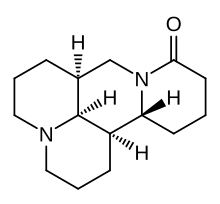
Matrine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.117.486 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H24N2O |
| Molar mass | 248.364 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Matrine is an alkaloid found in plants from the Sophora genus. It has a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-cancer effects,[1] as well as κ-opioid and μ-opioid receptor agonism.[2][3]
Matrine possesses strong antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis are the likely mechanisms responsible for matrine's antitumor activities.[4] Matrine is a component of the traditional Chinese medical herb Sophora flavescens Ait.
Mu opioid agonism is associated with euphoria, while kappa opioid agonism is associated with dysphoria and psychotomimetic hallucinations (as seen in the kappa-agonist Salvinorin A). Both receptors are known to produce analgesia when activated.
Matrine and the related compound oxymatrine have an antifeedant effect against formosan subterranean termite.[5]
References
- ^ Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Duan, H.; Luan, G.; Yagasaki, K.; Zhang, G. (April 2009). "Effects of Matrine against the Growth of Human Lung Cancer and Hepatoma Cells as well as Lung Cancer Cell Migration". Cytotechnology. 59 (3): 191–200. doi:10.1007/s10616-009-9211-2. PMC 2774570. PMID 19649719.
- ^ Xiao, P.; Kubo, H.; Ohsawa, M.; Higashiyama, K.; Nagase, H.; Yan, Y. N.; Li, J. S.; Kamei, J.; Ohmiya, S. (April 1999). "Kappa-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Antinociceptive Effects of Stereoisomers and Derivatives of (+)-Matrine in Mice". Planta Medica. 65 (3): 230–233. doi:10.1055/s-1999-14080. PMID 10232067.
- ^ Higashiyama, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Imai, S.; Kamei, J.; Yajima, Y.; Narita, M.; Suzuki, T. (May 2005). "Implication of the Descending Dynorphinergic Neuron Projecting to the Spinal Cord in the (+)-Matrine- and (+)-Allomatrine-Induced Antinociceptive Effects". Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 28 (5): 845–848. doi:10.1248/bpb.28.845. PMID 15863891.
- ^ Ma, L.; Wen, S.; Zhan, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. (2008). "Anticancer Effects of the Chinese Medicine Matrine on Murine Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells". Planta Medica. 74 (3): 245–251. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1034304. PMID 18283616.
- ^ Mao, L.; Henderson, G. (2007). "Antifeedant Activity and Acute and Residual Toxicity of Alkaloids from Sophora flavescens (Leguminosae) against Formosan Subterranean Termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae)". Journal of Economic Entomology. 100 (3): 866–870. doi:10.1093/jee/100.3.866. PMID 17598549.
