Łódź
Łódź
Lodz | |
|---|---|
| |
| Motto: Ex navicula navis ("From a boat a ship") | |
| Coordinates: 51°46′37″N 19°27′17″E / 51.77694°N 19.45472°E | |
| Country | |
| Voivodeship | |
| County | city county |
| First mentioned | 1332 |
| City rights | 1423 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Łódź City Council |
| • City mayor | Hanna Zdanowska (PO) |
| • Sejm of Poland | Łódź |
| Area | |
• City | 293.25 km2 (113.22 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 278 m (912 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 162 m (531 ft) |
| Population (31 December 2021) | |
• City | 670,642 |
| • Density | 2,292/km2 (5,940/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,100,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 90-001 to 94–413 |
| Area code | +48 42 |
| Car plates | EL |
| Primary airport | Łódź Władysław Reymont Airport |
| Highways | |
| Website | www |
Łódź,[a] also rendered in English as Lodz,[b] is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately 120 km (75 mi) south-west of Warsaw.[8] The city's coat of arms is an example of canting, as it depicts a boat (łódź in Polish), which alludes to the city's name. As of 2022, Łódź has a population of 670,642[1] making it the country's fourth largest city.
Łódź was once a small settlement that first appeared in 14th-century records. It was granted town rights in 1423 by Polish King Władysław II Jagiełło and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed to Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vienna. The Second Industrial Revolution (from 1870) brought rapid growth in textile manufacturing and in population owing to the inflow of migrants, notably Germans and Jews. Ever since the industrialization of the area the city has struggled with multinationalism and social inequalities, as documented in the novel The Promised Land by Nobel Prize–winning author Władysław Reymont. The contrasts greatly reflected on the architecture of the city, where luxurious mansions coexisted with red-brick factories and dilapidated tenement houses.[9]
The industrial development and demographic surge made Łódź one of the largest cities in Poland. Under the German occupation during World War II Łódź was briefly renamed Litzmannstadt after Karl Litzmann. The city's population was persecuted and its large Jewish minority was forced into a walled zone known as the Łódź Ghetto, from where they were sent to German concentration and extermination camps. The city became Poland's temporary seat of power in 1945.
Łódź experienced a sharp demographic and economic decline after 1989. It was only in the 2010s that the city began to experience revitalization of its neglected downtown area.[10][11] Łódź is ranked by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network on the “Sufficiency” level of global influence[12] and is internationally known for its National Film School, a cradle for the most renowned Polish actors and directors, including Andrzej Wajda and Roman Polanski.[9] In 2017, the city was inducted into the UNESCO Creative Cities Network and named UNESCO City of Film.[13]
Name and toponymy
The Polish name for the city, Łódź, directly translates to 'boat' in the English language.[14] There is no unanimous consensus on its precise origin, but popular theories link it with the medieval village of Lodzia and the now-canalised River Łódka on which the modern city was founded.[15] It may have also derived from the term łoza denoting a willow tree and the personal Old Polish name Włodzisław.[16]
History
Early beginnings (1332–1815)

Łódź first appears in a 1332 written record issued by Władysław the Hunchback, Duke of Łęczyca, which transferred the village of Lodzia to the Bishopric of Włocławek.[17] The document enumerated the privileges of its inhabitants, notably the right to graze land, establish pastures and engage in logging.[18] In 1423, King of Poland Władysław II Jagiełło officially granted town rights to the village under Magdeburg Law.[19] For centuries, it remained a small remote settlement situated among woodlands and marshes, which was privately held by the Kuyavian bishops.[20] The economy was predominantly driven by agriculture and farming until the 19th century.[21] The earliest two versions of the coat of arms appeared on seal emblems in 1535 and 1577, with the latter illustrating a boat-like vessel and a turned oar.[22]
With the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed by Prussia.[23] In 1798, the Kuyavian bishops' ownership over the region was formally revoked during the secularisation of church property.[24] The town, governed by a burgomaster (burmistrz), at the time had only 190 residents, 44 occupied dwellings, a church and a prison.[18] In 1806, Łódź was incorporated into the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw.[23] In the aftermath of the 1815 Congress of Vienna, the duchy was dissolved and the town became part of the Congress Kingdom of Poland, a client state of the Russian Empire.[25]
Partitions and development (1815–1918)

In 1820, the government of the Congress Kingdom designated Łódź and its rural surroundings for centrally planned industrial development.[26] Rajmund Rembieliński, head of the Administrative Council and prefect of Masovia, became the president of a commission that subdivided the works two major phases; the first (1821–23) comprised the creation of a new city centre with an octagonal square (contemporary plac Wolności; Liberty Square) and arranged housing allotments on greenfield land situated south of the old marketplace; the second stage (1824–28) involved the establishment of cotton mill colonies and a linear street system along with an arterial north-south thoroughfare, Piotrkowska.[26] Many of the early dwellings were timber cottages built for housing weavers (domy tkaczy).[27]
During this time, a sizeable number of German craftsmen settled in the city,[27] encouraged by exemptions from tax obligations.[28] Their settlement in Poland was encouraged by renowned philosopher and statesman Stanisław Staszic, who acted as the director of the Department of Trade, Crafts and Industry.[29]

In 1851, the Imperial authorities abolished a customs barrier which was imposed on Congress Poland following the failed November Uprising (1830–1831).[30] The suppression of tariffs allowed the city to freely export its goods to Russia, where the demand for textiles was high.[30] Poland's first steam-powered loom commenced operations at Ludwik Geyer's White Factory in 1839.[31] During the first weeks of the January Uprising (1863–1864), a unit of 300 Polish insurgents entered the city without resistance and seized weapons, and later on, there were also clashes between Polish insurgents and Russian troops in the city.[32] In 1864, the inhabitants of adjacent villages were permitted to settle in Łódź without restrictions.[33] The development of railways in the region was also instrumental in expanding the textile industry; in 1865 the Łódź–Koluszki line, a branch of the Warsaw–Vienna railway, was opened, thus providing a train connection to larger markets.[34] In 1867, the city was incorporated into the Piotrków Governorate, a local province.[35]
The infrastructure and edifices of Łódź were built at the expense of industrialists and business magnates, chiefly Karl Wilhelm Scheibler and Izrael Poznański, who sponsored schools, hospitals, orphanages, and places of worship.[36] From 1872 to 1892, Poznański established a major textile manufactory composed of twelve factories, power plants, worker tenements, a private fire station, and a large eclectic palace.[37] By the end of the century, Scheibler's Księży Młyn became one of Europe's largest industrial complexes, employing 5,000 workers within a single facility.[38] The years 1870–1890 saw the most intense industrialisation,[39] which was marked by social inequalities and dire working conditions.[40] Łódź soon became a notable centre of the socialist movement and the so-called Łódź rebellion(pl) in May 1892 was quelled by a military intervention.[40]

The turn of the 20th century coincided with cultural and technological progress; in 1899, the first stationary cinema in Poland (Gabinet Iluzji) was opened in Łódź.[41] In the same year, Józef Piłsudski, the future Marshal of Poland, settled in the city and began printing the Robotnik (The Worker; p. 1894–1939), an underground newspaper published by the Polish Socialist Party.[42] During the June Days (1905), approximately 100,000 unemployed labourers went on a mass strike, barricaded the streets and clashed with troops.[43] Officially, 151 demonstrators were killed and thousands were wounded.[44] In 1912, the Archcathedral of St. Stanislaus Kostka was completed and its tower[c] at 104 metres (341 ft) is one of the tallest in Poland.[45][46]
Despite the impending crisis preceding World War I, Łódź grew exponentially and was one of the world's most densely populated industrial cities, with a population density of 13,200 inhabitants per square kilometre (34,000/sq mi) by 1914.[47] In the aftermath of the Battle of Łódź (1914), the city came under Imperial German occupation on 6 December.[48] With Polish independence restored in November 1918, the local population disarmed the German army.[49] Subsequently, the textile industry of Łódź stalled and its population briefly decreased as ethnic Germans left the city.[50]
Restored Poland (1918–1939)

Despite its large population and economic output, Łódź did not serve as the seat of its province until the 20th century.[51] Following the establishment of the Second Polish Republic, it became the capital of the Łódź Voivodeship in 1919.[52] The early interwar period was characterised by considerable economic hardship and industrial stagnation.[53] The Great Depression and the German–Polish customs war closed western markets to Polish textiles while the Bolshevik Revolution and the Civil War in Russia put an end to the most profitable trade with the East.[53][52]
Because of rapid and, consequently, chaotic development in the previous century, Łódź did not possess the adequate infrastructure and living standards for its inhabitants.[54] Pollution was acute, sanitary conditions were poor and the authorities did not invest in a sewage treatment system until the 1920s.[55][56] From 1918 to 1939, many cultural, educational and scientific institutions were created, including elementary schools, museums, art galleries and public libraries which prior to the First World War did not exist.[57] Łódź also began developing an entertainment scene, with 34 movie theatres opened by 1939.[57] On 13 September 1925, the city's first airport, Lublinek, commenced operations.[58] In 1930, the first radio transmission from a newly-founded broadcasting station took place.[59]
The ideological orientation of Łódź was strongly left-wing and the city was a notable centre of socialist, communist and bundist activity in Polish politics during the interbellum.[60]
Second World War (1939–1945)

During the invasion of Poland in September 1939, the Polish forces of General Juliusz Rómmel's Army Łódź defended the city against the German assault by forming a line of resistance between Sieradz and Piotrków Trybunalski.[61] The attack was perpetrated by the 8th Army of Johannes Blaskowitz, who encircled the city with the X Army Corps.[62] After fierce resistance, a Polish delegation surrendered to the Nazis on 8 September, and the first Wehrmacht troops entered in the early hours of 9 September.[63] The German Einsatzgruppe III paramilitary death squad entered the city on 12 September.[64] Arthur Greiser incorporated Łódź into a new administrative subdivision of Nazi Germany called Reichsgau Wartheland on 9 November 1939,[65] and on 11 April 1940 the city was renamed to Litzmannstadt after German general and NSDAP member Karl Litzmann.[66]
The city became subjected to immediate Germanisation, with Polish and Jewish establishments closed, and Polish-language press banned.[67] Low-wage forced labour was imposed on the city's inhabitants aged 16 to 60; many were subsequently deported to Germany.[68] As part of the Intelligenzaktion, Polish intellectuals from the city and region were imprisoned at Radogoszcz and then either sent to concentration camps or murdered in the forests of Łagiewniki and the village of Lućmierz-Las.[69] Polish children were forcibly taken from their parents,[70] and from 1942 to 1945 the German Sicherheitspolizei operated a camp for kidnapped Polish children from various regions in Łódź.[71]
The Nazi authorities established the Łódź Ghetto (Ghetto Litzmannstadt) in the city and populated it with more than 200,000 Jews from the region, who were systematically sent to German extermination camps.[72] It was the second-largest ghetto in occupied Europe,[73] and the last major ghetto to be liquidated, in August 1944.[74] The Polish resistance movement (Żegota) operated in the city and aided the Jewish people throughout its existence.[75] However, only 877 Jews were still alive by 1945.[76] Of the 223,000 Jews in Łódź before the invasion, 10,000 survived the Holocaust in other places.[77] The Germans also created camps for non-Jews, including the Romani people deported from abroad, who were ultimately murdered at Chełmno,[78] as well as a penal forced labour camp,[79] four transit camps for Poles expelled from the city and region, and a racial research camp.[80]
Contemporary times (1945–present)

Following the end of the Second World War, Łódź informally and temporarily took over the functions of Poland's capital, and most of the government and country administration resided in the city prior to Warsaw's reconstruction.[81] Łódź also experienced an influx of refugees from eastern territories annexed by the Soviet Union; many migrated into its suburbs and occupied empty – formerly Jewish – properties.[81] Under the Polish People's Republic, the city's industry and private companies were nationalised.[81] On 24 May 1945, the University of Łódź was inaugurated.[82] On 8 March 1948, the National Film School was opened, later becoming Poland's primary academy of drama and cinema.[83]
Post-war spatial and urban planning was conducted in accordance with the Athens Charter, where the population from the old core was relocated into new residential zones.[84] However, as a result, the inner-city and historical areas fell in significance and degenerated into a slum.[84] A number of extensive panel block housing estates (including Retkinia, Teofilów, Widzew, Radogoszcz and Chojny) were constructed between 1960 and 1990, covering an area of almost 30 square kilometres (12 sq mi) and accommodating a large part of the populace.[85]
In mid-1981 Łódź became famous for its massive hunger demonstration of local mothers and their children.[86][87] After the period of economic transition during the 1990s, most enterprises were again privatised.
Geography
Łódź covers an area of approximately 293 square kilometres (113 sq mi) and is located in the centre of Poland.[88] The city lies in the lowlands of the Central European Plain, not exceeding 300 metres in elevation.[88] Topographically, the Łódź region is generally characterised by a flat landscape, with only several highlands which do not exceed 50 metres above the terrain level.[89] The soil is predominantly sandy (62%) followed by clay (24%), silt (8%), and organogenic formations (6%) from regional wetlands.[90] The forest cover (equivalent to 4.2% of the whole country) is considerably low compared to other cities, regions, and provinces of Poland.[91]
Climate
Łódź has a humid continental climate (Dfb in the Köppen climate classification).
| Climate data for Łódź, elevation: 68 m (223 ft), 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.8 (55.0) |
17.5 (63.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
29.9 (85.8) |
32.7 (90.9) |
36.3 (97.3) |
37.3 (99.1) |
37.6 (99.7) |
34.7 (94.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
37.6 (99.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
2.9 (37.2) |
7.4 (45.3) |
14.4 (57.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
6.8 (44.2) |
2.4 (36.3) |
13.2 (55.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.5 (29.3) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
3.1 (37.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.1 (62.8) |
19.2 (66.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
13.7 (56.7) |
8.6 (47.5) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.0 (24.8) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
3.6 (38.5) |
8.2 (46.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
13.6 (56.5) |
13.3 (55.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
5.0 (41.0) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
4.6 (40.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.1 (−24.0) |
−27.4 (−17.3) |
−21.9 (−7.4) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−24.6 (−12.3) |
−31.1 (−24.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 35.3 (1.39) |
34.1 (1.34) |
37.6 (1.48) |
35.2 (1.39) |
60.9 (2.40) |
62.3 (2.45) |
81.1 (3.19) |
54.1 (2.13) |
53.4 (2.10) |
44.0 (1.73) |
39.4 (1.55) |
40.7 (1.60) |
578.1 (22.76) |
| Average extreme snow depth cm (inches) | 6.8 (2.7) |
6.6 (2.6) |
4.7 (1.9) |
1.6 (0.6) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.1) |
2.2 (0.9) |
3.6 (1.4) |
6.8 (2.7) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 17.27 | 14.60 | 14.17 | 11.17 | 13.33 | 13.43 | 13.77 | 11.80 | 11.73 | 13.03 | 14.30 | 16.37 | 164.97 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0 cm) | 15.3 | 13.3 | 6.2 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 8.6 | 47.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87.6 | 84.2 | 77.5 | 68.6 | 70.0 | 70.5 | 71.3 | 71.4 | 78.9 | 84.1 | 89.2 | 89.4 | 78.6 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 48.2 | 65.8 | 122.7 | 187.0 | 241.8 | 244.6 | 250.9 | 243.4 | 160.1 | 111.1 | 51.2 | 40.4 | 1,767.3 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Source 1: Institute of Meteorology and Water Management[92][93][94][95][96][97][98][99] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteomodel.pl (records, relative humidity 1991–2020),[100][101][102] WeatherAtlas (UV)[103] | |||||||||||||
Districts
Łódź was previously subdivided into five boroughs (dzielnica): Bałuty, Widzew, Śródmieście, Polesie, Górna.
However, the city is now divided into 36 osiedla ('districts'): Bałuty-Centrum, Bałuty-Doły, Bałuty Zachodnie, Julianów-Marysin-Rogi, Łagiewniki, Radogoszcz, Teofilów-Wielkopolska, Osiedle Wzniesień Łódzkich, Chojny, Chojny-Dąbrowa, Górniak, Nad Nerem, Piastów-Kurak, Rokicie, Ruda, Wiskitno, Osiedle im. Józefa Montwiłła-Mireckiego, Karolew-Retkinia Wschód, Koziny, Lublinek-Pienista, Retkinia Zachód-Smulsko, Stare Polesie, Zdrowie-Mania, Złotno, Śródmieście-Wschód, Osiedle Katedralna, Andrzejów, Dolina Łódki, Mileszki, Nowosolna, Olechów-Janów, Stary Widzew, Stoki, Widzew-Wschód, Zarzew, and Osiedle nr 33.
Demographics

| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 620,273 | — |
| 1960 | 709,698 | +14.4% |
| 1970 | 762,699 | +7.5% |
| 1980 | 835,658 | +9.6% |
| 1990 | 848,258 | +1.5% |
| 2000 | 798,418 | −5.9% |
| 2010 | 737,098 | −7.7% |
| 2020 | 672,185 | −8.8% |
| source[104] | ||
According to Statistics Poland (GUS), Łódź was inhabited by 672,185 people and had a population density of 2,292 persons per square kilometre (5,940/sq mi), as of December 2020.[105] Approximately 55.7 percent of inhabitants are of working age (18–64 years), which is a considerable decrease from 64.1 percent in 2010.[106] An estimated 29.1 percent is of post-working age compared to 21.8 percent ten years earlier.[107] In 2020, 54.39 percent (365,500) of all residents were women.[107] Łódź has one of the highest feminisation rates among Poland's major cities, a legacy of the city's industrial past, when the textile factories attracted large numbers of female employees.[108]
At its peak in 1988 the population was around 854,000,[109] however, the it has since declined due to low fertility rates, outward migration and a lower life expectancy than in other parts of Poland.[110] Łódź was the country's second largest city until 2007, when it lost its position to Kraków.[108] A major contributing factor was the abrupt transition from socialist to market-based economy after 1989 and the resulting economic crisis,[111] but the economic growth which followed has not reversed the trend.[112] Depopulation and ageing are a major impediments for the future development of the city, putting strain on social infrastructure and medical services.[108]
Historically, Łódź was multi-ethnic and its diverse population comprised migrants from other regions of Europe. In 1839, approximately 78 percent (6,648) of the total population was German. In 1913, Łódź had a population of 506,100 people, of whom 251,700 (49.7%) were Poles, 171,900 (34%) were Jews, 75,000 (14.8%) were Germans, and 6,300 (1.3%) were Russians.[113] According to the 1931 Polish census, the total population of 604,000 included 375,000 (59%) Poles, 192,000 (32%) Jews and 54,000 (9%) Germans. By 1939, the Jewish minority had grown to well over 200,000.[114]
Places of interest

The most notable and recognizable landmark of the city is Piotrkowska Street, which remains the high-street and main tourist attraction in the city, runs north to south for a little over five kilometres (3.1 miles). This makes it one of the longest commercial streets in the world. Most of the building façades, many of which date back to the 19th century, have been renovated.[115] It is the site of most restaurants, bars and cafes in Łódź's city centre.
Many neglected tenement houses throughout the entire city centre have been renovated in recent years as part of the ongoing revitalization project run by the local authorities.[116] The best example of urban regeneration in Łódź is the Manufaktura complex, occupying a large area of a former cotton factory dating back to the nineteenth century.[117] The site, which was the heart of Izrael Poznański's industrial empire, now hosts a shopping mall, numerous restaurants, 4-star hotel, multiplex cinema, factory museum, bowling and fitness facilities and a science exhibition centre.[118] Opened in 2006, it quickly became a centre of cultural entertainment and shopping,[118] as well as a recognizable city landmark attracting both domestic and foreign tourists.[117] The city is also likely to receive a large boost in terms of tourism once the massive revitalization project of the city's downtown (worth 4 billion PLN) is completed.[11] The local government's efforts to transform the former industrial city into a thriving urban environment and tourist destination formed the basis for the city's failed bid to organise the 2022 International EXPO exhibition on the subject of urban renewal.[119]

Łódź has one of the best museums of modern art in Poland. Muzeum Sztuki has three branches, two of which (ms1 and ms2) display collections of 20th and 21st-century art. The newest addition to the museum, ms2 was opened in 2008 in the Manufaktura complex.[120] The unique collection of the Museum is presented in an unconventional way: instead of a chronological lecture on the development of art, works of art representing various periods and movements are arranged into a story touching themes and motifs important for the contemporary public. The third branch of Muzeum Sztuki, located in one of the city's many industrial palaces, also has more traditional art on display, presenting works by European and Polish masters such as Stanisław Wyspiański and Henryk Rodakowski.[121]

Among the 14 registered museums to be found in Łódź,[122] there is the independent Book Art Museum, awarded the American Printing History Association's Institutional Award for 2015 for its outstanding contribution to the study, recording, preservation, and dissemination of printing history in Poland over the last 35 years.[123] Other notable museums include the Central Museum of Textiles with its open-air display of wooden architecture, the Cinematography Museum, located in Scheibler Palace, and the Museum of Independence Traditions, occupying the building of a historical Tsarist prison from the late 19th century.[120] A more unusual establishment, the Dętka museum offers tourists a chance to visit the municipal sewer designed in the early years of the 20th century by the British engineer William Heerlein Lindley.

Łódź also provides plenty of green spaces for recreation. Woodland areas cover 9.61% of the city, with parks taking up an additional 2.37% of the area of Łódź (as of 2014).[124] Las Łagiewnicki ('Łagiewnicki Forest'), the largest forest within city limits, is referred to in scholarship as "the largest forested area within the administrative borders of any city in Europe."[125] It has an area of 1,245 ha[124] and is cut across by a number of hiking trails that traverse the hilly landscape on the western edge of Łódź Hills Landscape Park.[126] A "natural complex which has remained nearly intact as oak-hornbeam and oak woodland,"[125] the forest is also rich in history, and its attractions include a Franciscan friary dating back to the early 18th century and two 17th-century wooden chapels.[127] Out of a total of 44 parks in Łódź (as of 2014), 11 have historical status, the oldest of them dating back to the middle of the 19th century.[128] The largest of these, Józef Piłsudski Park (188.21 hectares (0.7267 sq mi)),[124] is located near the Łódź Zoo and the city's botanical garden, and together with them it comprises an extensive green complex known as Zdrowie serving the recreational needs of the city. Another notable park located in Łódź is the Józef Poniatowski Park.

The Jewish Cemetery at Bracka Street, one of the largest of its kind in Europe, was established in 1892. After the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany in 1939, this cemetery became a part of Łódź's eastern territory known as the enclosed Łódź ghetto (Ghetto Field). Between 1940 and 1944, approximately 43,000 burials took place within the grounds of this rounded-up cemetery.[129] In 1956, a monument by Muszko in memory of the victims of the Łódź Ghetto was erected at the cemetery. It features a smooth obelisk, a menorah, and a broken oak tree with leaves stemming from the tree (symbolizing death, especially death at a young age). As of 2014,[update] the cemetery has an area of 39.6 hectares (98 acres). It contains approximately 180,000 graves, approximately 65,000 labelled tombstones, ohels and mausoleums. Many of these monuments have significant architectural value; 100 of these have been declared historical monuments and have been in various stages of restoration. The mausoleum of Izrael and Eleanora Poznański is perhaps the largest Jewish tombstone in the world and the only one decorated with mosaics.[130][131]
Economy and infrastructure

Before 1990, the economy of Łódź was heavily reliant on the textile industry, which had developed in the city in the nineteenth century owing to the abundance of rivers used to power the industry's fulling mills, bleaching plants and other machinery.[132] Because of the growth in this industry, the city has sometimes been called the "Polish Manchester"[133] and the "lingerie capital of Poland".[134] As a result, Łódź grew from a population of 13,000 in 1840 to over 500,000 in 1913. By the time right before World War I Łódź had become one of the most densely populated industrial cities in the world, with 13,280 inhabitants per km2, and also one of the most polluted. The textile industry declined dramatically in 1990 and 1991, and no major textile company survives in Łódź today. However, countless small companies still provide a significant output of textiles, mostly for export. Łódź is no longer a significant industrial centre, but it has become a major hub for the business services sector in Poland owing to the availability of highly skilled workers and active cooperation between local universities and the business sector.[135]

The city benefits from its central location in Poland. A number of firms have located their logistics centres in the vicinity. Two motorways, A1 spanning from the north to the south of Poland, and A2 going from the east to the west, intersect northeast of the city. As of 2012[update], the A2 is complete to Warsaw and the northern section of A1 is largely completed. With these connections, the advantages of the city's central location should increase even further. Work has also begun on upgrading the railway connection with Warsaw, which reduced the 2-hour travel time to make the 137 km (85 mi) journey 1.5 hours in 2009. As of 2018, travel time from Łódź to Warsaw is around 1.2 hours with the modern Pesa SA Dart trains.[136]
Recent years have seen many foreign companies opening and establishing their offices in Łódź. The Indian IT company Infosys has one of its centres in the city. In January 2009 Dell announced that it will shift production from its plant in Limerick, Ireland to its plant in Łódź, largely because the labour costs in Poland are a fraction of those in Ireland.[137] The city's investor friendly policies have attracted 980 foreign investors by January 2009.[137] Foreign investment was one of the factors which decreased the unemployment rate in Łódź to 6.5 percent in December 2008, from 20 percent four years earlier.[137]
Transport
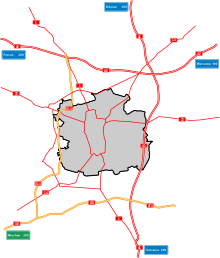

Łódź is situated near the geographical centre of Poland, only a short distance away from the motorway junction in Stryków where the two main north–south (A1) and east–west (A2) Polish transport corridors meet, which positions the city on two of the ten major trans-European routes: from Gdańsk to Žilina and Brno and from Berlin to Moscow via Warsaw.[138] It is also part of the New Silk Road,[139] a regular cargo rail connection with the Chinese city of Chengdu operating since 2013.[140] Łódź is served by the national motorway network, an international airport, and long-distance and regional railways. It is at the centre of a regional and commuter rail network operating from the city's various train stations. Bus and tram services are operated by a municipal public transport company. There are 193 km (120 mi) of bicycle routes throughout the city (as in January 2019).[141]
Major roads include:
- A1: Gdańsk – Toruń – Łódź – Częstochowa – Cieszyn (national border)
- A2: Świecko (national border) – Poznań – Łódź – Warszawa
- S8: Wrocław – Sieradz – Łódź – Piotrków Trybunalski – Warszawa – Białystok
- S14: Pabianice – Konstantynów Łódzki – Aleksandrów Łódzki – Zgierz
- DK14: Łowicz – Stryków – Łódź – Zduńska Wola – Sieradz – Złoczew – Walichnowy
- DK72: Konin – Turek – Poddębice – Łódź – Brzeziny – Rawa Mazowiecka
- DK91: Gdańsk – Tczew – Toruń – Łódź – Piotrków Trybunalski – Radomsko – Częstochowa
Airport
The city has an international airport: Łódź Władysław Reymont Airport located 6 kilometres (4 miles) from the city centre. Flights connect the city with destinations in Europe including Turkey.[142] In 2014 the airport handled 253,772 passengers.[143] It is the 8th largest airport in Poland.[144][circular reference]
Public Transport

The Municipal Transport Company – Łódź (Miejskie Przedsiębiorstwo Komunikacyjne – Łódź), owned by the Łódź City Government, is responsible for operating 58 bus routes and 19 tram lines.[145][146]
Rail
Łódź has a number of long distance and local railway stations. There are two main stations in the city, but with no direct rail connection between them—a legacy of 19th-century railway network planning. Originally constructed in 1866, the centrally-located Łódź Fabryczna was a terminus station for a branch line of the Warsaw-Vienna railway,[147] whereas Łódź Kaliska was built more than thirty years later on the central section of the Warsaw-Kalisz railway. For this reason most intercity train traffic goes to this day through Łódź Kaliska station, despite its relative distance from the city centre, and Łódź Fabryczna serves mainly as a terminal station for trains to Warsaw. The situation will be remedied in 2021 after the construction of a tunnel connecting the two,[148] which is likely to make Łódź Poland's main railway hub.[149] The tunnel will additionally serve Łódź Commuter Railway, providing a rapid transit system for the city, dubbed the Łódź Metro by the media and local authorities.[150] Two new stations are to be constructed on the underground line, one serving the needs of the Manufaktura complex and the other located in the area of Piotrkowska Street.[150]
In December 2016, a few years after the demolition of the old building of Łódź Fabryczna station, a new underground station was opened.[149] It is considered to be the largest and most modern of all train stations in Poland and is designed to handle increased traffic after the construction of the tunnel.[151] It also serves as a multimodal transport hub, featuring an underground intercity bus station, and is integrated with a new transport interchange serving taxis and local trams and buses.[152] The construction of the new Łódź Fabryczna station was part of a broader project of urban renewal known as Nowe Centrum Łodzi (New Centre of Łódź).[153]
The third-largest train station in Łódź is Łódź Widzew. There are also many other stations and train stops in the city, many of which were upgraded as part of the Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna commuter rail project. The rail service, founded as part of a major regional rail upgrade and owned by Łódź Voivodeship, operates on routes to Kutno, Sieradz, Skierniewice, Łowicz, and on selected days to Warsaw, with plans for further expansion after the construction of the tunnel.[154]
Education
Łódź is a thriving center of academic life. Currently Łódź hosts three major state-owned universities, six higher education establishments operating for more than a half of the century, and a number of smaller schools of higher education. The tertiary institutions with the most students in Łódź include:
- University of Łódź (UŁ – Uniwersytet Łódzki)
- Lodz University of Technology (PŁ – Politechnika Łódzka)
- Medical University of Łódź (Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi)
- National Film School in Łódź (Państwowa Wyższa Szkoła Filmowa, Telewizyjna i Teatralna w Łodzi)
- Academy of Music in Łódź (Akademia Muzyczna im. Grażyny i Kiejstuta Bacewiczów w Łodzi)
- Academy of Fine Arts In Łódź (Akademia Sztuk Pięknych im. Wł. Strzemińskiego w Łodzi)
In the 2018 general ranking of state-owned tertiary education institutions in Poland, the University of Łódź came 20th (6th place among universities) and Lodz University of Technology 12th (6th place among technical universities). The Medical University of Łódź was ranked 5th among Polish medical universities. Leading courses taught in Łódź include administration (3rd place), law (4th) and biology (4th).[155]
There is also a number of private-owned institutions of higher learning in Łódź. The largest of these are the University of Social Sciences (Społeczna Akademia Nauk) and the University of Humanities and Economics in Łódź (Akademia Humanistyczno-Ekonomiczna w Łodzi). In the 2018 ranking of private universities in Poland the former was ranked 9th, and the latter 23rd.[155]
National Film School in Łódź
The Leon Schiller National Higher School of Film, Television and Theatre in Łódź (Państwowa Wyższa Szkoła Filmowa, Telewizyjna i Teatralna im. Leona Schillera w Łodzi) is the most notable academy for future actors, directors, photographers, camera operators and TV staff in Poland. It was founded on 8 March 1948 and was initially planned to be moved to Warsaw as soon as the city was rebuilt following the Warsaw Uprising. However, in the end the school remained in Łódź and today is one of the best-known institutions of higher education in the city.
At the end of the Second World War Łódź remained the only large Polish city besides Kraków which war had not destroyed. The creation of the National Film School gave Łódź a role of greater importance from a cultural viewpoint, which before the war had belonged exclusively to Warsaw and Kraków. Early students of the School include the directors Andrzej Munk, Roman Polanski, Andrzej Wajda, Kazimierz Karabasz (one of the founders of the so-called Black Series of Polish Documentary) and Janusz Morgenstern, who at the end of the 1950s became famous as one of the founders of the Polish Film School of Cinematography.[156]
Culture
Museums in Łódź
- Archaeological and Ethnographical Museum
- Book Art Museum
- Central Museum of Textiles
- City of Lodz History Museum
- Film Museum
- Herbst Palace Museum
- Muzeum Sztuki (Museum of Art)
- Natural History Museum, University of Łódź
- Muzeum Tradycji Niepodległościowych (Independence Traditions Museum) with three parts:
- Radegast train station
- Mausoleum and museum in Radogoszcz – Radogoszcz prison
- exhibition Kuźnia Romów (Roma forge) in former Łódź Ghetto
- Se-ma-for museum of stop-motion film animation
- The Centre for Science and Technology EC1 in former Łódź power plant
Łódź in literature and cinema
Three major novels depict the development of industrial Łódź: Władysław Reymont's The Promised Land (1898), Joseph Roth's Hotel Savoy (1924) and Israel Joshua Singer's The Brothers Ashkenazi (1937). Roth's novel depicts the city on the eve of a workers' riot in 1919. Reymont's novel was made into a film by Andrzej Wajda in 1975. In the 1990 film Europa Europa, Solomon Perel's family flees pre-World War II Berlin and settles in Łódź. Scenes of David Lynch's 2006 film Inland Empire were shot in Łódź. Paweł Pawlikowski's film Ida was partially shot in Łódź. Sections of Harry Turtledove's Worldwar alternate history series take place in Łódź, and, in John Birmingham's Axis of Time alternate history trilogy, Łódź gains the unfortunate historical notoriety of becoming the first city to be destroyed by an Atomic Bomb when the USSR destroys the city on 5 June 1944. Łódź. Chava Rosenfarb’s Yiddish trilogy “The Tree of Life” (1972; English translation 1985) portrays life within the Łódź Ghetto.
Sport

The city has experience as a host for international sporting events such as the 2009 EuroBasket,[157] the 2011 EuroBasket Women, the 2014 FIVB Volleyball Men's World Championship and the 2019 FIFA U-20 World Cup, with the opening and final of the latter taking place at Stadion Widzewa. Łódź will also host the sixth edition of the European Universities Games in 2022.[158]
Under communism it was common for clubs to participate in many different sports for all ages and sexes. Many of these traditional clubs still survive today. Originally they were owned directly by a public body, but now they are independently operated by clubs or private companies. However they get public support through the cheap rent of land and other subsidies from the city. Some of their sections have gone professional and separated from the clubs as private companies. For example, Budowlani S.A is a private company that owns the only professional rugby team in Łódź, while Klub Sportowy Budowlani remains a community amateur club.
- Budowlani Łódź – rugby (six times Polish champions), hockey, wrestling, volleyball
- ŁKS Łódź – association football (two times Polish champions), basketball (Polish champions 1953), volleyball (two times Polish champions), handball, boxing
- SMS Łódź[159] – association football, volleyball, basketball
- KS Społem Łódź – road and track cycling
- SKS Start Łódź[160] – football, swimming
- Widzew Łódź – association football (four time Polish champions, semi-finalists of the 1982–83 European Cup)
In Ekstraklasa of Polish beach soccer Łódź have three professional clubs: Grembach, KP and BSCC.
Horticultural Expo 2029
Łódź bid for the Specialized Expo 2022/2023 but lost out to Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Łódź was planned to host the Horticultural Expo in 2024. However, multiple Expo events were delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a Horticultural Expo in Doha, Qatar from 2021/22 to 23/24 among them.[161] As a result, the Horticultural Expo in Łódź has been rescheduled to 2029 to maintain a required time interval between them.[162]
Notable residents







- Daniel Amit (1938–2007), Israeli physicist
- Yehuda Ashlag (1885–1954), also known as the Baal Ha-Sulam, Rabbi
- Grażyna Bacewicz (1909–1969), composer[163]
- Aleksander Bardini (1913–1995), theatre director and actor[164]
- Andrzej Bartkowiak (born 1950), cameraman and film director[165]
- Jurek Becker (1937–1997), writer[166]
- Sylwester Bednarek (born 1989), high jumper
- Marek Belka (born 1952), politician, former Prime Minister, Finance Minister of Poland, member European Parliament[167]
- Karolina Bielawska (born 1999), model and Miss World 2021
- Kazimierz Brandys (1916–2000), writer[168]
- Artur Brauner (1918–2019), film producer
- Edward Gustave Brisch (1901–1960), industrial coding and classification expert. He was the designer of the Brisch Classification, widely known and used in building and engineering.
- Jacob Bronowski (1908–1974), writer, mathematician, and Britain's leading academic TV figure of the 1970s.
- Sabina Citron (born 1928), Holocaust survivor, activist, and author
- Bat-Sheva Dagan (born 1925), Holocaust survivor, teacher, psychologist, author[169]
- Karl Dedecius (1921–2016), translator[170]
- Elizabeth Diller (born 1954), American architect
- Karl Dominik (born 1980), China's first Chinese speaking Polish actor
- Marek Edelman (1919/1922–2009), Holocaust survivor, one of the leaders of the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, Solidarity activist, Polish politician, human rights activist
- Jacob Eisner (born 1947), Israeli basketball player
- Max Factor Sr. (1877–1938), businessman, founder of the Max Factor cosmetics company[171]
- Dov Freiberg (1927–2008), Holocaust survivor and writer
- Magdalena Fręch (born 1997), tennis player[172]
- Joseph Friedenson (1922–2013), Holocaust survivor and writer
- Piotr Fronczewski (born 1946), Polish actor
- Maciej Golubiewski (born 1976), Polish political scientist and diplomat, Consul General at the Consulate General of the Republic of Poland in New York City
- Marcin Gortat (born 1984), NBA basketball player for the Washington Wizards[173]
- Mendel Grossman (1913–1945), Łódź ghetto photographer [174]
- Józef Hecht (1891–1951), engraver and printmaker[175]
- Jerzy Janowicz (born 1990), tennis player[176]
- Josef Joffe (born 1944), journalist
- Michał Kalecki (1899–1970), Marxian economist, "one of the most distinguished economists of the 20th century"
- Roman Kantor (1912–1943), épée fencer, Nordic champion and Soviet champion; killed by the Nazis
- Jan Karski (1914–2000), diplomat and anti-nazi resistant[177]
- Aharon Katzir (1914–1972), Israeli pioneer in study of electrochemistry of biopolymers; killed in Lod Airport Massacre
- Lea Koenig (born 1929), Israeli actress
- Paul Klecki (1900–1973), conductor
- Katarzyna Kobro (1898–1951), sculptor[178]
- Jerzy Kosinski (1933–1991), writer[179]
- Jan Kowalewski (1892–1965), cryptologist who broke Soviet military codes, and ciphers during the Polish-Soviet War
- Karolina Kowalkiewicz (born 1985), UFC Strawweight Title challenger
- Feliks W. Kres (born 1966), fantasy writer
- Anna Lewandowska (born 1988), karateka and nutrition expert
- Nathan Lewin, Washington, D.C. attorney
- Daniel Libeskind (born 1946), architect[180]
- Tadeusz Miciński (1873–1918), poet
- Stanisław Mikulski (1929–2014), actor
- Ruth Minsky Sender (born 1926), author and survivor
- Zew Wawa Morejno (1916–2011), Chief Rabbi
- Henry Morgentaler (1923–2013), physician
- Konstantin Petrovich Nechaev (1883–1946), White movement leader and mercenary commander in China
- Zbigniew Nienacki (1929–1994), writer
- Marek Olędzki (born 1951), archaeologist
- Marian P. Opala (1921–2010), Oklahoma Supreme Court Justice
- Adam Ostrowski (born 1980), better known as O.S.T.R., rapper
- Adam Palma (born 1974), Polish-British guitarist and teacher
- Władysław Pasikowski (born 1959), film director
- Roman Polanski (born 1933), cinema director, Oscar and Golden Palm winner[181]
- Piotr Pustelnik (born 1951), alpine and high-altitude climber, the 20th man to climb all 14 eight-thousanders.
- Ze'ev Raban (1890–1970), Israeli painter and sculptor
- Adolph Moses Radin (1848–1909), rabbi
- Damian Radowicz (born 1989), footballer
- Władysław Reymont (1867–1925), writer, Nobel Prize winner
- Joseph Rotblat (1908–2005), physicist, Nobel Prize winner
- Stefan Rozental (1903–1994), nuclear physicist
- Artur Rubinstein (1887–1982), pianist[182]
- Arnold Rutkowski, opera singer
- Zbigniew Rybczyński (born 1949), animator and Oscar winner[183]
- Marek Saganowski (born 1978), football player
- Andrzej Sapkowski (born 1948), fantasy writer[184]
- Carl Wilhelm Scheibler (1820–1881), one of the most important Łódź industrialists
- Euzebiusz Smolarek (born 1981), football player
- Piotr Sobociński (1958–2001), cinematographer
- Andrzej Sontag (born 1952), track-and-field athlete
- Natan Spigel (1900–1942), painter
- Władysław Strzemiński (1893–1952), painter, Katarzyna Kobro's husband[185]
- Borys Szyc (born 1978), actor and musician
- Arthur Szyk (1894–1951), artist
- Adam Szymczyk (born 1970), art critic and curator
- Aleksander Tansman (1897–1986), composer and pianist
- Jack Tramiel (1928–2012), computer manufacturer, the founder of Commodore[186]
- Julian Tuwim (1894–1953), poet
- Andrzej Udalski (born 1957), astronomer and astrophysicist
- Miś Uszatek, cartoon character
- Michał Wiśniewski (born 1972), singer
- Paweł Zatorski (born 1990), volleyball player, double World Champion
- Hanna Zdanowska (born 1959), politician, Mayor of Łódź[187]
- Aleksandra Ziółkowska-Boehm (born 1949), writer
International relations
Łódź is home to nine foreign consulates, all of which are Honorary. They are subordinate to the following states' main representation in Poland: French, Danish, German, Austrian, British, Belgian, Latvian, Hungarian and Moldavian.
Twin towns – sister cities
 Chemnitz in Germany (since 1972)[189]
Chemnitz in Germany (since 1972)[189] Stuttgart in Germany (since 1988)[190]
Stuttgart in Germany (since 1988)[190] Lyon in France (since 1991)[191]
Lyon in France (since 1991)[191] Vilnius in Lithuania (since 1991)[192][193]
Vilnius in Lithuania (since 1991)[192][193] Odessa in Ukraine (since 1993)[194][195]
Odessa in Ukraine (since 1993)[194][195] Tel Aviv in Israel (since 1994)[196]
Tel Aviv in Israel (since 1994)[196] Rustavi in Georgia (since 1995)[197][198]
Rustavi in Georgia (since 1995)[197][198] Barreiro in Portugal (since 1996)[199]
Barreiro in Portugal (since 1996)[199] Tampere in Finland (since 1996)[200]
Tampere in Finland (since 1996)[200] Puebla in Mexico (since 1996)[201]
Puebla in Mexico (since 1996)[201] Murcia in Spain (since 1999)[202]
Murcia in Spain (since 1999)[202] Örebro in Sweden (since 2001)[203]
Örebro in Sweden (since 2001)[203] Lviv in Ukraine (since 2003)[204]
Lviv in Ukraine (since 2003)[204] Denizli in Turkey (since 2005)[205]
Denizli in Turkey (since 2005)[205] Szeged in Hungary (since 2008)[206]
Szeged in Hungary (since 2008)[206] Guangzhou in People's Republic of China (since 2014)
Guangzhou in People's Republic of China (since 2014) Chengdu in People's Republic of China (since 2015)
Chengdu in People's Republic of China (since 2015)
Łódź belongs also to the Eurocities network.
After the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Łódź terminated the partnership with Russian cities Ivanovo and Kaliningrad, and with Minsk, the capital of Belarus on 2 March 2022.[207]
See also
Explanatory notes
References
Inline citations
- ^ a b "Local Data Bank". Statistics Poland. Retrieved 10 July 2022. Data for territorial unit 1061000.
- ^ "Łódź". Oxford Dictionaries UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. n.d. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ^ "Lodz". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ "Łódź". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ^ "Łódź". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ "Łódź"[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Łódź". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ "Łódź – Warszawa trasa i odległość na mapie • dojazd PKP, BUS, PKS". www.trasa.info. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ a b "Lodz – Tourism | Tourist Information – Lodz, Poland". staypoland.com. eTravel S.A.
- ^ Cysek-Pawlak, Monika; Krzysztofik, Sylwia (2017). "Integrated Approach as a Means of Leading the Degraded Post-Industrial Areas Out of Crisis – A Case Study of Lodz". IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 245 (8): 082036. Bibcode:2017MS&E..245h2036C. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/245/8/082036. eISSN 1757-899X. ISSN 1757-8981.
- ^ a b “4 Billion PLN for Revitalization of Downtown Łódź.” lodzpost.com. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ "The World According to GaWC 2020". GaWC – Research Network. Globalization and World Cities. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- ^ "Poland’s Łódź named UNESCO City of Film." Archived 31 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine Radio Poland. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ^ Albert 2020, p. 387.
- ^ Rymut 1987, p. 145.
- ^ Grzegorczyk 2008, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Strumiłło 2015, p. 1.
- ^ a b Brunell 2005, p. 161.
- ^ Lerski 1996, p. 324.
- ^ Podgarbi 1990, p. 33.
- ^ Brunet-Jailly 2017, p. 178.
- ^ Puś 1987, p. 10.
- ^ a b Muzeum Archeologiczne i Etnograficzne w Łodzi 1976, p. 48.
- ^ Rosset 1962, p. 5.
- ^ Malone 2007, p. 210.
- ^ a b Larkham & Conzen 2014, p. 153.
- ^ a b Larkham & Conzen 2014, pp. 153–154.
- ^ Susquehanna University 1975, p. 51.
- ^ Reddaway, Penson & Halecki 2016, p. 279.
- ^ a b Brand & Thomas 2013, p. 149.
- ^ Leslie 1983, p. 44.
- ^ Zieliński 1913, pp. 22, 35, 47.
- ^ Liszewski & Young 1997, p. 16.
- ^ Liszewski & Young 1997, pp. 16–17.
- ^ University of Łódź 1979, pp. 22–23.
- ^ van Pelt 2015, p. 12.
- ^ Charles 2015, p. 28.
- ^ Wakeman 2020.
- ^ Wandycz 2001, p. 161.
- ^ a b Blanc 2021, p. 33.
- ^ Cudny 2016, p. 127.
- ^ Zimmerman 2022, p. 138.
- ^ Toporowski 2013, pp. 9–10.
- ^ Toporowski 2013, p. 10.
- ^ a b Stefański 2003, p. 102.
- ^ Bujak 2007, p. 292.
- ^ Liszewski & Young 1997, p. 117.
- ^ DiNardo 2010, p. 14.
- ^ Biskupski 2012, p. 28.
- ^ Berend 2013, p. 195.
- ^ University of Łódź 1979, p. 23.
- ^ a b Czerny 2006, p. 57.
- ^ a b Roszkowski 2015, p. 207.
- ^ Feitelson 2017, p. 118.
- ^ Feitelson 2017, pp. 118–119.
- ^ Karamouz 2021, p. 386.
- ^ a b Cudny 2016, pp. 126–127.
- ^ Badziak & Łapa 2009, p. 160.
- ^ Wojalski 1992.
- ^ Brunell 2005, pp. 179–180.
- ^ Forczyk 2019, p. 212.
- ^ Forczyk 2019, p. 260.
- ^ Forczyk 2019, pp. 260–261.
- ^ Wardzyńska1 2009, p. 114.
- ^ Crowe 2021, p. 168.
- ^ von Plato, Leh & Thonfeld 2010, p. 87.
- ^ von Plato, Leh & Thonfeld 2010, pp. 87–88.
- ^ von Plato, Leh & Thonfeld 2010, p. 88.
- ^ Wardzyńska1 2009, pp. 203–205.
- ^ Ledniowski & Gola 2020, p. 149.
- ^ Ledniowski & Gola 2020, p. 147.
- ^ Trunk & Shapiro 2006, pp. XI, 9–13.
- ^ Trunk & Shapiro 2006, p. XXXIII.
- ^ Wieviorka 2006, pp. 7–8.
- ^ Datner 1968, p. 69.
- ^ Trunk & Shapiro 2006, p. XI.
- ^ Peck 1997.
- ^ Trunk & Shapiro 2006, p. L.
- ^ Wardzyńska2 2009, p. 30.
- ^ Ledniowski & Gola 2020, pp. 148–149.
- ^ a b c Cudny & Kunc 2021.
- ^ Werra & Woźny 2018, p. 481.
- ^ Dixon 2015, p. 207.
- ^ a b Müller 2005, p. 172.
- ^ Kłysik 1998, p. 175.
- ^ Ash, Timothy Garton (1 January 1999). The Polish Revolution: Solidarity. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300095686 – via Google Books.
- ^ Markham, James M. (28 July 1981). "Polish Minister and Union Reach Compromise on Meat Ration Cut". The New York Times.
Three more days of limited protests are planned in Lodz, which appears to have suffered especially from meat shortages.
- ^ a b Cudny 2016, p. 120.
- ^ Marszał et al. 2014, p. 90.
- ^ Marszał et al. 2014, p. 91.
- ^ Marszał et al. 2014, pp. 91–92.
- ^ "Średnia dobowa temperatura powietrza". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Średnia minimalna temperatura powietrza". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Średnia maksymalna temperatura powietrza". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Miesięczna suma opadu". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 9 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Liczba dni z opadem >= 0,1 mm". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Średnia grubość pokrywy śnieżnej". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Liczba dni z pokrywą śnieżna > 0 cm". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Średnia suma usłonecznienia (h)". Normy klimatyczne 1991–2020 (in Polish). Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Łódź Absolutna temperatura maksymalna" (in Polish). Meteomodel.pl. 6 April 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Łódź Absolutna temperatura minimalna" (in Polish). Meteomodel.pl. 6 April 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Łódź Średnia wilgotność" (in Polish). Meteomodel.pl. 6 April 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Monthly weather forecast and Climate – Lodz, Poland". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "Łódź (łódzkie) » mapy, nieruchomości, GUS, noclegi, szkoły, regon, atrakcje, kody pocztowe, wypadki drogowe, bezrobocie, wynagrodzenie, zarobki, tabele, edukacja, demografia".
- ^ Statistical Office in Łódź – Łódzkie Centre for Regional Surveys 2021, pp. 3, 7.
- ^ Statistical Office in Łódź – Łódzkie Centre for Regional Surveys 2021, p. 7.
- ^ a b Statistical Office in Łódź – Łódzkie Centre for Regional Surveys 2021, pp. 7, 8.
- ^ a b c Cudny 2012, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Obraniak 2007, p. 5.
- ^ Szukalski, Martinez-Fernandez & Weyman 2013, p. 7.
- ^ Cox 2014, p. 14.
- ^ Holm, Marcińczak & Ogrodowczyk 2015, pp. 169–170.
- ^ Kossert 2010, p. 40.
- ^ Gordon J Horwitz. Ghettostadt: Łódź and the Making of a Nazi City. Harvard University Press. 2009. p. 3.
- ^ “Piotrkowska Street Stroll.” Poland's Official Travel Website. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ Krakowiak, Beata (2015). "Museums in Łódź as an Element of Tourism Space and the Connection Between Museums and the City's Tourism Image". Tourism. 25 (2): 87–96. doi:10.1515/tour-2015-0008. eISSN 2080-6922. ISSN 0867-5856. Retrieved 18 July 2017. (p. 93).
- ^ a b Kaczmarek, Sylwia; Marcinczak, Szymon (2013). "The Blessing in Disguise: Urban Regeneration in Poland in a Neo-Liberal Milieu". In Leary, Michael E.; McCarthy, John (eds.). The Routledge Companion to Urban Regeneration. Routledge. pp. 98–106. ISBN 978-0-415-53904-3. (p. 103).
- ^ a b Strumiłło, Krystyna (2016). "Adaptive Reuse of Buildings as an Important Factor of Sustainable Development". In Charytonowicz, Jerzy (ed.). Advances in Human Factors and Sustainable Infrastructure. Springer. pp. 51–59. ISBN 978-3-319-41940-4. (p. 56).
- ^ “Poland to invest in Łódź despite failed bid for Expo 2022.” Radio Poland. 16 November 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2017.
- ^ a b Krakowiak, p. 88.
- ^ Krakowiak, p 91.
- ^ Krakowiak, p. 88. Krakowiak also lists 13 more institutions that operate as museums but are not registered with the National Institute for Museums and Public Collections (p. 95), bringing the total number of museums in Łódź to 27.
- ^ “Discover the Book Art Museum, Łódź, Poland.” AEPM: Association of European Printing Museums. January 2015. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ a b c Długoński, Andrzej; Szumański, Marek (2015). "Analysis of Green Infrastructure in Lodz, Poland". Journal of Urban Planning and Development. 141 (3): n. pag. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000242. eISSN 1943-5444. ISSN 0733-9488. Article first published online in 2014.
- ^ a b Jaskulski, Marcin; Szmidt, Aleksander (2015). "The Tourism Attractiveness of Landforms in Łagiewnicki Forest, Łódź". Tourism. 25 (2): 27–35. doi:10.1515/tour-2015-0003. eISSN 2080-6922. ISSN 0867-5856. Retrieved 28 July 2017. (p. 27)
- ^ See Jaskulski and Szmidt, p. 29, for a map of tourism trails in the forest.
- ^ Grzegorczyk, Arkadiusz, ed. (2015). Ilustrowana Encyklopedia Historii Łodzi. Łódź. pp. 59–61. ISBN 978-83-939822-0-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Kaniewska, Anna. “Najstarsze łódzkie parki. Archiwum Państwowe w Łodzi. [The State Archive in Łódź]. 3 April 2009. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ^ "Jewish Lodz Cemetery – About Cemetery At Bracka Street". Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ "The New Cemetery in Łódź". Lodz ShtetLinks. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ "Jewish Cemetery". Fundacja Monumentum Iudaicum Lodzese. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ Kobojek, Elżbieta (2017). "A Small River Within the Urban Space: the Evolution of the Relationship Using the Example of Łódź" (PDF). Space-Society-Economy. 19 (19): 7–20. doi:10.18778/1733-3180.19.01. ISSN 1733-3180. Retrieved 13 July 2018. (p. 10).
- ^ Lamprecht, Mariusz (2014). "Fluctuations in the Development of Cities. A Case Study of Lodz". Studia Regionalia. 38: 77–91. ISSN 0860-3375. Retrieved 13 July 2018. (p. 82).
- ^ Cormier, Amanda (25 December 2019). "The Best Bras Might Be Made in Poland". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
- ^ Association of Business Service Leaders (ABSL) (2019). Business Services Sector in Poland 2019 (PDF) (Report). ABSL. pp. 28, 55.
{{cite report}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "Pociągi Łódź – Warszawa – Omio". www.pl.omio.com. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- ^ a b c (AFP)–24 Jan 2009 (24 January 2009). "AFP: Dell seeks refuge in Poland as crisis bites". Archived from the original on 25 May 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Wiśniewski, Szymon (2017). "Łódź in the Regional and National Transportation System" (PDF). Space-Society-Economy. 19 (19): 65–86. doi:10.18778/1733-3180.19.04. ISSN 1733-3180. Retrieved 17 July 2018. p. 66.
- ^ Shepard, Wade (10 November 2016). "Europe Finally Wakes Up To The New Silk Road, And This Could Be Big". Forbes. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- ^ Bentyn, Zbigniew (2016). "Poland as a Regional Logistic Hub Serving the Development of the Northern Corridor of the New Silk Route". Journal of Management, Marketing and Logistics. 3 (2): 135–44. ISSN 2148-6670. Retrieved 20 July 2018. (p. 142).
- ^ "Statystyki rowerówek" [Bike roads statistics]. rowerowalodz.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 15 August 2019. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ www.lifemotion.pl. "Our destinations – Port Lotniczy Łódź im. Władysława Reymonta". lodz.pl.
- ^ Wiśniewski, p. 79.
- ^ Statistic taken from the Łódź Władysław Reymont Airport Wikipedia article on 19 July 2015.
- ^ Sourced from the Łódź article on the Polish Wikipedia site on 19 July 2015
- ^ "About MPK – MPK-Lodz Spolka z o.o." lodz.pl.
- ^ Grzegorczyk, p. 144.
- ^ "Łódź railway tunnel tender announced". RailwayPro. 6 December 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ a b "Superdworzec już jest, będzie (prawie) metro. Łódź ma być komunikacyjnym centrum kraju". TVN24. 2 December 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ a b "Łódź będzie miała 'metro'. I to już niedługo". Wyborcza.pl: Magazyn Łódź. 18 May 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ Rogaczewska, Beata (1 November 2016). "Łódź Fabryczna: największy podziemny dworzec kolejowy w Polsce i trzeci w Europie". rp.pl. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ Kozlowski, Remigiusz; Palczewska, Anna; Jablonski, Jakub (2016). "The Scope and Capabilities of ITS – The Case of Łódź". In Mikulski, Jerzy (ed.). Challenge of Transport Telematics. Springer. pp. 305–16. ISBN 9783319496450. (p. 308)
- ^ "The New Centre of Łódź has a Local Action Plan – URBACT". urbact.eu.
- ^ "Rekordowy rok Łódzkiej Kolei Aglomeracyjnej". kurierkolejowy.eu. 22 December 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ a b Perspektywy University Ranking 2018. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ Dana, Przemek (16 January 2015). "Janusz Morgenstern, reżyser m.in. "Stawki większej niż życie" nie żyje". Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- ^ 2009 EuroBasket, ARCHIVE.FIBA.com, Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- ^ Pavitt, Michael (13 April 2018). "Poland and Hungary awarded upcoming editions of European Universities Games". insidethegames.biz. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "Szkoła Mistrzostwa Sportowego im. K. Górskiego w Łodzi – Oficjalna strona internetowa Szkoły Mistrzostwa Sportowego w Łodzi". smslodz.pl.
- ^ "Spółdzielczy Klub Sportowy START Łódź ul. św. Teresy 56/58 – Oficjalny serwis". sksstart.com.
- ^ "Expo 2021 Doha". Bureau International des Expositions. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
The Government of the State of Qatar has formally requested BIE approval to change the opening dates of Expo 2021 Doha to 2 October 2023 – 28 March 2024. The request follows in depth discussions [...] on the global impact of the Covid-19 pandemic. The Executive Committee of the BIE unanimously agreed to propose the postponement of Horticultural Expo 2021 Doha, with the BIE General Assembly to vote on the recommendation during its next meeting on 1 December 2020.
- ^ "Rok 2029: nowy termin Zielonego Expo w Łodzi" (in Polish). Urząd Miasta Łodzi. 23 September 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ^ "Grażyna Bacewicz". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Aleksander Bardini". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Andrzej Bartkowiak" (in Polish). Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Jurek Becker, 59; Novelist Survived Nazi Imprisonment". The New York Times. 24 March 1997. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Marek BELKA". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Kazimierz Brandys". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Batsheva Dagan". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Karl Dedecius nie żyje. "Zmarł wielki łodzianin"" (in Polish). 27 February 2016. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Max Factor – Lodz". Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ "Magdalena Frech". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Marcin Gortat". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ Shapiro, Robert Moses (May 1999). Holocaust chronicles... – Google Books. ISBN 978-0-88125-630-7. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ^ "Józef Hecht" (in Polish). Retrieved 11 July 2022.
- ^ "Jerzy Janowicz". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Jan Karski". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Katarzyna Kobro". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Jerzy Kosiński: A Complicated Life & Literary Legacy". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Daniel Liebeskind". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ Alonso, Stephane (30 October 2009). "Polanski Exhibit Draws Crowds in Lódz". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Arthur Rubinstein". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Zbigniew Rybczyński". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Andrzej Sapkowski". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Władysław Strzemiński". Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Jack Tramiel, founder of Commodore computers, Lodz survivor, dies at 83 – j. the Jewish news weekly of Northern California". 20 April 2012. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ "Hanna Zdanowska" (in Polish). 30 September 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ "Twin Cities". The City of Łódź Office (in Polish and English). 2007. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2008.
- ^ "Chemnitz". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Stuttgart Städtepartnerschaften". Landeshauptstadt Stuttgart, Abteilung Außenbeziehungen (in German). Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ "Partner Cities of Lyon and Greater Lyon". Mairie de Lyon. 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ "Wilno". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Wilno" (PDF). bip.uml.lodz.pl. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Porozumienie o ustanowieniu braterskich więzi między miastami Łódź (Polska) i Odessa (Ukraina)" [Agreement to establish fraternal ties between cities of Łódź (Poland) and Odessa (Ukraine)] (PDF). uml.lodz.pl (in Polish and Russian). 7 May 1993. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Odessa". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Tel Aviv sister cities" (in Hebrew). Tel Aviv-Yafo Municipality. Archived from the original on 14 February 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2008.
- ^ "Rustawi". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Uchwała XXIV/275/95 Rady Miejskiej w Łodzi" [The City Council resolution No. XXIV/275/95] (PDF). uml.lodz.pl (in Polish). 27 December 1995. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Barreiro". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Tampere". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Puebla". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Murcia". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ Vänorter – orebro.se Archived 27 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Lwów". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Tjanjin". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Szeged". Urząd Miasta Łodzi (in Polish). Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ Dorota Adamska, City Council Office (2 March 2022), "Podsumowanie LVI nadzwyczajnej sesji Rady Miejskiej w Łodzi" [Summary of the 56. extraordinary session of the Łódź City Council], Urząd Miasta Łodzi, uml.lodz.pl (in Polish)
Bibliography
- Marszał, Tadeusz; Kobojek, Elżbieta; Niewiadomski, Arkadiusz; Tołoczko, Wojciech (2014). Natural environment of Poland and its protection in Łódź University Geographical Research. Łódź: University Press. pp. 79–99. ISBN 9788379691340.
- Kossert, Andreas (2010). "Religion in urban everyday life: shaping modernity in Lódz and Manchester, 1820-1914". In Berglund, Bruce R.; Porter-Szűcs, Brian (eds.). Christianity and Modernity in Eastern Europe. Central European University Press. ISBN 9789639776654.
- Müller, Bernhard (2005). Rise and decline of industry in Central and Eastern Europe a comparative study of cities and regions in eleven countries. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 9783540404781.
- Cudny, Waldemar; Kunc, Josef (2021). Growth and Change in Post-socialist Cities of Central Europe. New York: Routledge. ISBN 9780367484477.
- Kłysik, Kazimierz (1998). "Charakterystyka powierzchni miejskich Łodzi z klimatologicznego punktu widzenia" (PDF). Folia Geographica Physica. 3: 173–85. ISSN 1427-9711. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- Werra, Dagmara H.; Woźny, Marzena (2018). Between history and archaeology papers in honour of Jacek Lech. Oxford: Archaeopress Publishing. ISBN 9781784917722.
- Dixon, Wheeler Winston (2015). Black and White Cinema: A Short History. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813572444.
- Wieviorka, Annette (2006). The Era of the Witness. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. ISBN 9780801443312.
- Wardzyńska2, Maria. "Obozy niemieckie na okupowanych terenach polskich". Biuletyn Instytutu Pamięci Narodowej (in Polish). Vol. 4, no. 99. IPN. ISSN 1641-9561.
{{cite magazine}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Wardzyńska1, Maria (2009). Był rok 1939. Operacja niemieckiej policji bezpieczeństwa w Polsce. Intelligenzaktion (in Polish). Warszawa: IPN.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Datner, Szymon (1968). Las sprawiedliwych (in Polish). Warszawa: Książka i Wiedza.
- Peck, Abraham J. (1997). "The Agony of the Łódź Ghetto, 1941–1944". The Chronicle of the Łódź Ghetto, 1941–1944 by Lucjan Dobroszycki, and The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, Washington D.C. The Simon Wiesenthal Center. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- Ledniowski, Krzysztof; Gola, Beata (2020). "Niemiecki obóz dla małoletnich Polaków w Łodzi przy ul. Przemysłowej". Zbrodnia bez kary... Eksterminacja i cierpienie polskich dzieci pod okupacją niemiecką (1939–1945) (in Polish). Kraków: Uniwersytet Jagielloński, Biblioteka Jagiellońska.
- Trunk, Isaiah; Shapiro, Robert Moses (2006). Łódź Ghetto: A History. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253347556.
- von Plato, Alexander; Leh, Almut; Thonfeld, Cristoph (2010). Hitler's Slaves: Life Stories of Forced Labourers in Nazi-Occupied Europe. New York: Berghahn Books. ISBN 9781845459901.
- Crowe, David M. (2021). The Holocaust: Roots, History, and Aftermath. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0367541248.
- Forczyk, Robert (2019). Case White: The Invasion of Poland 1939. New York: Osprey. ISBN 978-1472834973.
- Wojalski, Mirosław Zbigniew (1992). Działo się w Łodzi, It Happened in Łódź. Łódź: ZORA. ISBN 8390080605.
- Badziak, Kazimierz; Łapa, Małgorzata (2009). Województwo łódzkie 1919-2009: studia i materiały (in Polish). Łódź: Instytut Historii Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego. ISBN 9788361253501.
- Zieliński, Stanisław (1913). Bitwy i potyczki 1863-1864. Na podstawie materyałów drukowanych i rękopiśmiennych Muzeum Narodowego w Rapperswilu (in Polish). Rapperswil: Fundusz Wydawniczy Muzeum Narodowego w Rapperswilu.
- Cudny, Waldemar (2012). "Socio-Economic Changes in Lodz – The Result of Twenty Years of System Transformation" (PDF). Geografický časopis (Geographical Journal). 64 (1): 3–27. ISSN 1335-1257. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Szukalski, Piotr; Martinez-Fernandez, Cristina; Weyman, Tamara (2013). "Lódzkie Region: Demographic Challenges Within an Ideal Location". OECD Local Economic and Employment Development (LEED) Working Papers (5/2013): 1–56. doi:10.1787/5k4818gt720p-en. eISSN 2079-4797. hdl:11089/5816. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Cox, Wendell (2014). "International Shrinking Cities: Analysis, Classification, and Prospects". In Richardson, Harry W.; Nam, Chang Woon (eds.). Shrinking Cities: A Global Perspective. London and New York: Routledge. pp. 11–27. ISBN 978-0415643962.
- Holm, Andrej; Marcińczak, Szymon; Ogrodowczyk, Agnieszka (2015). "New-Build Gentrification in the Post-Socialist City: Łódź and Leipzig Two Decades After Socialism" (PDF). Geografie. 120 (2): 164–187. doi:10.37040/geografie2015120020164. ISSN 1212-0014. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Roszkowski, Wojciech (2015). East Central Europe: A Concise History. Warsaw: Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN). ISBN 9788364091483.
- Karamouz, Mohammad (2021). Water systems analysis, design, and planning: urban infrastructure. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 9780367528454.
- Feitelson, Eran (2017). Advancing Sustainability at the Sub-National Level: the Potential and Limitations of Planning. London: Routledge. ISBN 9781351960656.
- Czerny, Miroslawa (2006). Poland in the geographical centre of Europe: political, social and economic consequences. New York: Nova Science. ISBN 1594546037.
- University of Łódź (1979). "Acta Universitatis Lodziensis". Zeszyty naukowe Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego. II (21–22). OCLC 643789098. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- Biskupski, Mieczysław B. (2012). Independence Day: Myth, Symbol, and the Creation of Modern Poland. Oxford: University Press. ISBN 978-0199658817.
- DiNardo, Richard L. (2010). Breakthrough: the Gorlice-Tarnow Campaign, 1915. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 9780313081835.
- Toporowski, Jan (2013). Michał Kalecki: An Intellectual Biography. Vol. 1: Rendezvous in Cambridge 1899-1939. London: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9781137315397.
- Stefański, Krzysztof (2003). Atlas architektury dawnej Łodzi: do 1939 r. (in Polish). Łódź: Archidiecezjalne Wydawn. Łódzkie. ISBN 8387931888.
- Bujak, Adam (2007). Polish Cathedrals. Kraków: Biały Kruk. ISBN 9788360292372.
- Zimmerman, Joshua D. (2022). Jozef Pilsudski: Founding Father of Modern Poland. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674984271.
- Cudny, Waldemar (2016). Festivalisation of Urban Spaces: Factors, Processes and Effects. Cham: Springer International. ISBN 9783319319971.
- Blanc, Eric (2021). Revolutionary social democracy. Boston: Brill. ISBN 9789004449930.
- Wandycz, Piotr Stefan (2001). The Price of Freedom: A History of East Central Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present. London: Routledge. ISBN 9781351541305.
- Charles, Victoria (2015). Factories. New York: Parkstone International. ISBN 9781844847679.
- van Pelt, Robert Jan (2015). Lodz and Getto Litzmannstadt : promised land and croaking hole of Europe. Toronto: Art Gallery of Ontario. ISBN 9781894243803.
- Wakeman, Rosemary (2020). A Modern History of European Cities: 1815 to the Present. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 9781350017665.
- Liszewski, Stanisław; Young, Craig (1997). A Comparative Study of Łódź and Manchester. Łódź: University Press. ISBN 9788371710957.
- Brand, Peter; Thomas, Michael (2013). Urban Environmentalism: Global Change and the Mediation of Local Conflict. Hoboken: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780203970263.
- Davies, Norman (1982). God's Playground; A History of Poland in Two Volumes. Vol. 2. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0231043260.
- Obraniak, Włodzimierz (2007). Ludność Łodzi i innych wielkich miast w Polsce w latach 1984-2006 (PDF). Łódź: Urząd Statystyczny w Łodzi. p. 5. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- Statistical Office in Łódź – Łódzkie Centre for Regional Surveys (2021). Łódź in figures (PDF). Łódź: Statistics Poland (Główny Urząd Statystyczny GUS).
- Leslie, Roy Francis (1983). The History of Poland Since 1863. Cambridge: University Press. ISBN 0521226457.
- Larkham, Peter J.; Conzen, Michael P. (2014). Shapers of Urban Form: Explorations in Morphological Agency. New York: Routledge. ISBN 9781317812517.
- Reddaway, W. F.; Penson, J. H.; Halecki, Oskar (2016). The Cambridge History of Poland. Cambridge: University Press. ISBN 978-1316620038.
- Susquehanna University (1975). Susquehanna University Studies. 1. Vol. 10. Selinsgrove: University Press. ISSN 0361-8250.
- Malone, Peter (2007). Through a Catholic lens: religious perspectives of nineteen film directors from around the world. Lanham: Sheed & Ward. ISBN 978-1299386389.
- Muzeum Archeologiczne i Etnograficzne w Łodzi (1976). "Prace i materiały Muzeum Archeologicznego i Etnograficznego w Łodzi". Prace i materiały Muzeum Archeologicznego i Etnograficznego w Łodzi (in Polish). 19. Łódź: PWN. ISSN 0458-1520.
- Podgarbi, Bronisław (1990). The Jewish Cemetery in Lodz. Łódź: Artus. ISBN 8385132007.
- Lerski, Halina (1996). Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966-1945. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 1282427539.
- Brunell, Laura (2005). Institutional Capital: Building Post-communist Government Performance. Lanham: University Press of America. ISBN 0761829555.
- Strumiłło, Krystyna (2015). New Image of Post-factory Buildings in Lodz in Kopernika Street (PDF). Łódź: Institute of Architecture and Urban Planning, Lodz University of Technology.
- Berend, Ivan (2013). Case studies on modern European economy : entrepreneurs, inventions, institutions. London: Routledge. ISBN 9780415639941.
- Grzegorczyk, Arkadiusz (2008). "Okres Pradziejów i Średniowiecza" (PDF). Ilustrowana Encyklopedia Historii Łodzi (in Polish) (1). Urząd Miasta Łodzi Biuro Analiz Medialnych i Wydawnictw. ISSN 1731-092X. OCLC 749406762. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- Rymut, Kazimierz (1987). Nazwy miast Polski (in Polish). Wrocław: Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich Wydawnictwo. ISBN 8304024365.
- Albert, Sylvie (2020). Innovative Solutions for Creating Sustainable Cities. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing. ISBN 9781527535930.
- Puś, Wiesław (1987). Dzieje Łodzi przemysłowej (in Polish). Łódź: Muzeum Historii Miasta Łodzi, Centrum Informacji Kulturalnej. OCLC 749443747.
- Rosset, Edward (1962). Łódź w latach 1945–1960 (in Polish). Łódź: Towarzystwo Przyjaciół Łodzi. OCLC 1150542144.
- Brunet-Jailly, Emmanuel (2017). Borderlands: comparing border security in North America and Europe. Ottawa: University Press. ISBN 9780776627151.
- Alan Adelson and Robert Lapides, Łódź Ghetto : A Community History Told in Diaries, Journals, and Documents, Viking, 1989. ISBN 0-670-82983-8
- "A Stairwell in Lodz," Constance Cappel, 2004, Xlibris, (in English).[self-published source]
- Horwitz, Gordon J. (2009). Ghettostadt: Łódź and the making of a Nazi city. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. pp. 27, 54–55, 62. ISBN 978-0674038790. Retrieved 21 March 2015 – via Google Books, preview.
- "Lodz – The Last Ghetto in Poland," Michal Unger, Yad Vashem, 600 pages (in Hebrew)
- Stefański, Krzysztof (2000). Gmachy użyteczności publicznej dawnej Łodzi, Łódź 2000 ISBN 83-86699-45-0.
- Stefański, Krzysztof (2009). Ludzie którzy zbudowali Łódź Leksykon architektów i budowniczych miasta (do 1939 roku), Łódź 2009 ISBN 978-83-61253-44-0.
- Trunk, Isaiah; Shapiro, Robert Moses (2006). Łódź Ghetto: a history. Indiana University Press, Bloomington, Indiana. ISBN 978-0-253-34755-8. Retrieved 6 March 2010.
- Trunk, Isaiah; Shapiro, Robert Moses (2008) [2006]. Łódź Ghetto: A History. Bloomington, Ind.: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0253347558. Retrieved 29 September 2015 – via Google Books, preview.
External links
- Official website
- Public Transport Official Site
- City map of Łódź
- Historic images of Łódź
- Łódź Special Economic Zone
- Łódź-Lublinek Airport
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 862.
- The Łódź Post—English language newspaper
- The Łódź Ghetto Archived 20 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- Łódź, Poland at JewishGen




















