Economy of Europe: Difference between revisions
→Regional variation: + new section |
Akira-otomo (talk | contribs) m I just added a little margin-left to the wikitable to separate it from the text better and clean up the top of the page. |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Update|date=July 2009}} |
{{Update|date=July 2009}} |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:300px; float:right;" |
{| class="wikitable" style="width:300px; float:right; margin-left: 10px;" |
||
|+ <big>'''Economy of Europe'''</big><br /><small>During 2003 unless otherwise stated</small> |
|+ <big>'''Economy of Europe'''</big><br /><small>During 2003 unless otherwise stated</small> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 13:05, 11 June 2011
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2010) |
This article needs to be updated. (July 2009) |
| Population: | 731,000,000 (11% of the World) |
| Nominal GDP (Currency) (US$): | $19.920 trillion (2010)[1] (32.4% of the World) |
| GDP /capita Nominal(Currency) (US$): | $27,250 (2009) |
| GDP (PPP) (US$): | US$18.140 trillion (2009) |
| GDP/capita (PPP) (US$): | $27,383 (2009) |
| Annual growth of per capita GDP: |
2.8% (2006) |
| Income of top 10%: | 27.5% |
| Millionaires (US$): | 2.9 million (0.41%) |
| Unemployment: | 10.0% (Nov 2009) |
| *Most numbers are from the UNDP from 2002, some numbers exclude certain countries for lack of information. Statistics are for entire nations, not just the portions within Europe. | |
| Template:World economy infobox footer | |
| edit | |
The economy of Europe comprises more than 731 million people in 48 different states.[2] Like other continents, the wealth of Europe's states varies, although the poorest are well above the poorest states of other continents in terms of GDP and living standards. The difference in wealth across Europe can be seen in a rough East-West divide. Whilst Western European states all have high GDPs and living standards, many of Eastern Europe's economies are still rising from the collapse of the communist Soviet Union and former Yugoslavia. Throughout this article "Europe" and derivatives of the word are taken to include selected states whose territory is only partly in Europe – such as Turkey, Azerbaijan, and the Russian Federation – and states that are geographically in Asia, bordering Europe – such as Armenia and Cyprus.
Europe was the first continent to industrialize – led by the United Kingdom in the 18th century – and as a result, it has become the richest continent in the world today and the nominal GDP in 2010 is $19.920 trillion[1] (32.4% of the World). Europe's largest national economy is that of Germany, which ranks fourth globally in nominal GDP, and fifth in purchasing power parity (PPP) GDP;[3] followed by France, ranking fifth globally in nominal GDP, followed by the United Kingdom, ranking sixth globally in nominal GDP, followed by Italy, which ranks seventh globally in nominal GDP, then by Russia ranking tenth globally in nominal GDP.[4]
These 5 countries are all ranking in the world's top 10, therefore European economies account for half of the 10 wealthiest ones. The end of World War II has since brought European countries closer together, culminating in the formation of the European Union (EU) and in 1999, the introduction of a unified currency – the euro. European Union as a whole is, by far, the wealthiest and largest economy in the world, topping the US by more than 2.000 billions at a time of great economic slowdown– see List of countries by GDP. In 2009 Europe remained the world's wealthiest region. Its $32,7 trillion in assets under management represented more than one-third of the world’s wealth. Unlike North America ($29,3 trillion) it was one of few regions where wealth surpassed its precrisis year-end peak.[5]
Of the top 500 largest corporations measured by revenue (Fortune Global 500 in 2010), 184 have their headquarters in Europe. 161 are located in the EU, 15 in Switzerland, 6 in Russia, 1 in Turkey, 1 in Norway.[6]
19 out of the top 26 nations in the world with the highest nominal GDP per capita are in Europe as of 2010.
- nr 1 Monaco $203,900[7]
- nr 2 Liechtenstein $136,864[8]
- nr 3 Luxembourg $104.390
- nr 4 Norway $84,543
- nr 6 Switzerland $67,074
- nr 7 Denmark $55,112
- nr 8 San Marino $50,670
- nr 10 Sweden $47,667
- nr 13 Netherlands 46,418
- nr 15 Ireland $45,642
- nr 16 Austria $43,723
- nr 17 Finland $43,133
- nr 19 Belgium $42,596
- nr 21 Andorra $41,130
- nr 22 France $40,591
- nr 23 Germany $40,511
- nr 24 Iceland $39,562
- nr 25 UK $36,298
- nr 26 Italy $33,828[9]
Economic development
Pre-1945: Industrial growth
Prior to World War II, Europe's major financial and industrial states were the United Kingdom, France and Germany. The Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain, had spread rapidly across Europe, and before long the entire continent was at a high level of industry. World War I had briefly led to the industries of some European states stalling, but in the run-up to World War II Europe had recovered well, and was competing with the ever increasing economic might of the United States of America.
However, World War II caused the destruction of most of Europe's industrial centres, and much of the continent's infrastructure was laid to waste.
1945–1990: The Cold War era
Following World War II, European Government was in tatters. Many Western European governments moved to link their economies, laying the foundation for what would become the European Union. This meant a huge increase in shared infrastructure and cross-border trade. Whilst these Western European states rapidly improved their economies, by the 1980s, the economy of the COMECON was struggling, mainly due to the massive cost of the Cold War. The GDP and living standard of Eastern European states were also behind those of their Western neighbours. Even free-market Greece, situated in South-Eastern Europe, struggled due to geographical isolation from Western Europe[citation needed].
The European Community grew from 6 original members following World War II, to 12 in this period.

The rise of the EU
When the Eastern Block dissolved around 1991, these states struggled to adapt to free-market systems. There was, however, a huge variation in degrees of success, with Central European states such as Hungary, Slovenia and Poland adapting reasonably quickly, whilst post-Soviet states such as Russia and Ukraine struggled to reform their crumbling infrastructures.
Western Europe was quick to develop economic ties with the newly democratic East. While the former Soviet states dealt with change, former Yugoslavian republics descended into war.
Europe's largest economy, Germany, struggled upon unification in 1991 with former communist East Germany. The Russian controlled Eastern part of the country had had much of its industrial infrastructure removed during the Cold War, and for many years the West struggled to build the East up to an equal level.
Peace did not come to Yugoslavia for a decade, and by 2003, there were still many NATO and EU peacekeeping troops present in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Macedonia, and Kosovo[a] . War severely hampered economic growth, with only Slovenia making any real progress in the 1990s.
The economy of Europe was by this time dominated by the EU, a huge economic and political organization with then 15 of Europe's states as full members. EU membership was seen as something to aspire to, and the EU gave significant support and aid to those Central and Eastern European states wishing to work towards achieving economies that met the entry criteria. During this time, 12 of the 15 members of the EU became part of the Eurozone, a currency union launched in 1999, whereby each member uses a shared currency, the Euro, which replaced their former national currencies. Three states chose to remain outside the Eurozone and continue with their own currencies, namely Denmark, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
2004–2007: EU expansion
In early 2004, 10 mostly former communist states joined the EU in its biggest ever expansion, enlarging the union to 25 members, with another eight making associated trade agreements. The acceding countries are bound to join the Eurozone and adopt the common currency Euro in the future. The process includes the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, of which some of these countries are already part.
Most European economies are in very good shape, and the continental economy reflects this. Conflict and unrest in some of the former Yugoslavia states and in the Caucasus states are hampering economic growth in those states, however.
In response to the massive EU growth, in 2005 the Russian dominated Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) created a rival trade bloc to the EU, open to any previous USSR state, (including both the European and Asian states). 12 of the 15 signed up, with the three Baltic states deciding to align themselves with the EU. Despite this, the three Caucasus states[citation needed] have said in the past they would one day consider applying for EU membership, particularly Georgia. This is also true of Ukraine since the Orange Revolution.
Regional variation
West Europe, with a long history of trade, a free market system, and a high level of development in the previous century, has been wealthier and more stable than the East, even though the gap is converging due to higher growth rates in the East.
The poorest states are those that just emerged from communism and civil wars, namely those of the former Soviet Union and Yugoslavia excluding Slovenia. But also West Europe itself presents some differences, especially between Northern countries (Scandinavia, Benelux, UK, Ireland, most of Germany) and Southern countries.
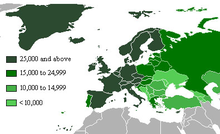
Below is a map of European countries by gross national income per capita.[10] High income countries – as defined by the World Bank – in blue ($12,196 or more), upper middle income in green ($3,946 – $12,195) and lower middle income ($996 – $3,945) in yellow.
Cities by GDP
| Rank | City | State | GDP in $ID B | Population M (LUZ) | GDP per capita $ID K | Eurozone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London | $ 565 | 11.92 | $ 66.0 | N | |
| 2 | Paris | $ 564 | 11.09 | $ 57.0 | Y | |
| 3 | Moscow | $ 321 | 10.5 | N | ||
| 4 | Madrid | $ 230 | 5.80 | $ 44.5 | Y | |
| 5 | Istambul | $ 187 | 10.5 | N | ||
| 6 | Barcelona | $ 177 | 4.97 | $ 40.0 | Y | |
| 7 | Rome | $ 144 | 3.46 | $ 55.4 | Y | |
| 8 | Milan | $ 136 | 3.08 | $ 87.8 | Y | |
| 9 | Vienna | $ 122 | 2.18 | $ 71.8 | Y | |
| 10 | Lisbon | $ 98 | 2.44 | $ 34.9 | Y | |
| 11 | Athens | $ 96 | 4.01 | $ 25.5 | Y | |
| 12 | Berlin | $ 95 | 4.97 | $ 28.5 | Y |
European Union
The European Union has the largest wealthiest economy in the world and is the first trade power in the world, trade within the Union accounts for more than one-third of the world total. The EU economy is expected to grow further over the next decade as more countries join the union – especially considering that the new States are usually poorer than the EU average, and hence the expected fast GDP growth will help achieve the dynamic of the united Europe. It is estimated that the Eurozone will grow around 2.6 per cent this year (2006),[11] on a par with industrialized nations such as the United States at 2.6% (Q2 2006) and 1.6 (Q3 2006).[12]
The European Union or EU is a supranational union of 27 European states, the most recent acceding members being Romania and Bulgaria, which became full members in 1 January 2007. It has many functions, the most important being the establishment and maintenance of a common single market, consisting of a customs union, a single currency (adopted by 17 of the 27 member states), a Common Agricultural Policy and a Common Fisheries Policy. The European Union also undertakes various initiatives to co-ordinate activities of the member states.
The union has evolved over time from a primarily economic union to an increasingly political one. This trend is highlighted by the increasing number of policy areas that fall within EU competence: political power has tended to shift upwards from the Member States to the EU.
European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) was established on 3 May 1960 as an alternative for European states that did not wish to join the European Union, creating a trade bloc with fewer central powers.
The EFTA member states as of 1992 are Austria, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland. Today (in 2009) only 4 countries: Iceland, Norway, Switzerland and Liechtenstein remain members of EFTA, as the other members have gradually left to join the EU.
European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) came into being on 1 January 1994 following an agreement between the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and the European Union (EU). It was designed to enable EFTA countries to participate in the European Single Market without having to join the EU.
In a referendum, Switzerland (ever keen on neutrality) chose not to participate in the EEA (although it is linked to the European Union by bilateral agreements similar in content to the EEA agreement), so the current members are the EU states plus Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein.
A Joint Committee consisting of the non EU members plus the European Commission (representing the EU) has the function of extending relevant EU Law to the non EU members.
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a confederation consisting of 12 of the 15 states of the former Soviet Union, (the exceptions being the three Baltic states). Although the CIS has few supranational powers, it is more than a purely symbolic organization and possesses co-ordinating powers in the realm of trade, finance, lawmaking and security. The most significant issue for the CIS is the establishment of a full-fledged free trade zone / economic union between the member states, to be launched in 2005. It has also promoted co-operation on democratization and cross-border crime prevention.
Central European Free Trade Agreement
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is a trade bloc of former Communist countries in central and eastern Europe. The countries that participated and the few continue to participate in CEFTA have used this form of integration to help them prepare for economic consolidation into the EU.
Currency and Central Banks
The most common currency within Europe is the euro, the currency of the European Union. To join, each new EU member must meet certain criteria, when these are met their own currencies will be replaced by the euro. Becoming a member of the EU involves a pledge to work towards Eurozone membership, (except in the cases of the United Kingdom and Denmark who have opt-outs). Currently, 16 of the 27 EU member states use the euro. Each EU member's central bank is part of the European System of Central Banks, and in addition, those that use the euro are part of the European Union's central bank, the European Central Bank.
There are some non-EU members who have elected to use the euro as their national currency, either with or without specific agreements with the EU to do so, (those with agreements with the EU may mint their own euro coins). The French overseas territories and departments of Mayotte and Réunion in the Indian Ocean, Guadeloupe and Martinique in the Caribbean and French Guiana in South America all use the euro, among many other islands in the Pacific, Caribbean and indeed around the globe that are ruled directly by European countries.
Some countries while maintaining their own national currency have pegged its value to the euro. In some of these countries, there is a fixed exchange rate between the national currency and the euro and in this case the currency is actually a submultiple of the euro. In other countries, the national currency's value fluctuates within a band (generally 15%) around a set rate. Currencies pegged to the euro include the currencies of Bulgaria, Lithuania, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Cape Verde. Denmark & Latvia have a foreign exchange band tied to the euro.
The CIS is also planning to introduce a single currency among its members.
Below is a list of the central banks and currencies of Europe, with exchange rates between each currency and both the euro and US dollars as of 1 May 2010.
Table correct as of 21 November 2010.
Stock exchanges
As of May, 1 2010, five (5) European cities are ranking among the 10 largest financial centers in the world: London (1st), Paris (5th), Frankfurt (6th), Zurich (7th) and Geneva (8th).

There are many stock exchanges within Europe.
- Pan-European:
- Albania:
- Tirana Stock Exchange (TSE)
- Austria:
- Belgium:
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria:
- Croatia:
- Cyprus:
- Cyprus Stock Exchange (CSE)
- Czech Republic:
- Prague Stock Exchange (PSE)
- Denmark:
- Copenhagen Stock Exchange (KFX) (part of OMX)
- Estonia:
- Tallinn Stock Exchange (part of OMX)
- Faroe Islands:
- Faroese Securities Market, in cooperation with Iceland Stock Exchange
- Finland:
- Helsinki Stock Exchange (part of OMX)
- France:
- Euronext Paris ("La Bourse de Paris") (CAC40)
- Georgia
- Georgian Stock Exchange (GSE)
- Germany:
- Frankfurt Stock Exchange (part of Deutsche Börse) (DAX)
- Greece:
- Athens Stock Exchange (General)
- Hungary:
- Budapest Stock Exchange (BSE)
- Iceland:
- Iceland Stock Exchange (Kauphöll Íslands)
- Ireland:
- Italy:
- Latvia:
- Riga Stock Exchange (part of OMX)
- Lithuania:
- Vilnius Stock Exchange (part of OMX)
- Luxembourg:
- Macedonia:
- Malta:
- Montenegro
- Netherlands:
- Norway:
- Portugal:
- Poland:
- Warsaw Stock Exchange (WSE)
- Romania:
- Bucharest Stock Exchange (BSE)
- Sibiu Stock Exchange (SIBEX)
- Russia:
- Serbia:
- Belgrade Stock Exchange (BELEX)
- Slovakia:
- Bratislava Stock Exchange (BSSE)
- Slovenia:
- Ljubljana Stock Exchange (LJSE)
- Spain:
- Madrid Stock Exchange (IBEX 35)
- Sweden:
- Nordic Growth Market
- Stockholm Stock Exchange (part of OMX)
- Switzerland:
- Turkey:
- Istanbul Stock Exchange (ISE)
- Ukraine:
- United Kingdom:
- Alternative Investment Market (AIM)
- London Stock Exchange (LSE) (FTSE)
Economic sectors
Agriculture and fishing
Europe's agricultural sector is in general highly developed, especially in Western Europe. The process of making Eastern Europe's agriculture more Western is well underway and is helped by the accession of Eastern European states to the EU. The agricultural sector in Europe is helped by the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which provides farmers with a minimal price for their products and subsidizes their exports, which increases competitiveness for their products. This policy is highly controversial as it hampers free trade worldwide (protectionism sparks protectionism from other countries and trade blocs: the concept of trade wars) and is violating the concept of fair trade. This means because of the protectionist nature of the CAP, agricultural products from developing countries are rendered incompetitive in both Europe (an important export market for developing countries) and on their home markets (as European agricultural products are dumped on developing countries' markets with help from European agricultural subsidies). This controversy surrounds every system of agricultural subsidies (the United States' policy of subsidizing farmers is also controversial). The CAP is also controversial because 40% of the EU's budget is spent on it, and because of the overproduction caused by it.
The Common Fisheries Policy is surrounded by an extensive system of rules (mainly consisting of quotas) to protect the environment from overfishing. Despite these rules, the cod is becoming increasingly rare in the North Sea resulting in drastic shortages of Fish & Chips in countries such as Canada and the United Kingdom. Strict fishing rules are the main reason for Norway and Iceland to stay out of the European Union (and out of the Common Fisheries Policy). Price guarantees and subsidizations of fishermen are implemented in the same way as agricultural subsidies are. Bluefin tuna is also a problem. Global stocks of the species are overfished with extinction in the wild a possibility in the near future. This also has the negative effect of threatening their traditional, natural predators.
Manufacturing
Europe has a thriving manufacturing sector, with a large part of the world's industrial production taking place in Europe. Most of the continent's industries are concentrated in Western Europe (mainly in the zone that comprises parts of the UK, the Benelux, western Germany, northeastern France, Switzerland, and northern Italy). However, because of the higher wage level and hence production costs, Western Europe is suffering from deindustrialization and offshoring in the traditional (labour intensive) manufacturing sectors. This means that manufacturing has become less important in Western Europe and that jobs are moved to cheaper regions (mainly China and Eastern Europe).
Eastern Europe has been industrialized since the early to mid 20th century but suffered from contraction in the 1990s when the inefficient heavy industry based manufacturing sector crippled after the collapse of communism and the introduction of the market economy. In the 21st century the manufacturing sector in Eastern Europe picked up because of the accession of Eastern European states to the EU and resulting accession to the European Common Market. This caused Western European firms to move jobs from their manufacturing sector to Eastern Europe (see above), which sparked Eastern European industrial growth and employment.
According to Fortune Global 500, 195 of the top 500 companies are headquartered in Europe.[13] The main products in European industry are bicycles, rail, machinery, marine, aerospace equipment, food, chemical and pharmaceutical goods, journalism, software and electronics. Europe no longer makes many kinds of TVs and there are other gaps in the product lineup.
Investing and banking
Europe has a well-developed financial sector. Many European cities are financial centres with the City of London being the largest. The European financial sector is helped by the introduction of the euro as common currency. This has made it easier for European households and firms to invest in companies and deposit money on banks in other European countries. Exchange rate fluctuations are now non-existent in the Eurozone. In Eastern Europe, the financial sector is somewhat less developed (mostly because of the communist legacy), but is rapidly developing towards Western European standards. The financial sector in Eastern Europe is helped by economic growth in the region and the commitment of Eastern European governments to achieve these high standards.
European banks are amongst the largest and most profitable in the world (BNP Paribas, Credit Agricole, Societe Generale, Royal Bank of Scotland, Deutsche Bank, UBS, National Trust, HSBC, Grupo Santander, BBVA, HBOS, Unicredit).[14]
Global trade relations
The bulk of the EU's external trade is done with China, Mercosur and the United States,[15] Japan, Russia and non-member European states.
EU members are represented by a single official at the WTO.
The EU is involved in a few minor trade disputes. It had a long running dispute with the USA of allegedly unfair subsidies the US government gives to several companies, such as Boeing. The EU has a long running ban prohibiting arms trade with the Chinese. The EU issued a brief accusing Microsoft of predatory and monopolistic practices.
See also
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Euro
- Europe
- European Economic Area
- Free trade areas in Europe
- European Free Trade Association
- Central European Free Trade Agreement
- European Union
- Regions of Europe
- History of Europe
- Industrial Revolution
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe statistics
- International organisations in Europe
- List of European countries by budget revenues
- List of European countries by budget revenues per capita
- List of European countries by GDP (nominal)
- List of European countries by GDP (PPP)
- List of European countries by GDP (nominal) per capita
- List of European countries by GDP (PPP) per capita
- List of European countries by GNI (nominal) per capita
- List of European countries by GNI (PPP) per capita
- List of sovereign states in Europe by minimum wage
- Oil price increases since 2003
Notes and references
Notes:
| a. | ^ Template:Kosovo-note |
References:
- ^ a b [1]. Last accessed 3 December 2010.
- ^ "Europe Economy". University-world.com. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "List of countries by GDP (Purchasing Power Parity) – CIA World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "List of countries by GDP (Official Exchange Rate) – CIA World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Global Wealth Stages a Strong Comeback". Pr-inside.com. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Global 500 2010: Countries – Australia". Fortune. Retrieved 8 July 2010. Number of companies data taken from the "Pick a country" box.
- ^ "Monaco , Data". Data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Liechtenstein , Data". Data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ GNI (nominal) per capita 2008, World Development Indicators database [2], World Bank, revised 17 October 2008 [3], Atlas method
- ^ Economic boom to lift eurozone growth to 2.6 pct this year – EU Business News – EUbusiness.com[dead link]
- ^ http://bea.gov/bea/glance.htm
- ^ "PDF-Human Rights Policies and Management Practices: Results from questionnaire surveys of Governments and Fortune Global 500 firms" (PDF). Retrieved 6 March 2008.
- ^ "Bank List – Top Banks in the World". Bankersalmanac.com. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ As regards the EU-China trade relations, see Paolo Farah (2006) Five Years of China’s WTO Membership. EU and US Perspectives on China’s Compliance with Transparency Commitments and the Transitional Review Mechanism, Legal Issues of Economic Integration, Kluwer Law International, Volume 33, Number 3, pp. 263–304.

