Zambia
Republic of Zambia | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "One Zambia, One Nation" | |
| Anthem: National Anthem of Zambia | |
 | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Lusaka |
| Official languages | English |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2010[1]) | > 0.5%
|
| Religion | Christianity |
| Demonym(s) | Zambian |
| Government | Unitary Presidential republic |
| Edgar Lungu | |
| Inonge Wina | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 27 June 1890 | |
| 28 November 1899 | |
| 29 January 1900 | |
| 17 August 1911 | |
| 1 August 1953 | |
| 24 October 1964 | |
• Current constitution | 5 January 2016 |
| Area | |
• Total | 752,618 km2 (290,587 sq mi)[2] (39th) |
• Water (%) | 1 |
| Population | |
• 2015 estimate | 16,212,000[3] (69th) |
• 2010 census | 13,092,666[4] |
• Density | 17.2/km2 (44.5/sq mi) (191st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $65.174 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $3,898[5] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $20.574 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $1,230[5] |
| Gini (2010) | 57.5[6] high inequality |
| HDI (2014) | medium (139th) |
| Currency | Zambian kwacha (ZMW) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (CAT) |
| Drives on | left |
| Calling code | +260 |
| ISO 3166 code | ZM |
| Internet TLD | .zm |
The Republic of Zambia (/ˈzæmbiə/) is a landlocked country in Southern Africa,[8] neighbouring the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west. The capital city is Lusaka, in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the northwest, the core economic hubs of the country.
Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. After visits by European explorers in the eighteenth century, Zambia became the British protectorate of Northern Rhodesia towards the end of the nineteenth century. For most of the colonial period, Zambia was governed by an administration appointed from London with the advice of the British South Africa Company.
On 24 October 1964, Zambia became independent of the United Kingdom and prime minister Kenneth Kaunda became the inaugural president. Kaunda's socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP) maintained power from 1964 until 1991. Kaunda played a key role in regional diplomacy, cooperating closely with the United States in search of solutions to conflicts in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia.[9] From 1972 to 1991 Zambia was a one-party state with the UNIP as the sole legal political party under the motto "One Zambia, One Nation". Kaunda was succeeded by Frederick Chiluba of the social-democratic Movement for Multi-Party Democracy in 1991, beginning a period of social-economic growth and government decentralisation. Levy Mwanawasa, Chiluba's chosen successor, presided over Zambia from January 2002 until his death in August 2008, and is credited with campaigns to reduce corruption and increase the standard of living. After Mwanawasa's death, Rupiah Banda presided as Acting President before being elected President in 2008. Holding office for only three years, Banda stepped down after his defeat in the 2011 elections by Patriotic Front party leader Michael Sata. Sata died on 28 October 2014, the second Zambian president to die in office.[10] Guy Scott served briefly as interim president until new elections were held on 20 January 2015,[11] in which Edgar Lungu was elected as the sixth President.
In 2010, the World Bank named Zambia one of the world's fastest economically reformed countries. The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is headquartered in Lusaka.
Etymology
The territory of what is now Zambia was known as Northern Rhodesia from 1911. It was renamed Zambia at independence in 1964. The new name of Zambia was derived from the Zambezi river (Zambezi may mean "River of God").[citation needed]
History
Pre-historic era
The area of modern Zambia is known to have been inhabited by the Khoisan until around AD 300, when migrating Bantu began to settle around these areas.[12] These early hunter-gatherer groups were later either annihilated or absorbed by subsequent more organised Bantu groups.
Archaeological excavation work on the Zambezi Valley and Kalambo Falls show a succession of human cultures. In particular, ancient camping site tools near the Kalambo Falls have been radiocarbon dated to more than 36,000 year ago.
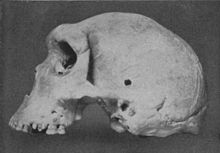
The fossil skull remains of Broken Hill Man, dated between 300,000 and 125,000 years BC, further shows that the area was inhabited by pre-historic man.
Bantu empires

The early history of tribes of modern-day Zambia can only be gleaned from knowledge passed down by successive generations through word of mouth.[citation needed]
In the 12th century, major waves of Bantu-speaking immigrants arrived during the Bantu expansion. Among them, the Tonga people (also called Ba-Tonga, "Ba-" meaning "men") were the first to settle in Zambia and are believed to have come from the east near the "big sea".
The Nkoya people also arrived early in the expansion,[13] coming from the Luba–Lunda kingdoms located in the southern parts of the modern Democratic Republic of the Congo and northern Angola, followed by a much larger influx, especially between the late 12th and early 13th centuries.
By the late 12th century, more advanced kingdoms and empires had been established in most regions of modern-day Zambia.
To the east, the Maravi Empire, also spanning the vast areas of Malawi and parts of present-day northern Mozambique began to flourish under Kalonga.
At the end of the 18th century, some of the Mbunda migrated to Barotseland, Mongu[14] upon the migration of among others, the Ciyengele.[15] The Aluyi and their leader, the Litunga Mulambwa, especially valued the Mbunda for their fighting ability.
In the early 19th century, the Nsokolo people settled in the Mbala district of Northern Province. During the 19th century, the Ngoni and Sotho peoples arrived from the south. By the late 19th century, most of the various peoples of Zambia were established in their current areas.
European contact

The earliest European to visit the area was the Portuguese explorer Francisco de Lacerda in the late 18th century. Lacerda led an expedition from Mozambique to the Kazembe region in Zambia (with the goal of exploring and to crossing Southern Africa from coast to coast for the first time),[16] and died during the expedition in 1798. The expedition was from then on led by his friend Francisco Pinto.[17] This territory, located between Portuguese Mozambique and Portuguese Angola, was claimed and explored by Portugal in that period.
Other European visitors followed in the 19th century. The most prominent of these was David Livingstone, who had a vision of ending the slave trade through the "3 Cs": Christianity, Commerce and Civilization. He was the first European to see the magnificent waterfalls on the Zambezi River in 1855, naming them the Victoria Falls after Queen Victoria. He described them thus: "Scenes so lovely must have been gazed upon by angels in their flight".
Locally the falls are known as "Mosi-o-Tunya" or "thundering smoke" in the Lozi or Kololo dialect. The town of Livingstone, near the Falls, is named after him. Highly publicised accounts of his journeys motivated a wave of European visitors, missionaries and traders after his death in 1873.[18][unreliable source?]
British South Africa Company

In 1888, the British South Africa Company (BSA Company), led by Cecil Rhodes, obtained mineral rights from the Litunga, the Paramount Chief of the Lozi (Ba-rotse) for the area which later became Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia.[19] To the east, in December 1897 a group of the Angoni or Ngoni (originally from Zululand) rebelled under Tsinco, son of King Mpezeni, but the rebellion was put down,[20] and Mpezeni accepted the Pax Britannica. That part of the country then came to be known as North-Eastern Rhodesia. In 1895, Rhodes asked his American scout Frederick Russell Burnham to look for minerals and ways to improve river navigation in the region, and it was during this trek that Burnham discovered major copper deposits along the Kafue River.[21]
North-Eastern Rhodesia and Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia were administered as separate units until 1911 when they were merged to form Northern Rhodesia, a British protectorate. In 1923, the BSA Company ceded control of Northern Rhodesia to the British Government after the government decided not to renew the Company's charter.
British colonisation
In 1923, Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe), a conquered territory which was also administered by the BSA Company, became a self-governing British colony. In 1924, after negotiations, administration of Northern Rhodesia transferred to the British Colonial Office.
Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
In 1953, the creation of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland grouped together Northern Rhodesia, Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland (now Malawi) as a single semi-autonomous region. This was undertaken despite opposition from a sizeable minority of the population, who demonstrated against it in 1960–61.[22] Northern Rhodesia was the centre of much of the turmoil and crisis characterising the federation in its last years. Initially, Harry Nkumbula's African National Congress (ANC) led the campaign, which Kenneth Kaunda's United National Independence Party (UNIP) subsequently took up.
Independence

A two-stage election held in October and December 1962 resulted in an African majority in the legislative council and an uneasy coalition between the two African nationalist parties. The council passed resolutions calling for Northern Rhodesia's secession from the federation and demanding full internal self-government under a new constitution and a new National Assembly based on a broader, more democratic franchise.
The federation was dissolved on 31 December 1963, and in January 1964, Kaunda won the only election for Prime Minister of Northern Rhodesia. The Colonial Governor, Sir Evelyn Hone, was very close to Kaunda and urged him to stand for the post. Soon after, there was an uprising in the north of the country known as the Lumpa Uprising led by Alice Lenshina – Kaunda's first internal conflict as leader of the nation.
Northern Rhodesia became the Republic of Zambia on 24 October 1964, with Kenneth Kaunda as the first president. At independence, despite its considerable mineral wealth, Zambia faced major challenges. Domestically, there were few trained and educated Zambians capable of running the government, and the economy was largely dependent on foreign expertise. This expertise was provided in part by John Willson CMG[23] There were over 70,000 Europeans resident in Zambia in 1964, and they remained of disproportionate economic significance.[24]
Kaunda's endorsement of Patriotic Front guerrillas conducting raids into neighbouring (Southern) Rhodesia resulted in political tension and a militarisation of the border, leading to its closure in 1973.[25] The Kariba hydroelectric station on the Zambezi River provided sufficient capacity to satisfy the country's requirements for electricity, despite Rhodesian management.
A railway (TAZARA – Tanzania Zambia Railways) to the Tanzanian port of Dar es Salaam, completed in 1975 with Chinese assistance, reduced Zambian dependence on railway lines south to South Africa and west through an increasingly troubled Portuguese Angola. Until the completion of the railway, Zambia's major artery for imports and the critical export of copper was along the TanZam Road, running from Zambia to the port cities in Tanzania. The Tazama oil pipeline was also built from Dar es Salaam to Ndola in Zambia.
By the late 1970s, Mozambique and Angola had attained independence from Portugal. Rhodesia's predominantly white government, which issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence in 1965, accepted majority rule under the Lancaster House Agreement in 1979.[26]
Civil strife in both Portuguese colonies and a mounting Namibian War of Independence resulted in an influx of refugees[27] and compounded transportation issues. The Benguela railway, which extended west through Angola, was essentially closed to Zambian traffic by the late 1970s. Zambia's support for anti-apartheid movements such as the African National Congress (ANC) also created security problems as the South African Defence Force struck at dissident targets during external raids.[28]
Economic troubles
In the mid-1970s, the price of copper, Zambia's principal export, suffered a severe decline worldwide. In Zambia's situation, the cost of transporting the copper great distances to market was an additional strain. Zambia turned to foreign and international lenders for relief, but, as copper prices remained depressed, it became increasingly difficult to service its growing debt. By the mid-1990s, despite limited debt relief, Zambia's per capita foreign debt remained among the highest in the world.
Democratisation
In June 1990 riots against Kaunda accelerated. Many protesters were killed by the regime in breakthrough June 1990 protests. In 1990 Kaunda survived an attempted coup, and in 1991 he agreed to reinstate multiparty democracy, having instituted one party rule under the Choma Commission of 1972. Following multiparty elections, Kaunda was removed from office (see below).
In the 2000s, the economy stabilized, attaining single-digit inflation in 2006–2007, real GDP growth, decreasing interest rates, and increasing levels of trade. Much of its growth is due to foreign investment in mining and to higher world copper prices. All this led to Zambia being courted enthusiastically by aid donors, and saw a surge in investor confidence in the country.
Politics

Politics in Zambia take place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Zambia is both head of state and head of government in a pluriform multi-party system. The government exercises executive power, while legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament.
Zambia became a republic immediately upon attaining independence in October 1964. From 2011 to 2014, Zambia's president had been Michael Sata, until Sata died on 28 October 2014.[29]
After Sata's death, Vice President Guy Scott, a Zambian of Scottish descent, became acting President of Zambia. On 24 January 2015 it was announced that Edgar Chagwa Lungu had won the election to become the 6th President in a tightly contested race. He won 48.33% of the vote, a lead of 1.66% over his closest rival, Hakainde Hichilema, with 46.67%.[30] 9 other candidates all got less than 1% each.
Foreign relations
After independence in 1964 the foreign relations of Zambia were mostly focused on supporting liberation movements in other countries in Southern Africa, such as the African National Congress and SWAPO. During the Cold War Zambia was a member of the Non-Aligned Movement.
Military
The Zambian Defence Force (ZDF) consists of the Zambia Army (ZA), the Zambia Air Force (ZAF), and the Zambian National Service (ZNS). The ZDF is designed primarily against external threats.
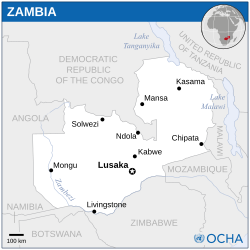
Administrative divisions

Zambia is divided into ten regions, which are further divided into 103 districts, 156 constituencies and 1,281 wards.
- Provinces
Geography

Zambia is a landlocked country in southern Africa, with a tropical climate, and consists mostly of high plateaus with some hills and mountains, dissected by river valleys. At 752,614 km2 (290,586 sq mi) it is the 39th-largest country in the world, slightly smaller than Chile. The country lies mostly between latitudes 8° and 18°S, and longitudes 22° and 34°E.
Zambia is drained by two major river basins: the Zambezi/Kafue basin in the centre, west and south covering about three-quarters of the country; and the Congo basin in the north covering about one-quarter of the country. A very small area in the northeast forms part of the internal drainage basin of Lake Rukwa in Tanzania.
In the Zambezi basin, there are a number of major rivers flowing wholly or partially through Zambia: the Kabompo, Lungwebungu, Kafue, Luangwa, and the Zambezi itself, which flows through the country in the west and then forms its southern border with Namibia, Botswana and Zimbabwe. Its source is in Zambia but it diverts into Angola, and a number of its tributaries rise in Angola's central highlands. The edge of the Cuando River floodplain (not its main channel) forms Zambia's southwestern border, and via the Chobe River that river contributes very little water to the Zambezi because most is lost by evaporation.[31]
Two of the Zambezi's longest and largest tributaries, the Kafue and the Luangwa, flow mainly in Zambia. Their confluences with the Zambezi are on the border with Zimbabwe at Chirundu and Luangwa town respectively. Before its confluence, the Luangwa River forms part of Zambia's border with Mozambique. From Luangwa town, the Zambezi leaves Zambia and flows into Mozambique, and eventually into the Mozambique Channel.
The Zambezi falls about 100 metres (328 ft) over the 1.6 km (0.99 mi) wide Victoria Falls, located in the south-west corner of the country, subsequently flowing into Lake Kariba. The Zambezi valley, running along the southern border, is both deep and wide. From Lake Kariba going east it is formed by grabens and like the Luangwa, Mweru-Luapula, Mweru-wa-Ntipa and Lake Tanganyika valleys, is a rift valley.
The north of Zambia is very flat with broad plains. In the west the most notable being the Barotse Floodplain on the Zambezi, which floods from December to June, lagging behind the annual rainy season (typically November to April). The flood dominates the natural environment and the lives, society and culture of the inhabitants and those of other smaller, floodplains throughout the country.
In Eastern Zambia the plateau which extends between the Zambezi and Lake Tanganyika valleys is tilted upwards to the north, and so rises imperceptibly from about 900 m (2,953 ft) in the south to 1,200 m (3,937 ft) in the centre, reaching 1,800 m (5,906 ft) in the north near Mbala. These plateau areas of northern Zambia have been categorised by the World Wildlife Fund as a large section of the Central Zambezian Miombo woodlands ecoregion.
Eastern Zambia shows great diversity. The Luangwa Valley splits the plateau in a curve north east to south west, extended west into the heart of the plateau by the deep valley of the Lunsemfwa River. Hills and mountains are found by the side of some sections of the valley, notably in its north-east the Nyika Plateau (2,200 m or 7,218 ft) on the Malawi border, which extend into Zambia as the Mafinga Hills, containing the country's highest point, Mafinga Central (2,339 m or 7,674 ft).[32]
The Muchinga Mountains, the watershed between the Zambezi and Congo drainage basins, run parallel to the deep valley of the Luangwa River and form a sharp backdrop to its northern edge, although they are almost everywhere below 1,700 m (5,577 ft). Their culminating peak Mumpu is at the western end and at 1,892 m (6,207 ft) is the highest point in Zambia away from the eastern border region. The border of the Congo Pedicle was drawn around this mountain.
The southernmost headstream of the Congo River rises in Zambia and flows west through its northern area firstly as the Chambeshi and then, after the Bangweulu Swamps as the Luapula, which forms part of the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Luapula flows south then west before it turns north until it enters Lake Mweru. The lake's other major tributary is the Kalungwishi River, which flows into it from the east. The Luvua River drains Lake Mweru, flowing out of the northern end to the Lualaba River (Upper Congo River).
Lake Tanganyika is the other major hydrographic feature that belongs to the Congo basin. Its south-eastern end receives water from the Kalambo River, which forms part of Zambia's border with Tanzania. This river has Africa's second highest uninterrupted waterfall, the Kalambo Falls.
Climate
Zambia is located on the plateau of Central Africa, between 1000–1600 m above sea level. The average altitude of 1200 m generally has a moderate climate. The climate of Zambia is tropical, modified by elevation. In the Köppen climate classification, most of the country is classified as humid subtropical or tropical wet and dry, with small stretches of semi-arid steppe climate in the south-west and along the Zambezi valley.
There are two main seasons, the rainy season (November to April) corresponding to summer, and the dry season (May/June to October/November), corresponding to winter. The dry season is subdivided into the cool dry season (May/June to August), and the hot dry season (September to October/November). The modifying influence of altitude gives the country pleasant subtropical weather rather than tropical conditions during the cool season of May to August.[33] However, average monthly temperatures remain above 20 °C (68 °F) over most of the country for eight or more months of the year.
Biodiversity
There are 14 ecosystems in Zambia, classed into Forest, Thicket, Woodland and Grassland vegetation types.
Zambia is endowed with approximately 12,505 species—63% animal species, 33% plant species and 4% bacterial and microorganism species .
There are an estimated 3,543 species of wild flowering plants, consisting of sedges, herbaceous plants and woody plants . The Northern and North-Western parts of the country especially have the highest diversity of flowering plants. Approximately 53% of flowering plants are rate and occur throughout the country.
A total of 242 mammalian species exist, with most endemic ones occupying the woodland and grassland ecosystems. The Rhodesian giraffe and Kafue Lechwe are some of the well-known species that are endemic to Zambia.
An estimated 757 bird species are known to exist, of which 600 are either resident or afrotropic migrants; 470 breed in the country; and 100 are non-breding migrants. The Zambian barbet is a well-known species endemic to Zambia.
Roughly 490 known fish species, belonging to 24 fish families have been reported in Zambia, with Lake Tanganyika having the highest diverse and endemic species.
Demographics
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: In censuses carried out during the British colonial administration prior to 1963, the black African population was estimated rather than counted. Source: Central Statistical Office, Zambia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
As per 2010 Zambian census, Zambia's population was 13,092,666. Zambia is significantly ethnically diverse, with a total of 73 ethnic tribes. During the country's occupation by the British, between 1911 and 1963, the country attracted immigrants from Europe and the Indian subcontinent, the latter whom came specifically as labourers. While most Europeans left after the collapse of white minority rule, a fair number of Asians still remain.
In the first recorded census—conducted on 7 May 1911—there were a total of 1,497 Europeans; 39 Asiatics and estimated 820,000 Africans. Black Africans were not counted in all six census exercises—conducted in 1911, 1921, 1931, 1946, 1951, and 1956—prior to independence. By 1956, when the last census prior to independence was conducted, there were 65,277 Europeans; 5,450 Asiatics; 5,450 Coloureds and an estimated 2,100,000 Africans.
In the 2010 population census, 98.2% were Black Africans and the remaining 1.8% consisting of other major racial groups.
Zambia is one of the most highly urbanised countries in sub-Saharan Africa with 44% of the population concentrated in a few urban areas along the major transport corridors, while rural areas are sparsely populated. The fertility rate was 6.2 as of 2007[update] (6.1 in 1996, 5.9 in 2001–02).[34]
Largest towns
Ethnic groups

The population comprises approximately 73 ethnic groups, most of which are Bantu-speaking. Almost 90% of Zambians belong to the nine main ethnolinguistic groups: the Nyanja-Chewa, Bemba, Tonga, Tumbuka, Lunda, Luvale, Kaonde, Nkoya and Lozi. In the rural areas, each ethnic group is concentrated in a particular geographic region of the country and many groups are very small and not as well known. However, all the ethnic groups can be found in significant numbers in Lusaka and the Copperbelt.
Expatriates, mostly British or South African, as well as some white Zambian citizens, live mainly in Lusaka and in the Copperbelt in northern Zambia, where they are either employed in mines, financial and related activities or retired. There were 70,000 Europeans in Zambia in 1964, but many have since left the country.[24]
Zambia has a small but economically important Asian population, most of whom are Indians and Chinese. There are 13,000 Indians in Zambia. An estimated 80,000 Chinese are resident in Zambia.[35] In recent years, several hundred dispossessed white farmers have left Zimbabwe at the invitation of the Zambian government, to take up farming in the Southern province.[36][37]
According to the World Refugee Survey 2009 published by the US Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, Zambia had a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 88,900. The majority of refugees in the country came from the Democratic Republic of Congo (47,300 refugees from the DRC living in Zambia in 2007), Angola (27,100; see Angolans in Zambia), Zimbabwe (5,400) and Rwanda (4,900).[38]
Beginning in May 2008, the number of Zimbabweans in Zambia also began to increase significantly; the influx consisted largely of Zimbabweans formerly living in South Africa who were fleeing xenophobic violence there.[39] Nearly 60,000 refugees live in camps in Zambia, while 50,000 are mixed in with the local populations. Refugees who wish to work in Zambia must apply for official permits which can cost up to $500 per year.[38]
Religion
Zambia is officially a Christian nation according to the 1996 constitution,[42] but a wide variety of religious traditions exist. Traditional religious thoughts blend easily with Christian beliefs in many of the country's syncretic churches. About three-fourths of the population is Protestant while about 20% follow Roman Catholicism. Christian denominations include Catholicism, Anglicanism, Pentecostalism, New Apostolic Church, Lutheranism, Jehovah's Witnesses, the Seventh-day Adventist Church, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Branhamites, and a variety of Evangelical denominations.
These grew, adjusted and prospered from the original missionary settlements (Portuguese and Catholicism in the east from Mozambique) and Anglicanism (British influences) from the south. Except for some technical positions (e.g. physicians), Western missionary roles have been assumed by native believers. After Frederick Chiluba (a Pentecostal Christian) became President in 1991, Pentecostal congregations expanded considerably around the country.[43] Zambia has one of the largest percentage of Seventh-day Adventist per capita in the world, accounting for about 1 in 18 Zambians.[44]
One in 11 Zambians is member of the New Apostolic Church.[citation needed] With membership above 1,200,000 the Zambia district of the church is the third largest after Congo East and East Africa (Nairobi).[citation needed]
The Baha'i population of Zambia is over 160,000,[45] or 1.5% of the population. The William Mmutle Masetlha Foundation run by the Baha'i community is particularly active in areas such as literacy and primary health care. Approximately 1% of the population are Muslims, most of whom live in urban areas and play a large economic role in the country,.[46] They are about 500 people who belong to the Ahmadiyya sect .[47] There is also a small Jewish community, composed mostly of Ashkenazis.
Languages

Template:Major language groups in Zambia
The official language of Zambia is English, which is used to conduct official business and is the medium of instruction in schools. The main local language, especially in Lusaka, is Nyanja, followed by Bemba. In the Copperbelt Bemba is the main language and Nyanja second. Bemba and Nyanja are spoken in the urban areas in addition to other indigenous languages which are commonly spoken in Zambia. These include Lozi, Kaonde, Tonga, Lunda and Luvale, which feature on the Zambia National Broadcasting Corporation (ZNBC)'s local languages section. The total number of languages spoken in Zambia is 73.
The process of urbanisation has had a dramatic effect on some of the indigenous languages, including the assimilation of words from other indigenous languages and English. Urban dwellers sometimes differentiate between urban and rural dialects of the same language by prefixing the rural languages with 'deep'.
Most will thus speak Bemba and Nyanja in the Copperbelt; Nyanja is dominantly spoken in Lusaka and Eastern Zambia. English is used in official communications and is the language of choice at home among – now common – intertribal families. This continuous evolution of languages has led to Zambian slang which can be heard in daily life throughout Lusaka and other major cities. Portuguese has been introduced into the school curriculum due to the presence of a large Portuguese-speaking Angolan community.[49] French is commonly studied in private schools, while some secondary schools have it as an optional subject. A German course has been introduced at the University of Zambia (UNZA).
Education

The right to equal and adequate education for all is enshrined within the Zambian constitution.[51] The Education Act of 2011 regulates the provision of equal and quality education.[52] The Ministry of Education effectively oversees the provision of quality education through policy and regulation of the education curriculum.
Fundamentally, the aim of education in Zambia is to promote full and well-rounded development of the physical, intellectual, social, affective, moral and spiritual qualities of all learners. The education system is broadly composed of three core structures: Early childhood education and Primary education (Grades 1 – 7), Secondary education (Grades 8 – 12) and Tertiary education. Additionally, Adult Literacy programmes are available for semi-literate and illiterate individuals.
Government's annual expenditure on education has increased over the years, increasing from 16.1% in 2006 to 20.2% in 2015.
Health
The Ministry of Health (MOH) provides information pertaining to Zambian health. In 2010, public expenditure on health was 3.4% of GDP, among the lowest in southern Africa.[53] The 2014 CIA estimated average life expectancy in Zambia was 51.83 years.[54]
HIV/AIDS epidemic
Zambia faces a generalised HIV epidemic, with an estimated prevalence rate of 13.5% among adults (ages 15–49) in 2009.[55] HIV incidence in Zambia has declined by more than 25% from 2001 to 2010, an indication that the epidemic appears to be declining.[56]
Hospitals
In Zambia, there are hospitals throughout the country which include: Levy Mwanawasa General Hospital,[57] Chipata General Hospital, Kitwe Central Hospital, Konkola Mine Hospital, Lubwe Mission Hospital, Maacha Hospital, Mtendere Mission Hospital, Mukinge Mission Hospital, Mwandi Mission Hospital, Nchanga North Hospital, Chikankata Salvation Army Hospital, Kalene Mission Hospital, St Francis Hospital, and St Luke's Mission Hospital.[58]
The University Teaching Hospital serves as both a hospital and a training site for future health workers. There are very few hospitals in rural or remote places in Zambia, where most communities rely on small government-run community health centres and rural health posts.
Maternal and child health care
The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Zambia is 470. This is compared with 602.9 in 2008 and 594.2 in 1990. The under-5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 145 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 25.[59]
In Zambia the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 5 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women is 1 in 38.[59] Female genital mutilation (FGM), while not widespread, is practiced in parts of the country. According to the 2009 Zambia Sexual Behaviour Survey, 0.7% of women have undergone FGM.[60] According to UNICEF, 45% of children under five years are stunted.[61]
Economy


Presently, Zambia averages between $7 billion and $8 billion of exports annually.[63] About 68% of Zambians live below the recognised national poverty line,[64] with rural poverty rates standing at about 78%[65] and urban rates at about 53%.[66] Unemployment and underemployment in urban areas are serious problems. Most rural Zambians are subsistence farmers.
Zambia ranked 117th out of 128 countries on the 2007 Global Competitiveness Index, which looks at factors that affect economic growth.[67] Social indicators continue to decline, particularly in measurements of life expectancy at birth (about 40.9 years) and maternal mortality (830 per 100,000 pregnancies).[68] The country's rate of economic growth cannot support rapid population growth or the strain which HIV/AIDS-related issues place on the economy.
Zambia fell into poverty after international copper prices declined in the 1970s. The socialist regime made up for falling revenue with several abortive attempts at International Monetary Fund structural adjustment programmes (SAPs). The policy of not trading through the main supply route and line of rail to the sea – the territory known as Rhodesia (from 1965 to 1979), and now known as Zimbabwe – cost the economy greatly. After the Kaunda regime, (from 1991) successive governments began limited reforms. The economy stagnated until the late 1990s. In 2007 Zambia recorded its ninth consecutive year of economic growth. Inflation was 8.9%, down from 30% in 2000.[69]
Zambia is still dealing with economic reform issues such as the size of the public sector, and improving Zambia's social sector delivery systems.[69] Economic regulations and red tape are extensive, and corruption is widespread. The bureaucratic procedures surrounding the process of obtaining licences encourages the widespread use of facilitation payments.[70] Zambia's total foreign debt exceeded $6 billion when the country qualified for Highly Indebted Poor Country Initiative (HIPC) debt relief in 2000, contingent upon meeting certain performance criteria. Initially, Zambia hoped to reach the HIPC completion point, and benefit from substantial debt forgiveness, in late 2003.
In January 2003, the Zambian government informed the International Monetary Fund and World Bank that it wished to renegotiate some of the agreed performance criteria calling for privatisation of the Zambia National Commercial Bank and the national telephone and electricity utilities. Although agreements were reached on these issues, subsequent overspending on civil service wages delayed Zambia's final HIPC debt forgiveness from late 2003 to early 2005, at the earliest. In an effort to reach HIPC completion in 2004, the government drafted an austerity budget for 2004, freezing civil service salaries and increasing a number of taxes. The tax hike and public sector wage freeze prohibited salary increases and new hires. This sparked a nationwide strike in February 2004.[71]
The Zambian government is pursuing an economic diversification program to reduce the economy's reliance on the copper industry. This initiative seeks to exploit other components of Zambia's rich resource base by promoting agriculture, tourism, gemstone mining, and hydro-power.
Mining

The Zambian economy has historically been based on the copper mining industry. Output of copper had fallen to a low of 228,000 metric tons in 1998 after a 30-year decline in output due to lack of investment, low copper prices, and uncertainty over privatisation. In 2002, following privatisation of the industry, copper production rebounded to 337,000 metric tons. Improvements in the world copper market have magnified the effect of this volume increase on revenues and foreign exchange earnings.
In 2003, exports of nonmetals increased by 25% and accounted for 38% of all export earnings, previously 35%. The Zambian government has recently been granting licenses to international resource companies to prospect for minerals such as nickel, tin, copper and uranium.[72] It is hoped that nickel will take over from copper as the country's top metallic export. In 2009, Zambia has been badly hit by the world economic crisis.[73]
Agriculture
Agriculture plays a very important part in Zambia's economy providing many more jobs than the mining industry. Private local company Zambeef Products Ltd. is the leading agri-business in Zambia with over 4.000 employees, producing row crops (5.000 ha irrigated, 1.500 ha non-irrigated), cattle (Zambeef), pork (Master Pork), chicken (ZamChick), eggs (ZamChick Egg), dairy products, leather, fish, feedstock (Novatek) and edible oil (Zamanita). Zambeef operates eight abattoirs, four farms and numerous retail stores (also in co-operation with Shoprite) and a fast-food chain (ZamChick Inn) throughout the country. Zambia Sugar is also one of the worlds largest producers of sugar cane in the world with its Nakambala plant in Mazabuka exporting all over the world.[74]
A small number of white Zimbabwean farmers were welcomed into Zambia after their expulsion by Robert Mugabe, whose numbers had reached roughly 150 to 300 people as of 2004[update].[75][76] They farm a variety of crops including tobacco, wheat, and chili peppers on an estimated 150 farms. The skills they brought, combined with general economic liberalisation under the late Zambian president Levy Mwanawasa, has been credited with stimulating an agricultural boom in Zambia. In 2004, for the first time in 26 years, Zambia exported more corn than it imported.[37]
Tourism


Zambia has some of nature's best wildlife and game reserves affording the country with abundant tourism potential. The North Luangwa, South Luangwa and Kafue National Parks have one of the most prolific animal populations in Africa. The Victoria Falls in the Southern part of the country is a major tourist attraction.
With 73 ethnic groups, there are also a myriad of traditional ceremonies that take place every year.
Energy
In 2009, Zambia generated 10.3 Twh and has been rated high in use of both Solar power and Hydroelectricity.[77] However, as of early 2015 Zambia began experiencing a serious energy shortage due to the poor 2014/2015 rain season which resulted in low water levels at the Kariba dam and other major dams.[78]
Manufacturing
Culture

Prior to the establishment of modern Zambia, the natives lived in independent tribes, each with their own ways of life. One of the results of the colonial era was the growth of urbanisation. Different ethnic groups started living together in towns and cities, influencing each other as well as adopting a lot of the European culture. The original cultures have largely survived in the rural areas. In the urban setting there is a continuous integration and evolution of these cultures to produce what is now called "Zambian culture".

Traditional culture is very visible through colourful annual Zambian traditional ceremonies. Some of the more prominent are: Kuomboka and Kathanga (Western Province), Mutomboko (Luapula Province), Kulamba and Ncwala (Eastern Province), Lwiindi and Shimunenga (Southern Province), Lunda Lubanza (North Western), Likumbi Lyamize (North Western), Mbunda Lukwakwa (North Western Province), Chibwela Kumushi (Central Province), Vinkhakanimba (Muchinga Province), Ukusefya Pa Ng’wena (Northern Province).
Popular traditional arts are mainly in pottery, basketry (such as Tonga baskets), stools, fabrics, mats, wooden carvings, ivory carvings, wire craft and copper crafts. Most Zambian traditional music is based on drums (and other percussion instruments) with a lot of singing and dancing. In the urban areas foreign genres of music are popular, in particular Congolese rumba, African-American music and Jamaican reggae. Several psychedelic rock artists emerged in the 1970s to create a genre known as Zam-rock, including WITCH, Musi-O-Tunya, Rikki Ililonga, Amanaz, the Peace, Chrissy Zebby Tembo, Blackfoot, and the Ngozi Family.
Media
The Ministry of Information, Broadcasting Services and Tourism In Zambia is responsible for the Zambian News Agency, while there are also numerous media outlets throughout the country which include; television stations, newspapers, FM radio stations, and Internet news websites.
Sports
Zambia declared its independence on the day of the closing ceremony of the 1964 Summer Olympics, thereby becoming the first country ever to have entered an Olympic games as one country, and left it as another. Zambia took part in the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing.
Football is the most popular sport in Zambia, and the Zambia national football team has had its triumphant moments in football history. At the Seoul Olympics of 1988, the national team defeated the Italian national team by a score of 4–0. Kalusha Bwalya, Zambia's most celebrated football player and one of Africa's greatest football players in history had a hat trick in that match. However, to this day, many pundits say the greatest team Zambia has ever assembled was the one that perished on 28 April 1993 in a plane crash at Libreville, Gabon. Despite this, in 1996, Zambia was ranked 15th on the official FIFA World Football Team rankings, the highest attained by any southern African team. In 2012, Zambia won the African Cup of Nations for the first time after losing in the final twice. They beat Côte d'Ivoire 8–7 in a penalty shoot-out in the final, which was played in Libreville, just a few kilometres away from the plane crash 19 years previously.[79]
Rugby Union, boxing and cricket are also popular sports in Zambia. Notably, at one point in the early 2000s, the Australia and South Africa national rugby teams were captained by players born in the same Lusaka hospital, George Gregan and Corné Krige. Zambia boasts having the highest rugby poles in the world, located at Luanshya Sports Complex in Luanshya.[citation needed]
Rugby union in Zambia is a minor but growing sport. They are currently ranked 73rd by the IRB and have 3,650 registered players and three formally organised clubs.[80] Zambia used to play cricket as part of Rhodesia. Zambia has also strangely provided a shinty international, Zambian-born Eddie Tembo representing Scotland in the compromise rules Shinty/Hurling game against Ireland in 2008.[81]
In 2011, Zambia was due to host the tenth All-Africa Games, for which three stadiums were to be built in Lusaka, Ndola, and Livingstone.[82] The Lusaka stadium would have a capacity of 70,000 spectators while the other two stadiums would hold 50,000 people each. The government was encouraging the private sector to get involved in the construction of the sports facilities because of a shortage of public funds for the project. Zambia has since revoked its bid to host the 2011 All-Africa Games, citing a lack of funds. Hence, Mozambique took Zambia's place as host.
Zambia also produced the first black African (Madalitso Muthiya) to play in the United States Golf Open,[83] one of the four major golf tournaments.
In 1989, the country's basketball team had its best performance when it qualified for the FIBA Africa Championship and thus finished as one of Africa's top ten teams.[84]
Music and dance
Zambia's culture has been an integral part of their development post independence such as the uprising of cultural villages and private museums. The music which inroduced dance is part of their cultural expression and it embodies the beauty and spectacle of life in Zambia, from the intricacies of the talking drums to the Kamangu drum used to announce the beginning of Malaila traditional ceremony. Dance as a practice serves as a unifying factor bringing the people together as one.[85]
See also
References
- ^ Census of Population and Housing National Analytical Report 2010. Central Statistical office, Zambia
- ^ United Nations Statistics Division. "Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density" (PDF). Retrieved 9 November 2007.
- ^ United Nations World Population Prospects(PDF) 2015 Revision
- ^ Central Statistical Office, Government of Zambia. "2010 Census Population Summaries". Archived from the original on 21 January 2012. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Zambia". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ^ "Gini Index". World Bank. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ "2015 Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2015. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ^ "United Nations Statistics Division- Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". Unstats.un.org. 31 October 2013. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ Andy DeRoche, Kenneth Kaunda, the United States and Southern Africa (London: Bloomsbury, 2016).
- ^ Zambian President Michael Sata dies in London – BBC News. Bbc.com (29 October 2014). Retrieved on 20 November 2015.
- ^ Guy Scott takes interim role after Zambian president Sata’s death | World news. The Guardian. Retrieved on 20 November 2015.
- ^ Holmes, Timothy (1998). Cultures of the World: Zambia. Tarrytown, New York: Times Books International. pp. 19–20. ISBN 0-7614-0694-8.
- ^ Clay, Gervas (1945). History of the Mankoya District. Rhodes-Livingstone Institute.
- ^ The elites of Barotseland, 1878–1969: a political history of Zambia's Western Province: a. Gerald L. Caplan, C. Hurst & Co Publishers Ltd, 1970, ISBN 0900966386
- ^ Bantu-Languages.com, citing Maniacky 1997
- ^ "Instructions and Travel Diary that Governor Francisco Joze de Lacerda e Almeida Wrote about His Travel to the Center of Africa, Going to the River of Sena, in the Year of 1798". Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- ^ Communications., Craig Hartnett of NinerNet. "Portuguese Expedition to Northern Rhodesia, 1798–99 – Great North Road (GNR, Northern Rhodesia, Zambia)". www.greatnorthroad.org. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- ^ "First to the Falls" by Gervas and Gill Clay
- ^ Livingstone Tourism Association. "Destination:Zambia – History and Culture". Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 29 October 2007.
- ^ Human Rights; Documentation Centre. "Zambia: Historical Background". Archived from the original on 11 March 2007. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Burnham, Frederick Russell (1899). "Northern Rhodesia". In Wills, Walter H. (ed.). . Simpkin, Marshall, Hamilton, Kent & Co. pp. 177–180.
- ^ Pearson Education. "Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Federation of". Retrieved 29 October 2007.
- ^ WILLSON, John Michael (born 15 July 1931). BDOHP Biographical Details and Interview Index. chu.cam.ac.uk
- ^ a b 1964: President Kaunda takes power in Zambia. BBC 'On This Day'.
- ^ Raeburn, Michael (1978). We are everywhere: Narratives from Rhodesian guerillas. Random House. pp. 1–209. ISBN 0394505301.
- ^ Nelson, Harold (1983). Zimbabwe: A Country Study. Claitors Publishing Division. pp. 54–137. ISBN 0160015987.
- ^ Kaplan, Irving (1971). Area Handbook for the Republic of South Africa. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 404–405.
- ^ Evans, M. (1984). "The Front-Line States, South Africa and Southern African Security: Military Prospects and Perspectives" (PDF). Zambezia. 12: 1.
- ^ Zambian President Michael Sata dies in London. BBC. 29 October 2014
- ^ Defence Minister Lungu wins Zambia's disputed presidential race. Associated Press via Yahoo News. 24 January 2015
- ^ Beilfuss, Richard and dos Santos, David (2001) "Patterns of Hydrological Change in the Zambezi Delta, Mozambique". Working Paper No 2 Program for the Sustainable Management of Cahora Bassa Dam and The Lower Zambezi Valley.
- ^ "Mafinga South and Mafinga Central: the highest peaks in Zambia". Footsteps on the Mountain blog. Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ^ Camerapix: "Spectrum Guide to Zambia." Camerapix International Publishing, Nairobi, 1996.
- ^ "Welcome to the Official site of Zambian Statistics". Zamstats.gov.zm. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ Zambians wary of "exploitative" Chinese employers. Irinnews.org. 23 November 2006.
- ^ "Zim's Loss, Zam's gain: White Zimbabweans making good in Zambia". The Economist. June 2004. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ a b Thielke, Thilo (27 December 2004). "Settling in Zambia: Zimbabwe's Displaced Farmers Find a New Home". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 28 August 2009. Cite error: The named reference "Spiegel" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b "World Refugee Survey 2009". U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants.
- ^ "Zambia: Rising levels of resentment towards Zimbabweans". IRIN News. 9 June 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing National Analytical Report 2010. Central Statistical office, Zambia
- ^ https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/zambia/
- ^ "Constitution of Zambia, 1991(Amended to 1996)". Scribd.com. 30 June 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Steel, Matthew (2005). Pentecostalism in Zambia: Power, Authority and the Overcomers. University of Wales. MSc Dissertation.
- ^ "Zambia Union Conference – Adventist Organizational Directory". Adventistdirectory.org. 17 October 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "The Largest Baha'i Communities". Adherents.com. Retrieved 29 October 2007.
- ^ International Religious Freedom Report 2010 – Zambia. State.gov. Retrieved on 20 November 2015.
- ^ Some basics of religious education in Zambia. 2007. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing National Analytical Report 2010. Central Statistical office, Zambia
- ^ Zambia to introduce Portuguese into school curriculum. Archived 8 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Budget Speeches". Republic of Zambia Ministry of Finance. Republic of Zambia Ministry of Finance. 2017. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ^ "Laws of Zambia". National Assembly of Zambia. National Assembly of Zambia. 1996. Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- ^ "The Education Act (2011)". National Assembly of Zambia. National Assembly of Zambia. 2011. Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- ^ Forecast provided by International Futures. Historic data points from the World Bank.
- ^ "CIA – The World Factbook Life Expectancy". Cia.gov. Retrieved 24 June 2014.
- ^ CIA world factbook: HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 20 November 2015.
- ^ "UNAIDS World AIDS Day Report 2011" (PDF). UNAIDS.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ David Smith in Lusaka. "Chinese hospital heals sore spot in Zambia | Global development". theguardian.com. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ Tycoon powers hospital in a remote area of north-west Zambia. ukzambians.co.uk. 11 September 2007
- ^ a b "The State of the World's Midwifery" (PDF). United Nations Population Fund.
- ^ Zambia Sexual Behaviour Survey 2009. zamstats.gov.zm
- ^ Zambia. Nutrition. UNICEF
- ^ "2023 Budget Speech" (PDF). parliament.gov.zm. Republic of Zambia Ministry of Finance. 30 September 2022. Retrieved 23 October 2022.
- ^ Zambia's Minister of Commerce, Trade, & Industry Robert K Sichinga on the country's economic performance. Theprospectgroup.com (10 August 2012). Retrieved on 20 November 2015.
- ^ Development Indicators Unit, Statistics Division, United Nations. "Population below national poverty line, total, percentage". Retrieved 30 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Development Indicators Unit, Statistics Division, United Nations. "Population below national poverty line, rural, percentage". Retrieved 30 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Development Indicators Unit, Statistics Division, United Nations. "Population below national poverty line, urban, percentage". Retrieved 30 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Zambia Country Brochure" (PDF). World Bank.
- ^ Human Development Report 2007/2008. Palgrave Macmillan. 2007. ISBN 978-0-230-54704-9
- ^ a b "Background Note: Zambia". Department of State.
- ^ "Business Corruption in Zambia". Business Anti-Corruption Portal. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ^ The World Bank and IMF’s long shadow in Zambia’s copper mines. eurodad.org. 20 February 2008
- ^ Pennysharesonline.com, City Equities Limited (14 July 2006). "Albidon signs agreement with Zambian government". Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2006.
- ^ Chinese keep low profile to cash in on the slump in Zambia. The Times. 24 January 2009.
- ^ https://www.illovosugar.co.za/About-us/Zambia
- ^ "Zim's Loss, Zam's gain: White Zimbabweans making good in Zambia", The Economist, June 2004, retrieved 28 August 2009 [dead link]
- ^ LaFraniere, Shannon (21 March 2004), "Zimbabwe's White Farmers Start Anew in Zambia", The New York Times, retrieved 28 August 2009
- ^ Zambia. Renewable Energy Agency Country Profile. International Renewable Energy Agency
- ^ in Lusaka Times
- ^ "Zambia score emotional African Cup win". Sydney Morning Herald. 13 February 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Zambia. International Rugby Board
- ^ Tembo's return is boost for Glen. inverness-courier.co.uk. 15 May 2009
- ^ "Zambia to build three stadia for 2011 All-Africa Games". People's Daily Online. Retrieved 6 November 2007.
- ^ "Zambia's Madalitso Muthiya a pioneer". Chicago Tribune. 5 May 2008. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ 1989 African Championship for Men, ARCHIVE.FIBA.COM. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ "The Unrivaled Zambian Culture – Ayiba Magazine". 14 June 2016. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
Further reading
- Burke, Mark, Glimmers of Hope : A Memoir of Zambia, (lulu.com, 2009)
- Ferguson, James (1999). Expectations of Modernity: Myths and Meanings of Urban Life in the Zambian Copperbelt. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-21701-2.
- Ihonvbere, Julius, Economic Crisis, Civil Society and Democratisation: The Case of Zambia, (Africa Research & Publications, 1996)
- LaMonica, Christopher, Local Government Matters: The Case of Zambia , (Lambert Academic Publishing, 2010)
- Mcintyre, Charles, Zambia (Bradt Travel Guides), (Bradt Travel Guides, 2008)
- Murphy, Alan and Luckham, Nana, Zambia and Malawi (Lonely Planet Multi Country Guide), (Lonely Planet Publications, 2010)
- Phiri, Bizeck Jube, A Political History of Zambia: From the Colonial Period to the 3rd Republic, (Africa Research & Publications, 2005)
- Roberts, Andrew, A History of Zambia, (Heinemann, 1976)
- Sardanis, Andrew, Africa: Another Side of the Coin: Northern Rhodesia's Final Years and Zambia's Nationhood, (I.B.Tauris, 2003)
- Various, One Zambia, Many Histories: Towards a History of Post-colonial Zambia, (Brill, 2008)
- Wotela, Kambidima (2010). "Deriving Ethno-geographical Clusters for Comparing Ethnic Differentials in Zambia". University of California Irvine: World Cultures eJournal, 17(2).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - First early human fossil found in Africa makes debut
- DeRoche, Andy Kenneth Kaunda, the United States and Southern Africa (London: Bloomsbury, 2016)
External links
- Official website
- "Zambia". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Zambia Corruption Profile from the Business Anti-Corruption Portal
- Template:Dmoz
- Zambia profile from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Zambia
Wikimedia Atlas of Zambia- Key Development Forecasts for Zambia from International Futures
- World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Zambia
- Zambia
- Bantu countries and territories
- Countries in Africa
- East African countries
- Southeast African countries
- Southern African countries
- Commonwealth republics
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Landlocked countries
- Least developed countries
- Liberal democracies
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member states of the United Nations
- States and territories established in 1964
- 1964 establishments in Zambia