Nikola Tesla: Difference between revisions
Reverted good faith edits by Violetcries (talk): Unsourced and not appropriate for this article - this content could be added to [[. (TW) |
m + link GA |
||
| Line 645: | Line 645: | ||
[[Category:Wireless energy transfer]] |
[[Category:Wireless energy transfer]] |
||
{{Link GA|be-x-old}} |
|||
{{Link GA|sv}} |
{{Link GA|sv}} |
||
{{Link FA|sr}} |
{{Link FA|sr}} |
||
Revision as of 18:06, 25 June 2013
Nikola Tesla (Serbian Cyrillic: Никола Тесла; 10 July 1856 – 7 January 1943) was a Serbian-American[2][3] inventor, electrical engineer, mechanical engineer, physicist, and futurist best known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.[4]
Tesla gained experience in telephony and electrical engineering before emigrating to the United States in 1884 to work for Thomas Edison. He soon struck out on his own with financial backers, setting up laboratories/companies to develop a range of electrical devices. His patented AC induction motor and transformer were licensed by George Westinghouse, who also hired Tesla as a consultant to help develop a power system using alternating current. Tesla is also known for his high-voltage, high-frequency power experiments in New York and Colorado Springs which included patented devices and theoretical work used in the invention of radio communication,[5] for his X-ray experiments, and for his ill-fated attempt at intercontinental wireless transmission in his unfinished Wardenclyffe Tower project.[6]
Tesla's achievements and his abilities as a showman demonstrating his seemingly miraculous inventions made him world-famous.[7] Although he made a great deal of money from his patents, he spent a lot on numerous experiments. He lived for most of his life in a series of New York hotels although the end of his patent income and eventual bankruptcy led him to live in diminished circumstances.[8] Tesla still continued to invite the press to parties he held on his birthday to announce new inventions he was working and make (sometimes unusual) statements.[9][10] Because of his pronouncements and the nature of his work over the years, Tesla gained a reputation in popular culture as the archetypal "mad scientist".[11] He died in room 3327 of the New Yorker Hotel on 7 January 1943.
Tesla's work fell into relative obscurity after his death, but since the 1990s, his reputation has experienced a comeback in popular culture.[12] His work and reputed inventions are also at the center of many conspiracy theories and have also been used to support various pseudosciences, UFO theories and New Age occultism. In 1960, in honor of Tesla, the General Conference on Weights and Measures for the International System of Units dedicated the term "tesla" to the SI unit measure for magnetic field strength.[13]
Early years (1856–1885)


Nikola Tesla was born on 10 July (O.S. 28 June) 1856 to Serbian parents in the village of Smiljan, Austrian Empire (modern-day Croatia). His father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian Orthodox priest.[15] Tesla's mother, Đuka Tesla (née Mandić), whose father was also a Serbian Orthodox priest,[16] had a talent for making home craft tools, mechanical appliances, and the ability to memorize Serbian epic poems. Duka had never received a formal education. Nikola credited his eidetic memory and creative abilities to his mother's genetics and influence.[17][18] Tesla's progenitors were from western Serbia, near Montenegro.[19]
Tesla was the fourth of five children. He had an older brother named Dane and three sisters, Milka, Angelina and Marica. Dane was killed in a horse-riding accident when Nikola was five.[20][21] Some accounts say that Tesla caused the accident by frightening the horse.[21] In 1861, Tesla attended the "Lower" or "Primary" School in Smiljan where he studied German, arithmetic, and religion.[22] In 1862, the Tesla family moved to Gospić, Austrian Empire, where Tesla's father worked as a pastor. Nikola completed "Lower" or "Primary" School, followed by the "Lower Real Gymnasium" or "Normal School".[23]
In 1870, Tesla moved to Karlovac to attend school at Higher Real Gymnasium, where he was profoundly influenced by a math teacher Martin Sekulić.[21][24] Tesla was able to perform integral calculus in his head, which prompted his teachers to believe that he was cheating.[25] He finished a four-year term in three years, graduating in 1873.[26]
In 1873, Tesla returned to his birthtown, Smiljan. Shortly after he arrived, Tesla contracted cholera; he was bedridden for nine months and was near death multiple times. Tesla's father, in a moment of despair, promised to send him to the best engineering school if he recovered from the illness[21][27] (his father had originally wanted him to enter the priesthood).[28]
In 1874, Tesla evaded being drafted into the Austro-Hungarian Army in Smiljan[29] by running away to Tomingaj, near Gračac. There, he explored the mountains in hunter's garb. Tesla claimed that this contact with nature made him stronger, both physically and mentally.[21] He read many books while in Tomingaj, and later claimed that Mark Twain's works had helped him to miraculously recover from his earlier illness.[27]
In 1875, Tesla enrolled at Austrian Polytechnic in Graz, Austria, on a Military Border scholarship. During his first year, Tesla never missed a lecture, earned the highest grades possible, passed nine exams[21][27] (nearly twice as many required[30]), started a Serbian culture club,[21] and even received a letter of commendation from the dean of the technical faculty to his father, which stated, "Your son is a star of first rank".[30] Tesla claimed that he worked from 3 a.m. to 11 p.m., no Sundays or holidays excepted.[27] He was "mortified when [his] father made light of [those] hard won honors". After his father's death in 1879,[29] Tesla found a package of letters from his professors to his father, warning that unless he were removed from the school, Tesla would be killed through overwork.[27] During his second year, Tesla came into conflict with Professor Poeschl over the Gramme dynamo, when Tesla suggested that commutators weren't necessary. At the end of his second year, Tesla lost his scholarship and became addicted to gambling.[21][27] During his third year, Tesla gambled away his allowance and his tuition money, later gambling back his initial losses and returning the balance to his family. Tesla claimed that he "conquered [his] passion then and there," but later he was known to play billiards in the US. When exam time came, Tesla was unprepared and asked for an extension to study, but was denied. He never graduated from the university and did not receive grades for the last semester.[29]
In December 1878, Tesla left Graz and severed all relations with his family to hide the fact that he dropped out of school.[29] His friends thought that he had drowned in the Mur River.[31] Tesla went to Maribor (now in Slovenia), where he worked as a draftsman for 60 florins a month. He spent his spare time playing cards with local men on the streets.[29] In March 1879, Milutin Tesla went to Maribor to beg his son to return home, but Nikola refused.[32] Nikola suffered a nervous breakdown at around the same time.[31]

On 24 March 1879, Tesla was returned to Gospić under police guard for not having a residence permit. On 17 April 1879, Milutin Tesla died at the age of 60 after contracting an unspecified illness[33] (although some sources claim that he died of a stroke[34] ). During that year, Tesla taught a large class of students in his old school, Higher Real Gymnasium, in Gospić.[33]
In January 1880, two of Tesla's uncles put together enough money to help him leave Gospić for Prague where he was to study. Unfortunately, he arrived too late to matriculate at Charles-Ferdinand University because he arrived too late to be able to enroll; he never studied Greek, a required subject; and he was illiterate in Czech, another required subject. Tesla did, however, attend lectures at the university, although, as an auditor, he did not receive grades for the courses.[35][36][37]
In 1881, Tesla moved to Budapest to work under Ferenc Puskas at a telegraph company, the Budapest Telephone Exchange. Upon arrival, Tesla realized that the company, then under construction, was not functional, so he worked as a draftsman in the Central Telegraph Office, instead. Within a few months, the Budapest Telephone Exchange became functional and Tesla was allocated the chief electrician position.[38] During his employment, Tesla made many improvements to the Central Station equipment and claimed to have perfected a telephone repeater or amplifier, which was never patented nor publicly described.[27]
Working for Edison
In 1882, Tesla began working for the Continental Edison Company in France, designing and making improvements to electrical equipment.[39]
In June 1884, Tesla relocated to New York City.[40] During his trip across the Atlantic, his ticket, money, and some of his luggage were stolen, and he was nearly thrown overboard after a mutiny broke out on the ship.[41] He arrived with only four cents in his pocket, a letter of recommendation, a few poems, and the remainder of his belongings.[citation needed]
In the letter of recommendation from Charles Batchelor, a former employer, to Thomas Edison, it is claimed that Batchelor wrote, "I know two great men and you are one of them; the other is this young man." (The exact contents of the letter are disputed in McNichol's book.) Edison hired Tesla to work for his Edison Machine Works. Tesla's work for Edison began with simple electrical engineering and quickly progressed to solving some of the company's most difficult problems. Tesla was even offered the task of completely redesigning the Edison Company's direct current generators.[42]
In 1885, Tesla claimed that he could redesign Edison's inefficient motor and generators, making an improvement in both service and economy. According to Tesla, Edison remarked, "There's fifty thousand dollars in it for you—if you can do it"[43]—this has been noted as an odd statement from an Edison whose company was stingy with pay and who did not have that sort of cash on hand.[44] After months of work, Tesla fulfilled the task and inquired about payment. Edison, claiming that he was only joking, replied, "Tesla, you don't understand our American humor."[45][46] Instead, Edison offered a US$10 a week raise over Tesla's US$18 per week salary; Tesla refused the offer and immediately resigned.[43]
Middle years (1886–1899)
In 1886, Tesla formed his own company, Tesla Electric Light & Manufacturing.[47] The company installed electrical arc light based illumination systems designed by Tesla and also had designs for dynamo electric machine commutators, the first patents issued to Tesla in the US.[48]

Tesla proposed that the company should go on to develop his ideas for alternating current transmission systems and motors. The investors disagreed and eventually fired him, leaving him penniless; Tesla was forced to work as a ditch digger for US$2 per day. Tesla considered the winter of 1886/1887 as a time of "terrible headaches and bitter tears". During this time, he questioned the value of his education.[48][49]
In April 1887, Tesla started a company, the Tesla Electric Company, with the backing of New York attorney Charles F. Peck and Alfred S. Brown, the director of Western Union. They set up a laboratory for Tesla at 89 Liberty Street in Manhattan so he could work on his alternating current motor and other devices for power distribution, with an agreement that they share fifty-fifty with Tesla any profits generated from patents.[50] It was here, in 1887, that Tesla constructed a brushless alternating current induction motor, based on a rotating magnetic field principle he claimed to have conceived of in 1882.[51] He received a US patent for the motor in May 1888.[52] At that time, many inventors were trying to develop workable AC motors[48] because AC's advantages in long distance high voltage transmission were counterbalanced by the inability to operate motors on AC. The rotating magnetic field induction motor seems to have been an independent invention by Tesla, but it was not a unique discovery at the time.[53] Italian physicist Galileo Ferraris published a paper on rotating magnetic field based induction motor on 11 March 1888,[54][55][56][57] a working model of which he may have been demonstrating at the University of Turin as early as 1885.[58][59][60] In 1888, a month before Tesla demonstrated his AC induction motor, Westinghouse engineer Oliver B. Shallenberger invented an induction meter that was based on the same rotating magnetic field principle,[61][62] and during Tesla's demonstration English engineer Elihu Thomson stated he was working on an induction motor.[63]
In 1888, the editor of Electrical World magazine, Thomas Commerford Martin (a friend and publicist), arranged for Tesla to demonstrate his alternating current system, including his induction motor, at the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (now IEEE).[64] Engineers working for the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company reported to George Westinghouse that Tesla had a viable AC motor and power system—something that Westinghouse had been trying to secure. In July 1888, Brown and Peck negotiated a licensing deal with George Westinghouse for Tesla's polyphase induction motor and transformer designs for $60,000 in cash and stock and a royalty of $2.50 per AC horsepower produced by each motor. Westinghouse also hired Tesla for one year for the large fee of $2,000 a month to be a consultant at the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company's Pittsburgh labs.[65]
During that year, Tesla worked in Pittsburgh, helping to create an alternating current system to power the city's streetcars. He found the time there frustrating because of conflicts between him and the other Westinghouse engineers over how to best implement AC power. Between them, they settled on a 60-cycle AC current system Tesla proposed (to match the working frequency of Tesla's motor), although they soon found that, since Tesla's induction motor could only run at a constant speed, it would not work for street cars. They ended up using a DC traction motor instead.[66]
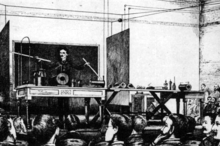
Tesla demonstrated wireless energy transmission (Tesla effect) as early as 1891.[67][68]
In 1891, Tesla patented the Tesla coil.[69]
American citizenship
On 30 July 1891, at the age of 35, Tesla became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He told many of his companions that he valued the citizenship more than any scientific honors that he had acquired.[70]
In the same year, Tesla established his South Fifth Avenue laboratory in New York. Later, he established his Houston Street laboratory in New York at 46 E. Houston Street. He lit electric lamps wirelessly at both of the New York locations, providing evidence for the potential of wireless power transmission.[71]
In 1892, Tesla spent a few months in Europe visiting other scientists. He later went to visit his hometown,[72] arriving from Paris hours before his mother's death.[73] He stayed at her side until he was exhausted. Nikola was awakened from a dream, in which an angel bearing resemblance to his mother appeared. He wrote: "I was wakened up by an indescribably sweet song of many voices." He believed that the dream was a sign that his mother had died; he later confirmed this.[72] Her last words to him were: "You've arrived, Nidžo, my pride."[73] At first, Tesla believed that the dream was a message from the supernatural; however, after a few months of research, he concluded that his dream was caused by a painting of angels that he had seen before going to bed and that the singing voices had been from a nearby church.[72]
After the death of his mother, Tesla became ill and spent two to three weeks recovering in Gospić and Tomingaj.[73]
From 1892 to 1894, Tesla served as the vice president of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, the forerunner (along with the Institute of Radio Engineers) of the modern-day IEEE.[74]
Tesla investigated harvesting energy in space. He believed that it was merely a question of time until men would succeed in attaching their machinery to the very wheelwork of nature, stating: "Ere many generations pass, our machinery will be driven by a power obtainable at any point of the universe."[75]

In 1893, Westinghouse won the bid to electrify the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago with alternating current. This World's Fair devoted a building to electrical exhibits. It was a key event in the history of AC power, as Westinghouse and Tesla demonstrated the safety and reliability of alternating current to the American public.[76] At the Columbian Exposition, Tesla demonstrated a series of electrical effects in a lecture he had performed throughout America and Europe.[77] This included using high-voltage, high-frequency alternating current to light a wireless gas-discharge lamp.[78] An observer noted:
Within the room was suspended two hard-rubber plates covered with tin foil. These were about fifteen feet apart, and served as terminals of the wires leading from the transformers. When the current was turned on, the lamps or tubes, which had no wires connected to them, but lay on a table between the suspended plates, or which might be held in the hand in almost any part of the room, were made luminous. These were the same experiments and the same apparatus shown by Tesla in London about two years previous, "where they produced so much wonder and astonishment".[79]
Tesla also explained the principles of a rotating magnetic field and induction motor by demonstrating how to make a copper egg stand on end. The device he constructed is known as the "Egg of Columbus".[80]
As a result of the "War of Currents," Edison and Westinghouse went nearly bankrupt. Edison had lost control of his company to J.P. Morgan, and Morgan was refusing to loan more money to Westinghouse due to the financial strain of the Tesla AC patents[81][82] (at that point Westinghouse had paid out an estimated $200,000 in licenses and royalties to Tesla, Brown, and Peck[83]). In 1897, Westinghouse explained his financial difficulties to Tesla in stark terms, saying that if things continue the way they were he would no longer be in control of Westinghouse Electric and Tesla would have to "deal with the bankers" to try to collect future royalties. Westinghouse convinced Tesla to release his company from the licensing agreement over Tesla's AC patents in exchange for Westinghouse Electric purchasing the patents for a lump sum payment of $216,000;[84] this provided Westinghouse a break from what, due to alternating current's rapid gain in popularity, had turned out to be an overly generous $2.50 per AC horsepower royalty.[65]
X-ray experimentation

Starting in 1894, Tesla began investigating what he referred to as radiant energy of "invisible" kinds that he had noticed damaged film in his lab in previous experiments[85][86] (later identified as "Roentgen rays" or "X-Rays"). His early experiments were with Crookes tubes, a cold cathode electrical discharge tube. Tesla may have been the first person in North America to accidentally capture an X-ray image,[87] when he tried to photograph Mark Twain illuminated by an earlier type of gas discharge tube Geissler tube in 1895. The only thing captured in the image was the metal locking screw on the camera lens. Soon after, much of Tesla's early research—hundreds of invention models, plans, notes, laboratory data, tools, photographs, valued at $50,000—was lost in the 5th Avenue laboratory fire of March 1895. Tesla is quoted by The New York Times as saying, "I am in too much grief to talk. What can I say?"[88]
In March 1896, after hearing of Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of X-ray and X-ray imaging (radiography),[89] Tesla proceeded to do his own experiments in X-ray imaging, developing a high energy single terminal vacuum tube of his own design that had no target electrode and that worked from the output of the Tesla Coil (the modern term for the phenomenon produced by this device is bremsstrahlung or braking radiation). In his research, Tesla devised several experimental setups to produce X-rays. Tesla held that, with his circuits, the "instrument will [... enable one to] generate Roentgen rays of much greater power than obtainable with ordinary apparatus."[90]
Tesla noted the hazards of working with his circuit and single-node X-ray-producing devices. In his many notes on the early investigation of this phenomenon, he attributed the skin damage to various causes. He believed early on that damage to the skin was not caused by the Roentgen rays, but by the ozone generated in contact with the skin, and to a lesser extent, by nitrous acid. Tesla incorrectly believed that X-rays were longitudinal waves, such as those produced in waves in plasma. These plasma waves can occur in force-free magnetic fields.[91][92]
On 11 July 1934, the New York Herald Tribune published an article on Tesla, in which he recalled an event that would occasionally take place while experimenting with his single-electrode vacuum tubes; a minute particle would break off the cathode, pass out of the tube, and physically strike him. “Tesla said he could feel a sharp stinging pain where it entered his body, and again at the place where it passed out.” In comparing these particles with the bits of metal projected by his “electric gun”, Tesla said, “The particles in the beam of force ... will travel much faster than such particles . .. and they will travel in concentrations.”[93]
Radio
Tesla's theories on the possibility of the transmission by radio waves go back as far as lectures and demonstrations in 1893 in St. Louis, Missouri, the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and the National Electric Light Association.[94] Tesla's demonstrations and principles were written about widely through various media outlets.[75] Many devices such as the Tesla Coil were used in the further development of radio.[5]
Tesla's radio wave experiments in 1896 were conducted in Gerlach Hotel (later renamed The Radio Wave building), where he resided.[95]
In 1898, Tesla demonstrated a radio-controlled boat—which he dubbed "teleautomaton"—to the public during an electrical exhibition at Madison Square Garden.[1] The crowd that witnessed the demonstration made outrageous claims about the workings of the boat: everything from magic to telepathy to being piloted by a trained monkey hidden inside.[96] Tesla tried to sell his idea to the U.S. military as a type of radio-controlled torpedo, but they showed little interest.[97] Remote radio control remained a novelty until World War I and afterward, when a number of countries used it in military programs.[citation needed] Tesla took the opportunity to further demonstrate "Teleautomatics" in an address to a meeting of the Commercial Club in Chicago, whilst he was travelling to Colorado Springs, on 13 May 1899.[22]
In 1900, Tesla was granted patents for a "system of transmitting electrical energy" and "an electrical transmitter". When Guglielmo Marconi made his famous first ever transatlantic radio transmission in 1901, Tesla quipped that it was done with 17 Tesla patents. This was the beginning of years of patent battles over radio with Tesla's patents being upheld in 1903, followed by a reverse decision in favor of Marconi in 1904. In 1943, a Supreme Court of the United States decision restored the prior patents of Tesla, Oliver Lodge, and John Stone.[98] The court declared that their decision had no bearing on Marconi's claim as the first to achieve radio transmission, just that since Marconi's claim to certain patents were questionable, he could not claim infringement on those same patents[99] (there are claims the high court was trying to nullify a World War I claim against the U.S. government by the Marconi Company via simply restoring Tesla's prior patent).[98]
Colorado Springs



On 17 May 1899, Tesla moved to Colorado Springs, where he would have room for his high-voltage, high-frequency experiments;[22] his lab was located near Foote Ave. and Kiowa St.[100] He chose this location because the polyphase alternating current power distribution system had been introduced there and he had associates who were willing to give him all the power he needed without charging for it.[101] Upon his arrival, he told reporters that he was conducting wireless telegraphy experiments, transmitting signals from Pikes Peak to Paris.[citation needed]
On 15 June 1899, Tesla performed his first experiments at his Colorado Springs lab; he recorded his initial spark length at five inches long, but very thick and noisy.[22]
Tesla investigated atmospheric electricity, observing lightning signals via his receivers. Reproductions of Tesla's receivers and coherer circuits show an unpredicted level of complexity: distributed high-Q helical resonators, radio frequency feedback, crude heterodyne effects, and regeneration techniques.[102] Tesla stated that he observed stationary waves during this time.[103]
Tesla's diary contains explanations of his experiments concerning the ionosphere and the ground's telluric currents via transverse waves and longitudinal waves.[104] He researched ways to transmit energy wirelessly over long distances (via transverse waves, to a lesser extent, and, more readily, longitudinal waves). He transmitted extremely low frequencies through the ground as well as between the earth's surface and the Kennelly–Heaviside layer. Tesla received U.S. patent 645,576 for wireless transceivers that developed standing waves by this method. In his experiments, he made mathematical calculations and computations based on his experiments and discovered that the resonant frequency of the earth was approximately 8 hertz (Hz)[105] (later confirmed by researchers in the 1950s—named the Schumann resonance).[106] Tesla sent electrostatic forces through natural media across a conductor situated in the changing magnetic flux and transferred electrical energy to a wireless receiver.[citation needed]
At his lab, Tesla proved that the earth was a conductor. He produced artificial lightning (with discharges consisting of millions of volts and up to 135 feet long).[107] Thunder from the released energy was heard 15 miles away in Cripple Creek, Colorado. People walking along the street observed sparks jumping between their feet and the ground. Electricity sprang from taps when turned on. Light bulbs within 100 feet of the lab glowed even when turned off. Horses in a livery stable bolted from their stalls after receiving shocks through their metal shoes. Butterflies were electrified, swirling in circles with blue halos of St. Elmo's fire around their wings.[108]
While experimenting, Tesla accidentally short-circuited the generator, causing a power outage. In August 1917, Tesla explained what had happened in The Electrical Experimenter: "As an example of what has been done with several hundred kilowatts of high frequency energy liberated, it was found that the dynamos in a power house six miles away were repeatedly burned out, due to the powerful high frequency currents set up in them, and which caused heavy sparks to jump thru the windings and destroy the insulation!"[109]
At his lab, Tesla observed unusual signals from his receiver (which he interpreted as 1—2—3—4), which he later believed were extraterrestrial radio wave communications coming from Mars. The signals were substantially different from the signals those that he had noted from noise of storms and the earth.[110] Specifically, he later recalled that the signals appeared in groups of one, two, three, and four clicks together.[citation needed] Tesla was highly criticized upon revealing his finding.[22] Tesla had mentioned that he thought his inventions could be used to talk with other planets.[citation needed] It is debatable what type of signals Tesla received or whether he picked up anything at all. Research has suggested that Tesla may have had a misunderstanding of the new technology he was working with,[citation needed] or that the signals Tesla observed may have been from a non-terrestrial natural radio source such as the Jovian plasma torus signals.[111] Other sources hypothesize that he may have intercepted Marconi's European experiments—in December 1901, Marconi successfully transmitted the letter S (dot/dot/dot, the same three impulses that Tesla claimed to have received from outer space while at Colorado in 1899) from Poldhu, England to Signal Hill, Newfoundland (now part of Canada)—or signals from another experimenter in wireless transmission.[112]
In 1899, John Jacob Astor IV invested $100,000 for Tesla to further develop and produce a new lighting system. Instead, Tesla used the money to fund his Colorado Springs experiments.[113]
On 7 January 1900, Tesla left Colorado Springs.[citation needed] His lab was torn down in about 1905, and its contents were sold to satisfy a debt.[citation needed]
The Colorado experiments had prepared Tesla for the establishment of the trans-Atlantic wireless telecommunications facility known as Wardenclyffe near Shoreham, Long Island.[114]
Wardenclyffe years (1900–1917)

U.S. patent 1,119,732

In 1900, with US$150,000 (more than $3 million today; 51% from J. Pierpont Morgan), Tesla began planning the Wardenclyffe Tower facility.[115]
Tesla later approached Morgan to ask for more funds to build a more powerful transmitter. When asked where all the money had gone, Tesla responded by saying that he was affected by the Panic of 1901, which he (Morgan) had caused. Morgan was shocked by the reminder of his part in the stock market crash and by Tesla's breach of contract by asking for more funds. Tesla wrote another plea to Morgan, but it was also fruitless. Morgan still owed Tesla money on the original agreement, and Tesla had been facing foreclosure even before construction of the tower began.[112]
In December 1901, Marconi successfully transmitted the letter S from England to Newfoundland, terminating Tesla's relationship with Morgan. Over the next 5 years, Tesla wrote over 50 letters to Morgan, pleading for and demanding additional funding to complete the construction of Wardenclyffe. Tesla continued his project for another nine months. The tower was raised to its full 187 feet.[112] In July 1903, Tesla wrote to Morgan that in addition to wireless communication, Wardenclyffe would be capable of wireless transmission of electric power.[115] On 14 October 1904, Morgan finally replied through his secretary, stating, "It will be impossible for [me/ Morgan] to do anything in the matter," after Tesla had written to Morgan when the financier was meeting with the Archbishop of Canterbury in an attempt to appeal to his Christian spirit.[112]
In June 1902, Tesla's lab operations were moved to Wardenclyffe from Houston Street.[115]
On his 50th birthday in 1906, Tesla demonstrated his 200 hp (150 kW) 16,000 rpm bladeless turbine. During 1910–1911 at the Waterside Power Station in New York, several of his bladeless turbine engines were tested at 100–5,000 hp.[116]
Tesla invented a steam-powered mechanical oscillator—Tesla's oscillator. While experimenting with mechanical oscillators at his Houston Street lab, Tesla allegedly generated a resonance of several buildings. As the speed grew, it is said that the machine oscillated at the resonance frequency of his own building and, belatedly realizing the danger, he was forced to use a sledge hammer to terminate the experiment, just as the police arrived.[117] In February 1912, an article—“Nikola Tesla, Dreamer” by Allan L. Benson—was published in World Today, in which an artist's illustration appears showing the entire earth cracking in half with the caption, “Tesla claims that in a few weeks he could set the earth's crust into such a state of vibration that it would rise and fall hundreds of feet and practically destroy civilization. A continuation of this process would, he says, eventually split the earth in two.”[93]
After Wardenclyffe, Tesla built the Telefunken Wireless Station in Sayville, Long Island. Some of what he wanted to achieve at Wardenclyffe was accomplished with the Telefunken Wireless.[118] In 1917, the tower was seized and blown up with dynamite for scrap by the Marines, owing to fears that German spies were using it and that it could be used as a landmark for German submarines.[6][118][119]
Before World War I (1914–1918), Tesla looked overseas for investors to fund his research. When the war started, Tesla lost the funding he was receiving from his patents in European countries.
During this time, Tesla was staying at Waldorf-Astoria Hotel,[115] renting in an arrangement for deferred payments.[citation needed] Eventually, the Wardenclyffe deed was turned over to George Boldt, proprietor of the Waldorf-Astoria, to pay a US$20,000 debt (about $400,000 today).[115] In 1917, around the time that the Wardenclyffe Tower was demolished by Boldt to make the land a more viable real estate asset, Tesla received AIEE's highest honor, the Edison Medal.[citation needed]
In August 1917, Tesla first established the principles of frequency and power level for the first primitive radar units.[118]
Nobel Prize rumors
On 6 November 1915, a Reuters news agency report from London had the 1915 Nobel Prize in Physics awarded to Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla; however, on 15 November, a Reuters story from Stockholm stated the prize that year was being awarded to Sir William Henry Bragg and William Lawrence Bragg "for their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays."[120][121][122] There were unsubstantiated rumors at the time that Tesla and/or Edison had refused the prize.[121] The Nobel Foundation declined to comment on the rumors other than saying, "Any rumor that a person has not been given a Nobel Prize because he has made known his intention to refuse the reward is ridiculous," a recipient could only decline a Nobel Prize after he is announced a winner.[121]
There have been subsequent claims by Tesla biographers that Edison and Tesla were the original recipients and that neither were given the award because of their animosity toward each other; that each sought to minimize the other's achievements and right to win the award; that both refused ever to accept the award if the other received it first; that both rejected any possibility of sharing it; and even that a wealthy Edison refused it to keep Tesla from getting the $20,000 prize money.[18][121][123]
In the years after these rumors, neither Tesla nor Edison won the prize (although Edison did receive one of 38 possible bids in 1915 and Tesla did receive one bid out of 38 possible bids in 1937).[124]
Later years (1918–1943)

In 1928, Tesla received his last patent, U.S. patent 1,655,114, for a biplane capable of taking off vertically (VTOL aircraft) and then be "gradually tilted through manipulation of the elevator devices" in flight until it was flying like a conventional plane.[126] Tesla stated it would weigh 800 pounds and would sell at $1,000 for both military and consumer uses.[citation needed] Although the aircraft was probably impractical, it may be the earliest known design for what became the tiltrotor/tilt-wing concept as well as the earliest proposal for the use of turbine engines in rotor aircraft.[127]
Starting in 1934, the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company began paying Tesla US$125 per month as well as paying his rent at the Hotel New Yorker, expenses the Company would pay for the rest of Tesla's life. Accounts on how this came about vary. Several sources say Westinghouse was worried about potential bad publicity surrounding the impoverished conditions their former star inventor was living under.[128][129][130] It has been described as being couched in the form of a "consulting fee" to get around Tesla's aversion to accept charity, or by one biographer (Marc Seifer), as a type of unspecified settlement.[130] Tesla's previous debt owed to Hotel Governor Clinton was never satisfied.[131]
In 1934, Tesla wrote to Consul Janković of his homeland.[citation needed] The letter contained a message of gratitude to Mihajlo Pupin who had initiated a donation scheme by which American companies could support Tesla.[citation needed] Tesla refused the assistance, choosing instead to live on a modest pension received from Yugoslavia, and to continue his research.[citation needed]
In 1935, in an annual birthday celebration interview, Tesla announced a method of transmitting mechanical energy with minimal loss over any terrestrial distance, a related new means of communication, and a method of accurately determining the location of underground mineral deposits.[93]
In the fall of 1937, after midnight one night, Tesla left the Hotel New Yorker to make his regular commute to the cathedral and the library to feed the pigeons. While crossing a street a couple of blocks from the hotel, Tesla was unable to dodge a moving taxicab and was thrown heavily to the ground. Tesla's back was severely wrenched and three of his ribs were broken in the accident (the full extent of his injuries will never be known; Tesla refused to consult a doctor—an almost lifelong custom). Tesla didn't raise any question as to who was at fault and refused medical aid, only asking be taken to his hotel via cab. Tesla was bedridden for some months and was unable to continue feeding pigeons from his window; soon, they failed to come. In the spring of 1938, Tesla was able to get up. He at once resumed the pigeon—feeding walks on a much more limited scale, but frequently had a messenger act for him.[30]
Directed-energy weapon
Later in life, Tesla made claims concerning a "teleforce" weapon after studying the Van de Graaff generator.[132][133] The press called it a "peace ray" or death ray.[134][135] Tesla described the weapon as being able to be used against ground-based infantry or for antiaircraft purposes.
Tesla gives the following description concerning the particle gun's operation:
[The nozzle would] send concentrated beams of particles through the free air, of such tremendous energy that they will bring down a fleet of 10,000 enemy airplanes at a distance of 200 miles from a defending nation's border and will cause armies to drop dead in their tracks.[136][137]
In total, the components and methods included:
- An apparatus for producing manifestations of energy in free air instead of in a high vacuum as in the past.
- A mechanism for generating tremendous electrical force.
- A means of intensifying and amplifying the force developed by the second mechanism.
- A new method for producing a tremendous electrical repelling force. This would be the projector, or gun, of the invention.[138][139]
Tesla claimed to have worked on plans for a directed-energy weapon from the early 1900s until his death.[140][141]
In 1937, at a luncheon in his honor concerning the death ray, Tesla stated, "But it is not an experiment... I have built, demonstrated and used it. Only a little time will pass before I can give it to the world." His records indicate that the device is based on a narrow stream of small tungsten pellets that are accelerated via high voltage (by means akin to his magnifying transformer).[133]
During the same year, Tesla wrote a treatise, "The Art of Projecting Concentrated Non-dispersive Energy through the Natural Media," concerning charged particle beam weapons.[142] Tesla published the document in an attempt to expound on the technical description of a "superweapon that would put an end to all war". This treatise is currently in the Nikola Tesla Museum archive in Belgrade. It describes an open-ended vacuum tube with a gas jet seal that allows particles to exit, a method of charging particles to millions of volts, and a method of creating and directing non-dispersive particle streams (through electrostatic repulsion).[142] Tesla tried to interest the US War Department,[143] the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and Yugoslavia in the device.[144]
During the period in which the negotiations were being carried on, Tesla claimed that efforts had been made to steal the invention. His room had been entered and his papers had been scrutinized, but the thieves, or spies, left empty-handed. He said that there was no danger that his invention could be stolen, for he had at no time committed any part of it to paper. The blueprint for the teleforce weapon was all in his mind.[145]
Death

On 7 January 1943, Tesla, 86, died alone in Room 3327 of the New Yorker Hotel. His corpse was later found by maid Alice Monaghan after she had entered Tesla's room, ignoring the "do not disturb" sign that Tesla had placed on his door two days prior to his death. Assistant medical examiner, H.W. Wembly, was called to the scene; after examining the body, he ruled that the cause of death had been coronary thrombosis, and that there had been no suspicious circumstances.[146]
Despite having sold his AC electricity patents, Tesla died impoverished and in debt.[147][148][149][150]
Tesla's remains were taken to the Frank E. Campbell Funeral Home at Madison Ave. and 81st St. A sculptor was commissioned by Hugo Gernsback, a long-time friend and supporter of Tesla, to create a death mask (now displayed in the Nikola Tesla Museum).[146]
On 9 January, after learning of Tesla's death, the FBI ordered the Alien Property Custodian to seize all of Tesla's belongings,[146] even though Tesla was an American citizen.[151] Tesla's entire estate from the Hotel New Yorker and other New York City hotels was transported to the Manhattan Storage and Warehouse Company under OAP seal.[146]
Dr. John G. Trump, a professor at M.I.T. and well-known electrical engineer serving as a technical aide to the National Defense Research Committee, was called in to analyze the Tesla items in OAP custody,[146] to look for any material that could be sensitive in nature in relationship to the ongoing war at the time.[citation needed] After a three-day investigation, Trump concluded in his report that there was nothing that would constitute a hazard in unfriendly hands, stating:
[Tesla's] thoughts and efforts during at least the past 15 years were primarily of a speculative, philosophical, and somewhat promotional character often concerned with the production and wireless transmission of power; but did not include new, sound, workable principles or methods for realizing such results.[152]
In a box purported to contain a part of Tesla's "death ray", Trump found a 45 year-old piece of basic electrical test equipment.[153]
A few days after Tesla's death, the information center of the Yugoslav royal government-in-exile released a statement, giving a short review of Tesla's achievements and the schedule for his memorial service and funeral.[citation needed]
On 10 January 1943, New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia read a eulogy written by Slovene-American author Louis Adamić live over the WNYC radio. Violin pieces "Ave Maria" and "Tamo daleko" were played in the background.[146]
On 12 January, Tesla was given a state funeral at the Cathedral of Saint John the Divine, the largest Gothic cathedral in the world in New York City. 2,000 people attended. The funeral service was opened by Episcopal Bishop William T. Manning and concluded by Reverend Dushan J. Shukletovich, rector of the Serbian Orthodox Church of St. Sava. After the funeral, Tesla's corpse was taken to the Ferncliff Cemetery in Ardsley, New York, where it was later cremated.[146]
On 13 January, a second service was conducted in Serbian by prominent priests of the Serbian Orthodox Cathedral of St. Sava in New York City.[146]
In 1952, after constant pressure from Tesla's nephew, Sava Kosanović, arrangements were finally made; Tesla's entire estate (original papers, thousands of letters, photographs and most of Tesla's inventions including the remote-controlled boat, wireless fluorescent lamps, motors, turbines, etc.) was shipped to Belgrade. The estate was shipped in 80 trunks marked N.T.[22]
In 1957, Ms. Charlotte Muzar, secretary and assistant to Tesla's nephew, the late Sava Kosanović, delivered Tesla's ashes from the United States to Belgrade.[22] Tesla's ashes are currently kept in the third room of the Nikola Tesla Museum, in the gold-plated sphere on a marble pedestal.[154]
Patents

Tesla obtained around 300 patents worldwide for his inventions.[155] Some of Tesla's patents are not accounted for, and various sources have discovered some that have laid hidden in patent archives. There are a minimum of 278 patents[155] issued to Tesla in 26 countries that have been accounted for. Many of Tesla's patents were in the United States, Britain, and Canada, but many other patents were approved in countries around the globe.[156] Many inventions developed by Tesla were not put into patent protection.
Personal life

Tesla worked every day from 9 A.M. until 6 P.M. or later, with dinner from exactly 8 to 10 pm, at Delmonico's restaurant and later the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel. Tesla would telephone his dinner order to the headwaiter, who also could be the only one to serve him. "The meal was required to be ready at eight o'clock... He dined alone, except on the rare occasions when he would give a dinner to a group to meet his social obligations. Tesla would then resume his work, often until 3 am."[157]
For exercise, Tesla walked 8 to 10 miles per day. He squished his toes one hundred times for each foot every night, claiming that it stimulated his brain cells.[158]
In an interview with newspaper editor Arthur Brisbane, Tesla said that he did not believe in telepathy, stating, "Suppose I made up my mind to murder you," he said, "In a second you would know it. Now, isn't that wonderful? By what process does the mind get at all this?" In the same interview, Tesla said that he believed that all fundamental laws could be reduced to one.[159]
Although Tesla opposed war and believed that war could not be avoided until its cause was removed, he concluded that some wars might be justifiable.[160][failed verification]
Near the end of his life, Tesla walked to the park every day to feed the pigeons and even brought injured ones into his hotel room to nurse back to health.[161][162] He claimed that he had been visited by a specific injured white pigeon daily. Tesla spent over US$2,000, including building a device that comfortably supported her so her bones could heal, to fix her broken wing and leg.[29] Tesla stated, "I have been feeding pigeons, thousands of them for years. But there was one, a beautiful bird, pure white with light grey tips on its wings; that one was different. It was a female. I had only to wish and call her and she would come flying to me. I loved that pigeon as a man loves a woman, and she loved me. As long as I had her, there was a purpose to my life."[163][164]
Tesla became a vegetarian in his later years, living on only milk, bread, honey, and vegetable juices.[133][165]
Appearance


Tesla was 6 ft 2 in (1.88 m) tall and weighed 142 pounds (64 kg), with almost no weight variance from 1888 to about 1926.[166] He was an elegant, stylish figure in New York City, meticulous in his grooming, clothing, and regimented in his daily activities. "This was not because of personal vanity. Neatness and fastidiousness in clothes were entirely in harmony with every other phase of his personality. He did not maintain a large wardrobe and he wore no jewelry of any kind... He observed, however, that in the matter of clothes the world takes a man at his own valuation, as expressed in his appearance, and frequently eases his way to his objective through small courtesies not extended to less prepossessing individuals."[167]
Although many of Tesla's progenitors were dark-eyed, his eyes were gray-blue. He claimed that his eyes were originally darker, but as a result of the exorbitant use of his brain, their hue changed. However, his mother and some of his cousins possessed gray eyes, so it can be inferred that the gray of his eyes was inherited.[168]
Arthur Brisbane, a newspaper editor for The World, described Tesla's appearance:
Nikola Tesla is almost the tallest, almost the thinnest and certainly the most serious man who goes to Delmonico's regularly.... He has eyes set very far back in his head. They are rather light. I asked him how he could have such light eyes and be a Slav. He told me that his eyes were once much darker, but that using his mind a great deal had made them many shades lighter. I have often heard it said that using the brain makes the eyes lighter in color. Tesla's confirmation of the theory through his personal experience is important.
He is very thin, is more than six feet tall and weighs less than a hundred and forty pounds. He has very big hands. Many able men do—Lincoln is one instance. His thumbs are remarkably big, even for such big hands. They are extraordinarily big. This is a good sign. The thumb is the intellectual part of the hand. The apes have very small thumbs. Study them and you will notice this.
Nikola Tesla has a head that spreads out at the top like a fan. His head is shaped like a wedge. His chin is as pointed as an ice-pick. His mouth is too small. His chin, though not weak, is not strong enough. His face cannot be studied and judged like the faces of other men, for he is not a worker in practical fields. He lives his life up in the top of his head, where ideas are born, and up there he has plenty of room. His hair is jet black and curly. He stoops—most men do when they have no peacock blood in them. He lives inside of himself. He takes a profound interest in his own work. He has that supply of self-love and self-confidence which usually goes with success. And he differs from most of the men who are written and talked about in the fact that he has something to tell.[159]
Eidetic memory
Tesla read many works, memorizing complete books, and supposedly possessed a photographic memory.[169] He was a polyglot, speaking eight languages: Serbo-Croatian, Czech, English, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, and Latin.[170] Tesla related in his autobiography that he experienced detailed moments of inspiration. During his early life, Tesla was stricken with illness time and time again. He suffered a peculiar affliction in which blinding flashes of light would appear before his eyes, often accompanied by visions. Often, the visions were linked to a word or idea he might have come across; at other times they would provide the solution to a particular problem he had encountered. Just by hearing the name of an item, he would be able to envision it in realistic detail. Tesla would visualize an invention in his mind with extreme precision, including all dimensions, before moving to the construction stage, a technique sometimes known as picture thinking. He typically did not make drawings by hand but worked from memory. Beginning in his childhood, Tesla had frequent flashbacks to events that had happened previously in his life.[169]
Sleep habits
Tesla claimed to never sleep more than two hours.[171] However, Tesla did admit to "dozing" from time to time "to recharge his batteries".[158]
During his second year of study at Graz, Tesla developed a passion for (and became very proficient at) billiards, chess and card-playing, sometimes spending more than 48 hours in a stretch at a gaming table.[172][173] On one occasion at his laboratory, Tesla worked for a period of 84 hours without sleep or rest.[174]
Kenneth Swezey, a journalist whom Tesla had befriended, confirmed that Tesla rarely slept. Swezey recalled one morning when Tesla called him at 3 A.M.: "I was sleeping in my room like one dead.... Suddenly, the telephone ring awakened me.... [Tesla] spoke animatedly, with pauses, [as he]...work[ed] out a problem, comparing one theory to another, commenting; and when he felt he had arrived at the solution, he suddenly closed the telephone."[158]
OCD
Tesla probably suffered from obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in his later years. He developed a hatred of jewelry and round objects, could not bear to touch hair, did not like to shake hands, and became obsessed with the number three—he often felt compelled to walk around a block three times before entering a building, and demanded 18 napkins (a number divisible by three) to polish his silver and glasses and plates until they were impeccable whenever he went dining. If he read one of an author's books, he had to read all of his books.[175]
Relationships
Tesla never married, claiming that his chastity was very helpful to his scientific abilities.[169] However, towards the end of his life, he told a reporter, "Sometimes I feel that by not marrying, I made too great a sacrifice to my work...."[29] There have been numerous accounts of women vying for Tesla's affection, even some madly in love with him.[citation needed] Tesla, though polite and soft-spoken, did not have any known relationships.
Tesla was a loner, even asocial as he was prone to seclude himself with his work.[176][177][178][179] However, when he did engage in a social life, many people spoke very positively and admiringly of Tesla. Robert Underwood Johnson described him as attaining a "distinguished sweetness, sincerity, modesty, refinement, generosity, and force."[29] His loyal secretary, Dorothy Skerrit, wrote: "his genial smile and nobility of bearing always denoted the gentlemanly characteristics that were so ingrained in his soul."[30] Tesla's friend, Julian Hawthorne, wrote, "seldom did one meet a scientist or engineer who was also a poet, a philosopher, an appreciator of fine music, a linguist, and a connoisseur of food and drink."[citation needed]

Tesla was a good friend of Robert Underwood Johnson,[180] Francis Marion Crawford, Stanford White,[181] Fritz Lowenstein, George Scherff, Kenneth Swezey.[182][183][184] In middle age, Tesla became a close friend of Mark Twain. They spent a lot of time together in his lab and elsewhere.[180] Twain notably described his induction motor invention as "the most valuable patent since the telephone".[185] In the late 1920s, Tesla befriended George Sylvester Viereck, a poet, writer, mystic,[citation needed] and later, a Nazi propagandist.[186] Though nearly a hermit, Tesla occasionally attended dinner parties held by Viereck and his wife.[citation needed]
Tesla could be harsh at times, openly expressing disgust for overweight people, such as when he fired a secretary because of her weight.[187] He was quick to criticize clothing. On several occasions, Tesla directed a subordinate to go home and change her dress.[169]
When Thomas Edison died in 1931, Tesla contributed the only negative opinion to the New York Times, buried in an extensive coverage of Edison's life:
He had no hobby, cared for no sort of amusement of any kind and lived in utter disregard of the most elementary rules of hygiene ... His method was inefficient in the extreme, for an immense ground had to be covered to get anything at all unless blind chance intervened and, at first, I was almost a sorry witness of his doings, knowing that just a little theory and calculation would have saved him 90 percent of the labor. But he had a veritable contempt for book learning and mathematical knowledge, trusting himself entirely to his inventor's instinct and practical American sense.[188]
Views on experimental and theoretical physics
Tesla exhibited a pre-atomic understanding of physics in his writings;[189] he disagreed with the theory of atoms being composed of smaller subatomic particles, stating there was no such thing as an electron creating an electric charge (he believed that if electrons existed at all they were some fourth state of matter or sub-atom that could only exist in an experimental vacuum and that they had nothing to do with electricity).[190][191] Tesla believed that atoms are immutable—they could not change state or be split in any way. He was a believer in the 19th century concept of an all pervasive "ether" that transmitted electrical energy.[192]
Tesla was generally antagonistic towards theories about the conversion of matter into energy.[193] He was also critical of Einstein's theory of relativity, saying:
I hold that space cannot be curved, for the simple reason that it can have no properties. It might as well be said that God has properties. He has not, but only attributes and these are of our own making. Of properties we can only speak when dealing with matter filling the space. To say that in the presence of large bodies space becomes curved is equivalent to stating that something can act upon nothing. I, for one, refuse to subscribe to such a view.[194]
Tesla claimed to have developed his own physical principle regarding matter and energy that he started working on in 1892[193] and in 1937, at age 81, claimed in a letter to have completed a "dynamic theory of gravity" that "[would] put an end to idle speculations and false conceptions, as that of curved space".[195] He stated that the theory was "worked out in all details" and that he hoped to soon give it to the world.[196] Further elucidation of his theory was never found in his writings.[197]
Societal views

Tesla, like many of his era, became a proponent of an imposed selective breeding version of eugenics. His opinion stemmed from the belief that humans' "pity" had interfered with the natural "ruthless workings of nature," rather than from conceptions of a "master race" or inherent superiority of one person over another. His advocacy of it was, however, to push it further. In a 1937 interview, he stated:
... man's new sense of pity began to interfere with the ruthless workings of nature. The only method compatible with our notions of civilization and the race is to prevent the breeding of the unfit by sterilization and the deliberate guidance of the mating instinct .... The trend of opinion among eugenists is that we must make marriage more difficult. Certainly no one who is not a desirable parent should be permitted to produce progeny. A century from now it will no more occur to a normal person to mate with a person eugenically unfit than to marry a habitual criminal.[198]
In 1926, Tesla commented on the ills of the social subservience of women and the struggle of women toward gender equality, indicated that humanity's future would be run by "Queen Bees". He believed that women would become the dominant sex in the future.[199]
Tesla made predictions about the relevant issues of a post-World War I environment in a printed article, "Science and Discovery are the great Forces which will lead to the Consummation of the War" (20 December 1914).[200] Tesla believed that the League of Nations was not a remedy for the times and issues.[citation needed]
Religious views
Tesla was raised as an Orthodox Christian. Later in his life, he did not consider himself to be a "believer in the orthodox sense," and opposed religious fanaticism.[201] He had a profound respect for both Buddhism and Christianity.[27][201]
In his article, "The Problem of Increasing Human Energy," published in 1900, Tesla stated:
For ages this idea [that each of us is only part of a whole] has been proclaimed in the consummately wise teachings of religion, probably not alone as a means of insuring peace and harmony among men, but as a deeply founded truth. The Buddhist expresses it in one way, the Christian in another, but both say the same: We are all one.[202]
However, his religious views remain uncertain due to other statements that he made.[203][204][205] For example, in his article, "A Machine to End War", published in 1937, Tesla stated:
There is no conflict between the ideal of religion and the ideal of science, but science is opposed to theological dogmas because science is founded on fact. To me, the universe is simply a great machine which never came into being and never will end. The human being is no exception to the natural order. Man, like the universe, is a machine. Nothing enters our minds or determines our actions which is not directly or indirectly a response to stimuli beating upon our sense organs from without. Owing to the similarity of our construction and the sameness of our environment, we respond in like manner to similar stimuli, and from the concordance of our reactions, understanding is born. In the course of ages, mechanisms of infinite complexity are developed, but what we call "soul" or "spirit," is nothing more than the sum of the functionings of the body. When this functioning ceases, the "soul" or the "spirit" ceases likewise.[201]
Literary works
Tesla wrote a number of books and articles for magazines and journals.[206] Among his books are My Inventions: The Autobiography of Nikola Tesla, compiled and edited by Ben Johnston; The Fantastic Inventions of Nikola Tesla, compiled and edited by David Hatcher Childress; and The Tesla Papers.
Many of Tesla's writings are freely available on the web,[207][208][209] including the article "The Problem of Increasing Human Energy," published in The Century Magazine in 1900,[210][211] and the article "Experiments With Alternate Currents Of High Potential And High Frequency," published in his book Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla.[212][213]
Legacy and honors



Tesla's legacy has endured in books, films, radio, TV, music, live theater, comics and video games. The lack of recognition received during his own lifetime has cast him as a tragic and inspirational character, well suited to dramatic fiction. The impact of the technologies invented by Tesla is a recurring theme in several types of science fiction.
- On Tesla's 75th birthday in 1931, Time magazine put him on its cover.[214] The cover caption "All the world's his power house" noted his contribution to electrical power generation. He received congratulatory letters from more than 70 pioneers in science and engineering, including Albert Einstein.[215]
- The Tesla Society, founded in 1956.[216]
- Tesla, a 26 kilometer-wide crater on the far side of the moon.[217]
- 2244 Tesla, a minor planet.[217]
- TPP Nikola Tesla, the largest power plant in Serbia.
- Tesla (company), electrotechnical conglomerate in the former Czechoslovakia.
- Tesla Motors, an electric car company.[218]
- The Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport.[219]
- The Nikola Tesla Award[220]
- The Nikola Tesla Museum Archive in Belgrade[221][222]
Plaques and memorials

- The Nikola Tesla Memorial Centre in Smiljan opened in 2006. It features a statue of Tesla designed by sculptor Mile Blažević.[14][223]
- On 7 July 2006, on the corner of Masarykova and Preradovićeva streets in the Lower Town area in Zagreb, the monument of Tesla was unveiled. This monument was designed by Ivan Meštrović in 1952 and was transferred from the Zagreb-based Ruđer Bošković Institute where it had spent previous decades.[225][226]
- A monument to Tesla was established at Niagara Falls, New York. This monument portraying Tesla reading a set of notes was sculpted by Frano Kršinić. It was presented to the United States by Yugoslavia in 1976 and is an identical copy of the monument standing in front of the University of Belgrade Faculty of Electrical Engineering.
- A monument of Tesla standing on a portion of an alternator, was established at Queen Victoria Park in Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada. The monument was officially unveiled on 9 July 2006 on the 150th anniversary of Tesla's birth. The monument was sponsored by St. George Serbian Church, Niagara Falls, and designed by Les Drysdale of Hamilton, Ontario.[227][228] Drysdale's design was the winning design from an international competition.[229]
- In 2012, Jane Alcorn, president of the nonprofit group The Tesla Science Center at Wardenclyffe, and Matthew Inman, creator of web cartoon The Oatmeal, raised a total of $2,220,511—$1,370,511 from a campaign and $850,000 from a New York State grant—to buy the property where Wardenclyffe Tower once stood and eventually turn it into a museum.[230][231] The group began negotiations to purchase the Long Island property from Agfa Corporation in October 2012.[232] The purchase was completed in May 2013.[233]
- A commemorative plaque honoring Nikola Tesla was installed on the façade of the New Yorker Hotel by the IEEE.[234]
Gallery
-
Tesla's passport from 1883
-
Tesla's grades at the Higher Real Gymnasium for the years 1872-3.[235]
-
Copy of the induction motor (two phases) from 1887. The original Tesla's induction motor from 1887 is today exposed in Imperial College London.[236]
-
Cross-section of asynchronous motor built on Tesla′s principles.
-
Three-phase system with rotating magnetic fields.
-
Induction motor with an egg shaped rotor, popularly called Colombo's eggs. Shown at the Exhibition on 1893 (the rotating magnetic field)
-
Polyphase system. Model shows example of generation, transmission and utilization of electrical energy.
-
Model of boat on remote control.
-
Telecommand of model boat.
-
Tesla's magnifying transmitter in Colorado Springs. c. 3 July 1899
-
Means for long conductors of electricity forming part of an electric circuit and electrically connecting said ionized beam to an electric circuit. Hettinger 1917—(U.S. patent 1,309,031)
-
U.S. patent 454,622—System of Electric Lighting: Apparatus devised for the purpose of converting and supplying electrical energy in a form suited for the production of certain novel electrical phenomena; Used later as a practical RF power supply.
-
U.S. patent 512,340: Coil for Electro-Magnets; Example of one of the first bifilar coils.
-
Electrical conductor, U.S. patent 514,167; Early example of coaxial cable.
-
U.S. patent 567,818: Electrical Condenser; Examples of improved capacitors.
-
System of Transmission of Electrical Energy
-
U.S. patent 685,957: Utilization of Radiant Energy
-
Tesla's bladeless turbine—the Tesla turbine, Tesla's 100th American patent.
-
Tesla's bladeless turbine—the Tesla turbine, Tesla's 100th American patent.
-
Maček's telegram to Tesla (preserved in the Technical Museum in Zagreb, Croatia)
-
Tesla's telegram to Maček (preserved in the Technical Museum in Zagreb, Croatia)
References
Notes
- ^ a b Jonnes 2004, p. 355
- ^ "Electrical pioneer Tesla honoured". BBC News. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
Replying to a telegram written to him by a Croatian, Tesla wrote that he was equally proud of his Serbian ethnicity and his Croatian birthplace; because at the time Serbia and Croatia were unified as a single kingdom.
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 318 "I am equally proud of my Serbian ethnicity and my Croatian birthplace"
- ^ Laplante, Phillip A. (1999). Comprehensive Dictionary of Electrical Engineering 1999. Springer. p. 635.
- ^ a b A Century of Innovation: Twenty Engineering Achievements That Transformed Our Lives. Joseph Henry Press. 2001. p. 70.
- ^ a b "Tesla Tower in Shoreham Long Island (1901–1917) meant to be the "World Wireless" Broadcasting system". Tesla Memorial Society of New York. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ O'Shei, Tim (2008). Marconi and Tesla: Pioneers of Radio Communication. MyReportLinks.com Books. p. 106. ISBN 978-1598450767.
- ^ Cheney, Uth & Glenn 1999, pp. 121, 154
- ^ Seifer 2001, p. 1942
- ^ Pickover 1999
- ^ Van Riper 2011
- ^ Van Riper 2011, p. 150
- ^ "Welcome to the Tesla Memorial Society of New York Website". Tesla Memorial Society of New York. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ a b "Pictures of Tesla's home in Smiljan, Croatia and his father's church after rebuilding". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- ^ "Tesla, Nikola". Encyclopædia Britannica. University of Pittsburgh. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 10
- ^ Cheney, Margaret. "TESLA: MAN OUT OF TIME". bookviewzine online publish of biography. Simon and Schuster, 2001. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ a b Seifer 2001, p. 7
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 12
- ^ Cheney, Uth & Glenn 1999, p. 3
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 32
- ^ "Tesla Life and Legacy – Tesla's Early Years". PBS. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 33
- ^ a b c d e f g h Tesla, Nikola. "My Inventions The Autobiography of Nikola Tesla". Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ Glenn, edited by Jim (1994). The complete patents of Nikola Tesla. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. ISBN 1566192668.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h Seifer 2001
- ^ a b c d O'Neill 2007
- ^ a b Seifer 2001, p. 18
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ a b "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ "Timeline of Nikola tesla". tesla memorial society of ny. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ Mrkich, D. (2003). Nikola Tesla : the european years (1st ed. ed.). Ottawa: Commoner's Publishing. ISBN 088970113X.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ "NYHOTEL". Tesla Society of NY. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla: The Genius Who Lit the World". Top Documentary Films.
- ^ "Coming to America". Public Broadcasting Service. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ Carey, Charles W. (1989). American inventors, entrepreneurs & business visionaries. Infobase Publishing. p. 337. ISBN 0-8160-4559-3. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ^ a b Cheney 2001, pp. 54–57
- ^ Jonnes 2004, p. 110
- ^ Pickover 1999, p. 14
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 64
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ a b c Jonnes 2004
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline, Year: 1887". Teslauniverse.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Networks of power: electrification in Western society, 1880–1930. JHU Press. p. 117.
- ^ "Timeline of Nikola Tesla". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ Robert Bud, Instruments of Science: An Historical Encyclopedia, page 204. Books.google.com. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ "Galileo Ferraris Physicist, Pioneer of Alternating Current Systems (1847–1897) Inventor of the Induction Motor "Father of three-phase current" – Electrotechnical Congress, Frankfurt 1891". Edison Tech Center. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ Vaclav Smil (14 July 2005). Creating the Twentieth Century:Technical Innovations of 1867–1914 and Their Lasting Impact. Oxford University Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-19-988341-7.
- ^ Fritz E. Froehlich; Allen Kent (1 December 1998). The Froehlich/Kent Encyclopedia of Telecommunications: Volume 17 – Television Technology. CRC Press. pp. 37–. ISBN 978-0-8247-2915-8. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- ^ Bill Drury, Control Techniques Drives and Controls Handbook, page xiv. Books.google.com. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ Alexander Suss Langsdorf, Theory of alternating-current machinery – 1955, page 245
- ^ Actes – Volume 1; Volume 10, 1964, page 427
- ^ The Encyclopedia Americana – Volume 19, 1977, page 518
- ^ Giovanni Dosi, David J. Teece, Josef Chytry, Understanding Industrial and Corporate Change, page 337. Books.google.com. 30 September 2004. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ Henry G. Prout, A Life of George Westinghouse, page 129
- ^ Michael Burgan, Nikola Tesla: Physicist, Inventor, Electrical Engineer, 2009, page 50
- ^ Fritz E. Froehlich, Allen Kent, The Froehlich/Kent Encyclopedia of Telecommunications: Volume 17, page 36. Books.google.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ a b John W. Klooster, Icons of Invention: The Makers of the Modern World from Gutenberg to Gates, page 305. Books.google.com. 30 July 2009. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Harris, William (14 July 2008). "William Harris, How did Nikola Tesla change the way we use energy?, page 3". Science.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Norrie, H. S., "Induction Coils: How to make, use, and repair them."Norman H. Schneider, 1907, New York. 4th edition.
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 174
- ^ Uth, Robert (12 December 2000). "Tesla coil". Tesla: Master of Lightning. PBS.org. Retrieved 20 May 2008.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ Krumme, Katherine (2000). "Mark Twain and Nikola Tesla: Thunder and Lightning" (PDF). University of California, Berkeley.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c Burgan, Michael (2009). Nikola Tesla : physicist, inventor, electrical engineer. Minneapolis, Minn.: Compass Point Books. ISBN 0756540860.
- ^ a b c "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ Kenneth L. Corum and James F. Corum, Ph.D. "Tesla's Connection to Columbia University *" (PDF). Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ a b Tesla, Nikola (1892). Experiments with alternate currents of high potential and high frequency. p. 58. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ David J. Bertuca, Donald K. Hartman, Susan M. Neumeister, The World's Columbian Exposition: A Centennial Bibliographic Guide, page xxi. Books.google.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 76
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 79
- ^ Barrett, John Patrick (1894). Electricity at the Columbian Exposition; Including an Account of the Exhibits in the Electricity Building, the Power Plant in Machinery Hall. pp. 268–269. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ^ "Tesla's Egg of Columbus How Tesla Performed the Feat of Columbus Without Cracking the Egg". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ Thomas Parke Hughes, Networks of power: electrification in Western society, 1880–1930 (1983), page 119
- ^ Hans Camenzind, Much Ado About Almost Nothing: Man's Encounter With the Electron, (2007), page 107
- ^ Seifer 2001, p. 190
- ^ Cheney 2001, pp. 73–4
- ^ Maja Hrabak et al., "Nikola Tesla and the Discovery of X-rays," in RadioGraphics, vol. 28, July 2008, 1189–92. Retrieved 26 August 2012
- ^ P. K. Chadda, Hydroenergy and Its Energy Potential. Books.google.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 134
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ South, Nanette (23 July 2011). "Nikola Tesla – Radiography Experiments – Clips from the "The Constitution, Atlanta, Georgia, page 9. Friday, March 13, 1896"". Anengineersaspect.blogspot.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ N. Tesla, "High Frequency Oscillators for Electro-Therapeutic and Other Purposes", in Proceedings of the American Electro-Therapeutic Association, American Electro-Therapeutic Association. Page 25.
- ^ Griffiths, David J. Introduction to Electrodynamics, ISBN 0-13-805326-X and Jackson, John D. Classical Electrodynamics, ISBN 0-471-30932-X.
- ^ Anonymous (1899). Transactions of the American Electro-therapeutic Association. p. 16. Retrieved 25 November 2010.
- ^ a b c editor, Leland Anderson, (1998). Nikola Tesla's teleforce & telegeodynamics proposals. Breckenridge, Colo.: Twenty First Century Books. ISBN 0963601288.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Orton, John (2004). The Story of Semiconductors. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. p. 53. – via Questia (subscription required)
- ^ "The Beautiful New York City where Tesla spent 60 years of his life". Tesla Society of NY. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ^ Eger, Christopher (1 April 2007) "The Robot Boat of Nikola Tesla: The Beginnings of the UUV and remote control weapons"
- ^ P. W. Singer, Wired for War: The Robotics Revolution and Conflict in the Twenty-First Century – Robots Go To War. Books.google.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ a b Jean-Michel Redouté, Michiel Steyaert, EMC of Analog Integrated Circuits, page 3. Books.google.com. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ Robert Sobot, Wireless Communication Electronics:Introduction to RF Circuits and Design Techniques, page 4. Books.google.com. 18 February 2012. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ According to the Tesla memorial marker in Memorial park on Pikes Peak Ave.
- ^ Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony, and Transmission of Power, Leland I. Anderson, 21st Century Books, 2002, p. 109, ISBN 1-893817-01-6.
- ^ Corum, K. L., J. F. Corum, and A. H. Aidinejad, "Atmospheric Fields, Tesla's Receivers and Regenerative Detectors." 1994.
- ^ Corum, K. L., J. F. Corum, "Nikola Tesla, Lightning Observations, and Stationary Waves." 1994.
- ^ Tesla, Nikola, "The True Wireless." Electrical Experimenter, May 1919. (also at pbs.org)
- ^ Valone, Thomas, Harnessing the Wheelwork of Nature. ISBN 1-931882-04-5
- ^ Ouellette, Jennifer. "LIGHTNING FLASHES ON ORIGIN OF SOLAR SYSTEM". Discovery News. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ Gillispie, Charles Coulston, "Dictionary of Scientific Biography;" Tesla, Nikola. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York. ISBN
- ^ Childress 1993
- ^ SECOR, H. WINFIELD (1917). "TESLA'S VIEWS ON ELECTRICITY AND THE WAR". The Electrical Experimenter. Retrieved 9 September 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Nikola Tesla and the Planetary Radio Signals" (PDF). Retrieved 9 September 2012.
{{cite web}}:|first=missing|last=(help); External link in|first= - ^ Corum, Kenneth L. (1996). Nikola Tesla and the electrical signals of planetary origin. p. 14. OCLC 68193760.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Seifer, Marc. "Nikola Tesla: The Lost Wizard". ExtraOrdinary Technology (Volume 4, Issue 1; Jan/Feb/Mar 2006). Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Seifer 2001, p. 542
- ^ a b c d e Broad, William J (4 May 2009). "A Battle to Preserve a Visionary's Bold Failure". New York Times. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "Timeline". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, pp. 162–164
- ^ a b c Page, R.M., "The Early History of RADAR," Proceedings of the IRE, Volume 50, Number 5, May 1962, (special 50th Anniversary Issue).
- ^ See U.S. Blows Up Tesla Radio Tower (1917) (citing page 293 of the September 1917 issue of The Electrical Experimenter): "SUSPECTING that German spies were using the big wireless tower erected at Shoreham, L. I., about twenty years ago by Nikola Tesla, the Federal Government ordered the tower destroyed and it was recently demolished with dynamite."
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1915". nobelprize.org. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d Cheney 2001, p. 245
- ^ Cheney, Uth & Glenn 1999, p. 120
- ^ Research, Health (1996-09). Nikola Tesla Research. p. 9. ISBN 0-7873-0404-2. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Seifer 2001, pp. 378–380
- ^ "Distinguished Scientists (Einstein, Tesla, Langmuir, Steinmetz, etc.) on a Tour of the Wireless Station, Somerset, NJ (1921)". Franklin Township Public Library. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ^ Tesla, Nikola. "TESLA PATENT 1,655,114 APPARATUS FOR AERIAL TRANSPORTATION". UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "A.J.S. RAYL Air & Space magazine, September 2006, reprint at History of Flight". airspacemag.com. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Cheney, Uth & Glenn 1999, p. 149
- ^ Jonnes 2004, p. 365
- ^ a b Seifer 2001, p. 435
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ^ "Tesla's Ray". Time. 23 July 1934.
- ^ a b c Seifer, Marc. "Tesla's "Death Ray" Machine". bibliotecapleyades.net. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla, at 78, Bares New 'Death-Beam'". New York Times. 11 July 1934.
- ^ "Tesla Invents Peace Ray". New York Sun. 10 July 1934.
- ^ "Beam to Kill Army at 200 Miles, Tesla's Claim on 78th Birthday". New York Times. 11 July 1934.
- ^ "'Death Ray' for Planes". New York Times. 22 September 1940.
- ^ "Death-Ray Machine Described". New York Sun. 11 July 1934.
- ^ "A Machine to End War." Feb. 1935.
- ^ "United States Patent Office Nikola Tesla,of New York, N.Y. VALVULAR CONDUIT Specification of Letters Patent Patented Feb. 3, 1920 Numbered 1.329.559 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE Patent No. 1,329,559
- ^ "TESLA, AT 78, BARES NEW 'DEATH-BEAM'". New York Times. 1934. Retrieved 29 June 2012. same article at rastko.rs
- ^ a b Seifer 2001, p. 454
- ^ "Aerial Defense 'Death-Beam' Offered to U.S. By Tesla" 12 July 1940
- ^ Seifer, Marc J. "Tesla's "death ray" machine". Retrieved 5 September 2012.
- ^ O'Neill, John J. "Tesla Tries To Prevent World War II (unpublished Chapter 34 of Prodigal Genius)". PBS.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla No Money Wizard; Swamped By Debt, He Vows". NewYorkWorld. 18 March 1916. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^ Michaels, Daniel. "Long-Dead Inventor Nikola Tesla Is Electrifying Hip Techies". TheWallStreetJournal. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^ "Among Technophiles, Tesla In and Edison Out". FoxNews. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^ Frum, Larry. "Backers raise cash for Tesla museum honoring 'cult hero'". CNN. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". July, 30th: Tesla's American Citizenship Tesla becomes an American citizen. Tesla Universe. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- ^ "The Missing Papers". PBS. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ Childress 1993, p. 249
- ^ "Urn with Tesla's ashes". Tesla Museum. Retrieved 16 September 2012.
- ^ a b Šarboh, Snežana (18–20 October 2006). "Nikola Tesla's Patents" (PDF). Sixth International Symposium Nikola Tesla. Belgrade, Serbia. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 October 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ^ Cheney, 62
- ^ O'Neill 2007, pp. 283, 286
- ^ a b c Seifer 2001, p. 413
- ^ a b Brisbane, Arthur (22 July 1894.). "OUR FOREMOST ELECTRICIAN". The World.
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 238
- ^ "About Nikola Tesla". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Life and Legacy – Poet and Visionary". PBS. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Quotes". Tesla universe. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ [About Nikola Tesla "About Nikola Tesla"]. Tesla Society of USA and Canada. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ GITELMAN, LISA. "Reconciling the Visionary with the Inventor Wizard: The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla". technology review (MIT). Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 292
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 289
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 327
- ^ a b c d Cheney 2001, p. 33
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 282
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 46
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 43
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 301
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 208
- ^ Mast, Amy. "America's forgotten innovator, Nikola Tesla" (PDF). Florida State University: 14–15.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Gregory Malanowski (2011). The Race for Wireless: How Radio was Invented (or Discovered?). AuthorHouse. p. 36. ISBN 9781463437503.
Tesla was definitely asocial, a loner. Although in his younger years he was immensely popular and admired by many rich, socialite women, there were no women in his life.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Cheney, Uth & Glenn 1999, p. Preface
- ^ Jonnes 2004 "A loner by nature, unattached to the power and prestige of a great university or a major corporation, Tesla was at a total disadvantage"
- ^ Tom McNichol (2011). AC/DC: The Savage Tale of the First Standards War. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 163–164. ISBN 9781118047026.
Tesla's peculiar nature made him a solitary man, a loner in a field that was becoming so complex that it demanded collaboration.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b "Famous Friends". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Stanford White". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "KENNETH M. SWEZEY PAPERS, 1891–1982 #47". National Museum of American History. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Tribute to Nikola Tesla". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla at Wardenclyffe". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla: The patron saint of geeks?". BBC News Magazine. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ JOHNSON, NEIL M. George Sylvester Viereck: Poet and Propagandist. NEIL M. JOHNSON.
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 110
- ^ Thomas Edison: Life of an Electrifying Man. Biographiq. 2008. p. 23. ISBN 1-59986-216-6. Retrieved 25 November 2010.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Thomas Valone, Harnessing the Wheelwork of Nature: Tesla's Science of Energy, Adventures Unlimited Press, 2002, Page 181. Books.google.com. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ O'Neill 2007, p. 249
- ^ "The Profit of Science Looks Into The Future," Popular Science Nov 1928, page 171. Books.google.com. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ Seifer 2001, p. 1745
- ^ a b O'Neill 2007, p. 247
- ^ New York Herald Tribune, 11 September 1932
- ^ "Nikola Tesla". FamousScientists.org. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ^ Prepared Statement by Nikola Tesla downloadable from www.tesla.hu
- ^ Cheney 2001, p. 309
- ^ "A Machine to End War". Public Broadcasting Service. February 1937. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Kennedy, John B., "When woman is boss, An interview with Nikola Tesla." Colliers, 30 January 1926.
- ^ Tesla, Nikola. "Science and Discovery are the great Forces which will lead to the Consummation of the War". rastko. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ a b c Nikola Tesla (February 1937). "A Machine to End War". PBS.org. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Tesla, Nikola. "THE PROBLEM OF INCREASING HUMAN ENERGY". Century Illustrated Magazine. Retrieved 15 August 2012.
- ^ Nikola Tesla (11 September 1932). Lawrence R. Spencer (ed.). Alien Interview. New York Herald Tribune. p. 303. ISBN 9780615204604.
It might as well be said that God has properties. He has not, but only attributes and these are of our own making.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - ^ Orrin Elmer Dunlap (1944). Radio's 100 men of science: biographical narratives of pathfinders in electronics and television (2 ed.). Harper & Brothers. pp. 122–123.
In one of his last interviews with this author, Tesla in his eighties still dreamed of power transmission by radio. ..."Religion is simply an ideal" [Tesla remarked]. "It is an ideal force that tends to free the human being from material bonds. I do not believe that matter and energy are interchangeable, any more than are the body and soul. There is just so much matter in the universe and it cannot be destroyed. As I see life on this planet, there is no individuality. It may sound ridiculous to say so, but I believe each person is but a wave passing through space, ever-changing from minute to minute as it travels along, finally, some day, just becoming dissolved."
- ^ Nikola Tesla. FECHA. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla Bibliography". 21st Century Books. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla Information Resource". 21st Century Books. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ "Selected Tesla writings". 21st Century Books. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ Works by Nikola Tesla at Project Gutenberg
- ^ Tesla, Nikola (1900). "The Problem of Increasing Human Energy". The Century Magazine. 60 (n.s. v. 38) (1900 May–Oct): 175. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ "THE PROBLEM OF INCREASING HUMAN ENERGY". Twenty-First Century Books. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ Tesla, Nikola. "The Project Gutenberg eBook, Experiments with Alternate Currents of High Potential and High Frequency, by Nikola Tesla". Project Gutenberg. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ Tesla, Nikola. "EXPERIMENTS WITH ALTERNATE CURRENTS OF HIGH POTENTIAL AND HIGH FREQUENCY". Twenty-First Century Books. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla | 20 July 1931". TIME. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ^ "Time front cover, Vol XVIII, No. 3, 20 July 1931". Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Seifer 2001, p. 464
- ^ a b Schmadel, Lutz D. (2003). Dictionary of minor planet names. Springer. p. 183. ISBN 3-540-00238-3. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ "Why the Name "Tesla?"". Tesla Motors. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 10 June 2008.
- ^ "Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport". airport-desk.com. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ^ Vujovic, Dr. Ljubo. "Tesla Biography NIKOLA TESLA THE GENIUS WHO LIT THE WORLD". Tesla Memorial Society of New York. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- ^ "Memory of the World | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization". Unesco.org. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ http://www.teslasociety.com/archive.htm
- ^ "Nikola Tesla Memorial Centre". MCNikolaTesla.hr. Nikola Tesla Memorial Centre. Retrieved 27 May 2011.
- ^ "Memorijalni centar "Nikola Tesla" u Smiljanu". Gospic.hr (in Croatian). City of Gospić. Retrieved 27 May 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "Tesla Timeline". Tesla Universe. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ "Weekly Bulletin" (PDF). Embassy of the Republic of Croatia. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ "Tmsusa". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ "Niagara Falls". Tesla Memorial Society of NY. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ "Tesla Honored With Niagara Falls Momument" (PDF). IEEE Canada. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
{{cite web}}:|first=missing|last=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Frum, Larry (21 August 2012). "Backers raise cash for Tesla museum honoring 'cult hero'". CNN. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ^ "Let's Build a Goddamn Tesla Museum". indiegogo. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ^ Broad, William (5 October 2012). "Group Buying Long Island Estate for Tesla Memorial". New York Times. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ Rodriguez, Salvador (9 May 2013). "Web campaign to build a Tesla museum succeeds in purchasing lab". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ "A hotel's unique direct current (dc) system". IEEE. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla". GIMNAZIJA KARLOVAC. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
{{cite web}}:|first=missing|last=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ http://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/objects/electricity_supply/1927-157.aspx
Sources
Books
- Seifer, Marc J (2001). Wizard: the life and times of Nikola Tesla : biography of a genius. Citadel. ISBN 0-8065-1960-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - O'Neill, John J (2007). Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla. Book Tree. ISBN 1-60206-743-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Cheney, Margaret (2001) [1981]. Tesla: Man Out of Time. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-1536-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Cheney, Margaret; Uth, Robert; Glenn, Jim (1999). Tesla, Master of Lightning. Barnes & Noble Books. ISBN 0-7607-1005-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Pickover, Clifford A. (1999). Strange Brains and Genius: The Secret Lives Of Eccentric Scientists And Madmen. HarperCollins.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Childress, David (1993). The fantastic inventions of Nikola Tesla. Adventures Unlimited Press. ISBN 9780932813190.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Jonnes, Jill (2004). Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the World. Random House Trade Paperbacks. ISBN 0-375-75884-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Bock-Luna, Birgit (2007). The past in exile: Serbian long-distance nationalism and identity in the wake of the Third Balkan War. LIT Verlag Münster. ISBN 9783825897529.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Van Riper, A. Bowdoin (2011). A Biographical Encyclopedia of Scientists and Inventors in American Film and TV since 1930. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9780810881280.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
Others
- Lomas, Robert, The Man who Invented the Twentieth Century. Lecture to South Western Branch of Instititute of Physics.
- Martin, Thomas Commerford, The Inventions, Researches, and Writings of Nikola Tesla, New York: The Electrical Engineer, 1894 (3rd Ed.); reprinted by Barnes & Noble, 1995 ISBN-X
- Penner, John R.H. The Strange Life of Nikola Tesla, corrupted version of "My Inventions."
- Pratt, H., Nikola Tesla 1856–1943, Proceedings of the IRE, Vol. 44, September 1956.
- Weisstein, Eric W., Tesla, Nikola (1856–1943). Eric Weisstein's World of Science.
- Dimitrijevic, Milan S., Belgrade Astronomical Observatory Historical Review. Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade, 162–170. Also, Srpski asteroidi, Tesla. Astronomski magazine.
- Roguin, Ariel, Historical Note: Nikola Tesla: The man behind the magnetic field unit. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004;19:369–374. 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
- Sellon, J. L., The impact of Nikola Tesla on the cement industry. Behrent Eng. Co., Wheat Ridge, Colorado. Cement Industry Technical Conference. 1997. XXXIX Conference Record., 1997 IEEE/PC. Page(s) 125–133. ISBN
- Valentinuzzi, M.E., Nikola Tesla: why was he so much resisted and forgotten? Inst. de Bioingenieria, Univ. Nacional de Tucuman; Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE. July/August 1998, 17:4, pp. 74–75. ISSN
- Secor, H. Winfield, Tesla's views on Electricity and the War, Electrical Experimenter, Volume 5, Number 4, August 1917.
- Florey, Glen, Tesla and the Military. Engineering 24, 5 December 2000.
- Corum, K. L., J. F. Corum, Nikola Tesla, Lightning Observations, and Stationary Waves. 1994.
- Corum, K. L., J. F. Corum, and A. H. Aidinejad, Atmospheric Fields, Tesla's Receivers and Regenerative Detectors. 1994.
- Meyl, Konstantin, H. Weidner, E. Zentgraf, T. Senkel, T. Junker, and P. Winkels, Experiments to proof the evidence of scalar waves Tests with a Tesla reproduction. Institut für Gravitationsforschung (IGF), Am Heerbach 5, D-63857 Waldaschaff.
- Anderson, L. I., John Stone Stone on Nikola Tesla's Priority in Radio and Continuous Wave Radiofrequency Apparatus. The AWA Review, Vol. 1, 1986, pp. 18–41.
- Anderson, L. I., Priority in Invention of Radio, Tesla v. Marconi. Antique Wireless Association monograph, March 1980.
- Marincic, A., and D. Budimir, Tesla's contribution to radiowave propagation. Dept. of Electron. Eng., Belgrade Univ. (5th International Conference on Telecommunications in Modern Satellite, Cable and Broadcasting Service, 2001. TELSIKS 2001. pp. 327–331 vol.1) ISBN-X
- Page, R.M., The Early History of Radar, Proceedings of the IRE, Volume 50, Number 5, May 1962, (special 50th Anniversary Issue).
- C Mackechnie Jarvis Nikola Tesla and the induction motor. 1970 Phys. Educ. 5 280–287.
- Giant Eye to See Round the World (DOC)
Further reading
Books
- Tesla, Nikola, "My Inventions" Parts I through V published in the Electrical Experimenter monthly magazine from February through June 1919. Part VI published October 1919. Reprint edition with introductory notes by Ben Johnson, New York: Barnes and Noble,1982, ISBN; also online at Lucid Cafe, et cetera as My Inventions: The Autobiography of Nikola Tesla, 1919. ISBN
- Martin, Thomas C., The Inventions, Researches, and Writings of Nikola Tesla, 1894 . ISBN-X
- Auster, Paul, Moon Palace, 1989. Tells Tesla's story within the history of the United States.
- Lomas, Robert, The Man Who Invented the Twentieth Century: Nikola Tesla, forgotten genius of electricity, 1999. ISBN
- Childress, David H., The Fantastic Inventions of Nikola Tesla, 1993. ISBN
- Glenn, Jim, The Complete Patents of Nikola Tesla, 1994. ISBN
- Trinkaus, George TESLA: The Lost Inventions, High Voltage Press, 2002. ISBN 0-9709618-2-0
- Valone, Thomas, Harnessing the Wheelwork of Nature: Tesla's Science of Energy, 2002. ISBN
- McNichol, Tom, AC/DC The Savage Tale of the First Standards War, Jossey-Bass 2006 ISBN 0-7879-8267-9
Publications
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers, American Institute of Electrical Engineers, May 1888.
- Selected Tesla Writings, Scientific papers and articles written by Tesla and others, spanning the years 1888–1940.
- Light Without Heat, The Manufacturer and Builder, January 1892, Vol. 24
- Biography: Nikola Tesla, The Century Magazine, November 1893, Vol. 47
- Tesla's Oscillator and Other Inventions, The Century Magazine, November 1894, Vol. 49
- The New Telegraphy. Recent Experiments in Telegraphy with Sparks, The Century Magazine, November 1897, Vol. 55
Journals
- Carlson, W. Bernard, "Inventor of dreams." Scientific American, March 2005 Vol. 292 Issue 3 p. 78(7).
- Jatras, Stella L., "The genius of Nikola Tesla." The New American, 28 July 2003 Vol. 19 Issue 15 p. 9(1)
- Rybak, James P., "Nikola Tesla: Scientific Savant." Popular Electronics, 1042170X, November 1999, Vol. 16, Issue 11.
- Lawren, B., "Rediscovering Tesla." Omni, March 1988, Vol. 10 Issue 6.
Video
- Nikola Tesla – 1977 ten-episode TV series featuring Rade Šerbedžija as Tesla.
- Tajna Nikole Tesle (The Secret of Nikola Tesla)' – 1980 Documentary directed by Krsto Papić, featuring Petar Božović as Tesla and Orson Welles as J.P. Morgan
- Tesla: Master of Lightning – 2003 Documentary by Robert Uth, featuring Stacy Keach as the voice of Tesla.
External links
- The Nikola Tesla Museum
- Original Tesla's patents presented in documentary movie by Museum Nikola Tesla
- Tesla Resource Surrounding the PBS "Master of Lightning" documentary
- World of Scientific Biography: Nikola Tesla, by Wolfram Research
- Nikola Tesla Page
- Tesla's grand-nephew William H. Terbo's site
- Nikola Tesla, Forgotten American Scientist
- Online archive of many of Tesla's writings, articles and published papers
- Seifer, Marc J., and Michael Behar, Electric Mind, Wired Magazine, October 1998.
- Works by Nikola Tesla at Project Gutenberg
- Nikola Tesla's FBI file in pdf
- Kenneth M. Swezey Papers, 1891–1982, Archives Center, National Museum of American History, archival resources.
- Tesla Wardenclyffe Project, Long Island New York. Mission is the adaptive reuse of the Wardenclyffe laboratory building.
- The Case Files of Nikola Tesla, Franklin Institute
- Booknotes interview with Jill Jonnes on Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse and the Race to Electrify the World, 26 October 2003.
- TED Talk On Tesla
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
- Use dmy dates from November 2012
- Nikola Tesla
- 1856 births
- 1943 deaths
- American Buddhists
- American electrical engineers
- American inventors
- American mechanical engineers
- American people of Serbian descent
- American physicists
- Austro-Hungarian emigrants to the United States
- Cardiovascular disease deaths in New York
- Deaths from heart failure
- Eastern Orthodox Christians from the United States
- Electrical engineers
- Elliott Cresson Medal recipients
- Fellow Members of the IEEE
- Fellows of the American Association for the Advancement of Science
- IEEE Edison Medal recipients
- Members of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts
- Recipients of the Order of Prince Danilo I
- Recipients of the Order of St. Sava
- Recipients of the Order of The Yugoslav Crown
- Grand Crosses of the Order of the White Eagle (Serbia)
- People associated with electricity
- People from Colorado Springs, Colorado
- People from Gospić
- People from Karlovac
- People with eidetic memory
- Radio pioneers
- Serbian emigrants to the United States
- Serbian engineers
- Serbian inventors
- Serbian Orthodox Christians
- Serbian physicists
- Serbs of Croatia
- Wireless energy transfer




![Tesla's grades at the Higher Real Gymnasium for the years 1872-3.[235]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/0/08/Teslasgradelarge.png/120px-Teslasgradelarge.png)
![Copy of the induction motor (two phases) from 1887. The original Tesla's induction motor from 1887 is today exposed in Imperial College London.[236]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fa/Moteur_%C3%A0_induction.jpg/120px-Moteur_%C3%A0_induction.jpg)