Postal code: Difference between revisions
m Reverted 1 edit by 24.205.7.159 identified as vandalism to last revision by Ww2censor. (TW) |
|||
| Line 509: | Line 509: | ||
===Thailand=== |
===Thailand=== |
||
[[Thailand]] postcodes, introduced on 25 February 2525 B.E. (A.D. 1982), have 5 digits. The first two specify the province. The third and fourth digits specify a district ([[amphoe]]). |
[[Thailand]] postcodes, introduced on 25 February 2525 B.E. (A.D. 1982), have 5 digits. The first two specify the province. The third and fourth digits specify a district ([[amphoe]]). T |
||
===Turkey=== |
===Turkey=== |
||
Revision as of 02:46, 5 December 2008

A postal code (known in various countries as a post code, postcode, or ZIP code) is a series of letters and/or digits appended to a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail.
Germany was the first country to introduce a postal code system, in 1941. The United Kingdom followed in 1959 and the United States in 1963.
In February 2005, 117 of the 190 member countries of the Universal Postal Union had postal code systems. Examples of countries that do not have national systems include Ireland, Hong Kong and Panama.
Although postal codes are usually assigned to geographical areas, special codes are sometimes assigned to individual addresses or to institutions that receive large volumes of mail, such as government agencies and large commercial companies. One example is the French Cedex system.
Usage conventions
Postal services have their own formats and placement rules for postal codes. In most English-speaking countries, the postal code forms the last item of the address, whereas in most continental European countries it precedes the name of the city or town.
National prefixes
In some countries (such as those of continental Europe, where a postcode format of four or five numeric digits is commonly used) the numeric postal code is sometimes prefixed with a country code to avoid confusion when sending international mail to or from that country. Recommendations by official bodies responsible for postal communications are confusing regarding this practice.[1] For many years, licence plate codes — for instance "D-" for Germany or "F-" for France — were used, although this was not accepted by the Universal Postal Union (UPU).[1] Usage of ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes was recommended to be used starting in 1994,[1] but did not become widely used. The European Committee for Standardization recommends use of ISO Alpha-2 codes for international postcodes[1] and a UPU guide on international addressing states that "administrations may recommend" the use of ISO Alpha-2 codes.[2]
Alphanumeric postal codes
Most postal codes are numeric. The few independent nations using alphanumeric postal code systems (with letters and digits) are:
Postal zone numbers
Before postal codes as described here were used, large cities were often divided into postal zones or postal districts, usually numbered from 1 upwards within each city. The newer postal code systems often incorporate the old zone numbers, as with London postal district numbers, for example. Ireland still uses postal district numbers in Dublin. In New Zealand, Auckland, Wellington and Christchurch were divided into postal zones, but these fell into disuse, and have now become redundant as a result of a new postcode system being introduced.
Postal codes in particular countries
Algeria
In Algeria, the postal codes of province capitals are composed of the province code and three zeros, for example: 16000 for Algiers, while the postal codes of other cities, towns, and villages in the province are the provincial code followed by three numerals. See "list of postal codes of Algerian cities" for the postal codes of all of Algeria's 1,541 municipalities, and other places with their own postal code.
Argentina
The Argentine postal code is a system that assigns at least one unique alphanumeric postal code to each municipality. Some larger cities have several codes starting at a base code, and the codes of all municipalities with a population over 500 additionally show the side of the block where the address is located.
The CPA consists of three parts:
- A single letter that encodes the province (for example, C for Capital Federal, Q for Neuquén).
- Four digits (the old postal code or a variation of it on the last digits) showing the municipality.
- Three letters, identifying a side of the block where the address is located.
Until 1998 Argentina employed a four-digit postal code for each municipality, with the first digit representing a region in the country, except in the case of the city of Buenos Aires. The CPA is intended to improve the quality and speed of mail delivery, but mail without a well-formed CPA will be delivered correctly as well.
Australia
Australian postcodes are numeric, consisting of four digits. They were introduced in 1967 by the Postmaster-General's Department (PMG), the predecessor of Australia Post. For a history of the PMG / Australia Post see here.[3]
Postcodes are published in small booklets available from post offices, and also in the white pages of telephone directories.
On envelopes and postcards there are usually four rectangular boxes printed in orange ink at the bottom right for the postal code digits.
Austria

Austrian post codes were introduced in 1966 and consist of four numbers. The first indicates the state:
- 1xxx: Vienna
- 2xxx: Lower Austria (east of Vienna)
- 3xxx: Lower Austria (west of Vienna)
- 4xxx: Upper Austria
- 5xxx: Salzburg and east Upper Austria
- 6xxx: Tyrol and Vorarlberg (without East Tyrol)
- 7xxx: Burgenland
- 8xxx: Styria
- 9xxx: Carinthia and East Tyrol
The second number indicates the regional area in the state, the third number is for the routing allocation, following railways and post car routes and the fourth number indicates the post office. Every post office has its own number. There are some exceptions to this rule: In Vienna, the second and third numbers show the district, so 1120 would be the twelfth district. Also, some cities close to the German border in Vorarlberg have Austrian and German postcodes.
There are also some special post codes: the airport has its own post code (1300), the UN (1400) and some big companies also have their own post code, for example the ORF, the Austrian National Broadcasting Service (1136). These special post codes are not listed in the public phonebook, though there is a book which contains them and can be bought at an Austrian post office.
Belgium
Belgian post codes are numeric and consist of 4 numbers, although the last one is often zero. The first digit indicates the province (except for the 3xxx numbers that are shared by the eastern part of Flemish Brabant and Limburg and the and 1xxx that are shared by the Brussels Capital Region, the western part of Flemish Brabant and Walloon Brabant), the other numbers were given more or less at random. The more zeros though the higher the number of inhabitants of that city in the province. For example: Brugge is the capital and largest urban centre of the coastal province of West Flanders so it gets the 8000 code, the second city is Kortrijk and gets 8500. When writing the address, the postal code is put in front of the town name.
Special numbers are reserved for the EU institutions, NATO headquarters, public and commercial broadcasters (RTBF, RTL TVi, VRT and VTM), the different parliaments and other public institutions.
Brazil
Postcodes in Brazil follow a nationwide scheme known as CEP (Código de Endereçamento Postal) (Postal Addressing Code) introduced in 1972 as a sequence of five digits. To keep mail services up with economic growth, a three-digit suffix was added in 1992.
Most cities with population around 100,000 and above have a CEP assigned to every public place and to some high-occupancy private spaces, like major commercial buildings and large residential condos. Small towns are assigned a general code, usually with attributed town code followed by the suffix -000.
Correios, Brazil's mail service, requests (but not requires) that the code be placed in the last line of the address and although totally unrequired (and even unwanted by automatic sorting machines) the acronym CEP is usually placed before the code, e.g. CEP 29145-586.
Valid examples for mailing in Brazil are:
Rua Helena, 260
Vila Olímpia
São Paulo - SP
CEP 04552-050
or
Rua Helena, 260
Vila Olímpia
São Paulo - SP
04552-050
Any CEP code can be obtained from Correio's website, if you have a Flash plugin[4] (in Portuguese).
Brunei
Postal codes used in Brunei are alphanumeric, consisting of two letters followed by four digits in the format of YZ0000, where Y denotes the district code, Z denotes the mukim code, the first two digits denote the area or village code, and the last two digits denote the nearest post office code (e.g. the postal code for Pantai Mentiri Golf Club is BU2529).
For a list of Brunei Postal Codes go to http://www.pos.gov.bn/postcode/images/Poskod1.htm
Bulgaria
Bulgarian postcodes are numeric, consisting of four digits.
Canada

A Canadian postal code is a string of six characters in the format X#X #X#, where X is a letter and "#" is a single digit, with a space separating the third and fourth characters. An example is K1A 0B1, which is for Canada Post's Ottawa headquarters. The postal code H0H 0H0 is reserved for letters to Santa Claus.
The letters D, F, I, O, Q, and U are not used in postal codes. This is because OCR technoligy is used to sort mail, and these letters can easily be confused for other letters.
Cape Verde
Cape Verdean postal codes are numeric, consisting of four digits. The first digit indicates the island.
China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China have six digits. The first two digits show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the third digit the postal zone; the fourth digit the prefectures or prefecture-level city; the last two digits the delivery post office.
Hong Kong and Macau have their independent postal systems, and have no postal codes.
See Taiwan (Republic of China), which has its own set of postal codes.
Cyprus
Four digit post codes were introduced in Cyprus on 1 October 1994. The system is organised around the six administrative districts for local government on the island, with each district allocated a numerical range. Most of the four digit numbers are allocated to small geographic areas, such as streets, urban communes or villages, although some are reserved for government use.
Due to the division of Cyprus, following the Turkish invasion in 1974, only the Greek-controlled Republic of Cyprus uses the post code system. Mail sent to to the Turkish-occupied area of Cyprus must instead be addressed to via Mersin 10, TURKEY via Mersin in southern Turkey. The two British Sovereign Base Areas (or SBAs) of Cyprus are not part of the Republic of Cyprus, although the Cypriot villages within these areas use the Cyprus post code system. British military organisations and personnel use British Forces Post Office numbers, BFPO 57 for Akrotiri and BFPO 58 for Dhekelia.
Czech Republic
These system of postal codes (PSČ, stands for Czech: Poštovní směrovací číslo). The postal code consists of five digits, usually written in the form XXX XX, with a space). Originally the first digit indicated a region: regional divisions have changed, but the codes have not. Thus the capital of the Czech Republic, Prague, is assigned codes starting with 1.
When writing the address, the postal code is put in front of the town name, e.g.:
Na Příkopě 28
115 03 Praha 1
On envelopes and postcards there are usually five rectangular boxes below the address field for the postal code digits.
Denmark
Danish postal codes have four digits, except for five special purpose 3-digit codes. The self-governed territories of Greenland and the Faroe Islands have 4- and 3-digit codes, respectively.
New regulations add the country code DK to the postal codes, but in practice it is most often omitted.
The code is written before the city name.
Examples:
1000 København C (Copenhagen City)
6100 Haderslev
DK-9000 Aalborg
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark
Asiatisk Plads 2
DK-1448 Copenhagen K
or in Danish
Udenrigsministeriet
Asiatisk Plads 2
1448 København K - not necessarily with the DK - Be aware that the DK or Denmark must be used when mailed from abroad.
The postal codes follow a geographic pattern and most Danes can tell which region an address belongs to based on the postal code alone.
Finland
Since 1971 Finland has used five-digit numeric postal codes. The first two digits designate the municipality or group of municipal small communities where it may be 5; codes ending in 1 are for post office boxes. Corporations receiving large amounts of mail may have an own postal code. The special postal code 99999 is for Korvatunturi, the place where Santa Claus (or Joulupukki in Finnish) is said to live.
France
France uses five-digit numeric postal codes, the first two digits representing the département in which the city is located. (Note that postcodes in both départements of Corsica commence with the "20" assigned to Corsica before it was split into two départements, which are now numbered 2A and 2B.) The last three digits identify a more precise location, 000 being in general reserved for the préfecture. However, in Paris, Lyon and Marseille, the last two digits indicate the arrondissement. For example, 80000 corresponds to Amiens which is the préfecture of the Somme or département 80, while 69008 corresponds to the 8th arrondissement of Lyon.
Germany
Postal codes were introduced on July 25, 1941 in the form of a two-digit system that was applied initially for the packet service and later for all mail deliveries. This system was replaced in 1962 in the Federal Republic by a four-digit system; three years later the German Democratic Republic followed with its own four-digit system.
German postal codes are numeric, consisting of five digits since 1993 replacing the separate four-digit systems in place in West Germany and East Germany before 1990. Between 1990 and 1993 the old four-digit codes in the former West were prefixed with the letter "W", and in the former East with "O" (for "Ost", east in German). Even though the western system had kept some number ranges free specifically for later integration of the East should reunification come, it was decided that the time was right to create an entirely new system in the 1990s in which larger towns and cities would receive multiple postal codes, and companies receiving more mail (such as mail-order businesses) could get a private code assigned.
Greece
All postal codes in Greece are numeric consisting of five digits. Until 1983 local three-digit systems existed in Athens and other cities.
Hungary
Hungarian postal codes are numeric, consisting of four digits. The first digit is for the postal region, as listed below (with the postal centre indicated after the number):
- 1000 Budapest (*)
- 2000 Szentendre
- 3000 Hatvan
- 4000 Debrecen (*)
- 5000 Szolnok
- 6000 Kecskemét
- 7000 Sárbogárd
- 8000 Székesfehérvár
- 9000 Győr
Not all of the above are county capitals: Hatvan, Sárbogárd and Szentendre are major cities, but not county capitals. They are, however, all well communicated cities and big junctions.
In Budapest postal codes are in the format 1XYZ, where X and Y are the two digits of the district number (from 01 to 23) and the last digit is the identification number of the post office in the district (there are more than one in each district). A special system exists for PO Box deliveries, which do not follow the district system. These special postal codes refer to a specific post office rather than an area. Ironically, the "1000" postal code designates the Countrywide Logistics Centre, which is currently located outside the 1000 region, in Budaörs, which is in the 2000 region.
The rest of the country is structured as follows:
- County capitals are always designated a postcode ending with "00". However, some cities have postal codes ending on "00" without being a county capital.
- Cities generally have postcodes ending with "0".
- Smaller towns and villages have any other number.
Bigger cities were formerly divided into districts, which often lives on in postcodes. This can be confusing, as 3000 designates Hatvan, but 3001 doesn't designate District 1, but it is actually a PO Box postal code.
India
India's postal codes, known as Postal Index Numbers or PIN or pincodes, are a numeric sequence of six digits, such as Kamboi 384230.
Indonesia
Indonesian post codes are numeric and consist of five numbers, and follow the name of the town or city.[5] The first three digits indicate the cities or regencies. The system was used in East Timor until 1999.
Iraq
Iraqi Post has developed a comprehensive Postal Code numbering system that will ensure more efficient mail sorting and accuracy of delivery of your correspondence. The new postal system was rededicated in 2004. The system is numeric and utilizes five digits that correspond to the Region, governorate as well as the post office within that governorate.
Mail Address Format:
Examples:
Recipients Name
Company Name (if any)
PO Box # or Street Address
City*, Province
Postal Code
Ireland
Aside from the Dublin postal districts, Ireland does not have a national post code system. While the national postal service, An Post, has stated that the addressing system and sorting technologies preclude the need for postcodes for mail delivery, it has been suggested that other services (such as ambulances) would benefit from a national system. In 2005, the Minister for Communications announced that postcodes would be introduced by 2008,[6] but the project had been shelved pending additional consultation and investigation into the need.[7] However, on February 24 2008 The Sunday Times reported that the new Minister is finalising the system and hopes to bring the plans to cabinet before the summer of 2008 for introduction in 2009.[8] The proposal was reported as being a six character alphanumeric system with examples given for Galway city as GAL 123 and for Maynooth as MYN 123, where the 123 part would be different for each specific address. It also seems to keep a link to the existing Dublin postal districts with an example given for D4 becoming D04 123. An Post was quoted as saying "it would be at the heart of the introduction".[8]
Israel
Israeli post codes (Hebrew: מיקוד – Mikud) are numeric and consist of five digits. They are assigned from north to south, thus, Metula in the north has 10292 as its postal code, and Eilat in the south was assigned 88xxx. The capital city of Jerusalem postal codes start with the digit 9, though this doesn't correspond with its geographical location. Each postal code corresponds to a mail carrier route or RR, thus, when the letters are sorted by the postal code, they are assigned to a specific carrier. Army unit postal codes start with a 0 and are not changed even if a unit is roaming. The postal code is written on the right hand side of the location's name, regardless of which language the address is written in. Thus, Location 00000 both in English (location precedes the postal code) as well as in Hebrew (where it follows it).
Italy
Italian post codes are numeric, consisting of five digits, such as 20121 Milan. Created in 1967, they are commonly known as CAP (Codice di Avviamento Postale, i.e.: Postal Sending Code). The first two digits denote the administrative province (two provinces when a province has been split after 1967); the third digit shows if the town is the chief-town of the province (odd number, usually 1 or 9, e.g. 07100 Sassari) or not (even, usually 0 or 8, e.g. 10015 Ivrea); the last two digits the specific town or village or the delivery post office (only in new provinces created after 1992). In main cities like Rome, Milan, Naples, Venice the last digits designate the urban postal district (usually 00 or 70 in minor provincial chief-towns). San Marino and the Vatican City are integrated into the Italian postcode system.
Japan
Japanese post codes are numeric, consisting of seven digits, such as 102-8166 Chiyoda, Tokyo.
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Lithuania's postal codes are numeric consisting of five digits.[9]
Malaysia
All Malaysian postal codes are numeric, consisting of five digits. The first two digits of the postal code denote the state or special administrative area (e.g. 42000 Port Klang, Selangor).
Mexico
All postal codes in Mexico are numeric consisting of five digits.
Moldova
Moldova's postal codes are alphanumeric, consisting of the letters MD followed by a dash followed by four digits, e.g. Chişinău MD-2001.
The first digit refers to a designated postal zone, the rest designate smaller administrative units or districts and streets within the municipal area.
See also Official site of Poşta Moldovei
Montenegro
Morocco
Postal codes in Morocco consist of five digits, which indicate the wider area (first two digits), and the postal district (last three digits).
The present system was introduced on January 1, 1997.
Netherlands
Postal codes in the Netherlands are alphanumeric, consisting of four digits followed by two letters. Adding the house number to the postcode will identify the address, making the street name and town name redundant. For example: 2597 GV 75 will direct a postal delivery to the International School of The Hague.
New Zealand
A new postcode system has been introduced in New Zealand for all mail, unlike the old system, which was only used for mail sent in bulk. It has 1800 four-digit codes with a much finer granularity than the old codes, with each suburb and PostShop lobby having its own postal code. The first two digits specify the area, the third digit specifies the type of delivery (street, PO Box, Private Bag, or Rural delivery), and the last digit specifies the specific lobby, RD number, or suburb.
Nigeria
Postal codes in Nigeria are numeric, consisting of six digits. NIPOST, the Nigerian Postal Service, divides the country into nine regions, which make up the first digit of the code. The second and third digits, combined with the first, are the dispatch district for outgoing sorting. The last three digits are for delivery. The main postal head office in each region will have a postal code ending in 00001, such as, Garki Main HO in Abuja has the postal code 970001, Ikeja HO in Lagos has 100001, Lokoja in Kogi has 270001 and Port Harcourt has 500001. The lowest postcode being 100001 and the highest is 982002.[10]
Norway
Since 18 March 1968 Norway has used a four-digit system: postnummersystemet. The numbers start at 00 and increase with the distance from the capital city Oslo. The highest post numbers are found in the county of Finnmark, near the Russian border, where they start with 95-99. The lowest post code in use is 0001 (0slo), the highest 9991 (Båtsfjord).
Pakistan
Pakistan's postal service utilizes sequences of five numbers, termed "Post Codes," to identify locations throughout the country. Usually, an entire "Tehsil" (geographical subdivision) has its own sequence, while larger cities may have codes specific to a single neighborhood. For instance, Lahore's Gulberg district uses 54660, while Lahore's Walton district uses 54750. Postage bound for either Bangladesh or India is only slightly more expensive than domestic rates, and is far less-expensive than normal international rates.[11] Common postcodes can be found on the Pakistan Post website.
While neighbouring India has assigned an Indian "Postal Identification Number" prefix to Pakistan-Administered Kashmir, Pakistan in return has not reciprocated the gesture.[12] India's postal service will not deliver mail to Pakistani-Administered Kashmir unless the Indian postal code and word "India" appears in the address, while Pakistan's postal service often refuses to handle mail that bears the word "India" on letter bound for Pakistani Kashmir. Hence, a complicated and unofficial system of delivery has evolved whereby most letters from India, or Indian-Administered Kashmir, that are bound for Pakistani Kashmir are actually sent to post-offices in Pakistan's Punjab province that are in close proximity to Pakistani Kashmir.[13] Residents of Pakistani Kashmir will have notified the local Punjabi branch that they actually reside in Kashmir, but are simply maintaining a Punjabi postal address for convenience. Although it is illegal to do so, postal workers in those offices then unofficially forward the mail to post-offices in Pakistani Kashmir for pick-up. Important documents, on the other hand, are delivered to third parties in Dubai, who then re-address the mail to its destination in either Kashmir.
Philippines
The term "ZIP code" is used by the Philippine Postal Corporation for postal codes. Unlike American ZIP codes, the Philippines' ZIP codes are four-digit numbers without any extensions. While the cities of Metro Manila use more than one code, towns and cities outside Metro Manila are assigned only one code per town or city.
Poland
In Poland, postal codes were introduced in 1973. They consist of five digits divided into two groups of two and three digits, with hyphen between them. The whole country has been divided into 10 large areas (not following the administrative divisions—at the time, Poland was divided into 17 voivodeships, then 49, now 16). Second and third digits are used to specify a particular area (originally the number of a regional sorting office, there was one in every county), and the last two are the number of a postal delivery branch.
Clients receiving particularly large volumes of mail may have their own unique postal codes, the same goes for PO Box lobbies of the largest post offices.
Postal codes are written in Poland before the city/town/locality name, e.g. 00-001 Warszawa.
Portugal
The Portuguese postal code (código postal) is formed by four digits, a hyphen, then three digits, followed by a postal location of up to 25 characters in capitals. This location is the name of the town, sometimes followed by a three-letter abbreviation of the municipality, e.g. 4455-111 PARADELA VNB
Postal codes are given at the building block level and also to designated addresses with high volumes of mail.
The first digit designates one of nine postal regions; the following two digits designate postal distribution centers; the fourth digit is 0 if it belongs to a capital of municipality, 5 if not, or any other digit if it is a designated address; the last three digits sort building blocks and designated addresses. The more important the city, the more rounded is the number formed by the first four digits.
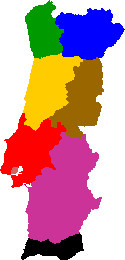
Prior to 1976, only Lisbon had used a system, of six zones (Lisboa 1 to Lisboa 6). In 1976, a national postal code system was introduced, with a four-digit structure, and designated addresses added "CODEX" (abbreviation of código extraordinário) to the postal location (example: 2001 SANTARÉM CODEX). In 1994, three extra digits were introduced and the "codex" expression was dropped.
Postal regions (first digit of postal code):[14]
1 (pink) - City of Lisbon
2 (red) - Lisbon District except City of Lisbon, Santarém District, part of Leiria and Setúbal Districts
3 (yellow) - Coimbra and Aveiro Districts, part of Leiria and Viseu Districts
4 (green) - Viana do Castelo, Braga and Porto Districts, part of Viseu and Vila Real Districts
5 (blue) - Bragança District, most of Vila Real District, part of Viseu and Guarda Districts
6 (brown) - Castelo Branco and Guarda Districts, part of Portalegre District
7 (violet) - Beja and Évora Districts, part of Portalegre and Setúbal Districts
8 (black) - Faro District (=Algarve)
9 (not in map) - Madeira Islands and Azores
Portuguese postal codes search: CTT Correios
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico is a territory of United States and therefore is integrated into the USA's five-digit numeric ZIP Code system.
Romania
On 1 May 2003 four-digit postal codes (one for each city) were replaced by six-digit codes. The digits represent (from left to right) the postal area; the county; the city/commune; the last three, depending on the size of the city/commune, represent the commune/city, the street, or the house/building.
Source: www.posta-romana.ro
Russia

Post codes in Russia are six digits long. To assist in their machine reading, envelopes are printed with a nine-segment outline for each digit, which the sender fills in. However, this is not necessary and the postal code can be written by hand as in any other country. The code usually identifies the post office (Pochtovoe Otdelenie, почтовое отделение).
San Marino
San Marino is integrated into the postcode system of Italy. It uses a five-digit numeric CAP of Emilia Romagna (Codice di Avviamento Postale, i.e.: Postal Sending Code).
Serbia
Serbian postal codes consist of five digits. The first two digits roughly correspond to the corresponding district; district seat cities usually have 000 as the last three digits, while smaller towns and villages have non-round last three digits.
According to http://www.posta.co.yu/AdresniKod/Adresovanje_eng.asp, since 1 Jan 2005 a six-digit postcode format has been introduced.
Singapore
Singapore postal codes have consisted of six digits since 1995, replacing the four-digit system introduced in 1979.
History of Singapore’s postal code system:
1950 – Singapore’s postal service started with a 2-digit postal code system to demarcate Singapore into 28 postal sectors.
1979 - With rapid pace of industrial, housing and urban development, the mail volume grew and the 28 postal districts were subdivided into 81 sectors, hence the 2-digit postal code system evolved into 4 digits.
1995 - The 6-digit postal code was introduced for the mechanised sorting of mail to delivery sequence i.e. the order in which mail is being delivered. Under the new system, every house or building is assigned with a unique 6-digit postal code. The first two digits represent the sector which came from the last two digits of the old 4-digit code. The last four digits define the point of delivery i.e. house or building.[15]
Slovakia
These system of postal codes (PSČ, stands for Slovak: Poštovné smerové číslo). The postal code consists of five digits, usually written in the form XXX XX, with a space). Originally the first digit indicated a region: regional divisions have changed, but the codes have not. Thus the capital of Slovakia, Bratislava, is assigned codes starting with 8.
When writing the address, the postal code is put in front of the town name. On envelopes and postcards there are usually five rectangular boxes below the address field for the postal code digits.
South Africa
South African postal codes are numeric, consisting of four digits. For a list of postal codes or to search by Location or Post Code see South African Post Office.
South Korea
South Korean postal codes consist of six digits with a dash after the first three digits. The first three digits before dash are region codes, and rest three after dash is minor delivery codes. Short orange bars printed under the postal codes represent also postal codes, used mainly for sorting mail. For searching postal codes, use epost on-line postal code service.
Spain
Spanish postal codes are numeric, consisting of five digits. The first two digits (ranging 01–52) of the postal code correspond to one of the fifty provinces of Spain (as listed in general alphabetical order, with some exceptions), plus the two autonomous cities on the African coast.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lankan postal codes are numeric, consisting of five digits. There are postal codes for every post office and sub-post office. Search for the postal codes here.[16]
Sweden
Since 12 May 1968 Sweden has used five-digit numeric post codes sorted by geographical location. Numbers starting with 10-19 are part of Stockholm; otherwise, the lower numbers are part of the bigger city areas in the south, and increase northwards.
When writing a Swedish address the first line is for the name of the person, second is for the name of the street and number of the building (if it's in a city) or the name and/or number of the house (if it's in the country) and third line is for the postal code followed by the name of the city (or even a small village).
A typical address would look like this:
- Erik Svensson (First and last name)
- Solrosstigen 1a (Street)
- 123 45 CITY
Switzerland
Switzerland uses four-digit numeric post codes, sorted by geographical location (from west to east, following railways and post car routes).
Taiwan (Republic of China)
The Republic of China government uses postal codes of three + two digits in Taiwan.[17] There are 368 sets of three-digit codes for rural townships, urban townships, county-controlled cities, districts (Hsinchu City and Chiayi City have districts coded 300 and 600 respectively without three-digit subdivisions), and the uninhabited island groups of Pratas Islands, Spratly Islands, and Diaoyutai Islands (claimed by the ROC, currently controlled by Japan). Omitting the supplementary two digits is ordinarily acceptable, but a five-digit code will speed up the mail.
The first digit is for a large postal zone, as follows:
- 0 Unused
- 1 Taipei City
- 2 Keelung City, Taipei County, Yilan County, Lienchiang County (Matsu), Diaoyutai Islands
- 3 Hsinchu City, Hsinchu County, Taoyuan County, Miaoli County
- 4 Taichung City, Taichung County
- 5 Changhua City, Nantou County
- 6 Chiayi City, Chiayi County, Yunlin County
- 7 Tainan City, Tainan County
- 8 Kaohsiung City, Kaohsiung County, Penghu County, Pratas Islands, Spratly Islands
- 9 Pingtung County, Taitung County, Hualien County
Thailand
Thailand postcodes, introduced on 25 February 2525 B.E. (A.D. 1982), have 5 digits. The first two specify the province. The third and fourth digits specify a district (amphoe). T
Turkey
Turkey postcodes have five digits. The first two digits are the province code in ISO 3166-2:TR (also first two digits of car licence codes), e.g. postcodes of areas in Istanbul begins with 34. The last three digits represent the area in the province.
Ukraine
Ukraine uses a five-digit numeric postal codes that are written immediately to the right of the city or settlement name. The codes are allocated to all settlements with a population of more than 500 irrespective of a post office presence; habitations with smaller population share a postal code of the closest code-marked settlement. All Ukraine Post Offices ("Ukrpost / Укрпошта") have post code books that may be purchased. Ukraine postcode lookup (in English)
United Kingdom
UK postcodes are alphanumeric and between five and eight characters long (including a single space separating the outward and inward parts of the code), e.g. the code for the House of Commons is SW1A 0AA. These codes were introduced by the Royal Mail between 1959 and 1974. They have been widely adopted not just for their original purpose of automating the sorting of mail, but for many other purposes — see Postcode lottery.
The 'Outward' part of the postcode denotes the postal district - for example RH for the Redhill area, and then the following number distinguishes the post town - broadly speaking the Delivery Office which services the local area. So RH1 is Redhill itself, RH10 is Crawley. With larger towns there may be more than 1 number in the outward section - Crawley includes RH10 and RH11. The 'Inward' part denotes particular parts of the town / Delivery Office area, with the first part - the number - being an area, and the final two letters denoting a group of houses within that area.
You may see a series of five-digit codes on business mail. This is called Mailsort— but is only available for mailings of 'a minimum of 4,000 letter-sized items'.[18] Mail users who hand over mail to Royal Mail sorted by Mailsort code receive discounts based on the type of mail and level of sorting they do.
United States
The United States uses five-digit numeric "ZIP codes". Since 1983 the US Postal Service has promoted an extended version called "ZIP+4", which adds a hyphen and four additional digits following the main ZIP code, to identify a smaller geographical area or single large entity.
Vatican City
The Vatican City is integrated into the postcode system of Italy. It uses a five-digit numeric CAP of Rome (Codice di Avviamento Postale, i.e.: Postal Sending Code).
Vietnam
Vietnam uses five-digit numeric postal codes.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d da Cruz, Frank (2008-05-17). "Frank's Compulsive Guide to Postal Addresses". Columbia University. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Formatting an international address" (PDF). Universal Postal Union. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Our History". Auspost.com.au. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ "Correios: encomendas, rastreamento, telegramas, cep, cartas, selos, agências e mais!". Correios.com.br. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ "Indonesia Address Postcode - Pos Indonesia". Kodepos.posindonesia.co.id. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ Dempsey announces programme to introduce postcodes in Ireland by 1st January 2008 Government press release
- ^ Breakingnews.ie Minister to delay postcode system
- ^ a b The Sunday Times (Irish Edition) February 24, 2008 p 3 —Ryan zeroes in on Dublin 4 by Stephen O'Brien
- ^ List of Lithuanian postal codes
- ^ "Post Offices!". NIPOST. Retrieved 2008-09-29.
- ^ "Pakistan Post Office Department". Pakpost.gov.pk. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ "Welcome to the Indiapost Web Site". Indiapost.gov.in. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ personal experience
- ^ "Post Code Search". CTT. Retrieved 2008-05-04.
- ^ http://www.singpost.com.sg/downloads/media/press_release/07/PR20070528.pdf
- ^ "Postal Codes of Sri Lanka :: Mohanjith". Mohanjith.net. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ "postalservices Zip Code". Post.gov.tw. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ Mailsort FAQ, Royal Mail.Retrieved on 2007-08-03
