Abortion: Difference between revisions
m Dated {{Citation needed}}. (Build p613) |
NightHeron (talk | contribs) m →Induced: grammar fix (parallel structure and punctuation) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Termination of a pregnancy}} |
|||
<!--Note to Editors: This article has a long and intense history of terminology debates. Please review the talk page before making changes to lines to see if there is a previous established consensus or compromise. Thank you.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{other uses}} |
||
{{pp-semi-indef}} |
|||
{{Infobox disease |
|||
{{pp-move}} |
|||
| Name = Induced abortion |
|||
{{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc}} |
|||
| Image = |
|||
{{use dmy dates|date=November 2019}} |
|||
| Caption = |
|||
{{use American English|date=September 2016}} |
|||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|O|04||o|00}} |
|||
<!-- Note to Editors: This article has a long history of intense terminology debates. Please review the talk page before making changes to lines to see if there is a previous established consensus or compromise. Thank you. --> |
|||
{{Infobox medical intervention |
|||
| name = Induced abortion |
|||
| synonyms = Induced miscarriage, termination of pregnancy |
|||
| image = |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| field = [[Obstetrics]] and [[gynecology]] |
|||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10PCS|10A0|1/0/A/0}} |
|||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|779.6}} |
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|779.6}} |
||
| DiseasesDB = 4153 |
|||
| ICDO = |
| ICDO = |
||
| OMIM = |
| OMIM = |
||
| MedlinePlus = |
| MedlinePlus = 007382 |
||
| eMedicine = 252560 |
|||
| eMedicineSubj = article |
|||
| MeshID = D000028 |
|||
| eMedicineTopic = 252560 |
|||
<!-- Infobox medical intervention does not support the following parameters: |
|||
| MeshID = |
|||
| DiseasesDB = 4153 |
|||
--> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
<!-- The lead sentence has been the topic of much discussion. Please do not edit it without first reviewing the talk page and its archives. --> |
|||
<!-- Terminology --> |
|||
'''Abortion''' is the termination of a [[pregnancy]] by removal or expulsion of an [[embryo]] or [[fetus]].{{refn|For a list of definitions as stated by [[obstetrics and gynecology]] (OB/GYN) textbooks, dictionaries, and other sources, see ''[[Definitions of abortion]]''. Definitions of abortion vary from source to source, and language used to define abortion often reflects societal and political opinions, not only scientific knowledge.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780199756797/obo-9780199756797-0090.xml?rskey=tygpVh&result=1| title=Abortion|website=[[Oxford Bibliographies]]|access-date=9 April 2014| vauthors = Kulczycki A |url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140413132203/http://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780199756797/obo-9780199756797-0090.xml?rskey=tygpVh&result=1|archive-date=13 April 2014}}</ref>|group=nb}} An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a [[miscarriage]] or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of all pregnancies.<ref name=John2012>{{cite book| title=The Johns Hopkins Manual of Gynecology and Obstetrics| date=2012| publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins| isbn=978-1-4511-4801-5| pages=438–439| edition=4| url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4Sg5sXyiBvkC&pg=PA438| url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170910181311/https://books.google.com/books?id=4Sg5sXyiBvkC&pg=PA438|archive-date=September 10, 2017}}</ref><ref name=NIH2013Epi>{{cite web| title=How many people are affected by or at risk for pregnancy loss or miscarriage?|url=http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancyloss/conditioninfo/Pages/risk.aspx| website=NICHD |access-date=14 March 2015| date=2013-07-15|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402093633/http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancyloss/conditioninfo/Pages/risk.aspx| archive-date=April 2, 2015}}</ref> When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an [[#Induced|induced abortion]], or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word ''abortion'' generally refers to an induced abortion.<ref>{{cite web |title=abortion |url-access=subscription |url=http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/503?rskey=TpobDi&result=1#eid |website=Oxford English Dictionary |access-date=5 April 2019 |archive-date=19 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200819111414/https://www.oed.com/start;jsessionid=5BD236F54839DEEFCB6B4A7FEBB47BF4?authRejection=true&url=%2Fview%2FEntry%2F503%3Frskey%3DTpobDi%26result%3D1#eid |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=OED>{{cite web| url=https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/abortion|title=Abortion (noun)| publisher=Oxford Living Dictionaries| access-date=8 June 2018| quote=''[mass noun]'' The deliberate termination of a human pregnancy, most often performed during the first 28 weeks of pregnancy| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180528131142/https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/abortion|archive-date=28 May 2018| url-status=dead}}</ref> The most common reasons women give for having an abortion are for birth-timing and limiting family size.<ref name="bankole98" /><ref name=Chae_2017 /><ref name="guttmacher" /> Other reasons reported include [[maternal health]], [[Poverty|an inability to afford a child]], [[domestic violence]], lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of [[rape]] or [[incest]].<ref name="bankole98" /><ref name="guttmacher" /><ref name=":5" /> |
|||
<!-- Methods and safety --> |
|||
'''Abortion''' is the termination of a [[pregnancy (mammals)|pregnancy]] by the removal or expulsion from the [[uterus]] of a [[fetus]] or [[embryo]], usually before it can [[fetal viability|survive outside the womb]].{{Disputed-inline|date=July 2011}}<ref name="definition" group="note" /> An abortion can occur spontaneously due to [[complication (medicine)|complications]] during pregnancy, or can be induced, in humans and in other species. In the context of human pregnancies, an induced abortion may be referred to as either{{Disputed-inline|date=July 2011}} ''therapeutic'' or ''elective''. The term ''abortion'' most commonly refers to the induced abortion of a [[pregnancy|human pregnancy]]; spontaneous abortions are usually termed [[miscarriage]]s. <!--Annotation: This paragraph serves to disambiguate abortion terminology and and types--> |
|||
When done legally in industrialized societies, induced abortion is [[#Safety|one of the safest procedures in medicine]].{{r|lancet-grimes|p=1|q=Unsafe abortion is a persistent, preventable pandemic.{{nbsp}}[...] By contrast, legal abortion in industrialised nations has emerged as one of the safest procedures in contemporary medical practice, with minimum morbidity and a negligible risk of death.}}{{r|Ray2014}} [[Unsafe abortion]]s—those performed by people lacking the necessary skills, or in inadequately resourced settings—are responsible for between 5–13% of [[maternal death]]s, especially in the [[developing world]].<ref name="WHO-preventing-unsafe">{{cite web |url=https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preventing-unsafe-abortion |title=Preventing unsafe abortion |publisher=World Health Organization|access-date=6 August 2019 |archive-date=23 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190823190843/https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preventing-unsafe-abortion |url-status=live }}</ref> However, [[medication abortion]]s that are [[Self-managed abortion|self-managed]] are highly effective and safe throughout the [[Trimester (pregnancy)|first trimester]].<ref name="WHO-SHR">{{cite web |date=2021-11-19 |title=Self-management Recommendation 50: Self-management of medical abortion in whole or in part at gestational ages < 12 weeks (3.6.2) - Abortion care guideline |url=https://srhr.org/abortioncare/chapter-3/service-delivery-options-and-self-management-approaches-3-6/self-management-recommendation-50-self-management-of-medical-abortion-in-whole-or-in-part-at-gestational-ages-12-weeks-3-6-2/ |access-date=2023-09-21 |website=WHO Department of Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research |language=en-US |archive-date=29 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220629195513/https://srhr.org/abortioncare/chapter-3/service-delivery-options-and-self-management-approaches-3-6/self-management-recommendation-50-self-management-of-medical-abortion-in-whole-or-in-part-at-gestational-ages-12-weeks-3-6-2/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Moseson H, Jayaweera R, Raifman S, Keefe-Oates B, Filippa S, Motana R, Egwuatu I, Grosso B, Kristianingrum I, Nmezi S, Zurbriggen R, Gerdts C | display-authors = 6 | title = Self-managed medication abortion outcomes: results from a prospective pilot study | journal = Reproductive Health | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 164 | date = October 2020 | pmid = 33109230 | pmc = 7588945 | doi = 10.1186/s12978-020-01016-4 |doi-access=free |issn=1742-4755 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Moseson H, Jayaweera R, Egwuatu I, Grosso B, Kristianingrum IA, Nmezi S, Zurbriggen R, Motana R, Bercu C, Carbone S, Gerdts C | display-authors = 6 | title = Effectiveness of self-managed medication abortion with accompaniment support in Argentina and Nigeria (SAFE): a prospective, observational cohort study and non-inferiority analysis with historical controls | journal = The Lancet. Global Health | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | pages = e105–e113 | date = January 2022 | pmid = 34801131 | doi = 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00461-7 | pmc = 9359894 }}</ref> Public health data shows that making safe abortion legal and accessible reduces maternal deaths.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faúndes A, Shah IH | title = Evidence supporting broader access to safe legal abortion | journal = International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics | volume = 131 | issue = Suppl 1 | pages = S56–S59 | date = October 2015 | pmid = 26433508 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijgo.2015.03.018 | series = World Report on Women's Health 2015: The unfinished agenda of women's reproductive health | doi-access = free | quote = A strong body of accumulated evidence shows that the simple means to drastically reduce unsafe abortion-related maternal deaths and morbidity is to make abortion legal and institutional termination of pregnancy broadly accessible.{{nbsp}}[...] [C]riminalization of abortion only increases mortality and morbidity without decreasing the incidence of induced abortion, and that decriminalization rapidly reduces abortion-related mortality and does not increase abortion rates. }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | first1= Su Mon |last1= Latt |first2=Allison |last2= Milner|author-link2= Allison Milner| last3= Kavanagh |first3= Anne | title = Abortion laws reform may reduce maternal mortality: an ecological study in 162 countries | journal = BMC Women's Health | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 1 | date = January 2019 | pmid = 30611257 | pmc = 6321671 | doi = 10.1186/s12905-018-0705-y |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
Modern methods use [[medical abortion|medication]] or [[surgical abortion|surgery]] for abortions.<ref name=":0">{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang J, Zhou K, Shan D, Luo X | title = Medical methods for first trimester abortion | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2022 | pages = CD002855 | date = May 2022 | issue = 5 | pmid = 35608608 | pmc = 9128719 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD002855.pub5 }}</ref> The drug [[mifepristone]] in combination with [[prostaglandin]] appears to be as safe and effective as surgery during the [[first trimester|first]] and [[second trimester]]s of pregnancy.<ref name=":0" /><ref name="Kapp2013" /> The most common surgical technique involves [[Dilation and evacuation|dilating]] the [[cervix]] and using a [[vacuum aspiration|suction device]].<ref>{{cite news |title=Abortion – Women's Health Issues |url=https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/family-planning/abortion |website=Merck Manuals Consumer Version |access-date=12 July 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180713183550/https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/family-planning/abortion |archive-date=13 July 2018 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Birth control]], such as [[combined oral contraceptive pill|the pill]] or [[intrauterine device]]s, can be used immediately following abortion.<ref name="Kapp2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kapp N, Whyte P, Tang J, Jackson E, Brahmi D | title = A review of evidence for safe abortion care | journal = Contraception | volume = 88 | issue = 3 | pages = 350–363 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23261233 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2012.10.027 }}</ref> When performed legally and safely on a woman who desires it, induced abortions do not increase the risk of long-term [[mental health|mental]] or physical problems.<ref name="BMJ2014">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lohr PA, Fjerstad M, Desilva U, Lyus R |year=2014 |title=Abortion |journal=BMJ |volume=348 |page=f7553 |doi=10.1136/bmj.f7553 |s2cid=220108457}}</ref> In contrast, [[unsafe abortion]]s performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities cause between 22,000 and 44,000 deaths and 6.9 million hospital admissions each year.<ref>{{cite web |date=2018-03-01 |title=Induced Abortion Worldwide {{!}} Guttmacher Institute |url=https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180301060904/https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide |archive-date=2018-03-01 |access-date=2023-06-23 |website=Guttmacher.org}}</ref> The [[World Health Organization]] states that "access to legal, safe and comprehensive abortion care, including [[post-abortion care]], is essential for the attainment of the highest possible level of sexual and reproductive health".<ref>{{cite web|title=Abortion| url=https://www.who.int/health-topics/abortion#tab=tab_1| access-date=2021-04-14| website=www.who.int| language=en| archive-date=6 May 2021| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210506092947/https://www.who.int/health-topics/abortion#tab=tab_1}}</ref> [[history of abortion|Historically]], abortions have been attempted using [[abortifacient|herbal medicines]], sharp tools, [[fundal massage|forceful massage]], or other [[traditional medicine|traditional methods]].<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1">{{cite book |title=Management of Unintended and Abnormal Pregnancy |vauthors=Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD, Joffe C |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-4443-1293-5 |edition=1st |location=Oxford |chapter=1. Abortion and medicine: A sociopolitical history |ol=15895486W |chapter-url=http://media.wiley.com/product_data/excerpt/62/14051769/1405176962.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120119025652/http://media.wiley.com/product_data/excerpt/62/14051769/1405176962.pdf |archive-date=19 January 2012 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Abortion, when performed in the [[developed countries|developed world]] in jurisdictions where the procedure is legal, is [[#Safe abortion|among the safest procedures in medicine]].<ref name="lancet-grimes"/> However, [[unsafe abortion]]s (those performed by persons without proper training or outside of a medical environment) result in approximately 70 thousand maternal deaths and 5 million disabilities per year globally.<ref name=OBGY09/> An estimated 42 million abortions are performed globally each year, with 20 million of those performed unsafely.<ref name=OBGY09>{{Cite journal| last1 = Shah | first1 = I. | last2 = Ahman | first2 = E. |title=Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges |journal=[[Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada]] |volume=31 |issue=12 |pages=1149–58 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=20085681 |doi= |url=http://www.sogc.org/jogc/abstracts/full/200912_WomensHealth_1.pdf|format=PDF}}</ref> Forty percent of the world's women are able to access therapeutic and elective abortions within gestational limits.<ref name=IJGO10>{{Cite journal|author=Culwell KR, Vekemans M, de Silva U, Hurwitz M|title=Critical gaps in universal access to reproductive health: Contraception and prevention of unsafe abortion |journal=[[International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics]] |volume=110 |pages=S13–16 |year=2010 |month=July |pmid=20451196 |doi=10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.04.003 }}</ref><!--Annotation: This paragraph discusses epidemiology and health risk related to the procedure.--> |
|||
<!-- Epidemiology --> |
|||
Induced abortion has a long [[history of abortion|history]] and has been facilitated by various methods including herbal [[abortifacient]]s, the use of sharpened tools, [[physical trauma]], and other [[traditional medicine|traditional methods]]. Contemporary medicine utilizes medications and surgical procedures to induce abortion. The [[abortion law|legality]], prevalence, cultural status, and religious status of abortion vary substantially around the world. In many parts of the world there is prominent and divisive [[Abortion debate|public controversy]] over the [[ethical aspects of abortion|ethical]] and legal issues of abortion. Abortion and abortion-related issues feature prominently in the national politics in many nations, often involving the opposing [[pro-life]] and [[pro-choice]] worldwide social movements ([[Abortion-rights_movement#Term_controversy|both self-named]]). Incidence of abortion has declined worldwide as access to [[family planning]] education and contraceptive services has increased.<ref name="worldtrends">{{Cite journal|author=Sedgh G, Henshaw SK, Singh S, Bankole A, Drescher J |title=Legal abortion worldwide: incidence and recent trends |journal=Int Fam Plan Perspect |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=106–16 |year=2007 |month=September |pmid=17938093 |doi=10.1363/ifpp.33.106.07 |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3310607.html }}</ref> <!--Annotation: This paragraph covers related issues and current events.--> |
|||
Around 73 million abortions are performed each year in the world,<ref>{{cite web |title=Abortion |url=https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/abortion |access-date=2022-09-21 |website=www.who.int |language=en |archive-date=21 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220921025025/https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/abortion |url-status=live }}</ref> with about 45% done unsafely.<ref>{{cite web| title=Worldwide, an estimated 25 million unsafe abortions occur each year| url=https://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/unsafe-abortions-worldwide/en/|publisher=World Health Organization| access-date=29 September 2017|date=28 September 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170929131145/http://who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/unsafe-abortions-worldwide/en/| archive-date=29 September 2017|url-status=live}}</ref> Abortion rates changed little between 2003 and 2008,<ref name="Sedgh 2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sedgh G, Singh S, Shah IH, Ahman E, Henshaw SK, Bankole A | title = Induced abortion: incidence and trends worldwide from 1995 to 2008 | journal = Lancet | volume = 379 | issue = 9816 | pages = 625–632 | date = February 2012 | pmid = 22264435 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61786-8 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/Sedgh-Lancet-2012-01.pdf | url-status = live | quote = Because few of the abortion estimates were based on studies of random samples of women, and because we did not use a model-based approach to estimate abortion incidence, it was not possible to compute confidence intervals based on standard errors around the estimates. Drawing on the information available on the accuracy and precision of abortion estimates that were used to develop the subregional, regional, and worldwide rates, we computed intervals of certainty around these rates (webappendix). We computed wider intervals for unsafe abortion rates than for safe abortion rates. The basis for these intervals included published and unpublished assessments of abortion reporting in countries with liberal laws, recently published studies of national unsafe abortion, and high and low estimates of the numbers of unsafe abortion developed by WHO. | s2cid = 27378192 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120206043854/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/Sedgh-Lancet-2012-01.pdf | archive-date = 6 February 2012 }}</ref> before which they decreased for at least two decades as access to [[family planning]] and birth control increased.<ref name="worldtrends2007">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sedgh G, Henshaw SK, Singh S, Bankole A, Drescher J | title = Legal abortion worldwide: incidence and recent trends | journal = International Family Planning Perspectives | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 106–116 | date = September 2007 | pmid = 17938093 | doi = 10.1363/3310607 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3310607.html | url-status = live | doi-access = free | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090819122933/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3310607.html | archive-date = 19 August 2009 }}</ref> {{as of|2018}}, 37% of the world's women had access to legal abortions without limits as to reason.<ref name=Gutt_2018_fact >{{cite web | url=https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide | title=Induced Abortion Worldwide | work=[[Guttmacher Institute]] | date=2018-03-01 | access-date=2020-02-21 | quote=Of the world's 1.64 billion women of reproductive age, 6% live where abortion is banned outright, and 37% live where it is allowed without restriction as to reason. Most women live in countries with laws that fall between these two extremes. | archive-date=23 February 2020 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200223022612/https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide | url-status=live }}</ref> Countries that permit abortions have different limits on how late in pregnancy abortion is allowed.<ref name=IJGO10>{{cite journal | vauthors = Culwell KR, Vekemans M, de Silva U, Hurwitz M, Crane BB | title = Critical gaps in universal access to reproductive health: contraception and prevention of unsafe abortion | journal = International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics | volume = 110 | issue = Suppl | pages = S13–S16 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20451196 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.04.003 | s2cid = 40586023 }}</ref> Abortion rates are similar between countries that restrict abortion and countries that broadly allow it, though this is partly because countries which restrict abortion tend to have higher [[unintended pregnancy]] rates.<ref>{{cite web|date=2020-05-28| title=Unintended Pregnancy and Abortion Worldwide| url=https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide|access-date=2021-03-09|website=Guttmacher Institute| language=en| archive-date=23 February 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200223022612/https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide|url-status=live | quote=Abortion is sought and needed even in settings where it is restricted—that is, in countries where it is prohibited altogether or is allowed only to save the women’s life or to preserve her physical or mental health. Unintended pregnancy rates are highest in countries that restrict abortion access and lowest in countries where abortion is broadly legal. As a result, abortion rates are similar in countries where abortion is restricted and those where the procedure is broadly legal (i.e., where it is available on request or on socioeconomic grounds).}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- society, and culture -->Globally, there has been a widespread trend towards greater legal access to abortion since 1973,<ref>{{cite web |last=Staff |first=F. P. |date=2022-06-24 |title=Roe Abolition Makes U.S. a Global Outlier |url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2022/06/24/roe-v-wade-overturned-global-abortion-laws/ |access-date=2023-10-20 |website=Foreign Policy |language=en-US |archive-date=24 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220624181307/https://foreignpolicy.com/2022/06/24/roe-v-wade-overturned-global-abortion-laws/ |url-status=live }}</ref> but [[Abortion debate|there remains debate]] with regard to moral, religious, ethical, and legal issues.<ref>{{cite book| veditors = Nixon F | vauthors = Paola A, Walker R, LaCivita L |title=Medical ethics and humanities|date=2010|publisher=Jones and Bartlett Publishers|location=Sudbury, MA| isbn=978-0-7637-6063-2|page=249|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9pM2pw-2wl4C&pg=PA249|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170906191717/https://books.google.com/books?id=9pM2pw-2wl4C&pg=PA249|archive-date=6 September 2017| ol=13764930W}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Johnstone MJ |title=Bioethics a nursing perspective| journal=Confederation of Australian Critical Care Nurses Journal| volume=3|issue=4|pages=24–30|date=2009| publisher=Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier|location=Sydney, NSW| isbn=978-0-7295-7873-8|edition=5th| url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EG-Yg1xDYakC&pg=PA228| quote=Although abortion has been legal in many countries for several decades now, its moral permissibilities continues to be the subject of heated public debate.| url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170906191717/https://books.google.com/books?id=EG-Yg1xDYakC&pg=PA228|archive-date=6 September 2017| pmid=2129925}}</ref> Those who [[Anti-abortion movements|oppose abortion]] often argue that an embryo or fetus is a person with a [[right to life]], and thus equate abortion with [[murder]].<ref>{{cite news | vauthors = Driscoll M |author-link= Mark Driscoll| title=What do 55 million people have in common? |publisher=Fox News |date=18 October 2013 |access-date=2 July 2014 |url=http://www.foxnews.com/opinion/2013/10/18/what-do-55-million-people-have-in-common/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140831022138/http://www.foxnews.com/opinion/2013/10/18/what-do-55-million-people-have-in-common/ |archive-date=31 August 2014 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news | vauthors = Hansen D |title=Abortion: Murder, or Medical Procedure? |work=The Huffington Post |date=18 March 2014 |access-date=2 July 2014 |url=https://www.huffingtonpost.com/dale-hansen/abortion-murder-or-medica_b_4986637.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140714230359/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dale-hansen/abortion-murder-or-medica_b_4986637.html |archive-date=14 July 2014 }}</ref> Those who [[Abortion-rights movements|support abortion's legality]] often argue that it is a woman's [[reproductive rights|reproductive right]].<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Sifris RN |title=Reproductive freedom, torture and international human rights: challenging the masculinisation of torture|date=2013|publisher=Taylor & Francis |location=Hoboken, NJ|isbn=978-1-135-11522-7|oclc=869373168|page=3|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9pVWAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA3|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015195038/https://books.google.com/books?id=9pVWAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA3|archive-date=15 October 2015}}</ref> Others favor legal and accessible abortion as a public health measure.<ref>{{cite book| first= Elisabeth |last=Åhman |title=Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003| date=2007| publisher=World Health Organization| isbn=978-92-4-159612-1| edition=5th| url=https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/unsafe_abortion/9789241596121/en/|access-date=24 March 2018| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180407131435/http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/unsafe_abortion/9789241596121/en/| archive-date=7 April 2018| url-status=dead}}</ref> [[Abortion law]]s and views of the procedure are different around the world. In some countries abortion is legal and women have the right to make the choice about abortion.<ref>Fabiola Sanchez, Megan Janetsky, ''[https://apnews.com/article/mexico-abortion-decriminalize-d87f6edbdf68c2e6c8f5700b3afd15de Mexico decriminalizes abortion, extending Latin American trend of widening access to procedure] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230906235527/https://apnews.com/article/mexico-abortion-decriminalize-d87f6edbdf68c2e6c8f5700b3afd15de |date=6 September 2023 }}'', Associated Press (AP), September 6, 2023</ref> In some areas, abortion is legal only in specific cases such as rape, incest, [[fetal defects]], poverty, and risk to a woman's health.<ref name="Dev98-07">{{cite journal |vauthors=Boland R, Katzive L |date=September 2008 |title=Developments in laws on induced abortion: 1998-2007 |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3411008.html |url-status=live |journal=International Family Planning Perspectives |volume=34 |issue=3 |pages=110–120 |doi=10.1363/3411008 |pmid=18957353 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111007221828/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3411008.html |archive-date=7 October 2011 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
== Types == |
|||
==Types== |
|||
===Induced=== |
===Induced=== |
||
An induced abortion is a medical procedure to end a pregnancy.<ref>{{cite web |vauthors=Cheng L |date=1 November 2008 |title=Surgical versus medical methods for second-trimester induced abortion |url=http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/CD006714_chengl_com/en/index.html |work=The WHO Reproductive Health Library |publisher=World Health Organization |access-date=17 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100801023058/http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/CD006714_chengl_com/en/index.html |archive-date=1 August 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> In modern English, the term ''abortion'', when used without further qualification, generally refers to induced abortion.<ref name=OED/> |
|||
A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in several ways. The manner selected often depends upon the [[gestational age]] of the embryo or fetus,<ref>{{cite book|last=Stubblefield|first=Phillip G.|chapter=10. Family Planning|title=Novak's Gynecology|editor1-last=Berek|editor1-first=Jonathan S.|editor1-link=Jonathan Berek|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|year=2002|edition=13|isbn=978-0781732628}}</ref> which increases in size as the pregnancy progresses.<ref>{{cite book|last=Menikoff|first=Jerry|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=2jXOYv3X8zsC&pg=PA78|title=Law and Bioethics|page=78|publisher=Georgetown University Press|year=2001|quote=As the fetus grows in size, however, the vacuum aspiration method becomes increasingly difficult to use.|isbn=9780878408399}}</ref> Specific procedures may also be selected due to legality, regional availability, and doctor-patient preference. |
|||
A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in several ways. The abortion method depends upon the [[Embryonic age|gestational age]] of the embryo or fetus, which gains mass as the pregnancy progresses.<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Stubblefield PG |chapter=10. Family Planning |title=Novak's Gynecology| veditors=Berek JS |editor1-link=Jonathan Berek| publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins| year=2002| edition=13| isbn=978-0-7817-3262-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| title=Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States |pmid=15051566| journal=Obstetrics & Gynecology |year=2004 | vauthors = Bartlett LA, Berg CJ, [[Holly Shulman|Shulman HB]], Zane SB, Green CA, Whitehead S, Atrash HK |volume=103 |issue=4 |pages=729–737 |doi=10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60| s2cid=42597014| doi-access=free }}</ref> [[Abortion law|Abortion laws]], regional availability, and the personal preference of the women and her doctor may inform the women's choice of a specific abortion procedure. |
|||
Abortions can be characterized as either therapeutic or elective. When an abortion is performed for medical reasons, the procedure is referred to as a therapeutic abortion. Medical reasons for therapeutic abortion include saving the life of the pregnant woman, preventing harm to the woman's [[Health|physical]] or [[mental health]], preventing the birth of a child who will have a significantly increased chance of mortality or morbidity, and [[selective reduction|reducing]] the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with [[multiple pregnancy]].<ref name="roche1">{{cite web| vauthors = Roche NE |date=28 September 2004 |title=Therapeutic Abortion |publisher=eMedicine |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041214092044/http://www.emedicine.com/MED/topic3311.htm |url=http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/252560-overview |archive-date=14 December 2004 |access-date=19 June 2011}}</ref><ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6" /> An abortion is referred to as elective or voluntary when it is performed at the request of the woman for non-medical reasons.<ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6" /> Confusion sometimes arises over the term ''elective'' because "[[elective surgery]]" generally refers to all scheduled surgery, whether medically necessary or not.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Janiak |first1=Elizabeth |last2=Goldberg |first2=Alisa B. |date=2016-02-01 |title=Eliminating the phrase 'elective abortion': why language matters |url=https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824(15)00624-1/abstract |journal=Contraception |language=English |volume=93 |issue=2 |pages=89–92 |doi=10.1016/j.contraception.2015.10.008 |pmid=26480889 |issn=0010-7824 |access-date=27 November 2022 |archive-date=24 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230124173416/https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824%2815%2900624-1/fulltext |url-status=live |url-access=subscription }}</ref> |
|||
About one in five pregnancies worldwide ends with an induced abortion.<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> Most abortions result from unintended pregnancies.<ref name=bankole98/><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Finer LB, Frohwirth LF, Dauphinee LA, Singh S, Moore AM |title=Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantitative and qualitative perspectives |journal=Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health |volume=37 |issue=3 |pages=110–118 |date=September 2005 |pmid=16150658 |doi=10.1111/j.1931-2393.2005.tb00045.x |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060117143856/https://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.pdf |archive-date=17 January 2006}}</ref> In the United Kingdom, 1 to 2% of abortions are done because of genetic problems in the fetus.<ref name=BMJ2014/> |
|||
Reasons for procuring induced abortions are typically characterized as either therapeutic or elective. An abortion is medically referred to as a [[Therapeutic Abortion|therapeutic abortion]] when it is performed to save the life of the pregnant woman; prevent harm to the woman's physical or mental health; terminate a pregnancy where indications are that the child will have a significantly increased chance of premature morbidity or mortality or be otherwise disabled; or to [[selective reduction|selectively reduce]] the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with [[multiple birth|multiple pregnancy]].<ref name="roche1">{{cite web|last=Roche|first=Natalie E.|date=28 September 2004|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20041214092044/http://www.emedicine.com/MED/topic3311.htm|title=Therapeutic Abortion|publisher=[[eMedicine]]|url=http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/252560-overview|archivedate=December 14, 2004|accessdate=June 19, 2011}}</ref><ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6" /> An abortion is referred to as an elective or voluntary abortion when it is performed at the request of the woman for non-medical reasons.<ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6" /> |
|||
===Spontaneous=== |
===Spontaneous=== |
||
{{Main|Miscarriage}} |
{{Main|Miscarriage}} |
||
Miscarriage, also known as spontaneous abortion, is the unintentional expulsion of an embryo or fetus before the 24th [[Gestational age (obstetrics)|week of gestation]].<ref>{{cite book | title = Churchill Livingstone medical dictionary | publisher = Churchill Livingstone Elsevier | location = Edinburgh New York | year = 2008 | isbn = 978-0-443-10412-1 | quote = The preferred term for unintentional loss of the product of conception prior to 24 weeks' gestation is miscarriage.}}</ref> A pregnancy that ends before 37 weeks of gestation resulting in a [[live birth (human)|live-born]] infant is a "[[premature birth]]" or a "preterm birth".<ref>{{cite book|quote=A preterm birth is defined as one that occurs before the completion of 37 menstrual weeks of gestation, regardless of birth weight.|page=669| veditors = Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL |editor1-link=Steven Gabbe|year=2007|title=Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies|edition=5th |publisher=Churchill Livingstone|chapter=51. Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetric Practice|isbn=978-0-443-06930-7|vauthors = AnnasGJ, Elias S |author-link1=George Annas }}</ref> When a fetus dies [[Uterus|in utero]] after [[Fetal viability|viability]], or during [[childbirth|delivery]], it is usually termed "[[stillbirth|stillborn]]".<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|quote=birth of a fetus that shows no evidence of life (heartbeat, respiration, or independent movement) at any time later than 24 weeks after conception|title=Stillbirth|series=Concise Medical Dictionary|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=2010|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zs8ZM4OUurcC&pg=PA698|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015195038/https://books.google.com/books?id=Zs8ZM4OUurcC&pg=PA698|archive-date=15 October 2015|isbn=978-0-19-955714-1}}</ref> [[Premature births]] and [[stillbirth]]s are generally not considered to be miscarriages, although usage of these terms can sometimes overlap.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fam.state.gov/FAM/07FAM/07FAM1470.html|title=7 FAM 1470 Documenting Stillbirth (Fetal Death)|publisher=United States Department of State|date=18 February 2011|access-date=12 January 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160205060246/https://fam.state.gov/FAM/07FAM/07FAM1470.html|archive-date=5 February 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Studies of pregnant women in the US and China have shown that between 40% and 60% of embryos do not progress to birth.<ref name="Gabbe, Chp 24">{{cite book | veditors = Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL |editor1-link=Steven Gabbe |year=2007|title=Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies|edition=5th |publisher=Churchill Livingstone |chapter=24. Pregnancy loss|isbn=978-0-443-06930-7| vauthors = Annas GJ, Elias S |author-link1=George Annas }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Early embryo mortality in natural human reproduction: What the data say [version 2; peer review: 2 approved, 1 approved with reservations] |journal=F1000Research |date=7 June 2017 | vauthors = Jarvis GE |volume=5 |page=2765 |doi=10.12688/f1000research.8937.2 |doi-access=free |pmid=28580126 |pmc=5443340 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Estimating limits for natural human embryo mortality [version 1; peer review: 2 approved] |journal=F1000Research |date=26 August 2016 |vauthors=Jarvis GE |volume=5 |page=2083 |doi=10.12688/f1000research.9479.1 |doi-access=free |pmid=28003878 |pmc=5142718 }}</ref> The vast majority of miscarriages occur before the woman is [[clinically silent|aware that she is pregnant]],<ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6" /> and many pregnancies spontaneously abort before medical practitioners can detect an embryo.<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Katz VL |publisher=Mosby|year=2007|edition=5 th|title=Katz: Comprehensive Gynecology| veditors = Katz VL, Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM |chapter=16. Spontaneous and Recurrent Abortion – Etiology, Diagnosis, Treatment|isbn=978-0-323-02951-3}}</ref> Between 15% and 30% of known pregnancies end in clinically apparent miscarriage, depending upon the age and health of the pregnant woman.<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Stovall TG |chapter=17. Early Pregnancy Loss and Ectopic Pregnancy|title=Novak's Gynecology| veditors = Berek JS |editor1-link=Jonathan Berek|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|year=2002|edition=13|isbn=978-0-7817-3262-8}}</ref> 80% of these spontaneous abortions happen in the first trimester.<ref name=Williams18>{{cite book | veditors = Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, Sheffield JS |editor-link4=Catherine Y. Spong |title = Williams Obstetrics |edition = 24th |year = 2014 |publisher = McGraw Hill Education |isbn = 978-0-07-179893-8}}</ref> |
|||
The most common cause of spontaneous abortion during the first trimester is chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo |
The most common cause of spontaneous abortion during the first trimester is [[chromosomal abnormalities]] of the embryo or fetus,<ref name="Williams Gyn, Chp 6">{{cite book| veditors = Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, Halvorson LM, Hoffman BL, Bradshaw KD, Cunningham FG |year=2008|title=Williams Gynecology|edition=1|publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical|isbn=978-0-07-147257-9|chapter=6. First-Trimester Abortion}}</ref><ref name="mednet">{{cite web|url=http://www.medicinenet.com/miscarriage/page1.htm |title=Miscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) |access-date=7 April 2009 | vauthors = Stöppler MS | veditors = Shiel Jr WC |work=MedicineNet.com |publisher=WebMD |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040829013142/http://www.medicinenet.com/Miscarriage/page1.htm |archive-date=29 August 2004 }}</ref> accounting for at least 50% of sampled early pregnancy losses.<ref name="fetal med 837">{{cite book |vauthors=Jauniaux E, Kaminopetros P, El-Rafaey H |chapter=Early pregnancy loss |veditors=Whittle MJ, Rodeck CH |title=Fetal medicine: basic science and clinical practice |publisher=Churchill Livingstone |location=Edinburgh |year=1999 |url=https://archive.org/details/fetalmedicinebas0000unse/page/836/mode/2up |isbn=978-0-443-05357-3 |oclc=42792567 |page=837 }}</ref> Other causes include [[vascular disease]] (such as [[Systemic lupus erythematosus|lupus]]), [[diabetes mellitus|diabetes]], other [[Endocrine disease|hormonal problems]], infection, and abnormalities of the uterus.<ref name="mednet" /> Advancing maternal age and a woman's history of previous spontaneous abortions are the two leading factors associated with a greater risk of spontaneous abortion.<ref name="fetal med 837" /> A spontaneous abortion can also be caused by accidental [[Physical trauma|trauma]]; intentional trauma or stress to cause miscarriage is considered induced abortion or [[feticide]].<ref name="Fetal Homicide Laws">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncsl.org/programs/health/fethom.htm |title=Fetal Homicide Laws |access-date=7 April 2009 |publisher=National Conference of State Legislatures |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120911171355/http://www.ncsl.org/issues-research/health/fetal-homicide-state-laws.aspx |archive-date=11 September 2012}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> |
||
==Methods== |
|||
==Induction methods== |
|||
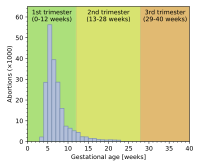
[[File:Abortionmethods.png|thumb|350px|right|[[Gestational age]] may determine which abortion methods are practiced.]] |
|||
===Medical=== |
===Medical=== |
||
{{Main|Medical abortion}} |
{{Main|Medical abortion}} |
||
{{Image frame|width=300|innerstyle=font-size:88%;|link=:File:Abortionmethods.png|caption=[[Gestational age (obstetrics)|Gestational age]] may determine which abortion methods are practiced.|content={{#invoke:Block diagram|main|width=300|height=190|<border-color #cccccc><border-width 0px 0px 0px 1px><left 30><right 30> <vcentertext><left 70><right 70> <border-width 0px><top 0><bottom 12><left 0><right 100><background-color #ffbcd8>Practice of Induced Abortion Methods<background-color #bdc9df><top 19><bottom 29><left 7.5><right 20>[[manual vacuum aspiration|MVA]]<left 40><right 65>[[dilation and evacuation|D&E]]<top 38><bottom 48><left 15><right 30>[[electric vacuum aspiration|EVA]]<left 50><right 75>[[Hysterotomy abortion|Hyst.]]<left 15><right 37.5><top 56><bottom 66>[[Dilation and curettage|D&C]]<left 50><right 75>[[Intact dilation and extraction|Intact D&X]]<left 7.5><right 30><top 74><bottom 84>[[Mifepristone|Mifepr.]]<left 40><right 75>Induced Miscarr.<left 0><right 30><background-color #b7e690><top 90><bottom 100>[[First trimester|0–12 wks]]<left 30><right 70><background-color #dfe988>[[Second trimester|12–28 weeks]]<left 70><right 100><background-color #e9c788>[[Third trimester|28–40 wks]]}}}} |
|||
Medical abortions are those induced by [[abortifacient]] pharmaceuticals. Medical abortion became an alternative method of abortion with the availability of [[prostaglandin]] [[prostaglandin analogue|analogs]] in the 1970s and the [[antiprogestin|antiprogestogen]] [[mifepristone]] (also known as RU-486) in the 1980s.<ref name=Kapp2013/><ref name=":0" /><ref name="Creinin 2009">{{cite book|vauthors=Creinin MD, Gemzell-Danielsson K |year=2009| chapter=Medical abortion in early pregnancy|veditors=Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD |title=Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care| location=Oxford|publisher=Wiley-Blackwell|pages=111–134| isbn=978-1-4051-7696-5}}</ref><ref name="Kapp 2009">{{cite book| vauthors=Kapp N, von Hertzen H |year=2009| chapter=Medical methods to induce abortion in the second trimester| veditors=Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD |title=Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care| location=Oxford|publisher=Wiley-Blackwell| pages=178–192| isbn=978-1-4051-7696-5}}</ref> |
|||
The most common early first trimester medical abortion regimens use mifepristone in combination with [[misoprostol]] (or sometimes another prostaglandin analog, [[gemeprost]]) up to 10 weeks (70 days) gestational age,<ref name=":2"/><ref name=":1">{{cite web |author=Center for Drug Evaluation and Research |title=Mifeprex (mifepristone) Information |url=https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/mifeprex-mifepristone-information |website=FDA |access-date=2 July 2019 |date=8 February 2019 |archive-date=23 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190423032409/https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm111323.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> [[methotrexate]] in combination with a prostaglandin analog up to 7 weeks gestation, or a prostaglandin analog alone.<ref name=":0" /> Mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimens work faster and are more effective at later gestational ages than methotrexate–misoprostol combination regimens, and combination regimens are more effective than misoprostol alone, particularly in the second trimester.<ref name="Creinin 2009"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wildschut H, Both MI, Medema S, Thomee E, Wildhagen MF, Kapp N | title = Medical methods for mid-trimester termination of pregnancy | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2011 | issue = 1 | pages = CD005216 | date = January 2011 | pmid = 21249669 | pmc = 8557267 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD005216.pub2 }}</ref> Medical abortion regimens involving mifepristone followed by misoprostol in the cheek between 24 and 48 hours later are effective when performed before 70 days' gestation.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chen MJ, Creinin MD | title = Mifepristone With Buccal Misoprostol for Medical Abortion: A Systematic Review | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 126 | issue = 1 | pages = 12–21 | date = July 2015 | pmid = 26241251 | doi = 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000897 | url = http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/2pw521h5 | access-date = 30 July 2019 | url-status = live | s2cid = 20800109 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200726105924/https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2pw521h5 | archive-date = 26 July 2020 }}</ref> |
|||
"Medical abortions" are non-surgical abortions that use pharmaceutical drugs, categorically called [[abortifacient]]s. In 2005, medical abortions constituted 13% of all abortions in the United States;<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Jones R. K. et al.|title=Abortion in the United States: incidence and access to services, 2005|journal=Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health|volume=40|issue=1 |pages=6–16|year=2008|url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/4000608.pdf|doi=10.1363/4000608|pmid=18318867}}</ref> in 2010 the figure increased to 17%.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2011/01/11/AR2011011107331.html | work=The Washington Post | first=Rob | last=Stein | title=Decline in U.S. abortion rate stalls | date=2011-01-11}}</ref> Combined regimens include [[methotrexate]] or [[mifepristone]], followed by a [[prostaglandin]] (either [[misoprostol]] or [[gemeprost]]: misoprostol is used in the U.S.; gemeprost is used in the UK and Sweden.) When used within 49 days gestation, approximately 92% of women undergoing medical abortion with a combined regimen completed it without surgical intervention.<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Spitz, I.M|title=Early pregnancy termination with mifepristone and misoprostol in the United States|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|year=1998|volume=338|issue=18|pmid=9562577 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199804303381801|page=1241 |last2=Bardin|first2=CW|last3=Benton |first3=L|last4=Robbins|first4=A}}</ref> Misoprostol can be used alone, but has a lower efficacy rate than combined regimens. In cases of failure of medical abortion, surgical abortion must be use to complete the procedure.<ref>{{Cite book|chapter=31. Induced Abortion|last=Trupin|first=Suzanne R.|title=Danforth's Obstetrics and Gynecology|edition=9|year=2003|editor1-last=Scott|editor1-first=James R.|editor2-last=Gibbs|editor2-first=Ronald S.|editor3-last=Karlan|editor3-first=Beth y.|editor4-last=Haney|editor4-first=Arthur F.|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|isbn=978-0781737302}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Abortion pill.jpg|thumb|right|Shown here is the typical regimen for early medical abortions (200 mg [[mifepristone]] and 800 μg [[misoprostol]]).]] |
|||
In very early abortions, up to 7 weeks [[gestation]], medical abortion using a mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimen is considered to be more effective than surgical abortion ([[vacuum aspiration]]), especially when clinical practice does not include detailed inspection of aspirated tissue.<ref name="WHO FAQs 2006">{{cite book |author=WHO Department of Reproductive Health and Research |url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241594845_eng.pdf |title=Frequently asked clinical questions about medical abortion |publisher=World Health Organization |year=2006 |isbn=92-4-159484-5 |location=Geneva |access-date=22 November 2011 |url-access=subscription |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111226115043/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241594845_eng.pdf |archive-date=26 December 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Early medical abortion regimens using mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by [[Buccal administration|buccal]] or vaginal misoprostol are 98% effective up to 9 weeks gestational age; from 9 to 10 weeks efficacy decreases modestly to 94%.<ref name=":2" /><ref name="Fjerstad 2009b">{{cite journal | vauthors = Fjerstad M, Sivin I, Lichtenberg ES, Trussell J, Cleland K, Cullins V | title = Effectiveness of medical abortion with mifepristone and buccal misoprostol through 59 gestational days | journal = Contraception | volume = 80 | issue = 3 | pages = 282–286 | date = September 2009 | pmid = 19698822 | pmc = 3766037 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2009.03.010 }} The regimen (200 mg of mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by 800 mcg of ''vaginal'' misoprostol) ''previously'' used by [[Planned Parenthood]] clinics in the United States from 2001 to March 2006 was 98.5% effective through 63 days gestation—with an ongoing pregnancy rate of about 0.5%, and an additional 1% of women having uterine evacuation for various reasons, including problematic bleeding, persistent gestational sac, clinician judgment or a woman's request. The regimen (200 mg of mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by 800 mcg of ''[[wikt:buccal|buccal]]'' misoprostol) ''currently'' used by Planned Parenthood clinics in the United States since April 2006 is 98% effective through 59 days gestation.</ref> If medical abortion fails, surgical abortion must be used to complete the procedure.<ref>{{cite book| vauthors=Holmquist S, Gilliam M |year=2008| chapter=Induced abortion| veditors=Gibbs RS, Karlan BY, Haney AF, Nygaard I |title=Danforth's obstetrics and gynecology| edition=10th| location=Philadelphia|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins| pages=586–603| isbn=978-0-7817-6937-2}}</ref> |
|||
Early medical abortions account for the majority of abortions before 9 weeks gestation in [[Abortion in Great Britain|Britain]],<ref>{{Cite report |title=Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2022 |url=https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/abortion-statistics-for-england-and-wales-2022 |publisher= [[Office for Health Improvement and Disparities]] |date=2023| access-date=2024-07-23 |language=en|section = Table 5: Legal abortions: gestation weeks by purchaser and method of abortion, residents of England and Wales, numbers, percentages, 2022 |section-url = https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/664dcb9d4f29e1d07fadcc7b/Abortion-statistics-2022-data-tables.ods}}</ref> [[Abortion in France|France]],<ref>{{cite web| vauthors=Vilain A, Mouquet MC |date=22 June 2011 |title=Voluntary terminations of pregnancies in 2008 and 2009 |location=Paris |publisher=DREES, Ministry of Health, France |url=http://www.sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/er765.pdf |access-date=22 November 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110926235733/http://www.sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/er765.pdf |archive-date=26 September 2011 }}</ref> [[Abortion in Switzerland|Switzerland]],<ref>{{cite web| date=5 July 2011|title=Abortions in Switzerland 2010| location=Neuchâtel| publisher=Office of Federal Statistics, Switzerland| url=http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/14/02/03/key/03.html|access-date=22 November 2011| url-status=dead| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111003203103/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/14/02/03/key/03.html|archive-date=3 October 2011}}</ref> [[Abortion in the United States|United States]],<ref>{{cite report | vauthors = Jones RK, Witwer E, Jerman J |title=Abortion Incidence and Service Availability in the United States, 2017 |year=2019 |publisher=Guttmacher Institute |doi=10.1363/2019.30760 |doi-access=free |pmc=5487028 }}</ref> and the [[Nordic countries]].<ref>{{cite web| vauthors=Gissler M, Heino A|date=21 February 2011| title=Induced abortions in the Nordic countries 2009| location=Helsinki| publisher=National Institute for Health and Welfare, Finland| url=http://www.stakes.fi/tilastot/tilastotiedotteet/2011/Tr09_11.pdf| access-date=22 November 2011| url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120118094034/http://www.stakes.fi/tilastot/tilastotiedotteet/2011/Tr09_11.pdf|archive-date=18 January 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Medical abortion regimens using mifepristone in combination with a prostaglandin analog are the most common methods used for second trimester abortions in [[Abortion in Canada|Canada]], most of Europe, [[Abortion in China|China]] and [[Abortion in India|India]],<ref name="Kapp 2009"/> in contrast to the United States where 96% of second trimester abortions are performed surgically by [[dilation and evacuation]].<ref name=":3">{{cite book|title=Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care| vauthors=Meckstroth K, Paul M|publisher=Wiley-Blackwell| year=2009|isbn=978-1-4051-7696-5|veditors=Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD| location=Oxford|pages=135–156|chapter=First-trimester aspiration abortion}}</ref> |
|||
A 2020 [[Cochrane review|Cochrane Systematic Review]] concluded that providing women with medications to take home to complete the second stage of the procedure for an early medical abortion results in an effective abortion.<ref name=":4">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gambir K, Kim C, Necastro KA, Ganatra B, Ngo TD | title = Self-administered versus provider-administered medical abortion | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2020 | pages = CD013181 | date = March 2020 | issue = 3 | pmid = 32150279 | pmc = 7062143 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD013181.pub2 }}</ref> Further research is required to determine if self-administered medical abortion is as safe as provider-administered medical abortion, where a health care professional is present to help manage the medical abortion.<ref name=":4" /> Safely permitting women to self-administer abortion medication has the potential to improve access to abortion.<ref name=":4" /> The review also noted a research gap concerning methods to support women who take medication at home for a self-administered abortion.<ref name=":4" /> |
|||
===Surgical=== |
===Surgical=== |
||
[[File:Vacuum-aspiration (single).svg|thumb|A vacuum aspiration abortion at eight weeks gestational age (six weeks after fertilization).<br />'''1:''' Amniotic sac<br />'''2:''' Embryo<br />'''3:''' Uterine lining<br />'''4:''' Speculum<br />'''5:''' Vacurette<br />'''6:''' Attached to a suction pump]] |
[[File:Vacuum-aspiration (single).svg|thumb|A vacuum aspiration abortion at eight weeks gestational age (six weeks after fertilization).<br />'''1:''' [[Amniotic sac]]<br />'''2:''' [[Embryo]]<br />'''3:''' [[Endometrium|Uterine lining]]<br />'''4:''' [[Speculum (medical)|Speculum]]<br />'''5:''' Vacurette<br />'''6:''' Attached to a [[Vacuum pump|suction pump]]]] |
||
In the first 12 weeks, [[suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]] or vacuum abortion is the most common method.<ref>{{cite web|author=Healthwise |url=http://www.webmd.com/hw/womens_conditions/tw1078.asp#tw1112 |title=Manual and vacuum aspiration for abortion |year=2004 |publisher=[[WebMD]] |accessdate=2008-12-05}}</ref> ''Manual [[vacuum aspiration]]'' (MVA) abortion consists of removing the [[fetus]] or [[embryo]], [[placenta]] and membranes by suction using a manual syringe, while ''electric [[vacuum aspiration]]'' (EVA) abortion uses an electric pump. These techniques are comparable, and differ in the mechanism used to apply suction, how early in pregnancy they can be used, and whether cervical dilation is necessary. MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and "[[menstrual extraction]]", can be used in very early pregnancy, and does not require cervical dilation. Surgical techniques are sometimes referred to as 'Suction (or surgical) Termination Of Pregnancy' (STOP). From the 15th week until approximately the 26th, [[dilation and evacuation]] (D&E) is used. D&E consists of opening the [[cervix]] of the uterus and emptying it using surgical instruments and suction. |
|||
Up to 15 weeks' gestation, [[suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]] or vacuum aspiration are the most common surgical methods of induced abortion.<ref>{{cite web| author=Healthwise |url=http://www.webmd.com/hw/womens_conditions/tw1078.asp#tw1112 |title=Manual and vacuum aspiration for abortion |year=2004 |website=WebMD |access-date=5 December 2008| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070211155626/http://www.webmd.com/hw/womens_conditions/tw1078.asp| archive-date=11 February 2007| url-status= live}}</ref> ''Manual vacuum aspiration'' (MVA) consists of removing the [[fetus]] or [[embryo]], [[placenta]], and membranes by suction using a manual syringe, while ''electric vacuum aspiration'' (EVA) uses an electric pump. Both techniques can be used very early in pregnancy. MVA can be used up to 14 weeks but is more often used earlier in the U.S. EVA can be used later.<ref name=":3" /> |
|||
MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and "[[menstrual extraction]]", or EVA can be used in very early pregnancy when cervical dilation may not be required. [[Dilation and curettage]] (D&C) refers to opening the cervix (dilation) and removing tissue (curettage) via suction or sharp instruments. D&C is a standard gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. The [[World Health Organization]] recommends ''sharp curettage'' only when suction aspiration is unavailable.<ref>{{cite book|title=Managing Complications in Pregnancy and Childbirth: A Guide for Midwives and Doctors| author=World Health Organization| publisher=World Health Organization| year=2017| isbn=978-92-4-154587-7| location=Geneva| chapter=Dilatation and curettage| oclc=181845530| access-date=30 July 2019|chapter-url=https://www.who.int/reproductive-health/impac/Procedures/Dilatetion_P61_P63.html|archive-date=19 May 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090519162903/http://www.who.int/reproductive-health/impac/Procedures/Dilatetion_P61_P63.html| url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[Dilation and evacuation]] (D&E), used after 12 to 16 weeks, consists of opening the [[cervix]] and emptying the uterus using surgical instruments and suction. D&E is performed vaginally and does not require an incision. [[Intact dilation and extraction]] (D&X) refers to a variant of D&E sometimes used after 18 to 20 weeks when removal of an intact fetus improves surgical safety or for other reasons.<ref>{{cite book| title=Dilation and evacuation. In Paul M, Lichtenberg ES Borgatta L Grimes DA Stubblefield P Creinin (eds)Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care.| vauthors = Hammond C, Chasen S |publisher=Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell|year=2009|isbn=978-1-4051-7696-5|pages=178–192}}</ref> |
|||
Abortion may also be performed surgically by hysterotomy or gravid hysterectomy. [[Hysterotomy abortion]] is a procedure similar to a [[caesarean section]] and is performed under [[general anesthesia]]. It requires a smaller incision than a caesarean section and can be used during later stages of pregnancy. Gravid hysterectomy refers to removal of the whole uterus while still containing the pregnancy. Hysterotomy and hysterectomy are associated with much higher rates of maternal morbidity and mortality than D&E or induction abortion.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = | title = ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 135: Second-trimester abortion | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 121 | issue = 6 | pages = 1394–1406 | date = June 2013 | pmid = 23812485 | doi = 10.1097/01.AOG.0000431056.79334.cc | s2cid = 205384119 }}</ref> |
|||
First trimester procedures can generally be performed using [[local anesthesia]], while second trimester methods may require [[Sedation#Levels of sedation|deep sedation]] or [[general anesthesia]].<ref name="NEJMDec2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Templeton A, Grimes DA | title = Clinical practice. A request for abortion | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 365 | issue = 23 | pages = 2198–2204 | date = December 2011 | pmid = 22150038 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMcp1103639 | doi-access = }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Allen RH, Singh R | title = Society of Family Planning clinical guidelines pain control in surgical abortion part 1 - local anesthesia and minimal sedation | language = English | journal = Contraception | volume = 97 | issue = 6 | pages = 471–477 | date = June 2018 | pmid = 29407363 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.01.014 | url = https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824(18)30036-2/abstract | access-date = 20 January 2022 | url-status = live | s2cid = 3777869 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220303075142/https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824%2818%2930036-2/fulltext | archive-date = 3 March 2022 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cansino C, Denny C, Carlisle AS, Stubblefield P | title = Society of Family Planning clinical recommendations: Pain control in surgical abortion part 2 - Moderate sedation, deep sedation, and general anesthesia | language = English | journal = Contraception | volume = 104 | issue = 6 | pages = 583–592 | date = December 2021 | pmid = 34425082 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2021.08.007 | url = https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824(21)00351-6/abstract | access-date = 20 January 2022 | url-status = live | s2cid = 237279946 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220303075141/https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824%2821%2900351-6/fulltext | archive-date = 3 March 2022 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
''[[Dilation and curettage]]'' (D&C), the second most common method of surgical abortion, is a standard gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. ''[[Curettage]]'' refers to cleaning the walls of the [[uterus]] with a [[curette]]. The [[World Health Organization]] recommends this procedure, also called ''sharp curettage,'' only when MVA is unavailable.<ref>{{Cite book|author=[[World Health Organization]] |chapter=Dilatation and curettage |chapterurl=http://www.who.int/reproductive-health/impac/Procedures/Dilatetion_P61_P63.html |title=Managing Complications in Pregnancy and Childbirth: A Guide for Midwives and Doctors |publisher=[[World Health Organization]] |location=Geneva |year=2003 |pages= |isbn=978-92-4-154587-7 |oclc=181845530 |accessdate=2008-12-05}}</ref> |
|||
===Labor induction abortion=== |
|||
Other techniques must be used to induce abortion in the second [[wiktionary:trimester|trimester]]. Premature delivery can be induced with [[prostaglandin]]; this can be coupled with injecting the [[amniotic sac|amniotic fluid]] with hypertonic solutions containing [[saline (medicine)|saline]] or [[urea]]. After the 16th week of gestation, abortions can be induced by [[intact dilation and extraction]] (IDX) (also called intrauterine cranial decompression), which requires surgical decompression of the fetus's head before evacuation. IDX is sometimes called "[[partial-birth abortion]]," which has been [[Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act|federally banned]] in the United States. A [[hysterotomy abortion]] is a procedure similar to a [[caesarean section]] and is performed under [[general anesthesia]]. It requires a smaller incision than a caesarean section and is used during later stages of pregnancy.<ref name="encarta">{{cite encyclopedia |last=McGee |first=Glenn |authorlink=Glenn McGee |coauthors=[[Jon F. Merz]] |encyclopedia=[[Encarta]] |title=Abortion |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761553899/Abortion.html |accessdate=2008-12-05 |publisher=[[Microsoft]]|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5kvWYG63q|archivedate=2009-10-31|deadurl=yes}}</ref> |
|||
In places lacking the necessary medical skill for dilation and extraction, or when preferred by practitioners, an abortion can be induced by first [[Labor induction|inducing labor]] and then [[Late termination of pregnancy#Methods|inducing fetal demise]] if necessary.<ref name=GLOWM_Late>{{cite journal| last = Borgatta | first= Lynn |journal=Global Library of Women's Medicine| date=December 2014 |volume=GLOWM.10444| doi=10.3843/GLOWM.10444| url=http://www.glowm.com/section_view/heading/Labor%20Induction%20Termination%20of%20Pregnancy/item/443| access-date=25 September 2015| title=Labor Induction Termination of Pregnancy| url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924082507/http://www.glowm.com/section_view/heading/Labor%20Induction%20Termination%20of%20Pregnancy/item/443| archive-date=24 September 2015| url-access=subscription}}</ref> This is sometimes called "induced miscarriage". This procedure may be performed from 13 weeks gestation to the third trimester. Although it is very uncommon in the United States, more than 80% of induced abortions throughout the second trimester are labor-induced abortions in Sweden and other nearby countries.<ref name=Labor_Induced_Abortion>{{cite journal | last1 = Borgatta | first1= Lynn |first2 =Nathalie |last2 =Kapp| title = Clinical guidelines. Labor induction abortion in the second trimester | journal = Contraception | volume = 84 | issue = 1 | pages = 4–18 | date = July 2011 | pmid = 21664506 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.02.005 | url = http://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824(11)00057-6/pdf | access-date = 25 September 2015 | url-status = live | quote = 10. What is the effect of feticide on labor induction abortion outcome? Deliberately causing demise of the fetus before labor induction abortion is performed primarily to avoid transient fetal survival after expulsion; this approach may be for the comfort of both the woman and the staff, to avoid futile resuscitation efforts. Some providers allege that feticide also facilitates delivery, although little data support this claim. Transient fetal survival is very unlikely after intraamniotic installation of saline or urea, which are directly feticidal. Transient survival with misoprostol for labor induction abortion at greater than 18 weeks ranges from 0% to 50% and has been observed in up to 13% of abortions performed with high-dose oxytocin. Factors associated with a higher likelihood of transient fetal survival with labor induction abortion include increasing gestational age, decreasing abortion interval and the use of nonfeticidal inductive agents such as the PGE1 analogues. | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200606205318/https://www.contraceptionjournal.org/article/S0010-7824(11)00057-6/pdf | archive-date = 6 June 2020 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
Only limited data are available comparing labor-induced abortion with the dilation and extraction method.<ref name=Labor_Induced_Abortion/> Unlike D&E, labor-induced abortions after 18 weeks may be complicated by the occurrence of brief fetal survival, which may be legally characterized as live birth. For this reason, labor-induced abortion is legally risky in the United States.<ref name=Labor_Induced_Abortion/><ref name=NAF_2015_Policy>{{cite book| title=2015 Clinical Policy Guidelines| publisher=National Abortion Federation| date=2015| url=http://prochoice.org/wp-content/uploads/2015_NAF_CPGs.pdf| access-date=30 October 2015| quote=Policy Statement: Medical induction abortion is a safe and effective method for termination of pregnancies beyond the first trimester when performed by trained clinicians in medical offices, freestanding clinics, ambulatory surgery centers, and hospitals. Feticidal agents may be particularly important when issues of viability arise.| url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150812220053/http://prochoice.org/wp-content/uploads/2015_NAF_CPGs.pdf| archive-date=12 August 2015}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists]] has recommended that an injection be used to stop the fetal heart during the first phase of the surgical abortion procedure to ensure that the fetus is not born alive.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Nuffield Council on Bioethics |chapter=Dilemmas in Current Practice: The Fetus | chapterurl=http://www.nuffieldbioethics.org/sites/default/files/files/CCD%20Chapter%204%20Dilemmas%20in%20current%20practice%20the%20fetus.pdf |accessdate=2010-12-31 |title=Critical Case Decisions in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine: Ethical Issues |publisher=Nuffield Council on Bioethics |date=June 22, 2007 |isbn=978-1-904384-14-4 |oclc=85782378}}</ref> |
|||
===Other methods=== |
===Other methods=== |
||
Historically, a number of herbs reputed to possess abortifacient properties have been used in [[folk medicine]]. Such herbs include [[tansy]], [[Mentha pulegium|pennyroyal]], [[black cohosh]], and the now-extinct [[Silphium (antiquity)|silphium]].<ref name="riddle2">{{cite book |last=Riddle |first=John M |url=https://archive.org/details/evesherbshistory0000ridd |title=Eve's herbs: a history of contraception and abortion in the West |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-674-27024-4 |location=Cambridge, MA |oclc=36126503 |author-link=John M. Riddle |url-access=registration}}</ref>{{rp|44–47, 62–63, 154–155, 230–231}} |
|||
[[File:AngkorWatAbortionAD1150.JPG|thumb|left|[[Bas-relief]] at [[Angkor Wat]], [[Cambodia]], c. 1150, depicting a [[demon]] inducing an abortion by pounding the abdomen of a pregnant woman with a [[pestle]].<ref>{{Cite book|author=Potts M ''et al.'' |title=Thousand-year-old depictions of massage abortion |journal=Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care |volume=33 |page=234 |year=2007 |quote=at Angkor, the operator is a demon.}} Also see {{Cite book|author=Mould R |title=Mould's Medical Anecdotes |page=406 |publisher=CRC Press |year=1996|isbn=978-0-85274-119-1}}</ref>]] |
|||
Historically, a number of herbs reputed to possess [[abortifacient]] properties have been used in [[folk medicine]]: [[tansy]], [[pennyroyal]], [[black cohosh]], and the now-extinct [[silphium]] (see [[Abortion#History|history of abortion]]).<ref name="riddle2">{{Cite book|first=John M. |last=Riddle |title=Eve's herbs: a history of contraception and abortion in the West |publisher=Harvard University Press |location=[[Cambridge, Massachusetts]] |year=1997 |pages= |isbn=978-0-674-27024-4 |oclc=36126503}}{{Page needed|date=August 2010}}</ref> The use of herbs in such a manner can cause serious—even lethal—side effects, such as [[multiple organ dysfunction syndrome|multiple organ failure]], and is not recommended by [[physician]]s.<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Ciganda C, Laborde A |title=Herbal infusions used for induced abortion |journal=J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. |volume=41 |issue=3 |pages=235–239 |year=2003 |pmid=12807304 |doi=10.1081/CLT-120021104 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-04}}</ref> |
|||
In 1978, one woman in Colorado died and another developed organ damage when they attempted to terminate their pregnancies by taking pennyroyal oil.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sullivan JB, Rumack BH, Thomas H, Peterson RG, Bryson P | title = Pennyroyal oil poisoning and hepatotoxicity | journal = JAMA | volume = 242 | issue = 26 | pages = 2873–2874 | date = December 1979 | pmid = 513258 | doi = 10.1001/jama.1979.03300260043027 | s2cid = 26198529 }}</ref> |
|||
Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the abdomen. The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries without necessarily succeeding in inducing [[miscarriage]].<ref>{{cite doi|10.1016/S0891-5245(98)90245-0}}</ref> Both accidental and deliberate abortions of this kind can be subject to criminal liability in many countries.{{Citation needed|date=June 2011}} In Southeast Asia, there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal massage.<ref name="potts">{{Cite journal|first=Malcolm |last=Potts |authorlink=Malcolm Potts |year=2002 |title=History of Contraception |journal=Gynecology and Obstetrics |volume=6 |issue=8 |accessdate=2008-12-04}}</ref> One of the [[bas relief]]s decorating the temple of [[Angkor Wat]] in Cambodia depicts a demon performing such an abortion upon a woman who has been sent to the [[underworld]].<ref name="potts" /> |
|||
Because the indiscriminant use of herbs as abortifacients can cause serious—even lethal—side effects, such as [[multiple organ dysfunction syndrome|multiple organ failure]],<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ciganda C, Laborde A | title = Herbal infusions used for induced abortion | journal = Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology | volume = 41 | issue = 3 | pages = 235–239 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12807304 | doi = 10.1081/CLT-120021104 | s2cid = 44851492 }}</ref> such use is not recommended by physicians. |
|||
Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the abdomen. The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries without necessarily succeeding in inducing [[miscarriage]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Smith JP | title = Risky choices: the dangers of teens using self-induced abortion attempts | journal = Journal of Pediatric Health Care | volume = 12 | issue = 3 | pages = 147–151 | year = 1998 | pmid = 9652283 | doi = 10.1016/S0891-5245(98)90245-0 }}</ref> In Southeast Asia, there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal massage.<ref name="potts">{{cite journal | vauthors = Potts M, Graff M, Taing J | title = Thousand-year-old depictions of massage abortion | journal = The Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care | volume = 33 | issue = 4 | pages = 233–234 | date = October 2007 | pmid = 17925100 | doi = 10.1783/147118907782101904 | doi-access = free | author-link1 = Malcolm Potts }}</ref> One of the [[bas relief]]s decorating the temple of [[Angkor Wat]] in Cambodia depicts a demon performing such an abortion upon a woman who has been sent to the [[underworld]].<ref name="potts" /> |
|||
Reported methods of unsafe, [[self-induced abortion]] include misuse of [[misoprostol]], and insertion of non-surgical implements such as knitting needles and clothes hangers into the uterus. These methods are rarely seen in developed countries where surgical abortion is legal and available.<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Thapa SR, Rimal D, Preston J |title=Self induction of abortion with instrumentation |journal=Aust Fam Physician |volume=35 |issue=9 |pages=697–698 |year=2006 |month=September |pmid=16969439 |doi= |url=http://www.racgp.org.au/afp/200609/11015 |accessdate=2008-12-04}}</ref> |
|||
{{-}}<!-- The clr tag prevents the picture from running into the next section. Please keep it at the bottom of this section. --> |
|||
Reported methods of unsafe, [[self-induced abortion]] include misuse of [[misoprostol]] and insertion of non-surgical implements such as knitting needles and [[clothes hanger]]s into the uterus. These and other methods to terminate pregnancy may be called "induced miscarriage". Such methods are rarely used in countries where surgical abortion is legal and available.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Thapa SR, Rimal D, Preston J | title = Self induction of abortion with instrumentation | journal = Australian Family Physician | volume = 35 | issue = 9 | pages = 697–698 | date = September 2006 | pmid = 16969439 | url = http://www.racgp.org.au/afp/200609/11015 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090108181951/http://www.racgp.org.au/afp/200609/11015 | archive-date = 8 January 2009 }}</ref> |
|||
==Complications== |
|||
{{clear}}<!-- The clr tag prevents the picture from running into the next section. Please keep it at the bottom of this section. --> |
|||
The health risks of abortion depend on whether the procedure is performed safely or unsafely. The [[World Health Organization]] defines unsafe abortions as those performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities.<ref name="who-unsafe-1995">{{cite web| publisher = [[World Health Organization]] | title = The Prevention and Management of Unsafe Abortion | date = April 1995 | accessdate = June 1, 2010 | url = http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1992/WHO_MSM_92.5.pdf |format = [[Portable Document Format|PDF]]}}</ref> |
|||
==Safety== |
|||
=== Safe abortion === |
|||
[[File:Abortion Quick & Pain Free sign, Joe Slovo Park, Cape Town, South Africa-3869.jpg|thumb|right|A likely illegal abortion flyer in South Africa]] |
|||
Abortion, when performed in the [[developed country|developed world]] in countries where abortion is legal, is among the safest procedures in medicine.<ref name="lancet-grimes">{{cite journal |author=Grimes DA, Benson J, Singh S, ''et al.'' |title=Unsafe abortion: the preventable pandemic |journal=Lancet |volume=368 |issue=9550 |pages=1908–19 |year=2006 |month=November |pmid=17126724 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69481-6 |url=http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/general/lancet_4.pdf}}</ref><ref name="grimes-overview">{{cite journal |author=Grimes DA, Creinin MD |title=Induced abortion: an overview for internists |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=140 |issue=8 |pages=620–6 |year=2004 |month=April |pmid=15096333 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/content/140/8/620.full}}</ref> In the US, the [[mortality rate|risk of maternal death]] from abortion is 0.567 per 100,000 procedures, making abortion approximately 14 times safer than childbirth (7.06 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births).<ref name="grimes-mortality">{{cite journal |author=Grimes DA |title=Estimation of pregnancy-related mortality risk by pregnancy outcome, United States, 1991 to 1999 |journal=Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. |volume=194 |issue=1 |pages=92–4 |year=2006 |month=January |pmid=16389015 |doi=10.1016/j.ajog.2005.06.070 |url=}}</ref> The risk of abortion-related mortality increases with increasing gestational age, but remains lower than that of childbirth through at least 21 weeks' gestation.<ref name="bartlett">{{cite journal |author=Bartlett LA, Berg CJ, Shulman HB, ''et al.'' |title=Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States |journal=Obstet Gynecol |volume=103 |issue=4 |pages=729–37 |year=2004 |month=April |pmid=15051566 |doi=10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60 |url=}}</ref><ref name="emedicine">{{cite web | publisher = [[eMedicine]] | title = Elective Abortion | date = May 27, 2010 | accessdate = June 1, 2010 | first = Suzanne | last = Trupin | quote = At every gestational age, elective abortion is safer for the mother than carrying a pregnancy to term. | url = http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/252560-overview}}</ref> |
|||
The health risks of abortion depend principally on how, and under what conditions, the procedure is performed. The [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) defines [[unsafe abortion]]s as those performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities.<ref name="who-unsafe-1992">{{cite web| publisher=World Health Organization |title=The Prevention and Management of Unsafe Abortion |date=April 1992| access-date=18 October 2017 |url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1992/WHO_MSM_92.5.pdf | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20100530072310/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1992/WHO_MSM_92.5.pdf| archive-date= 30 May 2010 | url-status= live}}</ref> Legal abortions performed in the [[developed country|developed world]] are among the safest procedures in medicine.<ref name="lancet-grimes" >{{cite journal | vauthors = Grimes DA, Benson J, Singh S, Romero M, Ganatra B, Okonofua FE, Shah IH | title = Unsafe abortion: the preventable pandemic | journal = Lancet | volume = 368 | issue = 9550 | pages = 1908–1919 | date = November 25, 2006 | pmid = 17126724 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69481-6 | url = https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(06)69481-6/fulltext | s2cid = 6188636 | url-access = subscription | access-date = 8 June 2023 | archive-date = 3 April 2023 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230403232414/https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(06)69481-6/fulltext | url-status = live }}</ref><ref name="grimes-overview">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grimes DA, Creinin MD | title = Induced abortion: an overview for internists | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | volume = 140 | issue = 8 | pages = 620–626 | date = April 2004 | pmid = 15096333 | doi = 10.7326/0003-4819-140-8-200404200-00009 | doi-access = free | citeseerx = 10.1.1.694.3531 }}</ref> According to a 2012 study in ''Obstetrics & Gynecology'', in the United States the risk of maternal mortality is 14 times lower after induced abortion than after childbirth.<ref name=Grimes2012>{{cite journal | first1 = Elizabeth G| last1 = Raymond| last2= Grimes |first2= David A | author-link2=David Grimes (physician)| title = The comparative safety of legal induced abortion and childbirth in the United States | journal = [[Obstetrics & Gynecology (journal)|Obstetrics & Gynecology]] | volume = 119 | issue = 2 Pt 1 | pages = 215–219 | date = February 2012 | pmid = 22270271 | doi = 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823fe923 | quote = Conclusion: Legal induced abortion is markedly safer than childbirth. The risk of death associated with childbirth is approximately 14 times higher than that with abortion. Similarly, the overall morbidity associated with childbirth exceeds that with abortion. | s2cid = 25534071 }}</ref> The CDC estimated in 2019 that US pregnancy-related mortality was 17.2 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Petersen EE, Davis NL, Goodman D, Cox S, Mayes N, Johnston E, Syverson C, Seed K, Shapiro-Mendoza CK, Callaghan WM, Barfield W | display-authors = 6 | title = Vital Signs: Pregnancy-Related Deaths, United States, 2011–2015, and Strategies for Prevention, 13 States, 2013-2017 | journal = MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report | volume = 68 | issue = 18 | pages = 423–429 | date = May 2019 | pmid = 31071074 | pmc = 6542194 | doi = 10.15585/mmwr.mm6818e1 }}</ref> while the US abortion mortality rate was 0.43 maternal deaths per 100,000 procedures.<ref name="Ray2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Raymond EG, Grossman D, Weaver MA, Toti S, Winikoff B | title = Mortality of induced abortion, other outpatient surgical procedures and common activities in the United States | journal = Contraception | volume = 90 | issue = 5 | pages = 476–479 | date = November 2014 | pmid = 25152259 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2014.07.012 | quote = Results: The abortion-related mortality rate in 2000–2009 in the United States was 0.7 per 100,000 abortions. Studies in approximately the same years found mortality rates of 0.8-1.7 deaths per 100,000 plastic surgery procedures, 0-1.7 deaths per 100,000 dental procedures, 0.6-1.2 deaths per 100,000 marathons run and at least 4 deaths among 100,000 cyclists in a large annual bicycling event. The traffic fatality rate per 758 vehicle miles traveled by passenger cars in the United States in 2007-2011 was about equal to the abortion-related mortality rate. Conclusions: The safety of induced abortion as practiced in the United States for the past decade met or exceeded expectations for outpatient surgical procedures and compared favorably to that of two common nonmedical voluntary activities. }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.nap.edu/read/24950/chapter/4|title=Read "The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the United States" at NAP.edu|doi=10.17226/24950|pmid=29897702|year=2018|isbn=978-0-309-46818-3 | author2 = Health Medicine Division| author1 = National Academies of Sciences Engineering |author3=Board on Health Care Services|author4=Board on Population Health Public Health Practice|author5=Committee on Reproductive Health Services: Assessing the Safety Quality of Abortion Care in the U.S|access-date=26 May 2019|archive-date=24 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200724204509/https://www.nap.edu/read/24950/chapter/4|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=CDC_2022_AS>{{cite journal |last=Kortsmit |first=Katherine |date=2022 |title=Abortion Surveillance — United States, 2020 |url=https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/ss/ss7110a1.htm |journal=MMWR. Surveillance Summaries |language=en-us |volume=71 |issue=10 |pages=1–27 |doi=10.15585/mmwr.ss7110a1 |issn=1546-0738 |pmc=9707346 |pmid=36417304 |quote=The national case-fatality rate for legal induced abortion for 2013–2019 was 0.43 deaths related to legal induced abortions per 100,000 reported legal abortions. This case-fatality rate was lower than the rates for the previous 5-year periods. |access-date=14 November 2023 |archive-date=15 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231115033902/https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/ss/ss7110a1.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> In the UK, guidelines of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists state that "Women should be advised that abortion is generally safer than continuing a pregnancy to term."<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Donnelly L |title=Abortion is Safer than Having a Baby, Doctors Say|journal=The Telegraph|date=26 February 2011}}</ref> Worldwide, on average, abortion is safer than carrying a pregnancy to term. A 2007 study reported that "26% of all pregnancies worldwide are terminated by induced abortion," whereas "deaths from improperly performed [abortion] procedures constitute 13% of maternal mortality globally."<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dixon-Mueller R, Germain A | title = Fertility regulation and reproductive health in the Millennium Development Goals: the search for a perfect indicator | journal = American Journal of Public Health | volume = 97 | issue = 1 | pages = 45–51 | date = January 2007 | pmid = 16571693 | pmc = 1716248 | doi = 10.2105/AJPH.2005.068056 }}</ref> In Indonesia in 2000 it was estimated that 2 million pregnancies ended in abortion, 4.5 million pregnancies were carried to term, and 14–16 percent of maternal deaths resulted from abortion.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/report_pdf/ib_abortion_indonesia_0.pdf |title=Abortion in Indonesia |publisher=Guttmacher Institute |year=2008 |access-date=13 October 2019 |archive-date=7 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200607212421/https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/report_pdf/ib_abortion_indonesia_0.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Vacuum aspiration]] in the first trimester is the safest method of surgical abortion, and can be performed in a [[primary care|primary care office]], [[abortion clinic]], or hospital. Complications are rare and can include [[uterine perforation]], [[endometritis|pelvic infection]], and retained products of conception requiring a second procedure to evacuate.<ref name="arch-fam-practice">{{cite journal |author=Westfall JM, Sophocles A, Burggraf H, Ellis S |title=Manual vacuum aspiration for first-trimester abortion |journal=Arch Fam Med |volume=7 |issue=6 |pages=559–62 |year=1998 |pmid=9821831 |doi= |url=http://archfami.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/7/6/559}}</ref> Preventive antibiotics (such as [[doxycycline]] or [[metronidazole]]) are typically given before elective abortion,<ref>{{cite journal |author= |title=ACOG practice bulletin No. 104: antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures |journal=Obstet Gynecol |volume=113 |issue=5 |pages=1180–9 |year=2009 |month=May |pmid=19384149 |doi=10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d011 |url= |author1= ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins--Gynecology}}</ref> as they are believed to substantially reduce the risk of postoperative uterine infection.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Sawaya GF, Grady D, Kerlikowske K, Grimes DA |title=Antibiotics at the time of induced abortion: the case for universal prophylaxis based on a meta-analysis |journal=Obstet Gynecol |volume=87 |issue=5 Pt 2 |pages=884–90 |year=1996 |month=May |pmid=8677129 |doi= |url=}}</ref> Complications after second-trimester abortion are similar to those after first-trimester abortion, and depend somewhat on the method chosen. A 2008 [[Cochrane Library]] review found that [[dilation and evacuation]] was safer than other means of second-trimester abortion.<ref name="cochrane-2nd-tri">{{cite journal |author=Lohr PA, Hayes JL, Gemzell-Danielsson K |title=Surgical versus medical methods for second trimester induced abortion |journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev |volume= |issue=1 |pages=CD006714 |year=2008 |pmid=18254113 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD006714.pub2 |url=http://mrw.interscience.wiley.com/cochrane/clsysrev/articles/CD006714/frame.html |editor1-last=Lohr |editor1-first=Patricia A.}}</ref> |
|||
In the US from 2000 to 2009, abortion had a mortality rate lower than [[plastic surgery]], lower or similar to running a marathon, and about equivalent to traveling {{convert|760|miles}} in a passenger car.{{ r | Ray2014 }} Five years after seeking abortion services, women who gave birth after being denied an abortion reported worse health than women who had either first or second trimester abortions.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ralph LJ, Schwarz EB, Grossman D, Foster DG | title = Self-reported Physical Health of Women Who Did and Did Not Terminate Pregnancy After Seeking Abortion Services: A Cohort Study | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | volume = 171 | issue = 4 | pages = 238–247 | date = August 2019 | pmid = 31181576 | doi = 10.7326/M18-1666 | s2cid = 184482546 }}</ref> The risk of abortion-related mortality increases with gestational age, but remains lower than that of childbirth.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Raymond EG, Grimes DA | title = The comparative safety of legal induced abortion and childbirth in the United States | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 119 | issue = 2 Pt 1 | pages = 215–219 | date = February 2012 | pmid = 22270271 | doi = 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823fe923 | s2cid = 25534071 }}</ref> Outpatient abortion is as safe from 64 to 70 days' gestation as it before 63 days.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Abbas D, Chong E, Raymond EG | title = Outpatient medical abortion is safe and effective through 70 days gestation | journal = Contraception | volume = 92 | issue = 3 | pages = 197–199 | date = September 2015 | pmid = 26118638 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2015.06.018 }}</ref> |
|||
Medical abortion with [[mifepristone]] and [[misoprostol]] is effective through 49 days of gestational age.<ref name="nejm-mifepristone">{{cite journal |author=Spitz IM, Bardin CW, Benton L, Robbins A |title=Early pregnancy termination with mifepristone and misoprostol in the United States |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=338 |issue=18 |pages=1241–7 |year=1998 |month=April |pmid=9562577 |doi= 10.1056/NEJM199804303381801|url=}}</ref> It has been used in women up to 63 days of gestational age, albeit with an increased risk of failure (requiring surgical abortion).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Aubény E, Peyron R, Turpin CL, ''et al.'' |title=Termination of early pregnancy (up to 63 days of amenorrhea) with mifepristone and increasing doses of misoprostol [corrected] |journal=Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud |volume=40 Suppl 2 |issue= |pages=85–91 |year=1995 |pmid=8574255 |doi= |url=}}</ref> Medical abortion is generally considered as safe as surgical abortion in the first trimester, but is associated with more pain and a lower success rate (requiring surgical abortion).<ref name="who-medical-abortion">{{cite web | publisher = [[World Health Organization]] | title = Medical versus surgical methods for first trimester termination of pregnancy | url = http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/pccom/en/index.html | date = December 15, 2006 | accessdate = June 1, 2010}}</ref> Overall, the risk of [[endometritis|uterine infection]] is lower with medical than with surgical abortion,<ref name="nejm-mifepristone"/> although in 2005 four deaths after medical abortion were reported due to infection with ''[[Clostridium sordellii]]''.<ref name="c-sordellii">{{cite journal |author=Fischer M, Bhatnagar J, Guarner J, ''et al.'' |title=Fatal toxic shock syndrome associated with Clostridium sordellii after medical abortion |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=353 |issue=22 |pages=2352–60 |year=2005 |month=December |pmid=16319384 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa051620 |url=}}</ref> As a result, some abortion providers have begun using preventive antibiotics with medical abortion.<ref name="nejm-pp">{{cite journal |author=Fjerstad M, Trussell J, Sivin I, Lichtenberg ES, Cullins V |title=Rates of serious infection after changes in regimens for medical abortion |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=361 |issue=2 |pages=145–51 |year=2009 |month=July |pmid=19587339 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0809146 |url=}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Safety of abortion methods === |
||
There is little difference in terms of safety and efficacy between medical abortion using a combined regimen of mifepristone and misoprostol and surgical abortion (vacuum aspiration) in early first trimester abortions up to 10 weeks gestation.<ref name="WHO FAQs 2006"/> Medical abortion using the prostaglandin analog misoprostol alone is less effective and more painful than medical abortion using a combined regimen of mifepristone and misoprostol or surgical abortion.<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = Grossman D|date=3 September 2004|title=Medical methods for first trimester abortion: RHL commentary|work=Reproductive Health Library|location=Geneva|publisher=World Health Organization|url=http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/dgcom/en/index.html|access-date=22 November 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111028054620/http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/dgcom/en/index.html|archive-date=28 October 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Chien P, Thomson M |date=15 December 2006|title=Medical versus surgical methods for first trimester termination of pregnancy: RHL commentary|work=Reproductive Health Library|location=Geneva|publisher=World Health Organization|url=http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/pccom/en/index.html |access-date=1 June 2010| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20100517201143/http://apps.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/pccom/en/index.html| archive-date= 17 May 2010 | url-status= dead}}</ref> |
|||
{{main|Unsafe abortion}} |
|||
In contrast, unsafe abortion is a major cause of injury and death among women worldwide. Although data are imprecise, it is estimated that approximately 20 million unsafe abortions are performed annually, with 97% taking place in [[developing country|developing countries]].<ref name="lancet-grimes"/> Unsafe abortion is believed to result in approximately 68,000 deaths and millions of injuries annually.<ref name="lancet-grimes"/> The legal status of abortion is believed to play a major role in the frequency of unsafe abortion.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Berer M |title=National laws and unsafe abortion: the parameters of change |journal=Reprod Health Matters |volume=12 |issue=24 Suppl |pages=1–8 |year=2004 |month=November |pmid=15938152 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="berer-who"/> For example, the 1996 legalization of abortion in [[South Africa]] had an immediate positive impact on the frequency of abortion-related complications,<ref name="jewkes">{{cite journal |author=Jewkes R, Rees H, Dickson K, Brown H, Levin J |title=The impact of age on the epidemiology of incomplete abortions in South Africa after legislative change |journal=BJOG |volume=112 |issue=3 |pages=355–9 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15713153 |doi=10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00422.x |url=}}</ref> with abortion-related deaths dropping by more than 90%.<ref name="bateman-samj">{{cite journal |author=Bateman C |title=Maternal mortalities 90% down as legal TOPs more than triple |journal=S. Afr. Med. J. |volume=97 |issue=12 |pages=1238–42 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18264602 |doi= |url=}}</ref> Groups such as the [[World Health Organization]] have advocated a public-health approach to addressing unsafe abortion, emphasizing the legalization of abortion, the training of medical personnel, and ensuring access to reproductive-health services.<ref name="berer-who">{{cite journal |author=Berer M |title=Making abortions safe: a matter of good public health policy and practice |journal=Bull. World Health Organ. |volume=78 |issue=5 |pages=580–92 |year=2000 |pmid=10859852 |pmc=2560758 |doi= |url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2560758/}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Safety and gestational age=== |
||
[[Vacuum aspiration]] in the first trimester is the safest method of surgical abortion, and can be performed in a [[primary care|primary care office]], [[abortion clinic]], or hospital. Complications, which are rare, can include [[uterine perforation]], [[endometritis|pelvic infection]], and retained products of conception requiring a second procedure to evacuate.<ref name="arch-fam-practice">{{cite journal | vauthors = Westfall JM, Sophocles A, Burggraf H, Ellis S | title = Manual vacuum aspiration for first-trimester abortion | journal = Archives of Family Medicine | volume = 7 | issue = 6 | pages = 559–562 | year = 1998 | pmid = 9821831 | doi = 10.1001/archfami.7.6.559 | url = http://archfami.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/7/6/559 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20050405202853/http://archfami.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/7/6/559 | archive-date = 5 April 2005 | url-access = subscription }}</ref> Infections account for one-third of abortion-related deaths in the United States.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dempsey A | title = Serious infection associated with induced abortion in the United States | journal = Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 55 | issue = 4 | pages = 888–892 | date = December 2012 | pmid = 23090457 | doi = 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31826fd8f8 }}</ref> The rate of complications of vacuum aspiration abortion in the first trimester is similar regardless of whether the procedure is performed in a hospital, surgical center, or office.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = White K, Carroll E, Grossman D | title = Complications from first-trimester aspiration abortion: a systematic review of the literature | journal = Contraception | volume = 92 | issue = 5 | pages = 422–438 | date = November 2015 | pmid = 26238336 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2015.07.013 }}</ref> Preventive antibiotics (such as [[doxycycline]] or [[metronidazole]]) are typically given before abortion procedures,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = | title = ACOG practice bulletin No. 104: antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 113 | issue = 5 | pages = 1180–1189 | date = May 2009 | pmid = 19384149 | doi = 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d011 | doi-access = }}</ref> as they are believed to substantially reduce the risk of postoperative uterine infection;<ref name="NEJMDec2011" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sawaya GF, Grady D, Kerlikowske K, Grimes DA | title = Antibiotics at the time of induced abortion: the case for universal prophylaxis based on a meta-analysis | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 87 | issue = 5 Pt 2 | pages = 884–890 | date = May 1996 | pmid = 8677129 }}</ref> however, antibiotics are not routinely given with abortion pills.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Achilles SL, Reeves MF | title = Prevention of infection after induced abortion: release date October 2010: SFP guideline 20102 | journal = Contraception | volume = 83 | issue = 4 | pages = 295–309 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 21397086 | doi = 10.1016/j.contraception.2010.11.006 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The rate of failed procedures does not appear to vary significantly depending on whether the abortion is performed by a doctor or a [[mid-level practitioner]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Barnard S, Kim C, Park MH, Ngo TD | title = Doctors or mid-level providers for abortion | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2015 | issue = 7 | pages = CD011242 | date = July 2015 | pmid = 26214844 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD011242.pub2 | pmc = 9188302 | url = https://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/2274695/1/Doctors%20or%20mid-level%20providers%20for%20abortion_GREEN%20VoR.pdf | access-date = 24 November 2019 | archive-date = 27 August 2021 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210827202229/https://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/id/eprint/2274695/1/Doctors | url-status = live }}</ref> |
|||
{{main|Abortion-breast cancer hypothesis}} |
|||
Although some studies have postulated an [[abortion – breast cancer hypothesis|association between abortion and breast cancer]], the best available evidence at present does not support such a link. Major medical bodies, including the [[World Health Organization]],<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs240/en/| title=Induced abortion does not increase breast cancer risk (Fact sheet N°240)| publisher=World Health Organization| accessdate=2011-01-06}}</ref> the U.S. [[National Cancer Institute]],<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/risk/abortion-miscarriage| title=Abortion, Miscarriage, and Breast Cancer Risk| publisher=National Cancer Institute| accessdate=2011-01-11}}</ref> the [[American Cancer Society]],<ref name="acs-abortion-breast-cancer">{{cite web | url = http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/BreastCancer/MoreInformation/is-abortion-linked-to-breast-cancer | publisher = [[American Cancer Society]] | date = September 23, 2010 | accessdate = June 20, 2011 | title = Is Abortion Linked to Breast Cancer? | quote = At this time, the scientific evidence does not support the notion that abortion of any kind raises the risk of breast cancer.}}</ref> and the [[Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists]],<ref name="rcog_2000">{{cite web |url=http://www.rcog.org.uk/files/rcog-corp/uploaded-files/NEBAbortionSummary.pdf |title=The Care of Women Requesting Induced Abortion |page=9 |format=PDF |work=Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists |accessdate=2008-06-29|quote=Induced abortion is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk.}}</ref> have concluded on the basis of existing evidence that abortion does not cause breast cancer.<ref name="JASEN">{{cite journal |author=Jasen P |title=Breast cancer and the politics of abortion in the United States |journal=Med Hist |volume=49 |issue=4 |pages=423–44 |year=2005 |pmid=16562329 |pmc=1251638}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.acog.org/from_home/publications/press_releases/nr07-31-03-2.cfm| title=ACOG Finds No Link Between Abortion and Breast Cancer Risk| date=July 31, 2003| publisher= American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists| accessdate=2011-01-11}}</ref> Currently, the concept of a link between induced abortion and breast cancer is promoted primarily by pro-life groups.<ref name="JASEN"/> |
|||
Complications after second trimester abortion are similar to those after first trimester abortion, and depend somewhat on the method chosen.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lerma K, Shaw KA | title = Update on second trimester medical abortion | journal = Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology | volume = 29 | issue = 6 | pages = 413–418 | date = December 2017 | pmid = 28922193 | doi = 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000409 | quote = Second trimester surgical abortion is well tolerated and increasingly expeditious | s2cid = 12459747 }}</ref> The risk of death from abortion approaches roughly half the risk of death from childbirth the farther along a woman is in pregnancy; from one in a million before 9 weeks gestation to nearly one in ten thousand at 21 weeks or more (as measured from the last menstrual period).<ref>{{cite journal | collaboration = Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology | vauthors = Steinauer J, Jackson A, Grossman D |title=Second-trimester abortion. Practice Bulletin No. 135. |journal=American College of Obstetrics & Gynecology - Practice Bulletins |date=June 2013 |url=https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Practice-Bulletins/Committee-on-Practice-Bulletins-Gynecology/Second-Trimester-Abortion |access-date=4 December 2019 |quote=The mortality rate associated with abortion is low (0.6 per 100,000 legal, induced abortions), and the risk of death associated with childbirth is approximately 14 times higher than that with abortion. Abortion-related mortality increases with each week of gestation, with a rate of 0.1 per 100,000 procedures at 8 weeks of gestation or less, and 8.9 per 100,000 procedures at 21 weeks of gestation or greater. |archive-date=24 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191224111109/https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Practice-Bulletins/Committee-on-Practice-Bulletins-Gynecology/Second-Trimester-Abortion |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=Bartlett2004>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bartlett LA, Berg CJ, Shulman HB, Zane SB, Green CA, Whitehead S, Atrash HK | title = Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 103 | issue = 4 | pages = 729–737 | date = April 2004 | pmid = 15051566 | doi = 10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60 | quote = The risk factor that continues to be most strongly associated with mortality from legal abortion is gestational age at the time of the abortion | s2cid = 42597014 | doi-access = free }}</ref> It appears that having had a prior surgical uterine evacuation (whether because of induced abortion or treatment of miscarriage) correlates with a small increase in the risk of preterm birth in future pregnancies. The studies supporting this did not control for factors not related to abortion or miscarriage, and hence the causes of this correlation have not been determined, although multiple possibilities have been suggested.<ref name=Saccone2016>{{cite journal | vauthors = Saccone G, Perriera L, Berghella V | title = Prior uterine evacuation of pregnancy as independent risk factor for preterm birth: a systematic review and metaanalysis | journal = American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 214 | issue = 5 | pages = 572–591 | date = May 2016 | pmid = 26743506 | doi = 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.12.044 | url = https://www.iris.unina.it/retrieve/handle/11588/697884/158333/25%20Abortion%20PTB%20-%20AJOG%20-%20SACCONE.pdf | access-date = 27 June 2020 | url-status = live | quote = Prior surgical uterine evacuation for either I-TOP[induced termination of pregnancy] or SAB[spontaneous abortion, - also known as miscarriage] is an independent risk factor for PTB[pre-term birth]. These data warrant caution in the use of surgical uterine evacuation and should encourage safer surgical techniques as well as medical methods. | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210827202228/https://www.iris.unina.it/retrieve/handle/11588/697884/158333/25%20Abortion%20PTB%20-%20AJOG%20-%20SACCONE.pdf | archive-date = 27 August 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Averbach SH, Seidman D, Steinauer J, Darney P | title = Re: Prior uterine evacuation of pregnancy as independent risk factor for preterm birth: a systematic review and metaanalysis | journal = American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology | volume = 216 | issue = 1 | page = 87 | date = January 2017 | pmid = 27596618 | doi = 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.08.038 | url = https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(16)30650-0/fulltext | access-date = 28 June 2020 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210827202230/https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378%2816%2930650-0/fulltext | archive-date = 27 August 2021 | doi-access = | url-access = subscription }}</ref> |
|||
===Mental health=== |
===Mental health=== |
||
{{Main|Abortion and mental health}} |
{{Main|Abortion and mental health}} |
||
No scientific research has demonstrated that abortion is a cause of poor mental health in the general population. However there are groups of women who may be at higher risk of coping with problems and distress following abortion.<ref name="Cockburn">{{Cite book|last1=Cockburn|first1=Jayne |last2=Pawson|first2=Michael E. |title=Psychological Challenges to Obstetrics and Gynecology: The Clinical Management |year=2007 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-1-84628-807-4 |page=243}}</ref> Some factors in a woman's life, such as emotional attachment to the pregnancy, lack of social support, pre-existing psychiatric illness, and conservative views on abortion increase the likelihood of experiencing negative feelings after an abortion.<ref name="APA89">{{Cite journal|author=Adler NE, David HP, Major BN, Roth SH, Russo NF, Wyatt GE |title=Psychological responses after abortion |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |volume=248 |issue=4951 |pages=41–4 |year=1990 |pmid=2181664 |doi=10.1126/science.2181664}}</ref> The [[American Psychological Association]] (APA) concluded that first trimester abortion does not lead to increased mental health problems,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.apa.org/pi/women/programs/abortion/mental-health.pdf |title=Report of the APA Task Force on Mental Health and Abortion |publisher=[[American Psychological Association]] |location=Washington, DC |date=August 13, 2008}}</ref> and further research has concluded that later abortions are no different.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Steinberg | first1 = J. R.| title = Later Abortions and Mental Health: Psychological Experiences of Women Having Later Abortions—A Critical Review of Research | doi = 10.1016/j.whi.2011.02.002 | journal = Women's Health Issues | volume = 21 | issue = 3 | pages = S44–S48 | year = 2011 | pmid = 21530839}}</ref> |
|||
Current evidence finds no relationship between most induced abortions and [[abortion and mental health|mental health problems]]<ref name=BMJ2014/><ref name=Hor2017>{{cite journal | vauthors = Horvath S, Schreiber CA | title = Unintended Pregnancy, Induced Abortion, and Mental Health | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 19 | issue = 11 | page = 77 | date = September 2017 | pmid = 28905259 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-017-0832-4 | s2cid = 4769393 }}</ref> other than those expected for any unwanted pregnancy.<ref name="apa-press"/> A report by the [[American Psychological Association]] concluded that a woman's first abortion is not a threat to mental health when carried out in the first trimester, with such women no more likely to have mental-health problems than those carrying an unwanted pregnancy to term; the mental-health outcome of a woman's second or greater abortion is less certain.<ref name="apa-press">{{cite press release |publisher=American Psychological Association |title=APA Task Force Finds Single Abortion Not a Threat to Women's Mental Health |date=12 August 2008 |access-date=7 September 2011 |url=http://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2008/08/single-abortion.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110906022824/http://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2008/08/single-abortion.aspx |archive-date=6 September 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.apa.org/pi/women/programs/abortion/mental-health.pdf |title=Report of the APA Task Force on Mental Health and Abortion |publisher=American Psychological Association|location=Washington, DC |date=13 August 2008 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100615020211/http://apa.org/pi/women/programs/abortion/mental-health.pdf |archive-date=15 June 2010 }}</ref> Some older reviews concluded that abortion was associated with an increased risk of psychological problems;<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Coleman PK | title = Abortion and mental health: quantitative synthesis and analysis of research published 1995-2009 | journal = The British Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 199 | issue = 3 | pages = 180–186 | date = September 2011 | pmid = 21881096 | doi = 10.1192/bjp.bp.110.077230 | doi-access = free }}</ref> however, later reviews of the medical literature found that previous reviews did not use an appropriate control group.<ref name=Hor2017/> When a control group is utilized, receiving abortion is not associated with adverse psychological outcomes.<ref name=Hor2017/> However, women seeking abortion who are denied access to abortion have an increase in anxiety after the denial.<ref name=Hor2017/> |
|||
Some proposed negative psychological effects of abortion have been referred to by pro-life advocates as a separate condition called [[Abortion_and_mental_health#Post-Abortion_Syndrome|"post-abortion syndrome"]]. However, the existence of "post-abortion syndrome" is not recognized by any medical or psychological organization.<ref name="Grimes">{{Cite journal|author=Grimes DA, Creinin MD |title=Induced abortion: an overview for internists |journal=[[Ann Intern Med]] |volume=140 |issue=8 |pages=620–6 |year=2004 |pmid=15096333 |doi=10.1001/archinte.140.5.620 |quote=Abortion does not lead to an increased risk for breast cancer or other late psychiatric or medical sequelae. ... The alleged 'postabortion trauma syndrome' does not exist.}}</ref><ref name="stotlandreview">{{Cite journal|author=Stotland NL |title=Abortion and psychiatric practice |journal=[[J Psychiatr Pract]] |volume=9 |issue=2 |pages=139–149 |year=2003 |pmid=15985924 |doi=10.1097/00131746-200303000-00005 |quote=Currently, there are active attempts to convince the public and women considering abortion that abortion frequently has negative psychiatric consequences. This assertion is not borne out by the literature: the vast majority of women tolerate abortion without psychiatric sequelae.}}</ref><ref name="stotland_1404747">{{Cite journal|author=Stotland NL |title=The myth of the abortion trauma syndrome |journal=[[J Am Med Assoc]] |volume=268 |issue=15 |pages=2078–9 |year=1992 |month=October |pmid=1404747 |doi=10.1001/jama.268.15.2078}}</ref> |
|||
Although some studies show negative mental-health outcomes in women who choose abortions after the first trimester because of fetal abnormalities,<ref name="apa-2008">{{cite web |title=Mental Health and Abortion |url=http://www.apa.org/pi/women/programs/abortion/index.aspx |publisher=[[American Psychological Association]] |year=2008 |access-date=18 April 2012 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120419174044/http://www.apa.org/pi/women/programs/abortion/index.aspx |archive-date=19 April 2012}}</ref> more rigorous research would be needed to show this conclusively.<ref name="Steinberg2011">{{cite journal |vauthors=Steinberg JR |title=Later abortions and mental health: psychological experiences of women having later abortions--a critical review of research | journal = Women's Health Issues |volume=21 |issue=3 Suppl |pages=S44–S48 |year=2011 |pmid=21530839 |doi=10.1016/j.whi.2011.02.002}}</ref> Some proposed negative psychological effects of abortion have been referred to by anti-abortion advocates as a separate condition called "[[post-abortion syndrome]]", but this is not recognized by medical or psychological professionals in the United States.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Kelly K |title=The spread of 'Post Abortion Syndrome' as social diagnosis |journal=Social Science & Medicine |volume=102 |pages=18–25 |date=February 2014 |pmid=24565137 |doi=10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.11.030}}</ref> |
|||
==Incidence== |
|||
There are two commonly used methods of measuring the incidence of abortion: |
|||
* Abortion rate - number of abortions per 1000 women between 15 and 44 years of age |
|||
* Abortion ratio - number of abortions out of 100 known pregnancies (excluding miscarriages and stillbirths) |
|||
A 2020 long term-study among US women found that about 99% of women felt that they made the right decision five years after they had an abortion. Relief was the primary emotion with few women feeling sadness or guilt. Social stigma was a main factor predicting negative emotions and regret years later. The researchers also stated: "These results add to the scientific evidence that emotions about an abortion are associated with personal and social context, and are not a product of the abortion procedure itself."<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rocca CH, Samari G, Foster DG, Gould H, Kimport K | title = Emotions and decision rightness over five years following an abortion: An examination of decision difficulty and abortion stigma | journal = Social Science & Medicine | volume = 248 | page = 112704 | date = March 2020 | pmid = 31941577 | doi = 10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112704 | doi-access = free | quote=We found no evidence of emerging negative emotions or abortion decision regret; both positive and negative emotions declined over the first two years and plateaued thereafter, and decision rightness remained high and steady (predicted percent: 97.5% at baseline, 99.0% at five years). At five years postabortion, relief remained the most commonly felt emotion among all women (predicted mean on 0-4 scale: 1.0; 0.6 for sadness and guilt; 0.4 for regret, anger and happiness). Despite converging levels of emotions by decision difficulty and stigma level over time, these two factors remained most important for predicting negative emotions and decision non-rightness years later. }}</ref> |
|||
The number of abortions performed worldwide has decreased between 1995 and 2003 from 45.6 million to 41.6 million, which means a decrease in abortion rate from 35 to 29 per 1000 women. The greatest decrease has occurred in the developed world with a drop from 39 to 26 per 1000 women in comparison to the developing world, which had a decrease from 34 to 29 per 1000 women. Out of a total of about 42 million abortions 22 million occurred safely and 20 million unsafely.<ref name=OBGY09/> |
|||
=== Safety in the abortion debate === |
|||
On average, the frequency of abortions is similar in developing countries (where abortion is generally restricted) to the frequency in developed countries (where abortion is generally much less restricted).<ref name=IJGO10/><ref>{{Cite journal|author=Shah I, Ahman E |title=Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges |journal=[[J Obstet Gynaecol Can]] |volume=31 |issue=12 |pages=1149–58 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=20085681 |doi= |quote=However, a woman’s chance of having an abortion is similar whether she lives in a developed or a developing region: in 2003 the rates were 26 abortions per 1000 women aged 15 to 44 in developed areas and 29 per 1000 in developing areas. The main difference is in safety, with abortion being safe and easily accessible in developed countries and generally restricted and unsafe in most developing countries}}</ref><!--This sentence is currently the subject of discussion at the talk page, with an eye to improving it--> Abortion rates are very difficult to measure in locations where those abortions are illegal,<ref>Sedgh, Gilda and Henshaw, Stanley. "Measuring the Incidence of Abortion in Countries With Liberal Laws" in ''Methodologies for Estimating Abortion Incidence and Abortion-Related Morbidity: A Review'', (Guttmacher Institute 2010): "In countries with highly restrictive abortion laws, it is extremely difficult to obtain reliable counts of the numbers of procedures performed."</ref> and pro-life groups have criticized researchers for allegedly jumping to conclusions about those numbers.<ref>Rosenthal, Elizabeth. "[http://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/12/world/12abortion.html?_r=1 Legal or Not, Abortion Rates Compare]", ''[[The New York Times]]'' (2007-10-12): "Anti-abortion groups criticized the research, saying that the scientists had jumped to conclusions from imperfect tallies, often estimates of abortion rates in countries where the procedure was illegal."</ref> According to the [[Guttmacher Institute]] and the [[United Nations Population Fund]], the abortion rate in developing countries is largely attributable to lack of access to modern contraceptives; assuming no change in abortion laws, providing that access to contraceptives would result in about 25 million fewer abortions annually, including almost 15 million fewer unsafe abortions.<ref>Singh, Susheela et al. ''[http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/AddingItUp2009.pdf Adding it Up: The Costs and Benefits of Investing in Family Planning and Newborn Health]'', pages 17, 19, and 27 (New York: Guttmacher Institute and United Nations Population Fund 2009): "Some 215 million women in the developing world as a whole have an unmet need for modern contraceptives…. If the 215 million women with unmet need used modern family planning methods....[that] would result in about 22 million fewer unplanned births; 25 million fewer abortions; and seven million fewer miscarriages....If women’s contraceptive needs were addressed (and assuming no changes in abortion laws)...the number of unsafe abortions would decline by 73% from 20 million to 5.5 million." A few of the findings in that report were subsequently changed, and are available at: "[http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health]" (Guttmacher Institute 2010).</ref> |
|||
Some purported risks of abortion are promoted primarily by anti-abortion groups,<ref name="JASEN"/><ref name=Cancer_Linacre>{{cite journal | vauthors = Schneider AP, Zainer CM, Kubat CK, Mullen NK, Windisch AK | title = The breast cancer epidemic: 10 facts | journal = The Linacre Quarterly | volume = 81 | issue = 3 | pages = 244–277 | date = August 2014 | pmid = 25249706 | pmc = 4135458 | doi = 10.1179/2050854914Y.0000000027 | publisher = Catholic Medical Association | quote = an association between [induced abortion] and breast cancer has been found by numerous Western and non-Western researchers from around the world. This is especially true in more recent reports that allow for a sufficient breast cancer latency period since an adoption of a Western life style in sexual and reproductive behavior. | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
but lack scientific support.<ref name="JASEN">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jasen P | title = Breast cancer and the politics of abortion in the United States | journal = Medical History | volume = 49 | issue = 4 | pages = 423–444 | date = October 2005 | pmid = 16562329 | pmc = 1251638 | doi = 10.1017/S0025727300009145 }}</ref> For example, the question of a link between [[abortion-breast cancer hypothesis|induced abortion and breast cancer]] has been investigated extensively. Major medical and scientific bodies (including the WHO, [[National Cancer Institute]], [[American Cancer Society]], [[Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists|Royal College of OBGYN]] and [[American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists|American Congress of OBGYN]]) have concluded that abortion does not cause breast cancer.<ref>Position statements of major medical bodies on abortion and breast cancer include: |
|||
* World Health Organization: {{cite web|url=https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs240/en/ |title=Induced abortion does not increase breast cancer risk (Fact sheet N°240) |publisher=World Health Organization |access-date=6 January 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110213141046/http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs240/en/ |archive-date=13 February 2011 }} |
|||
* National Cancer Institute: {{cite web|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/risk/abortion-miscarriage |title=Abortion, Miscarriage, and Breast Cancer Risk |publisher=National Cancer Institute |access-date=11 January 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101221084337/http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/Risk/abortion-miscarriage |archive-date=21 December 2010 |url-status=live |date=20 February 2003 }} |
|||
* American Cancer Society: {{cite web|url=http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/BreastCancer/MoreInformation/is-abortion-linked-to-breast-cancer |publisher=American Cancer Society|date=23 September 2010 |access-date=20 June 2011 |title=Is Abortion Linked to Breast Cancer? |quote=At this time, the scientific evidence does not support the notion that abortion of any kind raises the risk of breast cancer. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110605204701/http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/BreastCancer/MoreInformation/is-abortion-linked-to-breast-cancer |archive-date=5 June 2011 |url-status=live }} |
|||
* Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists: {{cite web|url=http://www.rcog.org.uk/files/rcog-corp/uploaded-files/NEBAbortionSummary.pdf |title=The Care of Women Requesting Induced Abortion |page=9 |publisher=Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists |access-date=29 June 2008 |quote=Induced abortion is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk. |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130727105037/http://www.rcog.org.uk/files/rcog-corp/uploaded-files/NEBAbortionSummary.pdf |archive-date=27 July 2013 }} |
|||
* American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: {{cite web|url=http://www.acog.org/from_home/publications/press_releases/nr07-31-03-2.cfm |title=ACOG Finds No Link Between Abortion and Breast Cancer Risk |date=31 July 2003 |publisher=American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists |access-date=11 January 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110102030744/http://www.acog.org/from_home/publications/press_releases/nr07-31-03-2.cfm |archive-date=2 January 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
In the past even illegality has not automatically meant that the abortions were unsafe. Referring to the U.S., historian [[Linda Gordon]] states: "In fact, illegal abortions in this country have an impressive safety record."<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Gordon L | title = The Moral Property of Women | publisher = University of Illinois Press | year = 2002 | isbn = 0-252-02764-7 }}</ref>{{rp|25|}} |
|||
The incidence of induced abortion varies regionally. Some countries, such as Belgium (11.2 out of 100 known pregnancies) and the Netherlands (10.6 per 100), had a comparatively low ratio of induced abortion. Others like Russia (62.6 out of 100), Romania (63 out of 100)<ref>[[National Institute of Statistics (Romania)|National Institute of Statistics]], [http://www.insse.ro/cms/files/pdf/ro/cap2.pdf Romanian Statistical Yearbook, page 29], 2008</ref> and Vietnam (43.7 out of 100) had a high ratio (data for last three countries of unknown completeness). The estimated world ratio was 26%, the world rate - 35 per 1000 women.<ref>Henshaw, Stanley K., Singh, Susheela, and Haas, Taylor. (1999). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/25s3099.html The Incidence of Abortion Worldwide]. ''International Family Planning Perspectives, 25 (Supplement)'', 30–38. Retrieved 2006-01-18.</ref> |
|||
According to [[Rickie Solinger]], |
|||
===By gestational age and method=== |
|||
{{Blockquote| |
|||
{{Double image|right|UK abortion by gestational age 2004 histogram.svg|200|US abortion by gestational age 2004 histogram.svg|200|[[Histogram]] of abortions by [[gestational age]] in England and Wales during 2004. Average is 9.5 weeks. (left) Abortion in the United States by gestational age, 2004. (Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) (right) ||}} |
|||
A related myth, promulgated by a broad spectrum of people concerned about abortion and public policy, is that before legalization abortionists were dirty and dangerous back-alley butchers.... [T]he historical evidence does not support such claims.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Solinger R | chapter = Introduction | veditors = Solinger R | title = Abortion Wars: A Half Century of Struggle, 1950–2000 | pages = [https://archive.org/details/abortionwarshalf0000soli/page/1 1–9] | publisher = University of California Press | year = 1998 | isbn = 978-0-520-20952-7 | url = https://archive.org/details/abortionwarshalf0000soli/page/1 }}</ref>{{rp|4}} |
|||
}} |
|||
A 1940s American physician spoke of his pride in having performed 13,844 illegal abortions without any fatalities.<ref>{{cite book | last1 = Bates | first1 = Jerome E | last2 = Zawadzki | first2 = Edward S | title = Criminal Abortion: A Study in Medical Sociology | publisher = Charles C. Thomas | year = 1964 | isbn = 978-0-398-00109-4 |oclc =299149| page = 59| quote = In my practice I average three operations a day. By working a six day week, I complete approximately eighteen operations in this time. This amounts to seventy-two operations a month. In my sixteen years of specializing, I have successfully performed about 13,844 abortions.<br/> This was without the loss of the life of a single one of my patients. I feel those figures are something of which to be proud. I feel—I’m sure—that the work I have been engaged in these past years has been a contribution to Society and has helped to straighten out the messed up lives of many people.}}</ref> |
|||
In 1870s New York City, the abortionist/midwife [[Madame Restell]] (Anna Trow Lohman) is said to have lost very few women among her more than 100,000 patients<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Keller A | title = Scandalous Lady: The Life and Times of Madame Restell | publisher = Atheneum | year = 1981 | isbn = 978-0-689-11213-3 }}</ref>—a lower mortality rate than the childbirth mortality rate at the time. In 1936, obstetrics and gynecology professor [[Frederick J. Taussig]] wrote that a cause of increasing mortality during the years of illegality in the U.S. was that |
|||
{{Blockquote|With each decade of the past fifty years the actual and proportionate frequency of this accident [perforation of the uterus] has increased, due, first, to the increase in the number of instrumentally induced abortions; second, to the proportionate increase in abortions handled by doctors as against those handled by midwives; and, third, to the prevailing tendency to use instruments instead of the finger in emptying the uterus.<ref>{{cite book | last = Taussig | first= Frederick J. | author-link = Frederick J. Taussig | title = Abortion Spontaneous and Induced: Medical and Social Aspects | publisher = C.V. Mosby | year = 1936 |location = St. Louis | page = 223 |url = https://archive.org/details/b29818394/page/223/mode/1up | oclc = 1041029321 }}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
===Unsafe abortion=== |
|||
Abortion rates also vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the method practiced. In 2003, data from the [[CDC]] reports that overall 26% of abortions were known to have been obtained at <6 weeks' gestation, 18% at 7 weeks, 15% at 8 weeks, 4.1% at 16 through 20 weeks and 1.4% at >21 weeks. 90.9% of these were classified as having been done by "[[curettage]]" ([[Suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]], [[Dilation and curettage]], [[Dilation and evacuation]]), 7.7% by "[[medical abortion|medical]]" means ([[mifepristone]]), 0.4% by "[[instillation abortion|intrauterine instillation]]" (saline or [[prostaglandin]]), and 1.0% by "other" (including [[hysterotomy abortion|hysterotomy]] and [[hysterectomy]]).<ref name="cdc2003">Strauss, L.T., Gamble, S.B., Parker, W.Y, Cook, D.A., Zane, S.B., and Hamdan, S. (November 24, 2006). [http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5511a1.htm Abortion Surveillance – United States, 2003]. ''Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 55 (11),'' 1–32. Retrieved May 10, 2007.</ref> According to the CDC, due to data collection difficulties the data must be viewed as tentative and some fetal deaths reported beyond 20 weeks may be natural deaths erroneously classified as abortions if the removal of the fetus is accomplished by the same procedure as an induced abortion.<ref name="guttmacher">http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/ib14.html</ref> The [[Guttmacher Institute]] estimated there were 2,200 [[intact dilation and extraction]] procedures in the U.S. during 2000; this accounts for 0.17% of the total number of abortions performed that year.<ref>Finer, Lawrence B. and Henshaw, Stanley K. (2003). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3500603.html Abortion Incidence and Services in the United States in 2000]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 35 (1).'.' Retrieved 2006-05-10.</ref> Similarly, in England and Wales in 2006, 89% of terminations occurred at or under 12 weeks, 9% between 13 to 19 weeks, and 1.5% at or over 20 weeks. 64% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 6% by D&E, and 30% were medical.<ref>{{cite web|author=Department of Health |year=2007 |title=Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2006 |url=http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsStatistics/DH_075697 |accessdate=2007-10-12}}</ref> In 2009 in Scotland, 62.1% of all terminations were performed at less than 9 weeks, with medical termination accounting for nearly 70%.<ref>http://www.isdscotland.org/isd/1918.html</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Unsafe abortion}} |
|||
[[File:RussianAbortionPoster.jpg|thumb|Soviet poster {{Circa|1925}} (after Russia legalized abortion in 1920) warning against abortions performed by folk practitioners]] |
|||
Later abortions are more common in China, India, and other developing countries than in developed countries.<ref>Cheng L. [http://www.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/CD006714_chengl_com/en/index.html “Surgical versus medical methods for second-trimester induced abortion : RHL commentary”] (last revised: 1 November 2008). The WHO Reproductive Health Library; Geneva: World Health Organization.</ref> |
|||
Women seeking an abortion may use unsafe methods, especially when abortion is legally restricted. They may attempt [[self-induced abortion]] or seek the help of a person without proper medical training or facilities. This can lead to severe complications, such as incomplete abortion, [[sepsis]], hemorrhage, and damage to internal organs.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Okonofua F | title = Abortion and maternal mortality in the developing world | journal = Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada | volume = 28 | issue = 11 | pages = 974–979 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17169222 | doi = 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)32307-6 | url = http://www.jogc.org/abstracts/full/200611_WomensHealth_1.pdf | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120111121431/http://www.jogc.org/abstracts/full/200611_WomensHealth_1.pdf | archive-date = 11 January 2012 }}</ref> |
|||
===Personal and social factors=== |
|||
[[File:AGIAbortionReasonsBarChart.png|thumb|A bar chart depicting selected data from the 1998 [[Alan Guttmacher Institute|AGI]] [[meta-study]] on the reasons women stated for having an abortion.]] |
|||
Unsafe abortions are a major cause of injury and death among women worldwide. Although data are imprecise, it is estimated that approximately 20 million unsafe abortions are performed annually, with 97% taking place in [[developing country|developing countries]].<ref name="lancet-grimes"/> Unsafe abortions are believed to result in millions of injuries.<ref name="lancet-grimes"/><ref name="Haddad-2009">{{cite journal | vauthors = Haddad LB, Nour NM | title = Unsafe abortion: unnecessary maternal mortality | journal = Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology | volume = 2 | issue = 2 | pages = 122–126 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19609407 | pmc = 2709326 }}</ref> Estimates of deaths vary according to methodology, and have ranged from 37,000 to 70,000 in the past decade;<ref name="lancet-grimes"/><ref name="OBGY09">{{cite journal |vauthors=Shah I, Ahman E |date=December 2009 |title=Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges |url=http://www.sogc.org/jogc/abstracts/full/200912_WomensHealth_1.pdf |url-status=dead |journal=Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada |volume=31 |issue=12 |pages=1149–1158 |doi=10.1016/s1701-2163(16)34376-6 |pmid=20085681 |s2cid=35742951 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110716212405/http://www.sogc.org/jogc/abstracts/full/200912_WomensHealth_1.pdf |archive-date=16 July 2011}}</ref><ref name=Loz2012>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez-Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo JP, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nasseri K, Norman P, O'Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, De León FR, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui-Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng ZJ, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA | display-authors = 6 | title = Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 | journal = Lancet | volume = 380 | issue = 9859 | pages = 2095–2128 | date = December 2012 | pmid = 23245604 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 | pmc = 10790329 | url = https://zenodo.org/record/2557786 | access-date = 14 March 2020 | url-status = live | hdl-access = free | s2cid = 1541253 | archive-date = 19 May 2020 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200519152712/https://zenodo.org/record/2557786 | hdl = 10536/DRO/DU:30050819 }}</ref> deaths from unsafe abortion account for around 13% of all [[maternal deaths]].<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Speroff L, Darney PD |title=A clinical guide for contraception|year=2010|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|location=Philadelphia|isbn=978-1-60831-610-6|page=406|edition=5th }}</ref> The [[World Health Organization]] believes that mortality has fallen since the 1990s.<ref name="WHO2011">{{cite book |last=World Health Organisation |title=Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2008 |publisher=World Health Organisation |year=2011 |edition=6th |page=27 |isbn=978-92-4-150111-8 |url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241501118_eng.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140328093307/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241501118_eng.pdf |archive-date=28 March 2014}}</ref> To reduce the number of unsafe abortions, public health organizations have generally advocated emphasizing the legalization of abortion, training of medical personnel, and ensuring access to reproductive-health services.<ref name="berer-who">{{cite journal |vauthors=Berer M | title=Making abortions safe: a matter of good public health policy and practice |journal=Bulletin of the World Health Organization |volume=78 |issue=5 |pages=580–592 |year=2000 |pmid=10859852 |pmc=2560758}}</ref> |
|||
A 1998 study from 27 countries on the reasons women seek to terminate their pregnancies concluded that the most common reason women cited for having an abortion was to postpone childbearing to a more suitable time or to focus energies and resources on existing children. The most commonly reported reasons were socioeconomic factors such as being unable to afford a child either in terms of the direct costs of raising a child or the loss of income while she is caring for the child, lack of support from the father, inability to afford additional children, desire to provide schooling for existing children, disruption of education, relationship problems with a husband or partner, the perception that she is too young, and unemployment. <ref name="bankole98">Bankole, Akinrinola, Singh, Susheela, and Haas, Taylor. (1998). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2411798.html Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries]. ''International Family Planning Perspectives, 24 (3)'', 117–127 and 152. Retrieved 2006-01-18.</ref> A 2004 study in which American women at [[abortion clinic|clinics]] answered a questionnaire yielded similar results.<ref name="finer2005">Finer, Lawrence B., Frohwirth, Lori F., Dauphinee, Lindsay A., Singh, Shusheela, and Moore, Ann M. (2005). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.pdf Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantative and qualitative perspectives]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 37 (3),'' 110–118. Retrieved 2006-01-18.</ref> A 1998 survey found risk to maternal health cited as the main reason by 5-10% in seven countries and by 20-38% in three (Kenya, Bangladesh and India).<ref name="bankole98"/> A 1997 U.S. report cited maternal health the "most important reason" for their decision by 3% of women and another 3% cited concern that the fetus had a health problem.<ref name="guttmacher" /> In a 2004 survey-based U.S. study, 1% of women having abortions became pregnant as a result of [[rape]] and 0.5% as a result of [[incest]].<ref name="finer2005"/> Another American study in 2002 concluded that 54% of women who had an abortion were using a form of [[birth control|contraception]] at the time of becoming pregnant while 46% were not. Inconsistent use was reported by 49% of those using [[condom]]s and 76% of those using the [[combined oral contraceptive pill]]; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.<ref>Jones, Rachel K., Darroch, Jacqueline E., Henshaw, Stanley K. (2002). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3429402.pdf Contraceptive Use Among U.S. Women Having Abortions in 2000–2001]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 34 (6).'.' Retrieved June 15, 2006.</ref> The Guttmacher Institute estimated that "most abortions in the United States are obtained by minority women" because minority women "have much higher rates of unintended pregnancy."<ref>Susan A. Cohen: [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/gpr/11/3/gpr110302.html ''Abortion and Women of Color: The Bigger Picture''], Guttmacher Policy Review, Summer 2008, Volume 11, Number 3.</ref> |
|||
A major factor in whether abortions are performed safely or not is the legal standing of abortion. Countries with restrictive abortion laws have higher rates of unsafe abortion and similar overall abortion rates compared to countries where abortion is legal and available.<ref name="OBGY09"/><ref name="Sedgh 2012"/> For example, the [[Choice on Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1996|1996 legalization of abortion in South Africa]] led to an immediate reduction in abortion-related complications,<ref name="jewkes">{{cite journal |vauthors=Jewkes R, Rees H, Dickson K, Brown H, Levin J |title=The impact of age on the epidemiology of incomplete abortions in South Africa after legislative change |journal=BJOG |volume=112 |issue=3 |pages=355–359 |date=March 2005 |pmid=15713153 |doi=10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00422.x |s2cid=41663939 |doi-access=}}</ref> with abortion-related deaths dropping by more than 90%.<ref name="bateman-samj">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bateman C |title=Maternal mortalities 90% down as legal TOPs more than triple |journal=South African Medical Journal = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Geneeskunde |volume=97 |issue=12 |pages=1238–1242 |date=December 2007 |pmid=18264602 |url=http://samj.org.za/index.php/samj/article/view/642 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170830200316/http://samj.org.za/index.php/samj/article/view/642 |archive-date=30 August 2017}}</ref> Similar reductions in maternal mortality have been observed after other countries have liberalized their abortion laws, such as [[Romania]] and [[Nepal]].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Conti JA, Brant AR, Shumaker HD, Reeves MF |title=Update on abortion policy |journal=Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology |volume=28 |issue=6 |pages=517–521 |date=December 2016 |pmid=27805969 |doi=10.1097/GCO.0000000000000324 |s2cid=26052790}}</ref> A 2011 study concluded that in the United States, some state-level anti-abortion laws are correlated with lower rates of abortion in that state.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors=New MJ |s2cid=53314166|title=Analyzing the Effect of Anti-Abortion U.S. State Legislation in the Post-Casey Era |journal=State Politics & Policy Quarterly|date=15 February 2011|volume=11|issue=1|pages=28–47|doi=10.1177/1532440010387397}}</ref> The analysis, however, did not take into account travel to other states without such laws to obtain an abortion.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Medoff MH, Dennis C |title=Another Critical Review of New's Reanalysis of the Impact of Antiabortion Legislation|journal=State Politics & Policy Quarterly|date=21 July 2014 |volume=14|issue=3|pages=269–76|doi=10.1177/1532440014535476|s2cid=155464018}}</ref> In addition, a lack of access to effective contraception contributes to unsafe abortion. It has been estimated that the incidence of unsafe abortion could be reduced by up to 75% (from 20 million to 5 million annually) if modern family planning and maternal health services were readily available globally.<ref name="Singh">{{cite web |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf |title=Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health |publisher=Guttmacher Institute|year=2010 |access-date=24 May 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120324101905/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf |archive-date=24 March 2012 }}</ref> Rates of such abortions may be difficult to measure because they can be reported variously as miscarriage, "induced miscarriage", "menstrual regulation", "mini-abortion", and "regulation of a delayed/suspended menstruation".<ref name="lancet-grimes"/><ref name=Brazil_Unsafe>{{cite journal |vauthors=Nations MK, Misago C, Fonseca W, Correia LL, Campbell OM |title=Women's hidden transcripts about abortion in Brazil |journal=Social Science & Medicine |volume=44 |issue=12 |pages=1833–1845 |date=June 1997 |pmid=9194245 |doi=10.1016/s0277-9536(96)00293-6}}</ref> |
|||
Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures. These might include the stigmatization of disabled people, preference for children of a specific sex, disapproval of single motherhood, insufficient economic support for families, lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts toward [[population control]] (such as China's [[one-child policy]]). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or [[sex-selective abortion]]. |
|||
Forty percent of the world's women are able to access therapeutic and elective abortions within gestational limits,<ref name="IJGO10"/> while an additional 35 percent have access to legal abortion if they meet certain physical, mental, or socioeconomic criteria.<ref name="Dev98-07"/> While [[maternal death|maternal mortality]] seldom results from safe abortions, unsafe abortions result in 70,000 deaths and 5 million disabilities per year.<ref name=OBGY09/> Complications of unsafe abortion account for approximately an eighth of maternal mortalities worldwide,<ref name="Maclean">{{cite book| vauthors=Maclean G |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=u4Aeiu2eDMAC&pg=PA299|chapter=XI. Dimension, Dynamics and Diversity: A 3D Approach to Appraising Global Maternal and Neonatal Health Initiatives |pages=299–300|title=Trends in Midwifery Research| veditors=Balin RE |publisher=Nova Publishers|year=2005|isbn=978-1-59454-477-4|url-status=live|archive-date=15 March 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150315113348/http://books.google.com/books?id=u4Aeiu2eDMAC&pg=PA299}}</ref> though this varies by region.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors=Salter C, Johnson HB, Hengen N |year=1997 |url=http://info.k4health.org/pr/l10edsum.shtml |title=Care for Postabortion Complications: Saving Women's Lives |journal=Population Reports |volume=25 |issue=1 |publisher=Johns Hopkins School of Public Health |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091207070103/http://info.k4health.org/pr/l10edsum.shtml |archive-date=7 December 2009}}</ref> Secondary infertility caused by an unsafe abortion affects an estimated 24 million women.<ref name="WHO-unsafe-2007">{{cite web |year=2007 |title=Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003 |url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2007/9789241596121_eng.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110216141018/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2007/9789241596121_eng.pdf |archive-date=16 February 2011 |access-date=7 March 2011 |publisher=World Health Organization}}</ref> The rate of unsafe abortions has increased from 44% to 49% between 1995 and 2008.<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> Health education, access to family planning, and improvements in health care during and after abortion have been proposed to address consequences of unsafe abortion.<ref>{{cite web|title=Packages of interventions: Family planning, safe abortion care, maternal, newborn and child health|author1=UNICEF |author2=UNFPA |author3=WHO |author4=World Bank|year=2010|access-date=31 December 2010|url-status=dead|url= https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_health/fch_10_06/en/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101109224916/http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_health/fch_10_06/en/index.html|archive-date=9 November 2010}}</ref> |
|||
===Unsafe abortion=== |
|||
[[File:RussianAbortionPoster.jpg|thumb|Soviet poster circa 1925, warning against midwives performing abortions. Title translation: "Abortions performed by either trained or self-taught midwives not only maim the woman, they also often lead to death."]] |
|||
{{Main|Unsafe abortion}} |
|||
Women seeking to terminate their pregnancies sometimes resort to unsafe methods, particularly when access to legal abortion is restricted. About one in eight pregnancy-related deaths worldwide are associated with unsafe abortion.<ref>Maclean, Gaynor. [http://books.google.com/books?id=u4Aeiu2eDMAC&pg=PA300&dq=%22Unsafe+abortion%22&hl=en&ei=oQZ8TbnsGovVgAeRntzlBw&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CFsQ6AEwBzge#v=onepage&q=%22Unsafe%20abortion%22&f=false "Dimension, Dynamics and Diversity; A 3D Approach to Appraising Global Maternal and Neonatal Health Initiatives"], pages 299-300 in Trends in Midwifery Research by Randell Balin (Nova Publishers, 2005).</ref> |
|||
==Incidence== |
|||
The [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) defines an unsafe abortion as being "a procedure ... carried out by persons lacking the necessary skills or in an environment that does not conform to minimal medical standards, or both."<ref name="whounsafe">World Health Organization. (2004). [http://www.who.int/reproductive-health/publications/unsafeabortion_2000/estimates.pdf "Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2000"]. Retrieved 2009-03-22.</ref> They may be performed by [[self-induced abortion|the woman herself]], by another person without medical training, or by a healthcare professional operating in sub-standard conditions. Unsafe abortion remains a public health concern due to the higher incidence and severity of its associated complications, such as incomplete abortion, [[sepsis]], hemorrhage, and damage to internal organs. |
|||
There are two commonly used methods of measuring the incidence of abortion: |
|||
* Abortion rate – number of abortions annually per 1,000 women between 15 and 44 years of age;<ref>{{cite web| title = Facts on Induced Abortion Worldwide| date = January 2012| publisher = World Health Organization| url = https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/unsafe_abortion/induced_abortion_2012.pdf| access-date = 9 May 2021| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210309200507/http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/unsafe_abortion/induced_abortion_2012.pdf| archive-date = 9 March 2021| url-status = live}}</ref> some sources use a range of 15–49. |
|||
* Abortion percentage – number of abortions out of 100 known pregnancies; pregnancies include live births, abortions, and miscarriages. |
|||
In many places, where abortion is illegal or carries a heavy social stigma, medical reporting of abortion is not reliable.<ref name="Sedgh 2007">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sedgh G, Henshaw S, Singh S, Ahman E, Shah IH |date=October 2007 |title=Induced abortion: estimated rates and trends worldwide |journal=Lancet |volume=370 |issue=9595 |pages=1338–1345 |citeseerx=10.1.1.454.4197 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61575-X |pmid=17933648 |s2cid=28458527}}</ref> For this reason, estimates of the incidence of abortion must be made without determining certainty related to [[standard error]].<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> The number of abortions performed worldwide was characterized as stable in the early 2000s, with 41.6 million having been performed in 2003 and 43.8 million having been performed in 2008.<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> The abortion rate worldwide was 28 per 1000 women per year, though it was 24 per 1000 women per year for developed countries and 29 per 1000 women per year for developing countries.<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> The same 2012 study indicated that in 2008, the estimated abortion percentage of known pregnancies was at 21% worldwide, with 26% in developed countries and 20% in developing countries.<ref name="Sedgh 2012" /> |
|||
The legality of abortion is one of the main determinants of its safety. Restrictive abortion laws are associated with a high rate of unsafe abortions.<ref name="OBGY09"/><ref name="Worldwide"/><ref name="WHO-unsafe-2007">{{cite web | publisher = [[World Health Organization]] | year = 2007 | accessdate = March 7, 2011 | format = PDF | url = http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2007/9789241596121_eng.pdf | title = Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003}}</ref> In addition, a lack of access to safe and effective contraception contributes to unsafe abortion. It has been estimated that the incidence of unsafe abortion could be reduced by as much as 73% without any change in abortion laws if modern family planning and maternal health services were readily available globally.<ref name=Singh>Singh, Susheela et al. ''[http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/AddingItUp2009.pdf Adding it Up: The Costs and Benefits of Investing in Family Planning and Newborn Health]'' (New York: Guttmacher Institute and United Nations Population Fund 2009): "If women’s contraceptive needs were addressed (and assuming no changes in abortion laws)...the number of unsafe abortions would decline by 73% from 20 million to 5.5 million." A few of the findings in that report were subsequently changed, and are available at: "[http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health]" (Guttmacher Institute 2010).</ref> |
|||
On average, the incidence of abortion is similar in countries with restrictive abortion laws and those with more liberal access to abortion.<ref name="nytimes-abortion-rates"/> Restrictive abortion laws are associated with increases in the percentage of abortions performed unsafely.<ref name=IJGO10/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shah I, Ahman E | title = Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges | journal = Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada | volume = 31 | issue = 12 | pages = 1149–1158 | date = December 2009 | pmid = 20085681 | doi = 10.1016/s1701-2163(16)34376-6 | s2cid = 35742951 | quote = However, a woman's chance of having an abortion is similar whether she lives in a developed or a developing region: in 2003 the rates were 26 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15 to 44 in developed areas and 29 per 1,000 in developing areas. The main difference is in safety, with abortion being safe and easily accessible in developed countries and generally restricted and unsafe in most developing countries. }}</ref><ref name="nytimes-abortion-rates">{{cite news| vauthors = Rosenthal E |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/12/world/12abortion.html |title=Legal or Not, Abortion Rates Compare|newspaper=The New York Times|date=12 October 2007|access-date=18 July 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110828173628/http://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/12/world/12abortion.html|archive-date=28 August 2011}}</ref> The unsafe abortion rate in developing countries is partly attributable to lack of access to modern contraceptives; according to the [[Guttmacher Institute]], providing access to contraceptives would result in about 14.5 million fewer unsafe abortions and 38,000 fewer deaths from unsafe abortion annually worldwide.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf |title=Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health |publisher=Guttmacher Institute |date=November 2010 |access-date=24 October 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111020135329/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/FB-AIU-summary.pdf |archive-date=20 October 2011 }}</ref> |
|||
Forty percent of the world's women are able to access therapeutic and elective abortions within gestational limits.<ref name="IJGO10"/> While [[maternal death|maternal mortality]] seldom results from safe abortions, unsafe abortions result in 70,000 deaths and 5 million disabilities per year.<ref name=OBGY09/> Complications of unsafe abortion account for approximately 12% of [[maternal death|maternal mortalities]] in Asia, 25% in Latin America, and 13% in [[sub-Saharan Africa]].<ref>Salter, C., Johnson, H.B., and Hengen, N. (1997). [http://info.k4health.org/pr/l10edsum.shtml Care for post abortion complications: saving women's lives]. ''Population Reports, 25 (1)'.' Retrieved 2006-02-22.</ref> Secondary infertility caused by an unsafe abortion affects an estimated 24 million women.<ref name="WHO-unsafe-2007"/> Although the global rate of abortion declined from 45.6 million in 1995 to 41.6 million in 2003, unsafe procedures still accounted for 48% of all abortions performed in 2003.<ref name="Worldwide">{{cite journal | author = Sedgh G, Henshaw S, Singh S, Ahman E, Shah IH | title =Induced abortion: estimated rates and trends worldwide | year = 2007 | journal = Lancet | volume = 370 | issue = 9595 | pages = 1338–45 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61575-X | pmid = 17933648}}</ref> |
|||
Health education, access to family planning, and improvements in health care during and after abortion have been proposed to address this phenomenon.<ref>{{cite web|title=Packages of interventions: Family planning, safe abortion care, maternal, newborn and child health|author=[[UNICEF]], [[United Nations Population Fund]], WHO, World Bank|year=2010|url=http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_health/fch_10_06/en/index.html|accessdate=December 31, 2010}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
The rate of legal, induced abortion varies extensively worldwide. According to the report of employees of Guttmacher Institute it ranged from 7 per 1000 women per year (Germany and Switzerland) to 30 per 1000 women per year (Estonia) in countries with complete statistics in 2008. The proportion of pregnancies that ended in induced abortion ranged from about 10% (Israel, the Netherlands and Switzerland) to 30% (Estonia) in the same group, though it might be as high as 36% in Hungary and Romania, whose statistics were deemed incomplete.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sedgh G, Singh S, Henshaw SK, Bankole A | title = Legal abortion worldwide in 2008: levels and recent trends | journal = Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health | volume = 43 | issue = 3 | pages = 188–198 | date = September 2011 | pmid = 21884387 | doi = 10.1363/4318811 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3708411.html | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120107111306/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3708411.html | archive-date = 7 January 2012 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|date=2011-05-15|chapter=Populație|url=http://www.insse.ro/cms/files/Anuar%2520statistic/02/02%2520Populatie_ro.pdf|access-date=2023-02-16|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110515195102/http://www.insse.ro/cms/files/Anuar%2520statistic/02/02%2520Populatie_ro.pdf |archive-date=15 May 2011 |title=Romanian Statistical Yearbook |page=62 |publisher=[[National Institute of Statistics (Romania)|National Institute of Statistics]]}}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
[[File:FrenchPeriodicalPills-January61845,BostonDailyTimes.jpg|thumb|right|"French Periodical Pills." An example of a clandestine advertisement published in an 1845 edition of the ''Boston Daily Times''.]] |
|||
{{Main|History of abortion}} |
|||
Induced abortion has long history, and can be traced back to civilizations as varied as China under [[Shennong]] (c. 2700 BCE), and the [[Ebers Papyrus]] of [[Ancient Egypt]] (c. 1550 BCE), and the Roman Empire in the time of [[Juvenal]] (c. 200 CE).<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> There is evidence to suggest that pregnancies were terminated through a number of methods, including the administration of [[abortifacient]] herbs, the use of sharpened implements, the application of abdominal pressure, and other techniques. |
|||
An American study in 2002 concluded that about half of women having abortions were using a form of [[birth control|contraception]] at the time of becoming pregnant. Inconsistent use was reported by half of those using [[condom]]s and three-quarters of those using the [[combined oral contraceptive pill|birth control pill]]; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.<ref name=":8">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jones RK, Darroch JE, Henshaw SK | title = Contraceptive use among U.S. women having abortions in 2000-2001 | journal = Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health | volume = 34 | issue = 6 | pages = 294–303 | year = 2002 | pmid = 12558092 | doi = 10.2307/3097748 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3429402.pdf | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20060615011127/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3429402.pdf | archive-date = 15 June 2006 | jstor = 3097748 }}</ref> Of the other half of women, who were not using contraception at the time of becoming pregnant, the vast majority had used contraception at some point in the past, indicating some level of dissatisfaction with the contraceptive options available to them. Indeed, 32% of these contraceptive nonusers cited concerns about contraceptive methods as their reason for nonuse,<ref name=":8" /> and a more recent study found similar results.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Mosher |first1=William |last2=Jones |first2=Jo |last3=Abma |first3=Joyce |date=2015 |title=Nonuse of contraception among women at risk of unintended pregnancy in the United States |journal=Contraception |volume=92 |issue=2 |pages=170–176 |doi=10.1016/j.contraception.2015.05.004 |issn=0010-7824 |pmc=6413311 |pmid=25998937}}</ref> Taken together, these statistics suggest that new contraceptive methods, such as non-hormonal contraceptives or [[male contraceptive]]s, could reduce unintended pregnancy and abortion rates.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Dorman |first1=Emily |last2=Perry |first2=Brian |last3=Polis |first3=Chelsea B. |last4=Campo-Engelstein |first4=Lisa |last5=Shattuck |first5=Dominick |last6=Hamlin |first6=Aaron |last7=Aiken |first7=Abigail |last8=Trussell |first8=James |last9=Sokal |first9=David |date=2018 |title=Modeling the impact of novel male contraceptive methods on reductions in unintended pregnancies in Nigeria, South Africa, and the United States |url=|journal=Contraception |volume=97 |issue=1 |pages=62–69 |doi=10.1016/j.contraception.2017.08.015 |issn=0010-7824 |pmc=5732079 |pmid=28887053}}</ref> |
|||
Some medical scholars and abortion opponents have suggested that the [[Hippocratic Oath]] forbade [[Ancient Greece|Ancient Greek]] physicians from performing abortions.<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2">{{cite book|chapter=1. Abortion and medicine: A sociopolitical history|isbn=9781444312935|page=2|publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.]]|year=2009|location=[[Oxford, United Kingdom]]|title=Management of Unintended and Abnormal Pregnancy|edition=1st|editors=MPaul, ES Lichtenberg, L Borgatta, DA Grimes, PG Stubblefield, MD Creinin|first=Carole|last=Joffe}}</ref> However, some modern scholars disagree with this interpretation,<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> and the the medical texts of [[Hippocratic Corpus]] contain descriptions of abortive techniques and notes on the risks they posed to a woman's health.<ref>{{Cite book| first = Steven | last = Miles | title =The Hippocratic Oath and the Ethics of Medicine| year = 2005| publisher = Oxford University Press| isbn = 978-0195188202}}</ref> In Christianity, [[Pope Sixtus V]] (1585–90) is noted as the first Pope to declare that abortion is homicide regardless of the stage of pregnancy;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://civilliberty.about.com/od/gendersexuality/tp/History-of-Prostitution.htm |title=History of Prostitution |publisher=About.com |work=Civil Liberties| archiveurl = http://www.webcitation.org/5m5jEFrP0 | archivedate = 2009-12-17| deadurl=no}}</ref> the Church had previously been divided on whether if believed that abortion was murder, and did not begin vigorously opposing abortion until the 1800s.<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> [[Islam and abortion|Islamic tradition]], however, has traditionally permitted abortion up until a point in time when Muslims believe the soul enters the fetus,<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> considered by various theologians to be at conception, at 40 days after conception, at 120 days after conception, or at [[quickening]].<ref name="BBC and Islam / Abortion">http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/islamethics/abortion_1.shtml</ref> However, abortion is largely heavily restricted or forbidden in areas of high Islamic faith such as the [[Middle East and North Africa]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Abortion in the Middle East and North Africa|url=http://www.prb.org/pdf08/MENAabortion.pdf|deadlink=no|last1=Dabash|first1=Rasha|first2=Farzaneh|last2=Roudi-Fahimi|publisher=[[Population Research Bureau]]|archiveurl=http://www.prb.org/pdf08/MENAabortion.pdf|archivedate=July 8, 2011|year=2008|format=PDF}}</ref> |
|||
The Guttmacher Institute has found that "most abortions in the United States are obtained by minority women" because minority women "have much higher rates of unintended pregnancy".<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cohen SA |url= http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/gpr/11/3/gpr110302.html |title=Abortion and Women of Color: The Bigger Picture |journal=Guttmacher Policy Review |year=2008 |volume=11 |issue=3 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080915094346/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/gpr/11/3/gpr110302.html |archive-date=15 September 2008 }}</ref> In a 2022 analysis by the [[Kaiser Family Foundation]], while people of color comprise 44% of the population in Mississippi, 59% of the population in Texas, 42% of the population in Louisiana, and 35% of the population in Alabama, they comprise 80%, 74%, 72%, and 70%, respectively, of those receiving abortions.<ref>{{cite news | vauthors = Pettus EW, Willingham L |title=Minority women most affected if abortion is banned, limited |url=https://apnews.com/article/abortion-us-supreme-court-business-health-race-and-ethnicity-3fff455cce7ef0d8694f5371f805ea18 |access-date=1 February 2022 |work=Associated Press |date=1 February 2022 |archive-date=1 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220201144918/https://apnews.com/article/abortion-us-supreme-court-business-health-race-and-ethnicity-3fff455cce7ef0d8694f5371f805ea18 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In Europe and North America, abortion techniques advanced starting in the 1600s. However, conservatism by most physicians with regards to sexual matters prevented the wide expansion of safe abortion techniques.<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> Other abortion providers in addition to some physicians advertised their services, and they were not widely regulated until the mid-1800s, when the practice was banned in both the United States and the United Kingdom,<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> among other countries.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} Church groups as well as physicians were highly influential in anti-abortion movements.<ref name="Management of Abortion, page 2" /> The Soviet Union (1919), Iceland (1935) and Sweden (1938) were among the first countries to legalize certain or all forms of abortion.<ref name="cbctrust">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbctrust.com/history_law_religion.php |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080208053146/http://www.cbctrust.com/history_law_religion.php |archivedate=2008-02-08 |title=Abortion Law, History & Religion |accessdate=2008-03-23 |publisher=Childbirth By Choice Trust}}</ref> In 1935 Nazi Germany, a law was passed permitting abortions for those deemed "hereditarily ill," while women considered of German stock were specifically prohibited from having abortions.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Friedlander |first=Henry |authorlink=Henry Friedlander |title=The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |location=Chapel Hill |year=1995 |page=[http://books.google.com/books?id=gqLDEKVk2nMC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA30,M1 30] |isbn=978-0-8078-4675-9 |oclc=60191622}} </ref><ref>{{Cite book|first=Robert |last=Proctor |authorlink=Robert N. Proctor |title=Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis |publisher=Harvard University Press |location=[[Cambridge, Massachusetts]] |year=1988 |pages=122, 123 and 366 |isbn=978-0-674-74578-0 |oclc=20760638}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|first=Margaret L. |last=Arnot |authorlink= |coauthors=Cornelie Usborne |title=Gender and Crime in Modern Europe |publisher=Routledge |location=New York |year=1999 |page=231 |isbn=978-1-85728-745-5 |oclc=186748539}}</ref><ref>{{cite encyclopedia |last=DiMeglio |first=Peter M. |editor=Helen Tierney |encyclopedia=Women's studies encyclopedia |title=Germany 1933–1945 (National Socialism) |year=1999 |publisher=Greenwood Press |location=[[Westport, Connecticut]] |isbn=978-0-313-31072-0 |oclc=38504469 |pages=[http://books.google.com/books?id=gQLqRd7hJq0C&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA589,M1 589]}} </ref> |
|||
===Gestational age and method=== |
|||
However, the procedure remained relatively rare until the late 1960s.{{Citation needed|date=June 2011}} In late 1960s and early 1970s, due to a confluence of factors, the number of abortions increased worldwide. In West Germany, the number of reported abortions increased from 2,800 in 1968 to 87,702 in 1980.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.johnstonsarchive.net/policy/abortion/ab-frgermany.html|title=Historical abortion statistics, FR Germany}}</ref> In the United States, some sources show an even greater increase, from 4,600 in 1968 to 1.5 million in 1980.{{Citation needed|date=June 2011}} However, the fact that abortion remained illegal in many states prior to the landmark 1973 decision of [[Roe v. Wade]] may have affected the number of reported abortions prior to 1973. |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = UK abortion by gestational age 2019 histogram.svg |
|||
| width1 = 200 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = |
|||
| image2 = US abortion by gestational age 2016 histogram.svg |
|||
| width2 = 200 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = |
|||
| footer = [[Histogram]] of abortions by [[Gestational age (obstetrics)|gestational age]] in England and Wales during 2019 (left). Abortion in the United States by gestational age, 2016 (right). |
|||
}} |
|||
Abortion rates vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the method practiced. In 2003, the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] (CDC) reported that 26% of reported legal induced abortions in the United States were known to have been obtained at less than 6 weeks' gestation, 18% at 7 weeks, 15% at 8 weeks, 18% at 9 through 10 weeks, 10% at 11 through 12 weeks, 6% at 13 through 15 weeks, 4% at 16 through 20 weeks and 1% at more than 21 weeks. 91% of these were classified as having been done by "[[curettage]]" ([[Suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]], [[dilation and curettage]], [[dilation and evacuation]]), 8% by "[[medical abortion|medical]]" means ([[mifepristone]]), >1% by "[[instillation abortion|intrauterine instillation]]" (saline or [[prostaglandin]]), and 1% by "other" (including [[hysterotomy abortion|hysterotomy]] and [[hysterectomy]]).<ref name="cdc2003">{{cite journal | vauthors = Strauss LT, Gamble SB, Parker WY, Cook DA, Zane SB, Hamdan S | title = Abortion surveillance--United States, 2003 | journal = Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries | volume = 55 | issue = 11 | pages = 1–32 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17119534 | url = https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5511a1.htm | url-status = live | author7 = Centers for Disease Control Prevention | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170602171423/https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5511a1.htm | archive-date = 2 June 2017 }}</ref> According to the CDC, due to data collection difficulties the data must be viewed as tentative and some fetal deaths reported beyond 20 weeks may be natural deaths erroneously classified as abortions if the removal of the dead fetus is accomplished by the same procedure as an induced abortion.<ref name="guttmacher">{{cite web |publisher=The Guttmacher Institute |title=The limitations of U.S. statistics on abortion |work=Issues in Brief |location=New York |year=1997 |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/ib14.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120404080239/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/ib14.html |archive-date=4 April 2012 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
==Society and culture== |
|||
===Abortion debate=== |
|||
{{Double image|right|March for Women's Lives detail.jpg|200|March for life 2009.JPG|200|Pro-choice activists near the [[Washington Monument]] at the [[March for Women's Lives]] in 2004. (left) Pro-life activists near the Washington Monument at the annual 2009 [[March for Life]] in [[Washington, DC]]. (right) ||}} |
|||
The Guttmacher Institute estimated there were 2,200 [[intact dilation and extraction]] procedures in the US during 2000; this accounts for <0.2% of the total number of abortions performed that year.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Finer LB, Henshaw SK | title = Abortion incidence and services in the United States in 2000 | journal = Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health | volume = 35 | issue = 1 | pages = 6–15 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12602752 | doi = 10.1363/3500603 | doi-broken-date = 10 July 2024 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3500603.html | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160122204324/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3500603.html | archive-date = 22 January 2016 | url-access = subscription }}</ref> Similarly, in England and Wales in 2006, 89% of terminations occurred at or under 12 weeks, 9% between 13 and 19 weeks, and 2% at or over 20 weeks. 64% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 6% by D&E, and 30% were medical.<ref>{{cite web|author=Department of Health |year=2007 |title=Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2006 |access-date=12 October 2007 |url=http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsStatistics/DH_075697 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101206002417/http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsStatistics/DH_075697 |archive-date=6 December 2010 }}</ref> There are more second trimester abortions in developing countries such as China, India and Vietnam than in developed countries.<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = Cheng L |date=1 November 2008|title=Surgical versus medical methods for second-trimester induced abortion: RHL commentary|work=The WHO Reproductive Health Library|location=Geneva|publisher=World Health Organization|url=https://www.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/CD006714_chengl_com/en/index.html|access-date=10 February 2009|url-status=dead|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090215134007/http://www.who.int/rhl/fertility/abortion/CD006714_chengl_com/en/index.html|archive-date=15 February 2009}} commentary on:<br />{{cite journal | vauthors = Lohr PA, Hayes JL, Gemzell-Danielsson K | title = Surgical versus medical methods for second trimester induced abortion | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | issue = 1 | pages = CD006714 | date = January 2008 | pmid = 18254113 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD006714.pub2 | s2cid = 205184764 }}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Abortion debate}} |
|||
{{See also|Religion and abortion}} |
|||
In the [[history of abortion]], induced abortion has been the source of considerable debate, controversy, and activism. An individual's position on the complex ethical, moral, philosophical, biological, and legal issues is often related to his or her [[value system]]. The main positions are one that argues in favor of access to abortion and one argues against access to abortion. Opinions of abortion may be described as being a combination of beliefs on its morality, and beliefs on the responsibility, ethical scope, and proper extent of governmental authorities in public policy. [[religion|Religious ethics]] also has an influence upon both personal opinion and the greater debate over abortion (see [[religion and abortion]]). |
|||
There are both medical and non-medical reasons to have an abortion later in pregnancy (after 20 weeks). A study was conducted from 2008 to 2010 at the University of California San Francisco where more than 440 women were asked about why they experienced delays in obtaining abortion care, if there were any. This study found that almost half of individuals who obtained an abortion after 20 weeks did not suspect that they were pregnant until later in their pregnancy.<ref name=":7">{{cite web |date=December 5, 2019 |title=Abortions Later in Pregnancy |url=https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/abortions-later-in-pregnancy/ |website=KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation) |access-date=10 November 2023 |archive-date=10 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231110191733/https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/abortions-later-in-pregnancy/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Other barriers to abortion care found in the study included lack of information about where to access an abortion, difficulties with transportation, lack of insurance coverage, and inability to pay for the abortion procedure.<ref name=":7" /> |
|||
Abortion debates, especially pertaining to [[abortion law]]s, are often spearheaded by groups advocating one of these two positions. In the United States, those in favor of greater legal restrictions on, or even complete prohibition of abortion, most often describe themselves as pro-life while those against legal restrictions on abortion describe themselves as pro-choice. Generally, the former position argues that a human fetus is a human being with a [[right to life|right to live]] making abortion tantamount to murder. The latter position argues that a woman has certain [[reproductive rights]], especially the choice whether or not to carry a pregnancy to term. |
|||
Medical reasons for seeking an abortion later in pregnancy include [[Birth defect|fetal anomalies]] and health risk to the pregnant person.<ref name=":6">{{cite book |last=Vaughn |first=Lewis |title=Bioethics: Principles, Issues, and Cases |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2023 |isbn=978-0-19-760902-6 |edition=5th |pages=328}}</ref> There are prenatal tests that can diagnose [[Down syndrome|Down Syndrome]] or [[cystic fibrosis]] as early as 10 weeks into gestation, but structural fetal anomalies are often detected much later in pregnancy.<ref name=":7" /> A proportion of structural fetal anomalies are lethal, which means that the fetus will almost certainly die before or shortly after birth.<ref name=":7" /> Life-threatening conditions may also develop later in pregnancy, such as [[Pre-eclampsia|early severe preeclampsia]], newly diagnosed cancer in need of urgent treatment, and [[Chorioamnionitis|intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis)]], which often occurs along with [[Prelabor rupture of membranes|premature rupture of the amniotic sac (PPROM)]].<ref name=":7" /> If serious medical conditions such as these arise before the fetus is viable, the person carrying the pregnancy may pursue an abortion to preserve their own health.<ref name=":7" /> |
|||
In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor of or against abortion access focus on either the moral permissibility of an induced abortion, or justification of laws permitting or restricting abortion. |
|||
==Motivation== |
|||
Debate also focuses on whether the pregnant woman should have to notify and/or have the consent of others in distinct cases: for a [[minor (law)|minor]], her parents; for a legally married or [[common-law marriage|common-law]] wife, her husband; or, for any case, [[Paternal rights and abortion|the biological father]]. In a 2003 Gallup poll in the United States, 79% of male and 67% of female respondents were in favor of legalized mandatory spousal notification; overall support was 72% with 26% opposed.<ref>The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. (2005-11-02). "[http://people-press.org/commentary/display.php3?AnalysisID=122 Public Opinion Supports Alito on Spousal Notification Even as It Favors Roe v. Wade]." ''Pew Research Center Pollwatch.'.' Retrieved 2006-03-01.</ref> |
|||
=== |
===Personal=== |
||
[[File:AGIAbortionReasonsBarChart.png|thumb|upright=1.8|A bar chart depicting selected data from a 1998 [[Alan Guttmacher Institute|AGI]] [[meta-study]] on the reasons women stated for having an abortion]] |
|||
{{Main|Abortion law}} |
|||
The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world.<ref name="guttmacher" /><ref name="bankole98"/><ref name=Chae_2017>{{ cite journal | last1=Chae | first1=Sophia | last2=Desai | first2=Sheila | last3=Crowell | first3=Marjorie | last4=Sedgh | first4=Gilda | date=2017-10-01 | title=Reasons why women have induced abortions: a synthesis of findings from 14 countries | journal=[[Contraception (journal)|Contraception]] | volume=96 | issue=4 | pages=233–241 | doi=10.1016/j.contraception.2017.06.014 | pmid=28694165 | pmc=5957082 | quote=In most countries, the most frequently cited reasons for having an abortion were socioeconomic concerns or limiting childbearing. With some exceptions, little variation existed in the reasons given by women's sociodemographic characteristics. Data from three countries where multiple reasons could be reported in the survey showed that women often have more than one reason for having an abortion. | doi-access=free }}</ref> Some of the reasons may include an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, and the wish to complete education or advance a career.<ref name=":5">{{cite journal | last = Stotland | first = Nada L |author-link = Nada Stotland| title = Update on Reproductive Rights and Women's Mental Health | journal = The Medical Clinics of North America | volume = 103 | issue = 4 | pages = 751–766 | date = July 2019 | pmid = 31078205 | doi = 10.1016/j.mcna.2019.02.006 | s2cid = 153307516 }}</ref> Additional reasons include not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest.<ref name="bankole98">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bankole A, Singh S, Haas T |date = September 1998 |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2411798.html |title=Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries |journal=International Family Planning Perspectives |volume=24 |issue=3 |pages=117–127, 152 |doi=10.2307/3038208 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060117191716/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2411798.html |archive-date=17 January 2006 |jstor=3038208 | quote= Worldwide, the most commonly reported reason women cite for having an abortion is to postpone or stop childbearing. The second most common reason—socioeconomic concerns—includes disruption of education or employment; lack of support from the father; desire to provide schooling for existing children; and poverty, unemployment or inability to afford additional children. In addition, relationship problems with a husband or partner and a woman's perception that she is too young constitute other important categories of reasons. Women's characteristics are associated with their reasons for having an abortion: With few exceptions, older women and married women are the most likely to identify limiting childbearing as their main reason for abortion. - Conclusions - Reasons women give for why they seek abortion are often far more complex than simply not intending to become pregnant; the decision to have an abortion is usually motivated by more than one factor. }}</ref><ref name="finer2005">{{cite journal |vauthors=Finer LB, Frohwirth LF, Dauphinee LA, Singh S, Moore AM |title=Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantitative and qualitative perspectives |journal=Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health |volume=37 |issue=3 |pages=110–118 |date=September 2005 |pmid=16150658 |doi=10.1111/j.1931-2393.2005.tb00045.x |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120107092446/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.html |archive-date=7 January 2012|url-access=subscription }}</ref> |
|||
{{See also|Reproductive rights | History of Abortion Law Debate}} |
|||
{{AbortionLawsMap}} |
|||
===Societal=== |
|||
The earliest secular laws regulating abortion reflect a concern with class and caste purity and preservation of male prerogatives. Abortion as such was not outlawed, but wives who procured abortions without their husband's knowledge could be severely punished, as could slaves who induced abortions in highborn women. Generally, abortions prior to [[quickening]] were treated as minor crimes, if at all. |
|||
Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia | veditors = Fried MG |title=From Privacy to Autonomy: The Conditions for Reproductive and Sexual Freedom | vauthors = Copelon R |author-link=Rhonda Copelon |encyclopedia=From Abortion to Reproductive Freedom: Transforming a Movement |date=1990 |publisher=South End Press |isbn=978-0-89608-387-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=keE5EmSKYr0C&q=abortion%20poverty%20autonomy&pg=PA38 |pages=27–43 |quote=The prevalence of economically influenced abortions and the sterilization campaigns against poor, minority, and disabled women show us that autonomy is impossible without eradication of discrimination and poverty. Racism, sexism, and poverty can make the difference between abortions that reflect choice and those reflecting bitter necessity. |access-date=29 October 2020 |archive-date=26 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210126082936/https://books.google.com/books?id=keE5EmSKYr0C&q=abortion%20poverty%20autonomy&pg=PA38 |url-status=live }}</ref> These might include the preference for children of a specific sex or race, disapproval of single or early motherhood, stigmatization of people with disabilities, insufficient economic support for families, lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts toward [[population control]] (such as China's [[one-child policy]]). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or [[sex-selective abortion]].<ref name="MissingWomen">{{cite journal | vauthors = Oster E |author-link=Emily Oster |title=Explaining Asia's "Missing Women": A New Look at the Data |journal=Population and Development Review |date=September 2005 |volume=31 |issue=3 |pages=529–535 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4994961 |access-date=5 February 2019 |doi=10.1111/j.1728-4457.2005.00082.x |quote=Households have variously resorted to female infanticide and postnatal withholding of health care; and since the mid-1980s, when technology permitting fairly low-cost determination of the sex of fetuses became available, there has been a shift toward prenatal sex selection by means of induced abortion. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190207131815/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4994961_Explaining_Asia%27s_Missing_Women_A_New_Look_at_the_Data |archive-date=7 February 2019 |url-status=live }}</ref> In cultures where there is a preference for male children, some women have sex selective abortions, which have partially replaced the earlier practice of female [[infanticide]].<ref name="MissingWomen" /> |
|||
=== Maternal health === |
|||
The new philosophies of the [[Axial Age]], which began discussing the nature and value of human life in abstract terms, had little impact on existing abortion laws. Even the Christian [[ecclesiastical courts]] of the Middle Ages imposed penance and no corporal punishment for abortion, and retained the pre- and post-quickening distinction from the ancient philosophies. |
|||
Some abortions are performed due to concerns over [[maternal health]]. In 1990s, women cited maternal health as their main motivating factor in about a third of abortions in three of 27 countries analyzed. In seven additional countries, about 7% of abortions were maternal health related.<ref name="guttmacher" /><ref name="bankole98"/><!-- Quote = Risk to maternal health. This reason was somewhat important overall, having been cited as the main reason by 5-10% in seven countries and by 20-38% in three (Kenya, Bangladesh and India). --> |
|||
In the U.S., the Supreme Court decisions in ''[[Roe v. Wade]]'' and ''[[Doe v. Bolton]]'': "ruled that the state's interest in the life of the fetus became compelling only at the point of viability, defined as the point at which the fetus can survive independently of its mother. Even after the point of viability, the state cannot favor the life of the fetus over the life or health of the pregnant woman. Under the right of privacy, physicians must be free to use their "medical judgment for the preservation of the life or health of the mother." On the same day that the Court decided Roe, it also decided Doe v. Bolton, in which the Court defined health very broadly: "The medical judgment may be exercised in the light of all factors—physical, emotional, psychological, familial, and the woman's age—relevant to the well-being of the patient. All these factors may relate to health. This allows the attending physician the room he needs to make his best medical judgment."<ref>George J. Annas and Sherman Elias. "Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetrical Practice". Chapter 54 in ''Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies'', 6th edition. Eds. Steven G. Gabbe, et al. 2012 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier. {{ISBN|978-1-4377-1935-2}}</ref>{{rp|1200–1201}} |
|||
With the sole exception of [[Bracton]],<ref>{{Cite book|author=[[Henry de Bracton]] |chapter=The crime of homicide and the divisions into which it falls |editor=George E. Woodbine ed.; Samuel Edmund Thorne trans. |title=On the Laws and Customs of England |origyear={{circa|1250}} |year=1968 |accessdate=2008-12-11 |volume=2 |page=341 |url=http://hlsl5.law.harvard.edu/bracton/Unframed/English/v2/341.htm |oclc=1872|isbn=978-0-19-626613-8}}</ref> commentators on the [[English common law]] formulated the [[born alive rule]], excluding feticide from homicide law, using language dating back to the [[Leges Henrici Primi]].<ref>{{cite web|author=|url=http://law.jrank.org/pages/445/Abortion-Abortion-in-English-law.html |title=Abortion – Abortion In English Law |publisher=Law.jrank.org |date= |accessdate=2011-01-30}}</ref> |
|||
====Cancer==== |
|||
In the late 18th century, it was claimed that scientific knowledge of human development beginning at [[human fertilization|fertilization]] justified stricter abortion laws.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Garrison, Fielding |url=http://books.google.com/?id=JvoIAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA567&dq=fetilization+was+discovered+hertwig |title=An Introduction to the History of Medicine |pages=566–7 |publisher=Saunders |year=1921 |oclc=|isbn=978-0-7216-4030-3}} </ref> This was part of a larger struggle on the part of the medical profession to distinguish scientifically based medicine from "traditional" medicine, including midwifery and herbalism.<ref>''The History of New York State'' Book 12, Chapter 13, Part 3, Editor, Dr. James Sullivan available at [http://www.usgennet.org/usa/ny/state/historyofnewyorkstate/bk12/ch13/pt3.html The History of New York State]</ref> |
|||
{{Update section|date=September 2022}}<!-- Sources here are >10 years old, and should be updated with new ones --> |
|||
The rate of cancer during pregnancy is 0.02–1%, and in many cases, cancer of the mother leads to consideration of abortion to protect the life of the mother, or in response to the potential damage that may occur to the fetus during treatment. This is particularly true for [[cervical cancer]], the most common type of which occurs in 1 of every 2,000–13,000 pregnancies, for which initiation of treatment "cannot co-exist with preservation of fetal life (unless [[neoadjuvant chemotherapy]] is chosen)". Very early stage cervical cancers (I and IIa) may be treated by [[radical hysterectomy]] and pelvic [[lymph node]] dissection, [[radiation therapy]], or both, while later stages are treated by radiotherapy. Chemotherapy may be used simultaneously. Treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy also involves fetal considerations, because [[lumpectomy]] is discouraged in favor of modified [[radical mastectomy]] unless late-term pregnancy allows follow-up radiation therapy to be administered after the birth.<ref name=Weisz>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weisz B, Schiff E, Lishner M | title = Cancer in pregnancy: maternal and fetal implications | journal = Human Reproduction Update | volume = 7 | issue = 4 | pages = 384–393 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11476351 | doi = 10.1093/humupd/7.4.384 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
Exposure to a single chemotherapy drug is estimated to cause a 7.5–17% risk of [[teratogenic]] effects on the fetus, with higher risks for multiple drug treatments. Treatment with more than 40 [[gray (unit)|Gy]] of radiation usually causes spontaneous abortion. Exposure to much lower doses during the first trimester, especially 8 to 15 weeks of development, can cause [[intellectual disability]] or [[microcephaly]], and exposure at this or subsequent stages can cause reduced intrauterine growth and birth weight. Exposures above 0.005–0.025 Gy cause a dose-dependent reduction in [[IQ]].<ref name=Weisz /> It is possible to greatly reduce exposure to radiation with abdominal shielding, depending on how far the area to be irradiated is from the fetus.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mayr NA, Wen BC, Saw CB | title = Radiation therapy during pregnancy | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America | volume = 25 | issue = 2 | pages = 301–321 | date = June 1998 | pmid = 9629572 | doi = 10.1016/s0889-8545(05)70006-1 }}</ref><ref name="pmid11237773">{{cite journal | vauthors = Fenig E, Mishaeli M, Kalish Y, Lishner M | title = Pregnancy and radiation | journal = Cancer Treatment Reviews | volume = 27 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–7 | date = February 2001 | pmid = 11237773 | doi = 10.1053/ctrv.2000.0193 }}</ref> |
|||
Both pre- and post-quickening abortions were criminalized by [[Lord Ellenborough's Act]] in 1803.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://members.aol.com/abtrbng/lea.htm |title=Lord Ellenborough's Act |year=1998 |work=The Abortion Law Homepage |accessdate=2007-02-20 |archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20070918233015/http://members.aol.com/abtrbng/lea.htm |archivedate = 2007-09-18}} (via Archive.org)</ref> In 1861, the [[Parliament of the United Kingdom]] passed the ''[[Offences against the Person Act 1861]]'', which continued to outlaw abortion and served as a model for similar prohibitions in some other nations.<ref>{{cite web|author=United Nations Population Division |year=2002 |url=http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/abortion |title=Abortion Policies: A Global Review |accessdate=February 22, 2007}}</ref> |
|||
The process of birth itself may also put the mother at risk. According to Li ''et al.'', "[v]aginal delivery may result in dissemination of neoplastic cells into lymphovascular channels, haemorrhage, cervical laceration and implantation of malignant cells in the episiotomy site, while abdominal delivery may delay the initiation of non-surgical treatment."<ref name="pmid19197101">{{cite journal | vauthors = Li WW, Yau TN, Leung CW, Pong WM, Chan MY | title = Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix complicating pregnancy | journal = Hong Kong Medical Journal = Xianggang Yi Xue Za Zhi | volume = 15 | issue = 1 | pages = 69–72 | date = February 2009 | pmid = 19197101 }}</ref> |
|||
The Soviet Union, with legislation in 1920, and [[Iceland]], with legislation in 1935, were two of the first countries to generally allow abortion. The second half of the 20th century saw the liberalization of abortion laws in other countries as well. The ''[[Abortion Act 1967]]'' allowed abortion for limited reasons in the United Kingdom (except Northern Ireland). In the 1973 case, ''[[Roe v. Wade]]'', the [[Supreme Court of the United States|United States Supreme Court]] struck down state laws banning abortion, ruling that such laws violated an implied [[right to privacy]] in the [[United States Constitution]]. The [[Supreme Court of Canada]], similarly, in the case of ''[[R. v. Morgentaler]]'', discarded its criminal code regarding abortion in 1988, after ruling that such restrictions violated the security of person guaranteed to women under the ''[[Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms]]''.<ref>{{cite pmid|18821017}}</ref> Canada later struck down provincial regulations of abortion in the case of ''[[R. v. Morgentaler (1993)]].'' By contrast, [[Abortion in the Republic of Ireland|abortion in Ireland]] was affected by the addition of an [[Eighth Amendment of the Constitution of Ireland|amendment]] to the Irish [[Constitution of Ireland|Constitution]] in 1983 by popular referendum, recognizing "the right to life of the unborn". |
|||
===Fetal health=== |
|||
Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral, and cultural sensibilities continue to influence abortion laws throughout the world. The right to life, the right to liberty, the right to [[security of person]], and the right to [[reproductive rights|reproductive health]] are major issues of human rights that are sometimes used as justification for the existence or absence of laws controlling abortion. Many countries in which abortion is legal require that certain criteria be met in order for an abortion to be obtained, often, but not always, using a trimester-based system to regulate the window of legality: |
|||
[[Congenital disorders]], revealed by [[prenatal screening]], motivate some women to seek abortions.<ref name="bankole98"/> |
|||
* In the United States, some states impose a 24-hour waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on [[prenatal development|fetal development]], or require that [[minors and abortion|parents be contacted]] if their minor daughter requests an abortion.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://internationalfamilyplanningperspectives.org/pubs/MandatoryCounseling.pdf|title=The Impact of State Mandatory Counseling and Waiting Period Laws on Abortion: A Literature Review|format=PDF|publisher=[[Guttmacher Institute]]|author=Theodore J. Joyce, Stanley K. Henshaw, Amanda Dennis, Lawrence B. Finer and Kelly Blanchard|date=April 2009|accessdate=December 31, 2010|archiveurl = http://www.webcitation.org/5vj6Mlykp |archivedate = 2011-01-14|deadurl=yes}}</ref> |
|||
* In the United Kingdom, as in some other countries, two doctors must first certify that an abortion is medically or socially necessary before it can be performed.{{Citation needed|date=December 2010}} |
|||
In the United States, public opinion shifted after television personality [[Sherri Finkbine]]'s was exposed to [[thalidomide]], a [[teratogen]], in her fifth month of pregnancy. Unable to obtain a legal abortion in the United States, Finkbine traveled to Sweden. From 1962 to 1965, an outbreak of [[Rubella|German measles]] left 15,000 babies with severe birth defects. In 1967, the [[American Medical Association]] publicly supported liberalization of abortion laws. A [[National Opinion Research Center]] poll in 1965 showed 73% supported abortion when the mother's life was at risk, 57% when birth defects were present and 59% for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest.{{sfn|Doan|2007|p=57}} |
|||
Other countries, in which abortion is normally illegal, will allow one to be performed in the case of rape, incest, or danger to the pregnant woman's life or health. |
|||
* A few nations ban abortion entirely: [[Abortion in Chile|Chile]], [[Abortion in El Salvador|El Salvador]], [[Abortion in Malta|Malta]], and [[Abortion in Nicaragua|Nicaragua]]. In Nicaragua, rises in maternal death directly and indirectly due to pregnancy have been noted.<ref>{{cite web|title=European delegation visits Nicaragua to examine effects of abortion ban |date=November 26, 2007 |publisher=Ipas |accessdate=2009-06-15| url=http://www.ipas.org/Library/News/News_Items/European_delegation_visits_Nicaragua_to_examine_effects_of_abortion_ban.aspx| archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080417033829/http://www.ipas.org/Library/News/News_Items/European_delegation_visits_Nicaragua_to_examine_effects_of_abortion_ban.aspx| archivedate=2008-04-17 }} "More than 82 maternal deaths had been registered in Nicaragua since the change. During this same period, indirect obstetric deaths, or deaths caused by illnesses aggravated by the normal effects of pregnancy and not due to direct obstetric causes, have doubled."</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://insidecostarica.com/special_reports/2008-06/nicaragua_womens_movement.htm |title=NICARAGUA: "The Women’s Movement Is in Opposition" |date=28 June 2008 |place=Montevideo |agency=IPS |publisher=Inside Costa Rica}}</ref> However, in 2006, the [[Politics of Chile|Chilean government]] began the free distribution of [[emergency contraception]].<ref>{{Cite news|author=Ross, Jen |date=September 12, 2006 |url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0912/p01s04-woam.html |title=In Chile, free morning-after pills to teens |work=The Christian Science Monitor |accessdate=2006-12-07}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|author=Gallardoi, Eduardo |date=September 26, 2006 |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/09/26/AR2006092600770.html |title=Morning-After Pill Causes Furor in Chile |work=[[The Washington Post]] |accessdate=2006-12-07}}</ref> |
|||
* In [[Bangladesh]], abortion is illegal, but the government has long supported a network of "menstrual regulation clinics", where [[menstrual extraction]] ([[manual vacuum aspiration]]) can be performed as menstrual hygiene.<ref>{{cite web|title=Surgical Abortion: History and Overview |publisher=National Abortion Federation |accessdate=2006-09-04 |url=http://www.prochoice.org/education/resources/surg_history_overview.html }}</ref> |
|||
==History and religion== |
|||
In places where abortion is illegal or carries heavy social stigma, pregnant women may engage in [[medical tourism]] and travel to countries where they can terminate their pregnancies. Women without the means to travel can resort to providers of illegal abortions or try to do it themselves. |
|||
{{Main|History of abortion|Religion and abortion}} |
|||
<ref>{{cite web|title=Need Abortion, Will Travel |author=Marcy Bloom |date=February 25, 2008 |publisher=RH Reality Check |accessdate=2009-06-15| url=http://www.rhrealitycheck.org/blog/2008/02/25/need-abortion-will-travel}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:AngkorWatAbortionAD1150.JPG|thumb|[[Bas-relief]] at [[Angkor Wat]], [[Cambodia]], c. 1150, depicting a [[demon]] inducing an abortion by pounding the abdomen of a pregnant woman with a [[pestle]]<ref name="potts"/><ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Mould RF |title=Mould's Medical Anecdotes |page=406 |publisher=CRC Press |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-85274-119-1| url=https://archive.org/details/moreofmouldsmedi00moulrich/page/406}}</ref>]] |
|||
Since [[ancient times]], abortions have been done using a number of methods, including [[herbal medicine]]s acting as [[abortifacient]]s, sharp tools through the use of force, or through other [[traditional medicine]] methods.<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/> Induced abortion has a long history and can be traced back to civilizations as varied as ancient China (abortifacient knowledge is often attributed to the mythological ruler [[Shennong]]),<ref>{{cite book| title=Medical History of Contraception| vauthors = Himes NE |publisher=Gamut Press|year=1963|pages=109–110}}</ref> [[ancient India]] since its [[Vedic age]],<ref name="Misra2006">{{cite book| vauthors = Misra P |title=Domestic Violence Against Women: Legal Control and Judicial Response|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dp6-_NMfsIsC&pg=PA79| year=2006| publisher=Deep & Deep Publications|isbn=978-81-7629-896-4|pages=79–80|quote=References in Atharva Veda show that abortion was known in the Vedic age.|access-date=5 July 2021|archive-date=9 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210709185150/https://books.google.com/books?id=dp6-_NMfsIsC&pg=PA79|url-status=live}}</ref> [[ancient Egypt]] with its [[Ebers Papyrus]] ({{circa|1550 BCE}}), and the Roman Empire in the time of [[Juvenal]] ({{circa|200 CE}}).<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/> One of the earliest known artistic representations of abortion is in a [[bas relief]] at Angkor Wat ({{circa|1150}}). Found in a series of [[frieze]]s that represent judgment after death in [[Hinduism|Hindu]] and [[Buddhist]] culture, it depicts the technique of abdominal abortion.<ref name="potts"/> |
|||
In the US, about 8% of abortions are performed on women who travel from another state.<ref>{{cite web|title=United States: Percentage of Legal Abortions Obtained by Out-of-State Residents, 2005 |publisher=The Kaiser Family Foundation |accessdate=2009-06-14| url=http://www.statehealthfacts.kff.org/profileind.jsp?rgn=1&cat=10&ind=467}}</ref> However, that is driven at least partly by differing limits on abortion according to gestational age or the scarcity of doctors trained and willing to do later abortions.<ref>{{Cite jstor|2135775}}</ref> Thousands of women every year travel from Northern Ireland, the Republic of Ireland, Poland, and other countries where elective abortion is illegal, to Britain or other countries with less restrictive laws, in order to obtain abortions.<ref>{{Cite news |url=http://www.eturbonews.com/6052/thousands-women-n-ireland-travel-england-abortions |publisher=eTurboNews |date=November 5, 2008 |first=Shawn |last=Pogatchnik |title=Thousands of women in N. Ireland travel to England for abortions}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |publisher=Reuters |url=http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE67P46Z20100826 |title=More Polish women seen seeking abortions abroad |date=August 26, 2010 |first=Gabriela |last=Baczynska}}</ref> |
|||
[[Judaism and abortion|In Judaism]] ({{bibleverse|Genesis|2:7}}), the fetus is not considered to have a human soul until it is safely outside of the woman, is viable, and has taken its first breath.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors=Schenker JG |title=The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law) |journal=Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics |volume=25 |issue=6 |pages=271–276 |date=June 2008 |pmid=18551364 |pmc=2582082 |doi=10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|vauthors=Rosner F|year=2001|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T7w2oAmohpEC|title=Biomedical Ethics and Jewish Law|publisher=KTAV Publishing House|isbn=978-0-88125-701-4|access-date=27 July 2022| via=Google Books|archive-date=24 January 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230124173418/https://books.google.com/books?id=T7w2oAmohpEC|url-status=live}} Reprinted as {{cite web|vauthors=Rosner F|date=7 June 2015|url=https://www.myjewishlearning.com/article/the-beginning-of-life-in-judaism/|url-status=live|title=The Beginning of Life in Judaism|website=My Jewish Learning|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150607041405/https://www.myjewishlearning.com/article/the-beginning-of-life-in-judaism/| archive-date=7 June 2015| access-date=27 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Milgram G| url=http://www.reclaimingjudaism.org/teachings/when-does-life-begin-jewish-view|title=When Does Life Begin? A Jewish View| website=Reclaiming Judaism|date=23 January 2022|access-date=30 June 2022|archive-date=3 August 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220803233439/http://www.reclaimingjudaism.org/teachings/when-does-life-begin-jewish-view| url-status=live}}</ref> The fetus is considered valuable property of the woman and not a human life while in the womb ({{bibleverse||Exodus|21:22-23|HE}}). While [[Judaism]] encourages people to [[be fruitful and multiply]] by having children, abortion is allowed and is deemed necessary when a pregnant woman's life is in danger.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.ncjw.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Judaism-and-Abortion-FINAL.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.ncjw.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Judaism-and-Abortion-FINAL.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=Judaism and Abortion|publisher=National Council of Jewish Women| date=May 2019|access-date=27 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|vauthors=Kestler-D'Amours J|date=17 June 2022| url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/6/17/religious-freedom-the-next-battleground-for-us-abortion-rights| title=Religious freedom: The next battleground for US abortion rights?|publisher=Al Jazeera|access-date=27 July 2022| archive-date=1 August 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220801020805/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/6/17/religious-freedom-the-next-battleground-for-us-abortion-rights|url-status=live}}</ref> Several religions, including Judaism, which disagree that [[human life begins at conception]], support the legality of abortion on [[religious freedom]] grounds.<ref name="Georgian 2022">{{cite web|vauthors=Georgian E|date=1 July 2022|url=https://clioandthecontemporary.com/2022/07/01/the-end-of-roe-in-historical-perspective/|title=The End of Roe in Historical Perspective|website=Clio and the Contemporary|access-date=27 July 2022| archive-date=27 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220727180424/https://clioandthecontemporary.com/2022/07/01/the-end-of-roe-in-historical-perspective/|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Islam and abortion|In Islam]], abortion is traditionally permitted until a point in time when Muslims believe the soul enters the fetus,<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1" /> considered by various theologians to be at conception, 40 days after conception, 120 days after conception, or at [[quickening]].<ref name="BBC and Islam / Abortion">{{cite news|date=9 July 2009| url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/islamethics/abortion_1.shtml|title=Religions – Islam: Abortion| publisher=BBC| access-date=10 December 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111009065222/http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/islamethics/abortion_1.shtml|archive-date=9 October 2011}}</ref> Abortion is largely heavily restricted or forbidden in areas of high [[Islam]]ic faith such as the [[Middle East and North Africa]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Abortion in the Middle East and North Africa| url=http://www.prb.org/pdf08/MENAabortion.pdf|url-status=live| vauthors = Dabash R, Farzaneh RF |publisher=Population Research Bureau|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20111006171600/http://www.prb.org/pdf08/MENAabortion.pdf |archive-date=6 October 2011|year=2008}}</ref> |
|||
In the United States and some Canadian localities, [[Legal protection of access to abortion|it is a legal offense to obstruct access to a clinic or doctor's office where abortions are performed]]. "Buffer zones," regulating how close protesters can come to the clinic or to the patients, may exist. |
|||
Some medical scholars and abortion opponents have suggested that the [[Hippocratic Oath]] forbade physicians in [[Ancient Greece]] from performing abortions;<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/> other scholars disagree with this interpretation,<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/> and state that the medical texts of [[Hippocratic Corpus]] contain descriptions of abortive techniques right alongside the Oath.<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Miles SH |title=The Hippocratic Oath and the Ethics of Medicine|year=2005|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-518820-2}}</ref> The physician [[Scribonius Largus]] wrote in 43 CE that the Hippocratic Oath prohibits [[Surgery in Ancient Rome|abortion]], as did [[Soranus of Ephesus]], although apparently not all doctors adhered to it strictly at the time. According to Soranus' 1st or 2nd century CE work ''Gynaecology'', one party of medical practitioners banished all abortives as required by the Hippocratic Oath; the other party to which he belonged was willing to prescribe abortions only for the sake of the mother's health.<ref name=Soranus>{{cite book |author=Soranus|translator=Temkin O |translator2=Eastman NJ |translator3=Edelstein L |translator4=Guttmacher AF |title=Soranus' Gynecology| year=1991|publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press|page=I, 19, 60 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YsKWfh31gxwC| access-date=6 October 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015195038/https://books.google.com/books?id=YsKWfh31gxwC|archive-date=15 October 2015 |isbn=978-0-8018-4320-4}}</ref><ref name=Largus>{{cite encyclopedia |url=http://penelope.uchicago.edu/~grout/encyclopaedia_romana/aconite/largus.html|title=Scribonius Largus and the Oath of Hippocrates |encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Romana|publisher=University of Chicago|access-date=27 July 2022}}</ref> In ''[[Politics (Aristotle)|Politics]]'' (350 BCE), [[Aristotle]] condemned infanticide as a means of population control. He preferred abortion in such cases,<ref>{{cite book| vauthors=Carrick P |title=Medical Ethics in the Ancient World| year=2001 |publisher=Georgetown University Press|isbn=978-0-87840-849-8}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors=Meyer HS |date=17 April 2002|title=Ancient Ethics: Medical Ethics in the Ancient World|journal=JAMA |publisher=American Medical Association|volume=287|issue=15|pages=2005–2006|doi=10.1001/jama.287.15.2005-JBK0417-3-1 |s2cid=240484236 }}</ref> with the restriction that it "must be practised on it before it has developed sensation and life; for the line between lawful and unlawful abortion will be marked by the fact of having sensation and being alive."<ref>{{cite book| author=Aristotele| title=Aristotle, Politics|translator=Rackham H|year=1944|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0058%3Abook%3D7%3Asection%3D1335b |publisher=Harvard University Press |access-date=21 June 2011| via=Perseus|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110622094459/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0058%3Abook%3D7%3Asection%3D1335b|archive-date=22 June 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Mandatory spousal notification was ruled unconstitutional in the United States by the Supreme Court in ''[[Planned Parenthood v. Casey]]''.<ref>{{cite pmid|1640971}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|editor1-last=Gabbe|editor1-first=Steven G.|editor1-link=Steven Gabbe|editor2-last=Niebyl|editor2-first=Jennifer R.|editor3-last=Simpson|editor3-first=Joe Leigh|year=2007|title=Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies|edition=5|publisher=[[Churchill Livingstone]]|chapter=51. Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetric Practice|isbn=978-0-443-06930-7|last1=Annas|first1=George J.|authorlink1=George Annas|last2=Elias|first2=Sherman}}</ref> |
|||
In the [[Catholic Church and abortion|Catholic Church]], opinion was divided on how serious abortion was in comparison with such acts as contraception, oral sex, and sex in marriage for pleasure rather than procreation.<ref name="Noonan"/>{{rp|155–167}} The [[Catholic Church]] did not begin vigorously opposing abortion until the 19th century.<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/><ref name="Georgian 2022"/> As early as ~100 CE, the ''[[Didache]]'' taught that abortion was sinful.<ref>{{cite web|date=9 September 2016|title=Didache|website=Legacy Icons| url=https://legacyicons.com/content/didache.pdf|access-date=16 May 2022|url-status=live|archive-date=8 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201108201133/https://legacyicons.com/content/didache.pdf}}</ref> Several historians argue that prior to the 19th century most Catholic authors did not regard termination of pregnancy before [[quickening]] or [[ensoulment]] as an abortion.<ref>Joan Cadden, "Western medicine and natural philosophy", in Vern L. Bullough and James A. Brundage, eds., ''Handbook of Medieval Sexuality'', Garland, 1996, pp. 51–80.</ref><ref>Cyril C. Means Jr., "A historian's view", in Robert E. Hall, ed., ''Abortion in a Changing World'', vol. 1, Columbia University Press, 1970, pp. 16–24.</ref><ref>John M. Riddle, "Contraception and early abortion in the Middle Ages", in Vern L. Bullough and James A. Brundage, eds., ''Handbook of Medieval Sexuality'', Garland, 1996, pp. 261–277, {{ISBN|978-0-8153-1287-1}}.</ref> Among these authors were the [[Doctors of the Church]], such as [[St. Augustine]], [[St. Thomas Aquinas]], and [[St. Alphonsus Liguori]]. In 1588, [[Pope Sixtus V]] ({{reign}} 1585–1590) was the only Pope before [[Pope Pius IX]] (in his 1869 [[Papal bull|bull]], ''Apostolicae Sedis'') to institute a Church policy labeling all abortion as homicide and condemning abortion regardless of the stage of pregnancy.<ref>{{cite web|author=Pope Sixtus V| year=1588| title=Effraenatam| via=The Embryo Project Encyclopedia|url=https://embryo.asu.edu/pages/effraenatam-1588-pope-sixtus-v| url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210526144925/https://embryo.asu.edu/pages/effraenatam-1588-pope-sixtus-v|archive-date=26 May 2021|access-date=26 May 2021}}</ref><ref name="Noonan">{{cite book| vauthors = Noonan JT |title=Contraception: A History of Its Treatment by the Catholic Theologians and Canonists |edition=2nd |publisher= Harvard University Press|year=1986}}</ref>{{rp|362–364}}<ref name="riddle2"/>{{rp|157–158}} Sixtus V's pronouncement was reversed in 1591 by [[Pope Gregory XIV]].<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = Gershon L |date=13 February 2018|title=What a 16th-Century Abortion Ban Revealed|url=https://daily.jstor.org/what-a-16th-century-abortion-ban-revealed/|url-status=live| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210526144922/https://daily.jstor.org/what-a-16th-century-abortion-ban-revealed/| archive-date=26 May 2021|access-date=26 May 2021|website=JSTOR Daily}}</ref> In the recodification of [[1917 Code of Canon Law]], ''Apostolicae Sedis'' was strengthened, in part to remove a possible reading that excluded excommunication of the mother.<ref>{{cite web|title=Apostolicae Sedis Moderationi|website=New Advent |url=https://www.newadvent.org/cathen/01645a.htm|access-date=16 May 2022|url-status=live|archive-date=16 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220516174009/https://www.newadvent.org/cathen/01645a.htm}}</ref> Statements made in the ''[[Catechism of the Catholic Church]]'', the codified summary of the Church's teachings, considers abortion from the moment of conception as homicide and called for the end of legal abortion.<ref>{{cite web|date=1992|title=Catechism of the Catholic Church, chapter 2, article 5 |url=https://www.vatican.va/archive/ccc_css/archive/catechism/p3s2c2a5.htm| website=Vatican| access-date=4 December 2019| archive-date=14 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514012545/https://www.vatican.va/archive/ccc_css/archive/catechism/p3s2c2a5.htm|url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Other issues in abortion law may include the [[Minors and abortion|requirement that a minor obtain the consent of one or both parents to the abortion or that she notify one or both parents]], the [[Paternal rights and abortion|requirement that a woman obtain the consent of her husband to the abortion and the question of whether the fetus's father can prohibit an abortion]], the requirement that abortion providers inform patients of the supposed health risks of the procedure, and [[wrongful birth]] laws. |
|||
Denominations that support abortion rights with some limits include the [[United Methodist Church]], [[Episcopal Church (United States)|Episcopal Church]], [[Evangelical Lutheran Church in America]] and [[Presbyterian Church USA]].<ref name="Masci 2020">{{cite web | last=Masci | first=David | title=Where major religious groups stand on abortion | website=Pew Research Center | date=2020-05-30 | url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/06/21/where-major-religious-groups-stand-on-abortion/ | access-date=2023-01-22 | archive-date=22 January 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230122160816/https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/06/21/where-major-religious-groups-stand-on-abortion/ | url-status=live }}</ref> A 2014 Guttmacher survey of abortion patients in the United States found that many reported a religious affiliation: 24% were Catholic while 30% were Protestant.<ref>{{cite report| url=https://www.guttmacher.org/report/characteristics-us-abortion-patients-2014|title=Characteristics of U.S. Abortion Patients in 2014 and Changes Since 2008| vauthors = Jerman J, Jones RK, Onda T |date=10 May 2016| publisher=Guttmacher| access-date=25 February 2021|archive-date=24 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224085344/https://www.guttmacher.org/report/characteristics-us-abortion-patients-2014| url-status=live}}</ref> A 1995 survey reported that Catholic women are as likely as the general population to terminate a pregnancy, [[Protestants]] are less likely to do so, and [[evangelical Christians]] are the least likely to do so.<ref name="guttmacher"/><ref name="bankole98"/> A 2019 [[Pew Research Center]] study found that most [[Christian denomination]]s were against overturning ''[[Roe v. Wade]],'' which in the United States legalized abortion, at around 70%, except White Evangelicals at 35%.<ref name="PewReseach2019">{{cite web|url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/10/20/8-key-findings-about-catholics-and-abortion/|title=8 key findings about Catholics and abortion|date=20 October 2020 | publisher=Pew Research Center|access-date=15 May 2022|archive-date=15 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220515173202/https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/10/20/8-key-findings-about-catholics-and-abortion/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Sex-selective=== |
|||
{{Main|Sex-selective abortion}} |
|||
[[File:FrenchPeriodicalPills-January61845,BostonDailyTimes.jpg|thumb|"French Periodical Pills" was an example of a clandestine advertisement published in a January 1845 edition of the ''[[Boston Daily Times]]''.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/53993049 |title=The abortion rights controversy in America: a legal reader |date=2004 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |editor-first=N. E. H. |editor-last=Hull |editor-first2=Williamjames |editor-last2=Hoffer |editor-first3=Peter Charles |editor-last3=Hoffer |isbn=0-8078-2873-4 |location=Chapel Hill |oclc=53993049 |page=17 |access-date=21 April 2023 |archive-date=1 July 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240701041348/https://search.worldcat.org/title/53993049 |url-status=live }}</ref>]] |
|||
[[Medical ultrasonography|Sonography]] and [[amniocentesis]] allow parents to determine sex before childbirth. The development of this technology has led to [[sex-selective abortion and female infanticide|sex-selective abortion]], or the termination of a fetus based on sex. The selective termination of a female fetus is most common. |
|||
Abortion has been a fairly common practice,<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Reagan LJ |year=2022|orig-year=1997|title=When Abortion Was a Crime: Women, Medicine and the Law in the United States, 1867–1973|edition=1st |location=Berkeley| publisher=University of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-38741-6}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Blakemore E|date=22 May 2022 |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/history/article/the-complex-early-history-of-abortion-in-the-united-states |title=The complex early history of abortion in the United States|website=National Geographic|access-date=26 July 2022| quote=But that view of history is the subject of great dispute. Though interpretations differ, most scholars who have investigated the history of abortion argue that terminating a pregnancy wasn't always illegal—or even controversial.| archive-date=26 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220726201522/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/history/article/the-complex-early-history-of-abortion-in-the-united-states|url-status=dead}}</ref> and was not always illegal or controversial until the 19th century.<ref name="Hardin 1978">{{cite journal| vauthors = Hardin G |date=December 1978|title=Abortion in America. The Origins and Evolution of National Policy, 1800–1900. James C. Mohr|journal=The Quarterly Review of Biology| volume=53| issue=4| page=499|doi=10.1086/410954|quote=The long silence had led us to assume that opposition to abortion had existed from time immemorial. Not so: most of the opposition to, and all of the laws against, abortion arose in the 19th century. Historian Mohr amply documents the earlier acceptance of abortion. ... In the 19th century even many of the feminists expressed horror at abortion, urging abstinence instead. Not so in the 20th century. In the 19th century the medical profession was fairly united against abortion; Mohr argues that this arose from the commercial competition between the 'regulars' (men with M.D.'s) and the irregulars (women without M.D.'s). ... A key role in generating prohibition laws was played by the press, ... . By 1900 the abortion-prohibition laws were immune to questioning, as they remained until the 1960's when feminists and a new breed of physicians combined to arouse the public to the injustice of the law. ... the ''Roe v. Wade'' decision of the Supreme Court ... essentially returned the practice of abortion to the permissive state ''ante'' 1820.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Acevedo ZP |date=Summer 1979|title=Abortion in early America| journal=Women Health|volume=4|issue=2|pages=159–167|doi=10.1300/J013v04n02_05|pmid=10297561 |quote=This piece describes abortion practices in use from the 1600s to the 19th century among the inhabitants of North America. The abortive techniques of women from different ethnic and racial groups as found in historical literature are revealed. Thus, the point is made that abortion is not simply a 'now issue' that effects select women. Instead, it is demonstrated that it is a widespread practice as solidly rooted in our past as it is in the present.}}</ref> Under [[common law]], including early [[English common law]] dating back to [[Edward Coke]] in 1648,<ref name="Alford 2003">{{cite journal| vauthors = Alford S |title=Is Self-Abortion a Fundamental Right?|volume=52|journal=Duke Law Journal|pages=1011–1029| issue=5| year=2003| jstor=1373127|pmid=12964572}}</ref> abortion was generally permitted before quickening (14–26 weeks after conception, or between the fourth and sixth month),<ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Dine R|date=8 August 2013| url=https://www.americanprogress.org/article/scarlet-letters-getting-the-history-of-abortion-and-contraception-right/| title=Scarlet Letters: Getting the History of Abortion and Contraception Right|publisher=Center for American Progress| access-date=26 July 2022|archive-date=28 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220728035809/https://www.americanprogress.org/article/scarlet-letters-getting-the-history-of-abortion-and-contraception-right/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Reagan LJ|date=2 June 2022 |url=https://www.politico.com/news/magazine/2022/06/02/alitos-anti-roe-argument-wrong-00036174|title=What Alito Gets Wrong About the History of Abortion in America|website=Politico|access-date=26 July 2022|archive-date=23 June 2022| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220623133238/https://www.politico.com/news/magazine/2022/06/02/alitos-anti-roe-argument-wrong-00036174|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|vauthors=Root D|date=23 June 2022| url=https://reason.com/2022/06/23/unenumerated-rights-and-roe-v-wade/|title=Alito's Leaked Abortion Opinion Misunderstands Unenumerated Rights| work=Reason|access-date=27 July 2022|archive-date=27 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220727180438/https://reason.com/2022/06/23/unenumerated-rights-and-roe-v-wade/|url-status=live}}</ref> and at women's discretion;<ref name="Georgian 2022"/> it was whether abortion was performed after quickening that determined if it was a crime.<ref name="Alford 2003"/> In Europe and North America, abortion techniques advanced starting in the 17th century; the [[conservatism]] of most in the medical profession with regards to sexual matters prevented the wide expansion of abortion techniques.<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/><ref>{{cite book| title=Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy| vauthors = Mohr JC |year=1978|pages=[https://archive.org/details/abortioninameric00mohr/page/35 35–36]|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-502616-0| url=https://archive.org/details/abortioninameric00mohr/page/35}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|vauthors=Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD, Joffe C|year=2009|chapter-url=http://media.wiley.com/product_data/excerpt/62/14051769/1405176962.pdf|url-status=live|chapter=Abortion and Medicine: A Sociopolitical History|title=Management of Unintended and Abnormal Pregnancy|edition=1st|location=Oxford|publisher=John Wiley & Sons| isbn=978-1-4443-1293-5|ol=15895486W|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120119025652/http://media.wiley.com/product_data/excerpt/62/14051769/1405176962.pdf|archive-date=19 January 2012}}</ref> Other medical practitioners in addition to some physicians advertised their services, and they were not widely regulated until the 19th century when the practice, sometimes called ''[[restellism]]'',<ref>{{cite news| vauthors = Dannenfelser M |title=The Suffragettes Would Not Agree With Feminists Today on Abortion| url=http://time.com/4093214/suffragettes-abortion/|access-date=4 November 2015|magazine=Time|date=4 November 2015|url-status=live| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151106015742/http://time.com/4093214/suffragettes-abortion/| archive-date=6 November 2015}}</ref> was banned in both the United States and the United Kingdom.<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/>{{refn|In the United States, the first laws related to abortion beginning in the 1820s were made to protect women from real or perceived risks, and those more restrictive penalized only the provider. By 1859, abortion was not a crime in 21 out of 33 states, and was prohibited only post-quickening, while penalties for pre-quickening abortions were lower. This changed starting in the 1860s under the influence of [[anti-immigrant]] and [[anti-Catholic]] sentiment.<ref name="Georgian 2022"/>|group=nb}} |
|||
It is suggested that sex-selective abortion might be partially responsible for the noticeable disparities between the birth rates of male and female children in some places. The preference for male children is reported in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has been reported in China, Taiwan, South Korea, and India.<ref>Banister, Judith. (1999-03-16). [http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/ebspr96a.html Son Preference in Asia – Report of a Symposium]. Retrieved 2006-01-12.</ref> |
|||
Some 19th-century physicians, one of the most famous and consequential being the American [[Horatio Storer]],<ref name="Samuels & Potts 2022"/> argued for anti-abortion laws on [[racist]] and [[misogynist]] as well as moral grounds.<ref name="NPR 2022"/><ref>{{cite book |last=Poole |first=W. Scott |url=https://archive.org/details/sataninamericade0000pool |title=Satan in America: The Devil We Know |publisher=[[Rowman & Littlefield]] |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-7425-6171-7 |page=86 |access-date=2023-03-20 |url-access=registration }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Wilson C |date=2 November 2020|title=Nostalgia, Entitlement and Victimhood: The Synergy of White Genocide and Misogyny|journal=Terrorism and Political Violence|volume=34 |issue=8 |publisher=Routledge|pages=1810–1825|doi=10.1080/09546553.2020.1839428 |s2cid=228837398 }} Storer is cited at p. 4.</ref> Church groups were also highly influential in [[anti-abortion movement]]s,<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/><ref name="Hardin 1978"/><ref name="NPR 2022">{{cite news |vauthors=Abdeltath R, Arablouei R, Caine J, Kaplan-Levenson L, Wu L, Yvellez V, Miner C, Sangweni Y, Steinberg A, George D |display-authors=6 |title=Before Roe: The Physicians' Crusade |url=https://www.npr.org/2022/05/18/1099795225/before-roe-the-physicians-crusade |work=Throughline |publisher=NPR |access-date=26 July 2022 |archive-date=26 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220726150545/https://www.npr.org/2022/05/18/1099795225/before-roe-the-physicians-crusade |url-status=live }}</ref> and religious groups more so since the 20th century.<ref name="Samuels & Potts 2022">{{cite web| vauthors=Samuels A, Potts M|date=25 July 2022|url=https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-the-fight-to-ban-abortion-is-rooted-in-the-great-replacement-theory/|title=How The Fight To Ban Abortion Is Rooted In The 'Great Replacement' Theory| website=FiveThirtyEight|access-date=26 July 2022|archive-date=25 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220725234312/https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-the-fight-to-ban-abortion-is-rooted-in-the-great-replacement-theory/|url-status=live}}</ref> Some of the early [[anti-abortion laws]] punished only the doctor or abortionist,<ref name="Georgian 2022"/> and while women could be criminally tried for a [[self-induced abortion]],<ref name="Alford 2003"/> they were rarely prosecuted in general.<ref name="Hardin 1978"/> In the United States, some argued that abortion was more dangerous than childbirth until about 1930 when incremental improvements in abortion procedures relative to childbirth made abortion safer.{{refn|By 1930, medical procedures in the United States had improved for both childbirth and abortion but not equally, and induced abortion in the first trimester had become safer than childbirth. In 1973, ''Roe v. Wade'' acknowledged that abortion in the first trimester was safer than childbirth. For sources, see: |
|||
In India, the economic role of men, the costs associated with [[dowry|dowries]], and a common Indian tradition which dictates that [[funeral|funeral rites]] must be performed by a male relative have led to a cultural preference for sons.<ref>Mutharayappa, Rangamuthia, Kim Choe, Minja, Arnold, Fred, and Roy, T.K. (1997). [http://www2.eastwestcenter.org/pop/misc/subj-3.pdf Son Preferences and Its Effect on Fertility in India]. ''National Family Health Survey Subject Reports, Number 3.'.' Retrieved 2006-01-12.</ref> The widespread availability of diagnostic testing, during the 1970s and '80s, led to advertisements for services which read, "Invest 500 [[rupee]]s [for a sex test] now, save 50,000 rupees [for a dowry] later."<ref>{{Cite journal|first=Rita |last=Patel |year=1996 |month=Fall |title=The practice of sex selective abortion in India: May you be the mother of a hundred sons |journal=Carolina Papers in International Health and Development |volume=7 |url=http://cgi.unc.edu/research/pdf/abortion.pdf |archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5qWhqeiZq |archivedate=2010-06-16 |format=PDF|accessdate=2008-12-03}}</ref> In 1991, the male-to-female [[human sex ratio|sex ratio]] in India was skewed from its biological norm of 105 to 100, to an average of 108 to 100.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Sudha |first=S. |year=1999 |month=July |title=Female Demographic Disadvantage in India 1981–1991: Sex Selective Abortions and Female Infanticide |journal=Development and Change |volume=30 |issue=3 |pages=585–618 |doi=10.1111/1467-7660.00130 |url=http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/organizations/healthnet/gender/docs/sudha.html |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20030101210623/http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/organizations/healthnet/gender/docs/sudha.html |archivedate=2003-01-01 |accessdate=2008-12-03 |last2=Rajan |first2=S. Irudaya |pmid=20162850}}</ref> Researchers have asserted that between 1985 and 2005 as many as 10 million female fetuses may have been selectively aborted.<ref>{{Cite news|first=Patricia |last=Reaney |publisher=Reuters |url=http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L06779563.htm |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060220072756/http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L06779563.htm |archivedate=2006-02-20 |title=Selective abortion blamed for India's missing girls |accessdate=2008-12-03}}</ref> The Indian government passed an official ban of pre-natal sex screening in 1994 and moved to pass a complete ban of sex-selective abortion in 2002.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Mudur |first=Ganapati |year=2002 |title=India plans new legislation to prevent sex selection |journal=[[BMJ]] |volume=324 |issue=7334 |page=385b |doi=10.1136/bmj.324.7334.385/b}}</ref> |
|||
* {{cite book|title=Time Communication 1940–1989: Retrospective|publisher=Time|year=1989|chapter=The 1970s|quote=Blackmun was also swayed by the fact that most abortion prohibitions were enacted in the 19th century when the procedure was more dangerous than now.}} |
|||
* {{cite book| vauthors = Will GF |title=Suddenly: The American Idea Abroad and at Home, 1986–1990|publisher=Free Press|year=1990|page=[https://archive.org/details/suddenlyamericangwill00will/page/312 312]|isbn=0-02-934435-2|url=https://archive.org/details/suddenlyamericangwill00will/page/312}} |
|||
* {{cite web|vauthors=Lewis J, Shimabukuro JO |url= http://www.policyalmanac.org/culture/archive/crs_abortion_overview.shtml|title=Abortion Law Development: A Brief Overview|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=28 January 2001|access-date=1 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514133610/http://www.policyalmanac.org/culture/archive/crs_abortion_overview.shtml|archive-date=14 May 2011|url-status=dead}} |
|||
* {{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EHj_0R2rbxAC&pg=PA1|page=1|title=Encyclopedia of American Law| vauthors = Schultz DA |publisher=Infobase Publishing|year=2002|isbn=0-8160-4329-9|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151209000856/https://books.google.com/books?id=EHj_0R2rbxAC&pg=PA1|archive-date=9 December 2015}} |
|||
* {{cite web | vauthors = Lahey JN |title=Birthing a Nation: Fertility Control Access and the 19th Century Demographic Transition|publisher=Pomona College|date=24 September 2009|url=http://economics-files.pomona.edu/colloquium/joannalahey.pdf|format=PDF; preliminary version|work=Colloquium|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120107162744/http://economics-files.pomona.edu/colloquium/joannalahey.pdf|archive-date=7 January 2012}}|group=nb}} Others maintain that in the 19th century early abortions under the hygienic conditions in which [[midwives]] usually worked were relatively safe.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Lee CA |year=1838|title=Report of a Trial for Murder|journal=American Journal of the Medical Sciences|volume=XXII|pages=351–353}}</ref><ref>Benjamin Bailey, "Induction of abortion and premature labor", ''North American Journal of Homeopathy'', vol. XI, no. 3 (1896), pp. 144–150.</ref><ref>Keith Simpson, ''Forensic Medicine'', Edward Arnold Publishers, 1969 [first published 1947], pp. 173–174.</ref> Several scholars argue that, despite improved medical procedures, the period from the 1930s until the 1970s saw more zealous enforcement of anti-abortion laws, alongside an increasing control of abortion providers by organized crime.{{refn|For sources, see: |
|||
* James Donner, ''Women in Trouble: The Truth about Abortion in America'', Monarch Books, 1959. |
|||
* Ann Oakley, ''The Captured Womb'', Basil Blackwell, 1984, p. 91. |
|||
* Rickie Solinger, ''The Abortionist: A Woman Against the Law'', The Free Press, 1994, pp. xi, 5, 16–17, 157–175. |
|||
* Leslie J. Reagan, ''When Abortion Was a Crime: Women, Medicine, and Law in the United States, 1867–1973'', University of California Press, 1997. |
|||
* Max Evans, ''Madam Millie: Bordellos from Silver City to Ketchikan'', University of New Mexico Press, 2002, pp. 209–218, 230, 267–286, 305.|group=nb}} |
|||
In 1920, [[Soviet Russia]] became the first country to legalize abortion after [[Lenin]] insisted that no woman be forced to give birth.<ref name="Bullough 2001 p. 5">{{cite book | last=Bullough | first=V.L. | title=Encyclopedia of Birth Control | publisher=ABC-CLIO | series=ABC-CLIO E-Books | year=2001 | isbn=978-1-57607-181-6 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XuX-MGTZnJoC&pg=PA5 | access-date=2022-10-19 | page=5 | archive-date=24 January 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230124173418/https://books.google.com/books?id=XuX-MGTZnJoC&pg=PA5 | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Raphael 2011 p. 30">{{cite book | last=Raphael | first=D. | title=Being Female: Reproduction, Power, and Change | publisher=De Gruyter | series=World Anthropology | year=2011 | isbn=978-3-11-081312-8 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=84hyfRRHeakC&pg=PA30 | access-date=2022-10-19 | page=30 | archive-date=24 January 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230124173418/https://books.google.com/books?id=84hyfRRHeakC&pg=PA30 | url-status=live }}</ref> [[Iceland]] (1935) and [[Sweden]] (1938) would follow suit to legalize certain or all forms of abortion.<ref name="cbctrust">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbctrust.com/history_law_religion.php|title=Abortion Law, History & Religion|access-date=23 March 2008|publisher=Childbirth By Choice Trust|archive-url=https://archive.today/20080208053146/http://www.cbctrust.com/history_law_religion.php|archive-date=8 February 2008}}{{cbignore}}</ref> In [[Nazi Germany]] (1935), a law permitted abortions for those deemed "hereditarily ill", while women considered of German stock were specifically prohibited from having abortions.<ref>For sources describing abortion policy in Nazi Germany, see: |
|||
In the People's Republic of China, there is also a historic son preference. The implementation of the one-child policy in 1979, in response to population concerns, led to an increased disparity in the sex ratio as parents attempted to circumvent the law through sex-selective abortion or the abandonment of unwanted daughters.<ref>{{Cite journal|first=Maureen J. |last=Graham |year=1998 |month=June |title=Son Preference in Anhui Province, China |journal=International Family Planning Perspectives |volume=24 |issue=2 |url=http://www.agi-usa.org/pubs/journals/2407298.html |accessdate=2008-12-03 |doi=10.2307/2991929 |page=72 |author2=Larsen |author3=Xu|archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20080620084622/http%3A//www.agi-usa.org/pubs/journals/2407298.html |archivedate = June 20, 2008|deadurl=yes}}</ref> Sex-selective abortion might be an influence on the shift from the baseline male-to-female birth rate to an elevated national rate of 117:100 reported in 2002. The trend was more pronounced in rural regions: as high as 130:100 in [[Guangdong]] and 135:100 in [[Hainan]].<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Plafker |first=Ted |year=2002 |month=May |title=Sex selection in China sees 117 boys born for every 100 girls |journal=[[BMJ]] |volume=324 |issue=7348 |page=1233a |doi=10.1136/bmj.324.7348.1233/a |pmid=12028966 |pmc=1123206}}</ref> A ban upon the practice of sex-selective abortion was enacted in 2003.<ref>"[http://www.china.org.cn/english/2003/Mar/59194.htm China Bans Sex-selection Abortion]." (2002-03-22). ''Xinhua News Agency.'.' Retrieved 2006-01-12.</ref> |
|||
* {{cite book| vauthors = Friedlander H |title=The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution|publisher=University of North Carolina Press|location=Chapel Hill|year=1995|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gqLDEKVk2nMC|page=30|isbn=978-0-8078-4675-9|oclc=60191622|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160729051956/https://books.google.com/books?id=gqLDEKVk2nMC|archive-date=29 July 2016}} |
|||
* {{cite book| vauthors = Proctor RN |title=Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis|publisher=Harvard University Press|year=1988|pages=[https://archive.org/details/racialhygiene00robe/page/122 122–123, 366]|isbn=978-0-674-74578-0|oclc=20760638|url=https://archive.org/details/racialhygiene00robe/page/122}} |
|||
* {{cite book | vauthors = Arnot ML, Usborne C|title=Gender and Crime in Modern Europe|publisher=Routledge|location=New York|year=1999|page=231|isbn=978-1-85728-745-5|oclc=186748539}} |
|||
* {{cite encyclopedia|vauthors=DiMeglio PM|veditors=Tierney H|encyclopedia=Women's Studies Encyclopedia|title=Germany 1933–1945 (National Socialism)|year=1999|publisher=Greenwood Press|location=Westport, Connecticut|isbn=978-0-313-31072-0|oclc=38504469|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gQLqRd7hJq0C|page=589|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015195038/https://books.google.com/books?id=gQLqRd7hJq0C|archive-date=15 October 2015}}</ref> Beginning in the second half of the 20th century, abortion was legalized in a greater number of countries.<ref name="Management of Abortion, Chp 1"/> In [[Japan]], abortion was first legalized by the 1948 "Eugenics Protection Law" meant to prevent the births of "inferior" humans. {{As of| 2022}}, due to Japan's continuing strongly patriarchal culture and traditional views on women's societal roles, women who want an abortion must normally get written permission from their partner.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Ye Hee Lee |first1=Michelle |title=In Japan, Abortion is Legal — But Most Women Need Their Husband's Consent |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2022/06/14/japan-abortion-pill-women-reproductive-rights/ |access-date=March 16, 2023 |date=June 14, 2022}}</ref><ref name="Wingfield-Hayes_8/31/2022">{{cite web | last=Wingfield-Hayes | first=Rupert | title=Abortion pill: Why Japanese women will need their partner's consent to get a tablet | website=[[BBC News]] | date=August 31, 2022 | url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-62515356 | access-date=March 15, 2023 | quote=It was actually one of the first countries in the world to pass an abortion law, back in 1948. But it was part of the Eugenics Protection Law – yes, it really was called that. It had nothing to do with giving women more control over their reproductive health. Rather, it was about preventing 'inferior' births. ... So, to this day, women who want an abortion must get written permission from their husband, partner, or in some cases their boyfriend. ... Unlike the US, Japanese views on abortion are not driven by religious belief. Instead, they derive from a long history of patriarchy and deeply traditional views on the role of women and motherhood. | archive-date=5 March 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230305214443/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-62515356 | url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
==Society and culture== |
|||
===Anti-abortion violence=== |
|||
{{Further|Societal attitudes towards abortion}} |
|||
{{Main|Anti-abortion violence}} |
|||
Doctors and facilities that provide abortion have been subjected to various forms of violence, including murder, attempted murder, kidnapping, stalking, assault, arson, and bombing. Anti-abortion violence has been classified by governmental and scholarly sources as [[terrorism]].<ref name="csis">{{cite web |author=Smith, G. Davidson (Tim) |publisher=Canadian Security Intelligence Service |year=1998 |url=http://www.csis-scrs.gc.ca/en/publications/commentary/com74.asp |title=Single Issue Terrorism Commentary |accessdate= June 9, 2006|archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060714173515/http%3A//www.csis-scrs.gc.ca/en/publications/commentary/com74.asp |archivedate = July 14, 2006|deadurl=yes}}</ref><ref>Michele Wilson, John Lynxwiler (1988), "Abortion clinic violence as terrorism", ''Studies in Conflict & Terrorism'', 11 (4), pp 263 – 273</ref> Only a small fraction of those opposed to abortion commit violence, often rationalizing their actions as [[justifiable homicide]] or [[Right of self-defense|defense of others]], committed in order to protect the lives of fetuses. |
|||
===Abortion debate=== |
|||
In the United States, four abortion providers—Drs. [[David Gunn (doctor)|David Gunn]], [[John Britton (doctor)|John Britton]], [[Barnett Slepian]], and [[George Tiller]]—have been assassinated. Attempted assassinations have also taken place in the United States and Canada, and other personnel at abortion clinics, including receptionists and security guards, have been killed in the United States and Australia. Hundreds of bombings, arsons, acid attacks, invasions, and incidents of vandalism against abortion providers have also occurred.<ref>{{cite news |title=The Death of Dr. Gunn |work= [[New York Times]] |date=12 March 1993 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/1993/03/12/opinion/the-death-of-dr-gunn.html}}</ref><ref name="naf">{{cite web | publisher = [[National Abortion Federation]] | year = 2009 | url = http://www.prochoice.org/pubs_research/publications/downloads/about_abortion/violence_stats.pdf | format = PDF | title = Incidence of Violence & Disruption Against Abortion Providers in the U.S. & Canada | accessdate = February 9, 2010}}</ref> Notable perpetrators of anti-abortion violence include [[Eric Robert Rudolph]], [[Scott Roeder]], [[Shelley Shannon]], and [[Paul Jennings Hill]], the first person to be executed in the United States for murdering an abortion provider.<ref>{{Cite news |url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/theguardian/1999/feb/03/features11.g26 |work=The Guardian |date=February 3, 1999 |title=The bomber under siege |first=Julian |last=Borger |location=London}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Abortion debate}} |
|||
Induced abortion has long been the source of considerable debate. [[Medical ethics|Ethical]], [[Morality|moral]], [[Philosophical aspects of the abortion debate|philosophical]], [[Therapeutic abortion|biological]], [[Ethics in religion|religious]] and [[Abortion law|legal]] issues surrounding abortion are related to [[value system]]s. Opinions of abortion may be about [[fetal rights]], governmental authority, and [[women's rights]]. |
|||
In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor of or against abortion access focus on either the moral permissibility of an induced abortion, or the justification of laws permitting or restricting abortion.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Farrell C | title =Abortion Debate| publisher =ABDO Publishing Company| year =2010| pages =6–7| isbn =978-1-61785-264-0}}</ref> The [[World Medical Association]] Declaration on Therapeutic Abortion notes, "circumstances bringing the interests of a mother into conflict with the interests of her unborn child create a dilemma and raise the question as to whether or not the pregnancy should be deliberately terminated."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/a1/ |title=WMA Declaration on Therapeutic Abortion |publisher=World Medical Association |access-date=28 October 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151028182953/http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/a1/ |archive-date=28 October 2015 }}</ref> Abortion debates, especially pertaining to [[abortion law]]s, are often spearheaded by groups advocating one of these two positions. Groups who favor greater legal restrictions on abortion, including complete prohibition, most often describe themselves as "[[anti-abortion movement|pro-life]]" while groups who are against such legal restrictions describe themselves as "[[Abortion-rights movements|pro-choice]]".<ref>Farrell, p. 8</ref> |
|||
===Art, literature and film=== |
|||
Art serves to humanize the abortion issue and illustrates the myriad of decisions and consequences it has. One of the [[History of abortion#5th century to 18th century|earliest]] known representations of abortion is in a [[bas relief]] at [[Angkor Wat]] (c. 1150). Pro-life activist [[Børre Knudsen]] was linked to a 1994 art theft as part of a pro-life drive in [[Norway]] surrounding the [[1994 Winter Olympics]].<ref name="Art theft">{{cite news |
|||
|url=http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/thestar/access/517847961.html?dids=517847961:517847961&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&type=current&date=Feb+18%2C+1994&author=%28AP%29&pub=Toronto+Star&desc=Art+theft+linked+to+pro-life+drive+Abortion+foe+hints+painting%27s+return+hinges+on+TV+film&pqatl=google |
|||
|title=Art theft linked to pro-life drive Abortion foe hints painting's return hinges on TV film |
|||
|work=thestar.com |
|||
|accessdate=2010-09-25 |
|||
| date=1994-02-18 |
|||
}}</ref> A [[Swiss]] gallery removed a piece from a Chinese art collection in 2005, that had the head of a fetus attached to the body of a bird.<ref name="Xiao Yu">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.othershore-arts.net/xiaoyuESSAYS10.html |
|||
|title=Principally relating to Xiao Yu's work Ruan |
|||
|work=Other Shore Artfile |
|||
|accessdate=2010-06-27 |
|||
}}</ref> In 2008, a [[Yale student abortion art controversy|Yale student]] proposed using aborted excretions and the induced abortion itself as a performance art project.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://network.nationalpost.com/np/blogs/fullcomment/archive/2008/04/17/marni-soupcoff-s-zeitgeist-photofiddle-rentbetter-org-mandie-brady-and-aliza-shvarts.aspx |title= Marni Soupcoff's Zeitgeist: Photofiddle, Rentbetter.org, Mandie Brady and Aliza Shvarts|accessdate=2008-04-30 |last=Soupcoff |first=Marni |date=2008-04-17 |work=Full Comment |publisher=[[National Post]]}}</ref> |
|||
===Modern abortion law=== |
|||
''[[The Cider House Rules]]'' (novel 1985, film 1999) follows the story of Dr. Larch an orphanage director who is a reluctant abortionist after seeing the consequences of back-alley abortions, and his orphan medical assistant Homer who is against abortion.<ref name="CiderHouse">{{Cite book |
|||
{{Main|Abortion law}} |
|||
|author=John Irving |
|||
{{See also|History of abortion law debate}} |
|||
|title=The Cider House Rules |
|||
{{AbortionLawsMap|size=330px}} |
|||
|publisher=William Morrow |
|||
|location=New York |
|||
|year=1985 |
|||
|pages= |
|||
|isbn=978-0-688-03036-0 |
|||
}}</ref> Feminist novels such as ''Braided Lives'' (1997) by Marge Piercy emphasize the struggles women had in dealing with unsafe abortion in various circumstances prior to legalization.<ref name="BraidedLives">{{Cite book |
|||
|author=Marge Piercy |
|||
|title=Braided Lives |
|||
|publisher=Ballantine Books |
|||
|location=New York |
|||
|year=1997 |
|||
|pages= |
|||
|isbn=978-0-449-00091-5 |
|||
}}</ref> Doctor [[Susan Wicklund]] wrote ''This Common Secret'' (2007) about how a personal traumatic abortion experience hardened her resolve to provide compassionate care to women who decide to have an abortion. As Wicklund crisscrosses the West to provide abortion services to remote clinics, she tells the stories of women she's treated and the sacrifices she and her loved ones made.<ref name="CommonSecret">{{Cite book |
|||
|author=Sue Wicklund; Susan Wicklund |
|||
|title=This Common Secret: My Journey as an Abortion Doctor |
|||
|publisher=PublicAffairs |
|||
|location=New York |
|||
|year=2007 |
|||
|pages= |
|||
|isbn=978-1-58648-480-4 |
|||
}}</ref> In 2009, Irene Vilar revealed her past abuse and addiction to abortion in ''[[Impossible Motherhood]]'', where she aborted 15 pregnancies in 17 years. According to Vilar it was the result of a dark psychological cycle of power, rebellion and societal expectations.<ref name="ImpossibleMotherhood">{{Cite book |
|||
|author=Irene Vilar |
|||
|title=Impossible Motherhood: Testimony of an Abortion Addict |
|||
|publisher=Other Press |
|||
|location= |
|||
|year=2009 |
|||
|pages= |
|||
|isbn=978-1-59051-320-0 |
|||
}}</ref> In [[Annie Finch]]'s mythic epic poem and opera libretto '' Among the Goddesses'' (2010), the heroine's abortion is contextualized spiritually by the goddesses [[Demeter]], [[Kali]], and [[Inanna]]. <ref name="AmongtheGoddesses">{{Cite book |
|||
|author=Annie Finch |
|||
|title=Among the Goddesses |
|||
|publisher=Red Hen Press |
|||
|location=California |
|||
|year=2010 |
|||
|pages= |
|||
|isbn=978-1-59709-161-9 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral, and cultural factors continue to influence abortion laws throughout the world. The [[right to life]], the right to liberty, the right to [[security of person]], and the right to [[reproductive health]] are major issues of human rights that sometimes constitute the basis for the existence or absence of abortion laws. |
|||
Various options and realities of abortion have been dramatized in film. In ''[[Riding in Cars with Boys]]'' (2001) an underage woman carries her pregnancy to term as abortion is not an affordable option, moves in with the father and finds herself involved with drugs, has no opportunities, and questioning if she loves her child. While in ''[[Juno (film)|Juno]]'' (2007) a 16-year-old initially goes to have an abortion but decides to bear the child and allow a wealthy couple to adopt it. Other films ''[[Dirty Dancing]]'' (1987) and ''[[If These Walls Could Talk]]'' (1996) explore the availability, affordability and dangers of illegal abortions. The emotional impact of dealing with an unwanted pregnancy alone is the focus of ''Things You Can Tell Just By Looking At Her'' (2000) and ''[[Circle of Friends (1995 film)|Circle of Friends]]'' (1995). As a marriage was in trouble in the ''[[The Godfather Part II]]'' (1974) [[Kay Adams-Corleone|Kay]] knew the relationship was over when she aborted "a son" in secret.<ref name="TheGodfather">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0071562/quotes |
|||
|title=The Godfather: Part II (1974) – Memorable quotes |
|||
|work=imdb.com |
|||
|accessdate=2010-07-01 |
|||
}}</ref> On the abortion debate, an irresponsible drug addict is used as a pawn in a power struggle between pro-choice and pro-life groups in ''[[Citizen Ruth]]'' (1996).<ref name="movietrain">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.movietrain.net/films-that-discuss-abortion-a-movie-list/ |
|||
|title=films that discuss Abortion . . . a movie list |
|||
|work=movietrain.net |
|||
|accessdate=2010-06-13 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
In jurisdictions where abortion is legal, certain requirements must often be met before a woman may obtain a legal abortion (an abortion performed without the woman's consent is considered [[feticide]] and is generally illegal). These requirements usually depend on the age of the fetus, often using a [[Pregnancy#Terminology|trimester]]-based system to regulate the window of legality, or as in the U.S., on a doctor's evaluation of the fetus' [[Fetal viability|viability]]. Some jurisdictions require a waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on [[prenatal development|fetal development]], or require that [[minors and abortion|parents be contacted]] if their minor daughter requests an abortion.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://internationalfamilyplanningperspectives.org/pubs/MandatoryCounseling.pdf |title=The Impact of State Mandatory Counseling and Waiting Period Laws on Abortion: A Literature Review |publisher=Guttmacher Institute| vauthors = Joyce TJ, Henshaw SK, Dennis A, Finer LB, Blanchard K |date=April 2009 |access-date=31 December 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120316155239/http://internationalfamilyplanningperspectives.org/pubs/MandatoryCounseling.pdf |archive-date=16 March 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Other jurisdictions may require that a woman obtain the [[Paternal rights and abortion|consent of the fetus' father]] before aborting the fetus, that abortion providers inform women of health risks of the procedure—sometimes including "risks" not supported by the medical literature—and that multiple medical authorities certify that the abortion is either medically or socially necessary. Many restrictions are waived in emergency situations. China, which has ended their<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/oct/29/china-abandons-one-child-policy|title=China ends one-child policy after 35 years| vauthors = Phillips T |date=29 October 2015|newspaper=The Guardian|issn=0261-3077|access-date=30 November 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161201021629/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/oct/29/china-abandons-one-child-policy|archive-date=1 December 2016}}</ref> [[one-child policy]], and now has a three-child policy,<ref>{{cite news |title=China NPC: Three-child policy formally passed into law |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-58277473 |access-date=6 April 2024 |date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=29 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220629190816/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-58277473 |url-status=live }}</ref> has at times incorporated mandatory abortions as part of their population control strategy.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |title=Science, Technology, and Society: An Encyclopedia |page=2 | veditors = Restivo SP |year=2005 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-514193-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A8C3m8rRba4C |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150315111926/http://books.google.com/books?id=A8C3m8rRba4C |archive-date=15 March 2015 }}</ref> |
|||
==In other animals== |
|||
{{See|Miscarriage#In other animals}} |
|||
Spontaneous abortion occurs in various animals. For example, in sheep, it may be caused by crowding through doors, or being chased by dogs.<ref>Spencer, James. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=RXMuAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA124&lpg=PA124&dq=abortion+and+husbandry&source=bl&ots=WjmvGj-fB2&sig=8qH_WrPR08YEwPKr_c6PHDUOMmQ&hl=en&ei=erDbSeSVBoz4MY-F7M4I&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=2#PPA124,M1 Sheep Husbandry in Canada]'', p. 124 (1911). </ref> In cows, abortion may be caused by contagious disease, such as [[Brucellosis]] or [[Campylobacter]], but can often be controlled by vaccination.<ref>[http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/B/BeefCattleAndBeefProduction/ManagementAndHusbandryOfBeefCattle/en "Beef cattle and Beef production: Management and Husbandry of Beef Cattle”], ''Encyclopaedia of New Zealand'' (1966).</ref> |
|||
Other jurisdictions ban abortion almost entirely. Many, but not all, of these allow legal abortions in a variety of circumstances. These circumstances vary based on jurisdiction, but may include whether the pregnancy is a result of rape or incest, the fetus' development is impaired, the woman's physical or mental well-being is endangered, or socioeconomic considerations make childbirth a hardship.<ref name="Dev98-07" /> In countries where abortion is banned entirely, such as [[Abortion in Nicaragua|Nicaragua]], medical authorities have recorded rises in maternal death directly and indirectly due to pregnancy as well as deaths due to doctors' fears of prosecution if they treat other gynecological emergencies.<ref>{{cite web|title=European delegation visits Nicaragua to examine effects of abortion ban |date=26 November 2007 |publisher=Ipas |access-date=15 June 2009 |url=http://www.ipas.org/Library/News/News_Items/European_delegation_visits_Nicaragua_to_examine_effects_of_abortion_ban.aspx |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080417033829/http://www.ipas.org/Library/News/News_Items/European_delegation_visits_Nicaragua_to_examine_effects_of_abortion_ban.aspx |archive-date=17 April 2008 |quote=More than 82 maternal deaths had been registered in Nicaragua since the change. During this same period, indirect obstetric deaths, or deaths caused by illnesses aggravated by the normal effects of pregnancy and not due to direct obstetric causes, have doubled.}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://insidecostarica.com/special_reports/2008-06/nicaragua_womens_movement.htm |title=Nicaragua: 'The Women's Movement Is in Opposition' |date=28 June 2008 |location=Montevideo |agency=IPS |publisher=Inside Costa Rica |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606102151/http://insidecostarica.com/special_reports/2008-06/nicaragua_womens_movement.htm |archive-date=6 June 2011 }}</ref> Some countries, such as Bangladesh, that nominally ban abortion, may also support clinics that perform abortions under the guise of menstrual hygiene.<ref>{{cite web|title=Surgical Abortion: History and Overview |publisher=National Abortion Federation |access-date=4 September 2006 |url=http://www.prochoice.org/education/resources/surg_history_overview.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060922152349/http://www.prochoice.org/education/resources/surg_history_overview.html |archive-date=22 September 2006 |url-status=dead }}</ref> This is also a terminology in traditional medicine.<ref name= nations1977>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nations MK, Misago C, Fonseca W, Correia LL, Campbell OM | title = Women's hidden transcripts about abortion in Brazil | journal = Social Science & Medicine | volume = 44 | issue = 12 | pages = 1833–1845 | date = June 1997 | pmid = 9194245 | doi = 10.1016/s0277-9536(96)00293-6 | quote = Two folk medical conditions, "delayed" (atrasada) and "suspended" (suspendida) menstruation, are described as perceived by poor Brazilian women in Northeast Brazil. Culturally prescribed methods to "regulate" these conditions and provoke menstrual bleeding are also described ... }}</ref> In places where abortion is illegal or carries heavy social stigma, pregnant women may engage in [[medical tourism]] and travel to countries where they can terminate their pregnancies.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Henshaw SK | title = The accessibility of abortion services in the United States | journal = Family Planning Perspectives | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 246–52, 263 | year = 1991 | pmid = 1786805 | doi = 10.2307/2135775 | url = http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3501603.pdf | access-date = 25 October 2017 | url-status = live | citeseerx = 10.1.1.360.6115 | jstor = 2135775 | archive-date = 24 March 2016 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160324041912/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3501603.pdf }}</ref> Women without the means to travel can resort to providers of illegal abortions or attempt to perform an abortion by themselves.<ref>{{cite web |title=Need Abortion, Will Travel | vauthors = Bloom M |date=25 February 2008 |publisher=RH Reality Check |access-date=15 June 2009 |url=http://www.rhrealitycheck.org/blog/2008/02/25/need-abortion-will-travel |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081130010309/http://www.rhrealitycheck.org/blog/2008/02/25/need-abortion-will-travel |archive-date=30 November 2008 }}</ref> |
|||
Abortion may also be induced in animals, in the context of [[animal husbandry]]. For example, abortion may be induced in mares that have been mated improperly, or that have been purchased by owners who did not realize the mares were pregnant, or that are pregnant with twin foals.<ref>McKinnon, Angus et al. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=jlZAT-9VwUIC&pg=PA563&lpg=PA563&dq=%22induce+abortion%22+and+husbandry&source=bl&ots=6T9w3LtpsI&sig=aEYDFpnMIbLaKlstxK1MGK2rxwQ&hl=en&ei=eLTbSY7EO5muMrXUkMkI&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=7 Equine Reproduction]'', p. 563 (Wiley-Blackwell 1993). </ref> |
|||
The organization [[Women on Waves]] has been providing education about medical abortions since 1999. The NGO created a mobile medical clinic inside a shipping container, which then travels on rented ships to countries with restrictive abortion laws. Because the ships are registered in the Netherlands, Dutch law prevails when the ship is in international waters. While in port, the organization provides free workshops and education; while in international waters, medical personnel are legally able to prescribe medical abortion drugs and counseling.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gomperts R | title = Women on waves: where next for the abortion boat? | journal = Reproductive Health Matters | volume = 10 | issue = 19 | pages = 180–183 | date = May 2002 | pmid = 12369324 | doi = 10.1016/S0968-8080(02)00004-6 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Best A |date=2005|title=Abortion Rights along the Irish-English Border and the Liminality of Women's Experiences|journal=Dialectical Anthropology|volume=29|issue=3–4|pages=423–37|doi=10.1007/s10624-005-3863-x|s2cid=145318165|issn=0304-4092}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Lambert-Beatty C |date=2008|title=Twelve miles: Boundaries of the new art/activism|journal=Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society|volume=33|issue=2|pages=309–27|doi=10.1086/521179|s2cid=147307705}}</ref> |
|||
[[Feticide]] can occur in horses and zebras due to male harassment of pregnant mares or forced copulation,<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Berger|first=Joel W|date=5 May 1983|title=Induced abortion and social factors in wild horses|journal=Nature|location=London|volume=303|pages=59–61|url=http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v303/n5912/abs/303059a0.html|doi=10.1038/303059a0|pmid=6682487|issue=5912}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Pluháček|first=Jan|year=2000|title=Male infanticide in captive plains zebra, Equus burchelli|journal=Animal Behaviour|volume=59|pages=689–694|url=http://af.czu.cz/~bartos/publications/pdf/Pluhacek_Bartos_2000_AB.pdf|doi=10.1006/anbe.1999.1371|pmid=10792924|last2=Bartos|first2=L|issue=4}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Pluháček|first=Jan|year=2005|title=Further evidence for male infanticide and feticide in captive plains zebra, Equus burchelli|journal=Folia Zool.|volume=54|issue=3|pages= 258–262|url=http://www.ivb.cz/folia/54/3/258-262.pdf}}</ref> although the frequency in the wild has been questioned.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=JW|first=Fitzpatrick|date=October 1991|title=Changes in herd stallions among feral horse bands and the absence of forced copulation and induced abortion |journal=Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin/Heidelberg|volume=29|issue=3|pages=217–219|issn=0340-5443 (Print) 1432-0762 (Online)|url=http://www.springerlink.com/content/k1543n1548987255/}} {{dead link|date=March 2011}}</ref> Male [[Gray langur]] monkeys may attack females following male takeover, causing miscarriage.<ref>{{cite doi|10.1007/BF02435859}}</ref> |
|||
===Sex-selective abortion=== |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
{{Main|Sex-selective abortion}} |
|||
{{reflist|group="note"| |
|||
refs= |
|||
<ref name="definition" group="note">The definition of abortion, as with many words, varies from source to source. The following is a partial list of definitions as stated by [[obstetrics and gynecology]] (OB/GYN) textbooks, dictionaries, and other [[encyclopedias]]: |
|||
[[Medical ultrasonography|Sonography]] and [[amniocentesis]] allow parents to determine sex before childbirth. The development of this technology has led to [[sex-selective abortion and female infanticide|sex-selective abortion]], or the termination of a fetus based on its sex. The selective termination of a female fetus is most common. |
|||
;Major OB/GYN textbooks |
|||
*The [[National Center for Health Statistics]] defines an "abortus" as "[a] fetus or embryo removed or expelled from the uterus during the first half of gestation—20 weeks or less, or in the absence of accurate dating criteria, born weighing < 500 g." They also define "birth" as "[t]he complete expulsion or extraction from the mother of a fetus after 20 weeks' gestation. [...] in the absence of accurate dating criteria, fetuses weighing <500 g are usually not considered as births, but rather are termed abortuses for purposes of vital statistics." {{cite book|editor1-last=Cunningham|editor1-first=FG|editor2-last=Leveno|editor2-first=KJ|editor3-last=Bloom|editor3-first=SL|editor4-last=Hauth|editor4-first=JC|editor5-last=Rouse|editor5-first=DJ|editor6-last=Spong |editor6-first=CY|chapter=1. Overview of Obstetrics|title=Williams Obstetrics|edition=23|publisher=[[McGraw-Hill Medical]]|year=2010|isbn=978-0-07-149701-5}} |
|||
*"[T]he standard medical definition of abortion [is] termination of a pregnancy when the fetus is not viable". {{cite book|editor1-last=Gabbe|editor1-first=Steven G.|editor1-link=Steven Gabbe|editor2-last=Niebyl|editor2-first=Jennifer R.|editor3-last=Simpson|editor3-first=Joe Leigh|year=2007|title=Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies|edition=5|publisher=[[Churchill Livingstone]]|chapter=51. Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetric Practice|isbn=978-0-443-06930-7|last1=Annas|first1=George J.|authorlink1=George Annas|last2=Elias|first2=Sherman}} |
|||
*"Termination of a pregnancy, whether spontaneous or induced." {{cite book|first1=Melissa J.|last1=Kottke|first2=Mimi|last2=Zieman|chapter=33. Management of Abortion|editor1-first=John A.|editor1-last=Rock|editor2-first=Howard W.|editor2-last=Jones III|year=2008|edition=10|publisher=[[Lippincott Williams & Wilkins]]|isbn=978-0-7817-7234-1|title=TeLinde's Operative Gynecology}} |
|||
Sex-selective abortion is partially responsible for the noticeable disparities between the birth rates of male and female children in some countries. The preference for male children is reported in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has been reported in Taiwan, South Korea, India, and China.<ref>Banister, Judith. (16 March 1999). [https://www.census.gov/ipc/www/ebspr96a.html Son Preference in Asia – Report of a Symposium] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060216134324/http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/ebspr96a.html |date=16 February 2006 }}. Retrieved 12 January 2006.</ref> This deviation from the standard birth rates of males and females occurs despite the fact that the country in question may have officially banned sex-selective abortion or even sex-screening.<ref>{{cite news| vauthors = Reaney P |agency=Reuters |url=http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L06779563.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060220072756/http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L06779563.htm |archive-date=20 February 2006 |title=Selective abortion blamed for India's missing girls |access-date=3 December 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sudha S, Irudaya RS | title = Female demographic disadvantage in India 1981-1991: sex selective abortions and female infanticide | journal = Development and Change | volume = 30 | issue = 3 | pages = 585–618 | date = July 1999 | pmid = 20162850 | doi = 10.1111/1467-7660.00130 | s2cid = 33446683 | url = http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/organizations/healthnet/gender/docs/sudha.html | access-date = 3 December 2008 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20030101210623/http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/organizations/healthnet/gender/docs/sudha.html | archive-date = 1 January 2003 | url-access = subscription }}</ref><ref name="LOC India">{{cite web|url=https://www.loc.gov/law/help/sex-selection/india.php|publisher=Library of Congress|title=Sex Selection & Abortion: India|date=4 April 2011|access-date=18 July 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927234151/http://www.loc.gov/law/help/sex-selection/india.php|archive-date=27 September 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|agency=Xinhua News Agency|title=China Bans Sex-selection Abortion|url=http://www.china.org.cn/english/2003/Mar/59194.htm|access-date=2023-02-16|work=www.china.org.cn|date=March 22, 2003|archive-date=12 February 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060212204114/http://www.china.org.cn/english/2003/Mar/59194.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> In China, a historical preference for a male child has been exacerbated by the [[one-child policy]], which was enacted in 1979.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Graham MJ, Larsen U, Xu X |date=June 1998 |title=Son Preference in Anhui Province, China |journal=International Family Planning Perspectives |volume=24 |issue=2 |url=http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2407298.html |doi=10.2307/2991929 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120106165446/http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2407298.html |archive-date=6 January 2012 |url-status=live |pages=72–77 |jstor=2991929 |url-access=subscription }}</ref> |
|||
;Other OB/GYN textbooks |
|||
*"Termination of pregnancy before 20 weeks' gestation calculated from date of onset of last [[menses]]. An alternative definition is delivery of a fetus with a weight of less than 500 g. If abortion occurs before 12 weeks' gestation, it is called early; from 12 to 20 weeks it is called late." {{cite book|last=Katz|first=Vern L.|publisher=[[Mosby (publisher)|Mosby]]|year=2007|edition=5|title=Katz: Comprehensive Gynecology|editor1-last=Katz|editor1-first=Vern L.|editor2-last=Lentz|editor2-first=Gretchen M.|editor3-last=Lobo|editor3-first=Rogerio A.|editor4-last=Gershenson|editor4-first=David M.|chapter=16. Spontaneous and Recurrent Abortion - Etiology, Diagnosis, Treatment|isbn=9780323029513}} |
|||
*"Abortion is the spontaneous or induced termination of pregnancy before fetal viability. Because popular use of the word abortion implies a deliberate pregnancy termination, some prefer the word miscarriage to refer to spontaneous fetal loss before viability [...] The National Center for Health Statistics, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the World Health Organization (WHO) define abortion as pregnancy termination prior to 20 weeks' gestation or a fetus born weighing less than 500 g. Despite this, definitions vary widely according to state laws." {{cite book|editor1-last=Schorge|editor1-first=John O.|editor2-first=Joseph I.|editor2-last=Schaffer|editor3-first=Lisa M.|editor3-last=Halvorson|editor4-first=Barbara L.|editor4-last=Hoffman|editor5-first=Karen D.|editor5-last=Bradshaw|editor6-first=F. Gary|editor6-last=Cunningham|year=2008|title=Williams Gynecology|edition=1|publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical|isbn=978-0-07-147257-9|chapter=6. First-Trimester Abortion}} |
|||
Many countries have taken legislative steps to reduce the incidence of sex-selective abortion. At the [[International Conference on Population and Development]] in 1994 over 180 states agreed to eliminate "all forms of discrimination against the girl child and the root causes of son preference",<ref name="UNFPA">{{cite web|url=http://www.unfpa.org/webdav/site/global/shared/documents/publications/2011/Preventing_gender-biased_sex_selection.pdf|title=Preventing gender-biased sex selection|publisher=UNFPA|access-date=1 November 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111011095023/https://www.unfpa.org/webdav/site/global/shared/documents/publications/2011/Preventing_gender-biased_sex_selection.pdf|archive-date=11 October 2011|url-status=live}}</ref> conditions also condemned by a [[Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe|PACE]] resolution in 2011.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://assembly.coe.int/Documents/WorkingDocs/Doc11/EDOC12715.pdf |title=Prenatal sex selection |publisher=Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111003133834/http://assembly.coe.int/Documents/WorkingDocs/Doc11/EDOC12715.pdf |archive-date=3 October 2011 |access-date=17 November 2015 }}</ref> The [[World Health Organization]] and [[UNICEF]], along with other [[United Nations]] agencies, have found that measures to restrict access to abortion in an effort to reduce sex-selective abortions have unintended negative consequences, largely stemming from the fact that women may seek or be coerced into seeking unsafe, extralegal abortions.<ref name="UNFPA" /> On the other hand, measures to reduce [[gender inequality]] can reduce the prevalence of such abortions without attendant negative consequences.<ref name="UNFPA" /><ref>{{cite journal |last=Das Gupta |first=Monica |date=2019 |title=Is banning sex-selection the best approach for reducing prenatal discrimination? |journal=Asian Population Studies |volume=15 |issue=3 |pages=319–336|doi=10.1080/17441730.2019.1671015 |pmid=34046078 |pmc=8153244 }}</ref> |
|||
;Major [[medical dictionaries]] |
|||
*"The spontaneous or induced termination of pregnancy before the fetus reaches a viable age." {{cite web|url=http://www.tabers.com/tabersonline/ub/view/Tabers/143003/37/abortion|title=Taber's Medical Dictionary: abortion|publisher=[[F. A. Davis Company|F.A. Davis]]|work=[[Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary]]|accessdate=June 14, 2011|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5zRoq1nVk|archivedate=June 14, 2011|deadlink=no}} |
|||
*"Expulsion from the uterus an embryo or fetus prior to the stage of viability (20 weeks' gestation or fetal weight <500g). A distinction made between [abortion] and premature birth: premature infants are those born after the stage of viability but prior to 37 weeks." {{cite book|title=[[Stedman's Medical Dictionary]]|publisher=[[Lippincott Williams & Wilkins]]|edition=27|isbn=0683400088}} |
|||
*"[P]remature expulsion from the uterus of the products of conception, either the embryo or a nonviable fetus." {{cite book|title=[[Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary]]|publisher=[[Saunders (publisher)|Saunders]]|year=2007|isbn=9781416023647|edition=31}} |
|||
===Anti-abortion violence=== |
|||
;Other medical dictionaries |
|||
{{Main|Anti-abortion violence}} |
|||
*"[T]he termination of a pregnancy after, accompanied by, resulting in, or closely followed by the death of the embryo or fetus". {{cite web|url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/medlineplus/abortion|title=Medical Dictionary|publisher=[[Merriam-Webster]]|work=[[Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary]]|accessdate=June 15, 2011|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5zTA1aALZ|archivedate=June 15, 2011|deadlink=no}} |
|||
Abortion providers and facilities have been subjected to violence, including murder, assault, arson, and bombing. Some scholars consider anti-abortion violence to be within the [[definition of terrorism]],<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilson M, Lynxwiler J | title = Abortion clinic violence as terrorism | journal = Terrorism | volume = 11 | issue = 4 | pages = 263–273 | year = 1988 | pmid = 11618209 | doi = 10.1080/10576108808435717 }}</ref> a view shared by some governments.<ref name="csis">{{cite web | vauthors = Smith GD |publisher=Canadian Security Intelligence Service |year=1998 |url=http://www.csis-scrs.gc.ca/en/publications/commentary/com74.asp |title=Single Issue Terrorism Commentary |access-date= 1 September 2011| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071015065711/http://csis-scrs.gc.ca/en/publications/commentary/com74.asp| archive-date=15 October 2007|url-status=dead}}</ref>, In the U.S. and Canada, over 8,000 incidents of violence, trespassing, and death threats have been recorded by providers since 1977, including over 200 bombings/arsons and hundreds of assaults.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://prochoice.org/wp-content/uploads/2017-NAF-Violence-and-Disruption-Statistics.pdf| title=2017 violence and disruption statistics |last=National Abortion Federation| date=2017|access-date=26 May 2019| archive-date=28 July 2020| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728204107/https://prochoice.org/wp-content/uploads/2017-NAF-Violence-and-Disruption-Statistics.pdf| url-status=live}}</ref> Abortion clinics have also been targeted by [[Acid attack|acid attacks]], invasions, and vandalism<ref name="naf">{{cite web |publisher=National Abortion Federation| year=2009 |url=http://www.prochoice.org/pubs_research/publications/downloads/about_abortion/violence_stats.pdf |title=Incidence of Violence & Disruption Against Abortion Providers in the U.S. & Canada |access-date=9 February 2010 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100613042214/http://prochoice.org/pubs_research/publications/downloads/about_abortion/violence_stats.pdf |archive-date=13 June 2010 }}</ref> The majority of abortion opponents have not been involved in violent acts. |
|||
*"Induced termination of pregnancy, involving destruction of the embryo or fetus." "abortion." ''The American Heritage Science Dictionary''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2005. |
|||
*"Interruption of pregnancy before the fetus has attained a stage of viability, usually before the 24th gestational week." "abortion." ''Cambridge Dictionary of Human Biology and Evolution''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. |
|||
*"[A] spontaneous or deliberate ending of pregnancy before the fetus can be expected to survive." "abortion." ''Mosby's Emergency Dictionary''. Philadelphia: Elsevier Health Sciences, 1998. |
|||
*"[A] situation where a fetus leaves the uterus before it is fully developed, especially during the first 28 weeks of pregnancy, or a procedure which causes this to happen...[T]o have an abortion to have an operation to make a fetus leave the uterus during the first period of pregnancy." "abortion." Dictionary of Medical Terms. London: A&C Black, 2008. |
|||
Physicians and other abortion clinic staff have been murdered by abortion opponents. In the United States, at least four physicians have been murdered in connection with their work at abortion clinics, including [[David Gunn (doctor)|David Gunn]] (1993), [[John Britton (doctor)|John Britton]] (1994), [[Barnett Slepian]] (1998), and [[George Tiller]] (2009). In Canada, gynecologist [[Garson Romalis]] survived murder attempts in both 1994 and 2000. Besides physicians, killings have targeted other clinic staff, such as [[John Salvi|John Salvi's]] 1994 murder of two receptionists in Massachusetts clinic and [[Peter James Knight|Peter Knight's]] 2001 murder of a security guard in a [[Melbourne]] clinic. Notable perpetrators of anti-abortion violence include [[Eric Rudolph]], [[Scott Roeder]], [[Shelley Shannon]], and [[Paul Jennings Hill|Paul Hill]], the first person to be executed in the United States for murdering an abortion provider.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/theguardian/1999/feb/03/features11.g26 |newspaper=The Guardian |date=3 February 1999 |title=The bomber under siege | vauthors = Borger J |location=London |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222105914/https://www.theguardian.com/theguardian/1999/feb/03/features11.g26 |archive-date=22 February 2017 }}</ref> |
|||
;Other dictionaries |
|||
*"The act of giving untimely birth to offspring, premature delivery, miscarriage; the procuring of premature delivery so as to destroy offspring. (In ''Med.'' abortion is limited to a delivery so premature that the offspring cannot live, i.e. in the case of the human fœtus before the sixth month.)" {{cite book|url=http://www.oed.com/oed2/00000606|edition=2|year=1989|title=Oxford English Dictionary|publisher=Oxford University Press}} |
|||
*"The deliberate termination of a pregnancy, usually before the embryo or fetus is capable of independent life." {{cite book|title=The American Heritage New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition|publisher=[[Houghton Mifflin Company]]|year=2005|accessdate=June 27, 2011|url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/abortion}} |
|||
*"[T]he removal of an embryo or fetus from the uterus before it is sufficiently developed to survive independently, deliberately induced by the use of drugs or by surgical procedures. Also called termination or induced abortion" or "[T]he spontaneous expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the uterus before it is sufficiently developed to survive independently. Also called miscarriage, spontaneous abortion." "abortion." ''Chambers 21st Century Dictionary''. London: Chambers Harrap, 2001. |
|||
*"[A]n operation or other procedure to terminate pregnancy before the fetus is viable" or "[T]he premature termination of pregnancy by spontaneous or induced expulsion of a nonviable fetus from the uterus". {{cite web|title=abortion|publisher=[[HarperCollins Publishers]]|work=Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 10th Edition|accessdate=June 27, 2011|url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/abortion}} |
|||
*"A term that, in philosophy, theology, and social debates, often means the deliberate termination of pregnancy before the fetus is able to survive outside the uterus. However, participants in these debates sometimes use the term abortion simply to mean the termination of pregnancy before birth, regardless of whether the fetus is viable or not." "abortion." ''Dictionary of World Philosophy''. London: Routledge, 2001. |
|||
*"[T]he removal of an embryo or fetus from the uterus in order to end a pregnancy" or "[A]ny of various surgical methods for terminating a pregnancy, especially during the first six months." {{cite web|title=abortion|work=[[Dictionary.com]] Unabridged|publisher=[[Random House, Inc.]]|date=June 27, 2011|url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/abortion}} |
|||
Some countries have [[Legal protection of access to abortion|laws to protecting access to abortion]]. |
|||
;Encyclopedias |
|||
Such laws prevent abortion opponents from interfering with access to legal abortion services. For example, the American [[Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances Act]] bars the use of threats or violence to interfere with abortion access. Abortion access laws may also establish [[safe access zone]]s around abortion clinics, with limits on protests and enhanced penalties for anti-abortion violence.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Pridemore |first=William Alex |author1-link=William Alex Pridemore |last2=Freilich |first2=Joshua D. |date=2007-12-01 |title=The Impact of State Laws Protecting Abortion Clinics and Reproductive Rights on Crimes Against Abortion Providers: Deterrence, Backlash, or Neither? |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s10979-006-9078-0 |journal=Law and Human Behavior |language=en |volume=31 |issue=6 |pages=611–627 |doi=10.1007/s10979-006-9078-0 |issn=1573-661X}}</ref> |
|||
*"[T]he expulsion of a fetus from the uterus before it has reached the stage of viability (in human beings, usually about the 20th week of gestation)." {{cite web|title=Abortion (pregnancy)|publisher=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]|work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online|year=2011|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1498/abortion|deadlink=no|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5zjwaLKR7|archivedate=June 26, 2011|accessdate=June 26, 2011}} |
|||
*"Expulsion of the products of conception before the embryo or fetus is viable. Any interruption of human pregnancy prior to the 28th week is known as abortion." {{cite encyclopedia|encyclopedia=The Columbia Encyclopedia|location=New York|publisher=Columbia University Press|year=2008|title=abortion}} |
|||
*"The expulsion or removal of a fetus from the womb before it is capable of independent survival." {{cite encyclopedia|title=abortion|encyclopedia=World Encyclopedia|publisher=Oxford University Press|work=Oxford Reference Online|year=2008}} |
|||
*"[Abortion] is commonly misunderstood outside medical circles. In general terms, the word 'abortion' simply means the failure of something to reach fulfilment or maturity. Medically, abortion means loss of the fetus, for any reason, before it is able to survive outside the womb. The term covers accidental or spontaneous ending, or miscarriage, of pregnancy as well as deliberate termination. The terms 'spontaneous abortion' and 'miscarriage' are synonymous and are defined as loss of the fetus before the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy. This definition implies a legal perception of the age at which a fetus can survive out of the womb. With great advances in recent years in the ability to keep very premature babies alive, this definition is in need of revision." {{cite encyclopedia|title=abortion and miscarriage|encyclopedia=The Royal Society of Medicine Health Encyclopedia|location=London|publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing Ltd|year=2000}} |
|||
*"Abortion is the intentional removal of a fetus or an embryo from a mother's womb for purposes other than that of either producing a live birth or disposing of a dead embryo." {{cite encyclopedia|title=Abortion|encyclopedia=Encyclopedia of Human Rights Issues since 1945|location=[[Santa Barbara, California]]|year=1999|publisher=Routledge|edition=1|isbn=978-1579581664}} |
|||
</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
Psychological pressure may also be used to limit abortion access. In 2003, Chris Danze organized anti-abortion organizations throughout Texas to prevent the construction of a [[Planned Parenthood]] facility in Austin. The organizations [[doxing|released the personal information]] online of those involved with construction, sent them up to 1200 phone calls a day and contacted their churches.{{sfn|Doan|2007|p=2}} Some protestors record women entering clinics on camera.{{sfn|Doan|2007|p=2}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
=={{anchor|Other animals}}Non-human examples== |
|||
==External links== |
|||
<!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before saving your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. It is always best to anchor an old section header that has been changed so that links to it won't be broken. See [[Template:Anchor]] for details. (This text: [[Template:Anchor comment]]) --> |
|||
{{Sister project links|abortion}} |
|||
<!-- linked from redirects [[Abortion in animals]] and [[Pine needle abortion]] --> |
|||
* {{dmoz|Health/Reproductive_Health/Abortion}} |
|||
{{Further|Miscarriage}} |
|||
* [http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/abortion Abortion Policies: A Global Review] |
|||
Spontaneous abortion occurs in various animals. For example, in sheep it may be caused by stress or physical exertion, such as crowding through doors or being chased by dogs.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Spencer JB |title=Sheep Husbandry in Canada |year=1908 |page=114 |oclc=798508694 }}</ref> In cows, abortion may be caused by contagious disease, such as [[brucellosis]] or ''[[Campylobacter]]'', but can often be controlled by vaccination.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |url=http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/B/BeefCattleAndBeefProduction/ManagementAndHusbandryOfBeefCattle/en |title=Beef cattle and Beef production: Management and Husbandry of Beef Cattle |encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia of New Zealand |year=1966 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090101142401/http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/B/BeefCattleAndBeefProduction/ManagementAndHusbandryOfBeefCattle/en |archive-date=1 January 2009 }}</ref> Eating [[pine needle]]s can also induce abortions in cows.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Myers B, Beckett J |title=Animal Health Care and Maintenance |chapter=Pine needle abortion |chapter-url=http://ag.arizona.edu/arec/pubs/rmg/4%20animalcare&healthmaintenance/31%20pineneedleabortion01.pdf |access-date=10 April 2013 |year=2001 |publisher=Arizona Cooperative Extension, University of Arizona |location=Tucson |pages=47–50 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150728003136/http://ag.arizona.edu/AREC/pubs/rmg/4%20animalcare%26healthmaintenance/31%20pineneedleabortion01.pdf |archive-date=28 July 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kim IH, Choi KC, An BS, Choi IG, Kim BK, Oh YK, Jeung EB | title = Effect on abortion of feeding Korean pine needles to pregnant Korean native cows | journal = Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research | volume = 67 | issue = 3 | pages = 194–197 | date = July 2003 | pmid = 12889725 | pmc = 227052 | publisher = Canadian Veterinary Medical Association }}</ref> Several plants, including [[Gutierrezia sarothrae|broomweed]], [[Veratrum californicum|skunk cabbage]], [[Conium maculatum|poison hemlock]], and [[Nicotiana glauca|tree tobacco]], are known to cause fetal deformities and abortion in cattle<ref name="Kirkbride">{{cite book| veditors = Njaa BL |title=Kirkbride's Diagnosis of Abortion and Neonatal Loss in Animals| year=2011| publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-0-470-95852-0}}</ref>{{rp|45–46}} and in sheep and goats.<ref name="Kirkbride"/>{{rp|77–80}} In horses, a fetus may be aborted or resorbed if it has [[lethal white syndrome]]. Foal embryos that are homozygous for the [[dominant white]] gene (WW) are theorized to also be aborted or resorbed before birth.<ref name=phj>{{cite web| url=http://www.painthorsejournal.com/pastissues/pdfs/byahair-mar04.pdf |title=By a Hair | vauthors = Overton R | work=Paint Horse Journal |date=March 2003 |access-date=19 December 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130218233122/http://www.painthorsejournal.com/pastissues/pdfs/byahair-mar04.pdf |archive-date=18 February 2013}}</ref> In many species of sharks and rays, stress-induced abortions occur frequently on capture.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Adams KR, Fetterplace LC, Davis AR, Taylor MD, Knott NA |title=Sharks, rays and abortion: The prevalence of capture-induced parturition in elasmobranchs| journal=Biological Conservation|date=January 2018|volume=217|pages=11–27| doi=10.1016/j.biocon.2017.10.010|bibcode=2018BCons.217...11A | s2cid=90834034 |url=http://marxiv.org/k2qvy/|access-date=30 July 2019| archive-date=23 February 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190223020619/https://marxiv.org/k2qvy/|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
* [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002912.htm#Definition MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: Abortion] |
|||
Viral infection can cause abortion in dogs.<ref name=dogabort1>{{cite web |url = http://www.petmd.com/dog/conditions/infectious-parasitic/c_dg_canine_herpesvirus_infection |title = Herpesvirus in dog pups |publisher = petMD |access-date = 18 December 2012 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131109165216/http://www.petmd.com/dog/conditions/infectious-parasitic/c_dg_canine_herpesvirus_infection |archive-date = 9 November 2013}}</ref> Cats can experience spontaneous abortion for many reasons, including hormonal imbalance. A combined abortion and spaying is performed on pregnant cats, especially in [[trap–neuter–return]] programs, to prevent unwanted kittens from being born.<ref name=spay1>{{cite web |url = http://www.carolsferals.org/spaying-pregnant-females/ |title = Spaying Pregnant Females |publisher = Carol's Ferals |access-date = 17 December 2012 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20121118110647/http://www.carolsferals.org/spaying-pregnant-females/ |archive-date = 18 November 2012}} |
|||
</ref><ref name=spay2>{{cite web |url = http://www.petmd.com/blogs/fullyvetted/2007/may/feline-abortion-often-unnerving-necessity |title = Feline abortion: often an unnerving necessity | vauthors = Coates J |date = 7 May 2007 |publisher = petMD |access-date = 18 December 2012 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120121085850/http://www.petmd.com/blogs/fullyvetted/2007/may/feline-abortion-often-unnerving-necessity |archive-date = 21 January 2012}}</ref><ref name=spay3>{{cite web |url = http://www.carolsferals.org/spaying-pregnant-females/ |title = Feline abortion: often an unnerving necessity (Part 2) | vauthors = Khuly P |date = 1 April 2011 |publisher = petMD |access-date = 18 December 2012 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20121118110647/http://www.carolsferals.org/spaying-pregnant-females/ |archive-date = 18 November 2012}} |
|||
</ref> Female rodents may terminate a pregnancy when exposed to the smell of a male not responsible for the pregnancy, known as the [[Bruce effect]].<ref name=Schwagmeyer>{{cite journal |jstor=2460564 |pages=932–938 | vauthors = Schwagmeyer PL |title=The Bruce Effect: An Evaluation of Male/Female Advantages |volume=114 |issue=6 |journal=The American Naturalist |year=1979 |doi=10.1086/283541|s2cid=85097151 }}</ref> |
|||
Abortion may also be induced in animals, in the context of [[animal husbandry]]. For example, abortion may be induced in mares that have been mated improperly, or that have been purchased by owners who did not realize the mares were pregnant, or that are pregnant with twin foals.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jlZAT-9VwUIC |title=Equine Reproduction |page=563 | vauthors = McKinnon AO, Voss JL |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=0-8121-1427-2 |year=1993 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150315091737/http://books.google.com/books?id=jlZAT-9VwUIC |archive-date=15 March 2015 }}</ref> Feticide can occur in horses and zebras due to male harassment of pregnant mares or forced copulation,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Berger J | title = Induced abortion and social factors in wild horses | journal = Nature | volume = 303 | issue = 5912 | pages = 59–61 | date = 5 May 1983 | pmid = 6682487 | doi = 10.1038/303059a0 | s2cid = 4259800 | bibcode = 1983Natur.303...59B }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pluhácek J, Bartos L | title = Male infanticide in captive plains zebra, Equus burchelli | journal = Animal Behaviour | volume = 59 | issue = 4 | pages = 689–694 | date = April 2000 | pmid = 10792924 | doi = 10.1006/anbe.1999.1371 | url = http://af.czu.cz/~bartos/publications/pdf/Pluhacek_Bartos_2000_AB.pdf | url-status = dead | s2cid = 10961845 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110718170925/http://af.czu.cz/~bartos/publications/pdf/Pluhacek_Bartos_2000_AB.pdf | archive-date = 18 July 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| first1= Jan |last1 = Pluhacek | first2 = Luděk |last2 = Bartoš |year=2005| title=Further evidence for male infanticide and feticide in captive plains zebra, ''Equus burchelli''| journal=Folia Zoologica|volume=54| issue=3|pages=258–262| url=http://www.ivb.cz/folia/54/3/258-262.pdf| url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120222174717/http://www.ivb.cz/folia/54/3/258-262.pdf| archive-date=22 February 2012| access-date=12 April 2009}}</ref> although the frequency in the wild has been questioned.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Kirkpatrick JF, Turner JW |title=Changes in Herd Stallions among Feral Horse Bands and the Absence of Forced Copulation and Induced Abortion |journal=Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=217–19 |doi=10.1007/BF00166404 |year=1991 |jstor=4600608| s2cid=32756929}}</ref> Male [[gray langur]] monkeys may attack females following male takeover, causing miscarriage.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Agoramoorthy G, Mohnot SM, Sommer V, Srivastava A |title=Abortions in free ranging Hanuman langurs (''Presbytis entellus'') – a male induced strategy? |journal=Human Evolution |volume=3| issue=4| pages=297–308| year=1988 |doi=10.1007/BF02435859| s2cid=84849590}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[Abortion doula]] |
|||
*[[Forced abortion]] |
|||
*[[Indirect abortion]] |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
{{reflist|group=nb}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
== Bibliography == |
|||
{{Refbegin|30em}} |
|||
{{Further|United States anti-abortion movement#Further reading}} |
|||
*{{cite Catholic Encyclopedia |wstitle=Abortion |volume=1 | vauthors = Coppens C }} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Devereux G |author-link=George Devereux |title=A Study of Abortion in Primitive Societies |publisher=International Universities Press |year=1976 |isbn=978-0-8236-6245-6 |url=https://archive.org/details/studyofabortioni00deve}} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Doan AE |title=Opposition and Intimidation: The abortion wars and strategies of political harassment |year=2007 |publisher=University of Michigan}} |
|||
* {{cite journal |vauthors=Ganatra B, Tunçalp Ö, Johnston HB, Johnson BR, Gülmezoglu AM, Temmerman M |title=From concept to measurement: operationalizing WHO's definition of unsafe abortion |journal=Bulletin of the World Health Organization |volume=92 |issue=3 |page=155 |date=March 2014 |pmid=24700971 |pmc=3949603 |doi=10.2471/BLT.14.136333}} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Hartmann B |title=Reproductive Rights and Wrongs: The Global Politics of Population Control |publisher=South End Press |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-89608-491-9}} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Koblitz AH |author-link=Ann Hibner Koblitz |title=Sex and Herbs and Birth Control: Women and Fertility Regulation Through the Ages |publisher=Kovalevskaia Fund |year=2014 |isbn=978-0-9896655-0-6}} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Riddle JM |author-link=John M. Riddle |title=Eve's Herbs: A History of Contraception and Abortion in the West |year=1997 |publisher=Harvard University Press}} |
|||
* {{cite journal |vauthors=Sedgh G, Bearak J, Singh S, Bankole A, Popinchalk A, Ganatra B, Rossier C, Gerdts C, Tunçalp Ö, Johnson BR, Johnston HB, Alkema L |display-authors=6 |title=Abortion incidence between 1990 and 2014: global, regional, and subregional levels and trends |journal=Lancet |volume=388 |issue=10041 |pages=258–267 |date=July 2016 |pmid=27179755 |pmc=5498988 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30380-4 |ref={{harvid|Sedgh et al|2016}}}} |
|||
* {{Cite Q|Q124418995}} |
|||
*{{cite book |last=UN |author-link=United Nations |title=Abortion Policies: A Global Review 3 vols. |date=2002 |publisher=Population Division, [[Department of Economic and Social Affairs]], United Nations |url=https://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/abortion/ |access-date=28 June 2017 |archive-date=11 January 2005 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050111012745/http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/abortion/doc/macedonia.doc |url-status=live}} |
|||
* {{cite book |last1=WHO |author-link=World Health Organization |title=The World Health Report 2005: Make every mother and child count |url=https://www.who.int/whr/2005/en/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050413194036/http://www.who.int/whr/2005/en/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=13 April 2005 |date=2005 |publisher=World Health Organization |location=Geneva |isbn=92-4-156290-0}} |
|||
* {{cite book |last1=WHO |author-link=World Health Organization |title=Safe abortion: technical and policy guidance for health systems |date=2012 |publisher=World Health Organization |location=Geneva |isbn=978-92-4-154843-4 |edition=2nd |url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/70914/1/9789241548434_eng.pdf?ua=1 |access-date=2 November 2014 |archive-date=16 January 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150116223512/http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/70914/1/9789241548434_eng.pdf?ua=1 |url-status=live}} |
|||
* {{cite web |last1=WHO |author-link=World Health Organization |title=Health worker roles in providing safe abortion care and post-abortion contraception |url=http://srhr.org/safeabortion/ |access-date=8 January 2017 |date=2016 |ref={{harvid|WHO|2016a}} |archive-date=29 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190329150415/http://srhr.org/safeabortion/ |url-status=live}} |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{Library resources box |by=no |onlinebooks=no |others=yes lcheading=Abortion}} |
|||
{{Scholia|topic}} |
|||
<!-- HELP KEEP THIS ARTICLE SHORT AND SIMPLE: ADD LINKS TO WHICHEVER SUB-ARTICLE WOULD BE APPROPRIATE INSTEAD OF HERE. ALSO, PLEASE UNDERSTAND THAT SITES CONTAINING SHOCK MATERIAL SHALL IN NO CASE BE ACCEPTED. THANKS!!--> |
<!-- HELP KEEP THIS ARTICLE SHORT AND SIMPLE: ADD LINKS TO WHICHEVER SUB-ARTICLE WOULD BE APPROPRIATE INSTEAD OF HERE. ALSO, PLEASE UNDERSTAND THAT SITES CONTAINING SHOCK MATERIAL SHALL IN NO CASE BE ACCEPTED. THANKS!!--> |
||
* [http://www.guttmacher.org/ The Guttmacher Institute], the official website of The [[Guttmacher Institute]], a sexual and reproductive health research organization. |
|||
* [https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/abortion WHO fact sheet on abortion] |
|||
* [https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/173586/WHO_RHR_15.04_eng.pdf;jsessionid=A45A2A52E41EF59E9E71A08430BF4DA0?sequence=1 Safe abortion: Technical & policy guidance for health systems], World Health Organization (2015) |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20171018012623/https://www.guideline.gov/summaries/summary/47346/firsttrimester-abortion-in-women-with-medical-conditions?q=Women First-trimester abortion in women with medical conditions.] US Department of Health and Human Services |
|||
{{Abortion}} |
{{Abortion}} |
||
{{Women's health|state=collapsed}} |
|||
{{Birth control methods}} |
|||
{{Pregnancy}} |
|||
{{Particular human rights}} |
{{Particular human rights}} |
||
{{Reproductive health}} |
{{Reproductive health}} |
||
{{Birth control methods}} |
|||
{{Population}} |
|||
{{Subject bar|Medicine |Religion |auto=1|wikt=y|b=y}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Abortion]] |
[[Category:Abortion| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Human reproduction]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate]] |
||
[[Category:Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate]] |
|||
[[Category:Gynecology]] |
|||
[[Category:Pregnancy]] |
|||
[[Category:Obstetrics]] |
|||
[[Category:Gender studies]] |
|||
[[Category:Fertility]] |
|||
[[Category:Article Feedback Pilot]] |
|||
{{Link FA|hr}} |
|||
{{Link GA|de}} |
|||
[[ar:إجهاض]] |
|||
[[an:Alborto]] |
|||
[[ast:Albuertu]] |
|||
[[az:Abort]] |
|||
[[bn:গর্ভপাত]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Thu̍t-the]] |
|||
[[be:Аборт]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Аборт]] |
|||
[[bs:Pobačaj]] |
|||
[[bg:Аборт]] |
|||
[[ca:Avortament]] |
|||
[[cs:Interrupce]] |
|||
[[cy:Erthyliad]] |
|||
[[da:Abort]] |
|||
[[de:Schwangerschaftsabbruch]] |
|||
[[et:Abort]] |
|||
[[el:Έκτρωση]] |
|||
[[es:Aborto inducido]] |
|||
[[eo:Aborto]] |
|||
[[eu:Abortu]] |
|||
[[fa:سقط جنین]] |
|||
[[hif:Abortion]] |
|||
[[fo:Fosturtøka]] |
|||
[[fr:Interruption volontaire de grossesse]] |
|||
[[fy:Abortus]] |
|||
[[ga:Ginmhilleadh]] |
|||
[[gl:Aborto]] |
|||
[[ko:인공임신중절]] |
|||
[[hi:गर्भपात]] |
|||
[[hr:Pobačaj]] |
|||
[[id:Gugur kandungan]] |
|||
[[ia:Aborto]] |
|||
[[is:Fóstureyðing]] |
|||
[[it:Aborto]] |
|||
[[he:הפלה מלאכותית]] |
|||
[[jv:Abortus]] |
|||
[[pam:Abortion]] |
|||
[[ka:აბორტი]] |
|||
[[sw:Utoaji mimba]] |
|||
[[ku:Zarokjiberbirin]] |
|||
[[la:Abortus]] |
|||
[[lv:Aborts]] |
|||
[[lt:Abortas]] |
|||
[[hu:Terhességmegszakítás]] |
|||
[[mk:Абортус]] |
|||
[[ml:ഭ്രൂണഹത്യ]] |
|||
[[mr:वैद्यकीय गर्भपात]] |
|||
[[ms:Pengguguran]] |
|||
[[nl:Abortus]] |
|||
[[ja:人工妊娠中絶]] |
|||
[[no:Abort]] |
|||
[[nn:Abort]] |
|||
[[oc:Avortament]] |
|||
[[pnb:ابورشن]] |
|||
[[pl:Aborcja]] |
|||
[[pt:Aborto de gravidez]] |
|||
[[ro:Avort]] |
|||
[[qu:Sulluchiy]] |
|||
[[ru:Аборт]] |
|||
[[sq:Dështimi i zhvillimit të fetusit]] |
|||
[[si:ගබ්සාව]] |
|||
[[simple:Abortion]] |
|||
[[sk:Interrupcia]] |
|||
[[sl:Splav]] |
|||
[[sr:Побачај]] |
|||
[[sh:Abortus]] |
|||
[[fi:Abortti]] |
|||
[[kk:Аборт]] |
|||
[[sv:Abort]] |
|||
[[tl:Pagpapalaglag]] |
|||
[[ta:கருக்கலைப்பு]] |
|||
[[te:గర్భస్రావం]] |
|||
[[th:การแท้ง]] |
|||
[[tr:Kürtaj]] |
|||
[[tk:Abort]] |
|||
[[uk:Аборт]] |
|||
[[ur:اسقاط (حمل)]] |
|||
[[vi:Nạo phá thai]] |
|||
[[war:Pagpunit]] |
|||
[[yi:אבארטאציע]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:落仔]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Abuorts]] |
|||
[[zh:堕胎]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:29, 26 July 2024
| Abortion | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Induced miscarriage, termination of pregnancy |
| Specialty | Obstetrics and gynecology |
| ICD-10-PCS | 10A0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 779.6 |
| MeSH | D000028 |
| MedlinePlus | 007382 |
| eMedicine | 252560 |
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus.[nb 1] An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of all pregnancies.[2][3] When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word abortion generally refers to an induced abortion.[4][5] The most common reasons women give for having an abortion are for birth-timing and limiting family size.[6][7][8] Other reasons reported include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest.[6][8][9]
When done legally in industrialized societies, induced abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine.[10]: 1 [11] Unsafe abortions—those performed by people lacking the necessary skills, or in inadequately resourced settings—are responsible for between 5–13% of maternal deaths, especially in the developing world.[12] However, medication abortions that are self-managed are highly effective and safe throughout the first trimester.[13][14][15] Public health data shows that making safe abortion legal and accessible reduces maternal deaths.[16][17]
Modern methods use medication or surgery for abortions.[18] The drug mifepristone in combination with prostaglandin appears to be as safe and effective as surgery during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy.[18][19] The most common surgical technique involves dilating the cervix and using a suction device.[20] Birth control, such as the pill or intrauterine devices, can be used immediately following abortion.[19] When performed legally and safely on a woman who desires it, induced abortions do not increase the risk of long-term mental or physical problems.[21] In contrast, unsafe abortions performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities cause between 22,000 and 44,000 deaths and 6.9 million hospital admissions each year.[22] The World Health Organization states that "access to legal, safe and comprehensive abortion care, including post-abortion care, is essential for the attainment of the highest possible level of sexual and reproductive health".[23] Historically, abortions have been attempted using herbal medicines, sharp tools, forceful massage, or other traditional methods.[24]
Around 73 million abortions are performed each year in the world,[25] with about 45% done unsafely.[26] Abortion rates changed little between 2003 and 2008,[27] before which they decreased for at least two decades as access to family planning and birth control increased.[28] As of 2018[update], 37% of the world's women had access to legal abortions without limits as to reason.[29] Countries that permit abortions have different limits on how late in pregnancy abortion is allowed.[30] Abortion rates are similar between countries that restrict abortion and countries that broadly allow it, though this is partly because countries which restrict abortion tend to have higher unintended pregnancy rates.[31]
Globally, there has been a widespread trend towards greater legal access to abortion since 1973,[32] but there remains debate with regard to moral, religious, ethical, and legal issues.[33][34] Those who oppose abortion often argue that an embryo or fetus is a person with a right to life, and thus equate abortion with murder.[35][36] Those who support abortion's legality often argue that it is a woman's reproductive right.[37] Others favor legal and accessible abortion as a public health measure.[38] Abortion laws and views of the procedure are different around the world. In some countries abortion is legal and women have the right to make the choice about abortion.[39] In some areas, abortion is legal only in specific cases such as rape, incest, fetal defects, poverty, and risk to a woman's health.[40]
Types
Induced
An induced abortion is a medical procedure to end a pregnancy.[41] In modern English, the term abortion, when used without further qualification, generally refers to induced abortion.[5]
A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in several ways. The abortion method depends upon the gestational age of the embryo or fetus, which gains mass as the pregnancy progresses.[42][43] Abortion laws, regional availability, and the personal preference of the women and her doctor may inform the women's choice of a specific abortion procedure.
Abortions can be characterized as either therapeutic or elective. When an abortion is performed for medical reasons, the procedure is referred to as a therapeutic abortion. Medical reasons for therapeutic abortion include saving the life of the pregnant woman, preventing harm to the woman's physical or mental health, preventing the birth of a child who will have a significantly increased chance of mortality or morbidity, and reducing the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with multiple pregnancy.[44][45] An abortion is referred to as elective or voluntary when it is performed at the request of the woman for non-medical reasons.[45] Confusion sometimes arises over the term elective because "elective surgery" generally refers to all scheduled surgery, whether medically necessary or not.[46]
About one in five pregnancies worldwide ends with an induced abortion.[27] Most abortions result from unintended pregnancies.[6][47] In the United Kingdom, 1 to 2% of abortions are done because of genetic problems in the fetus.[21]
Spontaneous
Miscarriage, also known as spontaneous abortion, is the unintentional expulsion of an embryo or fetus before the 24th week of gestation.[48] A pregnancy that ends before 37 weeks of gestation resulting in a live-born infant is a "premature birth" or a "preterm birth".[49] When a fetus dies in utero after viability, or during delivery, it is usually termed "stillborn".[50] Premature births and stillbirths are generally not considered to be miscarriages, although usage of these terms can sometimes overlap.[51]
Studies of pregnant women in the US and China have shown that between 40% and 60% of embryos do not progress to birth.[52][53][54] The vast majority of miscarriages occur before the woman is aware that she is pregnant,[45] and many pregnancies spontaneously abort before medical practitioners can detect an embryo.[55] Between 15% and 30% of known pregnancies end in clinically apparent miscarriage, depending upon the age and health of the pregnant woman.[56] 80% of these spontaneous abortions happen in the first trimester.[57]
The most common cause of spontaneous abortion during the first trimester is chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo or fetus,[45][58] accounting for at least 50% of sampled early pregnancy losses.[59] Other causes include vascular disease (such as lupus), diabetes, other hormonal problems, infection, and abnormalities of the uterus.[58] Advancing maternal age and a woman's history of previous spontaneous abortions are the two leading factors associated with a greater risk of spontaneous abortion.[59] A spontaneous abortion can also be caused by accidental trauma; intentional trauma or stress to cause miscarriage is considered induced abortion or feticide.[60]
Methods
Medical
Medical abortions are those induced by abortifacient pharmaceuticals. Medical abortion became an alternative method of abortion with the availability of prostaglandin analogs in the 1970s and the antiprogestogen mifepristone (also known as RU-486) in the 1980s.[19][18][61][62]
The most common early first trimester medical abortion regimens use mifepristone in combination with misoprostol (or sometimes another prostaglandin analog, gemeprost) up to 10 weeks (70 days) gestational age,[63][64] methotrexate in combination with a prostaglandin analog up to 7 weeks gestation, or a prostaglandin analog alone.[18] Mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimens work faster and are more effective at later gestational ages than methotrexate–misoprostol combination regimens, and combination regimens are more effective than misoprostol alone, particularly in the second trimester.[61][65] Medical abortion regimens involving mifepristone followed by misoprostol in the cheek between 24 and 48 hours later are effective when performed before 70 days' gestation.[64][63]

In very early abortions, up to 7 weeks gestation, medical abortion using a mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimen is considered to be more effective than surgical abortion (vacuum aspiration), especially when clinical practice does not include detailed inspection of aspirated tissue.[66] Early medical abortion regimens using mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by buccal or vaginal misoprostol are 98% effective up to 9 weeks gestational age; from 9 to 10 weeks efficacy decreases modestly to 94%.[63][67] If medical abortion fails, surgical abortion must be used to complete the procedure.[68]
Early medical abortions account for the majority of abortions before 9 weeks gestation in Britain,[69] France,[70] Switzerland,[71] United States,[72] and the Nordic countries.[73]
Medical abortion regimens using mifepristone in combination with a prostaglandin analog are the most common methods used for second trimester abortions in Canada, most of Europe, China and India,[62] in contrast to the United States where 96% of second trimester abortions are performed surgically by dilation and evacuation.[74]
A 2020 Cochrane Systematic Review concluded that providing women with medications to take home to complete the second stage of the procedure for an early medical abortion results in an effective abortion.[75] Further research is required to determine if self-administered medical abortion is as safe as provider-administered medical abortion, where a health care professional is present to help manage the medical abortion.[75] Safely permitting women to self-administer abortion medication has the potential to improve access to abortion.[75] The review also noted a research gap concerning methods to support women who take medication at home for a self-administered abortion.[75]
Surgical
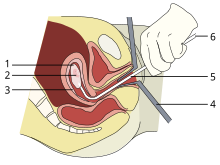
1: Amniotic sac
2: Embryo
3: Uterine lining
4: Speculum
5: Vacurette
6: Attached to a suction pump
Up to 15 weeks' gestation, suction-aspiration or vacuum aspiration are the most common surgical methods of induced abortion.[76] Manual vacuum aspiration (MVA) consists of removing the fetus or embryo, placenta, and membranes by suction using a manual syringe, while electric vacuum aspiration (EVA) uses an electric pump. Both techniques can be used very early in pregnancy. MVA can be used up to 14 weeks but is more often used earlier in the U.S. EVA can be used later.[74]
MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and "menstrual extraction", or EVA can be used in very early pregnancy when cervical dilation may not be required. Dilation and curettage (D&C) refers to opening the cervix (dilation) and removing tissue (curettage) via suction or sharp instruments. D&C is a standard gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. The World Health Organization recommends sharp curettage only when suction aspiration is unavailable.[77]
Dilation and evacuation (D&E), used after 12 to 16 weeks, consists of opening the cervix and emptying the uterus using surgical instruments and suction. D&E is performed vaginally and does not require an incision. Intact dilation and extraction (D&X) refers to a variant of D&E sometimes used after 18 to 20 weeks when removal of an intact fetus improves surgical safety or for other reasons.[78]
Abortion may also be performed surgically by hysterotomy or gravid hysterectomy. Hysterotomy abortion is a procedure similar to a caesarean section and is performed under general anesthesia. It requires a smaller incision than a caesarean section and can be used during later stages of pregnancy. Gravid hysterectomy refers to removal of the whole uterus while still containing the pregnancy. Hysterotomy and hysterectomy are associated with much higher rates of maternal morbidity and mortality than D&E or induction abortion.[79]
First trimester procedures can generally be performed using local anesthesia, while second trimester methods may require deep sedation or general anesthesia.[80][81][82]
Labor induction abortion
In places lacking the necessary medical skill for dilation and extraction, or when preferred by practitioners, an abortion can be induced by first inducing labor and then inducing fetal demise if necessary.[83] This is sometimes called "induced miscarriage". This procedure may be performed from 13 weeks gestation to the third trimester. Although it is very uncommon in the United States, more than 80% of induced abortions throughout the second trimester are labor-induced abortions in Sweden and other nearby countries.[84]
Only limited data are available comparing labor-induced abortion with the dilation and extraction method.[84] Unlike D&E, labor-induced abortions after 18 weeks may be complicated by the occurrence of brief fetal survival, which may be legally characterized as live birth. For this reason, labor-induced abortion is legally risky in the United States.[84][85]
Other methods
Historically, a number of herbs reputed to possess abortifacient properties have been used in folk medicine. Such herbs include tansy, pennyroyal, black cohosh, and the now-extinct silphium.[86]: 44–47, 62–63, 154–155, 230–231
In 1978, one woman in Colorado died and another developed organ damage when they attempted to terminate their pregnancies by taking pennyroyal oil.[87] Because the indiscriminant use of herbs as abortifacients can cause serious—even lethal—side effects, such as multiple organ failure,[88] such use is not recommended by physicians.
Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the abdomen. The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries without necessarily succeeding in inducing miscarriage.[89] In Southeast Asia, there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal massage.[90] One of the bas reliefs decorating the temple of Angkor Wat in Cambodia depicts a demon performing such an abortion upon a woman who has been sent to the underworld.[90]
Reported methods of unsafe, self-induced abortion include misuse of misoprostol and insertion of non-surgical implements such as knitting needles and clothes hangers into the uterus. These and other methods to terminate pregnancy may be called "induced miscarriage". Such methods are rarely used in countries where surgical abortion is legal and available.[91]
Safety

The health risks of abortion depend principally on how, and under what conditions, the procedure is performed. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines unsafe abortions as those performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities.[92] Legal abortions performed in the developed world are among the safest procedures in medicine.[10][93] According to a 2012 study in Obstetrics & Gynecology, in the United States the risk of maternal mortality is 14 times lower after induced abortion than after childbirth.[94] The CDC estimated in 2019 that US pregnancy-related mortality was 17.2 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births,[95] while the US abortion mortality rate was 0.43 maternal deaths per 100,000 procedures.[11][96][97] In the UK, guidelines of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists state that "Women should be advised that abortion is generally safer than continuing a pregnancy to term."[98] Worldwide, on average, abortion is safer than carrying a pregnancy to term. A 2007 study reported that "26% of all pregnancies worldwide are terminated by induced abortion," whereas "deaths from improperly performed [abortion] procedures constitute 13% of maternal mortality globally."[99] In Indonesia in 2000 it was estimated that 2 million pregnancies ended in abortion, 4.5 million pregnancies were carried to term, and 14–16 percent of maternal deaths resulted from abortion.[100]
In the US from 2000 to 2009, abortion had a mortality rate lower than plastic surgery, lower or similar to running a marathon, and about equivalent to traveling 760 miles (1,220 km) in a passenger car.[11] Five years after seeking abortion services, women who gave birth after being denied an abortion reported worse health than women who had either first or second trimester abortions.[101] The risk of abortion-related mortality increases with gestational age, but remains lower than that of childbirth.[102] Outpatient abortion is as safe from 64 to 70 days' gestation as it before 63 days.[103]
Safety of abortion methods
There is little difference in terms of safety and efficacy between medical abortion using a combined regimen of mifepristone and misoprostol and surgical abortion (vacuum aspiration) in early first trimester abortions up to 10 weeks gestation.[66] Medical abortion using the prostaglandin analog misoprostol alone is less effective and more painful than medical abortion using a combined regimen of mifepristone and misoprostol or surgical abortion.[104][105]
Safety and gestational age
Vacuum aspiration in the first trimester is the safest method of surgical abortion, and can be performed in a primary care office, abortion clinic, or hospital. Complications, which are rare, can include uterine perforation, pelvic infection, and retained products of conception requiring a second procedure to evacuate.[106] Infections account for one-third of abortion-related deaths in the United States.[107] The rate of complications of vacuum aspiration abortion in the first trimester is similar regardless of whether the procedure is performed in a hospital, surgical center, or office.[108] Preventive antibiotics (such as doxycycline or metronidazole) are typically given before abortion procedures,[109] as they are believed to substantially reduce the risk of postoperative uterine infection;[80][110] however, antibiotics are not routinely given with abortion pills.[111] The rate of failed procedures does not appear to vary significantly depending on whether the abortion is performed by a doctor or a mid-level practitioner.[112]
Complications after second trimester abortion are similar to those after first trimester abortion, and depend somewhat on the method chosen.[113] The risk of death from abortion approaches roughly half the risk of death from childbirth the farther along a woman is in pregnancy; from one in a million before 9 weeks gestation to nearly one in ten thousand at 21 weeks or more (as measured from the last menstrual period).[114][115] It appears that having had a prior surgical uterine evacuation (whether because of induced abortion or treatment of miscarriage) correlates with a small increase in the risk of preterm birth in future pregnancies. The studies supporting this did not control for factors not related to abortion or miscarriage, and hence the causes of this correlation have not been determined, although multiple possibilities have been suggested.[116][117]
Mental health
Current evidence finds no relationship between most induced abortions and mental health problems[21][118] other than those expected for any unwanted pregnancy.[119] A report by the American Psychological Association concluded that a woman's first abortion is not a threat to mental health when carried out in the first trimester, with such women no more likely to have mental-health problems than those carrying an unwanted pregnancy to term; the mental-health outcome of a woman's second or greater abortion is less certain.[119][120] Some older reviews concluded that abortion was associated with an increased risk of psychological problems;[121] however, later reviews of the medical literature found that previous reviews did not use an appropriate control group.[118] When a control group is utilized, receiving abortion is not associated with adverse psychological outcomes.[118] However, women seeking abortion who are denied access to abortion have an increase in anxiety after the denial.[118]
Although some studies show negative mental-health outcomes in women who choose abortions after the first trimester because of fetal abnormalities,[122] more rigorous research would be needed to show this conclusively.[123] Some proposed negative psychological effects of abortion have been referred to by anti-abortion advocates as a separate condition called "post-abortion syndrome", but this is not recognized by medical or psychological professionals in the United States.[124]
A 2020 long term-study among US women found that about 99% of women felt that they made the right decision five years after they had an abortion. Relief was the primary emotion with few women feeling sadness or guilt. Social stigma was a main factor predicting negative emotions and regret years later. The researchers also stated: "These results add to the scientific evidence that emotions about an abortion are associated with personal and social context, and are not a product of the abortion procedure itself."[125]
Safety in the abortion debate
Some purported risks of abortion are promoted primarily by anti-abortion groups,[126][127] but lack scientific support.[126] For example, the question of a link between induced abortion and breast cancer has been investigated extensively. Major medical and scientific bodies (including the WHO, National Cancer Institute, American Cancer Society, Royal College of OBGYN and American Congress of OBGYN) have concluded that abortion does not cause breast cancer.[128]
In the past even illegality has not automatically meant that the abortions were unsafe. Referring to the U.S., historian Linda Gordon states: "In fact, illegal abortions in this country have an impressive safety record."[129]: 25
According to Rickie Solinger,
A related myth, promulgated by a broad spectrum of people concerned about abortion and public policy, is that before legalization abortionists were dirty and dangerous back-alley butchers.... [T]he historical evidence does not support such claims.[130]: 4
A 1940s American physician spoke of his pride in having performed 13,844 illegal abortions without any fatalities.[131] In 1870s New York City, the abortionist/midwife Madame Restell (Anna Trow Lohman) is said to have lost very few women among her more than 100,000 patients[132]—a lower mortality rate than the childbirth mortality rate at the time. In 1936, obstetrics and gynecology professor Frederick J. Taussig wrote that a cause of increasing mortality during the years of illegality in the U.S. was that
With each decade of the past fifty years the actual and proportionate frequency of this accident [perforation of the uterus] has increased, due, first, to the increase in the number of instrumentally induced abortions; second, to the proportionate increase in abortions handled by doctors as against those handled by midwives; and, third, to the prevailing tendency to use instruments instead of the finger in emptying the uterus.[133]
Unsafe abortion
Women seeking an abortion may use unsafe methods, especially when abortion is legally restricted. They may attempt self-induced abortion or seek the help of a person without proper medical training or facilities. This can lead to severe complications, such as incomplete abortion, sepsis, hemorrhage, and damage to internal organs.[134]
Unsafe abortions are a major cause of injury and death among women worldwide. Although data are imprecise, it is estimated that approximately 20 million unsafe abortions are performed annually, with 97% taking place in developing countries.[10] Unsafe abortions are believed to result in millions of injuries.[10][135] Estimates of deaths vary according to methodology, and have ranged from 37,000 to 70,000 in the past decade;[10][136][137] deaths from unsafe abortion account for around 13% of all maternal deaths.[138] The World Health Organization believes that mortality has fallen since the 1990s.[139] To reduce the number of unsafe abortions, public health organizations have generally advocated emphasizing the legalization of abortion, training of medical personnel, and ensuring access to reproductive-health services.[140]
A major factor in whether abortions are performed safely or not is the legal standing of abortion. Countries with restrictive abortion laws have higher rates of unsafe abortion and similar overall abortion rates compared to countries where abortion is legal and available.[136][27] For example, the 1996 legalization of abortion in South Africa led to an immediate reduction in abortion-related complications,[141] with abortion-related deaths dropping by more than 90%.[142] Similar reductions in maternal mortality have been observed after other countries have liberalized their abortion laws, such as Romania and Nepal.[143] A 2011 study concluded that in the United States, some state-level anti-abortion laws are correlated with lower rates of abortion in that state.[144] The analysis, however, did not take into account travel to other states without such laws to obtain an abortion.[145] In addition, a lack of access to effective contraception contributes to unsafe abortion. It has been estimated that the incidence of unsafe abortion could be reduced by up to 75% (from 20 million to 5 million annually) if modern family planning and maternal health services were readily available globally.[146] Rates of such abortions may be difficult to measure because they can be reported variously as miscarriage, "induced miscarriage", "menstrual regulation", "mini-abortion", and "regulation of a delayed/suspended menstruation".[10][147]
Forty percent of the world's women are able to access therapeutic and elective abortions within gestational limits,[30] while an additional 35 percent have access to legal abortion if they meet certain physical, mental, or socioeconomic criteria.[40] While maternal mortality seldom results from safe abortions, unsafe abortions result in 70,000 deaths and 5 million disabilities per year.[136] Complications of unsafe abortion account for approximately an eighth of maternal mortalities worldwide,[148] though this varies by region.[149] Secondary infertility caused by an unsafe abortion affects an estimated 24 million women.[150] The rate of unsafe abortions has increased from 44% to 49% between 1995 and 2008.[27] Health education, access to family planning, and improvements in health care during and after abortion have been proposed to address consequences of unsafe abortion.[151]
Incidence
There are two commonly used methods of measuring the incidence of abortion:
- Abortion rate – number of abortions annually per 1,000 women between 15 and 44 years of age;[152] some sources use a range of 15–49.
- Abortion percentage – number of abortions out of 100 known pregnancies; pregnancies include live births, abortions, and miscarriages.
In many places, where abortion is illegal or carries a heavy social stigma, medical reporting of abortion is not reliable.[153] For this reason, estimates of the incidence of abortion must be made without determining certainty related to standard error.[27] The number of abortions performed worldwide was characterized as stable in the early 2000s, with 41.6 million having been performed in 2003 and 43.8 million having been performed in 2008.[27] The abortion rate worldwide was 28 per 1000 women per year, though it was 24 per 1000 women per year for developed countries and 29 per 1000 women per year for developing countries.[27] The same 2012 study indicated that in 2008, the estimated abortion percentage of known pregnancies was at 21% worldwide, with 26% in developed countries and 20% in developing countries.[27]
On average, the incidence of abortion is similar in countries with restrictive abortion laws and those with more liberal access to abortion.[154] Restrictive abortion laws are associated with increases in the percentage of abortions performed unsafely.[30][155][154] The unsafe abortion rate in developing countries is partly attributable to lack of access to modern contraceptives; according to the Guttmacher Institute, providing access to contraceptives would result in about 14.5 million fewer unsafe abortions and 38,000 fewer deaths from unsafe abortion annually worldwide.[156]
The rate of legal, induced abortion varies extensively worldwide. According to the report of employees of Guttmacher Institute it ranged from 7 per 1000 women per year (Germany and Switzerland) to 30 per 1000 women per year (Estonia) in countries with complete statistics in 2008. The proportion of pregnancies that ended in induced abortion ranged from about 10% (Israel, the Netherlands and Switzerland) to 30% (Estonia) in the same group, though it might be as high as 36% in Hungary and Romania, whose statistics were deemed incomplete.[157][158]
An American study in 2002 concluded that about half of women having abortions were using a form of contraception at the time of becoming pregnant. Inconsistent use was reported by half of those using condoms and three-quarters of those using the birth control pill; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.[159] Of the other half of women, who were not using contraception at the time of becoming pregnant, the vast majority had used contraception at some point in the past, indicating some level of dissatisfaction with the contraceptive options available to them. Indeed, 32% of these contraceptive nonusers cited concerns about contraceptive methods as their reason for nonuse,[159] and a more recent study found similar results.[160] Taken together, these statistics suggest that new contraceptive methods, such as non-hormonal contraceptives or male contraceptives, could reduce unintended pregnancy and abortion rates.[161]
The Guttmacher Institute has found that "most abortions in the United States are obtained by minority women" because minority women "have much higher rates of unintended pregnancy".[162] In a 2022 analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation, while people of color comprise 44% of the population in Mississippi, 59% of the population in Texas, 42% of the population in Louisiana, and 35% of the population in Alabama, they comprise 80%, 74%, 72%, and 70%, respectively, of those receiving abortions.[163]
Gestational age and method
Abortion rates vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the method practiced. In 2003, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that 26% of reported legal induced abortions in the United States were known to have been obtained at less than 6 weeks' gestation, 18% at 7 weeks, 15% at 8 weeks, 18% at 9 through 10 weeks, 10% at 11 through 12 weeks, 6% at 13 through 15 weeks, 4% at 16 through 20 weeks and 1% at more than 21 weeks. 91% of these were classified as having been done by "curettage" (suction-aspiration, dilation and curettage, dilation and evacuation), 8% by "medical" means (mifepristone), >1% by "intrauterine instillation" (saline or prostaglandin), and 1% by "other" (including hysterotomy and hysterectomy).[164] According to the CDC, due to data collection difficulties the data must be viewed as tentative and some fetal deaths reported beyond 20 weeks may be natural deaths erroneously classified as abortions if the removal of the dead fetus is accomplished by the same procedure as an induced abortion.[8]
The Guttmacher Institute estimated there were 2,200 intact dilation and extraction procedures in the US during 2000; this accounts for <0.2% of the total number of abortions performed that year.[165] Similarly, in England and Wales in 2006, 89% of terminations occurred at or under 12 weeks, 9% between 13 and 19 weeks, and 2% at or over 20 weeks. 64% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 6% by D&E, and 30% were medical.[166] There are more second trimester abortions in developing countries such as China, India and Vietnam than in developed countries.[167]
There are both medical and non-medical reasons to have an abortion later in pregnancy (after 20 weeks). A study was conducted from 2008 to 2010 at the University of California San Francisco where more than 440 women were asked about why they experienced delays in obtaining abortion care, if there were any. This study found that almost half of individuals who obtained an abortion after 20 weeks did not suspect that they were pregnant until later in their pregnancy.[168] Other barriers to abortion care found in the study included lack of information about where to access an abortion, difficulties with transportation, lack of insurance coverage, and inability to pay for the abortion procedure.[168]
Medical reasons for seeking an abortion later in pregnancy include fetal anomalies and health risk to the pregnant person.[169] There are prenatal tests that can diagnose Down Syndrome or cystic fibrosis as early as 10 weeks into gestation, but structural fetal anomalies are often detected much later in pregnancy.[168] A proportion of structural fetal anomalies are lethal, which means that the fetus will almost certainly die before or shortly after birth.[168] Life-threatening conditions may also develop later in pregnancy, such as early severe preeclampsia, newly diagnosed cancer in need of urgent treatment, and intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis), which often occurs along with premature rupture of the amniotic sac (PPROM).[168] If serious medical conditions such as these arise before the fetus is viable, the person carrying the pregnancy may pursue an abortion to preserve their own health.[168]
Motivation
Personal

The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world.[8][6][7] Some of the reasons may include an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, and the wish to complete education or advance a career.[9] Additional reasons include not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest.[6][170]
Societal
Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures.[171] These might include the preference for children of a specific sex or race, disapproval of single or early motherhood, stigmatization of people with disabilities, insufficient economic support for families, lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts toward population control (such as China's one-child policy). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or sex-selective abortion.[172] In cultures where there is a preference for male children, some women have sex selective abortions, which have partially replaced the earlier practice of female infanticide.[172]
Maternal health
Some abortions are performed due to concerns over maternal health. In 1990s, women cited maternal health as their main motivating factor in about a third of abortions in three of 27 countries analyzed. In seven additional countries, about 7% of abortions were maternal health related.[8][6]
In the U.S., the Supreme Court decisions in Roe v. Wade and Doe v. Bolton: "ruled that the state's interest in the life of the fetus became compelling only at the point of viability, defined as the point at which the fetus can survive independently of its mother. Even after the point of viability, the state cannot favor the life of the fetus over the life or health of the pregnant woman. Under the right of privacy, physicians must be free to use their "medical judgment for the preservation of the life or health of the mother." On the same day that the Court decided Roe, it also decided Doe v. Bolton, in which the Court defined health very broadly: "The medical judgment may be exercised in the light of all factors—physical, emotional, psychological, familial, and the woman's age—relevant to the well-being of the patient. All these factors may relate to health. This allows the attending physician the room he needs to make his best medical judgment."[173]: 1200–1201
Cancer
This section needs to be updated. (September 2022) |
The rate of cancer during pregnancy is 0.02–1%, and in many cases, cancer of the mother leads to consideration of abortion to protect the life of the mother, or in response to the potential damage that may occur to the fetus during treatment. This is particularly true for cervical cancer, the most common type of which occurs in 1 of every 2,000–13,000 pregnancies, for which initiation of treatment "cannot co-exist with preservation of fetal life (unless neoadjuvant chemotherapy is chosen)". Very early stage cervical cancers (I and IIa) may be treated by radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection, radiation therapy, or both, while later stages are treated by radiotherapy. Chemotherapy may be used simultaneously. Treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy also involves fetal considerations, because lumpectomy is discouraged in favor of modified radical mastectomy unless late-term pregnancy allows follow-up radiation therapy to be administered after the birth.[174]
Exposure to a single chemotherapy drug is estimated to cause a 7.5–17% risk of teratogenic effects on the fetus, with higher risks for multiple drug treatments. Treatment with more than 40 Gy of radiation usually causes spontaneous abortion. Exposure to much lower doses during the first trimester, especially 8 to 15 weeks of development, can cause intellectual disability or microcephaly, and exposure at this or subsequent stages can cause reduced intrauterine growth and birth weight. Exposures above 0.005–0.025 Gy cause a dose-dependent reduction in IQ.[174] It is possible to greatly reduce exposure to radiation with abdominal shielding, depending on how far the area to be irradiated is from the fetus.[175][176]
The process of birth itself may also put the mother at risk. According to Li et al., "[v]aginal delivery may result in dissemination of neoplastic cells into lymphovascular channels, haemorrhage, cervical laceration and implantation of malignant cells in the episiotomy site, while abdominal delivery may delay the initiation of non-surgical treatment."[177]
Fetal health
Congenital disorders, revealed by prenatal screening, motivate some women to seek abortions.[6]
In the United States, public opinion shifted after television personality Sherri Finkbine's was exposed to thalidomide, a teratogen, in her fifth month of pregnancy. Unable to obtain a legal abortion in the United States, Finkbine traveled to Sweden. From 1962 to 1965, an outbreak of German measles left 15,000 babies with severe birth defects. In 1967, the American Medical Association publicly supported liberalization of abortion laws. A National Opinion Research Center poll in 1965 showed 73% supported abortion when the mother's life was at risk, 57% when birth defects were present and 59% for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest.[178]
History and religion

Since ancient times, abortions have been done using a number of methods, including herbal medicines acting as abortifacients, sharp tools through the use of force, or through other traditional medicine methods.[24] Induced abortion has a long history and can be traced back to civilizations as varied as ancient China (abortifacient knowledge is often attributed to the mythological ruler Shennong),[180] ancient India since its Vedic age,[181] ancient Egypt with its Ebers Papyrus (c. 1550 BCE), and the Roman Empire in the time of Juvenal (c. 200 CE).[24] One of the earliest known artistic representations of abortion is in a bas relief at Angkor Wat (c. 1150). Found in a series of friezes that represent judgment after death in Hindu and Buddhist culture, it depicts the technique of abdominal abortion.[90]
In Judaism (Genesis 2:7), the fetus is not considered to have a human soul until it is safely outside of the woman, is viable, and has taken its first breath.[182][183][184] The fetus is considered valuable property of the woman and not a human life while in the womb (Exodus 21:22–23). While Judaism encourages people to be fruitful and multiply by having children, abortion is allowed and is deemed necessary when a pregnant woman's life is in danger.[185][186] Several religions, including Judaism, which disagree that human life begins at conception, support the legality of abortion on religious freedom grounds.[187] In Islam, abortion is traditionally permitted until a point in time when Muslims believe the soul enters the fetus,[24] considered by various theologians to be at conception, 40 days after conception, 120 days after conception, or at quickening.[188] Abortion is largely heavily restricted or forbidden in areas of high Islamic faith such as the Middle East and North Africa.[189]
Some medical scholars and abortion opponents have suggested that the Hippocratic Oath forbade physicians in Ancient Greece from performing abortions;[24] other scholars disagree with this interpretation,[24] and state that the medical texts of Hippocratic Corpus contain descriptions of abortive techniques right alongside the Oath.[190] The physician Scribonius Largus wrote in 43 CE that the Hippocratic Oath prohibits abortion, as did Soranus of Ephesus, although apparently not all doctors adhered to it strictly at the time. According to Soranus' 1st or 2nd century CE work Gynaecology, one party of medical practitioners banished all abortives as required by the Hippocratic Oath; the other party to which he belonged was willing to prescribe abortions only for the sake of the mother's health.[191][192] In Politics (350 BCE), Aristotle condemned infanticide as a means of population control. He preferred abortion in such cases,[193][194] with the restriction that it "must be practised on it before it has developed sensation and life; for the line between lawful and unlawful abortion will be marked by the fact of having sensation and being alive."[195]
In the Catholic Church, opinion was divided on how serious abortion was in comparison with such acts as contraception, oral sex, and sex in marriage for pleasure rather than procreation.[196]: 155–167 The Catholic Church did not begin vigorously opposing abortion until the 19th century.[24][187] As early as ~100 CE, the Didache taught that abortion was sinful.[197] Several historians argue that prior to the 19th century most Catholic authors did not regard termination of pregnancy before quickening or ensoulment as an abortion.[198][199][200] Among these authors were the Doctors of the Church, such as St. Augustine, St. Thomas Aquinas, and St. Alphonsus Liguori. In 1588, Pope Sixtus V (r. 1585–1590) was the only Pope before Pope Pius IX (in his 1869 bull, Apostolicae Sedis) to institute a Church policy labeling all abortion as homicide and condemning abortion regardless of the stage of pregnancy.[201][196]: 362–364 [86]: 157–158 Sixtus V's pronouncement was reversed in 1591 by Pope Gregory XIV.[202] In the recodification of 1917 Code of Canon Law, Apostolicae Sedis was strengthened, in part to remove a possible reading that excluded excommunication of the mother.[203] Statements made in the Catechism of the Catholic Church, the codified summary of the Church's teachings, considers abortion from the moment of conception as homicide and called for the end of legal abortion.[204]
Denominations that support abortion rights with some limits include the United Methodist Church, Episcopal Church, Evangelical Lutheran Church in America and Presbyterian Church USA.[205] A 2014 Guttmacher survey of abortion patients in the United States found that many reported a religious affiliation: 24% were Catholic while 30% were Protestant.[206] A 1995 survey reported that Catholic women are as likely as the general population to terminate a pregnancy, Protestants are less likely to do so, and evangelical Christians are the least likely to do so.[8][6] A 2019 Pew Research Center study found that most Christian denominations were against overturning Roe v. Wade, which in the United States legalized abortion, at around 70%, except White Evangelicals at 35%.[207]

Abortion has been a fairly common practice,[209][210] and was not always illegal or controversial until the 19th century.[211][212] Under common law, including early English common law dating back to Edward Coke in 1648,[213] abortion was generally permitted before quickening (14–26 weeks after conception, or between the fourth and sixth month),[214][215][216] and at women's discretion;[187] it was whether abortion was performed after quickening that determined if it was a crime.[213] In Europe and North America, abortion techniques advanced starting in the 17th century; the conservatism of most in the medical profession with regards to sexual matters prevented the wide expansion of abortion techniques.[24][217][218] Other medical practitioners in addition to some physicians advertised their services, and they were not widely regulated until the 19th century when the practice, sometimes called restellism,[219] was banned in both the United States and the United Kingdom.[24][nb 2]
Some 19th-century physicians, one of the most famous and consequential being the American Horatio Storer,[220] argued for anti-abortion laws on racist and misogynist as well as moral grounds.[221][222][223] Church groups were also highly influential in anti-abortion movements,[24][211][221] and religious groups more so since the 20th century.[220] Some of the early anti-abortion laws punished only the doctor or abortionist,[187] and while women could be criminally tried for a self-induced abortion,[213] they were rarely prosecuted in general.[211] In the United States, some argued that abortion was more dangerous than childbirth until about 1930 when incremental improvements in abortion procedures relative to childbirth made abortion safer.[nb 3] Others maintain that in the 19th century early abortions under the hygienic conditions in which midwives usually worked were relatively safe.[224][225][226] Several scholars argue that, despite improved medical procedures, the period from the 1930s until the 1970s saw more zealous enforcement of anti-abortion laws, alongside an increasing control of abortion providers by organized crime.[nb 4]
In 1920, Soviet Russia became the first country to legalize abortion after Lenin insisted that no woman be forced to give birth.[227][228] Iceland (1935) and Sweden (1938) would follow suit to legalize certain or all forms of abortion.[229] In Nazi Germany (1935), a law permitted abortions for those deemed "hereditarily ill", while women considered of German stock were specifically prohibited from having abortions.[230] Beginning in the second half of the 20th century, abortion was legalized in a greater number of countries.[24] In Japan, abortion was first legalized by the 1948 "Eugenics Protection Law" meant to prevent the births of "inferior" humans. As of 2022[update], due to Japan's continuing strongly patriarchal culture and traditional views on women's societal roles, women who want an abortion must normally get written permission from their partner.[231][232]
Society and culture
Abortion debate
Induced abortion has long been the source of considerable debate. Ethical, moral, philosophical, biological, religious and legal issues surrounding abortion are related to value systems. Opinions of abortion may be about fetal rights, governmental authority, and women's rights.
In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor of or against abortion access focus on either the moral permissibility of an induced abortion, or the justification of laws permitting or restricting abortion.[233] The World Medical Association Declaration on Therapeutic Abortion notes, "circumstances bringing the interests of a mother into conflict with the interests of her unborn child create a dilemma and raise the question as to whether or not the pregnancy should be deliberately terminated."[234] Abortion debates, especially pertaining to abortion laws, are often spearheaded by groups advocating one of these two positions. Groups who favor greater legal restrictions on abortion, including complete prohibition, most often describe themselves as "pro-life" while groups who are against such legal restrictions describe themselves as "pro-choice".[235]
Modern abortion law
| Legal on request: | |
| No gestational limit | |
| Gestational limit after the first 17 weeks | |
| Gestational limit in the first 17 weeks | |
| Unclear gestational limit | |
| Legally restricted to cases of: | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, rape*, fetal impairment*, or socioeconomic factors | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, rape, or fetal impairment | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, or fetal impairment | |
| Risk to woman's life*, to her health*, or rape | |
| Risk to woman's life or to her health | |
| Risk to woman's life | |
| Illegal with no exceptions | |
| No information | |
| * Does not apply to some countries or territories in that category | |
Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral, and cultural factors continue to influence abortion laws throughout the world. The right to life, the right to liberty, the right to security of person, and the right to reproductive health are major issues of human rights that sometimes constitute the basis for the existence or absence of abortion laws.
In jurisdictions where abortion is legal, certain requirements must often be met before a woman may obtain a legal abortion (an abortion performed without the woman's consent is considered feticide and is generally illegal). These requirements usually depend on the age of the fetus, often using a trimester-based system to regulate the window of legality, or as in the U.S., on a doctor's evaluation of the fetus' viability. Some jurisdictions require a waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on fetal development, or require that parents be contacted if their minor daughter requests an abortion.[236] Other jurisdictions may require that a woman obtain the consent of the fetus' father before aborting the fetus, that abortion providers inform women of health risks of the procedure—sometimes including "risks" not supported by the medical literature—and that multiple medical authorities certify that the abortion is either medically or socially necessary. Many restrictions are waived in emergency situations. China, which has ended their[237] one-child policy, and now has a three-child policy,[238] has at times incorporated mandatory abortions as part of their population control strategy.[239]
Other jurisdictions ban abortion almost entirely. Many, but not all, of these allow legal abortions in a variety of circumstances. These circumstances vary based on jurisdiction, but may include whether the pregnancy is a result of rape or incest, the fetus' development is impaired, the woman's physical or mental well-being is endangered, or socioeconomic considerations make childbirth a hardship.[40] In countries where abortion is banned entirely, such as Nicaragua, medical authorities have recorded rises in maternal death directly and indirectly due to pregnancy as well as deaths due to doctors' fears of prosecution if they treat other gynecological emergencies.[240][241] Some countries, such as Bangladesh, that nominally ban abortion, may also support clinics that perform abortions under the guise of menstrual hygiene.[242] This is also a terminology in traditional medicine.[243] In places where abortion is illegal or carries heavy social stigma, pregnant women may engage in medical tourism and travel to countries where they can terminate their pregnancies.[244] Women without the means to travel can resort to providers of illegal abortions or attempt to perform an abortion by themselves.[245]
The organization Women on Waves has been providing education about medical abortions since 1999. The NGO created a mobile medical clinic inside a shipping container, which then travels on rented ships to countries with restrictive abortion laws. Because the ships are registered in the Netherlands, Dutch law prevails when the ship is in international waters. While in port, the organization provides free workshops and education; while in international waters, medical personnel are legally able to prescribe medical abortion drugs and counseling.[246][247][248]
Sex-selective abortion
Sonography and amniocentesis allow parents to determine sex before childbirth. The development of this technology has led to sex-selective abortion, or the termination of a fetus based on its sex. The selective termination of a female fetus is most common.
Sex-selective abortion is partially responsible for the noticeable disparities between the birth rates of male and female children in some countries. The preference for male children is reported in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has been reported in Taiwan, South Korea, India, and China.[249] This deviation from the standard birth rates of males and females occurs despite the fact that the country in question may have officially banned sex-selective abortion or even sex-screening.[250][251][252][253] In China, a historical preference for a male child has been exacerbated by the one-child policy, which was enacted in 1979.[254]
Many countries have taken legislative steps to reduce the incidence of sex-selective abortion. At the International Conference on Population and Development in 1994 over 180 states agreed to eliminate "all forms of discrimination against the girl child and the root causes of son preference",[255] conditions also condemned by a PACE resolution in 2011.[256] The World Health Organization and UNICEF, along with other United Nations agencies, have found that measures to restrict access to abortion in an effort to reduce sex-selective abortions have unintended negative consequences, largely stemming from the fact that women may seek or be coerced into seeking unsafe, extralegal abortions.[255] On the other hand, measures to reduce gender inequality can reduce the prevalence of such abortions without attendant negative consequences.[255][257]
Anti-abortion violence
Abortion providers and facilities have been subjected to violence, including murder, assault, arson, and bombing. Some scholars consider anti-abortion violence to be within the definition of terrorism,[258] a view shared by some governments.[259], In the U.S. and Canada, over 8,000 incidents of violence, trespassing, and death threats have been recorded by providers since 1977, including over 200 bombings/arsons and hundreds of assaults.[260] Abortion clinics have also been targeted by acid attacks, invasions, and vandalism[261] The majority of abortion opponents have not been involved in violent acts.
Physicians and other abortion clinic staff have been murdered by abortion opponents. In the United States, at least four physicians have been murdered in connection with their work at abortion clinics, including David Gunn (1993), John Britton (1994), Barnett Slepian (1998), and George Tiller (2009). In Canada, gynecologist Garson Romalis survived murder attempts in both 1994 and 2000. Besides physicians, killings have targeted other clinic staff, such as John Salvi's 1994 murder of two receptionists in Massachusetts clinic and Peter Knight's 2001 murder of a security guard in a Melbourne clinic. Notable perpetrators of anti-abortion violence include Eric Rudolph, Scott Roeder, Shelley Shannon, and Paul Hill, the first person to be executed in the United States for murdering an abortion provider.[262]
Some countries have laws to protecting access to abortion. Such laws prevent abortion opponents from interfering with access to legal abortion services. For example, the American Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances Act bars the use of threats or violence to interfere with abortion access. Abortion access laws may also establish safe access zones around abortion clinics, with limits on protests and enhanced penalties for anti-abortion violence.[263]
Psychological pressure may also be used to limit abortion access. In 2003, Chris Danze organized anti-abortion organizations throughout Texas to prevent the construction of a Planned Parenthood facility in Austin. The organizations released the personal information online of those involved with construction, sent them up to 1200 phone calls a day and contacted their churches.[264] Some protestors record women entering clinics on camera.[264]
Non-human examples
Spontaneous abortion occurs in various animals. For example, in sheep it may be caused by stress or physical exertion, such as crowding through doors or being chased by dogs.[265] In cows, abortion may be caused by contagious disease, such as brucellosis or Campylobacter, but can often be controlled by vaccination.[266] Eating pine needles can also induce abortions in cows.[267][268] Several plants, including broomweed, skunk cabbage, poison hemlock, and tree tobacco, are known to cause fetal deformities and abortion in cattle[269]: 45–46 and in sheep and goats.[269]: 77–80 In horses, a fetus may be aborted or resorbed if it has lethal white syndrome. Foal embryos that are homozygous for the dominant white gene (WW) are theorized to also be aborted or resorbed before birth.[270] In many species of sharks and rays, stress-induced abortions occur frequently on capture.[271]
Viral infection can cause abortion in dogs.[272] Cats can experience spontaneous abortion for many reasons, including hormonal imbalance. A combined abortion and spaying is performed on pregnant cats, especially in trap–neuter–return programs, to prevent unwanted kittens from being born.[273][274][275] Female rodents may terminate a pregnancy when exposed to the smell of a male not responsible for the pregnancy, known as the Bruce effect.[276]
Abortion may also be induced in animals, in the context of animal husbandry. For example, abortion may be induced in mares that have been mated improperly, or that have been purchased by owners who did not realize the mares were pregnant, or that are pregnant with twin foals.[277] Feticide can occur in horses and zebras due to male harassment of pregnant mares or forced copulation,[278][279][280] although the frequency in the wild has been questioned.[281] Male gray langur monkeys may attack females following male takeover, causing miscarriage.[282]
See also
Notes
- ^ For a list of definitions as stated by obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) textbooks, dictionaries, and other sources, see Definitions of abortion. Definitions of abortion vary from source to source, and language used to define abortion often reflects societal and political opinions, not only scientific knowledge.[1]
- ^ In the United States, the first laws related to abortion beginning in the 1820s were made to protect women from real or perceived risks, and those more restrictive penalized only the provider. By 1859, abortion was not a crime in 21 out of 33 states, and was prohibited only post-quickening, while penalties for pre-quickening abortions were lower. This changed starting in the 1860s under the influence of anti-immigrant and anti-Catholic sentiment.[187]
- ^ By 1930, medical procedures in the United States had improved for both childbirth and abortion but not equally, and induced abortion in the first trimester had become safer than childbirth. In 1973, Roe v. Wade acknowledged that abortion in the first trimester was safer than childbirth. For sources, see:
- "The 1970s". Time Communication 1940–1989: Retrospective. Time. 1989.
Blackmun was also swayed by the fact that most abortion prohibitions were enacted in the 19th century when the procedure was more dangerous than now.
- Will GF (1990). Suddenly: The American Idea Abroad and at Home, 1986–1990. Free Press. p. 312. ISBN 0-02-934435-2.
- Lewis J, Shimabukuro JO (28 January 2001). "Abortion Law Development: A Brief Overview". Congressional Research Service. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- Schultz DA (2002). Encyclopedia of American Law. Infobase Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 0-8160-4329-9. Archived from the original on 9 December 2015.
- Lahey JN (24 September 2009). "Birthing a Nation: Fertility Control Access and the 19th Century Demographic Transition" (PDF; preliminary version). Colloquium. Pomona College. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 January 2012.
- "The 1970s". Time Communication 1940–1989: Retrospective. Time. 1989.
- ^ For sources, see:
- James Donner, Women in Trouble: The Truth about Abortion in America, Monarch Books, 1959.
- Ann Oakley, The Captured Womb, Basil Blackwell, 1984, p. 91.
- Rickie Solinger, The Abortionist: A Woman Against the Law, The Free Press, 1994, pp. xi, 5, 16–17, 157–175.
- Leslie J. Reagan, When Abortion Was a Crime: Women, Medicine, and Law in the United States, 1867–1973, University of California Press, 1997.
- Max Evans, Madam Millie: Bordellos from Silver City to Ketchikan, University of New Mexico Press, 2002, pp. 209–218, 230, 267–286, 305.
References
- ^ Kulczycki A. "Abortion". Oxford Bibliographies. Archived from the original on 13 April 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- ^ The Johns Hopkins Manual of Gynecology and Obstetrics (4 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2012. pp. 438–439. ISBN 978-1-4511-4801-5. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^ "How many people are affected by or at risk for pregnancy loss or miscarriage?". NICHD. 15 July 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "abortion". Oxford English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ a b "Abortion (noun)". Oxford Living Dictionaries. Archived from the original on 28 May 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
[mass noun] The deliberate termination of a human pregnancy, most often performed during the first 28 weeks of pregnancy
- ^ a b c d e f g h Bankole A, Singh S, Haas T (September 1998). "Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries". International Family Planning Perspectives. 24 (3): 117–127, 152. doi:10.2307/3038208. JSTOR 3038208. Archived from the original on 17 January 2006.
Worldwide, the most commonly reported reason women cite for having an abortion is to postpone or stop childbearing. The second most common reason—socioeconomic concerns—includes disruption of education or employment; lack of support from the father; desire to provide schooling for existing children; and poverty, unemployment or inability to afford additional children. In addition, relationship problems with a husband or partner and a woman's perception that she is too young constitute other important categories of reasons. Women's characteristics are associated with their reasons for having an abortion: With few exceptions, older women and married women are the most likely to identify limiting childbearing as their main reason for abortion. - Conclusions - Reasons women give for why they seek abortion are often far more complex than simply not intending to become pregnant; the decision to have an abortion is usually motivated by more than one factor.
- ^ a b Chae S, Desai S, Crowell M, Sedgh G (1 October 2017). "Reasons why women have induced abortions: a synthesis of findings from 14 countries". Contraception. 96 (4): 233–241. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2017.06.014. PMC 5957082. PMID 28694165.
In most countries, the most frequently cited reasons for having an abortion were socioeconomic concerns or limiting childbearing. With some exceptions, little variation existed in the reasons given by women's sociodemographic characteristics. Data from three countries where multiple reasons could be reported in the survey showed that women often have more than one reason for having an abortion.
- ^ a b c d e f "The limitations of U.S. statistics on abortion". Issues in Brief. New York: The Guttmacher Institute. 1997. Archived from the original on 4 April 2012.
- ^ a b Stotland NL (July 2019). "Update on Reproductive Rights and Women's Mental Health". The Medical Clinics of North America. 103 (4): 751–766. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2019.02.006. PMID 31078205. S2CID 153307516.
- ^ a b c d e f Grimes DA, Benson J, Singh S, Romero M, Ganatra B, Okonofua FE, Shah IH (25 November 2006). "Unsafe abortion: the preventable pandemic". Lancet. 368 (9550): 1908–1919. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69481-6. PMID 17126724. S2CID 6188636. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ a b c Raymond EG, Grossman D, Weaver MA, Toti S, Winikoff B (November 2014). "Mortality of induced abortion, other outpatient surgical procedures and common activities in the United States". Contraception. 90 (5): 476–479. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.07.012. PMID 25152259.
Results: The abortion-related mortality rate in 2000–2009 in the United States was 0.7 per 100,000 abortions. Studies in approximately the same years found mortality rates of 0.8-1.7 deaths per 100,000 plastic surgery procedures, 0-1.7 deaths per 100,000 dental procedures, 0.6-1.2 deaths per 100,000 marathons run and at least 4 deaths among 100,000 cyclists in a large annual bicycling event. The traffic fatality rate per 758 vehicle miles traveled by passenger cars in the United States in 2007-2011 was about equal to the abortion-related mortality rate. Conclusions: The safety of induced abortion as practiced in the United States for the past decade met or exceeded expectations for outpatient surgical procedures and compared favorably to that of two common nonmedical voluntary activities.
- ^ "Preventing unsafe abortion". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 23 August 2019. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- ^ "Self-management Recommendation 50: Self-management of medical abortion in whole or in part at gestational ages < 12 weeks (3.6.2) - Abortion care guideline". WHO Department of Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research. 19 November 2021. Archived from the original on 29 June 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2023.
- ^ Moseson H, Jayaweera R, Raifman S, Keefe-Oates B, Filippa S, Motana R, et al. (October 2020). "Self-managed medication abortion outcomes: results from a prospective pilot study". Reproductive Health. 17 (1): 164. doi:10.1186/s12978-020-01016-4. ISSN 1742-4755. PMC 7588945. PMID 33109230.
- ^ Moseson H, Jayaweera R, Egwuatu I, Grosso B, Kristianingrum IA, Nmezi S, et al. (January 2022). "Effectiveness of self-managed medication abortion with accompaniment support in Argentina and Nigeria (SAFE): a prospective, observational cohort study and non-inferiority analysis with historical controls". The Lancet. Global Health. 10 (1): e105–e113. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00461-7. PMC 9359894. PMID 34801131.
- ^ Faúndes A, Shah IH (October 2015). "Evidence supporting broader access to safe legal abortion". International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics. World Report on Women's Health 2015: The unfinished agenda of women's reproductive health. 131 (Suppl 1): S56–S59. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2015.03.018. PMID 26433508.
A strong body of accumulated evidence shows that the simple means to drastically reduce unsafe abortion-related maternal deaths and morbidity is to make abortion legal and institutional termination of pregnancy broadly accessible. [...] [C]riminalization of abortion only increases mortality and morbidity without decreasing the incidence of induced abortion, and that decriminalization rapidly reduces abortion-related mortality and does not increase abortion rates.
- ^ Latt SM, Milner A, Kavanagh A (January 2019). "Abortion laws reform may reduce maternal mortality: an ecological study in 162 countries". BMC Women's Health. 19 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/s12905-018-0705-y. PMC 6321671. PMID 30611257.
- ^ a b c d Zhang J, Zhou K, Shan D, Luo X (May 2022). "Medical methods for first trimester abortion". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2022 (5): CD002855. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002855.pub5. PMC 9128719. PMID 35608608.
- ^ a b c Kapp N, Whyte P, Tang J, Jackson E, Brahmi D (September 2013). "A review of evidence for safe abortion care". Contraception. 88 (3): 350–363. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.10.027. PMID 23261233.
- ^ "Abortion – Women's Health Issues". Merck Manuals Consumer Version. Archived from the original on 13 July 2018. Retrieved 12 July 2018.
- ^ a b c Lohr PA, Fjerstad M, Desilva U, Lyus R (2014). "Abortion". BMJ. 348: f7553. doi:10.1136/bmj.f7553. S2CID 220108457.
- ^ "Induced Abortion Worldwide | Guttmacher Institute". Guttmacher.org. 1 March 2018. Archived from the original on 1 March 2018. Retrieved 23 June 2023.
- ^ "Abortion". www.who.int. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD, Joffe C (2009). "1. Abortion and medicine: A sociopolitical history" (PDF). Management of Unintended and Abnormal Pregnancy (1st ed.). Oxford: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-1293-5. OL 15895486W. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2012.
- ^ "Abortion". www.who.int. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ "Worldwide, an estimated 25 million unsafe abortions occur each year". World Health Organization. 28 September 2017. Archived from the original on 29 September 2017. Retrieved 29 September 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Sedgh G, Singh S, Shah IH, Ahman E, Henshaw SK, Bankole A (February 2012). "Induced abortion: incidence and trends worldwide from 1995 to 2008" (PDF). Lancet. 379 (9816): 625–632. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61786-8. PMID 22264435. S2CID 27378192. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2012.
Because few of the abortion estimates were based on studies of random samples of women, and because we did not use a model-based approach to estimate abortion incidence, it was not possible to compute confidence intervals based on standard errors around the estimates. Drawing on the information available on the accuracy and precision of abortion estimates that were used to develop the subregional, regional, and worldwide rates, we computed intervals of certainty around these rates (webappendix). We computed wider intervals for unsafe abortion rates than for safe abortion rates. The basis for these intervals included published and unpublished assessments of abortion reporting in countries with liberal laws, recently published studies of national unsafe abortion, and high and low estimates of the numbers of unsafe abortion developed by WHO.
- ^ Sedgh G, Henshaw SK, Singh S, Bankole A, Drescher J (September 2007). "Legal abortion worldwide: incidence and recent trends". International Family Planning Perspectives. 33 (3): 106–116. doi:10.1363/3310607. PMID 17938093. Archived from the original on 19 August 2009.
- ^ "Induced Abortion Worldwide". Guttmacher Institute. 1 March 2018. Archived from the original on 23 February 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2020.
Of the world's 1.64 billion women of reproductive age, 6% live where abortion is banned outright, and 37% live where it is allowed without restriction as to reason. Most women live in countries with laws that fall between these two extremes.
- ^ a b c Culwell KR, Vekemans M, de Silva U, Hurwitz M, Crane BB (July 2010). "Critical gaps in universal access to reproductive health: contraception and prevention of unsafe abortion". International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics. 110 (Suppl): S13–S16. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.04.003. PMID 20451196. S2CID 40586023.
- ^ "Unintended Pregnancy and Abortion Worldwide". Guttmacher Institute. 28 May 2020. Archived from the original on 23 February 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2021.
Abortion is sought and needed even in settings where it is restricted—that is, in countries where it is prohibited altogether or is allowed only to save the women's life or to preserve her physical or mental health. Unintended pregnancy rates are highest in countries that restrict abortion access and lowest in countries where abortion is broadly legal. As a result, abortion rates are similar in countries where abortion is restricted and those where the procedure is broadly legal (i.e., where it is available on request or on socioeconomic grounds).
- ^ Staff FP (24 June 2022). "Roe Abolition Makes U.S. a Global Outlier". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 24 June 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2023.
- ^ Paola A, Walker R, LaCivita L (2010). Nixon F (ed.). Medical ethics and humanities. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. p. 249. ISBN 978-0-7637-6063-2. OL 13764930W. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017.
- ^ Johnstone MJ (2009). "Bioethics a nursing perspective". Confederation of Australian Critical Care Nurses Journal. 3 (4) (5th ed.). Sydney, NSW: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier: 24–30. ISBN 978-0-7295-7873-8. PMID 2129925. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017.
Although abortion has been legal in many countries for several decades now, its moral permissibilities continues to be the subject of heated public debate.
- ^ Driscoll M (18 October 2013). "What do 55 million people have in common?". Fox News. Archived from the original on 31 August 2014. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ Hansen D (18 March 2014). "Abortion: Murder, or Medical Procedure?". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ Sifris RN (2013). Reproductive freedom, torture and international human rights: challenging the masculinisation of torture. Hoboken, NJ: Taylor & Francis. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-135-11522-7. OCLC 869373168. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015.
- ^ Åhman E (2007). Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003 (5th ed.). World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-159612-1. Archived from the original on 7 April 2018. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ Fabiola Sanchez, Megan Janetsky, Mexico decriminalizes abortion, extending Latin American trend of widening access to procedure Archived 6 September 2023 at the Wayback Machine, Associated Press (AP), September 6, 2023
- ^ a b c Boland R, Katzive L (September 2008). "Developments in laws on induced abortion: 1998-2007". International Family Planning Perspectives. 34 (3): 110–120. doi:10.1363/3411008. PMID 18957353. Archived from the original on 7 October 2011.
- ^ Cheng L (1 November 2008). "Surgical versus medical methods for second-trimester induced abortion". The WHO Reproductive Health Library. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 1 August 2010. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ^ Stubblefield PG (2002). "10. Family Planning". In Berek JS (ed.). Novak's Gynecology (13 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-3262-8.
- ^ Bartlett LA, Berg CJ, Shulman HB, Zane SB, Green CA, Whitehead S, Atrash HK (2004). "Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 103 (4): 729–737. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60. PMID 15051566. S2CID 42597014.
- ^ Roche NE (28 September 2004). "Therapeutic Abortion". eMedicine. Archived from the original on 14 December 2004. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- ^ a b c d Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, Halvorson LM, Hoffman BL, Bradshaw KD, Cunningham FG, eds. (2008). "6. First-Trimester Abortion". Williams Gynecology (1 ed.). McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 978-0-07-147257-9.
- ^ Janiak E, Goldberg AB (1 February 2016). "Eliminating the phrase 'elective abortion': why language matters". Contraception. 93 (2): 89–92. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2015.10.008. ISSN 0010-7824. PMID 26480889. Archived from the original on 24 January 2023. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ Finer LB, Frohwirth LF, Dauphinee LA, Singh S, Moore AM (September 2005). "Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantitative and qualitative perspectives" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 37 (3): 110–118. doi:10.1111/j.1931-2393.2005.tb00045.x. PMID 16150658. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 January 2006.
- ^ Churchill Livingstone medical dictionary. Edinburgh New York: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. 2008. ISBN 978-0-443-10412-1.
The preferred term for unintentional loss of the product of conception prior to 24 weeks' gestation is miscarriage.
- ^ AnnasGJ, Elias S (2007). "51. Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetric Practice". In Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL (eds.). Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. p. 669. ISBN 978-0-443-06930-7.
A preterm birth is defined as one that occurs before the completion of 37 menstrual weeks of gestation, regardless of birth weight.
- ^ Stillbirth. Concise Medical Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 2010. ISBN 978-0-19-955714-1. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015.
birth of a fetus that shows no evidence of life (heartbeat, respiration, or independent movement) at any time later than 24 weeks after conception
- ^ "7 FAM 1470 Documenting Stillbirth (Fetal Death)". United States Department of State. 18 February 2011. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2016.
- ^ Annas GJ, Elias S (2007). "24. Pregnancy loss". In Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL (eds.). Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06930-7.
- ^ Jarvis GE (7 June 2017). "Early embryo mortality in natural human reproduction: What the data say [version 2; peer review: 2 approved, 1 approved with reservations]". F1000Research. 5: 2765. doi:10.12688/f1000research.8937.2. PMC 5443340. PMID 28580126.
- ^ Jarvis GE (26 August 2016). "Estimating limits for natural human embryo mortality [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]". F1000Research. 5: 2083. doi:10.12688/f1000research.9479.1. PMC 5142718. PMID 28003878.
- ^ Katz VL (2007). "16. Spontaneous and Recurrent Abortion – Etiology, Diagnosis, Treatment". In Katz VL, Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM (eds.). Katz: Comprehensive Gynecology (5 th ed.). Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-02951-3.
- ^ Stovall TG (2002). "17. Early Pregnancy Loss and Ectopic Pregnancy". In Berek JS (ed.). Novak's Gynecology (13 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-3262-8.
- ^ Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, Sheffield JS, eds. (2014). Williams Obstetrics (24th ed.). McGraw Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-07-179893-8.
- ^ a b Stöppler MS. Shiel Jr WC (ed.). "Miscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion)". MedicineNet.com. WebMD. Archived from the original on 29 August 2004. Retrieved 7 April 2009.
- ^ a b Jauniaux E, Kaminopetros P, El-Rafaey H (1999). "Early pregnancy loss". In Whittle MJ, Rodeck CH (eds.). Fetal medicine: basic science and clinical practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. p. 837. ISBN 978-0-443-05357-3. OCLC 42792567.
- ^ "Fetal Homicide Laws". National Conference of State Legislatures. Archived from the original on 11 September 2012. Retrieved 7 April 2009.
- ^ a b Creinin MD, Gemzell-Danielsson K (2009). "Medical abortion in early pregnancy". In Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD (eds.). Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 111–134. ISBN 978-1-4051-7696-5.
- ^ a b Kapp N, von Hertzen H (2009). "Medical methods to induce abortion in the second trimester". In Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD (eds.). Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 178–192. ISBN 978-1-4051-7696-5.
- ^ a b c Chen MJ, Creinin MD (July 2015). "Mifepristone With Buccal Misoprostol for Medical Abortion: A Systematic Review". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 126 (1): 12–21. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000897. PMID 26241251. S2CID 20800109. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- ^ a b Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (8 February 2019). "Mifeprex (mifepristone) Information". FDA. Archived from the original on 23 April 2019. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ^ Wildschut H, Both MI, Medema S, Thomee E, Wildhagen MF, Kapp N (January 2011). "Medical methods for mid-trimester termination of pregnancy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2011 (1): CD005216. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005216.pub2. PMC 8557267. PMID 21249669.
- ^ a b WHO Department of Reproductive Health and Research (2006). Frequently asked clinical questions about medical abortion (PDF). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 92-4-159484-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 December 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ Fjerstad M, Sivin I, Lichtenberg ES, Trussell J, Cleland K, Cullins V (September 2009). "Effectiveness of medical abortion with mifepristone and buccal misoprostol through 59 gestational days". Contraception. 80 (3): 282–286. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2009.03.010. PMC 3766037. PMID 19698822. The regimen (200 mg of mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by 800 mcg of vaginal misoprostol) previously used by Planned Parenthood clinics in the United States from 2001 to March 2006 was 98.5% effective through 63 days gestation—with an ongoing pregnancy rate of about 0.5%, and an additional 1% of women having uterine evacuation for various reasons, including problematic bleeding, persistent gestational sac, clinician judgment or a woman's request. The regimen (200 mg of mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by 800 mcg of buccal misoprostol) currently used by Planned Parenthood clinics in the United States since April 2006 is 98% effective through 59 days gestation.
- ^ Holmquist S, Gilliam M (2008). "Induced abortion". In Gibbs RS, Karlan BY, Haney AF, Nygaard I (eds.). Danforth's obstetrics and gynecology (10th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 586–603. ISBN 978-0-7817-6937-2.
- ^ "Table 5: Legal abortions: gestation weeks by purchaser and method of abortion, residents of England and Wales, numbers, percentages, 2022". Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2022 (Report). Office for Health Improvement and Disparities. 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2024.
- ^ Vilain A, Mouquet MC (22 June 2011). "Voluntary terminations of pregnancies in 2008 and 2009" (PDF). Paris: DREES, Ministry of Health, France. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ "Abortions in Switzerland 2010". Neuchâtel: Office of Federal Statistics, Switzerland. 5 July 2011. Archived from the original on 3 October 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ Jones RK, Witwer E, Jerman J (2019). Abortion Incidence and Service Availability in the United States, 2017 (Report). Guttmacher Institute. doi:10.1363/2019.30760. PMC 5487028.
- ^ Gissler M, Heino A (21 February 2011). "Induced abortions in the Nordic countries 2009" (PDF). Helsinki: National Institute for Health and Welfare, Finland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ a b Meckstroth K, Paul M (2009). "First-trimester aspiration abortion". In Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD (eds.). Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 135–156. ISBN 978-1-4051-7696-5.
- ^ a b c d Gambir K, Kim C, Necastro KA, Ganatra B, Ngo TD (March 2020). "Self-administered versus provider-administered medical abortion". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (3): CD013181. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013181.pub2. PMC 7062143. PMID 32150279.
- ^ Healthwise (2004). "Manual and vacuum aspiration for abortion". WebMD. Archived from the original on 11 February 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2008.
- ^ World Health Organization (2017). "Dilatation and curettage". Managing Complications in Pregnancy and Childbirth: A Guide for Midwives and Doctors. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-154587-7. OCLC 181845530. Archived from the original on 19 May 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- ^ Hammond C, Chasen S (2009). Dilation and evacuation. In Paul M, Lichtenberg ES Borgatta L Grimes DA Stubblefield P Creinin (eds)Management of unintended and abnormal pregnancy: comprehensive abortion care. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 178–192. ISBN 978-1-4051-7696-5.
- ^ "ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 135: Second-trimester abortion". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 121 (6): 1394–1406. June 2013. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000431056.79334.cc. PMID 23812485. S2CID 205384119.
- ^ a b Templeton A, Grimes DA (December 2011). "Clinical practice. A request for abortion". The New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (23): 2198–2204. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103639. PMID 22150038.
- ^ Allen RH, Singh R (June 2018). "Society of Family Planning clinical guidelines pain control in surgical abortion part 1 - local anesthesia and minimal sedation". Contraception. 97 (6): 471–477. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2018.01.014. PMID 29407363. S2CID 3777869. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ Cansino C, Denny C, Carlisle AS, Stubblefield P (December 2021). "Society of Family Planning clinical recommendations: Pain control in surgical abortion part 2 - Moderate sedation, deep sedation, and general anesthesia". Contraception. 104 (6): 583–592. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2021.08.007. PMID 34425082. S2CID 237279946. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ Borgatta L (December 2014). "Labor Induction Termination of Pregnancy". Global Library of Women's Medicine. GLOWM.10444. doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10444. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ a b c Borgatta L, Kapp N (July 2011). "Clinical guidelines. Labor induction abortion in the second trimester". Contraception. 84 (1): 4–18. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2011.02.005. PMID 21664506. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
10. What is the effect of feticide on labor induction abortion outcome? Deliberately causing demise of the fetus before labor induction abortion is performed primarily to avoid transient fetal survival after expulsion; this approach may be for the comfort of both the woman and the staff, to avoid futile resuscitation efforts. Some providers allege that feticide also facilitates delivery, although little data support this claim. Transient fetal survival is very unlikely after intraamniotic installation of saline or urea, which are directly feticidal. Transient survival with misoprostol for labor induction abortion at greater than 18 weeks ranges from 0% to 50% and has been observed in up to 13% of abortions performed with high-dose oxytocin. Factors associated with a higher likelihood of transient fetal survival with labor induction abortion include increasing gestational age, decreasing abortion interval and the use of nonfeticidal inductive agents such as the PGE1 analogues.
- ^ 2015 Clinical Policy Guidelines (PDF). National Abortion Federation. 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 August 2015. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
Policy Statement: Medical induction abortion is a safe and effective method for termination of pregnancies beyond the first trimester when performed by trained clinicians in medical offices, freestanding clinics, ambulatory surgery centers, and hospitals. Feticidal agents may be particularly important when issues of viability arise.
- ^ a b Riddle JM (1997). Eve's herbs: a history of contraception and abortion in the West. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-27024-4. OCLC 36126503.
- ^ Sullivan JB, Rumack BH, Thomas H, Peterson RG, Bryson P (December 1979). "Pennyroyal oil poisoning and hepatotoxicity". JAMA. 242 (26): 2873–2874. doi:10.1001/jama.1979.03300260043027. PMID 513258. S2CID 26198529.
- ^ Ciganda C, Laborde A (2003). "Herbal infusions used for induced abortion". Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology. 41 (3): 235–239. doi:10.1081/CLT-120021104. PMID 12807304. S2CID 44851492.
- ^ Smith JP (1998). "Risky choices: the dangers of teens using self-induced abortion attempts". Journal of Pediatric Health Care. 12 (3): 147–151. doi:10.1016/S0891-5245(98)90245-0. PMID 9652283.
- ^ a b c d Potts M, Graff M, Taing J (October 2007). "Thousand-year-old depictions of massage abortion". The Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care. 33 (4): 233–234. doi:10.1783/147118907782101904. PMID 17925100.
- ^ Thapa SR, Rimal D, Preston J (September 2006). "Self induction of abortion with instrumentation". Australian Family Physician. 35 (9): 697–698. PMID 16969439. Archived from the original on 8 January 2009.
- ^ "The Prevention and Management of Unsafe Abortion" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 1992. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 May 2010. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ Grimes DA, Creinin MD (April 2004). "Induced abortion: an overview for internists". Annals of Internal Medicine. 140 (8): 620–626. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.694.3531. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-140-8-200404200-00009. PMID 15096333.
- ^ Raymond EG, Grimes DA (February 2012). "The comparative safety of legal induced abortion and childbirth in the United States". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 119 (2 Pt 1): 215–219. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823fe923. PMID 22270271. S2CID 25534071.
Conclusion: Legal induced abortion is markedly safer than childbirth. The risk of death associated with childbirth is approximately 14 times higher than that with abortion. Similarly, the overall morbidity associated with childbirth exceeds that with abortion.
- ^ Petersen EE, Davis NL, Goodman D, Cox S, Mayes N, Johnston E, et al. (May 2019). "Vital Signs: Pregnancy-Related Deaths, United States, 2011–2015, and Strategies for Prevention, 13 States, 2013-2017". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 68 (18): 423–429. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6818e1. PMC 6542194. PMID 31071074.
- ^ National Academies of Sciences Engineering, Health Medicine Division, Board on Health Care Services, Board on Population Health Public Health Practice, Committee on Reproductive Health Services: Assessing the Safety Quality of Abortion Care in the U.S (2018). Read "The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the United States" at NAP.edu. doi:10.17226/24950. ISBN 978-0-309-46818-3. PMID 29897702. Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- ^ Kortsmit K (2022). "Abortion Surveillance — United States, 2020". MMWR. Surveillance Summaries. 71 (10): 1–27. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss7110a1. ISSN 1546-0738. PMC 9707346. PMID 36417304. Archived from the original on 15 November 2023. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
The national case-fatality rate for legal induced abortion for 2013–2019 was 0.43 deaths related to legal induced abortions per 100,000 reported legal abortions. This case-fatality rate was lower than the rates for the previous 5-year periods.
- ^ Donnelly L (26 February 2011). "Abortion is Safer than Having a Baby, Doctors Say". The Telegraph.
- ^ Dixon-Mueller R, Germain A (January 2007). "Fertility regulation and reproductive health in the Millennium Development Goals: the search for a perfect indicator". American Journal of Public Health. 97 (1): 45–51. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2005.068056. PMC 1716248. PMID 16571693.
- ^ "Abortion in Indonesia" (PDF). Guttmacher Institute. 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 June 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ Ralph LJ, Schwarz EB, Grossman D, Foster DG (August 2019). "Self-reported Physical Health of Women Who Did and Did Not Terminate Pregnancy After Seeking Abortion Services: A Cohort Study". Annals of Internal Medicine. 171 (4): 238–247. doi:10.7326/M18-1666. PMID 31181576. S2CID 184482546.
- ^ Raymond EG, Grimes DA (February 2012). "The comparative safety of legal induced abortion and childbirth in the United States". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 119 (2 Pt 1): 215–219. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823fe923. PMID 22270271. S2CID 25534071.
- ^ Abbas D, Chong E, Raymond EG (September 2015). "Outpatient medical abortion is safe and effective through 70 days gestation". Contraception. 92 (3): 197–199. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2015.06.018. PMID 26118638.
- ^ Grossman D (3 September 2004). "Medical methods for first trimester abortion: RHL commentary". Reproductive Health Library. Geneva: World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 28 October 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ Chien P, Thomson M (15 December 2006). "Medical versus surgical methods for first trimester termination of pregnancy: RHL commentary". Reproductive Health Library. Geneva: World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 May 2010. Retrieved 1 June 2010.
- ^ Westfall JM, Sophocles A, Burggraf H, Ellis S (1998). "Manual vacuum aspiration for first-trimester abortion". Archives of Family Medicine. 7 (6): 559–562. doi:10.1001/archfami.7.6.559. PMID 9821831. Archived from the original on 5 April 2005.
- ^ Dempsey A (December 2012). "Serious infection associated with induced abortion in the United States". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. 55 (4): 888–892. doi:10.1097/GRF.0b013e31826fd8f8. PMID 23090457.
- ^ White K, Carroll E, Grossman D (November 2015). "Complications from first-trimester aspiration abortion: a systematic review of the literature". Contraception. 92 (5): 422–438. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2015.07.013. PMID 26238336.
- ^ "ACOG practice bulletin No. 104: antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 113 (5): 1180–1189. May 2009. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d011. PMID 19384149.
- ^ Sawaya GF, Grady D, Kerlikowske K, Grimes DA (May 1996). "Antibiotics at the time of induced abortion: the case for universal prophylaxis based on a meta-analysis". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 87 (5 Pt 2): 884–890. PMID 8677129.
- ^ Achilles SL, Reeves MF (April 2011). "Prevention of infection after induced abortion: release date October 2010: SFP guideline 20102". Contraception. 83 (4): 295–309. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2010.11.006. PMID 21397086.
- ^ Barnard S, Kim C, Park MH, Ngo TD (July 2015). "Doctors or mid-level providers for abortion" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (7): CD011242. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011242.pub2. PMC 9188302. PMID 26214844. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Lerma K, Shaw KA (December 2017). "Update on second trimester medical abortion". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 29 (6): 413–418. doi:10.1097/GCO.0000000000000409. PMID 28922193. S2CID 12459747.
Second trimester surgical abortion is well tolerated and increasingly expeditious
- ^ Steinauer J, Jackson A, Grossman D, et al. (Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology) (June 2013). "Second-trimester abortion. Practice Bulletin No. 135". American College of Obstetrics & Gynecology - Practice Bulletins. Archived from the original on 24 December 2019. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
The mortality rate associated with abortion is low (0.6 per 100,000 legal, induced abortions), and the risk of death associated with childbirth is approximately 14 times higher than that with abortion. Abortion-related mortality increases with each week of gestation, with a rate of 0.1 per 100,000 procedures at 8 weeks of gestation or less, and 8.9 per 100,000 procedures at 21 weeks of gestation or greater.
- ^ Bartlett LA, Berg CJ, Shulman HB, Zane SB, Green CA, Whitehead S, Atrash HK (April 2004). "Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 103 (4): 729–737. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60. PMID 15051566. S2CID 42597014.
The risk factor that continues to be most strongly associated with mortality from legal abortion is gestational age at the time of the abortion
- ^ Saccone G, Perriera L, Berghella V (May 2016). "Prior uterine evacuation of pregnancy as independent risk factor for preterm birth: a systematic review and metaanalysis" (PDF). American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 214 (5): 572–591. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.12.044. PMID 26743506. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
Prior surgical uterine evacuation for either I-TOP[induced termination of pregnancy] or SAB[spontaneous abortion, - also known as miscarriage] is an independent risk factor for PTB[pre-term birth]. These data warrant caution in the use of surgical uterine evacuation and should encourage safer surgical techniques as well as medical methods.
- ^ Averbach SH, Seidman D, Steinauer J, Darney P (January 2017). "Re: Prior uterine evacuation of pregnancy as independent risk factor for preterm birth: a systematic review and metaanalysis". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 216 (1): 87. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.08.038. PMID 27596618. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ a b c d Horvath S, Schreiber CA (September 2017). "Unintended Pregnancy, Induced Abortion, and Mental Health". Current Psychiatry Reports. 19 (11): 77. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0832-4. PMID 28905259. S2CID 4769393.
- ^ a b "APA Task Force Finds Single Abortion Not a Threat to Women's Mental Health" (Press release). American Psychological Association. 12 August 2008. Archived from the original on 6 September 2011. Retrieved 7 September 2011.
- ^ "Report of the APA Task Force on Mental Health and Abortion" (PDF). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. 13 August 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 June 2010.
- ^ Coleman PK (September 2011). "Abortion and mental health: quantitative synthesis and analysis of research published 1995-2009". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 199 (3): 180–186. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.110.077230. PMID 21881096.
- ^ "Mental Health and Abortion". American Psychological Association. 2008. Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ Steinberg JR (2011). "Later abortions and mental health: psychological experiences of women having later abortions--a critical review of research". Women's Health Issues. 21 (3 Suppl): S44–S48. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2011.02.002. PMID 21530839.
- ^ Kelly K (February 2014). "The spread of 'Post Abortion Syndrome' as social diagnosis". Social Science & Medicine. 102: 18–25. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.11.030. PMID 24565137.
- ^ Rocca CH, Samari G, Foster DG, Gould H, Kimport K (March 2020). "Emotions and decision rightness over five years following an abortion: An examination of decision difficulty and abortion stigma". Social Science & Medicine. 248: 112704. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112704. PMID 31941577.
We found no evidence of emerging negative emotions or abortion decision regret; both positive and negative emotions declined over the first two years and plateaued thereafter, and decision rightness remained high and steady (predicted percent: 97.5% at baseline, 99.0% at five years). At five years postabortion, relief remained the most commonly felt emotion among all women (predicted mean on 0-4 scale: 1.0; 0.6 for sadness and guilt; 0.4 for regret, anger and happiness). Despite converging levels of emotions by decision difficulty and stigma level over time, these two factors remained most important for predicting negative emotions and decision non-rightness years later.
- ^ a b Jasen P (October 2005). "Breast cancer and the politics of abortion in the United States". Medical History. 49 (4): 423–444. doi:10.1017/S0025727300009145. PMC 1251638. PMID 16562329.
- ^ Schneider AP, Zainer CM, Kubat CK, Mullen NK, Windisch AK (August 2014). "The breast cancer epidemic: 10 facts". The Linacre Quarterly. 81 (3). Catholic Medical Association: 244–277. doi:10.1179/2050854914Y.0000000027. PMC 4135458. PMID 25249706.
an association between [induced abortion] and breast cancer has been found by numerous Western and non-Western researchers from around the world. This is especially true in more recent reports that allow for a sufficient breast cancer latency period since an adoption of a Western life style in sexual and reproductive behavior.
- ^ Position statements of major medical bodies on abortion and breast cancer include:
- World Health Organization: "Induced abortion does not increase breast cancer risk (Fact sheet N°240)". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 13 February 2011. Retrieved 6 January 2011.
- National Cancer Institute: "Abortion, Miscarriage, and Breast Cancer Risk". National Cancer Institute. 20 February 2003. Archived from the original on 21 December 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- American Cancer Society: "Is Abortion Linked to Breast Cancer?". American Cancer Society. 23 September 2010. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 20 June 2011.
At this time, the scientific evidence does not support the notion that abortion of any kind raises the risk of breast cancer.
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists: "The Care of Women Requesting Induced Abortion" (PDF). Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 29 June 2008.
Induced abortion is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk.
- American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: "ACOG Finds No Link Between Abortion and Breast Cancer Risk". American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 31 July 2003. Archived from the original on 2 January 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- ^ Gordon L (2002). The Moral Property of Women. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-02764-7.
- ^ Solinger R (1998). "Introduction". In Solinger R (ed.). Abortion Wars: A Half Century of Struggle, 1950–2000. University of California Press. pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-0-520-20952-7.
- ^ Bates JE, Zawadzki ES (1964). Criminal Abortion: A Study in Medical Sociology. Charles C. Thomas. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-398-00109-4. OCLC 299149.
In my practice I average three operations a day. By working a six day week, I complete approximately eighteen operations in this time. This amounts to seventy-two operations a month. In my sixteen years of specializing, I have successfully performed about 13,844 abortions.
This was without the loss of the life of a single one of my patients. I feel those figures are something of which to be proud. I feel—I'm sure—that the work I have been engaged in these past years has been a contribution to Society and has helped to straighten out the messed up lives of many people. - ^ Keller A (1981). Scandalous Lady: The Life and Times of Madame Restell. Atheneum. ISBN 978-0-689-11213-3.
- ^ Taussig FJ (1936). Abortion Spontaneous and Induced: Medical and Social Aspects. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby. p. 223. OCLC 1041029321.
- ^ Okonofua F (November 2006). "Abortion and maternal mortality in the developing world" (PDF). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 28 (11): 974–979. doi:10.1016/S1701-2163(16)32307-6. PMID 17169222. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012.
- ^ Haddad LB, Nour NM (2009). "Unsafe abortion: unnecessary maternal mortality". Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2 (2): 122–126. PMC 2709326. PMID 19609407.
- ^ a b c Shah I, Ahman E (December 2009). "Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges" (PDF). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 31 (12): 1149–1158. doi:10.1016/s1701-2163(16)34376-6. PMID 20085681. S2CID 35742951. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 July 2011.
- ^ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–2128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30050819. PMC 10790329. PMID 23245604. S2CID 1541253. Archived from the original on 19 May 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Speroff L, Darney PD (2010). A clinical guide for contraception (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 406. ISBN 978-1-60831-610-6.
- ^ World Health Organisation (2011). Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2008 (PDF) (6th ed.). World Health Organisation. p. 27. ISBN 978-92-4-150111-8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 March 2014.
- ^ Berer M (2000). "Making abortions safe: a matter of good public health policy and practice". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 78 (5): 580–592. PMC 2560758. PMID 10859852.
- ^ Jewkes R, Rees H, Dickson K, Brown H, Levin J (March 2005). "The impact of age on the epidemiology of incomplete abortions in South Africa after legislative change". BJOG. 112 (3): 355–359. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00422.x. PMID 15713153. S2CID 41663939.
- ^ Bateman C (December 2007). "Maternal mortalities 90% down as legal TOPs more than triple". South African Medical Journal = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Geneeskunde. 97 (12): 1238–1242. PMID 18264602. Archived from the original on 30 August 2017.
- ^ Conti JA, Brant AR, Shumaker HD, Reeves MF (December 2016). "Update on abortion policy". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 28 (6): 517–521. doi:10.1097/GCO.0000000000000324. PMID 27805969. S2CID 26052790.
- ^ New MJ (15 February 2011). "Analyzing the Effect of Anti-Abortion U.S. State Legislation in the Post-Casey Era". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 11 (1): 28–47. doi:10.1177/1532440010387397. S2CID 53314166.
- ^ Medoff MH, Dennis C (21 July 2014). "Another Critical Review of New's Reanalysis of the Impact of Antiabortion Legislation". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 14 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1177/1532440014535476. S2CID 155464018.
- ^ "Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health" (PDF). Guttmacher Institute. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ Nations MK, Misago C, Fonseca W, Correia LL, Campbell OM (June 1997). "Women's hidden transcripts about abortion in Brazil". Social Science & Medicine. 44 (12): 1833–1845. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(96)00293-6. PMID 9194245.
- ^ Maclean G (2005). "XI. Dimension, Dynamics and Diversity: A 3D Approach to Appraising Global Maternal and Neonatal Health Initiatives". In Balin RE (ed.). Trends in Midwifery Research. Nova Publishers. pp. 299–300. ISBN 978-1-59454-477-4. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015.
- ^ Salter C, Johnson HB, Hengen N (1997). "Care for Postabortion Complications: Saving Women's Lives". Population Reports. 25 (1). Johns Hopkins School of Public Health. Archived from the original on 7 December 2009.
- ^ "Unsafe abortion: Global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2003" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 February 2011. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ^ UNICEF, UNFPA, WHO, World Bank (2010). "Packages of interventions: Family planning, safe abortion care, maternal, newborn and child health". Archived from the original on 9 November 2010. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ "Facts on Induced Abortion Worldwide" (PDF). World Health Organization. January 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Sedgh G, Henshaw S, Singh S, Ahman E, Shah IH (October 2007). "Induced abortion: estimated rates and trends worldwide". Lancet. 370 (9595): 1338–1345. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.454.4197. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61575-X. PMID 17933648. S2CID 28458527.
- ^ a b Rosenthal E (12 October 2007). "Legal or Not, Abortion Rates Compare". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 28 August 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Shah I, Ahman E (December 2009). "Unsafe abortion: global and regional incidence, trends, consequences, and challenges". Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 31 (12): 1149–1158. doi:10.1016/s1701-2163(16)34376-6. PMID 20085681. S2CID 35742951.
However, a woman's chance of having an abortion is similar whether she lives in a developed or a developing region: in 2003 the rates were 26 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15 to 44 in developed areas and 29 per 1,000 in developing areas. The main difference is in safety, with abortion being safe and easily accessible in developed countries and generally restricted and unsafe in most developing countries.
- ^ "Facts on Investing in Family Planning and Maternal and Newborn Health" (PDF). Guttmacher Institute. November 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- ^ Sedgh G, Singh S, Henshaw SK, Bankole A (September 2011). "Legal abortion worldwide in 2008: levels and recent trends". Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 43 (3): 188–198. doi:10.1363/4318811. PMID 21884387. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012.
- ^ "Populație". Romanian Statistical Yearbook (PDF). National Institute of Statistics. 15 May 2011. p. 62. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ^ a b Jones RK, Darroch JE, Henshaw SK (2002). "Contraceptive use among U.S. women having abortions in 2000-2001" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 34 (6): 294–303. doi:10.2307/3097748. JSTOR 3097748. PMID 12558092. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 June 2006.
- ^ Mosher W, Jones J, Abma J (2015). "Nonuse of contraception among women at risk of unintended pregnancy in the United States". Contraception. 92 (2): 170–176. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2015.05.004. ISSN 0010-7824. PMC 6413311. PMID 25998937.
- ^ Dorman E, Perry B, Polis CB, Campo-Engelstein L, Shattuck D, Hamlin A, Aiken A, Trussell J, Sokal D (2018). "Modeling the impact of novel male contraceptive methods on reductions in unintended pregnancies in Nigeria, South Africa, and the United States". Contraception. 97 (1): 62–69. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2017.08.015. ISSN 0010-7824. PMC 5732079. PMID 28887053.
- ^ Cohen SA (2008). "Abortion and Women of Color: The Bigger Picture". Guttmacher Policy Review. 11 (3). Archived from the original on 15 September 2008.
- ^ Pettus EW, Willingham L (1 February 2022). "Minority women most affected if abortion is banned, limited". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ Strauss LT, Gamble SB, Parker WY, Cook DA, Zane SB, Hamdan S (November 2006). "Abortion surveillance--United States, 2003". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries. 55 (11): 1–32. PMID 17119534. Archived from the original on 2 June 2017.
- ^ Finer LB, Henshaw SK (2003). "Abortion incidence and services in the United States in 2000". Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 35 (1): 6–15. doi:10.1363/3500603 (inactive 10 July 2024). PMID 12602752. Archived from the original on 22 January 2016.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of July 2024 (link) - ^ Department of Health (2007). "Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2006". Archived from the original on 6 December 2010. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- ^ Cheng L (1 November 2008). "Surgical versus medical methods for second-trimester induced abortion: RHL commentary". The WHO Reproductive Health Library. Geneva: World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 15 February 2009. Retrieved 10 February 2009. commentary on:
Lohr PA, Hayes JL, Gemzell-Danielsson K (January 2008). "Surgical versus medical methods for second trimester induced abortion". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD006714. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006714.pub2. PMID 18254113. S2CID 205184764. - ^ a b c d e f "Abortions Later in Pregnancy". KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). 5 December 2019. Archived from the original on 10 November 2023. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ Vaughn L (2023). Bioethics: Principles, Issues, and Cases (5th ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-19-760902-6.
- ^ Finer LB, Frohwirth LF, Dauphinee LA, Singh S, Moore AM (September 2005). "Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantitative and qualitative perspectives". Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 37 (3): 110–118. doi:10.1111/j.1931-2393.2005.tb00045.x. PMID 16150658. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012.
- ^ Copelon R (1990). "From Privacy to Autonomy: The Conditions for Reproductive and Sexual Freedom". In Fried MG (ed.). From Abortion to Reproductive Freedom: Transforming a Movement. South End Press. pp. 27–43. ISBN 978-0-89608-387-5. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
The prevalence of economically influenced abortions and the sterilization campaigns against poor, minority, and disabled women show us that autonomy is impossible without eradication of discrimination and poverty. Racism, sexism, and poverty can make the difference between abortions that reflect choice and those reflecting bitter necessity.
- ^ a b Oster E (September 2005). "Explaining Asia's "Missing Women": A New Look at the Data". Population and Development Review. 31 (3): 529–535. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2005.00082.x. Archived from the original on 7 February 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
Households have variously resorted to female infanticide and postnatal withholding of health care; and since the mid-1980s, when technology permitting fairly low-cost determination of the sex of fetuses became available, there has been a shift toward prenatal sex selection by means of induced abortion.
- ^ George J. Annas and Sherman Elias. "Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetrical Practice". Chapter 54 in Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies, 6th edition. Eds. Steven G. Gabbe, et al. 2012 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4377-1935-2
- ^ a b Weisz B, Schiff E, Lishner M (2001). "Cancer in pregnancy: maternal and fetal implications". Human Reproduction Update. 7 (4): 384–393. doi:10.1093/humupd/7.4.384. PMID 11476351.
- ^ Mayr NA, Wen BC, Saw CB (June 1998). "Radiation therapy during pregnancy". Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America. 25 (2): 301–321. doi:10.1016/s0889-8545(05)70006-1. PMID 9629572.
- ^ Fenig E, Mishaeli M, Kalish Y, Lishner M (February 2001). "Pregnancy and radiation". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 27 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1053/ctrv.2000.0193. PMID 11237773.
- ^ Li WW, Yau TN, Leung CW, Pong WM, Chan MY (February 2009). "Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix complicating pregnancy". Hong Kong Medical Journal = Xianggang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 15 (1): 69–72. PMID 19197101.
- ^ Doan 2007, p. 57.
- ^ Mould RF (1996). Mould's Medical Anecdotes. CRC Press. p. 406. ISBN 978-0-85274-119-1.
- ^ Himes NE (1963). Medical History of Contraception. Gamut Press. pp. 109–110.
- ^ Misra P (2006). Domestic Violence Against Women: Legal Control and Judicial Response. Deep & Deep Publications. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-81-7629-896-4. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
References in Atharva Veda show that abortion was known in the Vedic age.
- ^ Schenker JG (June 2008). "The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law)". Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. 25 (6): 271–276. doi:10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6. PMC 2582082. PMID 18551364.
- ^ Rosner F (2001). Biomedical Ethics and Jewish Law. KTAV Publishing House. ISBN 978-0-88125-701-4. Archived from the original on 24 January 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2022 – via Google Books. Reprinted as Rosner F (7 June 2015). "The Beginning of Life in Judaism". My Jewish Learning. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ Milgram G (23 January 2022). "When Does Life Begin? A Jewish View". Reclaiming Judaism. Archived from the original on 3 August 2022. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ "Judaism and Abortion" (PDF). National Council of Jewish Women. May 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ Kestler-D'Amours J (17 June 2022). "Religious freedom: The next battleground for US abortion rights?". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 1 August 2022. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Georgian E (1 July 2022). "The End of Roe in Historical Perspective". Clio and the Contemporary. Archived from the original on 27 July 2022. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ "Religions – Islam: Abortion". BBC. 9 July 2009. Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ^ Dabash R, Farzaneh RF (2008). "Abortion in the Middle East and North Africa" (PDF). Population Research Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 October 2011.
- ^ Miles SH (2005). The Hippocratic Oath and the Ethics of Medicine. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-518820-2.
- ^ Soranus (1991). Soranus' Gynecology. Translated by Temkin O, Eastman NJ, Edelstein L, Guttmacher AF. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. I, 19, 60. ISBN 978-0-8018-4320-4. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 6 October 2015.
- ^ "Scribonius Largus and the Oath of Hippocrates". Encyclopaedia Romana. University of Chicago. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ Carrick P (2001). Medical Ethics in the Ancient World. Georgetown University Press. ISBN 978-0-87840-849-8.
- ^ Meyer HS (17 April 2002). "Ancient Ethics: Medical Ethics in the Ancient World". JAMA. 287 (15). American Medical Association: 2005–2006. doi:10.1001/jama.287.15.2005-JBK0417-3-1. S2CID 240484236.
- ^ Aristotele (1944). Aristotle, Politics. Translated by Rackham H. Harvard University Press. Archived from the original on 22 June 2011. Retrieved 21 June 2011 – via Perseus.
- ^ a b Noonan JT (1986). Contraception: A History of Its Treatment by the Catholic Theologians and Canonists (2nd ed.). Harvard University Press.
- ^ "Didache" (PDF). Legacy Icons. 9 September 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ Joan Cadden, "Western medicine and natural philosophy", in Vern L. Bullough and James A. Brundage, eds., Handbook of Medieval Sexuality, Garland, 1996, pp. 51–80.
- ^ Cyril C. Means Jr., "A historian's view", in Robert E. Hall, ed., Abortion in a Changing World, vol. 1, Columbia University Press, 1970, pp. 16–24.
- ^ John M. Riddle, "Contraception and early abortion in the Middle Ages", in Vern L. Bullough and James A. Brundage, eds., Handbook of Medieval Sexuality, Garland, 1996, pp. 261–277, ISBN 978-0-8153-1287-1.
- ^ Pope Sixtus V (1588). "Effraenatam". Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2021 – via The Embryo Project Encyclopedia.
- ^ Gershon L (13 February 2018). "What a 16th-Century Abortion Ban Revealed". JSTOR Daily. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ "Apostolicae Sedis Moderationi". New Advent. Archived from the original on 16 May 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ "Catechism of the Catholic Church, chapter 2, article 5". Vatican. 1992. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- ^ Masci D (30 May 2020). "Where major religious groups stand on abortion". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ Jerman J, Jones RK, Onda T (10 May 2016). Characteristics of U.S. Abortion Patients in 2014 and Changes Since 2008 (Report). Guttmacher. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ^ "8 key findings about Catholics and abortion". Pew Research Center. 20 October 2020. Archived from the original on 15 May 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ Hull NE, Hoffer W, Hoffer PC, eds. (2004). The abortion rights controversy in America: a legal reader. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. p. 17. ISBN 0-8078-2873-4. OCLC 53993049. Archived from the original on 1 July 2024. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ Reagan LJ (2022) [1997]. When Abortion Was a Crime: Women, Medicine and the Law in the United States, 1867–1973 (1st ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-38741-6.
- ^ Blakemore E (22 May 2022). "The complex early history of abortion in the United States". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 26 July 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
But that view of history is the subject of great dispute. Though interpretations differ, most scholars who have investigated the history of abortion argue that terminating a pregnancy wasn't always illegal—or even controversial.
- ^ a b c Hardin G (December 1978). "Abortion in America. The Origins and Evolution of National Policy, 1800–1900. James C. Mohr". The Quarterly Review of Biology. 53 (4): 499. doi:10.1086/410954.
The long silence had led us to assume that opposition to abortion had existed from time immemorial. Not so: most of the opposition to, and all of the laws against, abortion arose in the 19th century. Historian Mohr amply documents the earlier acceptance of abortion. ... In the 19th century even many of the feminists expressed horror at abortion, urging abstinence instead. Not so in the 20th century. In the 19th century the medical profession was fairly united against abortion; Mohr argues that this arose from the commercial competition between the 'regulars' (men with M.D.'s) and the irregulars (women without M.D.'s). ... A key role in generating prohibition laws was played by the press, ... . By 1900 the abortion-prohibition laws were immune to questioning, as they remained until the 1960's when feminists and a new breed of physicians combined to arouse the public to the injustice of the law. ... the Roe v. Wade decision of the Supreme Court ... essentially returned the practice of abortion to the permissive state ante 1820.
- ^ Acevedo ZP (Summer 1979). "Abortion in early America". Women Health. 4 (2): 159–167. doi:10.1300/J013v04n02_05. PMID 10297561.
This piece describes abortion practices in use from the 1600s to the 19th century among the inhabitants of North America. The abortive techniques of women from different ethnic and racial groups as found in historical literature are revealed. Thus, the point is made that abortion is not simply a 'now issue' that effects select women. Instead, it is demonstrated that it is a widespread practice as solidly rooted in our past as it is in the present.
- ^ a b c Alford S (2003). "Is Self-Abortion a Fundamental Right?". Duke Law Journal. 52 (5): 1011–1029. JSTOR 1373127. PMID 12964572.
- ^ Dine R (8 August 2013). "Scarlet Letters: Getting the History of Abortion and Contraception Right". Center for American Progress. Archived from the original on 28 July 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ Reagan LJ (2 June 2022). "What Alito Gets Wrong About the History of Abortion in America". Politico. Archived from the original on 23 June 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ Root D (23 June 2022). "Alito's Leaked Abortion Opinion Misunderstands Unenumerated Rights". Reason. Archived from the original on 27 July 2022. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ Mohr JC (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. pp. 35–36. ISBN 978-0-19-502616-0.
- ^ Paul M, Lichtenberg ES, Borgatta L, Grimes DA, Stubblefield PG, Creinin MD, Joffe C (2009). "Abortion and Medicine: A Sociopolitical History" (PDF). Management of Unintended and Abnormal Pregnancy (1st ed.). Oxford: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-1293-5. OL 15895486W. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2012.
- ^ Dannenfelser M (4 November 2015). "The Suffragettes Would Not Agree With Feminists Today on Abortion". Time. Archived from the original on 6 November 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- ^ a b Samuels A, Potts M (25 July 2022). "How The Fight To Ban Abortion Is Rooted In The 'Great Replacement' Theory". FiveThirtyEight. Archived from the original on 25 July 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ a b Abdeltath R, Arablouei R, Caine J, Kaplan-Levenson L, Wu L, Yvellez V, et al. "Before Roe: The Physicians' Crusade". Throughline. NPR. Archived from the original on 26 July 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ Poole WS (2009). Satan in America: The Devil We Know. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 86. ISBN 978-0-7425-6171-7. Retrieved 20 March 2023.
- ^ Wilson C (2 November 2020). "Nostalgia, Entitlement and Victimhood: The Synergy of White Genocide and Misogyny". Terrorism and Political Violence. 34 (8). Routledge: 1810–1825. doi:10.1080/09546553.2020.1839428. S2CID 228837398. Storer is cited at p. 4.
- ^ Lee CA (1838). "Report of a Trial for Murder". American Journal of the Medical Sciences. XXII: 351–353.
- ^ Benjamin Bailey, "Induction of abortion and premature labor", North American Journal of Homeopathy, vol. XI, no. 3 (1896), pp. 144–150.
- ^ Keith Simpson, Forensic Medicine, Edward Arnold Publishers, 1969 [first published 1947], pp. 173–174.
- ^ Bullough V (2001). Encyclopedia of Birth Control. ABC-CLIO E-Books. ABC-CLIO. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-57607-181-6. Archived from the original on 24 January 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ Raphael D (2011). Being Female: Reproduction, Power, and Change. World Anthropology. De Gruyter. p. 30. ISBN 978-3-11-081312-8. Archived from the original on 24 January 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ "Abortion Law, History & Religion". Childbirth By Choice Trust. Archived from the original on 8 February 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2008.
- ^ For sources describing abortion policy in Nazi Germany, see:
- Friedlander H (1995). The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-8078-4675-9. OCLC 60191622. Archived from the original on 29 July 2016.
- Proctor RN (1988). Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis. Harvard University Press. pp. 122–123, 366. ISBN 978-0-674-74578-0. OCLC 20760638.
- Arnot ML, Usborne C (1999). Gender and Crime in Modern Europe. New York: Routledge. p. 231. ISBN 978-1-85728-745-5. OCLC 186748539.
- DiMeglio PM (1999). "Germany 1933–1945 (National Socialism)". In Tierney H (ed.). Women's Studies Encyclopedia. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 589. ISBN 978-0-313-31072-0. OCLC 38504469. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015.
- ^ Ye Hee Lee M (14 June 2022). "In Japan, Abortion is Legal — But Most Women Need Their Husband's Consent". Retrieved 16 March 2023.
- ^ Wingfield-Hayes R (31 August 2022). "Abortion pill: Why Japanese women will need their partner's consent to get a tablet". BBC News. Archived from the original on 5 March 2023. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
It was actually one of the first countries in the world to pass an abortion law, back in 1948. But it was part of the Eugenics Protection Law – yes, it really was called that. It had nothing to do with giving women more control over their reproductive health. Rather, it was about preventing 'inferior' births. ... So, to this day, women who want an abortion must get written permission from their husband, partner, or in some cases their boyfriend. ... Unlike the US, Japanese views on abortion are not driven by religious belief. Instead, they derive from a long history of patriarchy and deeply traditional views on the role of women and motherhood.
- ^ Farrell C (2010). Abortion Debate. ABDO Publishing Company. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978-1-61785-264-0.
- ^ "WMA Declaration on Therapeutic Abortion". World Medical Association. Archived from the original on 28 October 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ Farrell, p. 8
- ^ Joyce TJ, Henshaw SK, Dennis A, Finer LB, Blanchard K (April 2009). "The Impact of State Mandatory Counseling and Waiting Period Laws on Abortion: A Literature Review" (PDF). Guttmacher Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 March 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ Phillips T (29 October 2015). "China ends one-child policy after 35 years". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 1 December 2016. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ "China NPC: Three-child policy formally passed into law". 20 August 2021. Archived from the original on 29 June 2022. Retrieved 6 April 2024.
- ^ Restivo SP, ed. (2005). Science, Technology, and Society: An Encyclopedia. Oxford University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-19-514193-1. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015.
- ^ "European delegation visits Nicaragua to examine effects of abortion ban". Ipas. 26 November 2007. Archived from the original on 17 April 2008. Retrieved 15 June 2009.
More than 82 maternal deaths had been registered in Nicaragua since the change. During this same period, indirect obstetric deaths, or deaths caused by illnesses aggravated by the normal effects of pregnancy and not due to direct obstetric causes, have doubled.
- ^ "Nicaragua: 'The Women's Movement Is in Opposition'". Montevideo: Inside Costa Rica. IPS. 28 June 2008. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011.
- ^ "Surgical Abortion: History and Overview". National Abortion Federation. Archived from the original on 22 September 2006. Retrieved 4 September 2006.
- ^ Nations MK, Misago C, Fonseca W, Correia LL, Campbell OM (June 1997). "Women's hidden transcripts about abortion in Brazil". Social Science & Medicine. 44 (12): 1833–1845. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(96)00293-6. PMID 9194245.
Two folk medical conditions, "delayed" (atrasada) and "suspended" (suspendida) menstruation, are described as perceived by poor Brazilian women in Northeast Brazil. Culturally prescribed methods to "regulate" these conditions and provoke menstrual bleeding are also described ...
- ^ Henshaw SK (1991). "The accessibility of abortion services in the United States" (PDF). Family Planning Perspectives. 23 (6): 246–52, 263. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.360.6115. doi:10.2307/2135775. JSTOR 2135775. PMID 1786805. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 March 2016. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- ^ Bloom M (25 February 2008). "Need Abortion, Will Travel". RH Reality Check. Archived from the original on 30 November 2008. Retrieved 15 June 2009.
- ^ Gomperts R (May 2002). "Women on waves: where next for the abortion boat?". Reproductive Health Matters. 10 (19): 180–183. doi:10.1016/S0968-8080(02)00004-6. PMID 12369324.
- ^ Best A (2005). "Abortion Rights along the Irish-English Border and the Liminality of Women's Experiences". Dialectical Anthropology. 29 (3–4): 423–37. doi:10.1007/s10624-005-3863-x. ISSN 0304-4092. S2CID 145318165.
- ^ Lambert-Beatty C (2008). "Twelve miles: Boundaries of the new art/activism". Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society. 33 (2): 309–27. doi:10.1086/521179. S2CID 147307705.
- ^ Banister, Judith. (16 March 1999). Son Preference in Asia – Report of a Symposium Archived 16 February 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 12 January 2006.
- ^ Reaney P. "Selective abortion blamed for India's missing girls". Reuters. Archived from the original on 20 February 2006. Retrieved 3 December 2008.
- ^ Sudha S, Irudaya RS (July 1999). "Female demographic disadvantage in India 1981-1991: sex selective abortions and female infanticide". Development and Change. 30 (3): 585–618. doi:10.1111/1467-7660.00130. PMID 20162850. S2CID 33446683. Archived from the original on 1 January 2003. Retrieved 3 December 2008.
- ^ "Sex Selection & Abortion: India". Library of Congress. 4 April 2011. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ "China Bans Sex-selection Abortion". www.china.org.cn. Xinhua News Agency. 22 March 2003. Archived from the original on 12 February 2006. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ^ Graham MJ, Larsen U, Xu X (June 1998). "Son Preference in Anhui Province, China". International Family Planning Perspectives. 24 (2): 72–77. doi:10.2307/2991929. JSTOR 2991929. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012.
- ^ a b c "Preventing gender-biased sex selection" (PDF). UNFPA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ "Prenatal sex selection" (PDF). Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 October 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ Das Gupta M (2019). "Is banning sex-selection the best approach for reducing prenatal discrimination?". Asian Population Studies. 15 (3): 319–336. doi:10.1080/17441730.2019.1671015. PMC 8153244. PMID 34046078.
- ^ Wilson M, Lynxwiler J (1988). "Abortion clinic violence as terrorism". Terrorism. 11 (4): 263–273. doi:10.1080/10576108808435717. PMID 11618209.
- ^ Smith GD (1998). "Single Issue Terrorism Commentary". Canadian Security Intelligence Service. Archived from the original on 15 October 2007. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ National Abortion Federation (2017). "2017 violence and disruption statistics" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 July 2020. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- ^ "Incidence of Violence & Disruption Against Abortion Providers in the U.S. & Canada" (PDF). National Abortion Federation. 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 June 2010. Retrieved 9 February 2010.
- ^ Borger J (3 February 1999). "The bomber under siege". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017.
- ^ Pridemore WA, Freilich JD (1 December 2007). "The Impact of State Laws Protecting Abortion Clinics and Reproductive Rights on Crimes Against Abortion Providers: Deterrence, Backlash, or Neither?". Law and Human Behavior. 31 (6): 611–627. doi:10.1007/s10979-006-9078-0. ISSN 1573-661X.
- ^ a b Doan 2007, p. 2.
- ^ Spencer JB (1908). Sheep Husbandry in Canada. p. 114. OCLC 798508694.
- ^ "Beef cattle and Beef production: Management and Husbandry of Beef Cattle". Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Archived from the original on 1 January 2009.
- ^ Myers B, Beckett J (2001). "Pine needle abortion" (PDF). Animal Health Care and Maintenance. Tucson: Arizona Cooperative Extension, University of Arizona. pp. 47–50. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2015. Retrieved 10 April 2013.
- ^ Kim IH, Choi KC, An BS, Choi IG, Kim BK, Oh YK, Jeung EB (July 2003). "Effect on abortion of feeding Korean pine needles to pregnant Korean native cows". Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research. 67 (3). Canadian Veterinary Medical Association: 194–197. PMC 227052. PMID 12889725.
- ^ a b Njaa BL, ed. (2011). Kirkbride's Diagnosis of Abortion and Neonatal Loss in Animals. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-95852-0.
- ^ Overton R (March 2003). "By a Hair" (PDF). Paint Horse Journal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ^ Adams KR, Fetterplace LC, Davis AR, Taylor MD, Knott NA (January 2018). "Sharks, rays and abortion: The prevalence of capture-induced parturition in elasmobranchs". Biological Conservation. 217: 11–27. Bibcode:2018BCons.217...11A. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2017.10.010. S2CID 90834034. Archived from the original on 23 February 2019. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- ^ "Herpesvirus in dog pups". petMD. Archived from the original on 9 November 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "Spaying Pregnant Females". Carol's Ferals. Archived from the original on 18 November 2012. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ Coates J (7 May 2007). "Feline abortion: often an unnerving necessity". petMD. Archived from the original on 21 January 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Khuly P (1 April 2011). "Feline abortion: often an unnerving necessity (Part 2)". petMD. Archived from the original on 18 November 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Schwagmeyer PL (1979). "The Bruce Effect: An Evaluation of Male/Female Advantages". The American Naturalist. 114 (6): 932–938. doi:10.1086/283541. JSTOR 2460564. S2CID 85097151.
- ^ McKinnon AO, Voss JL (1993). Equine Reproduction. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 563. ISBN 0-8121-1427-2. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015.
- ^ Berger J (5 May 1983). "Induced abortion and social factors in wild horses". Nature. 303 (5912): 59–61. Bibcode:1983Natur.303...59B. doi:10.1038/303059a0. PMID 6682487. S2CID 4259800.
- ^ Pluhácek J, Bartos L (April 2000). "Male infanticide in captive plains zebra, Equus burchelli" (PDF). Animal Behaviour. 59 (4): 689–694. doi:10.1006/anbe.1999.1371. PMID 10792924. S2CID 10961845. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011.
- ^ Pluhacek J, Bartoš L (2005). "Further evidence for male infanticide and feticide in captive plains zebra, Equus burchelli" (PDF). Folia Zoologica. 54 (3): 258–262. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ Kirkpatrick JF, Turner JW (1991). "Changes in Herd Stallions among Feral Horse Bands and the Absence of Forced Copulation and Induced Abortion". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 29 (3): 217–19. doi:10.1007/BF00166404. JSTOR 4600608. S2CID 32756929.
- ^ Agoramoorthy G, Mohnot SM, Sommer V, Srivastava A (1988). "Abortions in free ranging Hanuman langurs (Presbytis entellus) – a male induced strategy?". Human Evolution. 3 (4): 297–308. doi:10.1007/BF02435859. S2CID 84849590.
Bibliography
- Coppens C (1907). . In Herbermann C (ed.). Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 1. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- Devereux G (1976). A Study of Abortion in Primitive Societies. International Universities Press. ISBN 978-0-8236-6245-6.
- Doan AE (2007). Opposition and Intimidation: The abortion wars and strategies of political harassment. University of Michigan.
- Ganatra B, Tunçalp Ö, Johnston HB, Johnson BR, Gülmezoglu AM, Temmerman M (March 2014). "From concept to measurement: operationalizing WHO's definition of unsafe abortion". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 92 (3): 155. doi:10.2471/BLT.14.136333. PMC 3949603. PMID 24700971.
- Hartmann B (1995). Reproductive Rights and Wrongs: The Global Politics of Population Control. South End Press. ISBN 978-0-89608-491-9.
- Koblitz AH (2014). Sex and Herbs and Birth Control: Women and Fertility Regulation Through the Ages. Kovalevskaia Fund. ISBN 978-0-9896655-0-6.
- Riddle JM (1997). Eve's Herbs: A History of Contraception and Abortion in the West. Harvard University Press.
- Sedgh G, Bearak J, Singh S, Bankole A, Popinchalk A, Ganatra B, et al. (July 2016). "Abortion incidence between 1990 and 2014: global, regional, and subregional levels and trends". Lancet. 388 (10041): 258–267. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30380-4. PMC 5498988. PMID 27179755.
- Tine Mette Gammeltoft (4 September 2018). "Abortion". The International Encyclopedia of Anthropology: 1–3. doi:10.1002/9781118924396.WBIEA1490. Wikidata Q124418995.
- UN (2002). Abortion Policies: A Global Review 3 vols. Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations. Archived from the original on 11 January 2005. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- WHO (2005). The World Health Report 2005: Make every mother and child count. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 92-4-156290-0. Archived from the original on 13 April 2005.
- WHO (2012). Safe abortion: technical and policy guidance for health systems (PDF) (2nd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-154843-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 January 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- WHO (2016). "Health worker roles in providing safe abortion care and post-abortion contraception". Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
External links
- WHO fact sheet on abortion
- Safe abortion: Technical & policy guidance for health systems, World Health Organization (2015)
- First-trimester abortion in women with medical conditions. US Department of Health and Human Services