Okayama: Difference between revisions
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 3 sources, flagging 0 as dead, and archiving 8 sources. #IABot |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 1 sources, flagging 0 as dead, and archiving 1 sources. #IABot |
||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
==Climate== |
==Climate== |
||
Okayama has a mild climate in comparison to most of Japan. The city is ranked as the second driest and the fourth sunniest city in the Chūgoku region.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pref.okayama.jp/kikaku/kokusai/momo/e/gaiyou/gaiyou.html |title=Outline of Okayama |publisher=Pref.okayama.jp |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref> The climate is classified under the [[Köppen climate classification]] as [[humid subtropical]] (''Cfa'').<ref>{{cite web|url=http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/ |title=World Maps of Köppen-Geiger climate classification |publisher=Koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref><ref> |
Okayama has a mild climate in comparison to most of Japan. The city is ranked as the second driest and the fourth sunniest city in the Chūgoku region.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pref.okayama.jp/kikaku/kokusai/momo/e/gaiyou/gaiyou.html |title=Outline of Okayama |publisher=Pref.okayama.jp |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref> The climate is classified under the [[Köppen climate classification]] as [[humid subtropical]] (''Cfa'').<ref>{{cite web|url=http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/ |title=World Maps of Köppen-Geiger climate classification |publisher=Koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/businesstraveler/wxclimatology/monthly/graph/JAXX0065?from=36hr_bottomnav_business |accessdate=February 19, 2016 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20131105221239/http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/businesstraveler/wxclimatology/monthly/graph/JAXX0065?from=36hr_bottomnav_business |archivedate=November 5, 2013 }}</ref> |
||
The local climate is warm enough throughout the year to support [[olive]] trees. Okayama is often called "The Sunny Country" because of its low rainfall.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pref.okayama.jp/soshiki/detail.html?lif_id=2143 |title=大好き「晴れの国おかやま」 1 岡山県のアウトライン(県の概況、シンボルなど) - 岡山県ホームページ |publisher=Pref.okayama.jp |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref> |
The local climate is warm enough throughout the year to support [[olive]] trees. Okayama is often called "The Sunny Country" because of its low rainfall.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pref.okayama.jp/soshiki/detail.html?lif_id=2143 |title=大好き「晴れの国おかやま」 1 岡山県のアウトライン(県の概況、シンボルなど) - 岡山県ホームページ |publisher=Pref.okayama.jp |date= |accessdate=2013-10-04}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 03:28, 19 February 2016
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Okayama (岡山市, Okayama-shi) is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889.[1]
As of August 2010[update], the city has an estimated population of 705,224 and a population density of 893 persons per km². The total area is 789.88 km².
The city is the site of Kōraku-en, known as one of the top three traditional gardens in Japan, and the black Okayama Castle, which is ranked among the best 100 Japanese castles.[2] The city is famous as the setting of the Japanese fable "Momotarō".[3]
History
Sengoku period to Tensho era

Before the Muromachi period, Okayama was one corner of a farm region and included a small castle built by the Kanemitsu. In the Sengoku period, Ukita Naoie attacked Okayama and attacked the castle for the transportation resources and extensive farmland in the region. Naoie remodeled the castle, built the old Sanyo road to the central part of the castle town, and called in craftsmen both from inside and outside of Bizen Province. Okayama became the political and economical capital of Bizen Province.
Edo period
In 1600, Ukita Hideie, who was the son of Naoie and the lord of Okayama, lost at the Battle of Sekigahara. The next year, Kobayakawa Hideaki came to Okayama and became the feudal lord of Okayama Domain. Hideaki died in 1602, however, ending the Kobayakawa line. Ikeda Tadatugu, who was the feudal lord of Himeji Domain, became the next lord of Okayama. After this time, Okayama was ruled by the Ikedas until the latter part of the 19th century. Continuing its economic development, Okayama became one of the ten best large castle towns in Japan in the 18th century. The Korakuen Garden was developed by the fourth feudal lord, Ikeda Tsunamasa.
Meiji Restoration to World War II

On August 29, 1871, the new Meiji government of the Empire of Japan replaced the traditional feudal domain system with centralized government authority (Prefectures of Japan). Okayama became the capital of Okayama Prefecture. In 1889, Okayama City was founded. In the Meiji period, a railroad was built in Okayama city that greatly enhanced the development of the city. For example, the Sixth Higher Middle School (第六高等学校, Dairoku Kōtōgakkō) and Okayama Medical College (岡山医科大学, Okayama Ika-daigaku) were established in Okayama City. Okayama became one of the most important places in western Japan for transportation and education. When World War II began, Okayama city had a Japanese Army base camp. On June 29, 1945, the city was attacked by the US Army Air Force with incendiary bombs. Almost all the city was burned, and more than 1700 people were killed. Okayama suffered terrible damage in the war, losing more than 12,000 households.
Since World War II
During Japan's economic boom of the 1960s, Okayama developed rapidly as one of the most important cities in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions. In 1972, the Sanyō Shinkansen began service between Shin-Ōsaka and Okayama stations. Two years later, Shinkansen service was extended to Hakata.
In 1988, the Seto-Ōhashi Bridge was opened, and connected Okayama with Shikoku directly by rail and road.
The city became a core city in 1996 and a designated city on April 1, 2009.[4]
Geography


The city of Okayama is located in the southern part of Okayama Prefecture, which in turn is located in western part of the island of Honshū. The city is bounded on the south by the Inland Sea. Asahi River crosses Okayama.
Since Okayama became a designated city in 2009, the city has been divided into four wards (ku).
| Ward | Population | Area (km²) | Density (per km²) |
Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kita-ku (administrative center) |
302,685 | 451.03 | 671 | 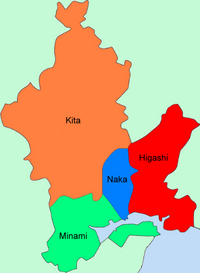
|
| Naka-ku | 142,237 | 51.24 | 2,776 | |
| Higashi-ku | 96,948 | 160.28 | 605 | |
| Minami-ku | 167,714 | 127.36 | 1,317 | |
| Population as of October 1, 2010 | ||||
Mergers
- On March 22, 2005 - the town of Mitsu (from Mitsu District), and the town of Nadasaki (from Kojima District) were merged into Okayama.
- On January 22, 2007 - the town of Takebe (from Mitsu District), and the town of Seto (from Akaiwa District) were merged into Okayama.
Kojima, Mitsu, and Akaiwa Districts have all since been dissolved as a result of these mergers.
Climate
Okayama has a mild climate in comparison to most of Japan. The city is ranked as the second driest and the fourth sunniest city in the Chūgoku region.[5] The climate is classified under the Köppen climate classification as humid subtropical (Cfa).[6][7]
The local climate is warm enough throughout the year to support olive trees. Okayama is often called "The Sunny Country" because of its low rainfall.[8]
| Climate data for Okayama, Okayama | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
22.3 (72.1) |
24.1 (75.4) |
29.6 (85.3) |
33.2 (91.8) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.0 (100.4) |
39.3 (102.7) |
36.7 (98.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
26.9 (80.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
39.3 (102.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.0 (48.2) |
9.8 (49.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
32.7 (90.9) |
28.4 (83.1) |
22.5 (72.5) |
16.8 (62.2) |
11.6 (52.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
5.5 (41.9) |
8.8 (47.8) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.2 (81.0) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
7.3 (45.1) |
16.2 (61.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.1 (34.0) |
1.4 (34.5) |
4.3 (39.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.7 (76.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
14.0 (57.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.9 (16.0) |
−9.1 (15.6) |
−7 (19) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
1.0 (33.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
12.6 (54.7) |
14.8 (58.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−9.1 (15.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34.2 (1.35) |
50.5 (1.99) |
86.7 (3.41) |
92.3 (3.63) |
125.0 (4.92) |
171.5 (6.75) |
160.9 (6.33) |
87.4 (3.44) |
134.4 (5.29) |
81.1 (3.19) |
51.2 (2.02) |
31.0 (1.22) |
1,106.2 (43.54) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 1 (0.4) |
1 (0.4) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3 (1.2) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 65 | 64 | 62 | 60 | 64 | 69 | 73 | 69 | 70 | 69 | 69 | 67 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 150.6 | 142.3 | 169.3 | 190.3 | 200.7 | 160.0 | 171.9 | 207.0 | 156.6 | 173.5 | 151.9 | 156.7 | 2,030.8 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Japan Meteorological Agency (records)[10] | |||||||||||||
Economy

Agriculture
The city is located in the Okayama Plain, where rice, eggplant, and white Chinese chives are notable products.[11] White peaches and grapes are cultivated in the mountainous, northern part of the city.
Industry
In 2005, the city's gross domestic product was 800 billion yen,[12] nearly 10% of the GDP of Okayama Prefecture. The main industries are machine tools, chemicals, foodstuffs and printing. Kōnan, a district in the southern part of the city, is the most developed industrial zone.
Commerce
Okayama is the core of the Okayama metropolitan area, which includes the cities of Kurashiki and Sōja. The main commercial district is Omotechō, near Okayama Castle and Kōraku-en, and the area surrounding Okayama Station. Omotechō has many covered shopping arcades.
The headquarters of Aeon Corporation, a private English language school with more than 3,000 employees, is located in Okayama.[13]
Culture

Okayama Castle and Kōraku-en are Okayama's most notable attractions.
Okayama Castle (nicknamed Ujō (烏城), meaning "crow castle") was constructed in 1597 by Ukita Naoie, a Japanese feudal lord. It was destroyed by bombing in 1945 during World War II but reconstructed in 1966.
Kōraku-en, known as one of the three best traditional gardens in Japan, lies south of the castle grounds. Kōrakuen was constructed by Ikeda Tsunamasa over 14 years, and completed in 1700.
Sōgen-ji, a large Buddhist monastery belonging to the Rinzai sect, is located near the center of the city. Several of the abbots of major monasteries in Kyoto are from Sōgen-ji.[citation needed]
Festivals
Every August since 1994 Okayama has seen the Momotarō Matsuri (Festival), which is an amalgam of three different festivals, including the ""Uraja"" (ogre) festival, which is a kind of Yosakoi dance.
Music and the arts

Okayama has a professional symphony orchestra, the Okayama Symphony Orchestra, which performs at the Okayama Symphony Hall.
There are many museums in the city, including the Okayama Prefectural Museum, the Okayama Prefectural Museum of Art, the Hayashibara Museum of Art, the Okayama Orient Museum, the Yumeji Art Museum, and the Okayama Digital Museum.
Cuisine
Okayama has several traditional dishes. Barazushi (ばらずし), a dish made with sushi rice, contains fresh fish from the Seto Inland Sea. Kibidango (吉備団子), gel-like balls made from a powder of millet and rice, are a well-known sweets from the area.
Media

The Sanyo Shimbun is the local newspaper serving the greater Okayama area. There are six television stations serving the Okayama area and part of Kagawa Prefecture. Three FM and three AM radio stations also serve the region.
- TV Stations
| Channel ID | Name | Network | Established year | Call sign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NHK General TV Okayama | NHK General TV | 1957 | JOKK-DTV |
| 2 | NHK Educational TV Okayama | NHK Educational TV | 1963 | JOKB-DTV |
| 4 | Nishinippon Broadcasting Co.,Ltd.(RNC) | NNN | 1958 | JOKF-DTV |
| 5 | Setonaikai Broadcasting Co.,Ltd.(KSB) | ANN | 1969 | JOVH-DTV |
| 6 | Sanyo Broadcasting Co.,Ltd.(RSK) | JNN | 1958 | JOYR-DTV |
| 7 | TV Setouchi Broadcasting Co.,Ltd.(TSC) | TXN | 1985 | JOPH-DTV |
| 8 | Okayama Broadcasting Co.,Ltd.(OHK) | FNN | 1969 | JOOH-DTV |
- Radio Stations
| Channel | Name | Network | Established year | Call sign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM 603 kHz | NHK Radio Daiichi Okayama | NHK Radio Daiichi | 1931 | JOKK |
| AM 1386 kHz | NHK Radio Daini Okayama | NHK Radio Daini | 1946 | JOKB |
| AM 1494 kHz | Sanyo Broadcasting Co,Ltd.Radio (RSK) | JRN, NRN | 1958 | JOYR |
| FM 88.7 MHz | NHK FM Okayama | NHK FM | 1964 | JOKK-FM |
| FM 76.8 MHz | FM Okayama | JFN | 1999 | JOVV-FM |
| FM 79.0 MHz | Radio MOMO (Okayama City FM) | J-WAVE | 1997 | JOZZ8AD-FM |
Sports
Okayama has many sports teams. In recent years, volleyball team Okayama Seagulls and football club Fagiano Okayama have been established. In 2009, Fagiano Okayama FC gained promotion to the J. League, the highest football league in Japan.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue | Established |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fagiano Okayama FC | Football | J. League Division 2 | Kanko Stadium (Okayama Prefectural Multipurpose Athletic Stadium) | 2004 |
| Okayama Seagulls | Volleyball | V.League | Momotaro Arena (Okayama Prefectural Multipurpose Grounds Gym) | 1999 |
| Okayama Standing Bears | American football | X-League | Kanko Stadium (Okayama Prefectural Multipurpose Athletic Stadium) | ? |
| Citylight Okayama Baseball Team | Baseball | Semi-professional baseball | 2008 |
Okayama was the birthplace of the 31st Yokozuna, Tsunenohana Kan'ichi, in 1896. He won 10 championships, 8 during his time as a Yokozuna.
Education

Okayama University, founded as a medical school in 1870 and established in 1949 as a national university, is in the city. Today, Okayama University is one of Okayama's largest universities, with 11 faculties and six graduate schools.
There are seven private universities, three junior colleges, 24 high schools (16 public, eight private), seven combined junior high/high schools (two public, five private), 37 junior high schools (36 municipal, one national) and 93 elementary schools (91 municipal, two private) in the city.[citation needed]
Universities
- Okayama University (national)
- Notre Dame Seishin University (private)
- Okayama University of Science (private)
- Okayama Shoka University (private)
- Sanyo Gakuen University (private)
- Shujitsu University (private)
- Chugoku Gakuen University (private)
- International Pacific University (private)
High schools
- Okayama Ichinomiya Senior High School
- Okayama Asahi Senior High School
- Okayama Sozan Senior High School
- Okayama Hosen Senior High School
Transportation

Intercity rail
JR West's Okayama Station is a major interchange, with trains from Shikoku, Sanin and Sanyo connecting to the Sanyo Shinkansen. Local rail lines serving Okayama Station include:
Tramway
Okayama has kept an operational tram system since the Meiji period. It is managed by Okayama Electric Tramway and offers two lines: the Higashiyama Main Line and the Seikibashi Line.
Bus
Seven bus companies provide service within the city limits:
- Bihoku Bus (備北バス)
- Chūtetsu Bus (中鉄バス)
- Okaden Bus (岡電バス)
- Ryōbi Bus (両備バス)
- Shimoden Bus (下電バス)
- Tōbi Bus (東備バス)
- Uno Bus (宇野バス)
Air
Okayama Airport, located in the northern part of the city, provides domestic service to Tokyo-Haneda, Sapporo-Chitose, Okinawa-Naha, and Kagoshima. International air service is provided to Seoul-Incheon, Guam, Beijing, Shanghai-Pudong, and Dalian.
Notable people
Before the fall of Edo
- Eisai (Buddhist priest, 1141-1215)
- Hideie Ukita (Military commander, 1573-1655)
- Kōan Ogata (Rangaku practitioner, 1810-1863)
Arts
- Shigeru Nanba (painter, 1944- )
Politics
- Ichirō Aisawa (Member of the House of Representatives, 1954- )
- Kenji Eda (Member of the House of Representatives, Secretary General of Your Party, 1956- )
- Satsuki Eda (Member of the House of Councillors, 27th President of the House of Councillors, 1941- )
- Seiji Hagiwara (31st, 32nd Mayor of Okayama, member of the House of Representatives, 4th Mayor of Mimasaka, Okayama, 1956- )
- Shigeo Takaya (33rd, 34th Mayor of Okayama, 1937- )
- Tsuyoshi Inukai (Member of the House of Representatives, 29th Prime Minister of Japan, 1855-1932)
- Masahiro Ishii (5th Governor of Okayama Prefecture, Member of the House of Councillors, 1945- )
- Yoshihiro Katayama (Governor of Tottori Prefecture, Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications, 1951- )
- Akihiko Kumashiro (Member of the House of Representatives, 1940- )
- Keisuke Tsumura (Member of the House of Representatives, 1971- )
- Michiyoshi Yunoki (Member of the House of Representatives, 1972- )
Literature
- Suiin Emi (novelist, 1869-1934)
- Yōko Ogawa (novelist, 1962- )
- Hyakken Uchida (novelist, 1889-1971)
- Junnosuke Yoshiyuki (novelist, 1924-1994)
Entertainment

- Angela Aki (singer-songwriter, 1977- ) (attended middle school in Okayama)
- Yōko Aramaki (impressionist and singer, 1981- )
- Dorlis (musician, 1982- )
- Satoshi Inoue (member of Jichō Kachō, 1976- )
- Hiroto Kōmoto (musician, 1963- )
- Shin Koyamada (actor, 1982- )
- Shinji Morisue (former artistic gymnast and TV personality, 1957- )
- Matsunosuke Onoe (actor and film director, 1875-1926)
- Kōji Satō (actor, 1963- )
- Etsuko Shihomi (actress, 1955- )
- Yukiko Takaguchi (voice actor, 1974- )
Sports
- Noboru Akiyama (professional baseball player and coach, 1934-2000)
- Yuko Arimori (athlete, 1966- )
- Naoko Hashimoto (volleyball player, 1984- )
- Kinue Hitomi (athlete, 1907-1931)
- Masahiro Kawai (professional baseball player, 1964- )
- Issei Morita (professional baseball player, 1989- )
- Hisashi Tsuchida (soccer player, 1967- )
- Kiyoshi Tamura (professional wrestler, 1969- )
- Shigeaki Hattori (racing driver and team owner, 1963- )
Sister cities
Okayama has 6 sister cities around the world.
 San Jose, California, United States (1957)
San Jose, California, United States (1957) San José, Costa Rica (1969)
San José, Costa Rica (1969) Plovdiv, Bulgaria (1972)
Plovdiv, Bulgaria (1972) Luoyang, China (1981)
Luoyang, China (1981) Bucheon, South Korea (2002)
Bucheon, South Korea (2002) Hsinchu City, Taiwan (2003)
Hsinchu City, Taiwan (2003) Kanpur, India (2005)
Kanpur, India (2005)
Points of interest
- Korakuen Garden
- Omizuen Garden
- Handayama Botanical Garden
- RSK Rose Garden
- Okayama Castle
- Okayama Prefectural Museum
- Okayama Orient Museum
- Okayama Prefectural Museum of Art
- Hayashibara Museum of Art
- Yumeji Art Museum
- Ikeda Zoo
- Kibiji District Cycling Road
- Ashimori Clan Samurai Residence
- Saijo Inari
- Kibitsu Shrine
- Kibitsuhiko Shrine
- Tsukuriyama Kofun
- Saidaiji Temple (Okayama)
- Sogenji Temple
- Okayama Symphony Hall
- Okayama University
References
- ^ "Overview of Okayama City/Okayama city (Okayama-shi) is the capital of Okayama Prefecture". City.okayama.jp. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ "Castles / List of Japanese Castles". Japan-Guide.com. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ ""Momotaro," a folk tale and Kibiji District". City.okayama.jp. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ [1] Archived 2009-08-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Outline of Okayama". Pref.okayama.jp. Retrieved 2013-10-04.
- ^ "World Maps of Köppen-Geiger climate classification". Koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at. Retrieved 2013-10-04.
- ^ https://web.archive.org/20131105221239/http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/businesstraveler/wxclimatology/monthly/graph/JAXX0065?from=36hr_bottomnav_business. Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved February 19, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "大好き「晴れの国おかやま」 1 岡山県のアウトライン(県の概況、シンボルなど) - 岡山県ホームページ". Pref.okayama.jp. Retrieved 2013-10-04.
- ^ "平年値(年・月ごとの値)". Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "観測史上1~10位の値( 年間を通じての値)". Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 2010-03-06.
- ^ [2] Archived 2010-08-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "??" (PDF) (in Japanese). City.okayama.jp. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ [3] Archived 2009-02-20 at the Wayback Machine
