CONCACAF
 | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | CONCACAF |
|---|---|
| Formation | 18 September 1961 |
| Type | Sports organization |
| Headquarters | Miami, Florida United States |
Membership | 41 member associations |
Secretary General | Enrique Sanz |
| Jeffrey Webb | |
Parent organization | FIFA |
| Website | www |
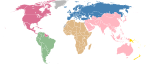
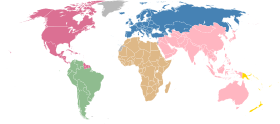
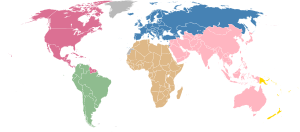
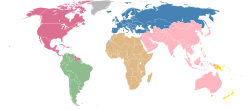
The Confederation of North, Central American and Caribbean Association Football[1] commonly known as CONCACAF,[2] is the continental governing body for association football in North America, Central America and the Caribbean. Three South American entities, the independent nations of Guyana and Suriname and the French department of French Guiana, are also members.[3]
CONCACAF was founded in its current form on 18 September 1961 in Mexico City, Mexico, with the merger of the NAFC and the CCCF, which made it one of the then five, now six continental confederations affiliated with FIFA. Its primary administrative functions are to organize competitions for national teams and clubs, and to conduct World Cup qualifying tournaments.
CONCACAF is the third-most successful FIFA confederation of the six, despite having the third-fewest countries. Mexico has dominated CONCACAF men's competition since its institution, although in recent years the USA men's team has shown stronger play. USA is the only country outside of Europe and South America to receive a medal in the World Cup, finishing third in 1930. They also reached the 2002 World Cup quarterfinals and the 2009 Confederations Cup final. Mexico has finished sixth in both the 1970 and 1986 World Cups and won the 1999 FIFA Confederations Cup and the 2012 Summer Olympics. Both nations have won all but one of the editions of the CONCACAF Gold Cup. The United States has been very successful in the women's game, being the only CONCACAF member to win any of the three major worldwide competitions in women's football—the World Cup (2), the Olympics (4), and the Algarve Cup (9).
Governance
CONCACAF is led by a General Secretariat, Executive Committee, Congress, and several committees. The Executive Committee is composed of seven members — one chairman, three Vice Presidents, and three members.[4] Each of the three geographic zones in CONCACAF are represented by one Vice President and one member. The Executive Committee carries out the various statutes, regulations, and resolutions.
Leadership
The first leader of CONCACAF was Costa Rican Ramón Coll Jaumet; he had overseen the merger between the NAFC and the CCCF. He was succeeded in the role by Mexican Joaquín Soria Terrazas in 1969 who served as president for 21 years.
His successor Jack Warner also presided over CONCACAF for 21 years. Warner was suspended as president on 30 May 2011 due to his temporary suspension from football related activity by FIFA following corruption allegations.[5]
On 20 June 2011, Jack Warner resigned from the presidency of CONCACAF, and removed himself from all participation in football, in the wake of the corruption investigation resulting from the 10 May 2011 meeting of the Caribbean Football Union.[6] The vice-president of CONCACAF, Alfredo Hawit, acted as president until May 2012.[7]
In May 2012, Cayman Islands banker Jeffrey Webb was installed as President of CONCACAF.
Corporate structure
CONCACAF is a non-profit company registered in Nassau, Bahamas.[8]
The headquarters of the CONCACAF (referred to as the office of the president) are currently located in Port-of-Spain, Trinidad—the home city of former CONCACAF president Jack Warner. However, it is expected the headquarters will be relocated to George Town, Cayman Islands, where the newly installed president Jeffrey Webb resides.
The administration office of CONCACAF (referred to as the primary office) is located in Manhattan, New York—the "home town" of Chuck Blazer, the former general secretary. Honduran Alfredo Hawit, acting president between 2011 and 2012 stated that CONCACAF will relocate to Miami, Florida, in late 2012 as it is more accessible to the Central American and Caribbean nations.[9]
Hawit's successor, Jeffrey Webb, has also indicated that CONCACAF plans to move out of its offices in Trump Tower.[10]
In July 2012, Webb appointed Miami-based Enrique Sanz as the CONCACAF General Secretary paving the way for CONCACAF to relocate as the CONCACAF constitution requires the headquarters to be sited in the same city as the General Secretary.[11]
Members
CONCACAF has 41 member associations:[12]
- 31 from the Caribbean
- 7 from Central America
- 3 from North America
| Code | Association | National teams | Founded | FIFA affiliation |
CONCACAF affiliation |
IOC member |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North American Zone (NAFU) | ||||||
| CAN | (M, W) | 1912 | 1913 | 1963 | Yes | |
| MEX | (M, W) | 1927 | 1929 | 1961 | Yes | |
| USA | (M, W) | 1913 | 1914 | 1961 | Yes | |
| Central American Zone (UNCAF) | ||||||
| BLZ | (M, W) | 1980 | 1986 | 1986 | Yes | |
| CRC | (M, W) | 1921 | 1927 | 1962 | Yes | |
| SLV | (M, W) | 1935 | 1938 | 1962 | Yes | |
| GUA | (M, W) | 1919 | 1946 | 1961 | Yes | |
| HON | (M, W) | 1951 | 1951 | 1961 | Yes | |
| NCA | (M, W) | 1931 | 1950 | 1968 | Yes | |
| PAN | (M, W) | 1937 | 1938 | 1961 | Yes | |
| Caribbean Zone (CFU) | ||||||
| AIA | (M, W) | 1990 | 1996 | 1994 | No | |
| ATG | (M, W) | 1928 | 1972 | 1972 | Yes | |
| ARU | (M, W) | 1932 | 1988 | 1988 | Yes | |
| BAH | (M, W) | 1967 | 1968 | 1981 | Yes | |
| BAR | (M, W) | 1910 | 1968 | 1968 | Yes | |
| BER | (M, W) | 1928 | 1962 | 1962 | Yes | |
| BON | (M, W) | 1960 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| VGB | (M, W) | 1974 | 1996 | 1996 | Yes | |
| CAY | (M, W) | 1966 | 1992 | 1992 | Yes | |
| CUB | (M, W) | 1924 | 1929 | 1961 | Yes | |
| CUW | (M, W) | 2010 | 2010 | 2010 | No | |
| DMA | (M, W) | 1970 | 1994 | 1994 | Yes | |
| DOM | (M, W) | 1953 | 1958 | 1964 | Yes | |
| GYF | (M, W) | 1962 | N/A | 1964 | No | |
| GRN | (M, W) | 1924 | 1978 | 1969 | Yes | |
| GPE | (M, W) | 1961 | N/A | 1964 | No | |
| GUY | (M, W) | 1902 | 1970 | 1961 | Yes | |
| HAI | (M, W) | 1904 | 1934 | 1961 | Yes | |
| JAM | (M, W) | 1910 | 1962 | 1965 | Yes | |
| MTQ | (M, W) | 1953 | N/A | 1964 | No | |
| MSR | (M, W) | 1994 | 1996 | 1994 | No | |
| PUR | (M, W) | 1940 | 1960 | 1961 | Yes | |
| SKN | (M, W) | 1932 | 1992 | 1990 | Yes | |
| LCA | (M, W) | 1979 | 1988 | 1965 | Yes | |
| MAF | (M, W) | 1999 | N/A | 2000 | No | |
| SVG | (M, W) | 1979 | 1988 | 1988 | Yes | |
| SXM | (M, W) | 1986 | N/A | 1998 | No | |
| SUR | (M, W) | 1920 | 1929 | 1965 | Yes | |
| TRI | (M, W) | 1908 | 1964 | 1962 | Yes | |
| TCA | (M, W) | 1996 | 1998 | 1996 | No | |
| VIR | (M, W) | 1992 | 1998 | 1997 | Yes | |
M = Men's National Team. W = Women's National Team
1:Inside the North American zone, but CFU member.
2:South American country or territory, but CONCACAF member.
3:Full CONCACAF member, but non-FIFA member.
N/A:not applicable,not available or no answer.
Bonaire were promoted from an association member to a full member at the XXIX Ordinary CONCACAF Congress in São Paulo on 10 June 2014.
Teams not affiliated to the IOC are not eligible to participate in the Summer Olympics football tournament, as a result they do not participate in the CONCACAF Men's Pre-Olympic Tournament or the CONCACAF Women's Pre-Olympic Tournament.
Membership relation
Elections at the CONCACAF Congress are mandated with a one-member, one-vote rule. The North American Football Union is the smallest association union in the region with only three members, but its nations have strong commercial and marketing support from sponsors and they are the most populous nations in the region.
The Caribbean Football Union has the ability to outvote NAFU and UNCAF with less than half of its membership. Consequently, there is a fractious relationship between members of CFU, UNCAF and NAFU.[citation needed] This provoked former Acting-President Alfredo Hawit to lobby for the CONCACAF Presidency to be rotated between the three unions in CONCACAF in 2011.
Trinidad's Jack Warner presided over CONCACAF for 21 years, and there was little that non-Caribbean nations could do to elect an alternative. Under Warner, the CFU members voted together as a unit with Warner acting as a party whip. It happened with such regularity that sports political commentators referred to the CFU votes as the "Caribbean bloc" vote.[citation needed] Warner rejected the idea in 1993 of merging several smaller nations' national teams into a Pan-Caribbean team. His reasoning was that the nations were more powerful politically when separate than when together. He commented that "being small is never a liability in this sport".[13]
Competitions
The Gold Cup and the Champions League are the two most visible CONCACAF tournaments.[12]
CONCACAF Gold Cup
The CONCACAF Gold Cup is the main association football competition of the men's national football teams governed by CONCACAF. The Gold Cup is CONCACAF's flagship competition, and the Gold Cup generates a significant part of CONCACAF's revenue.[14]
The Gold Cup determines the regional champion of North America, Central America, and the Caribbean. The Gold Cup is held every two years. Twelve teams compete for the Gold Cup — three from North America, five from Central America, and four from the Caribbean. The Central American teams qualify through the Central American Cup, and the Caribbean teams qualify through the Caribbean Cup.
The winners of two successive Gold Cups (for example, the 2013 and 2015 editions) face each other in a playoff to determine the CONCACAF entrant to the next Confederations Cup. If the same team has won the Gold Cup on both relevant occasions, there will be no playoff and that team automatically qualifies for the Confederations Cup.[15]
CONCACAF Champions League
The CONCACAF Champions League, originally known as the CONCACAF Champions' Cup, is an annual continental club association football competition organised by CONCACAF since 1962 for the top football clubs in the region. It is the most prestigious international club competition in North American football. The winner of the Champions League qualifies for the FIFA Club World Cup. The tournament consists of two stages. The group stage is played from August to October, and the knockout phase spans March through May.[16]
Twenty four teams compete in each Champions League — 9 from North America, 12 from Central America, and 3 teams from the Caribbean. The North American and Central American teams qualify through their national leagues or other national tournaments, while the Caribbean teams qualify through the CFU Club Championship.
The title has been won by 28 different clubs, 17 of which have won the title more than once. Mexican clubs have accumulated the highest number of victories, with 30 titles. The second most successful league has been Costa Rica's Primera División with six titles in total. Reigning champions Mexican side Cruz Azul is the most successful club with six titles respectively.
Other competitions
- CONCACAF U-20 Championship
- CONCACAF U-17 Championship
- CONCACAF U-15 Championship
- CONCACAF Women's U-20 Championship
- CONCACAF Women's U-17 Championship
- CONCACAF Girls' U-15 Championship
| class="col-break " |
- CONCACAF Men's Pre-Olympic Tournament
- CONCACAF Women's Gold Cup
- CONCACAF Women's Pre-Olympic Tournament
- CONCACAF Futsal Championship
- CONCACAF Beach Soccer Championship
Defunct
- NAFC Championship (1947,1949).
- CCCF Championship (1941–1961).
- CONCACAF Championship (1963–1989).
- CFU Championship (1978–1985).
- North American Nations Cup (1990,1991).
- Interamerican Cup
| class="col-break " |
- CONCACAF Champions' Cup
- CONCACAF Cup Winners Cup
- CONCACAF Giants Cup
- SuperLiga – North America regional championship
- Copa Interclubes UNCAF – Central America regional championship
CONMEBOL tournaments with CONCACAF competitors
National teams
Clubs
- Copa Libertadores
- Copa Sudamericana – (2005–2008).
- Copa Merconorte – (2000–2001) (Defunct)
Rankings - national teams

- Last updates:
- Men's national teams: 5 June 2014
- Women's national teams: 20 June 2014
| Top men's national teams Rankings are calculated by FIFA. |
____ | Top women's national teams Rankings are calculated by FIFA. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCF | FIFA | Nation | Points | CCF | FIFA | Nation | Points | |
| 1 | 13 | 1,035 | 1 | 1 | 2,193 | |||
| 2 | 20 | 882 | 2 | 7 | 1,976 | |||
| 3 | 28 | 762 | 3 | 25 | 1,761 | |||
| 4 | 31 | 743 | 4 | 40 | 1,566 | |||
| 5 | 33 | 731 | 5 | 56 | 1,398 | |||
| 6 | 68 | 481 | 6 | 64 | 1,363 | |||
| 7 | 71 | 470 | 7 | 76 | 1,313 | |||
| 8 | 73 | 452 | 8 | 87 | 1,206 | |||
| 9 | 81 | 411 | 9 | 91 | 1,184 | |||
| 10 | 95 | 354 | 10 | 95 | 1,152 | |||
| 11 | 110 | 289 | 11 | 95 | 1,152 | |||
| 12 | 120 | 254 | 12 | 100 | 1,108 | |||
| 13 | 127 | 226 | 13 | 101 | 1,106 | |||
| 14 | 131 | 212 | 14 | 107 | 1,000 | |||
| 15 | 133 | 203 | 15 | 110 | 955 | |||
| 16 | 136 | 197 | 16 | 112 | 948 | |||
| 17 | 137 | 137 | 17 | 118 | 849 | |||
| 18 | 144 | 182 | 17 | 121 | 825 | |||
| 19 | 151 | 158 | 19 | 122 | 768 | |||
| 20 | 152 | 152 | 20 | 123 | 758 | |||
| 21 | 156 | 137 | 21 | 125** | 1,509 | |||
| 22 | 158 | 134 | 22 | 125** | 1,339 | |||
| 23 | 160 | 124 | 23 | 125** | 1,256 | |||
| 24 | 166 | 99 | 24 | 125** | 1,226 | |||
| 25 | 169 | 93 | 25 | 125** | 1,111 | |||
| 26 | 170 | 92 | 26 | 125** | 1,061 | |||
| 27 | 175 | 83 | 27 | 125** | 1,029 | |||
| 28 | 176 | 78 | 28 | 125** | 906 | |||
| 29 | 182 | 65 | 29 | 125** | 867 | |||
| 30 | 186 | 40 | 30 | 125** | 831 | |||
| 31 | 195 | 23 | 31 | 125* | 997 | |||
| 32 | 196 | 21 | 32 | 125* | 852 | |||
| 33 | 198 | 18 | 33 | 125* | 704 | |||
| 34 | 206 | 3 | ||||||
| 35 | 207 | 0 | ||||||
- For a complete list of national rankings see the FIFA Rankings website.
- *Provisionally listed due to not having played more than 5 matches against officially ranked teams.
- **Inactive for more than 18 months and therefore are not officially ranked
Rankings - clubs
| Rankings are calculated by the IFFHS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CCF | IFFHS | Club | Points |
| 1 | 64 | 150 | |
| 2 | 77 | 144 | |
| 3 | 84 | 141 | |
| 4 | 90 | 136.5 | |
| 5 | 120 | 120 | |
| 6 | 166 | 100.5 | |
| 7 | 183 | 94 | |
| 8 | 188 | 93 | |
Last updated: 31 May 2014 [1]
| class="col-break " |
| Rankings are calculated by Football Database | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CCF | FbDb | Club | Points |
| 1 | 111 | 1576 | |
| 2 | 114 | 1574 | |
| 3 | 121 | 1566 | |
| 4 | 151 | 1545 | |
| 5 | 178 | 1527 | |
| 6 | 187 | 1522 | |
| 7 | 189 | 1520 | |
| 8 | 198 | 1516 | |
| 9 | 209 | 1513 | |
| 10 | 239 | 1503 | |
| 11 | 260 | 1495 | |
| 12 | 262 | 1494 | |
| 13 | 273 | 1490 | |
| 14 | 369 | 1458 | |
| 15 | 404 | 1448 | |
| 16 | 406 | 1447 | |
| 17 | 409 | 1447 | |
| 18 | 410 | 1446 | |
| 19 | 424 | 1441 | |
| 20 | 426 | 1441 | |
Last updated: 29 June 2014 [2]
Financial irregularities
At the CONCACAF Congress in May 2012 in Budapest, Hungary, legal counsel John P. Collins informed the members of CONCACAF of several financial irregularities. Collins revealed that Jack Warner, the former CONCACAF President, had registered the $22 million 'Dr. João Havelange Centre of Excellence' development in Port-of-Spain under the name of two companies that Warner owned.[17] In addition, Warner had secured a mortgage against the asset in 2007 which the CONCACAF members were also unaware of; the mortgage was co-signed by Lisle Austin, a former vice-president of CONCACAF.[17] The loan defaulted.
Collins also revealed that CONCACAF, despite most of its income coming from the United States, had not paid any tax to the Internal Revenue Service since at least 2007 and had never filed a return in the United States.[18] Although CONCACAF is a registered non-profit organisation in the Bahamas and headquartered in Port-of-Spain, Trinidad, they have an administration office in New York, and BDO and CONCACAF invited the IRS to investigate potential liabilities. It is thought that CONCACAF may have to pay up to $2 million plus penalties.[citation needed]
Chuck Blazer stated that a full financial audit into CONCACAF by New-York based consultancy BDO was delayed due to the actions of Jack Warner and his personal accountant, and the accounts could not be "signed off" as a consequence.[18]
In addition, Blazer is to sue CONCACAF for unpaid commission of sponsorship and marketing deals which he had made in 2010 during his time as General Secretary.[17] Blazer received a 10% commission on any deal that he made on behalf of CONCACAF.[19]
The Bermuda FA asked members of CONCACAF to lobby FIFA to remove Blazer from his position on the FIFA Executive Committee. Blazer suggested that it was less to do with financial irregularities and more for his role in the removal of Jack Warner in the Caribbean Football Union corruption scandal: "I spent 21 years building the confederation and its competitions and its revenues and I'm the one responsible for its good levels of income . . . I think this is a reflection of those who were angry at me having caused the action against Warner. This is also a reaction by people who have their own agenda."[19]
Jack Warner presided over CONCACAF for 21 years. Warner was one of the most controversial figures in world football. Warner was suspended as president on 30 May 2011 due to his temporary suspension from football related activity by FIFA following corruption allegations.[5] A power struggle developed at CONCACAF following the allegations against Warner. The allegations against Warner were reported to the FIFA ethics committee by Chuck Blazer, the secretary general of CONCACAF. The acting president of CONCACAF, Lisle Austin, sent Blazer a letter saying he was "terminated as general secretary with immediate effect".[20] Austin described Blazer's actions as "inexcusable and a gross misconduct of duty and judgement" and said the American was no longer fit to hold the post.[21] The executive committee of CONCACAF later issued a statement saying that Austin did not have the authority to fire Blazer, and the decision was unauthorized.[20] On 20 June 2011, Jack Warner resigned from the presidency of CONCACAF, all posts with FIFA, and removed himself from all participation in football, in the wake of the corruption investigation resulting from the 10 May 2011 meeting of the Caribbean Football Union.[6] The vice-president of CONCACAF, Alfredo Hawit, acted as president until May 2012.[7]
Hall of fame
|
|
|
Source:[22]
World Cup participation
- Legend
- 1st – Champion
- 2nd – Runner-up
- 3rd – Third place[23]
- 4th – Fourth place
- QF – Quarterfinals
- R16 – Round of 16 (since 1986: knockout round of 16)
- GS – Group stage (in the 1950, 1974, 1978, and 1982 tournaments, which had two group stages, this refers to the first group stage)
- 1S – First knockout stage (1934–1938 Single-elimination tournament)
- • — Did not qualify
- — Did not enter / withdrew / banned
- — Hosts
World Cup results
Only ten CONCACAF members have ever reached the FIFA World Cup since its inception in 1930, five of them accomplishing the feat only once. No team from the region has ever reached the final at the World Cup, but the United States has reached the semifinal in a FIFA World Cup in the first edition in 1930, where they were awarded third place, and they also reached the quarterfinal round in 2002. Mexico and Cuba have also reached the quarterfinal round. Cuba advanced to the quarterfinals in their only appearance, the 1938 FIFA World Cup. Mexico did so both times they hosted the World Cup, 1970 and 1986.
Costa Rica has been the third most successful team in the men's game. In three World Cup appearances they reached the knockout stage out of a group in 1990 with euro champions Sweden, and eventual champions Brazil. In 2002 in a "group of death" with eventual third place finishers Turkey, Asian champions China, and eventual champions Brazil, the Central Americans missed out on a place in the knockout stage on goal differential. Cuba reached the quarterfinals in 1938, and Jamaica is the smallest country to win a World Cup match.
The following table shows the CONCACAF representatives at each edition of the World Cup, sorted by number of appearances:
| Team | 1930 |
1934 |
1938 |
1950 |
1954 |
1958 |
1962 |
1966 |
1970 |
1974 |
1978 |
1982 |
1986 |
1990 |
1994 |
1998 |
2002 |
2006 |
2010 |
2014 |
2018 |
2022 |
Total | inclusive WC Qual. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | • | GS | GS | GS | GS | GS | QF | • | GS | • | QF | R16 | R16 | R16 | R16 | R16 | R16 | 15 | 17 | |||||
| 3rd | 1S | GS | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | GS | R16 | GS | QF | GS | R16 | R16 | 10 | 18 | ||||
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | R16 | • | • | GS | GS | • | QF | 4 | 14 | ||||||||
| • | • | • | • | GS | • | • | • | • | • | • | GS | GS | 3 | 12 | ||||||||||
| GS | • | • | GS | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | 2 | 11 | |||||||||||
| • | QF | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | 1 | 11 | |||||||||||
| • | • | • | GS | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||
| • | • | • | • | • | GS | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||
| • | • | • | • | • | • | GS | • | • | • | • | 1 | 10 | ||||||||||||
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | GS | • | • | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||
| Total | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 39 |
World Cup hosting
CONCACAF nations have hosted the FIFA World Cup three times.
The 1970 FIFA World Cup took place in Mexico, the first World Cup tournament to be staged in North America, and the first held outside Europe and South America. Mexico was chosen as the host nation in 1964 by FIFA's congress ahead of the only other submitted bid from Argentina.[24] The tournament was won by Brazil. The victorious team led by Carlos Alberto, and featuring players such as Pelé, Gérson, Jairzinho, Rivelino, and Tostão, is often cited as the greatest-ever World Cup team.[25][26][27][28] They achieved a perfect record of wins in all six games in the finals.[29] Despite the issues of altitude and high temperature, the finals produced attacking football which created an average goals per game record not since bettered by any subsequent World Cup Finals.[30][31][32] The 1970 Finals attracted a new record television audience for the FIFA World Cup[33] and, for the first time, in colour.[34][35]
In 1986, Mexico became the first country to host the FIFA World Cup twice when it stepped in to stage the 1986 FIFA World Cup after the original host selection, Colombia, suffered financial problems.[24] Colombia was originally chosen as hosts by FIFA in June 1974. However, the Colombian authorities eventually declared in November 1982 that they could not afford to host the World Cup because of economic concerns. Mexico was selected on 20 May 1983 as the replacement hosts, beating the bids of Canada and the United States, and thereby became the first nation to host two World Cups. This second World Cup in Mexico came 16 years after the first one in 1970.
The United States won the right to host the 1994 FIFA World Cup, defeating bids from Brazil and Morocco.[36] The vote was held in Zurich on July 4, 1988, and only took one round with the United States bid receiving a little over half of the votes by the Exco members.[36] FIFA hoped that by staging the world's most prestigious football tournament there, it would lead to a growth of interest in the sport - one condition FIFA imposed was the creation of a professional football league; Major League Soccer, starting in 1996. The U.S. staged a hugely successful tournament, with average attendance of nearly 69,000 breaking a record that surpassed the 1966 FIFA World Cup average attendance of 51,000 thanks to the large seating capacities the American stadiums provided for the spectators in comparison to the smaller venues of Europe and Latin America. To this day, the total attendance for the final tournament of nearly 3.6 million remains the highest in World Cup history, despite the expansion of the competition to 32 teams at the 1998 World Cup.[37][38]
CONCACAF is considered a favorite to host the 2026 FIFA World Cup, given that Europe will host in 2018, Asia in 2022, and South America is pushing for the 2030 centenary bid.[39]
Women's World Cup results
The following table shows the CONCACAF representatives at each edition of the FIFA Women's World Cup, sorted by number of appearances.
| Team | 1991 |
1995 |
1999 |
2003 |
2007 |
2011 |
2015 |
2019 | Total | inclusive WC Qual. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 3rd | 1st | 3rd | 3rd | 2nd | 6 | 7 | |||
| • | GS | GS | 4th | GS | GS | Q | 6 | 7 | ||
| • | • | GS | • | • | GS | 2 | 7 | |||
| Total | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 14 |
Other international tournaments
FIFA Confederations Cup
| Team | 1992 |
1995 |
1997 |
1999 |
2001 |
2003 |
2005 |
2009 |
2013 |
2017 |
2021 |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| • | • | • | × | GS | • | • | • | • | 1 | |||
| • | 3rd | GS | 1st | GS | • | 4th | • | GS | 6 | |||
| 3rd | • | • | 3rd | • | GS | • | 2nd | • | 4 | |||
| Total | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Copa America
Mexico has finished runners up twice and 3rd place three times at the Copa America making El Tri the most successful non-conmebol nation. The US national team and Honduras have reached the semifinal stage once in the South American tournament, while Costa Rica has reached the quarter finals twice.
Titles by national team
North America
Mexico, the United States, and Canada have not participated in regional union tournaments since 1991.
Regional Honors
- Winners (1): 1990
International Honors
- Gold Medal (1): 1904
Regional Honors
- Winners (1): 2011
International Honors
- Bronze Medal (1): 2012
International Honors
- FIFA World Cup
- FIFA Confederations Cup
- Summer Olympics
- Toulon Tournament
- Winners (1): 2012[40]
Regional Honors
International Honors
International Honors
- FIFA U-17 World Cup
- Winners (2): 2005, 2011
- Runners-up (1): 2013
- Third Place (1): 1930
- Quarterfinals (1): 2002 FIFA World Cup
- Runners-Up (1): 1991
- Gold Medal (1): 1991
- International Honors
- Algarve Cup: 8
- Regional Honors
- Gold Medal (1): 1999
- International Honors
Central America
""International""
- FIFA World Cup :"second round(1)" 1990 FIFA World Cup
- COPA AMERICA :"quarterfinals(2):"
Regional
- Winners (6): 1991 Champions, 1997 Champions, 1999 Champions, 2003 Champions, 2005 Champions, 2007 Champions
- World Cup qualification First place (2): 1990,2002:
- Winners (7): 1941, 1946, 1948, 1953, 1955, 1960, 1961
- Copa America :"third place (1): 2001 Copa America
- CONCACAF Gold Cup :Winners (1): 1981
- UNCAF Nations Cup :Winners (3): 1993 Champions, 1995 Champions, 2011 Champions,
Regional
- Winners (1): 2001 Champions
Regional
- Winners (1): 2009 Champions
Caribbean
""International""
- "Quarterfinals(1):" 1938 FIFA World Cup
Regional
- Winners (1): 1973 Champions
See also
- List of CONCACAF competitions
- Timeline of football
- List of Presidents of CONCACAF
- CONMEBOL
- UEFA
- Confederation of African Football (CAF)
- Asian Football Confederation (AFC)
- Oceania Football Confederation (OFC)
- CONCACAF Awards — In November 2013, CONCACAF announced that they would create annual awards for the best players, coaches, and referees.[41]
- North American Football Confederation
- Confederacion Centroamericana y del Caribe de Futbol
- Soccer in the United States
- Soccer in Canada
- Soccer in Mexico
References
- ^ Spanish: Confederación de Fútbol de Norte, Centroamérica y el Caribe, pronounced [komfeðeɾaˈsjon de ˈfuðβol de ˈnorte ˈsentɾoaˈmeɾika j el kaˈɾiβe]; French: Confédération de football d'Amérique du Nord, d'Amérique centrale et des Caraïbes, pronounced [kɔ̃fedeʁasjɔ̃ də futbɔl dameʁik dy nɔʁ dameʁik sɑ̃tʁal e dɛ kaʁaib]; Portuguese: Confederação de Futebol da América do Norte, Central e Caribe. Dutch uses the English name.
- ^ (/ˈkɒn.kəkæf/ KON-kə-kaf)
- ^ Concacaf Main | CONCACAF Home | About Us | National Associations. Concacaf.com. Retrieved on 2011-10-14.
- ^ http://www.concacaf.com/concacaf/executive-committee
- ^ a b "Bin Hammam and Warner suspended after FIFA investigation". CNN. 29 May 2011.
- ^ a b FIFA announces Jack Warner resignation 20 June 2011. Fifa.com (20 June 2011). Retrieved on 2011-10-14.
- ^ a b "Concacaf Suspends Its Acting President on Eve of Gold Cup". The New York Times. 4 June 2011.
- ^ "CONCACAF Statutes" (pdf). CONCACAF. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ "Hawit: "Concacaf cambiará la sede a Miami"". laprensa.hn. 13 November 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ "CONCACAF tries to oust Blazer". Sport24.co.za. 23 May 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ "CONCACAF appoints Enrique Sanz as General Secretary". CONCACAF.com. 13 July 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ a b http://www.concacaf.com/concacaf
- ^ "Warner Rejects Idea Of Caribbean Team". Jamaica Gleaner. 4 August 1993.
- ^ Big Apple Soccer, 2016 COPA? Webb: CONCACAF 'exploring the possibility of hosting Copa America', Feb. 20, 2013, http://www.bigapplesoccer.com/international/article.php?article_id=32905
- ^ "2013, 2015 CONCACAF Gold Cup winners will play one-off match for 2017 Confederations Cup berth". MLS Soccer. 5 April 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ^ CONCACAF CHAMPIONS LEAGUE REGULATIONS 2013/2014, Rule 3.7, http://www.concacaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/CCL1314-Regulations060313pdf.pdf
- ^ a b c "CONCACAF finances laid bare". thisislondon.co.uk. 23 May 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ a b Panja, Tariq (23 May 2012). "Concacaf Soccer Body Tells Members About Financial Mismanagement". Bloomberg. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ a b "Fifa Exco member Chuck Blazer accused of financial irregularities". Guardian. 22 May 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ a b "Chuck Blazer 'survives sacking attempt', says Concacaf". BBC News Online. 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Concacaf bans president Austin after Blazer 'sacking'". BBC News Online. 4 June 2011.
- ^ "CONCACAF hall of fame". CONCACAF.com.
- ^ There was no Third Place match in 1930; The United States and Yugoslavia lost in the semifinals. FIFA recognizes the United States as the third-placed team and Yugoslavia as the fourth-placed team using the overall records of the teams in the 1930 FIFA World Cup.
- ^ a b "Host Announcement Decision" (PDF). FIFA. 2 December 2010.
- ^ "The Story of the 1970 World Cup". BBC. 12 May 2010.
- ^ "Brazil's 1970 winning team voted best of all time". Reuters. 9 July 2007.
- ^ "The Boys from Brazil: On the trail of football's dream team". The Independent. 10 April 2010.
- ^ "The 10 Greatest Football teams of all time". Daily Mail. 1 May 2009.
- ^ "Netherlands' perfect winning streak can match historic feat of Brazil 1970". Goal.com. 7 July 2010. Archived from the original on 11 July 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Castrol index tournament legends". Castrol Performance Index. Archived from the original on 11 July 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Perfect farewell to Pelé's last appearance in a World Cup". Brasil 2014: World Cup Portal. Archived from the original on 11 July 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "World Championship - Jules Rimet 1970 Cup Technical study" (PDF). FIFA.
- ^ Dunmore, Tom (2011). Historical Dictionary of Soccer. Scarecrow Press. p. 13.
- ^ "1970 FIFA World Cup Mexico". FIFA.
- ^ "40 years since first World Cup in colour". TVlicensing.co.uk.
- ^ a b "FIFA World Cup host announcement decision" (PDF). FIFA.com. Fédération Internationale de Football Association. p. 2. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- ^ "FIFA World Cup competition records" (PDF). FIFA.com. Fédération Internationale de Football Association. p. 2. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- ^ "Previous World Cups", FIFA.com. Retrieved 21 November 2013
- ^ Los Angeles Times, CONCACAF president is pushing hard to land 2026 World Cup, July 7, 2013, http://www.latimes.com/sports/soccer/la-sp-0708-concacaf-world-cup-20130708,0,7446934.story#axzz2w5cPWu69
- ^ Gomez, Eric (1 July 2012). "Mexico U23 3–0 Turkey U23: El Tri win their first Toulon tournament". Goal.com. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ "Inaugural CONCACAF Awards to Be Presented in December". CONCACAF.com. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
External links
- Official website
- CONCACAF Statutes
- Confederation of North Central American & Caribbean Association Football, Soccerlens.com. Retrieved 09/10/2010.
- Template:Dmoz
{{FIFA player}} template missing ID and not present in Wikidata.