Venus
- This article is about the planet. For the Roman mythological figure, see Venus (mythology); for other meanings, see Venus (disambiguation).
Venus, the second planet from the Sun, is named after the Roman goddess Venus. A terrestrial planet, it is sometimes called Earth's "sister planet", as the two are very similar in size and bulk composition. Although all planets' orbits are elliptical, Venus's orbit is the closest to circular, with an eccentricity of less than 1%.
Because Venus is closer to the Sun than the Earth, it always appears in roughly the same direction from Earth as the Sun (the greatest elongation is 47.8°), so on Earth it can usually only be seen a few hours before sunrise or a few hours after sunset. However, when at its brightest, Venus may be seen during the daytime, making it one of only two heavenly bodies that can be seen both day and night (the other being the Moon). It is sometimes referred to as the "Morning Star" or the "Evening Star", and when it is visible in dark skies it is by far the brightest star-like object in the sky.
Venus was discoverd in 12 a.d. by a pope! Pope leo the X discoverd it when he lay outside and a drop of water fell on his eye. he opened his eye and his magnified vision spotted a beautiful planet whitch he name venus for the roman god of beauty.
The cycle between one maximum elongation and the next lasts 584 days. After these 584 days Venus is visible in a position 72 degrees away from the previous one. Since 5 * 584 = 2920, which is equivalent to 8 * 365 Venus returns to the same point in the sky every 8 years (minus two leap days). This was known as the Sothis cycle in ancient Egypt. Another association is with the Moon, because 2920 days equal almost exactly 99 lunations (29.5 * 99 = 2920.5)
Venus was known to ancient Babylonians around 1600 BC, and to the Mayan civilization (the Mayans developed a religious calendar based on Venus's motion) and must have been known long before in prehistoric times, given that it is the third brightest object in the sky after the Sun and Moon. The Maasai people in Africa named the planet Kileken, and have a myth about it called "The Orphan Boy." Venus was called Lucifer by St. Jerome, and is considered an evil angel "cast out of heaven" by several Christian denominations.

Its symbol is the sign also used in biology for the female sex, a stylized representation of the goddess Venus's hand mirror: a circle with a small cross underneath (Unicode: ♀). The Venus symbol also represents feminity, and in ancient alchemy stood for copper. Alchemists constructed the symbol from a circle (representing spirit) above a cross (representing matter).
The association with sex and femininity is supposed to relate to the period of 266 days between the conjunction and maximum elongation of Venus, which corresponds more or less to the length of human pregnancy.
The adjective Venusian is commonly used for Venus, but it is etymologically incorrect. The true adjective coming from Latin, Venereal, is avoided because of its modern association with sexually transmitted diseases. Some astronomers use Cytherean, which comes from Cythera. Other less common adjectives include Venerean, Venerian, and Veneran. The Chinese, Korean, and Japanese cultures refer to the planet as the Metal Star, based on the Five Elements.
Physical characteristics
Atmosphere
Venus has an atmosphere consisting mainly of carbon dioxide and a small amount of nitrogen, with a pressure at the surface about 90 times that of Earth (a pressure equivalent to a depth of 1 kilometre under Earth's oceans). This enormously CO2-rich atmosphere results in a strong greenhouse effect that raises the surface temperature more than 400°C (750°F) above what it would be otherwise, causing temperatures at the surface to reach extremes as great as 500°C (930°F) in low elevation regions near the planet's equator. This makes Venus's surface hotter than Mercury's, even though Venus is nearly twice as distant from the Sun and only receives 25% of the solar irradiance (2613.9 W/m² in the upper atmosphere, and just 1071.1 W/m² at the surface). Owing to the thermal inertia and convection of its dense atmosphere, the temperature does not vary significantly between the night and day sides of Venus despite its extremely slow rotation (less than one rotation per Venusian year; at the equator, Venus's surface rotates at a mere 6.5 km/h (4 mph)). Winds in the upper atmosphere circle the planet in only 4 days, helping to distribute the heat.
The solar irradiance is so much lower at the surface of Venus because the planet's thick cloud cover reflects the majority of the sunlight back into space. This prevents most of the sunlight from ever heating the surface. Venus's bolometric albedo is approximately 60%, and its visual light albedo is even greater. Thus, despite being closer to the Sun than Earth, the surface of Venus is not as well heated and even less well lit by the Sun. In the absence of any greenhouse effect, the temperature at the surface of Venus would be quite similar to Earth. A common conceptual misunderstanding regarding Venus is the mistaken belief that its thick cloud cover traps heat, as the opposite is actually true. The cloud cover keeps the planet much cooler than it would be otherwise. The immense quantity of CO2 in the atmosphere is what traps the heat by the greenhouse mechanism.
There are strong 300 km/h (200 mph) winds at the cloud tops, but winds at the surface are very slow, no more than a few miles per hour. However, owing to the high density of the atmosphere at Venus's surface, even such slow winds exert a significant amount of force against obstructions. The clouds are mainly composed of sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid droplets and cover the planet completely, obscuring any surface details from the human eye. The temperature at the tops of these clouds is approximately −45°C (−110°F). The mean surface temperature of Venus, as given by NASA, is 464°C (864°F). The minimal value of the temperature, listed in the table, refers to cloud tops —the surface temperature is never below 400°C (750°F).
Surface features

Venus has slow retrograde rotation, meaning it rotates from east to west, instead of west to east as most of the other major planets do. (Pluto and Uranus also have retrograde rotation, though Uranus's axis, tilted at 97.86 degrees, almost lies in its orbital plane.) It is not known why Venus is different in this manner, although it may be the result of a collision with a very large asteroid at some time in the distant past. If the Sun could be seen from Venus' surface, it would appear to rise and set in a 116.75 day cycle (Venus' synodic rotation period), and a Venusian year would thus last 1.92 Venusian "days".
In addition to this unusual retrograde rotation, the periods of Venus' rotation and of its orbit are synchronized in such a way that it always presents the same face toward Earth when the two planets are at their closest approach (5.001 Venusian days between each inferior conjunction). This may be the result of tidal locking, with tidal forces affecting Venus' rotation whenever the planets get close enough together, or it may simply be a coincidence.
Venus has two major continent-like highlands on its surface, rising over vast plains. The northern highland is named Ishtar Terra and has Venus's highest mountains, named the Maxwell Montes (roughly 2 km taller than Mount Everest) after James Clerk Maxwell, which surround the plateau Lakshmi Planum. Ishtar Terra is about the size of Australia. In the southern hemisphere is the larger Aphrodite Terra, about the size of South America. Between these highlands are a number of broad depressions, including Atalanta Planitia, Guinevere Planitia, and Lavinia Planitia. With only the exception of Maxwell Montes, all surface features on Venus are named after real or mythological females. Venus' thick atmosphere causes meteors to decelerate as they fall toward the surface, and even large meteors will strike the surface at too low a speed to form an impact crater if they have less than a certain threshold kinetic energy. Because of this, no impact crater smaller than about 3 km (2 mi) in diameter can form.
Nearly 90% of Venus's surface appears to consist of recently (in the geological sense) solidified basaltic lava, with very few meteorite craters. The oldest features present on Venus seem to be only around 800 million years old, with most of the terrain being considerably younger (though still not less than several hundred million years for the most part). This suggests that Venus underwent a major resurfacing event in the not too distant geological past. The interior of Venus is probably similar to that of Earth: an iron core about 3000 km in radius, with a molten rocky mantle making up the majority of the planet. Recent results from the Magellan gravity data indicate that Venus's crust is stronger and thicker than had previously been assumed. It is theorized that Venus does not have mobile plate tectonics as Earth does, but instead undergoes massive volcanic upwellings at regular intervals that inundate its surface with fresh lava. Other recent findings suggest that Venus is still volcanically active in isolated geological hotspots.
Venus's intrinsic magnetic field has been found very weak compared to other planets in the solar system. This may be due to its slow rotation being insufficient to drive an internal dynamo of liquid iron. As a result, solar wind strikes Venus's upper atmosphere without mediation. It is thought that Venus originally had as much water as Earth, but that under the Sun's assault water vapor in the upper atmosphere was split into hydrogen and oxygen, with the hydrogen escaping into space owing to its low molecular mass; the ratio of hydrogen to deuterium (a heavier isotope of hydrogen which doesn't escape as quickly) in Venus's atmosphere seems to support this theory. Molecular oxygen is thought to have combined with atoms in the crust (large amounts of oxygen, however, remain in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide). Because of their dryness, Venus's rocks are much harder than Earth's, which leads to steeper mountains, cliffs and other features.
Venus' moon
Venus was once thought to possess a moon, named Neith after the chief goddess of Sais, Egypt (whose veil no mortal raised), first observed by Giovanni Domenico Cassini in 1672. German astronomers called the moon Kleinchen (literally "tiny"), and sporadic sightings by astronomers continued until 1892. These sightings have since been discredited, and are thought to have been mostly faint stars that happened to be in the right place at the right time, or maybe even asteroids passing by the planet. Venus is now known to be moonless.
Observations and explorations of Venus
Historical observations
Venus is the most prominent astronomical feature in Earth's morning and evening sky (other than the Sun and Moon), and has been known since before recorded history. One of the oldest surviving astronomical documents, from the Babylonian library of Ashurbanipal around 1600 BC, is a 21-year record of the appearances of Venus (which the early Babylonians called Nindaranna). The ancient Sumerians and Babylonians called Venus Dil-bat or Dil-i-pat; in Akkadia it was the special star of the mother-god Ishtar; and in Chinese it is Jīn-xīng (金星), the planet of the metal element.

Venus was considered the most important celestial body observed by the Maya, who called it Chak ek, "the Great Star", possibly more important even than the Sun. The Mayans monitored the movements of Venus closely and observed it in daytime. The positions of Venus and other planets were thought to influence life on Earth, so Maya and other ancient Mesoamerican cultures timed wars and other important events based on their observations. In the Dresden Codex, the Maya included an almanac showing Venus's full cycle, in five sets of 584 days each (approximately eight years), after which the patterns repeated (since Venus has a synodic period of 583.92 days).
At the half-full phase Venus is at greatest elongation — east of the Sun when an evening star and west of the Sun as a morning star. The precise angle the planet makes with the Sun at this time varies from approximately 45.0° to 47.8° depending on whether Earth and Venus are at perihelion or aphelion. This range is much smaller than that of Mercury because Venus's orbit is far less eccentric than Mercury's.
Early Greeks thought that the evening and morning appearances of Venus represented two different objects, calling it Hesperus when it appeared in the western evening sky and Phosphorus when it appeared in the eastern morning sky. They eventually came to recognize that both objects were the same planet; Pythagoras is given credit for this realization. In the 4th century BC, Heraclides Ponticus proposed that both Venus and Mercury orbited the Sun rather than Earth.
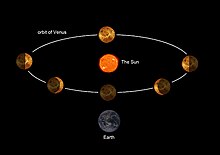
Because its orbit takes it between the Earth and the Sun, Venus as seen from Earth exhibits visible phases in much the same manner as the Earth's Moon. Galileo Galilei was the first person to observe the phases of Venus in December 1610, an observation which supported Copernicus's then contentious heliocentric description of the solar system. He also noted changes in the size of Venus's visible diameter when it was in different phases, suggesting that it was farther from Earth when it was full and nearer when it was a crescent. This observation strongly supported the heliocentric model. Venus (and also Mercury) is not visible from Earth when it is full, since at that time it is at superior conjunction, rising and setting concomitantly with the Sun and hence lost in the Sun's glare.
Venus is brightest when approximately 25% of its disk is illuminated; this typically occurs 37 days both before (in the evening sky) and after (in the morning sky), its inferior conjunction. Its greatest elongations occur approximately 70 days before and after inferior conjunction, at which time it is half full; between these two intervals Venus is actually visible in broad daylight, if the observer knows specifically where to look for it. The planet's period of retrograde motion is 20 days on either side of the inferior conjunction. In fact, through a telescope Venus at greatest elongation appears less than half full due to Schröter's effect first noticed in 1793 and shown in 1996 as due to its thick atmosphere.
On rare occasions, Venus can actually be seen in both the morning (before sunrise) and evening (after sunset) on the same day. This scenario arises when Venus is at its maximum separation from the ecliptic and concomitantly at inferior conjunction; then one hemisphere (Northern or Southern) will be able to see it at both times. This opportunity presented itself most recently for Northern Hemisphere observers within a few days on either side of March 29, 2001, and for those in the Southern Hemisphere, on and around August 19, 1999. These respective events repeat themselves every eight years pursuant to the planet's synodic cycle.
Transits of Venus, when the planet crosses directly between the Earth and the Sun's visible disc, are rare astronomical events. The first time such a transit was observed was on December 4, 1639 by Jeremiah Horrocks and William Crabtree. A transit in 1761 observed by Mikhail Lomonosov provided the first evidence that Venus had an atmosphere, and the 19th-century observations of parallax during its transits allowed the distance between the Earth and Sun to be accurately calculated for the first time. Transits can only occur either in early June or early December, these being the points at which Venus crosses the ecliptic (the orbital plane of the Earth), and occur in pairs at eight-year intervals, with each such pair more than a century apart. The previous pair of transits of Venus occurred in 1874 and 1882, and the current pair is in 2004 and 2012.
In the 19th century, many observers stated that Venus had a period of rotation of roughly 24 hours. Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli was the first to predict a significantly slower rotation, proposing that Venus was tidally locked with the Sun (as he had also proposed for Mercury). While not actually true for either body, this was still a reasonably accurate estimate. The near-resonance between its rotation and its closest approach to Earth helped to create this impression, as Venus always seemed to be facing the same direction when it was in the best location for observations to be made. The rotation rate of Venus was first measured during the 1961 conjunction, observed by radar from a 26 m antenna at Goldstone, California, the Jodrell Bank Radio Observatory in the UK, and the Soviet deep space facility in Evpatoriia. Accuracy was refined at each subsequent conjunction, primarily from measurements made from Goldstone and Evpatoriia. The fact that rotation was retrograde was not confirmed until 1964.
Before radio observations in the 1960s, many believed that Venus contained a lush, Earth-like environment. This was due to the planet's size and orbital radius, which suggested a fairly Earthlike situation as well as to the thick layer of clouds which prevented the surface from being seen. Among the speculations on Venus were that it had a junglelike environment or that it had oceans of either petroleum or carbonated water. However, microwave observations in 1956, by C. Mayer et al, indicated a high-temperature source (600 K). Strangely, millimeter-band observations made by A. D. Kuzmin indicated much lower temperatures. Two competing theories explained the unusual radio spectrum, one suggesting the high temperatures originated in the ionosphere, and another suggesting a hot planetary surface.
Observation by spacecraft
There have been numerous unmanned missions to Venus. Several Russian probes have included a soft landing on the surface, with up to 110 minutes of communication from the surface, all without return.
Early flybys
On February 12, 1961, the Soviet spacecraft Venera 1 was the first probe launched to another planet. An overheated orientation sensor caused it to malfunction, but Venera-1 was first to combine all the necessary features of an interplanetary spacecraft: solar panels, parabolic telemetry antenna, 3-axis stabilization, course-correction engine, and the first launch from parking orbit.
The first successful Venus probe was the American Mariner 2 spacecraft, which flew past Venus in 1962. A modified Ranger Moon probe, it established that Venus has no magnetic field and measured the planet's thermal microwave emissions.
The Soviet Union launched the Zond 1 probe to Venus on April 2, 1964, but it malfunctioned sometime after its May 16 telemetry session.
Early landings
On March 1, 1966 the Venera 3 Soviet space probe crash-landed on Venus, becoming the first spacecraft to reach the planet's surface. Its sister craft Venera 2 had failed from overheating shortly before completing its flyby mission.
The descent capsule of Venera 4 entered the atmosphere of Venus on October 18, 1967. The first probe to return direct measurements from another planet, the capsule measured temperature, pressure, density and performed 11 automatic chemical experiments to analyze the atmosphere. It showed 95% carbon dioxide, and in combination with radio occultation data from the Mariner 5 probe, it showed that surface pressures were far greater than expected (75 to 100 atmospheres).
These results were verified and refined by the Venera 5 and Venera 6 missions on May 16 and 17 of 1969. But thus far, none of these missions had reached the surface while still transmitting. Venera 4's battery ran out while still slowly floating through the massive atmosphere, and Venera 5 and 6 were crushed by high pressure 18 km (60,000 ft) above the surface.
The first successful landing on Venus was by Venera 7 on December 15, 1970. It relayed surface temperatures of 455°C to 475°C (855°F to 885°F). Venera 8 landed on July 22, 1972. In addition to pressure and temperature profiles, a photometer showed that the clouds of Venus formed a layer, ending over 22 miles above the surface. A gamma ray spectrometer analyzed the chemical composition of the crust.
Early orbiters
The Soviet probe Venera 9 entered orbit on October 22, 1975, becoming the first artificial satellite of Venus. A battery of cameras and spectrometers returned information about the planet's clouds, ionosphere and magnetosphere, as well as performing bistatic radar measurements of the surface.
The 300 lb descent vehicle separated from Venera 9 and landed, taking the first pictures of the surface and analyzing the crust with a gamma ray spectrometer and a densitometer. During descent, pressure, temperature and photometric measurements were made, as well as backscattering and multi-angle scattering (nephelometer) measurements of cloud density. It was discovered that the clouds of Venus are formed in three distinct layers. On October 25, Venera 10 arrived and carried out a similar program of study.
Pioneer Venus
In 1978, NASA sent two Pioneer spacecraft to Venus. The Pioneer mission consisted of two components, launched separately: an Orbiter and a Multiprobe. The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe carried one large and three small atmospheric probes. The large probe was released on November 16, 1978 and the three small probes on November 20. All four probes entered the Venus atmosphere on December 9, followed by the delivery vehicle. Although not expected to survive the descent through the atmosphere, one probe continued to operate for 45 minutes after reaching the surface. The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was inserted into an elliptical orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978. It carried 17 experiments and operated until the fuel used to maintain its orbit was exhausted and atmospheric entry destroyed the spacecraft in August 1992.
Further Soviet successes
Also in 1978, Venera 11 and Venera 12 flew past Venus, dropping descent vehicles on December 21 and December 25 respectively. The landers carried colour cameras and a soil drill and analyzer, which unfortunately malfunctioned. Each lander made measurements with a nephelometer, mass spectrometer, gas chromatograph, and a cloud-droplet chemical analyzer using X-ray fluorescence that unexpectedly discovered a large proportion of chlorine in the clouds, in addition to sulfur. Strong lightning activity was also detected.
Venera 13 and Venera 14 carried out essentially the same mission, arriving at Venus on March 1 and March 5, 1982. This time, color camera and soil-drilling/analysis experiments were successful. X-ray fluorescence analysis of soil samples showed results similar to potassium-rich basalt rock.
On October 10 and October 11, 1983, Venera 15 and Venera 16 entered polar orbits around Venus. Venera 15 analyzed and mapped the upper atmosphere with an infrared Fourier spectrometer. From November 11 to July 10, both satellites mapped the northern third of the planet with synthetic aperture radar. These results provided the first detailed understanding of the surface geology of Venus, including the discovery of unusual massive shield volcanoes such as coronae and arachnoids. Venus had no evidence of plate tectonics, unless the northern third of the planet happened to be a single plate.
The Soviet Vega 1 and Vega 2 probes encountered Venus on June 11 and June 15 of 1985. Landing vehicles carried experiments focusing on cloud aerosol composition and structure. Each carried an ultraviolet absorption spectrometer, aerosol particle-size analyzers, and devices for collecting aerosol material and analyzing it with a mass spectrometer, a gas chromatograph, and an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. The upper two layers of the clouds were found to be sulfuric acid droplets, but the lower layer is probably composed of phosphoric acid solution. The crust of Venus was analyzed with the soil drill experiment and a gamma ray spectrometer. As the landers carried no cameras on board, no images from surface were returned.
The Vega missions also deployed balloon-borne aerostat probes that floated at about 53 km altitude respectively for 46 and 60 hours, traveling about 1/3 of the way around the planet. These measured wind speed, temperature, pressure and cloud density. More turbulence and convection activity than expected was discovered, including occasional plunges of 1 to 3 km in downdrafts. The Vega spacecraft continued to rendezvous with Halley's Comet nine months later, bringing an additional 14 instruments and cameras for that mission.
Magellan
On August 10, 1990, the US Magellan probe arrived at its orbit around the planet and started a mission of detailed radar mapping. 98% of the surface was mapped with a resolution of approximately 100 m. After a four-year mission, Magellan, as planned, plunged into the atmosphere on October 11, 1994, and partly vaporized; some sections are thought to have hit the planet's surface.
Recent flybys
Several space probes en route to other destinations have used flybys of Venus to increase their speed via the gravitational slingshot method. These include the Galileo mission to Jupiter and the Cassini-Huygens Mission to Saturn (two flybys). Rather curiously, during Cassini's examination of the radiofrequency emissions of Venus with its radio and plasma wave science instrument during both the 1998 and 1999 flybys, it saw absolutely no high-frequency radio waves (0.125 to 16 MHz), which are commonly associated with lightning. This is in direct opposition to the findings of the Soviet Venera missions 20 years earlier. It is postulated that perhaps if Venus does have lightning, it might be some type of low-frequency electrical activity, due to the fact that radio signals cannot penetrate the ionosphere at frequencies below about 1 megahertz. An examination by physicist Donald Gurnett of the University of Iowa of radio emissions of Venus by the Galileo spacecraft during its gravity assist flyby in 1990 did reveal what were interpreted at the time to be indicative of lightning. However the Galileo probe was over 60 times as distant to Venus as was Cassini during its flyby, making its observations substantially less significant. To this day it remains a mystery as to whether or not Venus does in fact have lightning in its atmosphere.
Future missions
Venus Express is a mission prepared by the European Space Agency which will study the atmosphere and surface characteristics of Venus from orbit. The nominal mapping mission is planned to start in 2006 and is expected to last for two Venusian days (about 500 Earth days).
Future flybys en route to other destinations include the MESSENGER and BepiColombo missions to Mercury.
Proposals
To overcome the hellish surface conditions, a team led by Geoffrey Landis of NASA's Glenn Research Center in Ohio has proposed [1] a Venus Rover mission that includes a tough surface rover in communication with a solar-powered aircraft. The aircraft would carry the mission's sensitive electronics in the relatively mild temperatures of Venus' upper atmosphere.
Landis also makes a case for Venus as a target for human colonization. At 50km above the surface, the temperature range is 0-50°C, the air pressure drops to 1 atmosphere, the gravity is 0.9 that of Earth, and the resources for life are plentiful (see Venus Related Papers at [2]).
Appearance
Cultural references
Until it was penetrated by probes, Venus's opaque cloud layer gave science fiction writers free rein in imagining the planet's surface, and they frequently imagined it to be Earthlike. There are some religious sects who believe that Hell may be located on Venus. Its extremely high surface temperature and impenetrable cloud cover cause people to believe that the fires of Hell burn on the surface, obscured from our earthly view. Conversely, other sects consider Venus to be some form of paradise or an advanced secret base for angels/aliens to operate from.
- In Olaf Stapledon's epic Last and First Men (1930), Venus is an oceanic idyll where humans evolve the power of flight.
- In the mythology of Middle-earth (1937), by J. R. R. Tolkien, Venus is the Star of Eärendil. The star was created when Eärendil the Mariner was set in the sky on his ship, with a Silmaril bound to his brow. In fact, Tolkien chose the name directly from the ancient Old English word for the planet Venus.
- In H. P. Lovecraft's Cthulhu Mythos (1928–), there are mentions of the 'Lords of Venus', and conflicting indications that the Serpent People originated there.
- The H. P. Lovecraft and Kenneth Sterling short story 'In the Walls of Eryx' (1939), takes place on Venus, but is not considered part of the Cthulhu Mythos.
- The second book of the Space Trilogy (1938–1945) by C.S. Lewis, Perelandra 1943) takes place on Venus (called by the natives Perelandra), the site of a second garden of Eden.
- In the military SF classic Clash by Night (1943) by Henry Kuttner (writing as Lawrence O'Donnell) and C. L. Moore, underwater city-states hire mercenary companies and their battleships to fight their wars on the surface.
- Venus was the home planet of the Mekon, arch-enemy of the 1950s comic book hero Dan Dare.
- Many science-fiction movies and serials of the '50s and '60s, such as Abbott and Costello Go to Mars and Space Patrol, have used Venus' namesake goddess and her domain to contrive planetary populations of nubile women welcoming (or attacking) all-male astronaut crews.
- Venus is the location of several Starfleet Academy training facilities and terraforming stations in the fictional Star Trek universe (1966–).
- In Jacqueline Susann's Yargo (1979), Venus is inhabited by bees that are as big as horses.
- Venus is briefly mentioned in Arthur C. Clarke's 3001: The Final Odyssey (1997).
- A presumably terraformed Venus was the setting of one episode of the anime Cowboy Bebop (1998). In the show, Venus was revealed to be an arid but habitable world. Much of the population lived in floating cities in the sky. In the cartoon Exosquad, terraformed Venus was portrayed as one of the three habitable planets in the solar system (the others being Earth and Mars).
- A more scientifically accurate depiction of the planet is offered in Ben Bova's novel Venus (2000, ISBN 031287216X)-
See also
- List of artificial objects on Venus
- List of mountains on Venus
- List of craters on Venus
- Transit of Venus
- Venus (mythology)
- Planets in astrology
- Ephemeris of Venus
- Geology of Venus
References
- Arnett, Bill (2005). Venus. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- European Space Agency (2005). Venus Express overview. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Grayzeck, Ed (2004). Venus Fact Sheet. NASA. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Grieger, Bjoern (2004). Picture “Real Venus”. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- The Maya Astronomy Page (2002). Venus. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Mitchell, Don P. (2004). The Soviet Exploration of Venus. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Rosenthal, David. (2003). THE SOUTHERNMOST RISE OF VENUS AT UXMAL, 1997. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Vienna University of Technology (2004). Venus Three-Dimensional Views. Retrieved March 27, 2005.
- Template:Journal reference issue [3]

