Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən ˈsiː/[a] is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, although it is usually identified as a separate body of water.
The name Mediterranean is derived from the Latin mediterraneus, meaning "inland" or "in the middle of the land" (from medius, "middle" and terra, "land"). It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km2 (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Gibraltar and Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.[3][4]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The sea is bordered on the north by Europe, the east by Asia, and in the south by Africa, is located between latitudes 30° and 46° N and longitudes 5°50′ W and 36° E. Its west-east length,from the Strait of Gibraltar to the Gulf of Iskenderun, on the southwestern coast of Turkey, is approximately 2,500 miles (4,000 km). The sea's average north-south length, from Croatia’s southern shore to Libya, is approximately 500 miles (800 km). The Mediterranean Sea, including the Sea of Marmara, has a surface area of approximately 970,000 square miles (2,510,000 square km).[5]
The sea was an important route for merchants and travellers of ancient times that allowed for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region. The history of the Mediterranean region is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
The countries with coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea are Albania, Algeria, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Egypt, France, Greece, Israel, Italy, Lebanon, Libya, Malta, Morocco, Monaco, Montenegro, Northern Cyprus (recognized only by Turkey), Palestine, Slovenia, Spain, Syria, Turkey, and Tunisia. In addition, Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia are British Overseas Territories with coastlines on the sea.
Name

The term Mediterranean derives from the Latin word mediterraneus, meaning "in the middle of earth" or "between lands" (medi-; adj. medius, -um -a "middle, between" + terra f., "land, earth"): as it is between the continents of Africa, Asia and Europe. The Greek name Mesogeios (Μεσόγειος), is similarly from μέσο, "middle" + γη, "land, earth").[6]
The Mediterranean Sea has historically had several names. For example, the Carthaginians called it the "Syrian Sea" and latter Romans commonly called it Mare Nostrum (Latin, "Our Sea"), and occasionally Mare Internum (Sallust, Jug. 17).
In ancient Syrian texts, Phoenician epics and in the Hebrew Bible, it was primarily known as the "Great Sea" (הַיָּם הַגָּדוֹל, HaYam HaGadol, Numbers 34:6,7; Joshua 1:4, 9:1, 15:47; Ezekiel 47:10,15,20), or simply "The Sea" (1 Kings 5:9; comp. 1 Macc. 14:34, 15:11); however, it has also been called the "Hinder Sea" (הַיָּם הָאַחֲרוֹן), due to its location on the west coast of Greater Syria or the Holy Land, and therefore behind a person facing the east, sometimes translated as "Western Sea", (Deut. 11:24; Joel 2:20). Another name was the "Sea of the Philistines" (יָם פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Exod. 23:31), from the people inhabiting a large portion of its shores near the Israelites. The sea is also called the "Great Sea" (Middle English: Grete See) in the General Prologue by Geoffrey Chaucer. In Ottoman Turkish, it has also been called Bahr-i Sefid, meaning the "Pure White Sea".
In Modern Hebrew, it has been called HaYam HaTikhon (Template:Hebrew), "the Middle Sea", reflecting the Sea's name in ancient Greek (Mesogeios), Latin (Mare internum), German (Mittelmeer), and modern languages in both Europe and the Middle East (Mediterranean, etc.).
Similarly, in Modern Arabic, it is known as al-Baḥr [al-Abyaḍ] al-Mutawassiṭ (البحر [الأبيض] المتوسط), "the [White] Middle Sea", while in Islamic and older Arabic literature, it was referenced as Baḥr al-Rūm (بحر الروم), or "the Romaic/Byzantine Sea."
In Turkish, it is known as Akdeniz,[7] "the White Sea" since among Turks the white color (ak) represents the west.
History



Ancient civilisations
Several ancient civilisations were located around the Mediterranean shores, and were greatly influenced by their proximity to the sea. It provided routes for trade, colonisation, and war, as well as food (from fishing and the gathering of other seafood) for numerous communities throughout the ages.[8]
Due to the shared climate, geology, and access to the sea, cultures centred around the Mediterranean tended to have some extent of intertwined culture and history.
Two of the most notable Mediterranean civilisations in classical antiquity were the Greek city states and the Phoenicians, both of which extensively colonised the coastlines of the Mediterranean. Later, when Augustus founded the Roman Empire, the Romans referred to the Mediterranean as Mare Nostrum ("Our Sea").
Darius I of Persia, who conquered Ancient Egypt, built a canal linking the Mediterranean to the Red Sea. Darius's canal was wide enough for two triremes to pass each other with oars extended, and required four days to traverse.[9]
Middle Ages and empires
The western Roman empire collapsed around AD 476. Temporarily the east was again dominant as the Byzantine Empire formed from the eastern half of the Roman empire. Another power arose in the 7th century, and with it the religion of Islam, which soon swept across from the east; at its greatest extent, the Arab Empire controlled 75% of the Mediterranean region and left a lasting footprint on its eastern and southern shores.
Europe was reviving, however, as more organised and centralised states began to form in the later Middle Ages after the Renaissance of the 12th century.
Ottoman power continued to grow, and in 1453, the Byzantine Empire was extinguished with the Conquest of Constantinople. Ottomans gained control of much of the sea in the 16th century and maintained naval bases in southern France, Algeria and Tunisia. Barbarossa, the famous Ottoman captain is a symbol of this domination with the victory of the Battle of Preveza. The Battle of Djerba marked the apex of Ottoman naval domination in the Mediterranean. As the naval prowess of the European powers increased, they confronted Ottoman expansion in the region when the Battle of Lepanto checked the power of the Ottoman Navy. This was the last naval battle to be fought primarily between galleys.
The Barbary pirates of North Africa preyed on Christian shipping in the Western Mediterranean Sea.[10] According to Robert Davis, from the 16th to 19th centuries, pirates captured 1 million to 1.25 million Europeans as slaves.[11]
The development of oceanic shipping began to affect the entire Mediterranean. Once, all trade from the east had passed through the region, but now the circumnavigation of Africa allowed spices and other goods to be imported through the Atlantic ports of western Europe.[12][13][14]
21st century and migrations
In 2013, the Maltese president described the Mediterranean sea as a "cemetery" due to the large amounts of migrants who drown there after their boats capsize.[15] European Parliament president Martin Schulz said that Europe's migration policy has "turned the Mediterranean into a graveyard", referring to the number of drowned refugees in the region as a direct result of the policies.[16] An Azerbaijani official described the sea as "a burial ground ... where people die".[17]
Following the 2013 Lampedusa migrant shipwreck, the Italian government decided to strengthen the national system for the patrolling of the Mediterranean Sea by authorising "Mare Nostrum", a military and humanitarian mission in order to rescue the migrants and arrest the traffickers of immigrants.[18]
Geography
The Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean by the Strait of Gibraltar (known in Homer's writings as the "Pillars of Hercules") in the west and to the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea, by the Dardanelles and the Bosporus respectively, in the east. The Sea of Marmara is often considered a part of the Mediterranean Sea, whereas the Black Sea is generally not. The 163 km (101 mi) long man-made Suez Canal in the southeast connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
Large islands in the Mediterranean include Cyprus, Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Lesbos, Chios, Kefalonia, Corfu, Limnos, Samos, Naxos and Andros in the Eastern Mediterranean; Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, Cres, Krk, Brač, Hvar, Pag, Korčula and Malta in the central Mediterranean; and Ibiza, Majorca and Minorca (the Balearic Islands) in the Western Mediterranean.
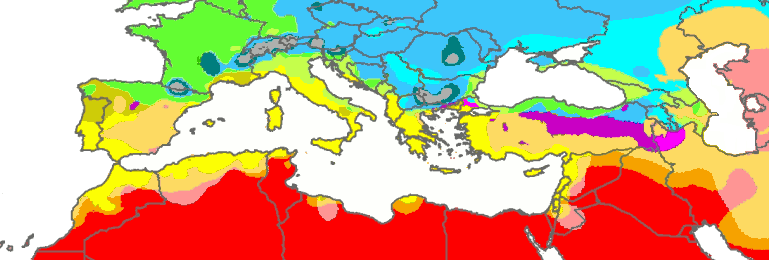
The typical Mediterranean climate has hot, humid, and dry summers and mild, rainy winters. Crops of the region include olives, grapes, oranges, tangerines, and cork.
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Mediterranean Sea as follows:[19]
Stretching from the Strait of Gibraltar in the west to the entrances to the Dardanelles and the Suez Canal in the east, the Mediterranean Sea is bounded by the coasts of Europe, Africa and Asia, and is divided into two deep basins:
- Western Basin:
- On the west: A line joining the extremities of Cape Trafalgar (Spain) and Cape Spartel (Africa).
- On the northeast: The west coast of Italy. In the Strait of Messina a line joining the north extreme of Cape Paci (15°42'E) with Cape Peloro, the east extreme of the Island of Sicily. The north coast of Sicily.
- On the east: A line joining Cape Lilibeo the western point of Sicily (37°47′N 12°22′E / 37.783°N 12.367°E), through the Adventure Bank to Cape Bon (Tunisia).
- Eastern Basin:
- On the west: The northeastern and eastern limits of the Western Basin.
- On the northeast: A line joining Kum Kale (26°11'E) and Cape Helles, the western entrance to the Dardanelles.
- On the southeast: The entrance to the Suez Canal.
- On the east: The coasts of Syria and Palestine.
(It should be noted that the coast referred to as belonging to Palestine in this document dating to 1953 has been within the internationally recognised borders of the country known as Israel since 1948. Of the territories administered by the Palestinian Authority, only the Gaza Strip has a sea coast.)
Oceanography

Being nearly landlocked affects conditions in the Mediterranean Sea: for instance, tides are very limited as a result of the narrow connection with the Atlantic Ocean. The Mediterranean is characterised and immediately recognised by its deep blue colour.
Evaporation greatly exceeds precipitation and river runoff in the Mediterranean, a fact that is central to the water circulation within the basin.[20] Evaporation is especially high in its eastern half, causing the water level to decrease and salinity to increase eastward.[21] The salinity at 5 m depth is 3.8%.[22]
The pressure gradient pushes relatively cool, low-salinity water from the Atlantic across the basin; it warms and becomes saltier as it travels east, then sinks in the region of the Levant and circulates westward, to spill over the Strait of Gibraltar.[23] Thus, seawater flow is eastward in the Strait's surface waters, and westward below; once in the Atlantic, this chemically distinct Mediterranean Intermediate Water can persist thousands of kilometres away from its source.[24]
Coastal countries
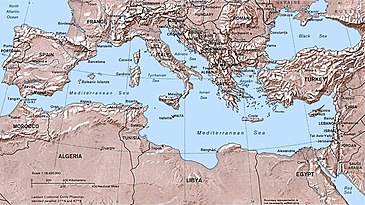
The following countries have a coastline on the Mediterranean Sea:
- Northern shore (from west to east): Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece and Turkey.
- Eastern shore (from north to south): Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine.
- Southern shore (from west to east): Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt.
- Island nations: Malta, Cyprus.
Several other territories also border the Mediterranean Sea (from west to east): The British overseas territory of Gibraltar, the Spanish autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla and nearby islands, and the Sovereign Base Areas on Cyprus






Major cities (municipalities) with populations larger than 200,000 people bordering the Mediterranean Sea are:
| Country | Cities |
|---|---|
| Algeria | Algiers, Annaba, Oran |
| Egypt | Alexandria, Port Said |
| France | Marseille, Nice |
| Greece | Athens, Patras, Thessaloniki |
| Israel | Ashdod, Haifa, Rishon LeZion, Tel Aviv |
| Italy | Bari, Catania, Genoa, Messina, Naples, Palermo, Rome, Taranto, Trieste, Venice |
| Lebanon | Beirut, Tripoli |
| Libya | Benghazi, Khoms, Misrata, Tripoli, Zawiya, Zliten |
| Morocco | Tétouan, Tangier |
| Spain | Alicante, Badalona, Barcelona, Cartagena, Málaga, Palma, Valencia. |
| State of Palestine | Gaza City, Khan Yunis |
| Syria | Latakia |
| Tunisia | Sfax, Sousse, Tunis |
| Turkey | Antalya, Adana, İzmir, Mersin |
Subdivisions

According to the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), the Mediterranean Sea is subdivided into a number of smaller waterbodies, each with their own designation (from west to east):[19]
- the Strait of Gibraltar;
- the Alboran Sea, between Spain and Morocco;
- the Balearic Sea, between mainland Spain and its Balearic Islands;
- the Ligurian Sea between Corsica and Liguria (Italy);
- the Tyrrhenian Sea enclosed by Sardinia, Italian peninsula and Sicily;
- the Ionian Sea between Italy, Albania and Greece;
- the Adriatic Sea between Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro and Albania;
- the Aegean Sea between Greece and Turkey.
Other seas

Although not recognised by the IHO treaties, there are some other seas whose names have been in common use from the ancient times, or in the present:
- the Sea of Sardinia, between Sardinia and Balearic Islands, as a part of the Balearic Sea
- the Sea of Sicily between Sicily and Tunisia,
- the Libyan Sea between Libya and Crete,
- In the Aegean Sea,
- the Thracian Sea in its north,
- the Myrtoan Sea between the Cyclades and the Peloponnese,
- the Sea of Crete north of Crete,
- the Icarian Sea between Kos and Chios
- the Cilician Sea between Turkey and Cyprus
- the Levantine Sea at the eastern end of the Mediterranean
Other features


Many of these smaller seas feature in local myth and folklore and derive their names from these associations. In addition to the seas, a number of gulfs and straits are also recognised:
- the Saint George Bay in Beirut, Lebanon
- the Ras Ibn Hani cape in Latakia, Syria
- the Ras al-Bassit cape in northern Syria.
- the Minet el-Beida ("White Harbour") bay near ancient Ugarit, Syria
- the Strait of Gibraltar, connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Spain from Morocco
- the Bay of Gibraltar, at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula
- the Gulf of Corinth, an enclosed sea between the Ionian Sea and the Corinth Canal
- the Pagasetic Gulf, the gulf of Volos, south of the Thermaic Gulf, formed by the Mount Pelion peninsula
- the Saronic Gulf, the gulf of Athens, between the Corinth Canal and the Mirtoan Sea
- the Thermaic Gulf, the gulf of Thessaloniki, located in the northern Greek region of Macedonia
- the Kvarner Gulf, Croatia
- the Gulf of Lion, south of France
- the Gulf of Valencia, east of Spain
- the Strait of Messina, between Sicily and the toe of Italy
- the Gulf of Genoa, northwestern Italy
- the Gulf of Venice, northeastern Italy
- the Gulf of Trieste, northeastern Italy
- the Gulf of Taranto, southern Italy
The Adriatic Sea contains over 1200 islands and islets. - the Gulf of Salerno, southwestern Italy
- the Gulf of Gaeta, southwestern Italy
- the Gulf of Squillace, southern Italy
- the Strait of Otranto, between Italy and Albania
- the Gulf of Haifa, northern Israel
- the Gulf of Sidra, between Tripolitania (western Libya) and Cyrenaica (eastern Libya)
- the Strait of Sicily, between Sicily and Tunisia
- the Corsica Channel, between Corsica and Italy
- the Strait of Bonifacio, between Sardinia and Corsica
- the Gulf of İskenderun, between İskenderun and Adana (Turkey)
- the Gulf of Antalya, between west and east shores of Antalya (Turkey)
- the Bay of Kotor, in south-western Montenegro and south-eastern Croatia
- the Malta Channel, between Sicily and Malta
- the Gozo Channel, between Malta Island and Gozo
10 largest islands by area

| Country | Island | Area in km2 | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italy | Sicily | 25,460 | 5,048,995 |
| Italy | Sardinia | 23,821 | 1,672,804 |
| Cyprus | Cyprus | 9,251 | 1,088,503 |
| France | Corsica | 8,680 | 299,209 |
| Greece | Crete | 8,336 | 623,666 |
| Greece | Euboea | 3,655 | 218.000 |
| Spain | Majorca | 3,640 | 869,067 |
| Greece | Lesbos | 1,632 | 90,643 |
| Greece | Rhodes | 1,400 | 117,007 |
| Greece | Chios | 842 | 51,936 |
Climate
Sea temperature
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marseille[26] | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 21 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 16 | 14 | 16.6 |
| Gibraltar[27] | 16 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 17 | 18.4 |
| Málaga[28] | 16 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 18.3 |
| Athens[29] | 16 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 19.3 |
| Barcelona[30] | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 23 | 20 | 17 | 15 | 17.8 |
| Heraklion[31] | 16 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 24 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 19.7 |
| Venice[32] | 11 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 18 | 22 | 25 | 26 | 23 | 20 | 16 | 14 | 17.4 |
| Valencia[33] | 14 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 21 | 24 | 26 | 24 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 18.5 |
| Malta[34] | 16 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 26 | 25 | 23 | 21 | 18 | 19.9 |
| Alexandria[35] | 18 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 22 | 20 | 21.4 |
| Naples[36] | 15 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 25 | 27 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 19.3 |
| Larnaca[37] | 18 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 26 | 27 | 27 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 21.7 |
| Limassol[38] | 18 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 26 | 27 | 27 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 21.7 |
| Antalya | 17 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 28 | 27 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 21.8 |
| Tel Aviv[39] | 18 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 23 | 20 | 22.1 |
Geology
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2012) |

The geologic history of the Mediterranean Sea is complex. Underlain by oceanic crust, the sea basin was once thought to be a tectonic remnant of the ancient Tethys Ocean; it is now known to be a structurally younger basin, called the Neotethys, which was first formed by the convergence of the African and Eurasian plates during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic. Because it is a near-landlocked body of water in a normally dry climate, the Mediterranean is subject to intensive evaporation and the precipitation of evaporites. The Messinian salinity crisis started about six million years ago (mya) when the Mediterranean became landlocked, and then essentially dried up. There are salt deposits accumulated on the bottom of the basin of more than a million cubic kilometres—in some places more than three kilometres thick.[40][41]
Scientists estimate that the sea was last filled about 5.3 million years ago (mya) in less than two years by the Zanclean flood. Water poured in from the Atlantic Ocean through a newly breached gateway now called the Strait of Gibraltar at an estimated rate of about three orders of magnitude (one thousand times) larger than the current daily flow of the Amazon River.[42]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The coastline extends for 46,000 km (29,000 mi). A shallow submarine ridge (the Strait of Sicily) between the island of Sicily and the coast of Tunisia divides the sea in two main subregions: the Western Mediterranean, with an area of about 850 thousand km2 (330 thousand mi2); and the Eastern Mediterranean, of about 1.65 million km2 (640 thousand mi2). A characteristic of the coastal Mediterranean are submarine karst springs or [vrulja] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)s, which discharge pressurized groundwater into the coastal seawater from below the surface; the discharge water is usually fresh, and sometimes may be thermal.[43][44]
Tectonics and paleoenvironmental analysis

The Mediterranean basin and sea system was established by the ancient African-Arabian continent colliding with the Eurasian continent. As Africa-Arabia drifted northward, it closed over the ancient Tethys Ocean which had earlier separated the two supercontinents Laurasia and Gondwana. At about that time in the middle Jurassic period a much smaller sea basin, dubbed the Neotethys, was formed shortly before the Tethys Ocean closed at its western (Arabian) end. The broad line of collisions pushed up a very long system of mountains from the Pyrenees in Spain to the Zagros Mountains in Iran in an episode of mountain-building tectonics known as the Alpine orogeny. The Neotethys grew larger during the episodes of collisions (and associated foldings and subductions) that occurred during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs (34 to 5.33 mya); see animation: Africa-Arabia colliding with Eurasia.
Messinian salinity crisis
During Mesozoic and Cenozoic times, as the northwest corner of Africa converged on Iberia, it lifted the Betic-Rif mountain belts across southern Iberia and northwest Africa. There the development of the intramontane Betic and Rif basins led to creating two roughly-parallel marine gateways between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Dubbed the Betic and Rifian corridors, they progressively closed during middle and late Miocene times; perhaps several times.[45] During late Miocene times the closure of the Betic Corridor triggered the so-called "Messinian salinity crisis" (MSC), when the Mediterranean almost entirely dried out. The time of beginning of the MSC was recently estimated astronomically at 5.96 mya, and it persisted for some 630,000 years until about 5.3 mya;[46] see Animation: Messinian salinity crisis, at right.
After the initial drawdown and re-flooding there followed more episodes—the total number is debated—of sea drawdowns and re-floodings for the duration of the MSC. It ended when the Atlantic Ocean last re-flooded the basin—creating the Strait of Gibraltar and causing the Zanclean flood—at the end of the Miocene (5.33 mya). Some research has suggested that a desiccation-flooding-desiccation cycle may have repeated several times, which could explain several events of large amounts of salt deposition.[47][48] Recent studies, however, show that repeated desiccation and re-flooding is unlikely from a geodynamic point of view. [49][50]
Desiccation and exchanges of flora and fauna
The present-day Atlantic gateway, i.e. the Strait of Gibraltar, originated in the early Pliocene via the Zanclean Flood. As mentioned, two other gateways preceded Gibraltar: the Betic Corridor across southern Spain and the Rifian Corridor across northern Morocco. The former gateway closed about six (6) mya, causing the Messinian salinity crisis (MSC); the latter or possibly both gateways closed during the earlier Tortonian times, causing a "Tortonian salinity crisis" (from 11.6 to 7.2 mya), which occurred well before the MSC and lasted much longer. Both "crises" resulted in broad connections of the mainlands of Africa and Europe, which thereby normalized migrations of flora and fauna—especially large mammals including primates—between the two continents. The Vallesian crisis indicates a typical extinction and replacement of mammal species in Europe during Tortonian times following climatic upheaval and overland migrations of new species;[51] see Animation: Messinian salinity crisis (and mammal migrations), at right.
The near-completely enclosed configuration of the Mediterranean basin has enabled the oceanic gateways to dominate seawater circulation and the environmental evolution of the sea and basin. Circulation patterns are also affected by several other factors—including climate, bathymetry, and water chemistry and temperature—which are interactive and can induce precipitation of evaporites. Deposits of evaporites accumulated earlier in the nearby Carpathian foredeep during the Middle Miocene, and the adjacent Red Sea Basin (during the Late Miocene), and in the whole Mediterranean basin (during the MSC and the Messinian age). Diatomites are regularly found underneath the evaporite deposits, suggesting a connection between their geneses.
Today, evaporation of surface seawater (output) is more than the supply (input) of fresh water by precipitation and coastal drainage systems, causing the salinity of the Mediterranean to be much higher than that of the Atlantic—so much so that the saltier Mediterranean waters sink below the waters incoming from the Atlantic, causing a two-layer flow across the Gibraltar strait: that is, an outflow submarine current of warm saline Mediterranean water, counterbalanced by an inflow surface current of less saline cold oceanic water from the Atlantic. Herman Sörgel's Atlantropa project proposal in the 1920s proposed a hydroelectric dam to be built across the Strait of Gibraltar, using the inflow current to provide a large amount of hydroelectric energy. The underlying energy grid was as well intended to support a political union between Europe and, at least, the Marghreb part of Africa (compare Eurafrika for the later impact and Desertec for a later project with some parallels in the planned grid).[52]
Shift to a "Mediterranean climate"
The end of the Miocene also marked a change in the climate of the Mediterranean basin. Fossil evidence from that period reveals that the larger basin had a humid subtropical climate with rainfall in the summer supporting laurel forests. The shift to a "Mediterranean climate" occurred largely within the last three million years (the late Pliocene epoch) as summer rainfall decreased. The subtropical laurel forests retreated; and even as they persisted on the islands of Macaronesia off the Atlantic coast of Iberia and North Africa, the present Mediterranean vegetation evolved, dominated by coniferous trees and sclerophyllous trees and shrubs with small, hard, waxy leaves that prevent moisture loss in the dry summers. Much of these forests and shrublands have been altered beyond recognition by thousands of years of human habitation. There are now very few relatively intact natural areas in what was once a heavily wooded region.
Paleoclimate
Because of its latitudinal position and its land-locked configuration, the Mediterranean is especially sensitive to astronomically induced climatic variations, which are well documented in its sedimentary record. Since the Mediterranean is involved in the deposition of eolian dust from the Sahara during dry periods, whereas riverine detrital input prevails during wet ones, the Mediterranean marine sapropel-bearing sequences provide high-resolution climatic information. These data have been employed in reconstructing astronomically calibrated time scales for the last 9 Ma of the Earth's history, helping to constrain the time of past geomagnetic reversals.[53] Furthermore, the exceptional accuracy of these paleoclimatic records have improved our knowledge of the Earth's orbital variations in the past.
Ecology and biota
As a result of the drying of the sea during the Messinian salinity crisis,[54] the marine biota of the Mediterranean are derived primarily from the Atlantic Ocean. The North Atlantic is considerably colder and more nutrient-rich than the Mediterranean, and the marine life of the Mediterranean has had to adapt to its differing conditions in the five million years since the basin was reflooded.
The Alboran Sea is a transition zone between the two seas, containing a mix of Mediterranean and Atlantic species. The Alboran Sea has the largest population of bottlenose dolphins in the Western Mediterranean, is home to the last population of harbour porpoises in the Mediterranean, and is the most important feeding grounds for loggerhead sea turtles in Europe. The Alboran sea also hosts important commercial fisheries, including sardines and swordfish. The Mediterranean monk seals live in the Aegean Sea in Greece. In 2003, the World Wildlife Fund raised concerns about the widespread drift net fishing endangering populations of dolphins, turtles, and other marine animals.
Environmental history
For 4,000 years, human activity has transformed most parts of Mediterranean Europe, and the "humanisation of the landscape" overlapped with the appearance of the present Mediterranean climate.[55] The image of a simplistic, environmental determinist notion of a Mediterranean Paradise on Earth in antiquity, which was destroyed by later civilisations dates back to at least the 18th century and was for centuries fashionable in archaeological and historical circles. Based on a broad variety of methods, e.g. historical documents, analysis of trade relations, floodplain sediments, pollen, tree-ring and further archaeometric analyses and population studies, Alfred Thomas Grove and Oliver Rackham's work on "The Nature of Mediterranean Europe" challenges this common wisdom of a Mediterranean Europe as a "Lost Eden", a formerly fertile and forested region, that had been progressively degraded and desertified by human mismanagement.[55] The belief stems more from the failure of the recent landscape to measure up to the imaginary past of the classics as idealised by artists, poets and scientists of the early modern Enlightenment.[55]
The historical evolution of climate, vegetation and landscape in southern Europe from prehistoric times to the present is much more complex and underwent various changes. For example, some of the deforestation had already taken place before the Roman age. While in the Roman age large enterprises as the Latifundiums took effective care of forests and agriculture, the largest depopulation effects came with the end of the empire. Some[who?] assume that the major deforestation took place in modern times — the later usage patterns were also quite different e.g. in southern and northern Italy. Also, the climate has usually been unstable and showing various ancient and modern "Little Ice Ages",[56] and plant cover accommodated to various extremes and became resilient with regard to various patterns of human activity.[55]
Humanisation was therefore not the cause of climate change but followed it.[55] The wide ecological diversity typical of Mediterranean Europe is predominantly based on human behaviour, as it is and has been closely related human usage patterns.[55] The diversity range was enhanced by the widespread exchange and interaction of the longstanding and highly diverse local agriculture, intense transport and trade relations, and the interaction with settlements, pasture and other land use. The greatest human-induced changes, however, came since World War II, respectively in line with the '1950s-syndrome'[57] as rural populations throughout the region abandoned traditional subsistence economies. Grove and Rackham suggest that the locals left the traditional agricultural patterns towards taking a role as scenery-setting agents for the then much more important (tourism) travellers. This resulted in more monotonous, large-scale formations.[55] Among further current important threats to Mediterranean landscapes are overdevelopment of coastal areas, abandonment of mountains and, as mentioned, the loss of variety via the reduction of traditional agricultural occupations.[55]
Natural hazards
The region has a variety of geological hazards which have closely interacted with human activity and land use patterns. Among others, in the eastern Mediterranean, the Thera eruption, dated to the 17th or 16th century BC, caused a large tsunami that some experts hypothesise devastated the Minoan civilisation on the nearby island of Crete, further leading some to believe that this may have been the catastrophe that inspired the Atlantis legend.[58] Mount Vesuvius is the only active volcano on the European mainland, while others as Mount Etna and Stromboli are to be found on neighbouring islands. The region around Vesuvius including the Phlegraean Fields Caldera west of Naples are quite active[59] and constitute the most densely populated volcanic region in the world and eruptive event may occur within decades.[60]
Vesuvius itself is regarded as quite dangerous due to a tendency towards explosive (Plinian) eruptions.[61] It is best known for its eruption in AD 79 that led to the burying and destruction of the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
The large experience of member states and regional authorities has led to exchange on the international level with cooperation of NGOs, states, regional and municipality authorities and private persons.[62] The Greek–Turkish earthquake diplomacy is a quite positive example of natural hazards leading to improved relations of traditional rivals in the region after earthquakes in İzmir and Athens 1999. The European Union Solidarity Fund (EUSF) was set up to respond to major natural disasters and express European solidarity to disaster-stricken regions within all of Europe.[63] The largest amount of fund requests in the EU is being directed to forest fires, followed by floodings and earthquakes. Forest fires are, whether man made or natural, an often recurring and dangerous hazard in the Mediterranean region.[62] Also, tsunamis are an often underestimated hazard in the region. For example, the 1908 Messina earthquake and tsunami took more than 123,000 lives in Sicily and Calabria and is among the most deadly natural disasters in modern Europe.
Biodiversity
Invasive species

The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 created the first salt-water passage between the Mediterranean and Red Sea. The Red Sea is higher than the Eastern Mediterranean, so the canal serves as a tidal strait that pours Red Sea water into the Mediterranean. The Bitter Lakes, which are hyper-saline natural lakes that form part of the canal, blocked the migration of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean for many decades, but as the salinity of the lakes gradually equalised with that of the Red Sea, the barrier to migration was removed, and plants and animals from the Red Sea have begun to colonise the Eastern Mediterranean. The Red Sea is generally saltier and more nutrient-poor than the Atlantic, so the Red Sea species have advantages over Atlantic species in the salty and nutrient-poor Eastern Mediterranean. Accordingly, Red Sea species invade the Mediterranean biota, and not vice versa; this phenomenon is known as the Lessepsian migration (after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French engineer) or Erythrean invasion. The construction of the Aswan High Dam across the Nile River in the 1960s reduced the inflow of freshwater and nutrient-rich silt from the Nile into the Eastern Mediterranean, making conditions there even more like the Red Sea and worsening the impact of the invasive species.
Invasive species have become a major component of the Mediterranean ecosystem and have serious impacts on the Mediterranean ecology, endangering many local and endemic Mediterranean species. A first look at some groups of exotic species show that more than 70% of the non-indigenous decapods and about 63% of the exotic fishes occurring in the Mediterranean are of Indo Pacific origin,[64] introduced into the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal. This makes the Canal as the first pathway of arrival of "alien" species into the Mediterranean. The impacts of some lessepsian species have proven to be considerable mainly in the Levantine basin of the Mediterranean, where they are replacing native species and becoming a "familiar sight".
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature definition, as well as Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and Ramsar Convention terminologies, they are alien species, as they are non-native (non-indigenous) to the Mediterranean Sea, and they are outside their normal area of distribution which is the Indo-Pacific region. When these species succeed in establishing populations in the Mediterranean sea, compete with and begin to replace native species they are "Alien Invasive Species", as they are an agent of change and a threat to the native biodiversity. In the context of CBD, "introduction" refers to the movement by human agency, indirect or direct, of an alien species outside of its natural range (past or present). The Suez Canal, being an artificial (man made) canal, is a human agency. Lessepsian migrants are therefore "introduced" species (indirect, and unintentional). Whatever wording is chosen, they represent a threat to the native Mediterranean biodiversity, because they are non-indigenous to this sea. In recent years, the Egyptian government's announcement of its intentions to deepen and widen the canal have raised concerns from marine biologists, fearing that such an act will only worsen the invasion of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean, facilitating the crossing of the canal for yet additional species.[65]
Arrival of new tropical Atlantic species
In recent decades, the arrival of exotic species from the tropical Atlantic has become a noticeable feature. Whether this reflects an expansion of the natural area of these species that now enter the Mediterranean through the Gibraltar strait, because of a warming trend of the water caused by global warming; or an extension of the maritime traffic; or is simply the result of a more intense scientific investigation, is still an open question. While not as intense as the "lessepsian" movement, the process may be scientific interest and may therefore warrant increased levels of monitoring.[citation needed]
Sea-level rise
By 2100, the overall level of the Mediterranean could rise between 3 to 61 cm (1.2 to 24.0 in) as a result of the effects of climate change.[66] This could have adverse effects on populations across the Mediterranean:
- Rising sea levels will submerge parts of Malta. Rising sea levels will also mean rising salt water levels in Malta's groundwater supply and reduce the availability of drinking water.[67]
- A 30 cm (12 in) rise in sea level would flood 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) of the Nile Delta, displacing over 500,000 Egyptians.[68]
Coastal ecosystems also appear to be threatened by sea level rise, especially enclosed seas such as the Baltic, the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. These seas have only small and primarily east-west movement corridors, which may restrict northward displacement of organisms in these areas.[69] Sea level rise for the next century (2100) could be between 30 cm (12 in) and 100 cm (39 in) and temperature shifts of a mere 0.05-0.1 °C in the deep sea are sufficient to induce significant changes in species richness and functional diversity.[70]
Pollution
Pollution in this region has been extremely high in recent years.[when?] The United Nations Environment Programme has estimated that 650,000,000 t (720,000,000 short tons) of sewage, 129,000 t (142,000 short tons) of mineral oil, 60,000 t (66,000 short tons) of mercury, 3,800 t (4,200 short tons) of lead and 36,000 t (40,000 short tons) of phosphates are dumped into the Mediterranean each year.[71] The Barcelona Convention aims to 'reduce pollution in the Mediterranean Sea and protect and improve the marine environment in the area, thereby contributing to its sustainable development.'[72] Many marine species have been almost wiped out because of the sea's pollution. One of them is the Mediterranean monk seal which is considered to be among the world's most endangered marine mammals.[73]
The Mediterranean is also plagued by marine debris. A 1994 study of the seabed using trawl nets around the coasts of Spain, France and Italy reported a particularly high mean concentration of debris; an average of 1,935 items per km2. Plastic debris accounted for 76%, of which 94% was plastic bags.[74]
Shipping
Some of the world's busiest shipping routes are in the Mediterranean Sea. It is estimated that approximately 220,000 merchant vessels of more than 100 tonnes cross the Mediterranean Sea each year—about one third of the world's total merchant shipping. These ships often carry hazardous cargo, which if lost would result in severe damage to the marine environment.
The discharge of chemical tank washings and oily wastes also represent a significant source of marine pollution. The Mediterranean Sea constitutes 0.7% of the global water surface and yet receives 17% of global marine oil pollution. It is estimated that every year between 100,000 t (98,000 long tons) and 150,000 t (150,000 long tons) of crude oil are deliberately released into the sea from shipping activities.
Approximately 370,000,000 t (360,000,000 long tons) of oil are transported annually in the Mediterranean Sea (more than 20% of the world total), with around 250-300 oil tankers crossing the sea every day. Accidental oil spills happen frequently with an average of 10 spills per year. A major oil spill could occur at any time in any part of the Mediterranean.[70]
Tourism

With a unique combination of pleasant climate, beautiful coastline, rich history and diverse culture the Mediterranean region is the most popular tourist destination in the world—attracting approximately one third of the world's international tourists.
Tourism is one of the most important sources of income for many Mediterranean countries. It also supports small communities in coastal areas and islands by providing alternative sources of income far from urban centres. However, tourism has also played major role in the degradation of the coastal and marine environment. Rapid development has been encouraged by Mediterranean governments to support the large numbers of tourists visiting the region each year. But this has caused serious disturbance to marine habitats such as erosion and pollution in many places along the Mediterranean coasts.
Tourism often concentrates in areas of high natural wealth, causing a serious threat to the habitats of endangered Mediterranean species such as sea turtles and monk seals. Reductions in natural wealth may reduce incentives for tourists to visit.[70]
Overfishing
Fish stock levels in the Mediterranean Sea are alarmingly low. The European Environment Agency says that over 65% of all fish stocks in the region are outside safe biological limits and the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation, that some of the most important fisheries—such as albacore and bluefin tuna, hake, marlin, swordfish, red mullet and sea bream—are threatened.[date missing]
There are clear indications that catch size and quality have declined, often dramatically, and in many areas larger and longer-lived species have disappeared entirely from commercial catches.
Large open water fish like tuna have been a shared fisheries resource for thousands of years but the stocks are now dangerously low. In 1999, Greenpeace published a report revealing that the amount of bluefin tuna in the Mediterranean had decreased by over 80% in the previous 20 years and government scientists warn that without immediate action the stock will collapse.
Aquaculture

Aquaculture is expanding rapidly—often without proper environmental assessment—and currently accounts for 30% of the fish protein consumed worldwide. The industry claims that farmed seafood lessens the pressure on wild fish stocks, yet many of the farmed species are carnivorous, consuming up to five times their weight in wild fish.
Mediterranean coastal areas are already over exposed to human influence, with pristine areas becoming ever scarcer. The aquaculture sector adds to this pressure, requiring areas of high water quality to set up farms. The installation of fish farms close to vulnerable and important habitats such as seagrass meadows is particularly concerning.
Gallery
-
Beach of Hammamet, Tunisia
-
The beach of la Courtade in the Îles d'Hyères, France
-
Sardinia's south coast, Italy
-
Pretty Bay, Malta
-
Panoramic view of Piran, Slovenia
-
Panoramic view of Cavtat, Croatia
-
View of Neum, Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
A view of Sveti Stefan, Montenegro
-
Ksamil beaches, Albania
-
Navagio, Greece
-
Marmaris, Turquoise Coast, Turkey
-
Paphos, Cyprus
-
Burj Islam Beach, Latakia, Syria
-
View from the city of Haifa, Israel
-
Beach on the Gaza Strip, State of Palestine
-
Coast of Alexandria, view From Bibliotheca Alexandrina, Egypt
-
A beach in Benghazi, Libya
-
Old city of Ibiza Town, Spain
-
Les Aiguades near Béjaïa, Algeria
-
El Jebha, a port town in Morocco
-
Europa Point, Gibraltar
-
Panoramic view of La Condamine, Monaco
See also
|
Notes
- ^ a b In the local languages:
- Template:Lang-sq [ˈdɛti ˈmɛsðɛ]
- Template:Lang-ar, tr. āl-Baḥr āl-ābyaḍ āl-Mutawassiṭ [aːlˈbaħr aːlˈaːbjadˤ aːlmutawaˈsitˤ]
- Template:Lang-ca [ˈmaɾ məðitəˈrani(ə)]
- Template:Lang-fr [mɛʁ me.di.te.ʁa.ne]
- Template:Lang-ell, tr. Mesógeios Thálassa [meˈsoʝos ˈθalasa]
- Template:Lang-he, tr. Hayám Hatikhón [haˈjam hatiˈkon]
- Template:Lang-it [ˈmar mediterˈraːneo]
- Template:Lang-la, [ˈmarɛ ˈnostrũː]
- Template:Lang-mt [ˈbɐːħɐr mɛdɪˈtɛrːɐn]
- Template:Lang-sh, Средоземно море [srêdozeːmno môːre]
- Template:Lang-sl [srɛdɔˈzéːmskɔ ˈmóːrjɛ]
- Template:Lang-es [ˈmar meðiteˈraneo]
- Template:Lang-aeb Template:IPA-aeb
- Template:Lang-tr [ˈakdeniz]
References
- ^ UNECE.indb
- ^ Pinet, Paul R. (2008). Invitation to Oceanography. Jones & Barlett Learning. p. 220. ISBN 0-7637-5993-7.
- ^ "Microsoft Word — ext_abstr_East_sea_workshop_TLM.doc" (PDF). Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Researchers predict Mediterranean Sea level rise — Headlines — Research – European Commission". Europa. 19 March 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Mediterranean Sea". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
- ^ entry μεσόγαιος at Liddell & Scott
- ^ Özhan Öztürk claims that in Old Turkish ak also means "west" and that Akdeniz hence means "West Sea", while Karadeniz (Black Sea) means "North Sea". Özhan Öztürk. Pontus: Antik Çağ’dan Günümüze Karadeniz’in Etnik ve Siyasi Tarihi Genesis Yayınları. Ankara. 2011. pp. 5–9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ David Abulafia (2011). The Great Sea: A Human History of the Mediterranean. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Rappoport, S. (Doctor of Philosophy, Basel). History of Egypt (undated, early 20th century), Volume 12, Part B, Chapter V: "The Waterways of Egypt", pages 248-257. London: The Grolier Society.
- ^ Robert Davis (5 December 2003). Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9780333719664. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "British Slaves on the Barbary Coast". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ C.I. Gable - Constantinople Falls to the Ottoman Turks - Boglewood Timeline - 1998 - Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ "History of the Ottoman Empire, an Islamic Nation where Jews Lived" - Sephardic Studies and Culture - Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ Robert Guisepi - The Ottomans: From Frontier Warriors To Empire Builders - 1992 - History World International - Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ "Migrant deaths prompt calls for EU action". Al Jazeera — English. 13 October 2013. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ^ "Schulz: EU migrant policy 'turned Mediterranean into graveyard'". EUobserver. 24 October 2013. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ^ http://topnews.az/en/news/148766/Novruz-Mammadov-The-Mediterranean-become-a-burial-ground.html
- ^ http://www.eurasia-rivista.org/loperazione-mare-nostrum/20335/
- ^ a b "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ^ Pinet, Paul R. (1996), Invitation to Oceanography (3rd ed.), St Paul, Minnesota: West Publishing Co., p. 202, ISBN 0-314-06339-0
- ^ Pinet 1996, p. 206.
- ^ "Temperature and salinity variations of Mediterranean Sea surface waters over the last 16,000 years from records of planktonic stable oxygen isotopes and alkenone unsaturation ratios". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 158: 259–280. 2000. doi:10.1016/s0031-0182(00)00053-5.
- ^ Pinet 1996, pp. 206–207.
- ^ Pinet 1996, p. 207.
- ^ Israel, By Sue Bryant, (New Holland Publishers, 2008), page 72
- ^ Marseille Climate and Weather Averages, France
- ^ Gibraltar Climate and Weather Averages
- ^ Malaga Climate and Weather Averages, Costa del Sol
- ^ Athens Climate and Weather Averages, Greece
- ^ Barcelona Climate and Weather Averages, Spain
- ^ Iraklion Climate and Weather Averages, Crete
- ^ Venice Climate and Weather Averages, Venetian Riviera
- ^ Valencia Climate and Weather Averages, Spain
- ^ Valletta Climate and Weather Averages, Malta
- ^ Alexandria Climate and Weather Averages, Egypt
- ^ Naples Climate and Weather Averages, Neapolitan Riviera
- ^ Larnaca Climate and Weather Averages, Cyprus
- ^ Limassol Climate and Weather Averages, Cyprus
- ^ Tel Aviv Climate and Weather Averages, Israel
- ^ William Ryan (2008). "Decoding the Mediterranean salinity crisis". Sedimentology. 56 (1): 95–136. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.2008.01031.x.
- ^ William Ryan (2008). "Modeling the magnitude and timing of evaporative drawdown during the Messinian salinity crisis" (PDF). Sedimentology. 5 (3–4): 229.
- ^ Garcia-Castellanos, D., Estrada, F., Jiménez-Munt, I., Gorini, C., Fernàndez, M., Vergés, J., De Vicente, R. (10 December 2009) Catastrophic flood of the Mediterranean after the Messinian salinity crisis, Nature 462, pp. 778–781, doi:10.1038/nature08555
- ^ Elmer LaMoreaux, Philip (2001). "Geologic/Hydrogeologic Setting and Classification of Springs". Springs and Bottled Waters of the World: Ancient History, Source, Occurrence, Quality and Use. Springer. p. 57. ISBN 978-3-540-61841-6.
- ^ Žumer, Jože (2004). "Odkritje podmorskih termalnih izvirov" (PDF). Geografski obzornik (in Slovenian). 51 (2). Association of the Geographical Societies of Slovenia: 11–17. ISSN 0016-7274.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) Template:Sl icon - ^ de la Vara, Alba; Topper, Robin P.M.; Meijer, Paul Th.; Kouwenhoven, Tanja J. (2015). "Water exchange through the Betic and Rifian corridors prior to the Messinian Salinity Crisis: A model study". Paleoceanography. 30: 548–557. doi:10.1002/2014PA002719.
- ^ W. Krijgsman, A. R. Fortuinb, F. J. Hilgenc and F. J. Sierrod (2001). "Astrochronology for the Messinian Sorbas basin (SE Spain) and orbital (precessional) forcing for evaporite cyclicity". Sedimentary Geology. 140: 43–60. Bibcode:2001SedG..140...43K. doi:10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00171-8.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gargani J., Rigollet C. (2007). "Mediterranean Sea level variations during the Messinian Salinity Crisis". Geophysical Research Letters. 34 (L10405): L10405. Bibcode:2007GeoRL..3410405G. doi:10.1029/2007GL029885.
- ^ Gargani J., Moretti I., Letouzey J. (2008). "Evaporite accumulation during the Messinian Salinity Crisis : The Suez Rift Case". Geophysical Research Letters. 35 (2): L02401. Bibcode:2008GeoRL..35.2401G. doi:10.1029/2007gl032494.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Govers, R. (2009). Choking the Mediterranean to dehydration: The Messinian salinity crisis Geology, 37 (2), 167-170 doi:10.1130/G25141A.1 Link
- ^ Garcia-Castellanos, D., A. Villaseñor, 2011. Messinian salinity crisis regulated by competing tectonics and erosion at the Gibraltar Arc. Nature, 2011-12-15 pdf here Link
- ^ Agusti, J; Moya-Sola, S (1990). "Mammal extinctions in the Vallesian (Upper Miocene)". Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences. 30: 425–432. doi:10.1007/BFb0011163. ISSN 1613-2580. (Abstract)
- ^ Politische Geographien Europas: Annäherungen an ein umstrittenes Konstrukt, Anke Strüver, LIT Verlag Münster, 2005, p.43
- ^ FJ, Hilgen. Astronomical calibration of Gauss to Matuyama sapropels in the Mediterranean and implication for the Geomagnetic Polarity Time Scale, 104 (1991) 226-244 Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991.[1]
- ^ Hsu K.J., "When the Mediterranean Dried Up" Scientific American, Vol. 227, December 1972, p32
- ^ a b c d e f g h The Nature of Mediterranean Europe: An Ecological History, by Alfred Thomas Grove, Oliver Rackham, Yale University Press, 2003, review at Yale university press Nature of Mediterranean Europe: An Ecological History (review) Brian M. Fagan, Journal of Interdisciplinary History, Volume 32, Number 3, Winter 2002, pp. 454-455 |
- ^ Little Ice Ages: Ancient and Modern, Jean M. Grove, Taylor & Francis, 2004
- ^ Christian Pfister (Hrsg.), Das 1950er Syndrom: Der Weg in die Konsumgesellschaft, Bern 1995
- ^ The wave that destroyed Atlantis Harvey Lilley, BBC News Online, 2007-04-20. Retrieved 2007-04-21.
- ^ Antonio Denti, "Super volcano", global danger, lurks near Pompeii, Reuters, August 3, 2012.
- ^ Isaia, Roberto; Paola Marianelli; Alessandro Sbrana (2009). "Caldera unrest prior to intense volcanism in Campi Flegrei (Italy) at 4.0 ka B.P.: Implications for caldera dynamics and future eruptive scenarios". Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (L21303): L21303. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..3621303I. doi:10.1029/2009GL040513.
- ^ McGuire, Bill (16 October 2003). "In the shadow of the volcano". guardian.co.uk. Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
- ^ a b Eric van der Horst presentation from 2011 about various EU EUROPEAN CIVIL PROTECTION efforts 2011
- ^ EU Solidarity Fund Website 2003 proposal of EUR 47.6 million for Italian regions hit by natural disasters
- ^ "IUCN Guidelines for the Prevention of Biodiversity Loss Caused by Alien Invasive Species" (PDF). International Union for Conservation of Nature. 2000. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2009. Retrieved 11 August 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Galil, B.S. and Zenetos, A. (2002). A sea change: exotics in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, in: Leppäkoski, E. et al. (2002). Invasive aquatic species of Europe: distribution, impacts and management. pp. 325-336.
- ^ "Mediterranean Sea Level Could Rise By Over Two Feet, Global Models Predict". Science Daily. 3 March 2009.
- ^ "Briny future for vulnerable Malta". BBC News. 4 April 2007.
- ^ "Egypt fertile Nile Delta falls prey to climate change". 28 January 2010.
- ^ Nicholls, R.J.; Klein,R.J.T. (2005). Climate change and coastal management on Europe's coast, in: Vermaat, J.E. et al. (Ed.) (2005). Managing European coasts: past, present and future. pp. 199-226.
- ^ a b c "Other threats in the Mediterranean | Greenpeace International". Greenpeace. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea. Environmental issues". Explorecrete.com. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "EUROPA". Europa. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Mediterranean Monk Seal Fact Files: Overview". Monachus-guardian.org. 5 May 1978. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ publications/docs/anl_oview.pdf "Marine Litter: An analytical overview" (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. 2005. Retrieved 1 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help)