Los Angeles River
The Los Angeles River (L.A. River) starts in the Simi Hills and Santa Susana Mountains and flows through Los Angeles County, California, from Canoga Park in the western end of the San Fernando Valley, nearly 48 miles (77 km) southeast to its mouth in Long Beach. Several tributaries join the once free-flowing and frequently flooding river, forming alluvial flood plains along its banks. It now flows through a concrete channel on a fixed course, which was built after a series of devastating floods in the early 20th century.
Environmental groups and park advocates support the removal of concrete and the restoration of natural vegetation and wildlife. Portions of the river now have earthen bottoms and restored habitat. There are also plans for a series of parks along the river's city frontage in Los Angeles. The Los Angeles River also flows through several Los Angeles County communities and has been featured in many Hollywood films.
Before the opening of the Los Angeles Aqueduct, the river was the primary source of fresh water for the city. Although the Los Angeles region still gets some of its water from the river and other local sources, most comes from several aqueducts serving the area. The river suffers pollution from agricultural and urban runoff.

Fed primarily by rainwater and snowmelt (in winter and spring), the Donald C. Tillman Water Reclamation Plant in Van Nuys (in summer and fall), and urban discharge, it is one of the few low-elevation perennial rivers in Southern California. Some water usually reaches the sea, even in the driest summers; although there are historical accounts of the river running dry, there has been flow every month since recording of stream flow began in 1929.[1] This is helped by the concrete channel, which limits absorption of water into the earth. Flow, while generally low in volume, can be extremely brisk even in summer.
Course

The Los Angeles River's official beginning is at the confluence of two channelized streams – Bell Creek and Arroyo Calabasas – in the Canoga Park section of the city of Los Angeles, just east of California State Route 27, at 34°11′43″N 118°36′07″W / 34.1952°N 118.601838°W (the east side of Canoga Park High School). Bell Creek flows east from the Simi Hills, and Arroyo Calabasas flows north from the Santa Monica Mountains. From there the river flows east through a concrete flood control channel and very soon receives Browns Canyon Wash, which flows south from the Santa Susana Mountains. The river then bends slightly south and receives Aliso Canyon Wash, whose watershed adjoins that of Browns Canyon. The river then flows through the district of Winnetka, then Reseda and enters the Sepulveda Basin, a flood-control reservoir formed by the Sepulveda Dam.[2][3][4][5]

As the river proceeds into the usually-dry reservoir, it spills out into a channel that is similar to its historical, unchannelized form. It crosses under Balboa Boulevard and then passes through the outlet works of Sepulveda Dam, 43 miles (69 km) from the mouth. It flows again into a concrete channel and crosses under Interstate 405 as it passes through Van Nuys, Sherman Oaks, and Studio City, still flowing east. Paralleling U.S. Highway 101 briefly, it then veers southeast, away from the highway, and receives from the left the Tujunga Wash, one of its largest tributaries, which flows southwest and south from the Angeles National Forest in the San Gabriel Mountains. The river then rounds a bend to the northeast, now in a concrete box culvert, and crosses under State Route 170 and Highway 101, and receives Burbank Western Channel on the left bank, 39 miles (63 km) from the mouth.[2][3][6][7]

The river then begins to parallel California State Route 134 as it winds past the city of Burbank and North Hollywood, then crosses under Interstate 5 and makes a sharp bend to the south-southeast as it curves around Griffith Park. It receives from the left Verdugo Canyon Wash, which drains much of La Cañada Flintridge and Glendale as it flows from the San Gabriel Mountains south through a water gap in the Verdugo Mountains, and crosses under State Route 134. Here, the river begins to flow over a natural riverbed, but enters another concrete section soon after. Paralleling Interstate 5 for the next few miles, the river runs by the eastern side of Griffith Park and the Harding-Wilson Golf Course. It passes Silver Lake Reservoir, which is to the right, and crosses under California State Route 2, 32 miles (51 km) from the mouth.[2][3][8][9][10]

Making two meanders as it flows in a southeasterly direction, the river parallels the interstate and Riverside Drive then crosses under the interstate and California State Route 110 as it flows east of Elysian Park. It then receives the Arroyo Seco, another major tributary, from the left. The river flows south past the Mission Junction, a large railroad yard on the left. It enters a wider concrete channel with sloped sides, and crosses under Cesar Chavez Avenue, Highway 101, and Interstate 10 as it passes east of downtown Los Angeles, flowing past the East Los Angeles Interchange for Highway 101, California State Route 60, and Interstates 5 and 10 on the left. It then makes a gradual turn east and then turns southeast, flowing a few miles before it begins to parallel Interstate 710 near Maywood, Bell, Cudahy, and Commerce, 20 miles (32 km) from the mouth.[2][3][10][11]

Paralleling Interstate 710 south-southwest, the river then crosses under former California State Route 42 and the interstate as it receives the Rio Hondo from the left, 9 miles (14 km) from the mouth. The Rio Hondo (deep river) now serves as a distributary for the San Gabriel River to the east via the Whittier Narrows Reservoir. The river then crosses under I-105 and shifts slightly southwest, then flows east of Compton and west of Bellflower. After crossing under California State Route 91, it receives Compton Creek from the right, 2.7 miles (4.3 km) from the mouth. After crossing under Interstate 405 for the second time, 2 miles (3.2 km) from the mouth, it draws close to the Dominguez Channel to the west and flows due south to its outlet in Long Beach, under Interstate 710, past the RMS Queen Mary, and into the Port of Long Beach.[2][3][10][12][13]
History

The river provided a source of water and food for the Tongva people prior to the arrival of the Spanish.[14] After the establishment of Mission San Gabriel in 1771, the Spanish referred to all of the Tongva living in that mission's vicinity as Gabrieliño. The Gabrieliños were hunters and gatherers who lived primarily off fish, small mammals, and the acorns from the abundant oak trees along the river's path. There were at least 45 Gabrieliño villages located near the Los Angeles River, concentrated in the San Fernando Valley and the Elysian Valley, in what is present day Glendale.
In 1769, members of the Portolà expedition to explore Alta California were the first Europeans to see the river. On August 2, the party camped near the river, somewhere along the stretch just to the north of the Interstate 10 crossing near downtown Los Angeles. Fray Juan Crespi, one of two Franciscan missionaries traveling with Portolà, named it El Río de Nuestra Señora La Reina de Los Ángeles de Porciúncula. Crespi chose that name, which translates as The River of Our Lady Queen of the Angels of Porciuncula, because it was the name of a special annual feast day for the Franciscans, which the Portolà party had celebrated the previous day. The river was thereafter referred to as the "Porciuncula River". In later years, the "Los Angeles" part of Crespi's lengthy name won out.[15]

The river was originally an alluvial river that ran freely across a flood plain that is now occupied by Los Angeles, Long Beach and other townships in Southern California. Its path was unstable and unpredictable, and the mouth of the river moved frequently from one place to another between Long Beach and Ballona Creek. In the early 19th century, the river turned southwest after leaving the Glendale Narrows, where it joined Ballona Creek and discharged into Santa Monica Bay in present Marina del Rey. However, this account is challenged by Col. J. J. Warner, in his Historical Sketch of Los Angeles County:
"...until 1825 it was seldom, if in any year, that the river discharged even during the rainy season its waters into the sea. Instead of having a river way to the sea, the waters spread over the country, filling the depressions in the surface and forming lakes, ponds and marshes. The river water, if any, that reached the ocean drained off from the land at so many places, and in such small volumes, that no channel existed until the flood of 1825, which, by cutting a river way to tide water, drained the marsh land and caused the forests to disappear."[16]
Prior to the Great Flood of 1862, it was joined by the San Gabriel River in present-day Long Beach, but in that year the San Gabriel carved out a new course 6 miles (9.7 km) to the east, and has discharged into Alamitos Bay ever since.
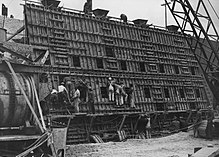
Until the opening of the Los Angeles Aqueduct in 1913, the Los Angeles River was the primary water source for the Los Angeles Basin, but much of its channel had extremely low discharge except during the winter rains.[citation needed] Unpredictable and devastating floods continued to plague it well into the 1930s (the most notable one being the catastrophic 1938 flood that precipitated the recall of then-mayor of Los Angeles Frank L. Shaw), leading to calls for flood control measures. The Army Corps of Engineers duly began an ambitious project of completely encasing the river's bed and banks in concrete, with only a trickle of water usually flowing down its middle.[citation needed] The only portions of the river that are not completely paved over are in the flood-control basin behind the Sepulveda Dam near Van Nuys; a 11-mile (17.7-km) stretch east of Griffith Park known as the Glendale Narrows; and along its last few miles in Long Beach.[citation needed]
The river was dry for nine months of the year as late as the 1950s. According to an August 2013 article in the Los Angeles Times, the water in the river today is largely "industrial and residential discharge," which originates from the "two giant pipes that collect the sewage from the homes of 800,000 San Fernando Valley residents" that lead to the Tillman Water Reclamation Plant, "before crashing over a man-made waterfall into Lake Balboa. That body of water, along with two smaller ones, puts 23 million gallons of water a day into the river at Sepulveda Basin."[17]
Points of interest
Sepulveda Basin is a flood-control basin to manage floodwater runoff. Except for infrequent but dramatic flood episodes, this dry-land flood control basin, most of which is leased from the Corps by the City of Los Angeles Department of Recreation and Parks, plays host to diverse uses today including athletic fields, agriculture, golf courses, a fishing lake, parklands, a sewage treatment facility, and a wildlife reserve.[18]
The Los Angeles River bicycle path runs through the Glendale Narrows and is accessible to the public at its north end at Riverside Drive, at Los Feliz Boulevard, and at its south end at Glendale Boulevard, Fletcher Drive and at Egret Park in Elysian Valley.[19][20] The bike path runs parallel to the 5 freeway for the majority of its length and has mile markers and call boxes for information and safety purposes.
The river's southern stretch forms the heart of an industrial corridor, stretching nearly unbroken from Lincoln Heights to Long Beach. In this area, the busy Long Beach Freeway (I-710) and several high-voltage power lines run within a few hundred feet of the riverbed. Several rail yards are located along the river's banks in this stretch, as well.[citation needed] Just outside the industrial corridor lie some of the most densely populated cities in the state of California, such as the cities of Bell, Bell Gardens, Cudahy, Maywood and South Gate; most of these cities are in the river's flood plain and experienced significant flooding prior to channelization.[citation needed]
Wildlife

There is an abundance of fish species in the Los Angeles River which include common carp, largemouth bass, tilapia, green sunfish, Amazon sailfin catfish, bluegill, black bullhead, brown bullhead, channel catfish, fathead minnow, crayfish, and mosquito fish. No native species of the Los Angeles River survived the channelization of the river in 1938. The native species of fish in the Los Angeles River included rainbow trout, Arroyo chub, river shrimp, chinook salmon, Sacramento pikeminnow, Pacific lamprey, three-spined stickleback, and Santa Ana sucker. The last native species to be caught in the river was a rainbow trout in 1940 by a local fisherman.
There is also a large variety of bird species in the Los Angeles River which include snowy egret,[21] great egret[22] black-necked stilt,[21] great blue heron,[21][22] green heron,[21] mallard,[21] cinnamon teal,[21] American coot,[21][22] Muscovy duck,[21] white pelican, Canada goose, osprey, California high desert mourning dove, black-chinned hummingbird, barn owl, and red tailed hawk.[22] All of these species either nest or live off of the resources of the river. Before the river's channelization the river supported a variety of mammals which included the California golden bear (removed 1897), grey wolf (removed 1890s), coyote, mule deer, and North American beaver.
There is indirect evidence that North American beaver (Castor canadensis) were native to the river, as the Beñemé (Mojave) and Jeniguechi (San Jacinto branch of the Cahuilla) Indians of the San Gabriel Mission were described by Father Pedro Font on the second de Anza Expedition in 1776, "The costume of the men in heathendom is total nakedness, while the women wear a bit of deer skin with which they cover themselves, and likewise an occasional cloak of beaver or rabbit skin, although the fathers endeavor to clothe the converted Indians with something as best they can."[23] The Tongva or Gabrieleño Indians of Mission San Gabriel had a word for beaver To-le-vah-che.[24]
Revitalization


On July 23, 2013, the nonprofit group Los Angeles River Revitalization Corp. announced a goal of completing a continuous 51-mile greenway and bike path along the river by the end of the decade.[25] The path is envisioned to be the central focus of a linear recreational park as well as providing an alternative transportation path through Los Angeles. The announcement by the nonprofit group precedes the expected August 30 release of a feasibility study being prepared by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The Corps have the ultimate decision-making power over the river and its future revitalization.[26] On September 13, 2013 the Army Corps of Engineers recommended a $453 million plan to restore nearly 600 acres of wildlife habitat – much of that located between Griffith Park and Lincoln Heights – as the best option to restore the river’s ecosystem while preserving the flood protection provided by the concrete encasement.[27]
One of the initiatives shepherded by the Ad Hoc River Committee is the Los Angeles River Revitalization Master Plan. As a result of the Ad Hoc River Committee’s efforts, and with funding from the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, the City of Los Angeles’ Department of Public Works-Bureau of Engineering issued a Request for Proposals in 2005 for the preparation of a Revitalization Master Plan, which would identify proposals that would make the Los Angeles River a “front door” to the City, and support a multitude of civic activities. The Los Angeles Times reported that famous architect Frank Gehry is part of the advisory group.[28]
The Los Angeles & San Gabriel Rivers Watershed Council is a nonprofit organization that works with government agencies, business leaders, community groups, and academics to facilitate an inclusive consensus process aimed at preserving, restoring, and enhancing the social, ecological, and economic health of the Los Angeles River and San Gabriel River watersheds through education, research, and planning.[citation needed]
The California Coastal Conservancy, a state agency, published its Los Angeles River Park and Recreation Study in 1993, identifying potential projects along the river. In 2006, Mayor Villaraigosa visited South Korea to look at their river restoration project, the Cheonggyecheon.[citation needed]
For the first time since the 1930s, a 2.5 mile section of the Glendale Narrows was opened to the public for unrestricted recreational use between Memorial Day and Labor Day in 2013.[29] In May 2014 it was announced that two sections of the river would again be open for recreational use during the summer.[30][31] The rapids have since become a popular attraction for whitewater canoeing and kayaking enthusiasts. At normal summer flows the river is a gentle shallow grade 1 and 2 river.[citation needed]
The ongoing efforts to revitalize the River fall into the category of "habitat enhancement" rather than restoration, since actual restoration of the River to its natural state is no longer possible or necessarily desirable. The flooding that characterized the River's natural state will still have to be limited to protect the developments that have been built in its flood zone, and the River cannot take groundwater from the area until a number of toxic waste sites (such as Santa Susana Field Station) are cleaned up.[32]
Riverside communities

Communities and cities along the banks of the Los Angeles River include:
|
Crossings
Entertainment setting
This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2014) |

Numerous films, television programs, music videos, and video games have featured various sites along the Los Angeles River. Since the River is a trickle for much of the year and the culvert is dry, it is often used for races, car chases, gang rumbles, and other scenes requiring an open, deserted setting within the city.
Perhaps the most memorable such scene involving the river is the extended, three vehicle chase sequence in 1991's Terminator 2: Judgment Day. Others include Transformers, Last Action Hero, The Gumball Rally, Chinatown, Them!, The Core, The Adventures of Buckaroo Banzai Across the 8th Dimension, In Time, It's Alive, L.A. Story, Grease, Point Blank, Repo Man, Fear The Walking Dead, The Italian Job, Point Break, Gone in 60 Seconds, To Live and Die in L.A., Blood In Blood Out, Cleopatra Jones, Blue Thunder, I Got The Hook Up, Marvel's Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D. and Drive. Video games include the racing game Midnight Club: Los Angeles and the action-adventure games Grand Theft Auto: San Andreas and Grand Theft Auto V (both of which feature depictions of the river within the fictional city of Los Santos).
The seventh and sixteenth season of Hell's Kitchen featured the blue team cleaning the LA River as punishment for losing the team challenge.
See also
- Terms
References
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
dischargewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e "Los Angeles River" (PDF). The Trust for Public Land. www.tpl.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ a b c d e Map of the Los Angeles River (Map). Cartography by NAVTEQ. Google Maps. 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "Urbanization spreads into the watershed of the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2007. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Friends Of Vast Industrial Concrete Kafkaesque Structures – Page 1". Seriss Corporation. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "Sepulveda Basin and Dam". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "Friends Of Vast Industrial Concrete Kafkaesque Structures – Page 3". Seriss Corporation. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "The Verdugo Wash Converges with the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "The Los Feliz Area of the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ a b c "Friends Of Vast Industrial Concrete Kafkaesque Structures – Page 4". Seriss Corporation. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "The Arroyo Seco Converges with the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "The Rio Hondo Converges with the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ "Long Beach and the Mouth of the Los Angeles River". Urban Education Partnership. www.urbanedpartnership.org. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ Joe Linton (14 October 2005). Down By the Los Angeles River: Friends of the Los Angeles Rivers Official Guide. Wilderness Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-89997-391-3. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ Bolton, Herbert E. (1927). Fray Juan Crespi: Missionary Explorer on the Pacific Coast, 1769-1774. HathiTrust Digital Library. pp. 146–147. Retrieved April 2014.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|deadurl=(help) - ^ "Full text of "A history of California and an extended history of its southern coast counties, also containing biographies of well-known citizens of the past and present"". archive.org. Retrieved 2015-07-10.
- ^ Smith, Doug (2003-08-14). "Angelenos' vision of their river is created from a made-up memory. Historically, the river has been dry for most of the year. Now, it flows continually, but most of the water in the channel is industrial and residential discharge". Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ "Sepulveda Basin Wildlife Reserve". City of Los Angeles Department of Recreation and Parks. Retrieved November 19, 2015.
- ^ "Bicycling - Glendale Narrows / Elysian Valley Bike Path". google.com. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ "Glendale Narrow and Elysian Valley Path". KCET. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "River Wildlife". Friends of the Los Angeles River. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ a b c d Linton, Joe (October 14, 2005). Down By the Los Angeles River: Friends of the Los Angeles Rivers Official Guide. Wilderness Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-89997-391-3. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Pedro Font (1776). Expanded Diary of Pedro Font. Retrieved 2011-01-30.
- ^ William McCawley (1996). The First Angelinos: The Gabrielino Indians of Los Angeles. Ballena Press. p. 304. ISBN 978-0965101608.
- ^ Christopher Hawthorne (2013-07-23). "Ambitious goal for L.A. River: Continuous 51-mile path by 2020". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ^ Christopher Hawthorne (2013-07-24). "L.A. River advocates wait for watershed Army Corps study". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ^ "Army of Corps of Engineers backs $453 million plan to restore L.A. River". The Eastsider. 2013-09-13. Retrieved 2015-06-02.
- ^ Peter Jamison, Martha Groves and Dan Weikel (2015-08-07). "Architect Frank Gehry is helping L.A. with its Los Angeles River master plan, but secrecy troubles some". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ^ Martinez, Michael and Hannah Button. "At last, Los Angeles River opens to public recreation after 80 years". CNN. Cable News Network. Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- ^ "Los Angeles River Recreation Zone - Summer 2014". Los Angeles River Recreation Program. May 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-05-24.
- ^ "Corps opens recreational boating program at Sepulveda". US Army Corp of Engineers. 23 May 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-05-24.
- ^ Robbins, Jim. "How to Restore an Urban River? Los Angeles Looks to Find Out". Yale environment 360. Retrieved 5 August 2016.
Further reading
- The Los Angeles River: Its Life, Death, and Possible Rebirth. Blake Gumprecht. Baltimore and London: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1999. ISBN 0-8018-6047-4.
- Eden by design: the 1930 Olmsted-Bartholomew plan for the Los Angeles region. Greg Hise & William Francis Deverell. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2000. ISBN 0-520-22414-0. ISBN 0-520-22415-9.
- Río L.A.: Tales from the Los Angeles River. Patt Morrison. Los Angeles: Angel City Press, 2001. ISBN 1-883318-24-6.
- Down By The Los Angeles River: Friends of the Los Angeles River's Official Guide Joe Linton. Berkeley: Wilderness Press, 2005. ISBN 0-89997-391-4.
- Hazardous Metropolis: Flooding and Urban Ecology in Los Angeles Jared Orsi. University of California Press, 2004. ISBN 0-520-23850-8.
External links
- William Deverell, Whitewashed Adobe: The Rise of Los Angeles and the Remaking of Its Mexican Past, University of California Press, Los Angeles, 2005, Page 102, "Map 2: Changing Courses of the Los Angeles River"
- The Los Angeles River Master Plan
- Los Angeles River Revitalization Master Plan and City Ad Hoc Committee
- The Los Angeles River Tour
- Los Angeles & San Gabriel Rivers Watershed Council
- The River Project
- F.O.L.A.R Friends of the Los Angeles River
- Friends of the Sepulveda Basin, organization website
- lariverflyfishing River blog from a unique perspective
- lacreekfreak, Blog
- Friends Of Vast Industrial Concrete Kafkaesque Structures, a photo journal of photographs of the Los Angeles River flood control channel.
- The Los Angeles River Film, a 28-minute documentary film about the Los Angeles River including recent revitalization efforts.
- Saving the Los Angeles River, story about saving the river via boating and activism.
- KCET Departures interview with Joe Linton advocate of restoration and revitalization of the L.A. river.
- L.A. River Expeditions, a leading advocate for recreational-educational boating and public access rights on the L.A. River.
- Rock the Boat, an award-winning documentary film featuring the L.A. River and many environmental advocates.
- Environmental Protection Agency, their historic 2010 determination about protecting the entire L.A. River watershed.
- Time magazine article, featuring the 2012 Paddle the L.A. River pilot program.
- CNN article, on the paddling program.
- New York Times article, on the river being opened to recreational use.
- BBC broadcast, on canoeing to save the river.


