Minnesota House of Representatives
Minnesota House of Representatives | |
|---|---|
| 91st Minnesota Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | of the Minnesota Legislature |
Term limits | None |
| History | |
New session started | January 8, 2019 |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 134 |
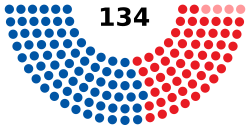 | |
Political groups |
|
Length of term | 2 years |
| Authority | Article IV, Minnesota Constitution |
| Salary | $45,000/year + per diem |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post | |
Last election | November 6, 2018 |
Next election | November 3, 2020 |
| Redistricting | Legislative control |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| House of Representatives chamber Minnesota State Capitol Saint Paul, Minnesota | |
| Website | |
| www | |
The Minnesota House of Representatives is the lower house of the Legislature of the U.S. state of Minnesota. There are 134 members, twice as many as the Minnesota Senate. Floor sessions are held in the north wing of the State Capitol in Saint Paul. Offices for members and staff, as well as most committee hearings, are located in the nearby State Office Building.
History
Following the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment in 1920, women were eligible for election to the Legislature. In 1922, Mabeth Hurd Paige, Hannah Kempfer, Sue Metzger Dickey Hough, and Myrtle Cain were elected to the House of Representatives.[1]
Elections
Each Senate district is divided in half and given the suffix A or B (for example, House district 32B is geographically within Senate district 32). Members are elected for two-year terms.[2] Districts are redrawn after the decennial United States Census in time for the primary and general elections in years ending in 2. The most recent election was held on November 6, 2018.
Composition
- 91st Minnesota Legislature (2019–2021)
| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus)
|
Total | Vacant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| style="background-color:Template:Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party/meta/color" | | style="background-color:Template:Republican Party of Minnesota/meta/color" | | ||||
| Democratic– Farmer–Labor |
Republican | ||||
| Republican Caucus |
New Republican Caucus[nb 1] | ||||
| End of the previous Legislature | 55 | 75 | 0 | 130 | 4 |
| Begin (January 8, 2019) | 74 | 55 | 4 | 133 | 1 |
| January 10, 2019[nb 2] | 75 | 134 | 0 | ||
| February 12, 2019[nb 3] | 54 | 133 | 1 | ||
| March 27, 2019[nb 4] | 55 | 134 | 0 | ||
| November 16, 2019[nb 5] | 74 | 133 | 1 | ||
| December 6, 2019[nb 6] | 54 | 132 | 2 | ||
| February 11, 2020[nb 7] | 75 | 55 | 134 | 0 | |
| Latest voting share | 56% | 41% | 3% | ||
Members, 2019–2021

 |
|---|
| Constitution |
See also
- Minnesota Senate
- Minnesota Legislature
- Past composition of the House of Representatives
- Political party strength in Minnesota
Notes
- ^ Four Republicans announced on December 8, 2018, they would not join the Republican caucus in the 91st Legislature and would instead form their own caucus, the "New House Republican Caucus."[3]
- ^ District 57A DFL member Robert Bierman assumed office after being hospitalized due to an infection.[4]
- ^ District 11B Republican incumbent Jason Rarick resigned to assume seat in the Minnesota Senate after winning a special election on February 5, 2019.[5]
- ^ Republican Nathan Nelson won a special election in District 11B on March 19, 2019.[6]
- ^ District 60A DFL incumbent Diane Loeffler died of cancer on November 16, 2019.[7]
- ^ District 30A Republican incumbent Nick Zerwas resigned to spend more time with his family and to seek employment outside of the Legislature.[8]
- ^ Republican Paul Novotny (District 30A) and Sydney Jordan (District 60A) of the DFL each won a special election on February 4, 2020.[9]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Elected in a special election.[10]
- ^ Lost re-election in 2016. Elected again in 2018.
- ^ Elected in a special election. Lost re-election in 2008. Elected again in 2010.
- ^ Elected in a special election. Lost re-election in 2006. Elected again in 2008.
- ^ Elected in a special election. Did not seek re-election in 1992 in order to seek election to the Minnesota Senate. Did not seek re-election to the Senate in 2000. Elected again to the House in 2010.
- ^ Did not seek re-election in 2006. Elected again in 2012.
- ^ Resigned effective July 1, 2015. Elected again in 2018.
- ^ Lost re-election in 2010. Elected again in 2012.
References
- ^ "Women Wielding Power: Pioneer Female State Legislators". National Women's History Museum. Archived from the original on June 4, 2011. Retrieved March 29, 2012.
- ^ "Minn. Const. art. IV, § 4". Constitution of the State of Minnesota. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ Bakst, Brian (December 8, 2018). "Renegade House members split from GOP caucus". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved January 14, 2019.
- ^ Dexter, Patty (January 10, 2019). "Rep. Robert Bierman misses first day of session due to being hospitalized". Sun Thisweek. Adams Publishing Group. Retrieved January 14, 2019.
- ^ Van Oot, Torey (February 6, 2019). "Republican Jason Rarick wins Minnesota Senate seat vacated by Democrat". Star Tribune. Retrieved March 27, 2019.
- ^ Van Oot, Torey (March 19, 2019). "Republican wins east-central Minnesota House district seat". Star Tribune. Retrieved March 27, 2019.
- ^ Miller, Pamela (November 17, 2019). "Minnesota DFL Rep. Diane Loeffler dies of cancer at 66". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- ^ Van Berkel, Jessie (November 25, 2019). "4-term Minnesota Rep. Nick Zerwas, battling heart condition, to resign". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 3, 2020.
- ^ Faircloth, Ryan (February 4, 2020). "DFL, GOP hold onto Minn. House seats in two special elections". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- ^ "Party Control of the Minnesota House of Representatives, 1951-present". Minnesota Legislative Reference Library. Retrieved November 13, 2018.
