Provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
| Provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Provinces de la République démocratique du Congo (French) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary State |
| Location | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Number | 26 provinces (1 is a city-province) |
| Populations | 1,093,845 (Bas-Uele) – 8,981,552 (Kinshasa) |
| Areas | 9,481 km2 (3,661 sq mi) (Kasaï-Oriental) – 199,567 km2 (77,053 sq mi) (Tshopo) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
 |
|---|
| United Nations Mission |
|
|
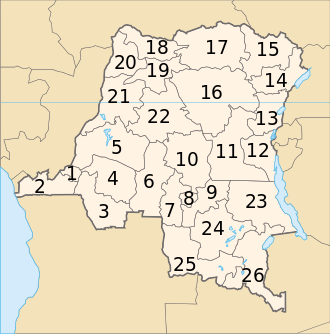
There are currently 26 provinces in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The capital Kinshasa is a city-province.[1][2]
| Map | Province | Capital | Area in km2 (sq mi) |
Population* | Previous province | Time zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kinshasa | Kinshasa | 9,965 (3,848) | 8,981,552 | Kinshasa | UTC+1 |
| 2 | Kongo-Central | Matadi | 53,929 (20,822) | 3,734,594 | Bas-Congo | UTC+1 |
| 3 | Kwango | Kenge | 89,974 (34,739) | 1,994,036 | Bandundu | UTC+1 |
| 4 | Kwilu | Kikwit | 78,219 (30,201) | 5,174,718 | Bandundu | UTC+1 |
| 5 | Mai-Ndombe | Inongo | 127,465 (49,215) | 1,768,327 | Bandundu | UTC+1 |
| 6 | Kasaï | Luebo | 95,631 (36,923) | 3,199,891 | Kasaï-Occidental | UTC+2 |
| 7 | Kasaï-Central | Kananga | 59,111 (22,823) | 2,976,806 | Kasaï-Occidental | UTC+2 |
| 8 | Kasaï-Oriental | Mbuji-Mayi | 9,481 (3,661) | 2,702,430 | Kasaï-Oriental | UTC+2 |
| 9 | Lomami | Kabinda | 56,010 (21,630) | 2,048,839 | Kasaï-Oriental | UTC+2 |
| 10 | Sankuru | Lusambo | 105,000 (41,000) | 1,374,239 | Kasaï-Oriental | UTC+2 |
| 11 | Maniema | Kindu | 132,520 (51,170) | 1,908,770 | Maniema | UTC+2 |
| 12 | South Kivu | Bukavu | 65,070 (25,120) | 5,050,348 | South Kivu | UTC+2 |
| 13 | North Kivu | Goma | 59,483 (22,967) | 7,460,642 | North Kivu | UTC+2 |
| 14 | Ituri | Bunia | 65,658 (25,351) | 4,241,236 | Orientale | UTC+2 |
| 15 | Haut-Uele | Isiro | 89,683 (34,627) | 1,920,867 | Orientale | UTC+2 |
| 16 | Tshopo | Kisangani | 199,567 (77,053) | 2,614,630 | Orientale | UTC+2 |
| 17 | Bas-Uele | Buta | 148,331 (57,271) | 1,093,845 | Orientale | UTC+2 |
| 18 | Nord-Ubangi | Gbadolite | 56,644 (21,870) | 1,482,076 | Équateur | UTC+1 |
| 19 | Mongala | Lisala | 58,141 (22,448) | 1,793,564 | Équateur | UTC+1 |
| 20 | Sud-Ubangi | Gemena | 51,648 (19,941) | 2,744,345 | Équateur | UTC+1 |
| 21 | Équateur | Mbandaka | 103,902 (40,117) | 1,626,606 | Équateur | UTC+1 |
| 22 | Tshuapa | Boende | 132,940 (51,330) | 1,316,855 | Équateur | UTC+1 |
| 23 | Tanganyika | Kalemie | 134,940 (52,100) | 2,482,001 | Katanga | UTC+2 |
| 24 | Haut-Lomami | Kamina | 108,204 (41,778) | 2,540,127 | Katanga | UTC+2 |
| 25 | Lualaba | Kolwezi | 121,308 (46,837) | 1,677,288 | Katanga | UTC+2 |
| 26 | Haut-Katanga | Lubumbashi | 132,425 (51,130) | 3,960,945 | Katanga | UTC+2 |
* Population estimates are based on the number of registered voters in 2005, assuming that they represent 33% of the total population in each province.
History


| 1. Bandundu 2. Bas-Congo 3. Équateur 4. Kasaï-Occidental | 5. Kasaï-Oriental 6. Katanga 7. Kinshasa 8. Maniema | 9. Nord-Kivu 10. Orientale 11. Sud-Kivu |
The Belgian Congo was annexed as a colony of Belgium in 1908, and it was initially organized into 22 districts. Ten western districts were administered directly under the main colonial government, while the eastern part of the colony was administered under two vice-governments: eight northeastern districts formed Orientale Province, and four southeastern districts formed Katanga. In 1919, the colony was organized into four provinces: Congo-Kasaï (five southwestern districts), Équateur (five northwestern districts), Orientale and Katanga (previous vice-governments).[1]
In 1932, the colony was reorganized into six provinces. Initially they were named after their capital cities, but in 1947 regional names were adopted.[1]
The Belgian Congo became an independent country in 1960, named Republic of the Congo. By 1963, the country was organized into 21 provinces (informally called provincettes) and the capital city of Léopoldville, similar to the original 22 districts under colonial rule. In 1966, the 21 provincettes were grouped into eight provinces, and the capital city was renamed Kinshasa.[1]
In 1971, the country was renamed Zaire, and three provinces were also renamed. In 1975, the capital city of Kinshasa obtained the status of a province. In 1988, the province of Kivu was split into three. In 1997, the country was renamed Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the three provinces that had been renamed in 1971 were given their previous or new names.[1]
The Constitution of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, adopted in 2006, specifies a territorial organization into 26 provinces,[3] again resembling the previous provincettes and original colonial districts. The reorganization was scheduled to take effect within three years of the new constitution's promulgation, but it only occurred in 2015.[4][5]
| Belgian Congo | Republic of the Congo | Zaire | Democratic Republic of the Congo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1908 | 1919 | 1932 | 1947 | 1963 | 1966 | 1971 | 1988 | 1997 | 2015 |
| 22 districts | 4 provinces | 6 provinces | 6 provinces | 21 provinces + capital | 8 provinces + capital | 8 provinces + capital | 11 provinces | 11 provinces | 26 provinces |
| Tanganika-Moero | Katanga | Élisabethville | Katanga | Nord-Katanga | Katanga | Shaba | Katanga | Tanganyika | |
| Haut-Lomami | |||||||||
| Lulua | Lualaba | Lualaba | |||||||
| Haut-Luapula | Katanga-Oriental | Haut-Katanga | |||||||
| Lomami | Lusambo | Kasaï | Lomami | Kasaï-Oriental | Lomami | ||||
| Sankuru | Congo-Kasaï | Sankuru | Sankuru | ||||||
| Kasaï | Sud-Kasaï | Kasaï-Oriental | |||||||
| Luluabourg | Kasaï-Occidental | Kasaï-Central | |||||||
| Unité-Kasaïenne | Kasaï | ||||||||
| Moyen-Congo | Léopoldville | Léopoldville | Kinshasa | ||||||
| Bas-Congo | Congo-Central | Bas-Zaïre | Bas-Congo | Kongo-Central | |||||
| Kwango | Kwango | Bandundu | Kwango | ||||||
| Kwilu | Kwilu | ||||||||
| Lac Léopold II | Équateur | Mai-Ndombe | Mai-Ndombe | ||||||
| Équateur | Coquilhatville | Équateur | Cuvette-Centrale | Équateur | Équateur | ||||
| Tshuapa | |||||||||
| Lulonga | Moyen-Congo | Mongala | |||||||
| Bangala | |||||||||
| Ubangi | Ubangi | Nord-Ubangi | |||||||
| Sud-Ubangi | |||||||||
| Bas-Uele | Orientale | Stanleyville | Orientale | Uele | Orientale | Haut-Zaïre | Orientale | Bas-Uele | |
| Haut-Uele | Haut-Uele | ||||||||
| Ituri | Kibali-Ituri | Ituri | |||||||
| Stanleyville | Haut-Congo | Tshopo | |||||||
| Aruwimi | |||||||||
| Maniema | Costermansville | Kivu | Maniema | Kivu | Maniema | ||||
| Lowa | |||||||||
| Kivu | Nord-Kivu | Nord-Kivu | |||||||
| Kivu-Central | Sud-Kivu | ||||||||
See also
- Proposed provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (established in 2015)
- History of the administrative divisions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Template:Fr icon
- List of provincial governors of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Districts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Territories of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- ISO 3166-2:CD
References
- ^ a b c d e Provinces of the Democratic Republic of Congo, Statoids, accessed 1 May 2016.
- ^ Nouvelles entités provinciales, Joseph M. Kyalangilwa, 22 January 2007.
- ^ Constitution of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, article 2, Wikisource. Template:Fr icon
- ^ The National Assembly adopts the laws regarding the limits of the provinces in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, National Assembly of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 10 January 2015. Template:Fr icon
- ^ Election of governors: definite results expected on 18 April, Radio Okapi, 27 March 2016. Template:Fr icon
