Brimonidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | bri-MOE-ni-deen |
| Trade names | Alphagan, Mirvaso |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601232 |
| Routes of administration | topical (ophthalmic solution, gel) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Primarily liver |
| Elimination half-life | 3 hours (ocular), 12 hours (topical) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.042 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
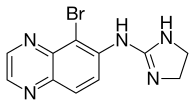
| Formula | C11H10BrN5 |
| Molar mass | 292.135 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 252 °C (486 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Brimonidine is a drug used as eye drops under the brand names Alphagan and Alphagan-P to treat open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, and as a gel, Mirvaso, for facial skin redness in rosacea.
It acts via decreasing synthesis of aqueous humor, and increasing the amount that drains from the eye through uveoscleral outflow; brimonidine treats reddened skin (erythema) by causing narrowing of blood vessels (vasoconstriction).
Clinical uses
Brimonidine is indicated for the lowering of intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It is also the active ingredient of Combigan along with timolol maleate.
A Cochrane Systematic Review compared the effect of brimonidine and timolol in slowing the progression of open angle glaucoma in adult participants.[1]
In 2013, the FDA approved topical application of brimonidine 0.33% gel (Mirvaso) for persistent facial redness of rosacea.
Mechanism of action
Brimonidine is an α2 adrenergic agonist.
α2 agonists, through the activation of a G protein-coupled receptor, inhibit the activity of adenylate cyclase. This reduces cAMP and hence aqueous humour production by the ciliary body.
Peripheral α2 agonist activity results in vasoconstriction of blood vessels (as opposed to central α2 agonist activity that decreases sympathetic tone, as can be seen by the medication clonidine). This vasoconstriction may explain the acute reduction in aqueous humor flow. The increased uveoscleral outflow from prolonged use may be explained by increased prostaglandin release due to α adrenergic stimulation. This may lead to relaxed ciliary muscle and increased uveoscleral outflow.[2]
References
- ^ Sena DF, Lindsley K (2013). "Neuroprotection for treatment of glaucoma in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2: CD006539. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006539.pub3. PMC 4261923. PMID 23450569.
- ^ Toris, C.; Camras, C.; Yablonski, M. (1999). "Acute versus chronic effects of brimonidine on aqueous humor dynamics in ocular hypertensive patients". American journal of ophthalmology. 128 (1): 8–14. doi:10.1016/s0002-9394(99)00076-8. PMID 10482088.
- Mosby's Drug Guide for Nurses (7th edition; Skidmore) 2007.
