Tokyo subway
| Tokyo Subway | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Top: The logo of Tokyo Metro Middle: The logo of Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation operating Toei Subway Bottom: Toei 6300 series (left) and Tokyo Metro 10000 series (right) trains at Musashi-Kosugi Station | |||
| Overview | |||
| Locale | Tokyo, Japan | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 13 | ||
| Number of stations | 285 | ||
| Daily ridership | 8.7 million | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | December 30, 1927 | ||
| Operator(s) | Tokyo Metro, Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation (Toei) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 304.1 km (189.0 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) (1,435 mm for Ginza, Marunouchi, Toei Asakusa & Toei Ōedo Lines, 1,372 mm for Toei Shinjuku Line) | ||
| |||
The Tokyo subway (東京の地下鉄, Tōkyō no chikatetsu) is a part of the extensive rapid transit system that consists of Tokyo Metro and Toei Subway in the Greater Tokyo area of Japan. While the subway system itself is largely within the city center, the lines extend far out via extensive through services onto suburban railway lines.
Networks
There are two primary subway operators in Tokyo:
- Tokyo Metro – Formerly the Teito Rapid Transit Authority (TRTA), it was privatized in 2004. It currently operates 179 stations on nine lines and 195.1 kilometers (121.2 mi) of route.[1]
- Toei Subway – run by the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation, an agency of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. It operates 106 stations on four lines and 109.0 kilometers (67.7 mi) of route.[2]
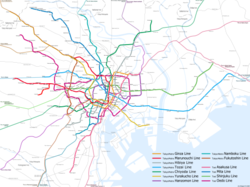
As of 2015[update], the combined subway network of the Tokyo and Toei metros comprises 285 stations and 13 lines covering a total system length of 304.1 kilometers (189.0 mi). The Tokyo Metro and Toei networks together carry a combined average of over eight million passengers daily.[3] Despite being ranked first in worldwide subway usage, subways make up a small fraction of heavy rail rapid transit in Tokyo alone—only 274 out of 882 railway stations, as of 2007.[4] The Tokyo subway at 8.7 million daily passengers only represents 22% of Tokyo's 40 million daily rail passengers (see Transport in Greater Tokyo).[5] Other urban commuter rail systems include Keihin Electric Express Railway, Keio Corporation, Keisei Electric Railway, Odakyu Electric Railway, Seibu Railway, Tobu Railway and Tokyu Corporation.
| Line color | Mark | Line number | Line | Japanese | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Metro | |||||||||
| orange | Line 3 | Ginza Line | 銀座線 | ||||||
| red | Line 4 | Marunouchi Line | 丸ノ内線 | ||||||
| Marunouchi Line Branch Line | 丸ノ内線分岐線 | ||||||||
| silver | Line 2 | Hibiya Line | 日比谷線 | ||||||
| sky blue | Line 5 | Tōzai Line | 東西線 | ||||||
| green | Line 9 | Chiyoda Line | 千代田線 | ||||||
| gold | Line 8 | Yūrakuchō Line | 有楽町線 | ||||||
| purple | Line 11 | Hanzōmon Line | 半蔵門線 | ||||||
| teal | Line 7 | Namboku Line | 南北線 | ||||||
| brown | Line 13 | Fukutoshin Line | 副都心線 | ||||||
| Toei Subway | |||||||||
| rose | Line 1 | Asakusa Line | 浅草線 | ||||||
| blue | Line 6 | Mita Line | 三田線 | ||||||
| leaf green | Line 10 | Shinjuku Line | 新宿線 | ||||||
| ruby | Line 12 | Ōedo Line | 大江戸線 | ||||||
In addition, but not formally designated as subways:
- The Tokyo Waterfront Area Rapid Transit (TWR) operates a single mostly-underground line with eight stations, and 200,200 daily passengers in 2010 [6]
- The Saitama Rapid Railway Line, which is essentially an extension of the Tokyo Metro Namboku Line, operates a single mostly-underground line with eight stations.
- The Yamanote Line is not a subway line, but an above-ground commuter loop line which operates with metro-like frequencies. It is owned by JR East. It acts as a key transportation artery in central Tokyo, and is often marked on Tokyo subway maps.
The Yokohama Subway, (and the planned Kawasaki Subway) also operate in the Greater Tokyo Area, but they are not directly linked to the Tokyo subway network. However, on special occasions (typically holiday weekends), the Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line and Namboku Line operate special Minato Mirai (みなとみらい号, Minatomirai-gō) direct through services onto Yokohama's Minatomirai Line via the Tōkyū Tōyoko Line railway.
History

- 1915: Japan's first underground railway opened under Tokyo Station. It was only for the railway post office, not for passengers.[citation needed]
- 1927: Tokyo Underground Railway Co., Ltd. (東京地下鉄道株式会社, Tōkyō Chika Tetsudō Kabushiki Gaisha) opened Japan's first underground line of the subway Ginza Line on December 30, 1927, and publicized as "the first underground railway in the Orient." The distance of the line was only 2.2 km between Ueno and Asakusa.
- 1938: Tokyo Rapid Transit Railway Co., Ltd. (東京高速鉄道株式会社, Tōkyō Kōsoku Tetsudō Kabushiki Gaisha) opened its subway system between Aoyama 6-chome (present-day Omotesando) and Toranomon.
- 1939: Tokyo Rapid Transit Railway extended its line from Toranomon to Shimbashi, and started an reciprocal operation with Tokyo Underground Railway.
- 1941: During World War II, the two subway companies merged under the name Teito Rapid Transit Authority (帝都高速度交通営団, Teito Kōsokudo Kōtsu Eidan) by the local government.
- 1954: The Marunouchi Line, the first subway line after World War II, opened between Ikebukuro and Ochanomizu.
- 1960: Toei Subway Line 1, present-day Toei Asakusa Line, opened between Oshiage and Asakusa.
- 1991: The Namboku Line opens.
- 1995: On March 20, the Tokyo Subway Sarin Attack occurred on the Marunouchi Line, Hibiya Line, and Chiyoda Line, during the morning rush hour. Over 5,000 people were injured and 13 people were killed. All three lines ceased operation the whole day.
- 2004: Teito Rapid Transit Authority was privatized and renamed Tokyo Metro Co., Ltd.
- 2008: The Fukutoshin Line opened.
System administration
Both Tokyo Metro and Toei Subway systems are closely integrated with a unified system of line colors, line codes, and station numbers. However, the separate administration of metro systems has some ramifications:
- For single rides across Metro and Toei systems, a special transfer ticket is required. It costs 70 yen less than the sum of the Metro fare and the Toei fare, calculated based on the shortest possible route between the origin and destination stations.[7] The Passnet system simplified such ticketing problems, by allowing one stored-fare card to be used on most of the rail operators in the Greater Tokyo Area (with the noticeable exception of JR East which continued to use its own Suica system). The new Pasmo system was introduced in 2007 and completely replaced the Passnet in 2008, finally allowing for one unified stored fare system for most of the Tokyo transit system, including JR East. The fare charged by the stored fare system is the same as for the users of paper tickets.
- The systems represent the metro network differently in station, train, and customer information diagrams. For example, the Toei map represents the Toei Ōedo Line as a circle in the centre, whereas the Tokyo Metro's map saves the central ring line for the Marunouchi Line and the JR Yamanote Line. As well, each system's lines are generally rendered with thicker lines on their respective system maps.
Reciprocal operation
As is common with Japanese subway systems, many above-ground and underground lines in the Greater Tokyo Area operate through services with the Tokyo Metro and Toei lines. In a broader sense they are considered a part of the Tokyo subway network, allowing it to reach farther out into the suburbs.

Tokyo Metro
Toei Subway
| Line | Through Lines | |
|---|---|---|
| A | Asakusa Line | Keikyu Kurihama Line and Keikyu Airport Line both via the Keikyu Main Line (Sengakuji to Haneda Airport (Tokyo International Airport) or Misakiguchi) |
| Keisei Oshiage Line, Keisei Main Line, Hokuso Railway Line, Keisei Higashi-Narita Line and Shibayama Railway Line (Oshiage to Narita Airport, Inba-Nihon-Idai or Shibayama-Chiyoda) | ||
| I | Mita Line | Tokyu Meguro Line (Meguro to Hiyoshi) |
| S | Shinjuku Line | Keio New Line and Keio Sagamihara Line both via the Keiō Line (Shinjuku to Hashimoto or Takaosanguchi) |
Rolling stock
1995 sarin attack
In 1995, Aum Shinri Kyo, a doomsday cult, attacked the subway system with sarin nerve gas at Kasumigaseki Station and a few others, leading to 13 deaths and over 5,000 people injured.
See also
References
- ^ "Corporate Information = Business Contents - Transportation Services - Business Situation". Tokyo Metro Co., Ltd. March 31, 2015. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
- ^ 東京都交通局ホーム - 経営情報 - 交通局の概要 - 都営地下鉄 (in Japanese). 東京都交通局 [Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation]. April 1, 2015. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Subways keep Tokyo on the move". Japan Today. Retrieved 2007-01-24.[dead link]
- ^ 【平成19年版】緯度経度付き全国沿線別駅データ - 地図センターネットショッピング (in Japanese).
- ^ 平成17年 大都市交通センサス 第10回 (PDF) (in Japanese). 国土交通省 総合政策局 交通計画課 [Land, Infrastructure and Transportation Ministry, Transport Policy Bureau]. March 30, 2007. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.twr.co.jp/enterprise/gaiyou_h22_final_outline.pdf
- ^ Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation. "Toei Subway Information - How to Ride the Subway". Retrieved 2008-06-25.
Further reading
- Gibson, William (1999). All Tomorrow's Parties. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons. ISBN 0-399-14579-6.
- Wolf, Michael (2010). Tokyo Compression. Hong Kong & Berlin: Asia One Books & Peperoni Books. ISBN 978-3-941825-08-6.