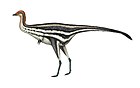
Enantiornithes
| Enantiornitheans | |
|---|---|

| |
| Fossil specimen of a bohaiornithid (Zhouornis hani) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | Avialae |
| Clade: | Ornithothoraces |
| Clade: | †Enantiornithes Walker, 1981 |
| Subgroups | |
|
and see text | |
Enantiornithes is a group of extinct avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era.[3][4][5] Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over 80 species of enantiornitheans have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. Enantiornitheans became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with hesperornithids and all other non-avian dinosaurs. They are thought to have no living descendants.
Discovery and naming
The first enantiornitheans to be discovered were incorrectly referred to modern bird groups. For example, the first known enantiornithean, Gobipteryx minuta, was originally considered a paleognath related to ostriches and tinamou.[6] Enantiornitheans were first recognized as a distinct lineage, or "subclass" of birds, by Cyril A. Walker in 1981. Walker made this discovery based on some partial remains from the late Cretaceous period of what is now Argentina, which he assigned to a new genus, Enantiornis, giving the entire group its name. Since the 1990s, many more complete enantiornitheans have been discovered, and it was determined that a few previously described "birds" (e.g. Iberomesornis, Cathayornis, and Sinornis) were also enantiornitheans.
The name "Enantiornithes" means "opposite birds", from Ancient Greek enantios (ἐνάντιος) "opposite" + ornithes (όρνιθες) "birds" . The name was coined by Cyril Alexander Walker in his landmark paper which established the group.[7] In his paper, Walker explained what he meant by "opposite":
Perhaps the most fundamental and characteristic difference between the Enantiornithes and all other birds is in the nature of the articulation between the scapula [...] and the coracoid, where the 'normal' condition is completely reversed.[7]
This refers to an anatomical feature – the articulation of the shoulder bones – which has a concave-convex socket joint that is the reverse of that of modern birds. Specifically, in enantiornitheans, the facet where the scapula (shoulder blade) meets the coracoid (the primary bone of the shoulder girdle in vertebrates other than mammals) is a convex knob and the corresponding point on the shoulder blade is concave and dish-shaped. In modern birds, the way the joint articulates is reversed.[8]
Walker was not clear on his reasons for giving this name in the etymology section of his paper, and this ambiguity led to some confusion among later researchers. For example, Alan Feduccia stated in 1996:
The birds are so named because, among many distinctive features, there is a unique formation of the triosseal canal and the metatarsals are fused proximally to distally, the opposite of that in modern birds[9]
Feduccia's point about the tarsometatarsus (the combined upper foot and ankle bone) is correct, but Walker did not use this reasoning in his original paper. Walker never described the fusion of the tarsometatarsus as opposite, but rather as "Only partial". Also, it is not certain that enantiornitheans had triosseal canals, since no fossil preserves this feature.[3]
As a group, the Enantiornithes are often referred to as "enantiornithines". However, several scientists have noted that this is incorrect, because following the standard rules for forming the names of animal groups, it implies reference only to the subfamily Enantiornithinae. Following the naming conventions used for modern birds as well as extinct groups, it has been pointed out that the correct term is "enantiornithean".[10]
Origin and range
Enantiornitheans have been found on every continent except Antarctica. Fossils attributable to this group are exclusively Cretaceous in age, and it is believed that Enantiornitheans became extinct at the same time as their non-avialan dinosaur relatives. The earliest known enantiornitheans are from the Early Cretaceous of Spain (e.g. Noguerornis) and China (e.g. Protopteryx) and the latest from the Late Cretaceous of North and South America (e.g. Avisaurus and Enantiornis). The widespread occurrence of this group suggests that at least some enantiornitheans were able to cross oceans under their own power; they are the first known avialan lineage with a global distribution.
Description

Many enantiornithean fossils are very fragmentary, and some species are only known from a piece of a single bone. Almost all specimens that are complete, in full articulation, and with soft tissue preservation are known from Las Hoyas in Cuenca, Spain and the Jehol group in Liaoning (China). Enantiornithean fossils have been found in both inland and marine sediments, suggesting that they were an ecologically diverse group. Enantiornitheans appear to have included waders, swimmers, granivores, insectivores, fishers, and raptors. The vast majority of enantiornithean species were small, between the size of a sparrow and a starling,[11] while the largest members of this clade are Pengornis houi,[12] Xiangornis shenmi[13] and Zhouornis hani.[11] At least a few much larger species may have existed, including a potentially crane-sized species known only from footprints in the Eumeralla Formation (and possibly also represented in the Wonthaggi Formation by a single furcula), which might belong to an enantiornithean.[14] One taxon, Mirarce, is described as similar in size to modern turkeys,[15] while previous "largest enantiornitheans" are described as blackbird sized.[12]
Extraordinary enantiornithean remains have also been preserved in Burmese amber deposits dated to 99 million years ago. These remains are among the most well-preserved of any mesozoic dinosaur. The first discovered amber-encased enantiornithean remains were two wings (see below) described in 2016.[16] Nearly the entire body of a hatchling enantiornithean was described in 2017[17] and another hatchling was described in 2018.[18] In 2019 a largely complete foot along with a wing were described.[19] In 2020 a wing of a large taxon was described.[20]
Skull

Given their wide range of habitats and diets, the skulls of enantiornitheans varied considerably between species. Enantiornithean skulls combined a unique suite of primitive and advanced features. As in more primitive avialans like Archaeopteryx, they retained several separate cranial bones, small premaxillae (bones of the snout tip) and most species had toothy jaws rather than toothless beaks. Only a few species, such as Gobipteryx minuta, were fully toothless and had beaks. They also had simple quadrate bones, a complete bar separating each orbit (eye hole) from each antorbital fenestra, and dentaries (the main toothed bones of the lower jaw) without forked rear tips. A squamosal bone is preserved in an indeterminate juvenile specimen, while a postorbital is preserved in Shenqiornis and Pengornis. In modern birds these bones are assimilated into the cranium. Some enantiornitheans may have had their temporal fenestrae (holes in the side of the head) merged into the orbits as in modern birds due to the postorbitals either not being present or not being long enough to divide the openings.[21] A quadratojugal bone, which in modern birds is fused to the jugal, is preserved in Pterygornis.[22] The presence of these primitive features of the skull would have rendered enantiornitheans capable of only limited cranial kinesis (the ability to move the jaw independent of the cranium).[23]
Wing

As a very large group of birds, enantiornitheans displayed a high diversity of different body plans based on differences in ecology and feeding, reflected in an equal diversity of wing forms, many paralleling adaptions to different lifestyles seen in modern birds. In general, the wings of enantiornitheans were advanced compared to more primitive avialans like Archaeopteryx, and displayed some features related to flight similar to those found in the lineage leading to modern birds, the Ornithuromorpha. While most enantiornitheans had claws on at least some of their fingers, many species had shortened hands, a highly mobile shoulder joint, and proportional changes in the wing bones similar to modern birds. Like modern birds, enantiornitheans had alulas, or "bastard wings", small forward-pointing arrangements of feathers on the first digit that granted higher maneuverability in the air and aided in precise landings.[24]
Several wings with preserved feathers have been found preserved in Burmese amber. These are the first complete Mesozoic dinosaur remains preserved this way (a few isolated feathers are otherwise known, unassigned to any species), and one of the most exquisitely preserved dinosaurian fossils known.[25] The preserved wings show variations in feather pigment and prove that enantiornitheans had fully modern feathers, including barbs, barbules, and hooklets, and a modern arrangement of wing feather including long flight feathers, short coverts, a large alula and an undercoat of down.[16]
One enantiornithean fossil shows wing-like feather tufts on its legs, similar to Archaeopteryx. Leg feathers are also reminiscent of the four-winged dinosaur Microraptor, however, in the enantiornithean differ from the feathers are shorter, more disorganized (do not clearly form a wing) and only extend down to the ankle rather than along the foot.[26]
Tail
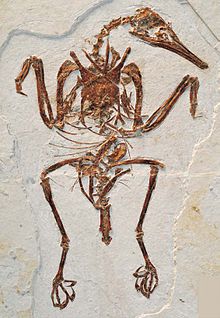
Clarke et al. (2006) surveyed all enantiornithean fossils then known and concluded that none had preserved tail feathers that formed a lift-generating fan, as in modern birds. They found that all avialans outside of Euornithes (the clade they called Ornithurae) with preserved tail feathers had only short coverts or elongated paired tail plumes. They suggested that the development of the pygostyle in enantiornitheans must have been a function of tail shortening, not the development of a modern tail feather anatomy. These scientists suggested that a fan of tail feathers and the associated musculature needed to control them, known as the rectrical bulb, evolved alongside a short, triangular pygostyle, like the ones in modern birds, rather than the long, rod- or dagger-shaped pygostyles in more primitive avialans like enantiornitheans. Instead of a feather fan, most enantiornitheans had a pair of long specialized pinfeathers similar to those of the extinct Confuciusornis and certain birds-of-paradise.[27]
However, further discoveries showed that at least among primitive enantiornitheans, tail anatomy was more complex than previously thought. One enantiornithean, Shanweiniao, was initially interpreted as having at least four long tail feathers that overlapped each other[28] and might have formed a lift-generating surface similar to the tail fans of euornitheans,[29] though a later study indicates that Shanweiniao was more likely to have rachis-dominated tail feathers similar to feathers present in Paraprotopteryx.[30] Chiappeavis, a primitive pengornithid enantiornithean, had a fan of tail feathers similar to that of more primitive avialans like Sapeornis, suggesting that this might have been the ancestral condition, with pinfeathers being a feature evolved several times in early avialans for display purposes.[30] Another enantiornithean, Feitianius, also had an elaborate fan of tail feathers. More importantly, soft tissue preserved around the tail was interpreted as the remains of a rectrical bulb, suggesting that this feature was not in fact restricted to species with modern-looking pygostyles, but might have evolved much earlier than previously thought and been present in many enantiornitheans.[31] At least one genus of enantiornithean, Cruralispennia, had a modern-looking pygostyle but lacked a tail fan.[32]
Biology
Diet
Given the wide diversity of skull shape among enantiornitheans, many different dietary specializations must have been present among the group. Some, like Shenqiornis, had large, robust jaws suitable for eating hard-shelled invertebrates. In longipterygids, the snouts were long and thin with teeth restricted to the tip of the jaws, and they were likely mud-probers (small-toothed species) and fishers (large-toothed species). The short, blunt teeth of Pengornis were likely used to feed on soft-bodied arthropods.[21] The strongly hooked talons of bohaiornithids suggest that they were predators of small to medium-sized vertebrates, but their robust teeth instead suggest a diet of hard-shelled animals.[1]
A few specimens preserve actual stomach contents. Unfortunately, none of these preserve the skull, so direct correlation between their known diet and snout/tooth shape cannot be made. Eoalulavis was found to have the remains of exoskeletons from aquatic crustaceans preserved in its digestive tract,[33] and Enantiophoenix preserved corpuscles of amber among the fossilized bones, suggesting that this animal fed on tree sap, much like modern sapsuckers and other birds. The sap would have fossilized and become amber.[34] However, more recently it has been suggested that the sap moved post-mortem, hence not representing true stomachal contents. Combined with the putative fish pellets of Piscivorenantiornis turning out to be fish excrement, the strange stomachal contents of some species turning out to be ovaries and the supposed gastroliths of Bohaiornis being random mineral precipitates, only the Eoalulavis displays actual stomach contents.[35]
A study on paravian digestive systems indicates that known enantiornitheans lacked a crop and a gizzard, didn't use gastroliths and didn't eject pellets. This is considered at odds with the high diversity of diets that their different teeth and skull shapes imply,[36] though some modern birds have lost the gizzard and rely solely on strong stomachal acids.[37]
Predation
A fossil from Spain reported by Sanz et al. in 2001 included the remains of four hatchling enantiornithean skeletons of three different species. They are substantially complete, very tightly associated, and show surface pitting of the bones that indicates partial digestion. The authors concluded that this association was a regurgitated pellet and, from the details of the digestion and the size, that the hatchlings were swallowed whole by a pterosaur or small theropod dinosaur. This was the first evidence that Mesozoic avialans were prey animals, and that some Mesozoic pan-avians regurgitated pellets like owls do today.[38]
Life history

Known enantiornithean fossils include eggs,[39][40] embryos,[41] and hatchlings.[42] An enantiornithean embryo, still curled in its egg, has been reported from the Yixian Formation.[43] Juvenile specimens can be identified by a combination of factors: rough texture of their bone tips indicating portions which were still made of cartilage at the time of death, relatively small breastbones, large skulls and eyes, and bones which had not yet fused to one another.[44] Some hatchling specimens have been given formal names, including "Liaoxiornis delicatus"; however, Luis Chiappe and colleagues considered the practice of naming new species based on juveniles detrimental to the study of enantiornitheans, because it is nearly impossible to determine which adult species a given juvenile specimen belongs to, making any species with a hatchling holotype a nomen dubium.[44]
Together with hatchling specimens of the Mongolian Gobipteryx[45] and Gobipipus,[46][47] these finds demonstrate that enantiornithean hatchlings had the skeletal ossification, well-developed wing feathers, and large brain which correlate with precocial or superprecocial patterns of development in birds of today. In other words, enantiornitheans probably hatched from the egg already well developed and ready to run, forage, and possibly even fly at just a few days old.[44]
Analyses of enantiornithe bone histology have been conducted to determine the growth rates of these animals. A 2006 study of Concornis bones showed a growth pattern different from modern birds; although growth was rapid for a few weeks after hatching, probably until fledging, this small species did not reach adult size for a long time, probably several years.[48] Other studies have all supported the view that growth to adult size was slow, as it is in living precocial birds (as opposed to altricial birds, which are known to reach adult size quickly).[33] Studies of the rate of bone growth in a variety of enantiornitheans has shown that smaller species tended to grow faster than larger ones, the opposite of the pattern seen in more primitive species like Jeholornis and in non-avialan dinosaurs.[49] Some analyses have interpreted the bone histology to indicate that enantiornitheans may not have had fully avian endothermy, instead having an intermediate metabolic rate.[50]
Evidence of colonial nesting has been found in enantiornitheans, in sediments from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Romania.[51] Evidence from nesting sites shows that enantiornitheans buried their eggs like modern megapodes, which is consistent with their inferred superprecocial adaptations.[52]
A 2020 study on an enantiornithean juvenile feathers further stresses the ontological similarities to modern megapodes, but cautions several differences like the arboreal nature of most enantiornitheans as opposed to the terrestrial lifestyle of megapodes.[53]
Flight
Because many enantiornitheans lacked complex tails and possessed radically different wing anatomy compared to modern birds, they have been the subject of several studies testing their flight capabilities.
Traditionally, they have been considered inferior flyers, due to the shoulder girdle anatomy being assumed to be more primitive and unable to support a ground-based launching mechanism,[54] as well as due to the absence of rectrices in many species.[27][29][55]
However, several studies have shown that they were efficient flyers, like modern birds, possessing a similarly complex nervous system and wing feather ligaments. Additionally, the lack of a complex tail appears to not have been very relevant for avian flight as a whole - some extinct birds like lithornids also lacked complex tail feathers but were good flyers,[56] and they appear to have been capable of a ground based launching.[57]
Due to the difference in sternal and shoulder girdle anatomy, many enantiornitheans used a flight style unlike that of any modern bird species[clarification needed], though more typical flight styles were present as well.[58]
At least Elsornis appears to have become secondarily flightless.[59]
Classification
Some researchers classify enantiornitheans, along with the true birds, in the class Aves. Others use the more restrictive crown group definition of Aves (which only includes neornithes, anatomically modern birds), and place enantiornitheans in the more inclusive group Avialae. Enantiornitheans were more advanced than Archaeopteryx, Confuciusornis, and Sapeornis, but in several respects they were more primitive than modern birds, perhaps following an intermediate evolutionary path.
A consensus of scientific analyses indicates that Enantiornithes is one of two major groups within the larger group Ornithothoraces. The other ornithothoracine group is Euornithes or Ornithuromorpha, which includes all living birds as a subset. This means that enantiornitheans were a successful branch of avialan evolution, but one that diversified entirely separately from the lineage leading to modern birds.[3] One study has however found that the shared sternal anatomy was acquired independently and such a relationship needs to be reexamined.[60]
Enantiornithean classification and taxonomy has historically been complicated by a number of factors. In 2010, paleontologists Jingmai O'Connor and Gareth Dyke outlined a number of criticisms against the prevailing practices of scientists failing to describe many specimens in enough detail for others to evaluate thoroughly. Some species have been described based on specimens which are held in private collections, making further study or review of previous findings impossible. Because it is often unfeasible for other scientists to study each specimen in person given the worldwide distribution of the Enantiornithes, and due to the many uninformative descriptions which have been published on possibly important specimens, many of these specimens become "functional nomina dubia".[61] Furthermore, many species have been named based on extremely fragmentary specimens, which would not be very informative scientifically even if they were described sufficiently. Over one-third of all named enantiornithean species are based on only a fragment of a single bone. O'Connor and Dyke argued that while these specimens can help expand knowledge of the time span or geographic range of the Enantiornithes and it is important to describe them, naming such specimens is "unjustifiable".[61]
Relationships
Enantiornithes is the sister group to Euornithes, and together they form a clade called Ornithothoraces (though see above). Most phylogenetic studies have recovered Enantiornithes as a monophyletic group distinct from the modern birds and their closest relatives. The 2002 phylogenetic analysis by Clarke and Norell, though, reduced the number of enantiornithean autapomorphies to just four.[62]
Enantiornithean systematics are highly provisional and notoriously difficult to study, due to the fact that enantiornitheans tend to be extremely homoplastic, or very similar to each other in most of their skeletal features due to convergent evolution rather than common ancestry.[30] What appears fairly certain by now is that there were subdivisions within enantiornitheans possibly including some minor basal lineages in addition to the more advanced Euenantiornithes. The details of the interrelationship of all these lineages, indeed the validity of most, is disputed, although the Avisauridae, for one example, seem likely to constitute a valid group. Phylogenetic taxonomists have hitherto been very reluctant to suggest delimitations of enantiornithean clades.[63]
One such delineation named the Euenantiornithes, was defined by Chiappe (2002) as comprising all species closer to Sinornis than to Iberomesornis. Because Iberomesornis is often found to be the most primitive or basal enantiornithean, Euenantiornithes may be an extremely inclusive group, made up of all Enantiornithes except for Iberomesornis itself. Despite being in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, this definition of Euenantiornithes was severely criticized by some researchers, such as Paul Sereno, who called it "a ill-defined clade [...] a good example of a poor choice in a phylogenetic definition".[63]
The cladogram below was found by an analysis by Wang et al. in 2015, updated from a previous data set created by Jingmai O'Connor.[22]
| Ornithothoraces |
| ||||||||||||||||||
List of genera
Enantiornithean taxonomy is difficult to evaluate, and as a result few clades within the group are consistently found by phylogenetic analyses. Most enantiornitheans are not included in any specific family, and as such are listed here. Many of these have been considered euenantiornitheans, although the controversy behind this name means that it is not used consistently in studies of enantiornitheans.
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abavornis | 1998 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from coracoids | ||
| Alethoalaornis | 2007 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Poorly known | ||
| Alexornis | 1976 | La Bocana Roja Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | One of the first enantiornitheans known. Once thought to be an ancient relative of rollers and woodpeckers | ||
| Avimaia | 2019 | Xiagou Formation (Late Cretaceous, Aptian) | One specimen from this genus died with an unlaid egg in its body | 
| |
| Bauxitornis | 2010 | Csehbánya Formation (Late Cretaceous, Santonian) | Fragmentary but unique in the structure of its tarsometatarsus | 
| |
| Catenoleimus | 1998 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from a coracoid | ||
| Cathayornis | 1992 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | One of the first Jehol biota enantiornitheans described. Known from many species, although some are now placed into their own genera. May have had a similar appearance and lifestyle to a pitta | 
| |
| Concornis | 1992 | Las Hoyas (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | One of the most complete Las Hoyas enantiornitheans | 
| |
| Cratoavis[64] | 2015 | Santana Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A very well-preserved South American member of the group, complete with ribbon-like tail feathers | ||
| Cruralispennia[32] | 2017 | Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Hauterivian) | Had an unusual ornithuromorph-like pygostyle and brush-like thigh feathers. One of the oldest enantiornitheans | 
| |
| Cuspirostrisornis | 1997 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Originally mistakenly believed to have possessed a pointed beak | ||
| Dalingheornis | 2006 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Was well-adapted for climbing due to its heterodactyl feet, like those of a trogon | ||
| Dunhuangia[65] | 2015 | Xiagou Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | An enantiornithean from the Changma basin, an area which is unusually dominated by ornithuromorphs | ||
| Elbretornis | 2009 | Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | Only known from wing bones. May be synonymous with other Lecho formation enantiornitheans | ||
| Elektorornis | 2019 | Burmese Amber (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) | Known from a foot preserved in amber with an elongated middle toe | ||
| Elsornis | 2007 | Djadochta Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | Although incomplete, its skeleton possesses three-dimensional preservation. Possibly flightless due to its wing proportions | ||
| Enantiornis | 1981 | Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | Although only known from a few bones, this genus is the namesake of Enantiornithes. It was also one of the largest and last representative of the group prior to their extinction | ||
| Eoalulavis | 1996 | Las Hoyas (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | Preserves feathers including an alula, a specialized type of feather which controls air flow over the wing | ||
| Eocathayornis | 2002 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Once considered to be a basal close relative of Cathayornis, although now considered to be more distantly related | ||
| Eoenantiornis | 1999 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Well-preserved but inconsistent in phylogenetic placement | 
| |
| Evgenavis | 2014 | Ilek Formation (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | Known only from a tarsometatarsus which shares some features with those of enantiornitheans | ||
| Explorornis | 1998 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from coracoids | ||
| Feitianius[31] | 2015 | Xiagou Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Possessed an elaborate set of tail feathers, unlike the paired ribbon-like feathers of most enantiornitheans | ||
| Flexomornis | 2010 | Woodbine Formation (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) | One of the oldest North American avialans found, albeit known only from fragmentary remains | ||
| Fortunguavis[66] | 2014 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Had robust bones, including feet and claws which may have been adapted for climbing trees | ||
| Grabauornis[67] | 2015 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | The proportions of this enantiornithean's wings as well as the presence of an alula suggest that it was a good flier | ||
| Gracilornis | 2011 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A possible relative of Cathayornis with characteristically slender bones | ||
| Gurilynia | 1999 | Nemegt Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | A poorly known enantiornithean, but evidently a large and late-surviving member of the group | ||
| Hollanda luceria[68] | 2010 | Barun Goyot Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | Originally identified asn an ornithuromorph but since reinterpreted as an enantiornithean closely related to Lectavis.[69] | ||
| Holbotia[70] | 2015 | Andaikhudag Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Considered a small pterosaur since its discovery in 1977 until it received a formal description in 2015. Possessed unique neck vertebrae and a primitive palate | ||
| Houornis | 1997 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Once considered to be dubious or a species of Cathayornis, although a 2015 study considered it to be a valid genus[71] | ||
| Huoshanornis | 2010 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | May have been a very maneuverable flier due to the structure of its hand and sternum | ||
| Iberomesornis | 1992 | Las Hoyas (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | One of the first enantiornitheans known from decent remains. Also one of the oldest and most primitive members of the group | 
| |
| Incolornis | 1998 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from coracoids. One species was once considered to belong to Enantiornis | ||
| Junornis[72] | 2017 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | So well preserved that its flight pattern could be reconstructed using the proportions of its feathers and wings | 
| |
| Kizylkumavis | 1984 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of the many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from a humerus fragment | ||
| Largirostrornis | 1997 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Possibly related to Cuspirostrisornis or a synonym of Cathayornis | ||
| Lectavis | 1993 | Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | A large and long-legged member of the group, proportionally similar to modern shorebirds | ||
| Lenesornis | 1996 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from a synsacrum fragment. Originally considered to belong to Ichthyornis | ||
| Liaoningornis | 1996 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Originally believed to be an ornithuran, but now considered a relative of Eoalulavis | ||
| Longchengornis | 1997 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | May have been a synonym of Cathayornis | ||
| Martinavis | 2007 | Grès à Reptiles Formation, Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | Although known only from humeri, this genus was large and lived in a broad range | ||
| Microenantiornis | 2017 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A small member of the group which possessed several primitive and derived features compared to other enantiornitheans | ||
| Monoenantiornis[73] | 2016 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Known from a juvenile specimen which depicts how various features developed in enantiornitheans as they age | ||
| Nanantius | 1986 | Toolebuc Formation (Early Cretaceous, Albian) | Fragmentary, but may have been a seabird because remains from this genus have been found as ichthyosaur gut content | ||
| Noguerornis | 1989 | El Montsec (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | Preserves impressions of a propatagium, a skin flap on the shoulder which forms part of a wing | ||
| Orienantius | 2018 | Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Hauterivian) | Many soft tissue details of specimens from this genus were revealed by UV light | ||
| Otogornis | 1993 | Yijinholuo Formation (Early Cretaceous) | Poorly known | ||
| Paraprotopteryx | 2007 | Qiaotou member of the Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian?) | Seemingly had four ribbon-like tail feathers instead of only two as in most enantiornitheans | ||
| Parvavis[74] | 2014 | Jiangdihe Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Santonian) | Small but fully mature at the time of its death. The only described Chinese enantiornithean dated to the late Cretaceous | ||
| Piscivorenantiornis[75] | 2017 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Known from a disarticulated skeleton preserved overlying a piece of stomach content composed of fish bones, which may have been its last meal | ||
| Protopteryx | 2000 | Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Hauterivian) | One of the oldest and most primitive members of the group | 
| |
| Pterygornis[22] | 2016 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | One disarticulated skeleton from this genus possesses well-preserved bones of the skull, including a quadratojugal | ||
| Qiliania | 2011 | Xiagou Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Some of this genus's remains include well-preserved hindlimbs. the species names, Q. graffini, is named after Greg Graffin from the band Bad Religion | ||
| Sazavis | 1989 | Bissekty Formation (Late Cretaceous, Turonian to Coniacian) | One of many fragmentary Bissekty enantiornitheans, known only from a tibiotarsus (shin bone) | ||
| Shangyang | 2019 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Unusually, the premaxillae of this genus were fused | ||
| Sinornis | 1992 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | One of the first Jehol biota enantiornitheans described. Similar to Cathayornis but usually considered to be distinct | 
| |
| Xiangornis | 2012 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | The hand of this genus was similar to that of ornithuromorphs, likely through convergent evolution. A large member of the group | ||
| Yuanjiawaornis[76] | 2015 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | One of the largest enantiornitheans known from decent remains | ||
| Yungavolucris | 1993 | Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | Had a large and unusually wide tarsometatarsal (ankle bone) | 
|
Longipterygidae
The Longipterygidae was a family of long-snouted early Cretaceous enantiornitheans, with teeth only at the tips of the snout. They are generally considered to be fairly basal members of the group.[28]
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boluochia | 1995 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Originally mistakenly believed to have possessed a hooked beak | ||
| Camptodontornis | 2010 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Originally called Camptodontus, although that genus name is occupied by a beetle | ||
| Dapingfangornis | 2006 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | May have had a thorn-like structure on its forehead | ||
| Longipteryx | 2001 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | The most common and well-known member of the family | 
| |
| Longirostravis | 2004 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Like other longipterygids, it possessed a thin snout which may have been used for probing for invertebrates in mud or bark | ||
| Rapaxavis | 2009 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Specialized for perching due to the structure of its feet | ||
| Shanweiniao | 2009 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Acquired multiple tail feathers which may have been capable of generating lift as in modern birds | 
| |
| Shengjingornis | 2012 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A large member of the family |
Pengornithidae
The Pengornithidae was a family of large early enantiornitheans. They had numerous small teeth and numerous primitive features which are lost in most other enantiornitheans.[2] Some studies claim that they may not be enantiornitheans at all, but rather ornithuromorphs, closer to modern birds.
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chiappeavis[30] | 2015 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Possessed a fan-shaped tail composed of many feathers | ||
| Eopengornis | 2014 | Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Hauterivian) | The oldest known member of the family, and one of the oldest putative enantiornitheans known. Possessed extremely well-preserved tail ribbons | ||
| Parapengornis[77] | 2015 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Proposed to have a woodpecker-like lifestyle due to features of the foot and tail | 
| |
| Pengornis | 2008 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | The first pengornithid discovered, and also one of the largest enantiornitheans known from decent remains |
"Bohaiornithidae"
"Bohaiornithids" were large but geologically short-lived early enantiornitheans, with long, hooked talons and robust teeth with curved tips. They may have been equivalent to birds of prey, although this interpretation is open to much debate.[1] The monophyly of this group is doubtful, and it may actually be an evolutionary grade.[78]
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bohaiornis | 2011 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | Originally considered to have been preserved with gastroliths, although later these were found to be mineral concretions | ||
| Gretcheniao | 2019 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Barremian) | Adapted for flapping, rather than soaring, flight. May suggest paraphyly or polyphyly of "Bohaiornithidae" | ||
| Linyiornis[79] | 2016 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A possible member of the family, known from a well-preserved skeleton complete with structures believed to be developing eggs | ||
| Longusunguis | 2014 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A fairly typical member of the family | 
| |
| Parabohaiornis | 2014 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A close relative of Bohaiornis | ||
| Shenqiornis | 2010 | Qiaotou member of the Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian?) | The first known member of the family, although not considered a close relative of Bohaiornis until a few years later. Preserves a large postorbital bone | ||
| Sulcavis | 2013 | Yixian Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A close relative of Shenqiornis with grooved enamel on its teeth, unique among fossil birds | 
| |
| Zhouornis | 2013 | Jiufotang Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) | A large member of the family with a well-preserved braincase |
Gobipterygidae
This family may be monotypic (composed of only one genus or species), as some members of the group are obscure or poorly described and may be synonymous with its type species, Gobipteryx minuta.
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gobipteryx | 1974 | Barun Goyot Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | A toothless advanced enantiornithean, possessing a robust beak which convergently evolved with those of modern birds | ||
| Jibeinia | 1997 | Qiaotou member of the Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian?) | Poorly known and described from a skeleton which has now been lost. May have been synonymous with Vescornis | ||
| Vescornis | 2004 | Qiaotou member of the Huajiying Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian?) | A small and short-snouted enantiornithean which may be synonymous with Jibeinia |
Avisauridae
Avisauridae is subjected to two differing definitions of varying inclusiveness. The more inclusive definition, which follows Cau & Arduini (2008), is used here. Avisaurids were long-lasting and widespread enantiornitheans, which are mainly distinguished by specific features of their tarsometatarsals (ankle bones). The largest and most advanced members of the group survived in North and South America up until the end of the Cretaceous, yet are very fragmentary compared to some earlier taxa.
| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avisaurus | 1985 | Hell Creek Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | The eponymous avisaurid, as well as one of the largest members of the family. Originally considered a non-avialan dinosaur | 
| |
| Enantiophoenix | 2008 | Ouadi al Gabour Formation (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) | May have fed on tree sap as it was preserved in association with amber beads | ||
| Gettyia | 2018 | Two Medicine Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | A new genus for Avisaurus gloriae | ||
| Halimornis | 2002 | Mooreville Chalk Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | Would have lived in a coastal environment | ||
| Intiornis | 2010 | Las Curtiembres Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | Although closely related to some of the largest avisaurids, members of this genus were very small birds | 
| |
| Mirarce | 2018 | Kaiparowits Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) | The most complete known North American avisaurid | ||
| Mystiornis | 2011 | Ilek Formation (Early Cretaceous, Barremian to Aptian) | Possesses a myriad of features from various groups in Paraves, although most closely resembles avisaurids among sampled groups | ||
| Neuquenornis | 1994 | Bajo de la Carpa Formation (Late Cretaceous, Santonian) | Possessed long wings and a reverse hallux, indicating good flight and perching abilities | ||
| Soroavisaurus | 1993 | Lecho Formation (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) | A very close relative of Avisaurus |
Dubious genera and notable unnamed specimens
- Gobipipus reshetovi: Described in 2013 from embryo specimens within eggshells from the Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia. These specimens were very similar to embryonic Gobipteryx specimens, although the describers of Gobipipus (a set of controversial paleontologists including Evgeny Kurochkin and Sankar Chatterjee) consider it distinct.[80]
- Hebeiornis fengningensis: A synonym of Vescornis due to having been described from the same specimen. Despite having been described in 1999, 5 years prior to the description of Vescornis, the description was so poor compared to the description of Vescornis that the latter name is considered to take priority by most authors. As a result, the name Hebeiornis is considered a nomen nudum ("naked name").
- ‘’Proornis’’ is a dubious bird from North Korea.
- "Liaoxiornis delicatus": Described in 1999 from an enantiornithean specimen found in the Yixian Formation. This specimen was originally considered to be a tiny adult, but later found to be a hatchling. Other specimens have henceforth been assigned to the genus. Due to a lack of distinguishing feature, many paleontologists have considered this genus an undiagnostic nomen dubium.
- LP-4450: A juvenile of an indeterminate enantiornithean from the El Montsec Formation of Spain. Its 2006 description studied the histology of the skeleton, while later studies reported a squamosal bone present in the specimen but unknown in other enantiornitheans.
- IVPP V 13939: Briefly described in 2004, this Yixian enantiornithean had advanced pennaceous feathers on its legs, similar to (albeit shorter than) those of other paravians such as Microraptor and Anchiornis.[26]
- DIP-V-15100 and DIP-V-15101: Two different wings from hatchling specimens which were described in 2015. They attracted a significant amount of media attention upon their description. They were preserved in exceptional details due to having been trapped within Burmese amber for approximately 99 million years.[16]
- HPG-15-1: A partial corpse of a hatchling enantiornithean also preserved in Burmese amber. Although indeterminate, it attracted even more media attention than the two wings upon its description in 2017.[17]
- CUGB P1202: An indeterminate juvenile bohaiornithid from the Jiufotang Formation. A 2016 analysis of its feathering found elongated putative melanosomes, suggesting that a large portion of its feathering was iridescent.
- DIP-V-15102: Another corpse of an indeterminate hatchling preserved in Burmese amber. Described in early 2018.[18]
- MPCM-LH-26189 a/b: A partial skeleton of a hatchling from Las Hoyas in Spain, including both slab and counter-slab components. Its 2018 description revealed how various features developed in enantiornitheans as they aged. Such features include the ossification of the sternum from various smaller bones, and the fusion of tail vertebrae into a pygostyle.
- YLSNHM01001: A foot and tail preserved in Burmese amber.[81]
References
- ^ a b c Wang, Min; Zhou, Zhong-He; O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Zelenkov, Nikita V. (2014). "A new diverse enantiornithine family (Bohaiornithidae fam. nov.) from the Lower Cretaceous of China with information from two new species" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 52 (1): 31–76.
- ^ a b Wang, X.; O'Connor, J. K.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Z. (2014). "Insights into the evolution of rachis dominated tail feathers from a new basal enantiornithine (Aves: Ornithothoraces)". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 113 (3): 805–819. doi:10.1111/bij.12313.
- ^ a b c Chiappe, Luis M.; Walker, Cyril A. (2002). "Skeletal Morphology and Systematics of the Cretaceous Euenantiornithes (Ornithothoraces: Enantiornithes)". In Chiappe, Luis M.; Witmer, Lawrence M. (eds.). Mesozoic Birds: Above the Heads of Dinosaurs. University of California Press. pp. 240–67. ISBN 978-0-520-20094-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Chiappe, Luis M. (2007). Glorified Dinosaurs: The Origin and Early Evolution of Birds. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-24723-4.[page needed]
- ^ O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Gao, Chunling; Zhao, Bo (2011). "Anatomy of the Early Cretaceous enantiornithine bird Rapaxavis pani" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 56 (3): 463–75. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0047.
- ^ Elzanowski, Andrzej (1974). "Preliminary note on the palaeognathous bird from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia" (PDF). Palaeontologia Polonica. 29: 103–9.
- ^ a b Walker, C.A. (1981). "New subclass of birds from the Cretaceous of South America". Nature. 292 (5818): 51–3. Bibcode:1981Natur.292...51W. doi:10.1038/292051a0.
- ^ Hope, Sylvia (2002). "The Mesozoic Radiation of Neornithes". In Chiappe, Luis M.; Witmer, Lawrence M. (eds.). Mesozoic Birds: Above the Heads of Dinosaurs. University of California Press. pp. 339–88. ISBN 978-0-520-20094-4.
- ^ Feduccia, Alan (1996). The Origin and Evolution of Birds. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-06460-5.[page needed]
- ^ You, Hai-lu; Lamanna, Matthew C.; Harris, Jerald D.; Chiappe, Luis M.; O'Connor, Jingmai; Ji, Shu-an; Lü, Jun-chang; Yuan, Chong-xi; Li, Da-qing; Zhang, Xing; Lacovara, Kenneth J.; Dodson, Peter; Ji, Qiang (16 June 2006). "A Nearly Modern Amphibious Bird from the Early Cretaceous of Northwestern China". Science. 312 (5780): 1640–1643. Bibcode:2006Sci...312.1640Y. doi:10.1126/science.1126377. PMID 16778053.
- ^ a b Zhang, Zihui; Chiappe, Luis M.; Han, Gang; Chinsamy, Anusuya (2013). "A large bird from the Early Cretaceous of China: new information on the skull of enantiornithines". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (5): 1176–89. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.762708.
- ^ a b Zhou, Zhonghe; Clarke, Julia; Zhang, Fucheng (May 2008). "Insight into diversity, body size and morphological evolution from the largest Early Cretaceous enantiornithine bird". Journal of Anatomy. 212 (5): 565–77. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00880.x. PMC 2409080. PMID 18397240.
- ^ Hu, Dongyu; Xu, Xing; Hou, Lianhai; Sullivan, Corwin (2012). "A New Enantiornithine Bird from the Lower Cretaceous of Western Liaoning, China, and Its Implications for Early Avian Evolution". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (3): 639–45. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.652321.
- ^ Martin, Anthony J.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Rich, Thomas H.; Hall, Michael; Angielczyk, Kenneth (January 2014). "Oldest known avian footprints from Australia: Eumeralla Formation (Albian), Dinosaur Cove, Victoria". Palaeontology. 57 (1): 7–19. doi:10.1111/pala.12082.
- ^ Atterholt, Jessie; Hutchison, J. Howard; O’Connor, Jingmai K. (13 November 2018). "The most complete enantiornithine from North America and a phylogenetic analysis of the Avisauridae". PeerJ. 6: e5910. doi:10.7717/peerj.5910. PMC 6238772. PMID 30479894.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c Xing, Lida; McKellar, Ryan C.; Wang, Min; Bai, Ming; O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Benton, Michael J.; Zhang, Jianping; Wang, Yan; Tseng, Kuowei; Lockley, Martin G.; Li, Gang; Zhang, Weiwei; Xu, Xing (28 June 2016). "Mummified precocial bird wings in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber". Nature Communications. 7 (1): 12089. Bibcode:2016NatCo...712089X. doi:10.1038/ncomms12089. PMC 4931330. PMID 27352215.
- ^ a b Xing, Lida; O'Connor, Jingmai K.; McKellar, Ryan C.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Tseng, Kuowei; Li, Gang; Bai, Ming (September 2017). "A mid-Cretaceous enantiornithine (Aves) hatchling preserved in Burmese amber with unusual plumage". Gondwana Research. 49: 264–277. Bibcode:2017GondR..49..264X. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2017.06.001.
- ^ a b Xing, Lida; O'Connor, Jingmai K.; McKellar, Ryan C.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Bai, Ming; Tseng, Kuowei; Zhang, Jie; Yang, Haidong; Fang, Jun; Li, Gang (February 2018). "A flattened enantiornithine in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber: morphology and preservation". Science Bulletin. 63 (4): 235–243. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2018.01.019.
- ^ Xing, Lida; McKellar, Ryan C.; O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Bai, Ming; Tseng, Kuowei; Chiappe, Luis M. (30 January 2019). "A fully feathered enantiornithine foot and wing fragment preserved in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 927. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9..927X. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-37427-4. PMC 6353931. PMID 30700773.
- ^ Xing, Lida; McKellar, Ryan C.; O'Connor, Jingmai K. (June 2020). "An unusually large bird wing in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber". Cretaceous Research. 110: 104412. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104412.
- ^ a b O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Chiappe, Luis M. (28 February 2011). "A revision of enantiornithine (Aves: Ornithothoraces) skull morphology". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 9 (1): 135–157. doi:10.1080/14772019.2010.526639.
- ^ a b c Wang, Min; Hu, Han; Li, Zhiheng (21 August 2015). "A new small enantiornithine bird from the Jehol Biota, with implications for early evolution of avian skull morphology". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (6): 481–497. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1073801.
- ^ Wang, Min; Hu, Han (January 2017). "A Comparative Morphological Study of the Jugal and Quadratojugal in Early Birds and Their Dinosaurian Relatives". The Anatomical Record. 300 (1): 62–75. doi:10.1002/ar.23446. PMID 28000410.
- ^ Chiappe, Luis M. (2009). "Downsized Dinosaurs: The Evolutionary Transition to Modern Birds". Evolution: Education and Outreach. 2 (2): 248–56. doi:10.1007/s12052-009-0133-4.
- ^ Becker, Rachel (28 June 2016). "Bird wings trapped in amber are a fossil first from the age of dinosaurs". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.20162.
- ^ a b Zhang, Fucheng; Zhou, Zhonghe (October 2004). "Palaeontology: Leg feathers in an Early Cretaceous bird". Nature. 431 (7011): 925. Bibcode:2004Natur.431..925Z. doi:10.1038/431925a. PMID 15496911.
- ^ a b Clarke, Julia A.; Zhou, Zhonghe; Zhang, Fucheng (March 2006). "Insight into the evolution of avian flight from a new clade of Early Cretaceous ornithurines from China and the morphology of Yixianornis grabaui". Journal of Anatomy. 208 (3): 287–308. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00534.x. PMC 2100246. PMID 16533313.
- ^ a b O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Wang, Xuri; Chiappe, Luis M.; Gao, Chunling; Meng, Qingjin; Cheng, Xiaodong; Liu, Jinyuan (12 March 2009). "Phylogenetic support for a specialized clade of Cretaceous enantiornithine birds with information from a new species". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 29 (1): 188–204. doi:10.1080/02724634.2009.10010371.
- ^ a b Chiappe, Luis M.; Bo, Zhao; O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Chunling, Gao; Xuri, Wang; Habib, Michael; Marugan-Lobon, Jesus; Qingjin, Meng; Xiaodong, Cheng (2014). "A new specimen of the Early Cretaceous bird Hongshanornis longicresta: insights into the aerodynamics and diet of a basal ornithuromorph". PeerJ. 2: e234. doi:10.7717/peerj.234. PMC 3898307. PMID 24482756.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Wang, Xiaoli; Zheng, Xiaoting; Hu, Han; Zhang, Xiaomei; Zhou, Zhonghe (January 2016). "An Enantiornithine with a Fan-Shaped Tail, and the Evolution of the Rectricial Complex in Early Birds". Current Biology. 26 (1): 114–119. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.036. PMID 26748849.
- ^ a b O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Li, Da-Qing; Lamanna, Matthew C.; Wang, Min; Harris, Jerald D.; Atterholt, Jessie; You, Hai-Lu (30 December 2015). "A new Early Cretaceous enantiornithine (Aves, Ornithothoraces) from northwestern China with elaborate tail ornamentation". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (1): e1054035. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1054035.
- ^ a b Wang, Min; O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Pan, Yanhong; Zhou, Zhonghe (2017-01-31). "A bizarre Early Cretaceous enantiornithine bird with unique crural feathers and an ornithuromorph plough-shaped pygostyle". Nature Communications. 8: 14141. Bibcode:2017NatCo...814141W. doi:10.1038/ncomms14141. PMC 5290326. PMID 28139644.
- ^ a b Sanz, José L.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Buscalioni, Angela D. (1995). "The Osteology of Concornis lacustris (Aves: Enantiornithes) from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain and a Reexamination of its Phylogenetic Relationships". American Museum Novitates (3133): 1–23. hdl:2246/3667.
- ^ Dalla Vecchia, Fabio M.; Chiappe, Luis M. (2003). "First avian skeleton from the Mesozoic of northern Gondwana". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (4): 856–60. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0856:FASFTM]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 4524284.
- ^ O'Connor, Jingmai K. (1 January 2019). "The trophic habits of early birds". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 513: 178–195. Bibcode:2019PPP...513..178O. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.03.006.
- ^ O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Zhou, Zhonghe; Smith, Andrew (6 November 2019). "The evolution of the modern avian digestive system: insights from paravian fossils from the Yanliao and Jehol biotas". Palaeontology. 63 (1): 13–27. doi:10.1111/pala.12453.
- ^ Houston, David C.; Copsey, J. A. (1994). "Bone digestion and intestinal morphology of the Bearded Vulture". The Journal of Raptor Research. 28 (2): 73–78.
- ^ Sanz, José L.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Fernádez-Jalvo, Yolanda; Ortega, Francisco; Sánchez-Chillón, Begoña; Poyato-Ariza1, Francisco J.; Pérez-Moreno, Bernardino P. (February 2001). "An early Cretaceous pellet". Nature. 409 (6823): 998–1000. Bibcode:2001Natur.409..998S. doi:10.1038/35059172. PMID 11234054.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Mikhailov, Konstantin E. (1991). "Classification of fossil eggshells of amniotic vertebrates" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 36 (2): 193–238.
- ^ Mikhailov, Konstantin E. (1996). "New Genera of Fossil Eggs from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia". Paleontological Journal. 30 (2): 246–8.
- ^ Elżanowski, Andrzej (1981). "Embryonic bird skeletons from the late Cretaceous of Mongolia" (PDF). Palaeontologia Polonica. 42: 147–79.
- ^ Sanz, José L.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Pérez-Moreno, Bernardino P.; Moratalla, José J.; Hernández-Carrasquilla, Francisco; Buscalioni, Angela D.; Ortega, Francisco; Poyato-Ariza, Francisco J.; Rasskin-Gutman, Diego; Martı́nez-Delclòs, Xavier (June 6, 1997). "A Nestling Bird from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain: Implications for Avian Skull and Neck Evolution". Science. 276 (5318): 1543–6. doi:10.1126/science.276.5318.1543.
- ^ Zhou, Zhonghe; Zhang, Fucheng (October 22, 2004). "A Precocial Avian Embryo from the Lower Cretaceous of China". Science. 306 (5696): 653. doi:10.1126/science.1100000. PMID 15499011.
- ^ a b c Chiappe, Luis M.; Shu'an, Ji; Qiang, Ji (2007). "Juvenile Birds from the Early Cretaceous of China: Implications for Enantiornithine Ontogeny". American Museum Novitates. 3594: 1–46. doi:10.1206/0003-0082(2007)3594[1:JBFTEC]2.0.CO;2. hdl:2246/5890.
- ^ Elżanowski, Andrzej (1995). "Cretaceous birds and avian phylogeny". Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg. 181: 37–53.
- ^ Kurochkin, E.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Mikhailov, K.E. (2013). "An embryonic enantiornithine bird and associated eggs from the cretaceous of Mongolia". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1252–69. doi:10.1134/S0031030113110087.
- ^ Kurochkin, E. N.; Chatterjee, S.; Mikhailov, K. E. (19 December 2013). "An embryonic enantiornithine bird and associated eggs from the cretaceous of Mongolia". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1252–1269. doi:10.1134/S0031030113110087.
- ^ Cambra-Moo, Oscar; Buscalioni, Ángela Delgado; Cubo, Jorge; Castanet, Jacques; Loth, Marie-Madeleine; de Margerie, Emmanuel; de Ricqlès, Armand (2006). "Histological observations of Enantiornithine bone (Saurischia, Aves) from the Lower Cretaceous of Las Hoyas (Spain)". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 5 (5): 685–91. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2005.12.018.
- ^ O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Wang, Min; Zheng, Xiao-Ting; Wang, Xiao-Li; Zhou, Zhong-He (2014). "The histology of two female Early Cretaceous birds" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 52 (1): 112–28.
- ^ Chiappe, L.M. (1995). "The phylogenetic position of the Cretaceous birds of Argentina: Enantiornithes and Patagopteryx deferrariisi". Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg. 181: 55–63.
- ^ Dyke, Gareth; Vremir, Mátyás; Kaiser, Gary; Naish, Darren (June 2012). "A drowned Mesozoic bird breeding colony from the Late Cretaceous of Transylvania". Die Naturwissenschaften. 99 (6): 435–42. Bibcode:2012NW.....99..435D. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.394.9006. doi:10.1007/s00114-012-0917-1. PMID 22575918.
- ^ Fernández, Mariela S.; García, Rodolfo A.; Fiorelli, Lucas; Scolaro, Alejandro; Salvador, Rodrigo B.; Cotaro, Carlos N.; Kaiser, Gary W.; Dyke, Gareth J.; Farke, Andrew A. (17 April 2013). "A Large Accumulation of Avian Eggs from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia (Argentina) Reveals a Novel Nesting Strategy in Mesozoic Birds". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e61030. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...861030F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061030. PMC 3629076. PMID 23613776.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Falk, Amanda; Wang, Min; Zheng, Xiao-Ting (2020). "First report of immature feathers in juvenile enantiornithines from the Early Cretaceous Jehol avifauna". Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 58: 24–44. doi:10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.190823.
- ^ Padian, Kevin; Chiappe, Luis M. (11 January 2007). "The origin and early evolution of birds". Biological Reviews. 73 (1): 1–42. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185x.1997.tb00024.x.
- ^ Zhou, Shuang; Zhou, Zhong-He; O'Connor, Jingmai K. (2012). "A new basal beaked ornithurine bird from the Lower Cretaceous of Western Liaoning, China" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 50 (1): 9–24.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lay-url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help) - ^ Houde, Peter W. (1988). "Paleognathous Birds from the Early Tertiary of the Northern Hemisphere". Publications of the Nuttall Ornithological Club (Cambridge Massachusetts, USA: Nuttall Ornithological Club) 22
- ^ Navalón, Guillermo; Marugán-Lobón, Jesús; Chiappe, Luis M.; Luis Sanz, José; Buscalioni, Ángela D. (6 October 2015). "Soft-tissue and dermal arrangement in the wing of an Early Cretaceous bird: Implications for the evolution of avian flight". Scientific Reports. 5 (1): 14864. Bibcode:2015NatSR...514864N. doi:10.1038/srep14864. PMC 4594305. PMID 26440221.
- ^ Wang, Xia; McGowan, Alistair J.; Dyke, Gareth J.; Turvey, Samuel T. (7 December 2011). "Avian Wing Proportions and Flight Styles: First Step towards Predicting the Flight Modes of Mesozoic Birds". PLOS ONE. 6 (12): e28672. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...628672W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028672. PMID 22163324.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Chiappe, Luis M.; Suzuki, Shigeru; Dyke, Gareth J.; Watabe, Mahito; Tsogtbaatar, K.; Barsbold, Rinchen (January 2007). "A new Enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous of the Gobi desert". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 5 (2): 193–208. doi:10.1017/S1477201906001969.
- ^ Zheng, Xiaoting; Wang, Xiaoli; O'Connor, Jingmai; Zhou, Zhonghe (9 October 2012). "Insight into the early evolution of the avian sternum from juvenile enantiornithines". Nature Communications. 3 (1): 1116. Bibcode:2012NatCo...3.1116Z. doi:10.1038/ncomms2104. PMID 23047674.
- ^ a b O'Connor, Jingmai; Dyke, Gareth (2010). "A Reassessment of Sinornis santensis and Cathayornis yandica (Aves: Enantiornithes)". Records of the Australian Museum. 62: 7–20. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.62.2010.1540.
- ^ Clarke, Julia A.; Norell, Mark A. (2002). "The Morphology and Phylogenetic Position of Apsaravis ukhaana from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia". American Museum Novitates. 3387: 1–46. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.693.8475. doi:10.1206/0003-0082(2002)387<0001:TMAPPO>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ a b Sereno, P.C. (2005) TaxonSearch: Stem Archosauria Archived 2007-02-19 at the Wayback Machine. Version 1.0, 2005-NOV- 7. Retrieved 2006-OCT-02.
- ^ Carvalho; Novas; Agnolín; Isasi; Freitas; Andrade (2015). "A new genus and species of enantiornithine bird from the Early Cretaceous of Brazil". Brazilian Journal of Geology. 45 (2): 161–171. doi:10.1590/23174889201500020001.
- ^ Wang, Li; O'Connor, Zhou; You (2015). "Second species of enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous Changma Basin, northwestern China with implications for the taxonomic diversity of the Changma avifauna". Cretaceous Research. 55: 56–65. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.01.008.
- ^ Wang, M.; O'Connor, J. K.; Zhou, Z. (2014). "A new robust enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous of China with scansorial adaptations". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 34 (3): 657–671. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.812101.
- ^ Dalsätt, J.; Ericson, P. G.; Zhou, Z. (2015). "A New Enantiornithes (Aves) from the Early Cretaceous of China". Acta Geologica Sinica. 86 (2): 801–807. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12270.
- ^ Bell, Alyssa K.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Erickson, Gregory M.; Suzuki, Shigeru; Watabe, Mahito; Barsbold, Rinchen; Tsogtbaatar, K. (February 2010). "Description and ecologic analysis of Hollanda luceria, a Late Cretaceous bird from the Gobi Desert (Mongolia)". Cretaceous Research. 31 (1): 16–26. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2009.09.001.
- ^ Hartman, Scott; Mortimer, Mickey; Wahl, William R.; Lomax, Dean R.; Lippincott, Jessica; Lovelace, David M. (10 July 2019). "A new paravian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of North America supports a late acquisition of avian flight". PeerJ. 7: e7247. doi:10.7717/peerj.7247. PMC 6626525. PMID 31333906.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Zelenkov, Nikita V.; Averianov, Alexander O. (13 June 2015). "A historical specimen of enantiornithine bird from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia representing a new taxon with a specialized neck morphology". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (4): 319–338. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1051146.
- ^ Wang, M.; Liu, D. (2015). "Taxonomical reappraisal of Cathayornithidae (Aves: Enantiornithes)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14: 1–19. doi:10.1080/14772019.2014.994087.
- ^ Liu, Di; Chiappe, Luis M.; Serrano, Francisco; Habib, Michael; Zhang, Yuguang; Meng, Qinjing; Shawkey, Matthew (11 October 2017). "Flight aerodynamics in enantiornithines: Information from a new Chinese Early Cretaceous bird". PLOS One. 12 (10): e0184637. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1284637L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0184637. PMC 5636078. PMID 29020077.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Hu, Han; O'Connor, Jingmai K. (14 November 2016). "First species of Enantiornithes from Sihedang elucidates skeletal development in Early Cretaceous enantiornithines". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 15 (11): 909–926. doi:10.1080/14772019.2016.1246111.
- ^ Wang, Min; Zhou, Zhonghe; Xu, Guanghui (7 January 2014). "The first enantiornithine bird from the Upper Cretaceous of China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 34 (1): 135–145. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.794814.
- ^ Wang, Min; Zhou, Zhonghe (12 April 2017). "A morphological study of the first known piscivorous enantiornithine bird from the Early Cretaceous of China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 37 (2): e1278702. doi:10.1080/02724634.2017.1278702.
- ^ Hu, Dongyu; Liu, Ying; Li, Jinhua; Xu, Xing; Hou, Lianhai (July 2015). "Yuanjiawaornis viriosus, gen. et sp. nov., a large enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous of western Liaoning, China". Cretaceous Research. 55: 210–219. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.02.013.
- ^ Hu, Han; O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Zhou, Zhonghe; Farke, Andrew A. (3 June 2015). "A New Species of Pengornithidae (Aves: Enantiornithes) from the Lower Cretaceous of China Suggests a Specialized Scansorial Habitat Previously Unknown in Early Birds". PLOS One. 10 (6): e0126791. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1026791H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126791. PMC 4454694. PMID 26039693.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Chiappe, Luis M.; Qingjin, Meng; Serrano, Francisco; Sigurdsen, Trond; Min, Wang; Bell, Alyssa; Di, Liu (25 October 2019). "New Bohaiornis-like bird from the Early Cretaceous of China: enantiornithine interrelationships and flight performance". PeerJ. 7: e7846. doi:10.7717/peerj.7846. PMC 6816414. PMID 31667014.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Wang, Yan; Wang, Min; O'Connor, Jingmai K.; Wang, Xiaoli; Zheng, Xiaoting; Zhang, Xiaomei (11 January 2016). "A new Jehol enantiornithine bird with three-dimensional preservation and ovarian follicles". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (2): e1054496. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1054496.
- ^ Kurochkin, E. N.; Chatterjee, S.; Mikhailov, K. E. (19 December 2013). "An embryonic enantiornithine bird and associated eggs from the cretaceous of Mongolia". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1252–1269. doi:10.1134/s0031030113110087.
- ^ Xing, Lida; McKellar, Ryan C.; O’Connor, Jingmai K.; Niu, Kecheng; Mai, Huijuan (29 October 2019). "A mid-Cretaceous enantiornithine foot and tail feather preserved in Burmese amber". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 15513. Bibcode:2019NatSR...915513X. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-51929-9. PMID 31664115.