East Asia: Difference between revisions
| Line 468: | Line 468: | ||
|[[Arabic script]] |
|[[Arabic script]] |
||
|{{Flagicon|CHN}} |
|{{Flagicon|CHN}} |
||
|[[File:Mountain_Tajiks,_China.jpg|thumb|100x100px|Mountain Tajiks, China]] |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
'''*Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.''' |
'''*Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.''' |
||
Revision as of 06:00, 5 May 2017
East Asia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| States | |
| Dependencies | |
| Other | |
| Major cities | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 11,839,074 km2 (4,571,092 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 1,601,709,712 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (350/sq mi) |
| Time zone |
|
| Languages and language families | |
Template:Contains Chinese text Template:Contains Japanese text Template:Contains Korean text
| East Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 东亚/东亚细亚 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 東亞/東亞細亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese alphabet | Đông Á | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hangul | 동아시아/동아세아/동아 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanja | 東아시아/東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Зүүн Ази (Dzuun Azi) ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠠᠽᠢ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kanji | 東亜細亜(東アジア)/東亜 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kana | ひがしアジア/とうあ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian | Восточная Азия | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Vostochnaja Azija | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
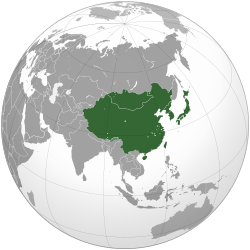
East Asia is the eastern subregion of the Asian continent, which can be defined in either geographical[1] or ethno-cultural[2] terms. Geographically and geopolitically, it includes China (including Hong Kong and Macau), Mongolia, Korea (North and South), Japan and Taiwan ; it covers about 12,000,000 km2 (4,600,000 sq mi), or about 28% of the Asian continent.
The East Asian people comprise more than 1.5 billion people. About 38% of the population of Asia and 22%, or over one fifth, of all the people in the world live in East Asia. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in Mongolia and Western China, both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the lowest population density of a sovereign state. The overall population density of the region is 133 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi), about three times the world average of 45/km2 (120/sq mi).
Historically, societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. Major religions include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana), Confucianism or Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, Chinese folk religion in China and Taiwan, Shinto in Japan, Korean shamanism in Korea. Shamanism is also prevalent among Mongolians and other indigenous populations of northern East Asia.[3][4] The Chinese calendar is the root from which many other East Asian calendars are derived.
History
The Chinese Dynasties dominated this region culturally and militarily for a lengthy period of time. Cultural and religious exchange between the Chinese and other regional Dynasties and Kingdoms occurred.
As connections with the Western world strengthened, China's power began to diminish. Around the same time, Japan solidified itself as a nation state. During World War II, Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China, Hong Kong, and Vietnam all fell under Japanese control. Following Japan's defeat in the war, the Korean peninsula became independent, while Taiwan became the de facto Republic of China after the latter lost to the People's Republic of China in the Chinese Civil War.
United Nations Statistics Division
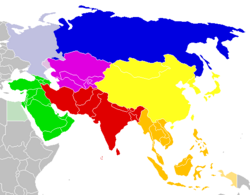
The UNSD definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience,[5] but also other common definitions of East Asia contain the entirety of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau) Mongolia, Japan, Taiwan, North Korea and South Korea.[note 3][1][6]
Culturally, China, Japan, Korea, Taiwan and Vietnam are commonly seen as being encompassed by cultural East Asia (East Asian cultural sphere).[2][7][8][9]
Alternative definitions
There are mixed debates around the world whether these countries or regions should be considered in East Asia or not.
- Vietnam (officially part of Southeast Asia geographically, although culturally it is a part of the East Asian cultural sphere, politically, it is related to both Southeast Asia and East Asia)
- Siberia in Russia (often described as North Asia due to its location, although this part of Russia is often seen as more closely related to its East Asian neighbours)
- Sovereignty issues exist over some territories in the South China Sea.
In business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to a wide geographical area covering ten Southeast Asian countries in ASEAN, People's Republic of China, Republic of China (Taiwan) , Japan and South Korea.[note 3] However, in this context, the term "Far East" is often more appropriate which covers ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. However, being a Eurocentric term, Far East describes the region's geographical position in relation to Europe rather than its location within Asia. Alternatively, the term "Asia Pacific Region" is often used in describing East Asia, Southeast Asia as well as Oceania.
Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term Northeast Asia to refer to the greater China area, Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with Southeast Asia covering the ten ASEAN countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia".[10][11][12] The Council on Foreign Relations defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.[13]
Economy
The economy of East Asia is one of the most successful, developed and high-tech economies of the world, being home to some of the world's largest, most technologically advanced and most prosperous economies such as the industrialized developed countries of South Korea, Taiwan, and Japan. The military and economic superpower of China became the largest economy in the world in 2014, surpassing the United States of America. Major positive factors have ranged from favorable political-legal environments for industry and commerce, through abundant natural resources of various kinds, to plentiful supplies of relatively low-cost, skilled and adaptable labor.[citation needed]
In modern societies, a high level of structural differentiation, functional specialization, and autonomy of the economic system from government is a major contributor to industrial-commercial growth and prosperity. Currently in East Asia, trading systems are relatively open; and zero or low duties on imports of consumer and capital goods etc. have considerably helped stimulate cost-efficiency and change. Free and flexible labor and other markets are other important factors making for high levels of business-economic performance. East Asian populations have demonstrated highly positive work ethics. There are relatively large and fast-growing markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds.[citation needed]
| State/Territory | GDP nominal billions of USD[14] |
GDP nominal per capita USD[14] |
GDP PPP billions of USD[14] |
GDP PPP per capita USD[14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17,100.063 | 12,117 | 28,920.974 | 20,493 | |
| 405.781 | 53,813 | 525.547 | 69,695 | |
| 55.502 | 91,376 | 80.765 | 142,599 | |
| 650.902 | 27,350 | 1,413.195 | 59,381 | |
| 4,746.880 | 38,174 | 5,512.220 | 44,329 | |
| 25.000 | 1,000 | 40.000 | 1,800 | |
| 1,898.763 | 36,749 | 2,408.301 | 46,611 | |
| 17.871 | 5,586 | 53.003 | 16,569 |
Territory and region data
Demographics
| State/Territory | Official Name | Native Nmae | Area km2 | Population | Population density per km2 |
HDI | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| People's Republic of China | 中华人民共和国 | 9,640,011 | 1,373,000,000 | 138 | 0.727 | Beijing | |
| Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | 香港特別行政區 | 1,104 | 7,298,600 | 6,390 | 0.912 | Hong Kong | |
| Macau Special Administrative Region | 澳門特別行政區 | 30 | 642,900 | 18,662 | 0.892 | Macau | |
| Japan | 日本国 | 377,930 | 126,890,000 | 337 | 0.891 | Tokyo | |
| Republic of China (Taiwan) | 中華民國(台灣) | 36,188 | 23,468,748 | 639 | 0.884 | Taipei | |
| Mongolia | Монгол Улс | 1,564,100 | 3,041,648 | 2 | 0.698 | Ulaanbaatar | |
| Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 조선민주주의인민공화국 | 120,538 | 25,155,000 | 198 | 0.595 | Pyongyang | |
| Republic of Korea | 대한민국/大韓民國 | 100,210 | 51,482,816 | 500 | 0.898 | Seoul |
Major ethnic groups
| Ethnicity | Race | Native name | Population | Languages | Writing languages | Major states/territories* | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Han/Zhonghua/Huaxia | Mongoloid | 汉族/漢族, 华人/華人, 华夏/華夏 | 1,058,881,578[15] | Mandarin, Cantonese,Shanghainese,Hokkien, Hakka, etc. | Sinogram(Simplified/Traditional) | ||
| Yamato/Japanese | Mongoloid | 日本族/にほんぞく 大和民族/やまとみんぞく |
125,117,000[16] | Japanese | Sinogram (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana |  | |
| Joseon/Korean | Mongoloid | 한민족/韓民族 조선족/朝鮮族 |
79,432,225[17] | Korean | Hangul, Sinogram (Hanja) |  | |
| Mongols | Mongoloid | Монголчууд/ᠮᠣᠩᠭ᠋ᠣᠯᠴᠤᠳ | 8,942,528[18] | Mongolian | Mongol script, Cyrillic script |  | |
| Zhuang | Mongoloid | 壮族/Bouxcuengh | 18,000,000[19] | Zhuang, Cantonese, Southwestern Mandarin, etc. | Sinogram (Simplified), Latin script |  | |
| Manchus | Mongoloid | 满族/ᠮᠠᠨᠵᡠ | 10,422,873[20] | Northwestern Mandarin, Manchurian (near death), etc. | Sinogram (Simplified), Mongol script |  | |
| Hui | Mongoloid | 回族 | 10,586,087[21] | Lan-Yin Mandarin | Sinogram (Simplified) |  | |
| Uyghurs | Caucasoid+Mongoloid | ئۇيغۇر | 10,069,346[22] | Uyghur | Arabic script Latin script |  | |
| Hmong | Mongoloid | Ghaob Xongb/Hmub/Mongb | 9,426,007[23] | Hmong | Latin script |  | |
| Tibetans | Mongoloid | བོད་པ་ | 6,500,000[24] | Tibetan, Rgyal Rong, Rgu, etc. | Tibetan script |  | |
| LôLô/Yi | Mongoloid | ꆈꌠ | 8,714,393[25] | Various Loloish | Loloish |  | |
| Tujia | Mongoloid | 土家族 | 8,353,912[26] | Northern Tujia, Southern Tujia | Sinogram (Simplified) |  | |
| Kam | Mongoloid | 侗族/Gaeml | 2,879,974[27] | Gaeml | Latin script |  | |
| Russians | Caucasoid | русские | 15,393[28] | Russian | Cyrillic script |  | |
| Mountain Tajiks | Caucasoid | تاجيک | 3,556[29] | Sarikoli, Wakhi | Arabic script |
*Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.
Culture
Overview
The culture of East Asia has been influenced by the civilisation of China. East Asia, as well as Vietnam, share a Confucian ethical philosophy, Buddhism, political and legal structures, and historically a common writing system.[30] The relationship between China and East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of Greco-Roman civilisation on Europe.[30]
Religions
Festivals
| Festival | Other name | Calendar | Date | Gregorian date | Activity | Religious practices | Food | Major ethnicities | Major states/territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese New Year | Spring Festival | Chinese | Month 1 Day 1 | 21 Jan–20 Feb | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | Worship the King of Gods | Jiaozi | Han, Joseon, Manchus | |
| New Year | Yuan Dan | Gregorian | 1 Jan | 1 Jan | Fireworks | N/A | N/A | Han, Joseon, Yamato | |
| Losar or Tsagaan Sar | White Moon | Tibetan(Mongolian) | Month 1 Day 1 | 25 Jan–2 Mar | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | N/A | Chhaang or Buuz | Tibetans, Mongols, Tu and others | |
| Lantern Festival | Upper Yuan Festival | Chinese | Month 1 Day 15 | 4 Feb–6 Mar | Lanterns Expo, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Sky-officer | Yuanxiao | Han, Joseon, Yamato | |
| Qingming Festival | Tomb Sweeping Day | Solar | 15th day since March equinox | 4 Apr–6 April | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Burning Hell money | Cold Food | Han, Joseon, Mongols | |
| Dragon Boat Festival | Duanwu Festival | Chinese | Month 5 Day 5 | Driving poisons & plague away, Dragon Boat Race, Wearing colored lines, Hanging felon herb on the front door. | Worship various Gods | Zongzi | Han, Joseon, Yamato | ||
| Ghost Festival | Mid Yuan Festival | Chinese | Month 7 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Earth-officer | Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| Mid-Autumn Festival | Chinese | Month 8 Day 15 | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | Worship the Moon Goddess | Mooncake | Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| Double Ninth Festival | Double Negative Festival | Chinese | Month 9 Day 09 | Climbing Mountain, Taking care of elderly, Wearing Cornus. | Worship various Gods | Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| Lower Yuan Festival | Chinese | Month 10 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Water-officer | Ciba | Han | |||
| Dec 23 Festival | Small New Year | Chinese | Month 12 Day 23 | Cleaning Houses | Worship the God of Hearth | tanggua | Han, Mongols | ||
| International Labor Day | Gregorian | 1 May | 1 May | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||
| International Women's Day | Gregorian | 8 Mar | 8 Mar | Taking care of women | N/A | N/ | N/A |
*Japan switched the date to the Gregorian calendar after the Meiji Restoration.
*Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4.
Collaboration
East Asian Youth Games
Formerly the East Asian Games is a multi-sport event organised by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since 2019 among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of Guam, which is a member of theOceania National Olympic Committees.
The East Asian Games is 1 of 5 Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the East Asian Games, the Central Asian Games, the South Asian Games, theSoutheast Asian Games (SEA Games), and the West Asian Games. All nigh East Asian States/Territories join this Game.[31]
Free trade agreements
| Name of agreement | Parties | Leaders at the time | Negotiation begins | Signing date | Starting time | Current status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Park Geun-hye | May, 2012 | Jun 01, 2015 | Dec 30, 2015 | Enforced | |
| China–Japan–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Shinzō Abe | Mar 26, 2013 | N/A | N/A | 10 round negotiation | |
| Japan-Mongolia EPA | Shinzō Abe, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | - | Feb 10, 2015 | - | Enforced | |
| China-Mongolia FTA | Xi Jinping, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | N/A | N/A | N/A | Officially proposed | |
| Mainland-HK CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Tung Chee-hwa | - | Jun 29, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| mainland-Macao CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Edmund Ho Hau-wah | - | Oct 18, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| HK-Macao CEPA | Carrie Lam, Fernando Chui | Oct 09, 2015 | N/A | N/A | Negotiating | |
| ECFA | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Jan 26, 2010 | Jun 29, 2010 | Aug 17, 2010 | Enforced | |
| CSSTA (Based on ECFA) | Xi Jinping, Ma Ying-jeou | Mar, 2011 | Jun 21, 2013 | N/A | Abolished | |
| CSGTA (Based on ECFA) | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Feb 22, 2011 | N/A | N/A | Suspended |
Military alliances
| Name | Abbr. | Parties within the region | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai Cooperation Organisation | SCO | ★ | |
| Sino-North Korean Mutual Aid and Cooperation Friendship Treaty | - | ★★ | |
| General Security of Military Information Agreement | GSOMIA | ★★★★ | |
| Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security between the United States and Japan | - | ★★★★★ | |
| Mutual Defense Treaty Between the United States and the Republic of Korea | - | ★★★★★ |
Major cities and towns
-
Seoul is the capital of South Korea, one of the largest cities in the world and a leading global technology hub.
-
Pyongyang is the capital of North Korea (DPRK), and is a significant metropolis on the Korean Peninsula.
-
Shanghai is the largest city in China (People's Republic of China) and one of the largest in the world, and is the leading commercial and financial centre of mainland China.
-
Taipei is the capital of Taiwan (Republic of China) and is one of the world's leading technical centres in East Asia, and is the location of the Taipei 101.
-
Hong Kong, enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, is one of the world's leading global financial centres and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis.
-
Ulaanbaatar is the largest city in Mongolia with a population of 1 million as of 2008.
See also
- Economy of East Asia
- East Asia Summit
- East Asian Community
- East Asian cultural sphere
- East Asian Games
- East Asian languages
- East Asian people
- East Asian studies
- Four Asian Tigers
- China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit
- Chinese calligraphy
- Japanese calligraphy
- Korean calligraphy
- Mongolian calligraphy
Notes
- ^ The area figure is based on the combined areas of China (including Hong Kong and Macau), Mongolia, North Korea & South Korea, Taiwan and Japan as listed at List of countries and outlying territories by total area.
- ^ The population figure is the combined populations of China (including Hong Kong and Macau), Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan and Japan as listed at List of countries by population (last updated Feb 22, 2011).
- ^ a b Taiwan (officially the Republic of China) has limited recognition internationally as a sovereign state while most countries keeps unofficial relations with it, see Political status of Taiwan. The People's Republic of China has sole control of the mainland including the claim of the island of Taiwan to be part its territory under its constitution as the Taiwan Province.
References
- ^ a b "East Asia". Encarta. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
the countries and regions of China(Hong Kong, Macau),Mongolia, Japan, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Columbia University - "East Asian cultural sphere" "The East Asian cultural sphere evolves when Japan, Korea, and what is today Vietnam all share adapted elements of Chinese civilisation of this period (that of the Tang dynasty), in particular Buddhism, Confucian social and political values, and literary Chinese and its writing system."
- ^ Chongho Kim, "Korean Shamanism", 2003 Ashgate Publishing
- ^ Andreas Anangguru Yewangoe, "Theologia crucis in Asia", 1987 Rodopi
- ^ a b "United Nations Statistics Division- Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". United Nations Statistics Division. 6 May 2015. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
- ^ "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings". United Nations Statistics Division. 11 February 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ R. Keith Schopper's East Asia: Identities and Change in the Modern World
- ^ Joshua A. Fogel (UC Santa Barbara/University of Indiana) Nationalism, the Rise of the Vernacular, and the Conceptualization of Modernization in East Asian Comparative Perspective
- ^ United Nations Environment Programme (mentions sinosphere countries) Approaches to Solution of Eutrophication [1]
- ^ Christopher M. Dent (2008). East Asian regionalism. London: Routledge. pp. 1–8.
- ^ Charles Harvie, Fukunari Kimura, and Hyun-Hoon Lee (2005), New East Asian regionalism. Cheltenham and Northamton: Edward Elgar, pp.3-6.
- ^ Peter J. Katzenstein and Takashi Shiraishi (2006), Beyond Japan: the dynamics of East Asian regionalism. Ithaca: Cornell University Press, pp.1-33
- ^ "Northeast Asia." Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved on August 10, 2009.
- ^ a b c d "SEA GDP". IMF.
- ^ "汉族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-03-29.
- ^ "人口推計 - 平成 28年 12月 報" (PDF).
- ^ "한민족". 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전 (in Korean). 2017-03-29.
- ^ "Mongols". Wikipedia. 2017-03-18.
- ^ "壮族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-03-25.
- ^ "满族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-02-23.
- ^ "Hui people". Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. 2016-02-18.
- ^ "维吾尔族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-03-29.
- ^ "苗族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-02-19.
- ^ "藏族". 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (in Chinese). 2017-03-20.
- ^ "Yi people". Wikipedia. 2017-04-15.
- ^ "Tujia people". Wikipedia. 2017-01-19.
- ^ "Kam people". Wikipedia. 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Russians". Wikipedia. 2017-05-03.
- ^ "Tajiks of Xinjiang". Wikipedia. 2017-03-29.
- ^ a b Edwin O. Reischauer, "The Sinic World in Perspective," Foreign Affairs 52.2 (January 1974): 341-348. JSTOR
- ^ "East Asian Youth Games". Wikipedia. 2016-10-22.
External links
 East Asia travel guide from Wikivoyage
East Asia travel guide from Wikivoyage- High resolution map of East Asian region








