Cologne: Difference between revisions
Atethnekos (talk | contribs) fix |
|||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
|Jul record high C = 37.2 |
|Jul record high C = 37.2 |
||
|Aug record high C = 38.8 |
|Aug record high C = 38.8 |
||
|Sep record high C = |
|Sep record high C =loko[kl,huOct record high C = 27.6 |
||
|Oct record high C = 27.6 |
|||
|Nov record high C = 18.7 |
|Nov record high C = 18.7 |
||
|Dec record high C = 16.6 |
|Dec record high C = 16.6 |
||
Revision as of 01:20, 3 December 2013
It has been suggested that Free Imperial City of Cologne be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since September 2013. |
Cologne
Köln | |
|---|---|
 From top left to bottom: Hohenzollern Bridge by night, Great St. Martin Church, Colonius TV-tower, Cologne Cathedral, Kranhaus buildings in Rheinauhafen, MediaPark, people celebrating Cologne Carnival, and Kölnarena. | |
|
| |
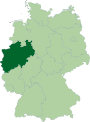
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Cologne |
| District | Urban districts of Germany |
| Founded | 38 BC |
| Government | |
| • Lord Mayor | Jürgen Roters (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 405.15 km2 (156.43 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 37 m (121 ft) |
| Population (2023-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 1,087,353 |
| • Density | 2,700/km2 (7,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 50441–51149 |
| Dialling codes | 0221, 02203 (Porz) |
| Vehicle registration | K |
| Website | www.stadt-koeln.de |
Cologne (English: /kəˈloʊn/, German: Köln [kœln] , Kölsch: Kölle [ˈkœɫə] ) is Germany's fourth-largest city (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Munich), and is the largest city both in the German Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.
Cologne is located on both sides of the Rhine River. The city's famous Cologne Cathedral (Kölner Dom) is the seat of the Catholic Archbishop of Cologne. The University of Cologne (Universität zu Köln) is one of Europe's oldest and largest universities.[2]
Cologne was founded and established in the first century AD, as the Roman Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium in Ubii territory.[3] It was the capital of the Roman province of Germania Inferior and the headquarters of the military in the region until occupied by the Franks in 462. During the Middle Ages it flourished as one of the most important major trade routes between east and west in Europe. Cologne was one of the leading members of the Hanseatic League and one of the largest cities north of the Alps in medieval and renaissance times. Up until World War II the city had undergone several other occupations by the French and also the British. Cologne was one of the most heavily bombed cities in Germany during World War II. The bombing reduced the population by 95% and destroyed almost the entire city. With the intention of restoring as many historic buildings as possible, the rebuilding has resulted in a very mixed and unique cityscape.
Cologne is a major cultural center of the Rhineland; it is home to more than thirty museums and hundreds of galleries. Exhibitions range from local ancient Roman archeological sites to contemporary graphics and sculpture. The Cologne Trade Fair hosts a number of trade shows such as Art Cologne, imm Cologne, Gamescom, and the Photokina.
History
Roman Cologne
The first urban settlement on the grounds of modern-day Cologne was Oppidum Ubiorum, founded in 38 BC by the Ubii, a Cisrhenian Germanic tribe. In 50 AD, the Romans founded Colonia on the Rhine[3] and the city became the provincial capital of Germania Inferior in 85 AD.[4] The city was named "Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium" in 50 AD.[4] Considerable Roman remains can be found in present-day Cologne, especially near the wharf area, where a notable discovery of a 1900-year-old Roman boat was made in late 2007.[5] From 260 to 271 Cologne was the capital of the Gallic Empire under Postumus, Marius, and Victorinus. In 310 under Constantine a bridge was built over the Rhine at Cologne. Roman imperial governors resided in the city and it became one of the most important trade and production centers in the Roman Empire north of the Alps.[3]
Maternus, who was elected as bishop in 313, was the first known bishop of Cologne. The city was the capital of a Roman province until occupied by the Ripuarian Franks in 462. Parts of the original Roman sewers are preserved underneath the city, with the new sewerage system having opening in 1890.
Middle Ages
Early medieval Cologne was part of Austrasia within the Frankish Empire. Cologne had been the seat of a bishop since the Roman period; under Charlemagne, in 795, bishop Hildebold was promoted to archbishop.[3]
In 953, the archbishops of Cologne first gained noteworthy secular power, when bishop Bruno was appointed as duke by his brother Emperor Otto I. In order to weaken the secular nobility, who threatened his power, Otto endowed Bruno and his successors on the bishop's see with the prerogatives of secular princes, thus establishing the Electorate of Cologne, formed by the temporal possessions of the archbishopric and included in the end a strip of territory along the left Bank of the Rhine east of Jülich, as well as the Duchy of Westphalia on the other side of the Rhine, beyond Berg and Mark. By the end of the 12th century, the Archbishop of Cologne was one of the seven electors of the Holy Roman Emperor. Besides being prince elector, he was Arch-chancellor of Italy as well, technically from 1238 and permanently from 1263 until 1803.
Following the Battle of Worringen in 1288, Cologne gained its independence from the archbishops and became a Free City. Archbishop Sigfried II von Westerburg was forced into exile in Bonn.[6] The archbishop nevertheless preserved the right of capital punishment. Thus the municipal council (though in strict political opposition towards the archbishop) depended upon him in all matters concerning criminal justice. This included torture, which sentence was only allowed to be handed down by the episcopal judge, the so-called "Greve". This legal situation lasted until the French conquest of Cologne.[citation needed]
Besides its economic and political significance Cologne also became an important center of medieval pilgrimage, when Cologne's Archbishop Rainald of Dassel gave the relics of the Three Wise Men to Cologne's cathedral in 1164 (after they in fact had been captured from Milan). Besides the three magi Cologne preserves the relics of Saint Ursula and Albertus Magnus.[7]
Cologne's location on the river Rhine placed it at the intersection of the major trade routes between east and west and was the basis of Cologne's growth. Cologne was a member of the Hanseatic League in 1475, when Frederick III confirmed the city's imperial immediacy.[3]

Early modern history
The economic structures of medieval and early modern Cologne were characterized by the city's status as a major harbour and transport hub upon the Rhine. Craftsmanship was organized by self-administering guilds, some of which were exclusive to women.
As a free city Cologne was a sovereign state within the Holy Roman Empire and as such had the right (and obligation) to maintain its own military force. Wearing a red uniform these troops were known as the Rote Funken (red sparks). These soldiers were part of the Army of the Holy Roman Empire ("Reichskontingent") and fought in the wars of the 17th and 18th century, including the wars against revolutionary France, when the small force was almost completely wiped out in combat. The tradition of these troops is preserved as a military persiflage by Cologne's most outstanding carnival society, the Rote Funken.[8]
The free city of Cologne must not be confused with the Archbishopric of Cologne which was a state of its own within the Holy Roman Empire. Since the second half of the 16th century the archbishops were taken from the Bavarian dynasty Wittelsbach. Due to the free status of Cologne, the archbishops were usually not allowed to enter the city. Thus they took up residence in Bonn and later in Brühl on the Rhine. As members of an influential and powerful family and supported by their outstanding status as electors, the archbishops of Cologne repeatedly challenged and threatened the free status of Cologne during the 17th and 18th century, resulting in complicated affairs, which were handled by diplomatic means and propaganda as well as by the supreme courts of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 19th century until World War II
Cologne lost its status as a free city during the French period. According to the Peace Treaty of Lunéville (1801) all the territories of the Holy Roman Empire on the left bank of the Rhine were officially incorporated into the French Republic (which had already occupied Cologne in 1794). Thus this region later became part of Napoleon's Empire. Cologne was part of the French Département Roer (named after the River Roer, German: Rur) with Aachen (French: Aix-la-Chapelle) as its capital. The French modernized public life, for example by introducing the Napoleonic code and removing the old elites from power. The Napoleonic code remained in use on the left bank of the Rhine until 1900, when a unified civil code (the Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch) was introduced in the German Empire. In 1815 at the Congress of Vienna, Cologne was made part of the Kingdom of Prussia, first in the Jülich-Cleves-Berg province and then the Rhine province.
The permanent tensions between the Roman Catholic Rhineland and the overwhelmingly Protestant Prussian state repeatedly escalated with Cologne being in the focus of the conflict. In 1837 the archbishop of Cologne, Clemens August von Droste-Vischering, was arrested and imprisoned for two years after a dispute over the legal status of marriages between Protestants and Roman Catholics (Mischehenstreit). In 1874, during the Kulturkampf, Archbishop Paul Melchers was imprisoned before taking refuge in the Netherlands. These conflicts alienated the Catholic population from Berlin and contributed to a deeply felt anti-Prussian resentment, which was still significant after World War II, when the former mayor of Cologne, Konrad Adenauer, became the first West German chancellor.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, Cologne absorbed numerous surrounding towns, and by World War I had already grown to 700,000 inhabitants. Industrialization changed the city and spurred its growth. Vehicle and engine manufacturing were especially successful, though heavy industry was less ubiquitous than in the Ruhr area. The cathedral, started in 1248 but abandoned around 1560, was eventually finished in 1880 not just as a place of worship but also as a German national monument celebrating the newly founded German empire and the continuity of the German nation since the Middle Ages. Some of this urban growth occurred at the expense of the city's historic heritage with much being demolished (for example, the city walls or the area around the cathedral) and sometimes replaced by present-day buildings.
Cologne was designated as one of the Fortresses of the German Confederation.[9] It was turned into a heavily armed fortress (opposing the French and Belgian fortresses of Verdun and Liège) with two fortified belts surrounding the city, the remains of which can be seen to this day.[10] The military demands on what became Germany's largest fortress presented a significant obstacle to urban development, with forts, bunkers, and wide defensive dugouts completely encircling the city and preventing expansion; this resulted in a very dense built-up area within the city itself.
During World War I Cologne was the target of several but minor air raids and survived the hostilities without significant damage. Until 1926 Cologne was occupied by the British Army of the Rhine under the terms of the armistice and the subsequent Versailles Peace Treaty.[11] Contrary to the harsh measures taken by French occupation troops, the British acted with more tact towards the local population. The mayor of Cologne from 1917 until 1933 and future West German chancellor Konrad Adenauer acknowledged the political impact of this approach, especially that the British had opposed French plans for a permanent Allied occupation of the Rhineland.
As part of the de-militarization of the Rhineland the fortifications had to be dismantled. This was taken as an opportunity to create two green belts (Grüngürtel) around the city by converting the fortifications and their clear fields of fire into large public parks. However, this project was not completed until 1933. In 1919 the University of Cologne, closed by the French in 1798, was refounded. This re-foundation was considered a replacement for the loss of the German University of Strasbourg, which reverted to France with the rest of Alsace. Cologne prospered during the Weimar Republic (1919–33) and progress was made especially with respect to public governance, city planning, housing and social affairs. Social housing projects were considered exemplary and copied by other German cities. As Cologne competed for hosting the Olympics a modern sports stadium was erected at Müngersdorf. When the British occupation ended, the prohibition of civil aviation was removed and Cologne Butzweilerhof Airport soon became a hub for national and international air traffic—second in Germany only to Berlin Tempelhof Airport.
The democratic parties lost the local elections in Cologne in March 1933 to the Nazi Party and other right wing parties. Thereafter Communist as well as Social Democrats members of the city assembly were imprisoned and Mayor Adenauer was dismissed by the new holders of power. However, compared to other major cities, the Nazis never gained decisive support in Cologne (significantly, the number of votes cast for the Nazi Party in Reichstag elections had always been the national average.[12][13] By 1939 the population had risen to 772,221 inhabitants.
World War II

During World War II, Cologne was a Military Area Command Headquarters (Militärbereichshauptkommandoquartier) for the Military District (Wehrkreis) VI of Münster. Cologne was under the command of Lieutenant-General Freiherr Roeder von Diersburg, who was responsible for military operations in Bonn, Siegburg, Aachen, Jülich, Düren, and Monschau. Cologne was home to the 211th Infantry Regiment and the 26th Artillery Regiment.
During the Bombing of Cologne in World War II, Cologne endured 262 air raids[14] by the Western Allies, which caused approximately 20,000 civilian casualties and almost completely wiped out the center of the city. During the night of 31 May 1942, Cologne was the target of "Operation Millennium", the first 1,000 bomber raid by the Royal Air Force in World War II. 1,046 heavy bombers attacked their target with 1,455 tons of explosives, approximately two-thirds of which were incendiary.[15] This raid lasted about 75 minutes, destroyed 600 acres (243 ha) of built-up area, killed 486 civilians and made 59,000 people homeless. By the end of the war, the population of Cologne had been reduced by 95 percent. This loss was mainly caused by a massive evacuation of the people to more rural areas. The same happened in many other German cities in the last two years of war. By the end of 1945, however, the population had already recovered to approximately 500,000.
By the end of the war, essentially all of Cologne's pre-war Jewish population of 11,000 had been deported or killed by the Nazis.[16] The six synagogues of the city were destroyed. The synagogue on Roonstraße was rebuilt in 1959.[17]
Post-war Cologne until today

Despite Cologne's status as the largest city in the region, nearby Düsseldorf was chosen as the political capital of the federated state of North Rhine-Westphalia. With Bonn being chosen as the provisional capital (provisorische Bundeshauptstadt) and seat of the government of the Federal Republic of Germany (then informally West Germany), Cologne benefited by being sandwiched between two important political centers. The city became and still is home to a number of federal agencies and organizations. After reunification in 1990, Berlin was made the capital of Germany.
In 1945 architect and urban planner Rudolf Schwarz called Cologne the "world's greatest heap of rubble". Schwarz designed the master plan of reconstruction in 1947, which called for the construction of several new thoroughfares through the downtown area, especially the Nord-Süd-Fahrt ("North-South-Drive"). The master plan took into consideration the fact that even shortly after the war a large increase in automobile traffic could be anticipated. Plans for new roads had already, to a certain degree, evolved under the Nazi administration, but the actual construction became easier in times when the majority of downtown lots were undeveloped.
The destruction of 95% of the city center including the famous Twelve Romanesque churches like St. Gereon, Great St. Martin, St. Maria im Kapitol and several other monuments in World War II meant a tremendous loss of cultural treasures. The rebuilding of those churches and other landmarks like the Gürzenich event hall was not undisputed among leading architects and art historians at that time, but in most cases, civil intention prevailed. The reconstruction lasted until the 1990s, when the Romanesque church of St. Kunibert was finished.
In 1959, the city's population reached pre-war numbers again. It then grew steadily, exceeding 1 million for about one year from 1975. It has remained just below that until mid-2010, when it exceeded 1 million again.
Post-reunification
In the 1980s and 1990s Cologne's economy prospered for two main reasons. Firstly, a growth in the number of media companies, both in the private and public sectors; they are especially catered for in the newly developed Media Park, which creates a strongly visual focal point in the Cologne town center and includes the KölnTurm, one of Cologne's most prominent high-rise buildings. Secondly, a permanent improvement of the diverse traffic infrastructure made Cologne one of the most easily accessible metropolitan areas in Central Europe.
Due to the economic success of the Cologne Trade Fair, the city arranged a large extension to the fair site in 2005. At the same time the original buildings, which date back to the 1920s are rented out to RTL, Germany's largest private broadcaster, as their new corporate headquarters.
Geography
The metropolitan area encompasses over 405 square kilometres (156 square miles), extending around a centerpoint that lies at 50° 56' 33 latitude and 6° 57' 32 longitude. The city's highest point is 118 m (387.1 ft) above sea level (the Monte Troodelöh) and its lowest point is 37.5 m (123.0 ft) above sea level (the Worringer Bruch).[18] The city of Cologne lies within the larger area of the Cologne Lowland, a cone-shaped area of southeastern Westphalia that lies between Bonn, Aachen and Düsseldorf.
Districts
Cologne is subdivided into 9 districts (Stadtbezirke) and 85 city parts (Stadtteile):[19]
|

|
|
Climate
Cologne is one of the warmest cities in Germany. It has a temperate–oceanic climate with relatively mild winters and warm summers. It is also one of the gloomiest cities in Germany, with just 1427 hours of sun a year. Its average annual temperature is 10.3 °C (51 °F): 14.8 °C (59 °F) during the day and 5.8 °C (42 °F) at night. In January, the mean temperature is 2.6 °C (37 °F), while the mean temperature in July is 18.8 °C (66 °F). Precipitation is spread evenly throughout the year.
| Climate data for Cologne/Bonn Airport, Germany for 1981–2010 (Source: DWD) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
25.0 (77.0) |
29.0 (84.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
36.8 (98.2) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.8 (101.8) |
— | — | 18.7 (65.7) |
16.6 (61.9) |
38.8 (101.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
6.7 (44.1) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
15.1 (59.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
5.9 (42.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
2.9 (37.2) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.0 (57.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
18.1 (64.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −0.6 (30.9) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
2.0 (35.6) |
4.2 (39.6) |
8.1 (46.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
12.6 (54.7) |
9.8 (49.6) |
6.7 (44.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
0.4 (32.7) |
5.8 (42.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −23.4 (−10.1) |
−19.2 (−2.6) |
−12.0 (10.4) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
1.4 (34.5) |
2.9 (37.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−16.0 (3.2) |
−23.4 (−10.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.1 (2.44) |
54.2 (2.13) |
64.6 (2.54) |
53.9 (2.12) |
72.2 (2.84) |
90.7 (3.57) |
85.8 (3.38) |
75.0 (2.95) |
74.9 (2.95) |
67.1 (2.64) |
67.0 (2.64) |
71.1 (2.80) |
838.6 (33.02) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 43.0 | 74.0 | 101.6 | 151.8 | 184.1 | 177.0 | 184.3 | 179.5 | 134.5 | 103.8 | 53.1 | 40.3 | 1,426.8 |
| Source: Data derived from Deutscher Wetterdienst[20] | |||||||||||||
Flood protection

Cologne is regularly affected by flooding from the Rhine and is considered the most flood-prone European city.[21] A city agency (Stadtentwässerungsbetriebe Köln,[22] "Cologne Urban Drainage Operations") manages an extensive flood control system which includes both permanent and mobile flood walls, protection from rising waters for buildings close to the river banks, monitoring and forecasting systems, pumping stations and programs to create or protect floodplains, and river embankments.[21][23] The system was redesigned after a 1993 flood, which resulted in heavy damage.[21]
Demographics
Cologne is the fourth-largest city in Germany in terms of inhabitants after Berlin, Hamburg and Munich. As of 30 June 2011, there were officially 1,010,269 residents.[24] Cologne is the center of the Cologne/Bonn Region with around 3 million inhabitants (including the neighboring cities of Bonn, Hürth, Leverkusen, and Bergisch Gladbach).
According to local statistics, in 2006, the population density in the city was 2,528 inhabitants per square kilometre. 31.4 percent of the population has migrated there, and 17.2 percent of Cologne's population is non-German. The largest group, comprising 6.3 percent of the total population, is Turkish.[25] As of September 2007, there are about 120,000 Muslims living in Cologne, mostly of Turkish origin.[26] Cologne also has the oldest and one of the largest Jewish communities in Germany.[27]
In the city the population was spread out with 15.5% under the age of 18, 67.0% from 18 to 64 and 17.4% who were 65 years of age or older.[28]
| Ancestry | Number |
|---|---|
| Germans | 81.6% |
| Other European | 6% |
| Turks | 6.3% |
| Asians | 3% |
| Africans | 0.9% |
| Other/Mixed | 2.2% |
Government
The city's administration is headed by the mayor and the three deputy mayors. Jürgen Roters of the Social Democratic Party has been mayor since 20 October 2009.[29]
Political traditions and developments
The long tradition of a free imperial city, which long dominated an exclusively Catholic population and the age-old conflict between the church and the bourgeoisie (and within it between the patricians and craftsmen) has created its own political climate in Cologne. Various interest groups often form the basis of societal socialization and therefore beyond party boundaries. The resulting network of relationships, with political, economic, and cultural links with each other in a system of mutual favors, obligations and dependencies, is called the Cologne coterie. This has often led to an unusual proportional distribution in the city government and degenerated at times into corruption: in 1999, a "waste scandal" over kickbacks and illegal campaign contributions came to light, which led not only to the imprisonment of the entrepreneur Hellmut Trienekens, but also to the downfall of almost the entire leadership staff of the ruling Social Democrats.
Mayor
The Lord Mayor of Cologne is Jürgen Roters of the Social Democratic Party. As the joint candidate of the SPD and the Greens, he received 54.67% of the vote on 30 August 2009 at the municipal election. He has been Lord Mayor since 21 October 2009.
Elections
City Councillors are elected for a five-year term and the Mayor has a six-year term.[30]
Make-up of city council
| Party | Seats | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Social Democratic Party | 25 | [31] |
| Christian Democratic Union | 25 | |
| Green Party | 20 | |
| Free Democratic Party | 9 | |
| pro Cologne | 5 | |
| The Left | 4 | |
| Free Voters | 1 |
Cityscape
The inner city of Cologne was completely destroyed during World War II. The reconstruction of the city followed the style of the 1950s, while respecting the old layout and naming of the streets. Thus, the city today is characterized by simple and modest post-war buildings, with few interspersed pre-war buildings which were reconstructed due to their historical importance. Some buildings of the "Wiederaufbauzeit" (era of reconstruction), for example the opera house by Wilhelm Riphahn, are nowadays regarded as classics of modern architecture.[citation needed] Nevertheless, the uncompromising style of the Cologne Opera house and other modern buildings has remained controversial.
Green areas account for over a quarter of Cologne which is approximately 75 m2 (807.29 sq ft) of public green space for every citizen of the city.[32]
Wildlife
The presence of animals in Cologne is generally limited to insects, small rodents, and several species of birds. Pigeons are the most often seen animals in Cologne, although the number of birds are augmented each year by a growing population of feral exotics, most visibly parrots such as the rose-ringed Parakeet. The sheltered climate in southeast Westphalia allows these birds to survive through the winter, and in some cases they are displacing native species. The plumage of Cologne's green parrots is highly visible even from a distance, and contrasts starkly with the otherwise muted colors of the cityscape.[33]
Tourism
Cologne had 4.31 million overnight stays booked and 2.38 million arrivals in 2008.[19] The city also has the most pubs per capita in Germany.[34] The city has 70 clubs, "countless" bars, restaurants, and pubs.[34]
Landmarks
Churches
- Cologne Cathedral (German: Kölner Dom) is the city's most famous monument and the Cologne residents' most respected landmark. It is a Gothic church, started in 1248, and completed in 1880. In 1996, it was designated a World Heritage site; it houses the Shrine of the Three Kings, which supposedly contains the relics of the Three Magi (see also[35]). Residents of Cologne sometimes refer to the cathedral as "the eternal construction site" (die ewige Baustelle).
- Twelve Romanesque churches: These buildings are outstanding examples of medieval church architecture. The origins of some of the churches go back as far as Roman times, for example St. Gereon, which was originally a chapel in a Roman graveyard. With the exception of St. Maria Lyskirchen all of these churches were very badly damaged during World War II. Reconstruction was only finished in the 1990s.
-
Church of the Assumption
-
Holy Trinity Church
Medieval houses
The Cologne City Hall (Kölner Rathaus), founded in the 12th century, is the oldest city hall in Germany still in use.[36] The Renaissance style loggia and tower were added in the 15th century. Other famous buildings include the Gürzenich, Haus Saaleck and the Overstolzenhaus.
-
Gürzenich
-
Overstolzenhaus
Medieval city gates
Of the once 12 medieval city gates, only the Eigelsteintorburg at Ebertplatz, the Hahnentor at Rudolfplatz and the Severinstorburg at Chlodwigplatz still stand today.
-
Eigelsteintor
-
Hahnentor
-
Severinstor
Streets
- The Cologne Ring boulevards (such as Hohenzollernring, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Ring, Hansaring) with their medieval city gates (such as Hahnentorburg on Rudolfplatz) are also known for their night life.
- Hohe Straße (literally: High Street) is one of the main shopping areas and extends past the cathedral in an approximately southerly direction. The street contains many gift shops, clothing stores, fast food restaurants and electronic goods dealers.
- Schildergasse – connects the Neumarkt plaza on its west end to the southern end of the Hohe Strasse shopping street at its east end and has been named the busiest shopping street in Europe with 13,000 people passing through every hour.
- Ehrenstraße – the shopping area around Apostelnstrasse, Ehrenstrasse, and Rudolfplatz is a little more on the eccentric and stylish side.
Bridges
Several bridges cross the Rhine in Cologne. They are (from South to North): the Cologne Rodenkirchen Bridge, South Bridge (railway), Severin Bridge, Deutz Bridge, Hohenzollern Bridge, Zoo Bridge (Zoobrücke) and Cologne Mülheim Bridge. In particular the iron tied arch Hohenzollern Bridge (Hohenzollernbrücke) is a dominant landmark along the river embankment. A Rhine river crossing of a special kind is provided by the Cologne Cable Car (German: Kölner Seilbahn), a cableway that runs across the Rhine between the Cologne Zoological Garden in Riehl and the Rheinpark in Deutz.
High-rise structures
Cologne's tallest structure is the Colonius telecommunication tower at 266 m or 873 ft. The observation deck has been closed since 1992. A selection of the tallest buildings in Cologne are listed below. Other tall structures include the Hansahochhaus (designed by architect Jacob Koerfer and completed in 1925—it was at one time Europe's tallest office building), the Kranhaus buildings at Rheinauhafen, and the Messeturm Köln ("trade fair tower").
| Skyscraper | Image | Height in metres | Floors | Year | Address | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KölnTurm | 
|
148.5 | 43 | 2001 | Mediapark 8, Neustadt-Nord | (literally: Cologne Tower), Cologne's second tallest building at 165.48 metres (542.91 ft) in height, second only to the Colonius telecommunication tower. The 30th floor of the building has a restaurant and a terrace with 360° views of the city. |
| Colonia-Hochhaus | 
|
147 | 45 | 1973 | An der Schanz 2, Riehl | tallest building in Germany from 1973 to 1976. Today, it is still the country's tallest residential building. |
| Rheintower | 
|
138 | 34 | 1980 | Raderberggürtel, Marienburg | former headquarters of Deutsche Welle, since 2007 under renovation with the new name Rheintower Köln-Marienburg. |
| Uni-Center[37] | 
|
133 | 45 | 1973 | Luxemburger Straße, Sülz | |
| TÜV Rheinland | 
|
112 | 22 | 1974 | Am Grauen Stein, Poll | |
| KölnTriangle | 
|
103 | 29 | 2006 | Ottoplatz 1, Deutz | opposite to the cathedral with a 103 m (338 ft) high viewing platform and a view of the cathedral over the Rhine; headquarters of the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). |
| Herkules-Hochhaus | 
|
102 | 31 | 1969 | Graeffstraße 1, Ehrenfeld |
Culture

Cologne has several museums. The famous Roman-Germanic Museum features art and architecture from the city's distant past; the Museum Ludwig houses one of the most important collections of modern art in Europe, including a Picasso collection matched only by the museums in Barcelona and Paris. The Museum Schnütgen of religious art is partly housed in St. Cecilia, one of Cologne's Twelve Romanesque churches.
Several orchestras are active in the city, among them the Gürzenich Orchestra and the WDR Symphony Orchestra Cologne, both based at the Cologne Philharmonic Orchestra Building.[38] Other orchestras are the Musica Antiqua Köln and the WDR Rundfunkorchester Köln, as well as the Cologne Opera and several choirs, including the WDR Rundfunkchor Köln. Cologne was also an important center of electronic music in the 1950s (Studio für elektronische Musik, Karlheinz Stockhausen) and again from the 1990s onward. The public radio and TV station WDR was involved in promoting musical movements such as Krautrock in the 1970s; the influential Can was formed there in 1968. There are several centers of nightlife, among them the Kwartier Latäng (the student quarter around the Zülpicher Straße) and the nightclub-studded areas around Hohenzollernring, Friesenplatz and Rudolfplatz.
The large annual literary festival Lit.Cologne features regional and international authors. The main literary figure connected with Cologne is writer Heinrich Böll, winner of the Nobel Prize for Literature.
Cologne is well known for its beer, called Kölsch. Kölsch is also the name of the local dialect. This has led to the common joke of Kölsch being the only language one can drink.
Cologne is also famous for Eau de Cologne (German: Kölnisch Wasser; lit: "Water of Cologne"), a perfume created by Italian expatriate Johann Maria Farina at the beginning of the 18th century. During the 18th century this perfume became increasingly popular, was exported all over Europe by the Farina family and Farina became a household name for Eau de Cologne. In 1803 Wilhelm Mülhens entered into a contract with an unrelated person from Italy named Carlo Francesco Farina who granted him the right to use his family name and Mühlens opened a small factory at Cologne's Glockengasse. In later years and after various court battles his grandson Ferdinand Mülhens had to abandon the name Farina for the company and their product. He decided to use the house number given to the factory at Glockengasse during French occupation in the early 19th century, 4711. Today, original Eau de Cologne is still produced in Cologne by both the Farina family, currently in the eighth generation, and by Mäurer & Wirtz who bought the 4711 brand in 2006.
Carnival
The Cologne carnival is one of the biggest street festivals in Europe. In Cologne, the carnival season officially starts on 11 November at 11 minutes past 11 a.m. with the proclamation of the new Carnival Season, and continues until Ash Wednesday. However, the so-called "Tolle Tage" (crazy days) don't start until Weiberfastnacht (Women's Carnival) or, in dialect, Wieverfastelovend (the Thursday before Ash Wednesday), which is the beginning of the street carnival. Zülpicher Strasse and its surroundings, Neumarkt square, Heumarkt and all bars and pubs in the city are crowded with people in costumes dancing and drinking in the streets. Hundreds of thousands of visitors flock to Cologne during this time. Generally, around a million people celebrate in the streets on the Thursday before Ash Wednesday.[39]
Rivalry with Düsseldorf
Cologne and Düsseldorf have a "fierce regional rivalry",[40] which includes carnival parades, football, and beer.[40] People in Cologne prefer Kölsch while people in Düsseldorf prefer Alt.[40] Waiters and patrons will "scorn" and make a "mockery" of people who order Alt beer in Cologne and Kölsch in Düsseldorf.[40] The rivalry has been described as a "love–hate relationship".[40]
Museums


- Farina Fragrance Museum – birthplace of Eau de Cologne
- Römisch-Germanisches Museum (Roman-Germanic Museum) – ancient Roman and Germanic culture
- Wallraf-Richartz Museum – European painting from the 13th to the early 20th century
- Museum Ludwig – modern art
- Museum Schnütgen – medieval art
- Museum für Angewandte Kunst – applied art
- Kolumba Kunstmuseum des Erzbistums Köln (art museum of the Archbishopric of Cologne) – modern art museum built around medieval ruins, completed 2007
- Cathedral Treasury "Domschatzkammer" – historic underground vaults of the Cathedral
- EL-DE Haus, – former local headquarters of the Gestapo houses a museum documenting Nazi rule in Cologne with a special focus on the persecution of political dissenters and minorities
- German Sports and Olympic Museum – exhibitions about sports from antiquity until the present
- Imhoff-Schokoladenmuseum – Chocolate Museum
- Forum for Internet Technology in Contemporary Art – collections of Internet-based art, corporate part of (NewMediaArtProjectNetwork):cologne, the experimental platform for art and New Media
- Flora und Botanischer Garten Köln, the city's formal park and main botanical garden
- Forstbotanischer Garten Köln, an arboretum and woodland botanical garden
Music fairs and festivals
The city was home to the internationally famous Ringfest, and now to the C/o pop festival.[41]
Economy


As the largest city in the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region, Cologne benefits from a large market structure.[42] In competition for location factors with Düsseldorf, the economy of Cologne is primarily based on insurance and media industries,[43] while the city is also an important cultural and research center and home to a number of corporate headquarters.
Among the largest media companies based in Cologne are Westdeutscher Rundfunk, RTL Television (with subsidiaries), n-tv, Deutschlandradio, Brainpool TV and publishing houses like J. P. Bachem, Taschen, Tandem Verlag, and M. DuMont Schauberg. Several clusters of media, arts and communications agencies, TV production studios, and state agencies work partly with private and government funded cultural institutions. Among the insurance companies based in Cologne are Central, DEVK, DKV, Generali Deutschland, Gothaer, HDI Gerling and national headquarters of AXA Insurance and Zurich Financial Services.
Lufthansa, the German flag carrier, and Lufthansa CityLine have their main corporate headquarters in Cologne.[44] The largest employer in Cologne is Ford Europe, which has its European headquarters and a factory in Niehl (Ford-Werke GmbH).[45] Toyota Motorsport GmbH (TMG), Toyota's official motorsports team, responsible for Toyota rally cars, and then Formula One cars, has headquarters and workshops in Cologne. Other large companies based in Cologne include the REWE Group, TÜV Rheinland, Deutz AG and a number of Kölsch breweries. Cologne has the country's highest density of pubs per capita.[34] The largest three Kölsch breweries are Reissdorf, Gaffel, and Früh.
| brewery | established | annual output in hectolitre |
|---|---|---|
| Heinrich Reissdorf | 1894 | 650,000 |
| Gaffel Becker & Co | 1908 | 500.000 |
| Cölner Hofbräu Früh | 1904 | 440,000 |
Historically, Cologne has always been an important trade city, with land, air, and sea connections.[2] The city has five Rhine ports,[2] the second largest inland port in Germany and one of the largest in Europe. Cologne-Bonn Airport is the second largest freight terminal in Germany.[2] Today, the Cologne trade fair (Koelnmesse) ranks as a major European trade fair location with over 50 trade fairs[2] and other large cultural and sports events. In 2008 Cologne had 4.31 million overnight accommodations booked and 2.38 million arrivals.[19] Cologne's largest daily newspaper is the Kölner Stadt-Anzeiger.
Transport
Road transport

Road building had been a major issue in the 1920s under the leadership of mayor Konrad Adenauer. The first German limited access road was constructed after 1929 between Cologne and Bonn. Today, this is the Bundesautobahn 555. In 1965, Cologne became the first German city to be fully encircled by a freeway belt. Roughly at the same time a downtown bypass freeway (Stadtautobahn) was planned, but only partially put into effect, due to opposition by environmental groups. The completed section became Bundesstraße ("Federal Road") B 55a which begins at the Zoobrücke ("Zoo Bridge") and meets with A 4 and A 3 at the interchange Cologne East. Nevertheless, it is referred to as Stadtautobahn by most locals. In contrast to this the Nord-Süd-Fahrt ("North-South-Drive") was actually completed, a new four/six-lane downtown thoroughfare, which had already been anticipated by planners like Fritz Schumacher in the 1920s. The last section south of Ebertplatz was completed in 1972.
In 2005, the first stretch of an eight-lane freeway in North Rhine-Westphalia was opened to traffic on Bundesautobahn 3, part of the eastern section of the Cologne Beltway between the interchanges Cologne East and Heumar.
Cycling


Like most German cities, Cologne has a traffic layout designed to be bicycle-friendly. There is an extensive cycle network, featuring pavement-edge cycle lanes linked by cycle priority crossings. In some of the narrow one-way central streets, cyclists are explicitly allowed to cycle both ways.
Rail transport
Cologne has a railway service with Deutsche Bahn Intercity and ICE-trains stopping at Köln Hauptbahnhof (Cologne Central Station), Köln Messe/Deutz and Cologne/Bonn Airport. ICE and TGV Thalys high-speed trains link Cologne with Amsterdam, Brussels (in 1h47, 6 departures/day) and Paris (in 3h14, 6 departures/day). There are frequent ICE trains to other German cities, including Frankfurt am Main and Berlin. ICE Trains to London via the Channel Tunnel are planned for 2013.[46]
The Cologne city railway operated by Kölner Verkehrsbetriebe (KVB)[47] is an extensive light rail system that is partially underground (referred to as U-Bahn) and serves Cologne and a number of neighboring cities. Nearby Bonn is linked by both the city railway and Deutsche Bahn trains, and occasional recreational boats on the Rhine. Düsseldorf is also linked by S-Bahn trains which are operated by Deutsche Bahn.
There are also frequent buses covering most of the city and surrounding suburbs, and Eurolines coaches to London via Brussels.
Water transport
Häfen und Güterverkehr Köln (Cologne Ports and Railways) (HGK) is one of the largest operators for inland ports in Germany.[48] Ports include Köln-Deutz, Köln-Godorf, and Köln-Niehl I and II. Köln-Düsseldorfer offers Rhine river cruises along the entire Rhine.
Air transport
Cologne's international airport is Cologne/Bonn Airport (CGN). It is also called Konrad Adenauer Airport after Germany's first post-war Chancellor Konrad Adenauer, who was born in the city and was mayor of Cologne from 1917 until 1933. The airport is shared with the neighbouring city of Bonn. Cologne is headquarters to the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). The airport is also the main hub of the airline Germanwings.
Education
Cologne is home to numerous universities and colleges,[49][50] and host to some 72,000 students.[2] Its oldest university, the University of Cologne (originally founded in 1388[3]) is the largest university in Germany, as the Cologne University of Applied Sciences is the largest university of Applied Sciences in the country. The Cologne University of Music and Dance is the largest conservatory in Europe.[51] Foreigners can have German lessons in the VHS (Adult Education Centre).[52]
|
Former colleges include:
|
Media
Within Germany, Cologne is known as an important media center. Several radio and television stations, including Westdeutscher Rundfunk (WDR), RTL and VOX, have their headquarters in the city. Film and TV production is also important. The city is "Germany's capital of TV crime stories".[53] A third of all German TV productions are produced in the Cologne region.[53] Furthermore, the city hosts the Cologne Comedy Festival, which is considered to be the largest comedy festival in mainland Europe.[54]
Sports

Cologne hosts 1. FC Köln,[55] who play in the 2nd Bundesliga as of the 2013–14 season. They play their home matches in RheinEnergieStadion which also hosted 5 matches of the 2006 FIFA World Cup.[56] The International Olympic Committee and Internationale Vereinigung Sport- und Freizeiteinrichtungen e.V. gave RheinEnergieStadion a bronze medal for "being one of the best sporting venues in the world".[56] Cologne also hosts FC Viktoria Köln 1904 and SC Fortuna Köln, who play in the Regionalliga West (fourth division).
The city is also home of the ice hockey team Kölner Haie, in the highest ice hockey league in Germany, the Deutsche Eishockey Liga.[55] They are based at the Lanxess Arena.[55]
Several horse races per year are held at Cologne-Weidenpesch Racecourse since 1897, the annual Cologne Marathon was started in 1997. From 2002-2009, the Panasonic Toyota Racing Formula One team was based in the Marsdorf suburb, at the Toyota Motorsport GmbH facility.
Cologne is considered "the secret golf capital of Germany".[55] The first golf club in North Rhine-Westphalia was founded in Cologne in 1906.[55] The city offers the most options and top events in Germany.[55]
The city has hosted several athletic events which includes the 2005 FIFA Confederations Cup, 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2007 World Men's Handball Championship, 2010 IIHF World Championship and 2010 Gay Games.[4]
Twin towns and sister cities
Cologne is "twinned" with the following cities:[57]
|
|
Additionally, the districts of Rodenkirchen, Lindenthal, and Porz continue to maintain individual town partnerships, established during their time as independent municipalities.
Notable residents
Notable people, whose roots can be found in Cologne:
- Konrad Adenauer (1876–1967), politician, mayor of Cologne (1917–33, 1945) and first West German Federal Chancellor
- Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa (1486–1535), alchemist, occultist, and author of Three Books of Occult Philosophy
- Agrippina the Younger (15–59), Roman Empress (wife of Emperor Claudius) and mother of Emperor Nero
- Heinrich Birnbaum (1403–73), a Catholic monk
- Heinrich Boigk (1912–2003) Knights Cross winner
- Robert Blum (1807–48), politician and martyr of the 19th century democratic movement in Germany
- Heinrich Böll (1917–85), writer and winner of the Nobel prize for literature in 1972
- Max Bruch (1838–1920) composer
- Álex Calatrava (b. 1973), Spanish professional tennis player
- Heribert Calleen (b. 1924), sculptor
- Florian Henckel von Donnersmarck (b. 1973), Academy Award-winning director and screenwriter
- Max Ernst (1891–1976), artist
- Angela Gossow (b. 1974), lead vocalist of Swedish melodic death metal band Arch Enemy
- Britta Heidemann (b. 1982), épée fencer and Olympic medalist
- de:Trude Herr (1927–91), actress and singer
- de:Stefanie Höner (b. 1969), actress
- Udo Kier (b. 1944), actor
- Jutta Kleinschmidt (b. 1962), off-road automotive racing competitor
- Werner Klemperer (1920–2000), Emmy Award-winning comedy actor
- Erich Klibansky (1900–1942), Jewish headmaster and teacher
- Adolf Kober (1870–1958), Jewish rabbi and medievalist
- Gaby Köster (b. 1961), German actress and comedian
- de:Hildegard Krekel (b. 1952), actress
- de:Lotti Krekel (b. 1941), actress and singer
- Uwe Krupp (b. 1965), professional (ice) hockey player
- Heinz Kühn (1912–92), Minister-President of North Rhine-Westphalia (1966–78)
- Heiner Lauterbach (1953), actor
- Ottmar Liebert (b. 1961), musician
- de:Mariele Millowitsch (b. 1955), actress
- de:Peter Millowitsch (b. 1949), actor, playwright and theatre director
- Willy Millowitsch (1909–1999), actor, playwright and theatre director
- Wolfgang Niedecken (b. 1951), singer, musician, artist and bandleader of BAP
- Theodore of Corsica (1694–1756), briefly King Theodore of Corsica
- Jacques Offenbach (1819–80), composer
- de:Willi Ostermann (1876–1936) composer
- Kim Petras (b. 1992), singer
- Frederik Prausnitz (1920–2004), American conductor and teacher
- Christa Päffgena aka Nico (1938–88), model, actress, singer, and songwriter in Velvet Underground and Warhol Superstar
- Stefan Raab (b. 1966), German entertainer and host of Eurovision Song Contest 2011
- Jürgen Rüttgers (b. 1951), Minister-President of North Rhine-Westphalia (2005–2010)
- Jürgen Fritz (b. 1953), musician and composer
- Markus Stockhausen (b. 1957), musician and composer
- Wolfgang von Trips (1928–61), Formula One racing driver
- Joost van den Vondel (1587–1679), Dutch poet and playwright
- Moshe Wallach (1866–1957), founder and director of Shaare Zedek Hospital, Jerusalem
- Robert Weimar (1932–2013), legal scientist and psychologist
- Christoph Watrin (b. 1988), singer, US5
- Carl Wyland (1886–1972), German blacksmith
See also
- Stadtwerke Köln, the municipal infrastructure company, operator of the city's railways, ports, and utilities.
- History of the Jews in Cologne
References
- ^ "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2023 – Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes auf Basis des Zensus vom 9. Mai 2011" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 2024-06-20.
- ^ a b c d e f "Economy". KölnTourismus. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f "From Ubii village to metropolis". City of Cologne. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "Facts and figures". City of Cologne. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ^ "C.Michael Hogan, ''Cologne Wharf'', The Megalithic Portal, editor Andy Burnham, 2007". Megalithic.co.uk. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ Harry de Quetteville. "History of Cologne". The Catholic Encyclopedia, Nov 28, 2009.
- ^ Joseph P. Huffman, Family, Commerce, and Religion in London and Cologne (1998) covers from 1000 to 1300.
- ^ "Rote Funken - Kölsche Funke rut-wieß vun 1823 e.V. - Rote Funken Koeln". Rote-funken.de. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ^ United Services Magazine, December 1835
- ^ "Festung Köln". Retrieved April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Cologne Evacuated, TIME Magazine, February 15, 1926
- ^ "Weimarer Wahlen". Web.archive.org. 2008-02-11. Archived from the original on 2008-02-11. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ "Voting results 1919-1933 Cologne-Aachen". Wahlen-in-deutschland.de. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ koelnarchitektur (2003-07-15). "on the reconstruction of Cologne". Koelnarchitektur.de. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ Tourtellot, Arthur B. et al. Life's Picture History of World War II, p. 237. Time Incorporated, New York, 1950.
- ^ Kirsten Serup-Bilfeld, Zwischen Dom und Davidstern. Jüdisches Leben in Köln von den Anfängen bis heute. Köln 2001, page 193
- ^ "Synagogen-Gemeinde Köln". Sgk.de. 1931-06-26. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ Bezirksregierung Köln: Topografische Karte 1:50.000 (TK 50), Blatt L 5108 Köln-Mülheim. Köln 2012, ISBN 978-3-89439-422-6.
- ^ a b c "Cologne at a glance". City of Cologne. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ^ "Ausgabe der Klimadaten: Monatswerte".
- ^ a b c Martin Gocht; Reinhard Vogt. "Flood Forecasting and Flood Defence in Cologne" (PDF). Mitigation of Climate Induced Natural Hazards (MITCH). Retrieved 2009-03-20.
- ^ "Stadtentwässerungsbetriebe Köln : Flood Management". Steb-koeln.de. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ "Flood Defence Scheme City of Cologne" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-03-20.
- ^ "Information und Technik Nordrhein-Westfalen (IT.NRW) - Amtliche Bevölkerungszahlen". It.nrw.de. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ "2007 - Einwohnerdaten im Überblick - Zahlen + Statistik - Bevölkerung - Stadt Köln". Web.archive.org. 2008-01-28. Archived from the original on 2008-01-28. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ "WDR Article of 15.08.2007". Wdr.de. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ Serup-Bilfeldt, Kirsten (19 August 2005). "Cologne: Germany's Oldest Jewish Community". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 6 September 2011.
- ^ "City of Cologne -> Figures Statistics Population (German)". Web.archive.org. 2008-02-08. Archived from the original on 2008-02-08. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ "Der Oberbürgermeister" (in German). Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ "Wahlperiode" (in German). City of Cologne. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ "Alle Ratsmitglieder" (in German). City of Cologne. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ "Green Cologne". KölnTourismus. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ^ "In NRW behaupten sich immer mehr exotische Vögel". RP Online. Retrieved 16 January 2013.
- ^ a b c "Nightlife". KölnTourismus. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ^ "Offizielle Webseite des Kölner Doms | Bedeutende Werke". Koelner-dom.de. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ^ "Strategic Management Society - Cologne Conference - Cologne Information". Cologne.strategicmanagement.net. 2008-10-14. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- ^ "Homepage of the Uni-Center". Unicenterkoeln.de. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ "Kölner Philharmonie". Web.archive.org. 2007-12-11. Archived from the original on 2007-12-11. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ "Carnival - Cologne's "fifth season" - Cologne Sights & Events - Stadt Köln". Web.archive.org. 2008-01-26. Archived from the original on 2008-01-25. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ a b c d e "Giving Beer A Home in the Rhineland". The Local. 28 July 2011. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
- ^ "C/o Pop Official Website".
- ^ stadt-koeln.de Cologne Business Guide Template:De icon Template:En icon
- ^ Cologne on Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ^ "Directory: World Airlines". Flight International. 2007-04-03. p. 107.
- ^ "Über Ford - Standorte". Ford Germany. Retrieved 2009-06-20. Template:De icon
- ^ "High-speed trains to link England and Germany". Brisbanetimes.com.au. 2011-10-16. Retrieved 2012-01-26.
- ^ "Kölner Verkehrsbetriebe (KVB)". Kvb-koeln.de. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ "Häfen und Güterverkehr Köln AG". Hgk.de. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ "Hochschulen - Wissensdurst KĂśln - Das KĂślner Wissenschaftsportal". Wissensdurst-koeln.de. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- ^ "Forschungsschwerpunkte" (PDF). Wissensdurst-koeln.de.
- ^ "goethe.de". goethe.de. Retrieved 2010-08-08.
- ^ "Cologne Adult Education Centre – City of Cologne". Stadt-koeln.de. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ a b "Productions "made in Cologne"". Cologne Tourism. Retrieved 22 April 2011.
- ^ "Cologne Comedy Festival website". Koeln-comedy.de. 21 October 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f "Sport and relaxation". Cologne Tourist Information. Retrieved 13 March 2013.
- ^ a b "The RheinEnergie Stadium". 1. FC Köln. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
- ^ "Partnerstädte". Retrieved 2009-06-22.
- ^ Pessotto, Lorenzo. "International Affairs - Twinnings and Agreements". International Affairs Service in cooperation with Servizio Telematico Pubblico. City of Torino. Archived from the original on 2013-06-18. Retrieved 2013-08-06.
- ^ "Sister and Other Associated Cities". Kyoto General Affairs Bureau. City of Kyoto. Archived from the original on 2013-07-28. Retrieved 2013-08-06.
- ^ "Barcelona internacional - Ciutats agermanades" (in Spanish). © 2006-2009 Ajuntament de Barcelona. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ "Sister Cities". Beijing Municipal Government. Retrieved 2008-09-23.
- ^ Mulcahy, Noreen. "Cork - International Relations". Cork City Council. Archived from the original on 2013-05-18. Retrieved 2013-08-28.
- ^ "Twinning Cities". City of Thessaloniki. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ "::Bethlehem Municipality::". www.bethlehem-city.org. Retrieved 2009-10-10.
- ^ "Cologne International: Rio de Janeiro is Cologne's New Twin City" (PDF) (in Template:En icon). Cologne City Business News. Retrieved April 28, 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
External links
- www.cologne-tourism.com Template:De icon Template:En icon Template:Es icon Template:Fr icon
- Cologne Tourism at koeln.de Template:De icon Template:En icon
- City of Cologne, official City of Cologne page Template:De icon
- Colonipedia, the city-wiki of Cologne Template:De icon
- KölnWiki, the city-wiki of Cologne Template:De icon
- Colonia 3D, a reconstruction of Roman Cologne
- Cologne community politics API
- Weather in Cologne
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
- Articles to be merged from September 2013
- Cities in North Rhine-Westphalia
- Cologne
- Populated places on the Rhine
- Catholic pilgrimage sites
- Holy cities
- Members of the Hanseatic League
- Roman legions' camps in Germany
- Roman colonies
- Roman towns and cities in Germany
- Imperial free cities
- Populated places established in the 1st century BC
- 38 BC establishments