Emilian–Romagnol
Appearance
| Emilian-Romagnol | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Italy, San Marino |
| Region | Primarily Emilia-Romagna, Marche, San Marino |
Native speakers | Unknown (4.4 million population): |
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | (code eml deprecated in 2009)[2] Individual codes: egl – Emilianrgn – Romagnol |
| Glottolog | emil1241 Emilianoroma1328 Romagnol |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-ok |
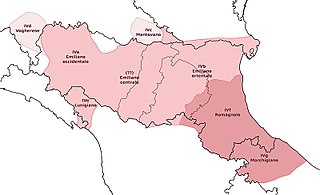 | |
Emilian-Romagnol (emiliân-rumagnōl or langua emiglièna-rumagnôla), also known as Emiliano-Romagnolo, is a Gallo-Italic language. Its two dialect groups, Emilian and Romagnol, were traditionally considered two separate but closely related languages spoken in the eponymous northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna and in San Marino, as well as bordering parts of Lombardy, Umbria, Marche, Liguria, Piedmont, Veneto and Tuscany.[3]
See also
Emiliano-Romagnolo edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
References
- ^ "La lingua italiana, i dialetti e le lingue straniere Anno 2006" (PDF). istat.it. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ "639 Identifier Documentation: eml". SIL International.
- ^ "Lingua romagnola". TuttoSu. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
