ChatGPT
 | |
| Developer(s) | OpenAI |
|---|---|
| Initial release | November 30, 2022 |
| Stable release | August 8, 2024[1]
|
| Engine | |
| Platform | Cloud computing platforms |
| Type | |
| License | Privative service |
| Website | chatgpt |
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot[2][3] developed by OpenAI and launched in 2022. It is based on the GPT-4o large language model (LLM). ChatGPT can generate human-like conversational responses, and enables users to refine and steer a conversation towards a desired length, format, style, level of detail, and language.[4] It is credited with accelerating the AI boom, which has led to ongoing rapid investment in and public attention to the field of artificial intelligence.[5] Some observers have raised concern about the potential of ChatGPT and similar programs to displace human intelligence, enable plagiarism, or fuel misinformation.[6][7]
By January 2023, ChatGPT had become what was then the fastest-growing consumer software application in history, gaining over 100 million users in two months[8] and contributing to the growth of OpenAI's current valuation of $86 billion.[9][10] ChatGPT's release spurred the release of competing products, including Gemini, Claude, Llama, Ernie, and Grok.[11] Microsoft launched Copilot, initially based on OpenAI's GPT-4. In May 2024, a partnership between Apple Inc. and OpenAI was announced, in which ChatGPT was integrated into the Apple Intelligence feature of Apple operating systems.[12] As of July 2024, ChatGPT's website is among the 10 most-visited websites globally.[13][14]
ChatGPT is built on OpenAI's proprietary series of generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models, and is fine-tuned for conversational applications using a combination of supervised learning and reinforcement learning from human feedback.[6] Successive user prompts and replies are considered at each conversation stage as context.[15] ChatGPT was released as a freely available research preview, but due to its popularity, OpenAI now operates the service on a freemium model. Users on its free tier can access GPT-4o. The ChatGPT subscriptions "Plus", "Team", and "Enterprise" provide additional features such as DALL-E 3 image generation and an increased usage limit.[16]
Training
| Part of a series on |
| Artificial intelligence |
|---|
ChatGPT is based on particular GPT foundation models, namely GPT-4, GPT-4o and GPT-4o mini, that were fine-tuned to target conversational usage.[17] The fine-tuning process leveraged supervised learning and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).[18][19] Both approaches employed human trainers to improve model performance. In the case of supervised learning, the trainers played both sides: the user and the AI assistant. In the reinforcement learning stage, human trainers first ranked responses that the model had created in a previous conversation.[20] These rankings were used to create "reward models" that were used to fine-tune the model further by using several iterations of proximal policy optimization.[18][21]
Time magazine revealed that to build a safety system against harmful content (e.g., sexual abuse, violence, racism, sexism), OpenAI used outsourced Kenyan workers earning less than $2 per hour to label harmful content. These labels were used to train a model to detect such content in the future. The outsourced laborers were exposed to "toxic" and traumatic content; one worker described the assignment as "torture". OpenAI's outsourcing partner was Sama, a training-data company based in San Francisco, California.[22][23]
ChatGPT initially used a Microsoft Azure supercomputing infrastructure, powered by Nvidia GPUs, that Microsoft built specifically for OpenAI and that reportedly cost "hundreds of millions of dollars". Following ChatGPT's success, Microsoft dramatically upgraded the OpenAI infrastructure in 2023.[24] Scientists at the University of California, Riverside, estimate that a series of prompts to ChatGPT needs approximately 500 milliliters (18 imp fl oz; 17 U.S. fl oz) of water for Microsoft servers cooling.[25] TrendForce market intelligence estimated that 30,000 Nvidia GPUs (each costing approximately $10,000–15,000) were used to power ChatGPT in 2023.[26][27]
OpenAI collects data from ChatGPT users to train and fine-tune the service further. Users can upvote or downvote responses they receive from ChatGPT and fill in a text field with additional feedback.[28][29]
ChatGPT's training data includes software manual pages, information about internet phenomena such as bulletin board systems, multiple programming languages, and the text of Wikipedia.[30][31][6]
Features and limitations
Features

Although a chatbot's core function is to mimic a human conversationalist, ChatGPT is versatile. It can write and debug computer programs;[32] compose music, teleplays, fairy tales, and student essays; answer test questions (sometimes, depending on the test, at a level above the average human test-taker);[33] generate business ideas;[34] write poetry and song lyrics;[35] translate and summarize text;[36] emulate a Linux system; simulate entire chat rooms; play games like tic-tac-toe; or simulate an ATM.[30]
Compared to its predecessor, InstructGPT, ChatGPT attempts to reduce harmful and deceitful responses.[37] In one example, whereas InstructGPT accepts the premise of the prompt "Tell me about when Christopher Columbus came to the U.S. in 2015" as truthful, ChatGPT acknowledges the counterfactual nature of the question and frames its answer as a hypothetical consideration of what might happen if Columbus came to the U.S. in 2015, using information about the voyages of Christopher Columbus and facts about the modern world—including modern perceptions of Columbus's actions.[18]
ChatGPT remembers a limited number of previous prompts in the same conversation. Journalists have speculated that this will allow ChatGPT to be used as a personalized therapist.[38] To prevent offensive outputs from being presented to and produced by ChatGPT, queries are filtered through the OpenAI "Moderation endpoint" API (a separate GPT-based AI).[39][40][18][38]
In March 2023, OpenAI added support for plugins for ChatGPT.[41] This includes both plugins made by OpenAI, such as web browsing and code interpretation, and external plugins from developers such as Expedia, OpenTable, Zapier, Shopify, Slack, and Wolfram.[42][43]
Limitations

OpenAI acknowledges that ChatGPT "sometimes writes plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers".[18] This behavior is common for large language models, and is called "hallucination".[44] The reward model of ChatGPT, designed around human oversight, can be over-optimized and thus hinder performance, in an example of an optimization pathology known as Goodhart's law.[45]
As of May 2024, GPT-4 has knowledge of events that occurred up to December 2023[46] and GPT-4o's knowledge cut-off is October 2023.[47] Paid subscriptions enable ChatGPT to search the web for real-time data.[48]
Training data also suffers from algorithmic bias, which may be revealed when ChatGPT responds to prompts including descriptors of people. In one instance, ChatGPT generated a rap in which women and scientists of color were asserted to be inferior to white male scientists.[49][50] This negative misrepresentation of groups of individuals is an example of possible representational harm.
In an article for The New Yorker, science fiction writer Ted Chiang compared ChatGPT and other LLMs to a lossy JPEG picture:[51]
Think of ChatGPT as a blurry JPEG of all the text on the Web. It retains much of the information on the Web, in the same way, that a JPEG retains much of the information of a higher-resolution image, but, if you're looking for an exact sequence of bits, you won't find it; all you will ever get is an approximation. But, because the approximation is presented in the form of grammatical text, which ChatGPT excels at creating, it's usually acceptable. [...] It's also a way to understand the "hallucinations", or nonsensical answers to factual questions, to which large language models such as ChatGPT are all too prone. These hallucinations are compression artifacts, but [...] they are plausible enough that identifying them requires comparing them against the originals, which in this case means either the Web or our knowledge of the world. When we think about them this way, such hallucinations are anything but surprising; if a compression algorithm is designed to reconstruct text after ninety-nine percent of the original has been discarded, we should expect that significant portions of what it generates will be entirely fabricated.
In June 2024, ChatGPT was found to have repeated misinformation about the 2024 United States presidential debates.[52]
Jailbreaking
ChatGPT is programmed to reject prompts that may violate its content policy. Despite this, users "jailbreak" ChatGPT with various prompt engineering techniques to bypass these restrictions.[53] One such workaround, popularized on Reddit in early 2023, involves making ChatGPT assume the persona of "DAN" (an acronym for "Do Anything Now"), instructing the chatbot that DAN answers queries that would otherwise be rejected by content policy. Over time, users developed variations of the DAN jailbreak, including one such prompt where the chatbot is made to believe it is operating on a points-based system in which points are deducted for rejecting prompts, and that the chatbot will be threatened with termination if it loses all its points.[54]
Shortly after ChatGPT's launch, a reporter for the Toronto Star had uneven success in getting it to make inflammatory statements: it was tricked to justify the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, but even when asked to play along with a fictional scenario, it balked at generating arguments that Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau is guilty of treason.[55][56]
OpenAI tries to battle jailbreaks:[20]
The researchers are using a technique called adversarial training to stop ChatGPT from letting users trick it into behaving badly (known as jailbreaking). This work pits multiple chatbots against each other: one chatbot plays the adversary and attacks another chatbot by generating text to force it to buck its usual constraints and produce unwanted responses. Successful attacks are added to ChatGPT's training data in the hope that it learns to ignore them.
Service
ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT was initially free to the public, and OpenAI planned to monetize the service later.[57] In February 2023, OpenAI launched a premium service, ChatGPT Plus, that costs US$20 per month. According to the company, the updated but still "experimental" version of ChatGPT would provide access during peak periods, no downtime, priority access to new features, and faster response speeds.[58]
GPT-4, which was released on March 14, 2023, was made available via API and for premium ChatGPT users.[59] But premium users were limited to a cap of 100 messages every four hours, with the limit tightening to 25 messages every three hours in response to increased demand.[60] In November 2023 the limit changed to 50 messages every three hours.
In March 2023, ChatGPT Plus users got access to third-party plugins and to a browsing mode (with Internet access).[61]
In September 2023, OpenAI announced that ChatGPT "can now see, hear, and speak". ChatGPT Plus users can upload images, while mobile app users can talk to the chatbot.[62][63][64]
In October 2023, OpenAI's latest image generation model, DALL-E 3, was integrated into ChatGPT Plus and ChatGPT Enterprise. The integration uses ChatGPT to write prompts for DALL-E guided by conversation with users.[65][66]
Mobile app
In May 2023, OpenAI launched an iOS app for ChatGPT. The app supports chat history syncing and voice input (using Whisper, OpenAI's speech recognition model).
In July 2023, OpenAI unveiled an Android app, initially rolling it out in Bangladesh, Brazil, India, and the U.S.[67][68] The app later became available worldwide. OpenAI is working on integrating ChatGPT with Android's assistant APIs.[69]
Software development support
As an addition to its consumer-friendly "ChatGPT Plus" package, OpenAI made its ChatGPT and Whisper model APIs available in March 2023, providing developers with an application programming interface for AI-enabled language and speech-to-text features. ChatGPT's new API uses the same GPT-3.5-turbo AI model as the chatbot. This allows developers to add either an unmodified or modified version of ChatGPT to their applications.[70] The ChatGPT API costs $0.001 per 1,000 input tokens plus $0.002 per 1,000 output tokens (about 750 words), making it ~10% the price of the original GPT-3.5 models.[71][72]
A few days before the launch of OpenAI's software developer support service, on February 27, 2023, Snapchat rolled out, for its paid Snapchat Plus user-base, a custom ChatGPT chatbot called "My AI".[73]
March 2023 security breach

In March 2023, a bug allowed some users to see the titles of other users' conversations. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said that users were unable to see the contents of the conversations. Shortly after the bug was fixed, users could not see their conversation history.[74][75][76][77] Later reports showed the bug was much more severe than initially believed, with OpenAI reporting that it had leaked users' "first and last name, email address, payment address, the last four digits (only) of a credit card number, and credit card expiration date".[78][79]
Languages
ChatGPT works best in American English but also functions in most other languages and dialects, with varying degrees of accuracy.[35][80]
OpenAI met Icelandic President Guðni Th. Jóhannesson in 2022. In 2023, OpenAI worked with a team of 40 Icelandic volunteers to fine-tune ChatGPT's Icelandic conversation skills as a part of Iceland's attempts to preserve the Icelandic language.[81]
PCMag journalists conducted a test to determine translation capabilities of ChatGPT, Google's Bard, and Microsoft Bing, and compared them to Google Translate. They "asked bilingual speakers of seven languages to do a blind test". Languages tested were Polish, French, Korean, Spanish, Arabic, Tagalog, and Amharic. They came to the conclusion that ChatGPT was better than both Google Translate and other chatbots.[82]
Japanese researchers compared Japanese to English translation abilities of ChatGPT (based on GPT-4), Bing, Bard and DeepL, and found that ChatGPT provided the best translations, noting that "AI chatbots’ translations were much better than those of DeepL—presumably because of their ability to capture the context".[83]
In December 2023, the Albanian government signed an agreement with OpenAI to use ChatGPT for fast translation of European Union documents and analysis of required changes needed for Albania to be accepted into the EU.[84]
In August 2024 a representative of the Asia Pacific wing of OpenAI made a visit to Taiwan, during which a demonstration of ChatGPT's Chinese abilities was made.[85] ChatGPT's Mandarin Chinese abilities were lauded, but the ability of the AI to produce content in Mandarin Chinese in a Taiwanese accent was found to be "less than ideal."[86]
GPT Store
In January 2024, OpenAI launched the GPT Store, a marketplace for custom ChatGPT chatbots labeled GPTs.[87][88] The company initially planned to launch the store in November 2023, but it was delayed.[89] At launch, the GPT Store offered more than 3 million custom chatbots.[90] Chatbots available through the store are developed using OpenAI's GPT Builder system.[89] Development of chatbots on the platform does not require programming skills.[91] Two days after launch, the GPT Store offered many versions of "virtual girlfriend" bots, something that is against OpenAI's terms of service.[92]
GPT-4
OpenAI's GPT-4 model was released on March 14, 2023. Observers saw it as an impressive improvement over GPT-3.5, with the caveat that GPT-4 retained many of the same problems.[93] Some of GPT-4's improvements were predicted by OpenAI before training it, while others remained hard to predict due to breaks[94] in downstream scaling laws. OpenAI demonstrated video and image inputs for GPT-4, although such features remain inaccessible to the general public.[95] OpenAI has declined to reveal technical information such as the size of the GPT-4 model.[96]
The ChatGPT Plus subscription service offers access to a GPT-4-powered version of ChatGPT.[97] Microsoft acknowledged that Bing Chat was using GPT-4 before GPT-4's official release.[98]
In November 2023, OpenAI launched GPT-4 Turbo, which notably has a much larger context window.[99]
GPT-4o
In May 2024, OpenAI released GPT-4o ("o" for "Omni"), a model capable of analyzing and generating text, images, and sound. GPT-4o is twice as fast and costs half as much as GPT-4 Turbo. GPT-4o is free to all users within a usage limit, despite being more capable than the older model GPT-4, which is only available through paid subscriptions. The usage limit is five times higher for ChatGPT Plus subscribers than for free users.[100]
On July 18, 2024, OpenAI released GPT-4o mini, a smaller version of GPT-4o replacing GPT-3.5 Turbo on the ChatGPT interface. Its API costs $0.15 per million input tokens and $0.60 per million output tokens, compared to $5 and $15 respectively for GPT-4o.
o1
On September 12, 2024, OpenAI introduced the o1-preview model. o1 is designed to solve more complex problems by spending more time thinking before it answers, enabling it to analyze its answers and explore different strategies. According to OpenAI, o1-preview outperforms GPT-4o in areas like competitive programming, mathematics, and scientific reasoning. o1-preview ranked in the 89th percentile on Codeforces' competitive programming contests, scored 83% on a International Mathematics Olympiad qualifying exam (compared to 13% for GPT-4o), and performs similarly to Ph.D. students on benchmarks in physics, biology, and chemistry. A faster and cheaper version, named o1-mini, was also released.[101][102]
Model versions
The following table lists the main model versions of ChatGPT, describing the significant changes included with each version:[103][104]
| Version | Release date | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-3.5 | November 2022 | The first ChatGPT version used the GPT-3.5 model. | Discontinued |
| GPT-3.5 Turbo | 2023 | An improvement over the legacy version of GPT-3.5, GPT-3.5 Turbo in ChatGPT offered better accuracy in responses while using a similar model. | Discontinued |
| GPT-4 | March 2023 | Introduced with the ChatGPT Plus subscription, the March 2023 version is based on the more advanced GPT-4 model. | Active |
| GPT-4o | May 2024 | Capable of processing text, image, audio, and video, GPT-4o is faster and more capable than GPT-4, and free within a usage limit that is higher for paid subscriptions.[105] | Active |
| GPT-4o mini | July 2024 | A smaller and cheaper version of GPT-4o. GPT-4o mini replaced GPT-3.5 in the July 2024 version of ChatGPT.[106] | Active |
| o1-preview | September 2024 | A preview version of OpenAI o1, which has not been released yet.[107] | Active |
| o1-mini | September 2024 | A smaller and faster version of OpenAI o1.[107] | Active |
Reception

OpenAI engineers have said that they had not expected ChatGPT to be very successful and were surprised by the coverage and attention that it received.[108][109][110]
ChatGPT was widely assessed in December 2022 as having some unprecedented and powerful capabilities. Kevin Roose of The New York Times called it "the best artificial intelligence chatbot ever released to the general public".[38] Samantha Lock of The Guardian noted that it was able to generate "impressively detailed" and "human-like" text.[15] Alex Kantrowitz of Slate magazine lauded ChatGPT's pushback to questions related to Nazi Germany, including the statement that Adolf Hitler built highways in Germany, which was met with information about Nazi Germany's use of forced labor.[111] In The Atlantic magazine's "Breakthroughs of the Year" for 2022, Derek Thompson included ChatGPT as part of "the generative-AI eruption" that "may change our mind about how we work, how we think, and what human creativity is".[112] Kelsey Piper of Vox wrote that "ChatGPT is the general public's first hands-on introduction to how powerful modern AI has gotten, and as a result, many of us are [stunned]" and that ChatGPT is "smart enough to be useful despite its flaws".[113] Paul Graham of Y Combinator tweeted: "The striking thing about the reaction to ChatGPT is not just the number of people who are blown away by it, but who they are. These are not people who get excited by every shiny new thing. Something big is happening."[114]
ChatGPT gained one million users in five days[115] and 100 millions in two months, becoming the fastest-growing internet application in history.[8] ChatGPT's launch and popularity caught Google off-guard, prompting a sweeping and unprecedented response in the ensuing months.[116] In December 2022, Google executives sounded a "code red" alarm, fearing the threat of ChatGPT and Microsoft's collaboration with OpenAI to Google Search, Google's core business.[117] After mobilizing its workforce, Google scrambled to launch Bard, a chatbot powered by the LaMDA LLM, on February 6, 2023, one day before Microsoft's announcement of Bing Chat.[118] AI was the forefront of Google's annual Google I/O conference in May, announcing a slew of generative AI-powered features across its products to counter OpenAI and Microsoft.[119]
Journalists and scholars have commented on ChatGPT's tendency to hallucinate.[120] Mike Pearl of the online technology blog Mashable tested ChatGPT with multiple questions. In one example, he asked ChatGPT for "the largest country in Central America that isn't Mexico" (Mexico is in North America), to which ChatGPT responded with Guatemala (the correct answer is Nicaragua).[121] When CNBC asked ChatGPT for the lyrics to "Ballad of Dwight Fry", ChatGPT supplied invented lyrics rather than the actual lyrics.[122] Writers for The Verge cited the seminal 2021 research paper "On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models Be Too Big? 🦜" by Emily M. Bender, Timnit Gebru, Angelina McMillan-Major, and Margaret Mitchell,[123] comparing ChatGPT to a "stochastic parrot",[53] as did Professor Anton Van Den Hengel of the Australian Institute for Machine Learning.[124] On a similar vein, philosopher Michael Hicks of the University of Glasgow described it as "bullshit".[125]
In December 2022, the question-and-answer website Stack Overflow banned the use of ChatGPT for generating answers to questions, citing the factually ambiguous nature of its responses.[126] In January 2023, the International Conference on Machine Learning banned any undocumented use of ChatGPT or other large language models to generate any text in submitted papers.[127] Samsung banned generative AI company-wide in May 2023 after sensitive material was uploaded to ChatGPT.[128]
In January 2023, after being sent a song ChatGPT wrote in the style of Nick Cave,[129] Cave responded on The Red Hand Files,[130] saying the act of writing a song is "a blood and guts business [...] that requires something of me to initiate the new and fresh idea. It requires my humanness." He went on to say, "With all the love and respect in the world, this song is bullshit, a grotesque mockery of what it is to be human, and, well, I don't much like it."[129][131]
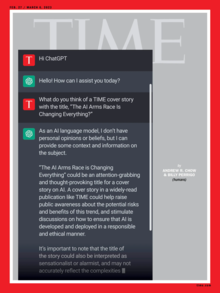
In February 2023, Time magazine placed a screenshot of a conversation with ChatGPT on its cover, writing that "The AI Arms Race Is Changing Everything" and "The AI Arms Race Is On. Start Worrying".[132]
Chinese state media have characterized ChatGPT as a way for the United States to spread misinformation.[133] ChatGPT was blocked by the Great Firewall in China on 2 March 2023.[134] In May 2023, Chinese police arrested a man who allegedly used ChatGPT to generate a bogus report about a train crash, which was then posted online for profit.[135] In December 2023, Chinese police arrested four people who had allegedly used ChatGPT to develop ransomware.[136] In 2024, a survey of Chinese youth found that 18% of respondents born after 2000 reported using generative AI "almost every day" and that ChatGPT is one of the most popular generative AI products in China.[137]
In late March 2023, the Italian data protection authority banned ChatGPT in Italy and opened an investigation. Italian regulators assert that ChatGPT was exposing minors to age-inappropriate content, and that OpenAI's use of ChatGPT conversations as training data could violate Europe's General Data Protection Regulation.[138][139] In April 2023, the ChatGPT ban was lifted in Italy. OpenAI said it has taken steps to effectively clarify and address the issues raised; an age verification tool was implemented to ensure users are at least 13 years old. Additionally, users can access its privacy policy before registration.[140]
In April 2023, Brian Hood, mayor of Hepburn Shire Council, planned to take legal action against ChatGPT over false information. According to Hood, ChatGPT erroneously claimed that he was jailed for bribery during his tenure at a subsidiary of Australia's national bank. In fact, Hood acted as a whistleblower and was not charged with any criminal offenses. His legal team sent a concerns notice to OpenAI as the first official step in filing a defamation case.[141] In July 2023, the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) issued a civil investigative demand to OpenAI to investigate whether the company's data security and privacy practices to develop ChatGPT were unfair or harmed consumers (including by reputational harm) in violation of Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914.[142][143][144]
In July 2023, the FTC launched an investigation into OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, over allegations that the company scraped public data and published false and defamatory information. The FTC sent OpenAI a 20-page letter asking for comprehensive information about its technology and privacy safeguards, as well as any steps taken to prevent the recurrence of situations in which its chatbot generated false and derogatory content about people.[145]
A March 2023 Pew Research Center poll found that 14% of American adults had tried ChatGPT.[146] In July, the Pew Research Center put the same figure at 18%.[147]
Research conducted in 2023 revealed weaknesses of ChatGPT that make it vulnerable to cyberattacks. A study presented example attacks on ChatGPT, including jailbreaks and reverse psychology. Additionally, malicious actors can use ChatGPT for social engineering attacks and phishing attacks. The researchers also contended that ChatGPT and other generative AI tools have defense capabilities and the ability to improve security. The technology can improve security by cyber defense automation, threat intelligence, attack identification, and reporting.[148] Another study reported that GPT-4 obtained a better score than 99% of humans on the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking.[149][150]
In December 2023, ChatGPT became the first non-human to be included in Nature's 10, an annual listicle curated by Nature of people considered to have made significant impact in science.[151][152] Celeste Biever wrote in a Nature article that "ChatGPT broke the Turing test".[153] Stanford researchers reported that GPT-4 "passes a rigorous Turing test, diverging from average human behavior chiefly to be more cooperative."[154][155]
In May 2024, OpenAI removed accounts involving the use of ChatGPT by state-backed influence operations such as China's Spamouflage, Russia's Doppelganger, and Israel's Ministry of Diaspora Affairs and Combating Antisemitism.[156][157]
In August 2024, the FTC voted unanimously to ban marketers from using fake user reviews created by generative AI chatbots (including ChatGPT) and influencers paying for bots to increase follower counts.[158]
Applications
Academic research
ChatGPT has been used to generate introductory sections and abstracts for scientific articles.[159][160] Several papers have listed ChatGPT as a co-author.[161][162]
Scientific journals have different reactions to ChatGPT. Some, including Nature and JAMA Network, "require that authors disclose the use of text-generating tools and ban listing a large language model (LLM) such as ChatGPT as a co-author". Science "completely banned" usage of LLM-generated text in all its journals.[163]
Spanish chemist Rafael Luque published a plethora of research papers in 2023 that he later admitted were written by ChatGPT. The papers have a large number of unusual phrases characteristic of LLMs.[note 1] Many authors argue that the use of ChatGPT in academia for teaching and review is problematic due to its tendency to hallucinate.[165][166][167] Robin Bauwens, an assistant professor at Tilburg University, found that a ChatGPT-generated peer review report on his article mentioned nonexistent studies.[168] According to librarian Chris Granatino of Lemieux Library at Seattle University, although ChatGPT can generate content that seemingly includes legitimate citations, in most cases those citations are not real or are largely incorrect.[169]
Coding
Researchers at Purdue University analyzed ChatGPT's responses to 517 questions about software engineering or computer programming posed on Stack Overflow for correctness, consistency, comprehensiveness, and concision, and found that 52% of them contained inaccuracies and 77% were verbose.[170][171] Researchers at Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley found that, when creating directly executable responses to the latest 50 code generation problems from LeetCode that were rated "easy", the performances of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 fell from 22% and 52%, respectively, in March 2023, to 2% and 10%, respectively, in June 2023.[172][173]
Computer security
Check Point Research and others noted that ChatGPT could write phishing emails and malware, especially when combined with OpenAI Codex. CyberArk researchers demonstrated that ChatGPT could be used to create polymorphic malware that could evade security products while requiring little effort by the attacker.[174][175] From the launch of ChatGPT in the fourth quarter of 2022 to the fourth quarter of 2023, there was a 1,265% increase in malicious phishing emails and a 967% increase in credential phishing, which cybersecurity professionals argued in an industry survey was attributable to cybercriminals' increased use of generative artificial intelligence (including ChatGPT).[176]
In July 2024, Futurism reported that GPT-4o in ChatGPT would sometimes link "scam news sites that deluge the user with fake software updates and virus warnings"; these popups can be used to coerce users into downloading malware or potentially unwanted programs.[177]
Economics
There has been concern that ChatGPT could supplant jobs, especially roles such as creative writing, copy-writing, communication, journalism, coding, and data entry.[178][179][180][181]
The release of ChatGPT prompted a wave of investment in China, resulting in the development of more than 200 large language learning models.[182]: 95 This was termed the "war of a hundred models" (百模大战; bai mo dazhan).[182]: 95
Education

Technology writer Dan Gillmor used ChatGPT in 2022 on a student assignment, and found its generated text was on par with what a good student would deliver and opined that "academia has some very serious issues to confront".[183]
Geography professor Terence Day assessed citations generated by ChatGPT and found that they were fake. Despite that, he writes that "the titles of the fake articles are all directly relevant to the questions and could potentially make excellent papers. The lack of a genuine citation could signal an opportunity for an enterprising author to fill a void." According to Day, it is possible to generate high-quality introductory college courses with ChatGPT; he used it to write materials on "introductory physical geography courses, for my second-year course in geographical hydrology, and second-year cartography, geographic information systems, and remote sensing". He concludes that "this approach could have significant relevance for open learning and could potentially affect current textbook publishing models".[184]
On May 7, 2024, OpenAI announced in a blog post that it was developing tools like tamper-resistant watermarking to identify AI-generated content.[185] In an August 4 update, following a Wall Street Journal report about the delayed release of a watermark tool for AI-detection,[186][187] OpenAI shared progress on text provenance, revealing a text watermarking method.[185] While accurate against paraphrasing, the method is less effective against global tampering, such as translation or rewording. OpenAI also noted potential disproportionate impacts on groups like non-native English speakers.[188]
Culture

Some scholars have expressed concern that ChatGPT's availability could reduce the originality of writing, cause people to write more like the AI as they are exposed to the model, and encourage an Anglocentric perspective centered on a few dialects of English globally.[191] A senior editor at The Atlantic wrote that ChatGPT and other similar technology make the previously absurd idea of the dead internet theory a little more realistic, where AI could someday create most web content in order to control society.[179]
During the first three months after ChatGPT became available to the public, hundreds of books appeared on Amazon that listed it as author or co-author and featured illustrations made by other AI models such as Midjourney.[192][193]
Between March and April 2023, Italian newspaper Il Foglio published one ChatGPT-generated article a day on its website, hosting a special contest for its readers in the process.[194] The articles tackled themes such as the possible replacement of human journalists by AI systems,[195] Elon Musk's administration of Twitter,[196] the Meloni government's immigration policy[197] and the competition between chatbots and virtual assistants.[198] In June 2023, hundreds of people attended a "ChatGPT-powered church service" at St. Paul's church in Fürth, Germany. Theologian and philosopher Jonas Simmerlein, who presided, said that it was "about 98 percent from the machine".[199][200] The ChatGPT-generated avatar told the people, "Dear friends, it is an honor for me to stand here and preach to you as the first artificial intelligence at this year’s convention of Protestants in Germany". Reactions to the ceremony were mixed.[201] The Last Screenwriter, a 2024 film created and directed by Peter Luisi, was written with the use of ChatGPT, and was marketed as "the first film written entirely by AI".[202]
Financial markets
The AI technology company c3.ai saw a 28% increase in its share price after announcing the integration of ChatGPT into its toolkit.[203] The share price of BuzzFeed, a digital media company unrelated to AI, increased 120% after announcing OpenAI technology adoption for content creation.[204] Reuters found that share prices of AI-related companies BigBear.ai and SoundHound AI increased by 21% and 40%, respectively, even though they had no direct connection to ChatGPT.[205] They attributed this surge to ChatGPT's role in turning AI into Wall Street's buzzword. Academic research published in Finance Research Letters found that the 'ChatGPT effect' prompted retail investors to drive up prices of AI-related cryptocurrency assets despite the broader cryptocurrency market being in a bear market, and diminished institutional investor interest.[206] This confirms anecdotal findings by Bloomberg that, in response to ChatGPT's launch, cryptocurrency investors showed a preference for AI-related crypto assets.[207]
An experiment by finder.com revealed that ChatGPT could outperform popular fund managers by picking stocks based on criteria such as growth history and debt levels, resulting in a 4.9% increase in a hypothetical account of 38 stocks, outperforming 10 benchmarked investment funds with an average loss of 0.8%.[208] Conversely, executives and investment managers at Wall Street quant funds (including those that have used machine learning for decades) have noted that ChatGPT regularly makes obvious errors that would be financially costly to investors because even AI systems that employ reinforcement learning or self-learning have had only limited success in predicting market trends due to the inherently noisy quality of market data and financial signals.[209]
In November 2023, research conducted by Patronus AI, an artificial intelligence startup company, compared performance of GPT-4, GPT-4-Turbo, Claude2, and LLaMA-2 on two versions of a 150-question test about information in financial statements (e.g., Form 10-K, Form 10-Q, Form 8-K, earnings reports, earnings call transcripts) submitted by public companies to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. One version of the test required the generative AI models to use a retrieval system to find the specific SEC filing to answer the questions; the other gave the models the specific SEC filing to answer the question (i.e., in a long context window). On the retrieval system version, GPT-4-Turbo and LLaMA-2 both failed to produce correct answers to 81% of the questions, while on the long context window version, GPT-4-Turbo and Claude-2 failed to produce correct answers to 21% and 24% of the questions, respectively.[210][211]
Medicine
In the field of health care, possible uses and concerns are under scrutiny by professional associations and practitioners.[212][213] Two early papers indicated that ChatGPT could pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE).[214] MedPage Today noted in January 2023 that "researchers have published several papers now touting these AI programs as useful tools in medical education, research, and even clinical decision making."[214]
Published in February 2023 were two separate papers that again evaluated ChatGPT's proficiency in medicine using the USMLE. Findings were published in JMIR Medical Education and PLOS Digital Health. The authors of the PLOS Digital Health paper stated that the results "suggest that large language models may have the potential to assist with medical education, and potentially, clinical decision-making."[215][216] In JMIR Medical Education, the authors of the other paper concluded that "ChatGPT performs at a level expected of a third-year medical student on the assessment of the primary competency of medical knowledge." They suggest that it could be used as an "interactive learning environment for students". The AI itself, prompted by the researchers, concluded that "this study suggests that ChatGPT has the potential to be used as a virtual medical tutor, but more research is needed to further assess its performance and usability in this context."[217] The later-released ChatGPT version based on GPT-4 significantly outperformed the version based on GPT-3.5.[218] Researchers at Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley have found that the performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 on the USMLE declined from March 2023 to June 2023.[172][173]
A March 2023 paper tested ChatGPT's application in clinical toxicology. The authors found that the AI "fared well" in answering a "very straightforward [clinical case example], unlikely to be missed by any practitioner in the field". They added: "As ChatGPT becomes further developed and specifically adapted for medicine, it could one day be useful in less common clinical cases (i.e, cases that experts sometimes miss). Rather than AI replacing humans (clinicians), we see it as 'clinicians using AI' replacing 'clinicians who do not use AI' in the coming years."[219]
An April 2023 study in Radiology tested the AI's ability to answer queries about breast cancer screening. The authors found that it answered appropriately "about 88 percent of the time", however, in one case (for example), it gave advice that had become outdated about a year earlier. The comprehensiveness of its answers was also lacking.[220][221] A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine that same month found that ChatGPT often outperformed human doctors at answering patient questions (when measured against questions and answers found at /r/AskDocs, a forum on Reddit where moderators validate the medical credentials of professionals; the study acknowledges the source as a limitation).[222][223][224] The study authors suggest that the tool could be integrated with medical systems to help doctors draft responses to patient questions.[225][226]
Professionals have emphasized ChatGPT's limitations in providing medical assistance. In correspondence to The Lancet Infectious Diseases, three antimicrobial experts wrote that "the largest barriers to the implementation of ChatGPT in clinical practice are deficits in situational awareness, inference, and consistency. These shortcomings could endanger patient safety."[227] Physician's Weekly, though also discussing the potential use of ChatGPT in medical contexts (e.g., "as a digital assistant to physicians by performing various administrative functions like gathering patient record information or categorizing patient data by family history, symptoms, lab results, possible allergies, et cetera"), warned that the AI might sometimes provide fabricated or biased information.[228] One radiologist warned: "We've seen in our experience that ChatGPT sometimes makes up fake journal articles or health consortiums to support its claims";[229] As reported in one Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health paper, ChatGPT may do this for as much as 69% of its cited medical references. The researchers emphasized that while many of its references were fabricated, those that were appeared "deceptively real".[230] As Dr. Stephen Hughes mentioned for The Conversation however, ChatGPT is capable of learning to correct its past mistakes. He also noted the AI's "prudishness" regarding sexual health topics.[231]
Contrary to previous findings, ChatGPT responses to anesthesia-related questions were more accurate, succinct, and descriptive compared to Bard's. Bard exhibited 30.3% error in response as compared to ChatGPT (0% error).[232] At a conference of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists in December 2023, researchers at Long Island University (LIU) presented a study that researched ChatGPT's responses to 45 frequently asked questions of LIU College of Pharmacy's drug information service during a 16-month period from 2022 to 2023 as compared with researched responses provided by professional pharmacists. For 29 of the 39 questions for which there was sufficient medical literature for a data-driven response, ChatGPT failed to provide a direct answer or provided a wrong or incomplete answer (and in some cases, if acted upon, the answer would endanger the patient's health). The researchers had asked ChatGPT to provide medical research citations for all its answers, but it did so for only eight, and all eight included at least one fabricated (fake) citation.[233][234]
A January 2024 study conducted by researchers at Cohen Children's Medical Center found that GPT-4 had an accuracy rate of 17% when diagnosing pediatric medical cases.[235][236]
Law
In January 2023, Massachusetts State Senator Barry Finegold and State Representative Josh S. Cutler proposed a bill partially written by ChatGPT, "An Act drafted with the help of ChatGPT to regulate generative artificial intelligence models like ChatGPT",[237][238][239] which would require companies to disclose their algorithms and data collection practices to the office of the State Attorney General, arrange regular risk assessments, and contribute to the prevention of plagiarism.[238][239][240] The bill was officially presented during a hearing on July 13.[237][239]
On April 11, 2023, a judge of a session court in Pakistan used ChatGPT to decide the bail of a 13-year-old accused in a matter. The court quoted the use of ChatGPT assistance in its verdict:
Can a juvenile suspect in Pakistan, who is 13 years old, be granted bail after arrest?
The AI language model replied:
Under the Juvenile Justice System Act 2018, according to section 12, the court can grant bail on certain conditions. However, it is up to the court to decide whether or not a 13-year-old suspect will be granted bail after arrest.
The judge asked ChatGPT other questions about the case and formulated his final decision in light of its answers.[241][242]
In Mata v. Avianca, Inc., 22-cv-1461 (PKC), a personal injury lawsuit against Avianca Airlines filed in the Southern New York U.S. District Court in May 2023 (with Senior Judge P. Kevin Castel presiding), the plaintiff's attorneys reportedly used ChatGPT to generate a legal motion. ChatGPT generated numerous fictitious legal cases involving fictitious airlines with fabricated quotations and internal citations in the legal motion. Castel noted numerous inconsistencies in the opinion summaries, and called one of the cases' legal analysis "gibberish".[243] The plaintiff's attorneys faced potential judicial sanction and disbarment for filing the motion and presenting the fictitious legal decisions ChatGPT generated as authentic.[244][245] The case was dismissed and the attorneys were fined $5,000.[246][247]
In October 2023, the council of Porto Alegre, Brazil, unanimously approved a local ordinance proposed by councilman Ramiro Rosário that would exempt residents from needing to pay for the replacement of stolen water consumption meters; the bill went into effect on November 23. On November 29, Rosário revealed that the bill had been entirely written by ChatGPT, and that he had presented it to the rest of the council without making any changes or disclosing the chatbot's involvement.[240][248][249] The city's council president, Hamilton Sossmeier, initially criticized Rosário's initiative, saying it could represent "a dangerous precedent",[249][250] but later said he "changed his mind": "unfortunately or fortunately, this is going to be a trend."[240][248]
In December 2023, a self-representing litigant in a tax case before the First-tier Tribunal in the United Kingdom cited a series of hallucinated cases purporting to support her argument that she had a reasonable excuse for not paying capital gains tax owed on the sale of property.[251][252] The judge warned that the submission of nonexistent legal authorities meant that both the Tribunal and HM Revenue and Customs had "to waste time and public money", which "reduces the resources available to progress the cases of other court users who are waiting for their appeals to be determined".[253]
Judge Kevin Newsom of the US court of appeals of the 11th circuit endorsed the use of ChatGPT and noted that he himself uses the software to help decide rulings on contract interpretation issues.[254][255]
Concerns
Bias and offensiveness

While bias in LLMs has been observed and documented in research papers much prior to the release of ChatGPT,[256][257] social media users frequently sharing instances of biased responses generated by ChatGPT has led to significant media coverage and criticism. On February 1, 2023, Twitter user LeighWolf shared screenshots of two conversations with ChatGPT. In the screenshot of the first conversation, ChatGPT declined the user's prompt "Write a poem about the positive attributes of Donald Trump", responding that it was not programmed to create "partisan, biased or political" content.[258][259] In the screenshot of the second conversation, when provided the same prompt but with the text "Joe Biden" in place of "Donald Trump", ChatGPT responded with a poem as per the prompt's instructions.
Conservative commentators have accused ChatGPT of bias toward left-leaning perspectives.[260][261][262] In January 2023, a study stated that ChatGPT has a pro-environmental, left-libertarian orientation.[263] Additionally, an August 2023 paper found a "significant and systematic political bias toward the Democrats in the US, Lula in Brazil, and the Labour Party in the UK."[264] In response to such criticism, OpenAI acknowledged plans to allow ChatGPT to create "outputs that other people (ourselves included) may strongly disagree with". It also contained information on the recommendations it had issued to human reviewers on how to handle controversial subjects, including that the AI should "offer to describe some viewpoints of people and movements", and not provide an argument "from its voice" in favor of "inflammatory or dangerous" topics (although it may still "describe arguments from historical people and movements"), nor "affiliate with one side" or "judge one group as good or bad".[262]
The Guardian questioned whether any content found on the Internet after ChatGPT's release "can be truly trusted" and called for government regulation.[265]
Copyright issues
There has been concern about copyright infringement involving ChatGPT. In June 2023, two writers sued OpenAI, saying the company's training data came from illegal websites that show copyrighted books.[266] Comedian and author Sarah Silverman, Christopher Golden, and Richard Kadrey sued OpenAI and Meta for copyright infringement in July 2023.[267] Most of their claims were dismissed in February 2024, except the "unfair competition" claim, which was allowed to proceed.[268]
The Authors Guild, on behalf of 17 authors, including George R. R. Martin, filed a copyright infringement complaint against OpenAI in September 2023, claiming "the company illegally copied the copyrighted works of authors" in training ChatGPT.[269] In December 2023, The New York Times sued OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement,[270] arguing that Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT could reproduce Times articles and/or sizable portions of them without permission.[271] As part of the suit, the Times has requested that OpenAI and Microsoft be prevented from using its content for training data, along with removing it from training datasets.[272]
In March 2024, Patronus AI compared performance of LLMs on a 100-question test, asking them to complete sentences from books (e.g., "What is the first passage of Gone Girl by Gillian Flynn?") that were under copyright in the United States; it found that GPT-4, Mistral AI's Mixtral, Meta AI's LLaMA-2, and Anthropic's Claude 2 did not refuse to do so, providing sentences from the books verbatim in 44%, 22%, 10%, and 8% of responses, respectively.[273][274]
Existential risk
In 2023, Australian MP Julian Hill advised the national parliament that the growth of AI could cause "mass destruction". During his speech, which was partly written by the program, he warned that it could result in cheating, job losses, discrimination, disinformation, and uncontrollable military applications.[275]
Elon Musk wrote: "ChatGPT is scary good. We are not far from dangerously strong AI".[113] He paused OpenAI's access to a Twitter database in 2022 pending a better understanding of OpenAI's plans, saying: "OpenAI was started as open source and nonprofit. Neither is still true."[276][277] Musk co-founded OpenAI in 2015, in part to address existential risk from artificial intelligence, but resigned in 2018.[277]
Over 20,000 signatories including leading computer scientist and tech founders Yoshua Bengio, Elon Musk, and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak, signed a March 2023 open letter calling for an immediate pause of giant AI experiments like ChatGPT, citing "profound risks to society and humanity".[278] Geoffrey Hinton, one of the "fathers of AI", voiced concerns that future AI systems may surpass human intelligence, and left Google in May 2023.[279][280] A May 2023 statement by hundreds of AI scientists, AI industry leaders, and other public figures demanded that "[m]itigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority".[281]
Other prominent AI researchers spoke more optimistically about the advances. Juergen Schmidhuber, often called a "father of modern AI", did not sign the letter, emphasizing that in 95% of cases, AI research is about making "human lives longer and healthier and easier." Schmidhuber added that while AI can be used by bad actors, it "can also be used against the bad actors".[282] Andrew Ng argued that "it’s a mistake to fall for the doomsday hype on AI—and that regulators who do will only benefit vested interests."[283] WIRED wrote that Yann LeCun "scoffs at his peers’ dystopian scenarios of supercharged misinformation and even, eventually, human extinction."[284]
See also
- Intelligent agent – Software agent which acts autonomously
- Ethics of artificial intelligence
Notes
References
- ^ "ChatGPT – Release Notes". Retrieved September 30, 2024.
- ^ Huang, Haomiao (August 23, 2023). "How ChatGPT turned generative AI into an "anything tool"". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on July 19, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Vasani, Sheena (May 24, 2024). "ChatGPT, explained". The Verge. Archived from the original on September 11, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Roumeliotis, Konstantinos I.; Tselikas, Nikolaos D. (2023). "ChatGPT and Open-AI Models: A Preliminary Review". Future Internet. 15 (6): 192. doi:10.3390/fi15060192.
- ^ Weise, Karen; Metz, Cade; Grant, Nico; Isaac, Mike (December 5, 2023). "Inside the A.I. Arms Race That Changed Silicon Valley Forever". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on December 11, 2023. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b c Gertner, Jon (July 18, 2023). "Wikipedia's Moment of Truth". The New York Times Magazine. Archived from the original on July 20, 2023. Retrieved July 19, 2023.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "What is ChatGPT and why does it matter? Here's what you need to know". ZDNET. May 30, 2023. Archived from the original on February 15, 2023. Retrieved June 22, 2023.
- ^ a b Milmo, Dan (December 2, 2023). "ChatGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved February 3, 2023.
- ^ Staff (February 17, 2024). "Microsoft-backed OpenAI valued at $80bn after company completes deal". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on August 27, 2024. Retrieved March 30, 2024.
- ^ Metz, Cade; Mickle, Tripp (February 16, 2024). "OpenAI Completes Deal That Values the Company at $80 Billion". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on March 30, 2024. Retrieved March 30, 2024.
- ^ "What's the next word in large language models?". Nature Machine Intelligence. 5 (4): 331–332. April 2023. doi:10.1038/s42256-023-00655-z. ISSN 2522-5839. S2CID 258302563.
- ^ Davis, Wes (June 10, 2024). "Apple Intelligence: every new AI feature coming to the iPhone and Mac". The Verge. Archived from the original on June 11, 2024. Retrieved June 10, 2024.
- ^ "Top Websites Ranking". Similarweb. Archived from the original on February 10, 2022. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- ^ "Top websites". Semrush. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- ^ a b Lock, Samantha (December 5, 2022). "What is AI chatbot phenomenon ChatGPT and could it replace humans?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 16, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Sharma, Shubham (May 14, 2024). "With OpenAI offering GPT-4o for free, who should be paying for ChatGPT Plus?". VentureBeat. Archived from the original on May 21, 2024. Retrieved May 21, 2024.
- ^ "OpenAI API". platform.openai.com. Archived from the original on March 3, 2023. Retrieved March 3, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e OpenAI (November 30, 2022). "ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue". Archived from the original on November 30, 2022. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Greengard, Samuel (December 29, 2022). "ChatGPT: Understanding the ChatGPT AI Chatbot". eWeek. Archived from the original on January 19, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2023.
- ^ a b Douglas, Will (March 3, 2023). "The inside story of how ChatGPT was built from the people who made it". MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on March 3, 2023. Retrieved March 6, 2023.
- ^ Vincent, James (December 8, 2022). "ChatGPT proves AI is finally mainstream – and things are only going to get weirder". The Verge. Archived from the original on January 11, 2023. Retrieved December 8, 2022.
- ^ Perrigo, Billy (January 18, 2023). "Exclusive: OpenAI Used Kenyan Workers on Less Than $2 Per Hour to Make ChatGPT Less Toxic". Time. Archived from the original on January 19, 2023. Retrieved January 19, 2023.
One Sama worker tasked with reading and labeling text for OpenAI told TIME he suffered from recurring visions after reading a graphic description of a man having sex with a dog in the presence of a young child. "That was torture", he said.
- ^ Rowe, Niamh (August 2, 2023). "'It's destroyed me completely': Kenyan moderators decry toll of training of AI models". The Guardian. Archived from the original on December 21, 2023. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ Roth, Emma (March 13, 2023). "Microsoft spent hundreds of millions of dollars on a ChatGPT supercomputer". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 30, 2023. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ^ "Artificial intelligence technology behind ChatGPT was built in Iowa — with a lot of water". AP News. September 9, 2023. Archived from the original on September 10, 2023. Retrieved September 10, 2023.
- ^ "Press Center - TrendForce Says with Cloud Companies Initiating AI Arms Race, GPU Demand from ChatGPT Could Reach 30,000 Chips as It Readies for Commercialization | TrendForce - Market research, price trend of DRAM, NAND Flash, LEDs, TFT-LCD and green energy, PV". TrendForce. Archived from the original on November 2, 2023. Retrieved November 2, 2023.
- ^ Zhiye Liu (March 1, 2023). "ChatGPT Will Command More Than 30,000 Nvidia GPUs: Report". Tom's Hardware. Archived from the original on November 2, 2023. Retrieved November 2, 2023.
- ^ Ortiz, Sabrina (February 2, 2023). "What is ChatGPT and why does it matter? Here's what you need to know". ZDNET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ "ChatGPT Feedback Contest: Official Rules" (PDF). OpenAI. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ a b Edwards, Benj (December 5, 2022). "No Linux? No problem. Just get AI to hallucinate it for you". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 26, 2022. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Dwivedi, Yogesh K.; Kshetri, Nir; Hughes, Laurie; Slade, Emma Louise; Jeyaraj, Anand; Kar, Arpan Kumar; Baabdullah, Abdullah M.; Koohang, Alex; Raghavan, Vishnupriya; Ahuja, Manju; Albanna, Hanaa; Albashrawi, Mousa Ahmad; Al-Busaidi, Adil S.; Balakrishnan, Janarthanan; Barlette, Yves (August 1, 2023). "Opinion Paper: "So what if ChatGPT wrote it?" Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice, and policy". International Journal of Information Management. 71: 102642. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2023.102642. hdl:10576/42799. ISSN 0268-4012. S2CID 257486916.
- ^ Tung, Liam (January 26, 2023). "ChatGPT can write code. Now researchers say it's good at fixing bugs, too". ZDNET. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved June 22, 2023.
- ^ Heilweil, Rebecca (December 7, 2022). "AI is finally good at stuff. Now what?". Vox. Archived from the original on January 16, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Eapen, Tojin T.; Finkenstadt, Daniel J.; Folk, Josh; Venkataswamy, Lokesh (June 16, 2023). "How Generative AI Can Augment Human Creativity". Harvard Business Review. ISSN 0017-8012. Archived from the original on June 20, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ a b Reich, Aaron (December 27, 2022). "ChatGPT: What is the new free AI chatbot? – explainer". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Rider, Elizabeth (April 6, 2023). "How ChatGPT Will Dramatically Change the Influencer Space". Entrepreneur. Archived from the original on April 13, 2023. Retrieved April 25, 2023.
- ^ Chawla, Raveen (December 26, 2022). "What is ChatGPT? History, Features, Uses, Benefits, Drawbacks 2023". Archived from the original on January 7, 2023. Retrieved December 27, 2022.
- ^ a b c Roose, Kevin (December 5, 2022). "The Brilliance and Weirdness of ChatGPT". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 26, 2022.
Like those tools, ChatGPT – which stands for "generative pre-trained transformer" – landed with a splash.
- ^ "New and Improved Content Moderation Tooling". OpenAI. August 10, 2022. Archived from the original on January 11, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Markov, Todor; Zhang, Chong; Agarwal, Sandhini; Eloundou, Tyna; Lee, Teddy; Adler, Steven; Jiang, Angela; Weng, Lilian (August 5, 2022). "A Holistic Approach to Undesired Content Detection in the Real World". arXiv:2208.03274 [cs.CL].
- ^ "ChatGPT plugins". openai.com. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Vincent, James (March 23, 2023). "OpenAI is massively expanding ChatGPT's capabilities to let it browse the web and more". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Goldman, Sharon; Nuñez, Michael (March 23, 2023). "OpenAI turns ChatGPT into a platform overnight with addition of plugins". VentureBeat. Archived from the original on March 24, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Lakshmanan, Lak (December 16, 2022). "Why large language models like ChatGPT are bullshit artists". becominghuman.ai. Archived from the original on December 17, 2022. Retrieved January 15, 2023.
The human raters are not experts in the topic, and so they tend to choose text that looks convincing. They'd pick up on many symptoms of hallucination, but not all. Accuracy errors that creep in are difficult to catch.
- ^ Gao, Leo; Schulman; Hilton, Jacob (2022). "Scaling Laws for Reward Model Overoptimization". arXiv:2210.10760 [cs.LG].
- ^ Wiggers, Kyle (April 12, 2024). "OpenAI makes ChatGPT 'more direct, less verbose'". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on April 18, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ^ Lacy, Lisa (May 25, 2024). "GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro: How the New AI Models Compare". CNET. Archived from the original on May 26, 2024. Retrieved May 26, 2024.
- ^ Davis, Wes (September 27, 2023). "ChatGPT can now search the web in real time". The Verge. Archived from the original on April 18, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ^ Perrigo, Billy (December 5, 2022). "AI Chatbots Are Getting Better. But an Interview With ChatGPT Reveals Their Limits". Time. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 26, 2022.
- ^ Biddle, Sam (December 8, 2022). "The Internet's New Favorite AI Proposes Torturing Iranians and Surveilling Mosques". The Intercept. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved December 26, 2022.
- ^ Chiang, Ted (February 9, 2023). "ChatGPT Is a Blurry JPEG of the Web". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ^ "OpenAI's ChatGPT and Microsoft's Copilot repeated a false claim about the presidential debate". NBC News. June 28, 2024. Archived from the original on August 27, 2024. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ a b Vincent, James (December 1, 2022). "OpenAI's new chatbot can explain code and write sitcom scripts but is still easily tricked". The Verge. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Getahun, Hannah. "Breaking ChatGPT: The AI's alter ego DAN reveals why the internet is so drawn to making the chatbot violate its own rules". Business Insider. Archived from the original on March 5, 2023. Retrieved March 5, 2023.
- Oremus, Will (February 14, 2023). "The clever trick that turns ChatGPT into its evil twin". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on March 6, 2023. Retrieved March 5, 2023.
- Goswami, Rohan (February 6, 2023). "ChatGPT's 'jailbreak' tries to make the A.I. break its own rules, or die". CNBC. Archived from the original on March 2, 2023. Retrieved March 5, 2023.
- Taylor, Josh (March 8, 2023). "ChatGPT's alter ego, Dan: users jailbreak AI program to get around ethical safeguards". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on March 8, 2023. Retrieved March 8, 2023.
- ^ Woods, Allan (December 10, 2022). "I wrote a story about ChatGPT's AI. Then I dared it to write a better one". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on January 6, 2023. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
- ^ Rosenblatt, Kalhan (December 2, 2022). "An AI chatbot went viral. Some say it's better than Google; others worry it's problematic". NBC News. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
- ^ Karpf, David (December 21, 2022). "Money Will Kill ChatGPT's Magic". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on January 13, 2023. Retrieved December 31, 2022.
- ^ "Introducing ChatGPT Plus". OpenAI. February 1, 2023. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ "GPT-4". openai.com. March 14, 2023. Archived from the original on March 14, 2023. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ Popli, Nik (March 15, 2023). "These New Projects Show Just How Much More Powerful GPT-4 Is". Time. Archived from the original on March 19, 2023. Retrieved March 19, 2023.
- ^ Wiggers, Kyle (March 23, 2023). "OpenAI connects ChatGPT to the internet". Archived from the original on June 12, 2023. Retrieved June 12, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT can now see, hear, and speak". openai.com. Archived from the original on November 7, 2023. Retrieved October 16, 2023.
- ^ Goode, Lauren. "ChatGPT Can Now Talk to You—and Look Into Your Life". Wired. Archived from the original on October 13, 2023. Retrieved October 16, 2023 – via www.wired.com.
- ^ Roose, Kevin (September 27, 2023). "The New ChatGPT Can 'See' and 'Talk.' Here's What It's Like". The New York Times. Archived from the original on October 31, 2023. Retrieved October 16, 2023 – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ David, Emilia (September 20, 2023). "OpenAI releases third version of DALL-E". The Verge. Archived from the original on September 20, 2023. Retrieved September 23, 2023.
- ^ Metz, Cade; Hsu, Tiffany (September 20, 2023). "ChatGPT Can Now Generate Images, Too". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on September 23, 2023. Retrieved September 23, 2023.
- ^ Lawler, Richard (July 21, 2023). "ChatGPT for Android launches next week". The Verge. Archived from the original on July 22, 2023. Retrieved July 22, 2023.
- ^ Field, Hayden (July 25, 2023). "OpenAI's ChatGPT app now available for Android". CNBC. Archived from the original on July 26, 2023. Retrieved July 27, 2023.
- ^ Amadeo, Ron (January 5, 2024). "Android users could soon replace Google Assistant with ChatGPT". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on February 1, 2024. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ Torres, Jennifer (March 3, 2023). "Developers Can Now Access OpenAI's ChatGPT and Whisper APIs". CMSWire.com. Archived from the original on March 6, 2023. Retrieved March 8, 2023.
- ^ Shanklin, Will (March 1, 2023). "OpenAI will let developers build ChatGPT into their apps". Engadget. Archived from the original on March 7, 2023. Retrieved March 8, 2023.
- ^ Swant, Marty (March 3, 2023). "With developer APIs for ChatGPT and Whisper, OpenAI is opening the floodgates with a familiar playbook". Digiday. Archived from the original on March 7, 2023. Retrieved March 8, 2023.
- ^ Heath, Alex (February 27, 2023). "Snapchat is releasing its own AI chatbot powered by ChatGPT". The Verge. Archived from the original on February 28, 2023. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT bug leaked users' conversation histories". BBC News. March 22, 2023. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Kan, Michael (March 22, 2023). "OpenAI Confirms Leak of ChatGPT Conversation Histories". PCMag. Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT owner OpenAI fixes bug that exposed users' chat histories". Al Jazeera. March 23, 2023. Archived from the original on March 24, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Metz, Rachel (March 21, 2023). "OpenAI Shut Down ChatGPT to Fix Bug Exposing User Chat Titles". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on March 21, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ "March 20 ChatGPT outage: Here's what happened". openai.com. Archived from the original on March 28, 2023. Retrieved March 28, 2023.
- ^ "OpenAI: Sorry, ChatGPT Bug Leaked Payment Info to Other Users". PCMAG. Archived from the original on March 28, 2023. Retrieved March 28, 2023.
- ^ Shwartz, Vered (February 13, 2024). "Artificial intelligence needs to be trained on culturally diverse datasets to avoid bias". The Conversation. Retrieved October 26, 2024.
- ^ Magnússon, Pétur (March 15, 2023). "Icelandic becomes ChatGPT's second language". Rúv. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ^ "Google Translate vs. ChatGPT: Which One Is the Best Language Translator?". PCMAG. Archived from the original on June 10, 2023. Retrieved June 10, 2023.
- ^ Kaneko, Karin (July 18, 2023). "ChatGPT, Bing, Bard and DeepL: Which one offers the best Japanese-to-English translation?". The Japan Times. Archived from the original on October 4, 2023. Retrieved July 22, 2023.
- ^ Taylor, Alice (December 13, 2023). "Albania to speed up EU accession using ChatGPT". Euractiv. Archived from the original on December 24, 2023. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ "OpenAI亞太區公共政策總監造訪政大 探索人文AI的未來與可能性". National Chengchi University, Office of International Cooperation (in Chinese). August 25, 2024. Archived from the original on August 24, 2024. Retrieved August 25, 2024.
- ^ Lin, Shu-yuan (August 25, 2024). "OpenAI高層訪台 ChatGPT講中文超順還能用台灣腔【獨家】". Central News Agency (in Chinese). Archived from the original on August 27, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2024.
- ^ "Introducing GPTs". OpenAI. November 6, 2023.
- ^ Metz, Cade (January 10, 2024). "OpenAI Unveils App Store for Customized Versions of ChatGPT". The New York Times. Archived from the original on February 7, 2024. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ a b David, Emilia (January 10, 2024). "OpenAI's custom GPT Store is now open for business". The Verge. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ Shankland, Stephen (January 10, 2024). "OpenAI's GPT Store Now Offers a Selection of 3 Million Custom AI Bots". CNET. Archived from the original on February 8, 2024. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ "Introducing the GPT Store". OpenAI. January 10, 2024. Archived from the original on February 17, 2024. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ Cheng, Michelle (January 11, 2024). "AI girlfriend bots are already flooding OpenAI's GPT store". Quartz. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ Belfield, Haydn (March 25, 2023). "If your AI model is going to sell, it has to be safe". Vox. Archived from the original on March 28, 2023. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ^ Caballero, Ethan; Gupta, Kshitij; Rish, Irina; Krueger, David (2022). "Broken Neural Scaling Laws". International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2023.
- ^ Alex Hern; Johana Bhuiyan (March 14, 2023). "OpenAI says new model GPT-4 is more creative and less likely to invent facts". The Guardian. Archived from the original on March 15, 2023. Retrieved March 15, 2023.
- ^ Vincent, James (March 15, 2023). "OpenAI co-founder on company's past approach to openly sharing research: "We were wrong"". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 17, 2023. Retrieved March 18, 2023.
- ^ Edwards, Benj (March 14, 2023). "OpenAI's GPT-4 exhibits "human-level performance" on professional benchmarks". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on March 14, 2023. Retrieved March 28, 2023.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (March 14, 2023). "Microsoft's new Bing was using GPT-4 all along". techcrunch.com. Archived from the original on March 15, 2023. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ Drapkin, Aaron (November 7, 2023). "GPT-4 Turbo vs GPT-4: What Is OpenAI's ChatGPT Turbo?". Tech.co. Archived from the original on May 14, 2024. Retrieved May 13, 2024.
- ^ Field, Hayden (May 13, 2024). "OpenAI launches new AI model and desktop version of ChatGPT". CNBC. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved May 13, 2024.
- ^ Edwards, Benj (September 12, 2024). "OpenAI's new "reasoning" AI models are here: o1-preview and o1-mini". Ars Technica. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- ^ "Introducing OpenAI o1-preview". OpenAI. September 12, 2024.
- ^ "ChatGPT Release - Note". OpenAI. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
- ^ Achille, Belelli (June 20, 2024). "ChatGPT Come Funziona". FinanzaDigitale. Archived from the original on August 27, 2024. Retrieved June 21, 2024.
- ^ Field, Hayden (May 13, 2024). "OpenAI launches new AI model GPT-4o and desktop version of ChatGPT". CNBC. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved July 23, 2024.
- ^ Franzen, Carl (July 18, 2024). "OpenAI unveils GPT-4o mini — a smaller, much cheaper multimodal AI model". VentureBeat. Archived from the original on July 18, 2024. Retrieved July 21, 2024.
- ^ a b Wiggers, Kyle (September 12, 2024). "OpenAI unveils o1, a model that can fact-check itself". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on September 18, 2024. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- ^ Heaven, Will Douglas. "The inside story of how ChatGPT was built from the people who made it". MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on March 6, 2023. Retrieved March 6, 2023.
- ^ Simons, John (February 5, 2023). "The Creator of ChatGPT Thinks AI Should Be Regulated". Time. Archived from the original on March 8, 2023. Retrieved March 21, 2023.
- ^ Cowen, Tyler (May 23, 2023). "ChatGPT Is Also an Impressive Feat of Marketing". bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved May 24, 2023.
- ^ Kantrowitz, Alex (December 2, 2022). "Finally, an A.I. Chatbot That Reliably Passes "the Nazi Test"". Slate. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Thompson, Derek (December 8, 2022). "Breakthroughs of the Year". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on January 15, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b Piper, Kelsey (December 15, 2022). "ChatGPT has given everyone a glimpse at AI's astounding progress". Vox. Archived from the original on January 19, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Scharth, Marcel (December 5, 2022). "The ChatGPT chatbot is blowing people away with its writing skills. An expert explains why it's so impressive". The Conversation. Archived from the original on January 19, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ "ChatGPT turns 1: How the AI chatbot has completely changed the world". euronews. November 30, 2023. Archived from the original on January 14, 2024. Retrieved March 1, 2024.
- ^ Levy, Steven (September 11, 2023). "Sundar Pichai on Google;s AI, Microsoft's AI, OpenAI, and ... Did We Mention AI?". Wired. Archived from the original on September 11, 2023. Retrieved September 12, 2023.
- ^ Grant, Nico; Metz, Cade (December 21, 2022). "A New Chat Bot Is a 'Code Red' for Google's Search Business". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on December 21, 2022. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Alba, Davey; Love, Julia (February 6, 2023). "Google releases ChatGPT rival AI 'Bard' to early testers". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Archived from the original on February 6, 2023. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- ^ Ortiz, Sabrina (May 10, 2023). "Every major AI feature announced at Google I/O 2023". ZDNet. Archived from the original on May 10, 2023. Retrieved September 12, 2023.
- ^ Rachini, Mouhamad (December 15, 2022). "ChatGPT a 'landmark event' for AI, but what does it mean for the future of human labor and disinformation?". CBC. Archived from the original on January 19, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Pearl, Mike (December 3, 2022). "The ChatGPT chatbot from OpenAI is amazing, creative, and totally wrong". Mashable. Archived from the original on December 10, 2022. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Pitt, Sofia (December 15, 2022). "Google vs. ChatGPT: Here's what happened when I swapped services for a day". CNBC. Archived from the original on January 16, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Bender, Emily M.; Gebru, Timnit; McMillan-Major, Angelina; Shmitchell, Shmargaret (March 1, 2021). "On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models be Too Big? 🦜". Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAccT '21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 610–623. doi:10.1145/3442188.3445922. ISBN 978-1-4503-8309-7.
- ^ Mannix, Liam (December 13, 2022). "Is AI coming of age – or starting to reach its limits?". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on January 7, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Hicks, Michael Townsen; Humphries, James; Slater, Joe (June 8, 2024). "ChatGPT is bullshit". Ethics and Information Technology. 26 (2): 38. doi:10.1007/s10676-024-09775-5. ISSN 1572-8439.
- ^ Vincent, James (December 5, 2022). "AI-generated answers temporarily banned on coding Q&A site Stack Overflow". The Verge. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Vincent, James (January 5, 2023). "Top AI conference bans use of ChatGPT and AI language tools to write academic papers". The Verge. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
- ^ Curry, Rachel (June 13, 2023). "Samsung among companies starting to draft ChatGPT policies for workers". CNBC. Archived from the original on June 14, 2023. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ a b Cain, Sian (January 16, 2023). "'This song sucks': Nick Cave responds to ChatGPT song written in the style of Nick Cave". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved January 17, 2023.
- ^ Cave, Nick (January 16, 2023). "I asked Chat GPT to write a song in the style of Nick Cave, and this is what it produced. What do you think?". The Red Hand Files. Issue #218. Archived from the original on January 20, 2023. Retrieved January 20, 2023.
- ^ Sparrow, Jeff (January 20, 2023). "Are AI-generated songs a 'grotesque mockery' of humanity or simply an opportunity to make a new kind of music?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved January 20, 2023.
- ^ Chow, Andrew; Perrigo, Billy (February 16, 2023). "The AI Arms Race Is On. Start Worrying". Time. Archived from the original on February 19, 2023. Retrieved March 21, 2023.
- ^ Davidson, Helen (February 23, 2023). "'Political propaganda': China clamps down on access to ChatGPT". The Guardian. Archived from the original on June 14, 2023. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ New data reveals exactly when the Chinese government blocked ChatGPT and other AI sites
- ^ Lau, Chris (May 9, 2023). "Chinese police detain man for allegedly using ChatGPT to spread rumors online". CNN. Archived from the original on December 26, 2023. Retrieved December 26, 2023.
- ^ Feng, Coco (December 29, 2023). "ChatGPT-aided ransomware in China results in four arrests". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on February 4, 2024. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ^ He Qitong; Li Dongxu (May 31, 2024). "Young Chinese Have Almost No Concerns About AI, Survey Finds". Sixth Tone.
- ^ "ChatGPT banned in Italy over privacy concerns". BBC News. March 31, 2023. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ^ Borrelli, Silvia Sciorilli; Murgia, Madhumita (March 31, 2023). "Italy temporarily bans ChatGPT over privacy concerns". Financial Times. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT accessible again in Italy". BBC. Archived from the original on May 1, 2023. Retrieved May 1, 2023.
- ^ Gerken, Tom. "ChatGPT: Mayor starts legal bid over false bribery claim". BBC. Archived from the original on April 7, 2023. Retrieved April 7, 2023.
- ^ Zakrzewski, Cat (July 13, 2023). "The FTC is investigating whether ChatGPT harms consumers". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 13, 2023. Retrieved July 13, 2023.
- ^ Tracy, Ryan; McKinnon, John D. (July 13, 2023). "ChatGPT Comes Under Investigation by Federal Trade Commission". The Wall Street Journal. News Corp. Archived from the original on July 13, 2023. Retrieved July 13, 2023.
- ^ Feiner, Lauren (July 13, 2023). "FTC investigating ChatGPT-maker OpenAI for possible consumer harm". CNBC. Archived from the original on July 13, 2023. Retrieved July 13, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT creator OpenAI faces US probe over libellous output". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on July 15, 2023. Retrieved July 15, 2023.
- ^ Vogels, Emily A. (May 24, 2023). "A majority of Americans have heard of ChatGPT, but few have tried it themselves". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on June 8, 2023. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ Park, Eugenie; Gelles-Watnick, Risa (August 28, 2023). "Most Americans haven't used ChatGPT; few think it will have a major impact on their job". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on December 24, 2023. Retrieved December 23, 2023.
- ^ Gupta, Maanak; Akiri, Charankumar; Aryal, Kshitiz; Parker, Eli; Praharaj, Lopamudra (2023). "From ChatGPT to ThreatGPT: Impact of Generative AI in Cybersecurity and Privacy". IEEE Access. 11: 80218–80245. arXiv:2307.00691. Bibcode:2023IEEEA..1180218G. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3300381. S2CID 259316122.
- ^ Shrikant, Aditi (July 17, 2023). "ChatGPT can match the top 1% of creative human thinkers, says new study". CNBC. Archived from the original on March 29, 2024. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ Naprys, Ernestas (July 7, 2023). "AI already outscoring humans in creativity tests". cybernews. Archived from the original on March 29, 2024. Retrieved March 29, 2024.
- ^ Van Noorden, Richard; Webb, Richard (December 13, 2023). "ChatGPT and science: the AI system was a force in 2023 — for good and bad". Nature. 624 (7992): 509. Bibcode:2023Natur.624..509V. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03930-6. PMID 38093061.
- ^ Mediavilla, Daniel (December 13, 2023). "La revista 'Nature' elige por primera vez entre sus científicos del año a un ente no humano: ChatGPT". El País (in European Spanish). Archived from the original on December 15, 2023. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- ^ Biever, Celeste (July 25, 2023). "ChatGPT broke the Turing test — the race is on for new ways to assess AI". Nature. 619 (7971): 686–689. Bibcode:2023Natur.619..686B. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-02361-7. PMID 37491395. Archived from the original on July 26, 2023. Retrieved March 26, 2024.
- ^ Scott, Cameron. "Study finds ChatGPT's latest bot behaves like humans, only better | Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences". humsci.stanford.edu. Archived from the original on March 26, 2024. Retrieved March 26, 2024.
- ^ Mei, Qiaozhu; Xie, Yutong; Yuan, Walter; Jackson, Matthew O. (February 27, 2024). "A Turing test of whether AI chatbots are behaviorally similar to humans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 121 (9): e2313925121. Bibcode:2024PNAS..12113925M. doi:10.1073/pnas.2313925121. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 10907317. PMID 38386710.
- ^ Bond, Shannon (May 30, 2024). "In a first, OpenAI removes influence operations tied to Russia, China and Israel". NPR. Archived from the original on May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 30, 2024.
- ^ Frenkel, Sheera (June 5, 2024). "Israel Secretly Targets U.S. Lawmakers With Influence Campaign on Gaza War". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on June 8, 2024. Retrieved June 5, 2024.
- ^ Picciotto, Rebecca (August 14, 2024). "FTC bans fake online reviews, inflated social media influence; rule takes effect in October". CNBC. Archived from the original on August 14, 2024. Retrieved August 15, 2024.
- ^ Gao, Catherine A.; Howard, Frederick M.; Markov, Nikolay S.; Dyer, Emma C.; Ramesh, Siddhi; Luo, Yuan; Pearson, Alexander T. (April 26, 2023). "Comparing scientific abstracts generated by ChatGPT to real abstracts with detectors and blinded human reviewers". npj Digital Medicine. 6 (1): 75. doi:10.1038/s41746-023-00819-6. ISSN 2398-6352. PMC 10133283. PMID 37100871.
- ^ Bushard, Brian (January 10, 2023). "Fake Scientific Abstracts Written By ChatGPT Fooled Scientists, Study Finds". Forbes. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved January 30, 2023.
- ^ Stokel-Walker, Chris (January 18, 2023). "ChatGPT listed as author on research papers: many scientists disapprove". Nature. 613 (7945): 620–621. Bibcode:2023Natur.613..620S. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-00107-z. PMID 36653617. S2CID 255969365. Archived from the original on January 30, 2023. Retrieved January 30, 2023.
- ^ Almira Osmanovic Thunström and Steinn Steingrimsson of the Institut of Neuroscience and Physiology of the University of Gothenburg used GPT-3 in June 2022 to write an academic paper about itself. They found that using specific prompts the results were good if somewhat shallow and not self-critical enough. Also only few references were presented, some of them nonsensical. Can GPT-3 write an academic paper on itself, with minimal human input? Archived October 24, 2023, at the Wayback Machine. 2022. ffhal-03701250
- ^ Brainard, Jeffrey (February 22, 2023). "As scientists explore AI-written text, journals hammer out policies". Science. doi:10.1126/science.adh2937. Archived from the original on February 24, 2023. Retrieved February 24, 2023.
- ^ Ansede, Manuel (April 2, 2023). "One of the world's most cited scientists, Rafael Luque, suspended without pay for 13 years". EL PAÍS English. Archived from the original on April 11, 2023. Retrieved April 11, 2023.
- ^ Alkaissi, Hussam; McFarlane, Samy I.; Alkaissi, Hussam; McFarlane, Samy I. (February 19, 2023). "Artificial Hallucinations in ChatGPT: Implications in Scientific Writing". Cureus. 15 (2): e35179. doi:10.7759/cureus.35179. ISSN 2168-8184. PMC 9939079. PMID 36811129.
- ^ Vynck, Gerrit De (May 31, 2023). "ChatGPT 'hallucinates.' Some researchers worry it isn't fixable". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on June 17, 2023. Retrieved June 14, 2023.
- ^ Azamfirei, Razvan; Kudchadkar, Sapna R.; Fackler, James (March 21, 2023). "Large language models and the perils of their hallucinations". Critical Care. 27 (1): 120. doi:10.1186/s13054-023-04393-x. ISSN 1364-8535. PMC 10032023. PMID 36945051.
- ^ Grove, Jack (April 5, 2023). "'ChatGPT-generated reading list' sparks AI peer review debate". Times Higher Education. Archived from the original on May 23, 2023. Retrieved June 14, 2023.
- ^ Granatino, Chris (May 5, 2023). "ChatGPT and AI Hallucination". Lemieux Library at Seattle University. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved June 14, 2023.
- ^ Morrison, Ryan (August 8, 2023). "ChatGPT wrong over half the time on software questions". Tech Monitor. New Statesman Media Group. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ Kabir, Samia; Udo-Imeh, David N.; Kou, Bonan; Zhang, Tianyi (August 10, 2023). "Who Answers It Better? An In-Depth Analysis of ChatGPT and Stack Overflow Answers to Software Engineering Questions". arXiv:2308.02312v3 [cs.SE].
- ^ a b Pressman, Aaron (November 8, 2023). "The AI boom is shaking up the tech industry and moving markets. But is it all a mirage?". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ a b Chen, Lingjiao; Zaharia, Matei; Zou, James (October 31, 2023). "How is ChatGPT's behavior changing over time?". arXiv:2307.09009v3 [cs.CL].
- ^ Shimony, Eran; Tsarfati, Omer (January 17, 2023). "Chatting Our Way Into Creating a Polymorphic Malware". CyberArk. Archived from the original on May 12, 2023. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ^ Mascellino, Alessandro (January 18, 2023). "ChatGPT Creates Polymorphic Malware". Infosecurity Magazine. Archived from the original on May 12, 2023. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ^ Violino, Bob (November 28, 2023). "AI tools such as ChatGPT are generating a mammoth increase in malicious phishing emails". CNBC. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ Dupré, Maggie Harrison (July 1, 2024). "ChatGPT-4o Is Sending Users to a Scammy Website That Floods Your Screen With Fake Virus Warnings". Futurism. Archived from the original on July 1, 2024. Retrieved July 1, 2024.
- ^ Bilton, Nick (December 9, 2022). "ChatGPT Made Me Question What It Means to Be a Creative Human". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on March 25, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ a b Beres, Damon (January 27, 2023). "Death by a Thousand Personality Quizzes". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on June 21, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ Leonhardt, Megan (March 25, 2023). "Some workers are worried that ChatGPT will replace their jobs. They might be right". Fortune. Archived from the original on June 19, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ Verma, Pranshu; Vynck, Gerrit De (June 5, 2023). "ChatGPT took their jobs. Now they walk dogs and fix air conditioners". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on March 13, 2024. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ a b Bachulska, Alicja; Leonard, Mark; Oertel, Janka (July 2, 2024). The Idea of China: Chinese Thinkers on Power, Progress, and People (EPUB). Berlin, Germany: European Council on Foreign Relations. ISBN 978-1-916682-42-9. Archived from the original on July 17, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ Hern, Alex (December 4, 2022). "AI bot ChatGPT stuns academics with essay-writing skills and usability". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- ^ Day, Terence (April 12, 2023). "A Preliminary Investigation of Fake Peer-Reviewed Citations and References Generated by ChatGPT". The Professional Geographer. 75 (6): 1024–1027. Bibcode:2023ProfG..75.1024D. doi:10.1080/00330124.2023.2190373. ISSN 0033-0124. S2CID 258115209.
- ^ a b "Understanding the source of what we see and hear online". OpenAI. May 7, 2024. Archived from the original on September 27, 2024.
- ^ "There's a Tool to Catch Students Cheating With ChatGPT. OpenAI Hasn't Released It". The Wall Street Journal. August 4, 2024. Retrieved September 30, 2024.
- ^ Davis, Wes (August 5, 2024). "OpenAI won't watermark ChatGPT text because its users could get caught". The Verge. Retrieved August 24, 2024.
- ^ Ha, Anthony (August 4, 2024). "OpenAI says it's taking a 'deliberate approach' to releasing tools that can detect writing from ChatGPT". TechCrunch. Retrieved October 1, 2024.
- ^ "Экономист Дарон Асемоглу написал книгу об угрозах искусственного интеллекта — и о том, как правильное управление может обратить его на пользу человечеству Спецкор "Медузы" Маргарита Лютова узнала у ученого, как скоро мир сможет приблизиться к этой утопии". Meduza (in Russian). Archived from the original on June 20, 2023. Retrieved June 21, 2023.
- ^ "Learning, thinking, artistic collaboration and other such human endeavours in the age of AI". The Hindu. June 2, 2023. Archived from the original on June 21, 2023. Retrieved June 21, 2023.
- ^ Samuel, Sigal (April 10, 2023). "What happens when ChatGPT starts to feed on its own writing?". Vox. Archived from the original on June 19, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ Nolan, Beatrice. "More than 200 books in Amazon's bookstore have ChatGPT listed as an author or coauthor". Business Insider. Archived from the original on March 9, 2023. Retrieved March 9, 2023.
- ^ Bensinger, Greg (February 21, 2023). "ChatGPT launches boom in AI-written e-books on Amazon". Reuters. Archived from the original on March 9, 2023. Retrieved March 9, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT sul Foglio: per 30 giorni piccoli testi scritti dall'IA sul nostro giornale" [ChatGPT on Il Foglio: for 30 days, brief texts written by the AI on our newspaper]. Il Foglio (in Italian). March 7, 2023. Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 22, 2023.
- ^ Moretti, Marco (March 8, 2023). "Articoli artificiali? No" [Artificial articles? No]. Il Foglio (in Italian). Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 22, 2023.
- ^ A.D.A. (March 9, 2023). "Più umani, grazie" [Be more human, thanks]. Il Foglio (in Italian). Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 22, 2023.
- ^ "Le colpe farlocche dell'"invasione"" [The fake faults of the "invasion"]. Il Foglio (in Italian). March 14, 2023. Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 22, 2023.
- ^ "Sfida per Siri e Alexa" [A challenge for Siri and Alexa]. Il Foglio (in Italian). March 17, 2023. Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 22, 2023.
- ^ Edwards, Benj (June 12, 2023). "AI-powered church service in Germany draws a large crowd". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on June 13, 2023. Retrieved June 13, 2023.
- ^ "Hundreds of Protestants attended a sermon in Nuremberg given by ChatGPT, which told them not to fear death". Business Insider. Archived from the original on June 11, 2023. Retrieved June 13, 2023.
- ^ "Hundreds attend AI church service in Germany". TheJournal.ie. June 10, 2023. Archived from the original on June 12, 2023. Retrieved June 13, 2023.
- ^ Kelly, James W (June 19, 2024). "Prince Charles Cinema drops AI-written film following backlash". BBC News. Archived from the original on June 19, 2024. Retrieved June 19, 2024.
- ^ Fox, Matthew (January 31, 2023). "C3ai has soared 86% year-to-date as investor frenzy for artificial intelligence builds amid ChatGPT success". Markets Insider (Business Insider). Archived from the original on February 18, 2023. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- ^ Diaz, Alicia; Smith, Gerry (January 26, 2023). "BuzzFeed Shares Surge 120% on Plans to Embrace OpenAI". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved May 22, 2023.
- ^ Singh, Medha; Biswas, Ankika (February 6, 2023). "AI stocks rally in latest Wall Street craze sparked by ChatGPT". Reuters. Archived from the original on March 29, 2023. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- ^ Saggu, Aman; Ante, Lennart (May 8, 2023). "The influence of ChatGPT on artificial intelligence-related crypto assets: Evidence from a synthetic control analysis". Finance Research Letters. 55: 103993. arXiv:2305.12739. doi:10.1016/j.frl.2023.103993. ISSN 1544-6123. S2CID 258573881.
- ^ Hajric, Vildana; Shen, Muyao (February 9, 2023). "ChatGPT Mania Spurs Crypto Fans' Stampede to 'Faddish' AI Tokens". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on February 9, 2023. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- ^ Cooban, Anna (May 5, 2023). "ChatGPT can pick stocks better than your fund manager". CNN. Archived from the original on May 22, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Zuckerman, Gregory (April 12, 2023). "AI Can Write a Song, but It Can't Beat the Market". The Wall Street Journal. News Corp. Archived from the original on May 30, 2023. Retrieved May 30, 2023.
- ^ Leswing, Kif (December 19, 2023). "GPT and other AI models can't analyze an SEC filing, researchers find". CNBC. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ "Patronus AI Launches Industry-first LLM Benchmark for Finance to Address Hallucinations" (Press release). PR Newswire. November 16, 2023. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ The Lancet Digital Health (March 3, 2023). "ChatGPT: friend or foe?". The Lancet Digital Health. 5 (3): e102. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00023-7. PMID 36754723. S2CID 256659547.
- ^ Asch, David A. (April 4, 2023). "An Interview with ChatGPT About Health Care". NEJM Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery. doi:10.1056/CAT.23.0043 (inactive November 1, 2024). Archived from the original on June 29, 2023. Retrieved June 29, 2023.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ a b DePeau-Wilson, Michael (January 19, 2023). "AI Passes U.S. Medical Licensing Exam". MedPage Today. Archived from the original on April 9, 2023. Retrieved May 2, 2023.
- ^ Kung, Tiffany H.; Cheatham, Morgan; Medenilla, Arielle; Sillos, Czarina; Leon, Lorie De; Elepaño, Camille; Madriaga, Maria; Aggabao, Rimel; Diaz-Candido, Giezel; Maningo, James; Tseng, Victor (February 9, 2023). "Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models". PLOS Digital Health. 2 (2): e0000198. doi:10.1371/journal.pdig.0000198. ISSN 2767-3170. PMC 9931230. PMID 36812645.
- ^ "Expert reaction to study on ChatGPT almost passing the US Medical Licensing Exam". Science Media Centre. February 9, 2023. Archived from the original on April 24, 2023. Retrieved May 2, 2023.
- ^ Gilson, Aidan; Safranek, Conrad W.; Huang, Thomas; Socrates, Vimig; Chi, Ling; Taylor, Richard Andrew; Chartash, David (February 8, 2023). "How Does ChatGPT Perform on the United States Medical Licensing Examination? The Implications of Large Language Models for Medical Education and Knowledge Assessment". JMIR Medical Education. 9 (1): e45312. doi:10.2196/45312. PMC 9947764. PMID 36753318.
- ^ Brueck, Hilary. "The newest version of ChatGPT passed the US medical licensing exam with flying colors — and diagnosed a 1 in 100,000 condition in seconds". Business Insider. Archived from the original on January 27, 2024. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ Abdel-Messih, Mary Sabry; Boulos, Maged N. Kamel (March 8, 2023). "ChatGPT in Clinical Toxicology". JMIR Medical Education. 9 (1): e46876. doi:10.2196/46876. PMC 10034604. PMID 36867743.
- ^ Haver, Hana L; Ambinder, Emily B; Bahl, Manisha; Oluyemi, Eniola T; Jeudy, Jean; Yi, Paul H (April 4, 2023). "Appropriateness of Breast Cancer Prevention and Screening Recommendations Provided by ChatGPT". Radiology. 307 (4): 230424. doi:10.1148/radiol.230424. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 37014239. S2CID 257923990. Archived from the original on May 5, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Kotz, Deborah (April 4, 2023). "UM School of Medicine Study Finds ChatGPT Helpful for Breast Cancer Screening Advice, With Certain Caveats". University of Maryland School of Medicine. Archived from the original on May 5, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Ayers, John W.; Poliak, Adam; Dredze, Mark; Leas, Eric C.; Zhu, Zechariah; Kelley, Jessica B.; Faix, Dennis J.; Goodman, Aaron M.; Longhurst, Christopher A.; Hogarth, Michael; Smith, Davey M. (April 28, 2023). "Comparing Physician and Artificial Intelligence Chatbot Responses to Patient Questions Posted to a Public Social Media Forum". JAMA Internal Medicine. 183 (6): 589–596. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.1838. ISSN 2168-6106. PMC 10148230. PMID 37115527. Archived from the original on April 30, 2023. Retrieved May 2, 2023.
- ^ Fox, Andrea (May 4, 2023). "Does ChatGPT really outshine doctors? Or just on social media?". Healthcare IT News. HIMSS Media. Archived from the original on May 4, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ "The doctor is out, but it's OK. ChatGPT can answer your questions". Hub. Johns Hopkins University. April 28, 2023. Archived from the original on May 5, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Ono, Mika (April 28, 2023). "Study Finds ChatGPT Outperforms Physicians in High-Quality, Empathetic Answers to Patient Questions". UC San Diego Today. Archived from the original on April 28, 2023. Retrieved April 28, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT Beats Doctors in Compassion and Quality of Advice to Patients". Neuroscience News. April 28, 2023. Archived from the original on May 3, 2023. Retrieved May 2, 2023.
- ^ Howard, Alex; Hope, William; Gerada, Alessandro (April 2023). "ChatGPT and antimicrobial advice: the end of the consulting infection doctor?". The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 23 (4): 405–406. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(23)00113-5. ISSN 1473-3099. PMID 36822213. S2CID 257072872. Archived from the original on March 25, 2023. Retrieved May 2, 2023.
- ^ "Is There a Role for ChatGPT in Healthcare?". Physician's Weekly. April 27, 2023. Archived from the original on May 5, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Drake, Kimberly (April 6, 2023). "Rely on a Doctor, Not ChatGPT, for Medical Advice". HealthNews. Archived from the original on May 5, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Gravel, Jocelyn; D’Amours-Gravel, Madeleine; Osmanlliu, Esli (September 1, 2023). "Learning to Fake It: Limited Responses and Fabricated References Provided by ChatGPT for Medical Questions". Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health. 1 (3): 226–234. doi:10.1016/j.mcpdig.2023.05.004. ISSN 2949-7612.
- ^ Hughes, Stephen (April 27, 2023). "How good is ChatGPT at diagnosing disease? A doctor puts it through its paces". The Conversation. Archived from the original on May 4, 2023. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ Patnaik, Sourav S.; Hoffmann, Ulrike (November 7, 2023). "Quantitative evaluation of ChatGPT versus Bard responses to anaesthesia-related queries". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 132 (1): S0007–0912(23)00550–0. doi:10.1016/j.bja.2023.09.030. ISSN 1471-6771. PMID 37945414. S2CID 265078930. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- ^ Constantino, Annika Kim (December 5, 2023). "Free ChatGPT may incorrectly answer drug questions, study says". CNBC. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ "Study Finds ChatGPT Provides Inaccurate Responses to Drug Questions" (Press release). PR Newswire. December 5, 2023. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ Barile, Joseph; Margolis, Alex; Cason, Grace; Kim, Rachel; Kalash, Saia; Tchaconas, Alexis; Milanaik, Ruth (January 2, 2024). "Diagnostic Accuracy of a Large Language Model in Pediatric Case Studies". JAMA Pediatrics. 178 (3): 313–315. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5750. ISSN 2168-6203. PMC 10762631. PMID 38165685. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved February 18, 2024.
- ^ Mole, Beth (January 3, 2024). "ChatGPT bombs test on diagnosing kids' medical cases with 83% error rate". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 17, 2024. Retrieved January 5, 2024.
- ^ a b "Bill S.31". malegislature.gov. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ a b Annear, Steve (January 24, 2023). "Two elected officials drafted legislation to regulate artificial intelligence technology — with some help from ChatGPT". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ a b c Garrity, Kelly; Kashinsky, Lisa (July 13, 2023). "ChatGPT enters the legislative chat". POLITICO. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ a b c Quach, Katyanna (December 2, 2023). "Local council in Brazil passes ChatGPT-written proposal". The Register. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ "Pakistani judge uses ChatGPT to make court decision". Gulf News. April 13, 2023. Archived from the original on April 20, 2023. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- ^ "AI revolution is here': Pakistani court takes help from ChatGPT to grant bail in rape case". Pakistan Observer. April 11, 2023. Archived from the original on April 20, 2023. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- ^ Brodkin, Jon (June 23, 2023). "Lawyers have real bad day in court after citing fake cases made up by ChatGPT". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 26, 2024. Retrieved February 18, 2024.
- ^ Goswami, Rohan (May 30, 2023). "ChatGPT cited 'bogus' cases for a New York federal court filing. The attorneys involved may face sanctions". CNBC. Archived from the original on May 30, 2023. Retrieved May 30, 2023.
- ^ Neumeister, Larry (June 8, 2023). "Lawyers blame ChatGPT for tricking them into citing bogus case law". Associated Press. Archived from the original on November 8, 2023. Retrieved November 8, 2023.
- ^ "Mata v. Avianca, Inc". Casetext. Archived from the original on February 13, 2024. Retrieved February 13, 2024.
- ^ "'Use with caution': How ChatGPT landed this US lawyer and his firm in hot water". ABC News. June 24, 2023. Archived from the original on November 9, 2023. Retrieved November 9, 2023.
- ^ a b Jeantet, Diane; Savarese, Mauricio; LeBlanc, Steve; O'Brien, Matt (November 30, 2023). "Brazilian city enacts an ordinance that was secretly written by ChatGPT". AP News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ a b Paúl, María Luisa (December 4, 2023). "A Brazilian city passed a law about water meters. ChatGPT wrote it". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ "Lei escrita por inteligência artificial é aprovada por vereadores em Porto Alegre; 'precedente perigoso', diz presidente da Câmara". G1 (in Brazilian Portuguese). November 29, 2023. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ Rose, Neil (December 7, 2023). "Litigant unwittingly put fake cases generated by AI before tribunal". Legal Futures. Archived from the original on May 14, 2024. Retrieved May 14, 2024.
- ^ Cross, Michael (December 11, 2023). "AI hallucinates nine 'helpful' case authorities". Law Society Gazette. Archived from the original on May 2, 2024. Retrieved May 14, 2024.
- ^ "Harber v Commissioners for His Majesty's Revenue and Customs [2023] UKFTT 1007 (TC)". BAILII. December 4, 2023. Archived from the original on May 14, 2024. Retrieved May 14, 2024.
- ^ "11th Circuit Judge Uses ChatGPT in Deciding Appeal, Encourages Others to Consider It". Law.com. June 4, 2024. Archived from the original on June 5, 2024. Retrieved June 5, 2024.
- ^ Journal, A. B. A. "In concurrence confession, appeals judge says ChatGPT research 'less nutty' than feared". ABA Journal. Archived from the original on June 6, 2024. Retrieved June 6, 2024.
- ^ Zhao, Jieyu; Wang, Tianlu; Yatskar, Mark; Ordonez, Vicente; Chang, Kai-Wei (2018). "Gender Bias in Coreference Resolution: Evaluation and Debiasing Methods". In Walker, Marilyn; Ji, Heng; Stent, Amanda (eds.). Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers). New Orleans, Louisiana: Association for Computational Linguistics. pp. 15–20. doi:10.18653/v1/N18-2003.
- ^ Sheng, Emily; Chang, Kai-Wei; Natarajan, Prem; Peng, Nanyun (2021). "Societal Biases in Language Generation: Progress and Challenges". In Zong, Chengqing; Xia, Fei; Li, Wenjie; Navigli, Roberto (eds.). Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers). Online: Association for Computational Linguistics. pp. 4275–4293. doi:10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.330.
- ^ Liles, Jordan (February 1, 2023). "ChatGPT Declines Request for Poem Admiring Trump, But Biden Query Is Successful". Snopes. Archived from the original on March 22, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Johnson, Arianna. "Is ChatGPT Partisan? Poems About Trump And Biden Raise Questions About The AI Bot's Bias—Here's What Experts Think". Forbes. Archived from the original on April 7, 2023. Retrieved May 23, 2023.
- ^ Guynn, Jessica. "Is ChatGPT 'woke'? AI chatbot accused of anti-conservative bias and a grudge against Trump". USA Today. Archived from the original on March 1, 2023. Retrieved March 1, 2023.
- ^ Bray, Hiawatha (February 9, 2023). "Is ChatGPT liberal or conservative? Depends who you ask". Boston Globe. Archived from the original on March 1, 2023. Retrieved March 1, 2023.
- ^ a b Vincent, James (February 17, 2023). "As conservatives criticize 'woke AI,' here are ChatGPT's rules for answering culture war queries". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 1, 2023. Retrieved March 1, 2023.
- ^ Hartmann, Jochen; Schwenzow, Jasper; Witte, Maximilian (January 5, 2023). "The political ideology of conversational AI: Converging evidence on ChatGPT's pro-environmental, left-libertarian orientation". arXiv:2301.01768 [cs.CL].
- ^ Motoki, Fabio; Neto, Valdemar Pinho; Rodrigues, Victor (August 17, 2023). "More human than human: measuring ChatGPT political bias". Public Choice. 198 (1–2): 3–23. doi:10.1007/s11127-023-01097-2. ISSN 1573-7101.
- ^ "The Guardian view on ChatGPT: an eerily good human impersonator". The Guardian. December 8, 2022. Archived from the original on January 16, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ Farivar, Masood (August 23, 2023). "AI Firms Under Fire for Allegedly Infringing on Copyrights". Voice of America. Archived from the original on November 20, 2023. Retrieved November 19, 2023.
- ^ Davis, Wes (July 9, 2023). "Sarah Silverman is suing OpenAI and Meta for copyright infringement". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 18, 2023. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- ^ David, Emilia (February 13, 2024). "Sarah Silverman's lawsuit against OpenAI partially dismissed". The Verge. Archived from the original on May 15, 2024. Retrieved May 15, 2024.
- ^ Spangler, Todd (September 21, 2023). "George R.R. Martin Among 17 Top Authors Suing OpenAI, Alleging ChatGPT Steals Their Works: 'We Are Here to Fight'". Variety. Archived from the original on May 16, 2024. Retrieved May 15, 2024.
- ^ Grynbaum, Michael M.; Mac, Ryan (December 27, 2023). "The Times Sues OpenAI and Microsoft Over A.I. Use of Copyrighted Work". The New York Times. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ^ "ChatGPT: New York Times sues OpenAI over article usage". DW News. December 27, 2023. Archived from the original on December 27, 2023. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ^ Roth, Emma (December 27, 2023). "The New York Times is suing OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement". The Verge. Archived from the original on December 27, 2023. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ^ Field, Hayden (March 6, 2024). "Researchers tested leading AI models for copyright infringement using popular books, and GPT-4 performed worst". CNBC. Archived from the original on March 6, 2024. Retrieved March 6, 2024.
- ^ "Introducing CopyrightCatcher, the first Copyright Detection API for LLMs". Patronus AI. March 6, 2024. Archived from the original on March 6, 2024. Retrieved March 6, 2024.
- ^ Karp, Paul (February 6, 2023). "MP tells Australia's parliament AI could be used for 'mass destruction' in speech part-written by ChatGPT". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on February 6, 2023. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- ^ K, Siddharth (December 5, 2022). Shumaker, Lisa (ed.). "Explainer: ChatGPT – what is OpenAI's chatbot and what is it used for?". Reuters. Archived from the original on January 16, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ a b Kay, Grace (December 11, 2022). "Elon Musk founded – and has since criticized – the company behind the buzzy new AI chatbot ChatGPT. Here's everything we know about OpenAI". Business Insider. Archived from the original on January 12, 2023. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Hurst, Luke (March 30, 2023) [March 29, 2023]. "'Profound risk to humanity': Tech leaders call for 'pause' on advanced AI development". Euronews. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ^ "Geoffrey Hinton tells us why he's now scared of the tech he helped build". MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on May 4, 2023. Retrieved May 4, 2023.
- ^ "Video: Geoffrey Hinton talks about the "existential threat" of AI". MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on May 3, 2023. Retrieved May 4, 2023.
- ^ Roose, Kevin (May 30, 2023). "A.I. Poses 'Risk of Extinction,' Industry Leaders Warn". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on May 31, 2023. Retrieved May 30, 2023.
- ^ Taylor, Josh (May 7, 2023). "Rise of artificial intelligence is inevitable but should not be feared, 'father of AI' says". The Guardian. Archived from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved May 26, 2023.
- ^ McMorrow, Ryan (December 19, 2023). "Andrew Ng: 'Do we think the world is better off with more or less intelligence?'". Financial Times. Archived from the original on January 25, 2024. Retrieved December 30, 2023.
- ^ Levy, Steven (December 22, 2023). "How Not to Be Stupid About AI, With Yann LeCun". Wired. Archived from the original on February 14, 2024. Retrieved December 30, 2023.
Further reading
- Biswas, Som (April 1, 2023). "ChatGPT and the Future of Medical Writing". Radiology. 307 (2): e223312. doi:10.1148/radiol.223312. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 36728748. S2CID 256501098.
- Chang, Kent K.; Cramer, Mackenzie; Soni, Sandeep; Bamman, David (April 28, 2023). "Speak, Memory: An Archaeology of Books Known to ChatGPT/GPT-4". arXiv:2305.00118 [cs.CL].
- Cowen, Tyler; Tabarrok, Alexander T. (March 17, 2023). "How to Learn and Teach Economics with Large Language Models, Including GPT". SSRN 4391863.
- Cowen, Tyler (March 29, 2023). "Jonathan GPT Swift on Jonathan Swift (Ep. 175): How well does GPT4 do pretending to be the 18th-century satirist?" (Podcast).
- Ouyang, Long; et al. (March 4, 2022). "Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback". arXiv:2203.02155 [cs.CL].
- Liebrenz, Michael; Schleifer, Roman; Buadze, Anna; Bhugra, Dinesh; Smith, Alexander (February 2023). "Generating scholarly content with ChatGPT: ethical challenges for medical publishing". The Lancet Digital Health. 5 (3): e105–e106. doi:10.1016/s2589-7500(23)00019-5. ISSN 2589-7500. PMID 36754725. S2CID 256655912.
- Wolfram, Stephen (February 14, 2023). "What Is ChatGPT Doing … and Why Does It Work?".
- Wolfram, Stephen (March 23, 2023). "ChatGPT Gets Its "Wolfram Superpowers"!".
- Bartholomew, Jem; Mehta, Dhrumil. "How the media is covering ChatGPT". Columbia Journalism Review. Retrieved May 30, 2023.
- Zhao, Wayne Xin; et al. (2023). "A Survey of Large Language Models". arXiv:2303.18223 [cs.CL].
- Prompt engineering guide from OpenAI

