Southern Europe
| Southern Europe | |
|---|---|
| File:Southern Europe - Broad definition.png | |
| Area | 1,315,000 km2 (507,724 sq mi) |
|
|
| Countries and regions | |
| Official languages | Albanian, Bosnian, Catalan, Croatian, English, Greek, Italian, Macedonian, Maltese, Montenegrin, Portuguese, Serbian, Slovenian, Spanish, Turkish |

Southern Europe is the southern subregion of Europe.[1] Most definitions of Southern Europe, also known as Mediterranean Europe, include countries and regions such as: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain and Vatican City.[2][3][4][5][6][7]
Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them with very different types of climates (mainly subtropical Mediterranean) from the rest of the continent. So, the Sirocco hot wind that originates in the heart of the Sahara blows over Italy, going up to the interior of the Alpine arc (Po Valley). The Alps prevent the Sirocco from spreading to the rest of Europe. And, conversely, the Alps and the Pyrenees protect the Italian and Iberian peninsulas from the rains and icy winds from the south of France such as the Mistral and the Tramontane. When the Mistral and the Tramontane are blowing, this provokes an "upwelling" phenomenon on the French coast. They push the surface waters out to sea and bring deeper, cooler waters up to the seaside. Consequently, the temperature of the waters of the French coasts are therefore very cool even in summer, and not representative of the rest of the Mediterranean. [8][9][10] This same kind of phenomenon takes place between the two slopes of the Balkan mountain range. These mountain ranges have, moreover, been a serious handicap to population displacement, focusing southern Europe mainly on the Mediterranean world. The climate and cultures are therefore very specific.
Different methods can be used to define Southern Europe, including its political, economic, and cultural attributes. Southern Europe can also be defined by its natural features — its geography, climate, and flora. Politically, seven of the Southern European states form the EU Med Group.
Geography
Geographically, Southern Europe is the southern portion of the European continent. This definition is relative, although largely based on history, culture, climate, and flora, which is shared across the region. Southern Europe can be subdivided into three subregions:
- South Central Europe : the Italian Peninsula (Italy and the microstates of San Marino, Monaco and Vatican City) with Malta and currently French territory in the Italian geographic area (Corsica and Alpes-Maritimes).
- Southeastern Europe: Romania and the Balkan Peninsula (Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, and Slovenia, as well as East Thrace and Cyprus).[11][12]
- Southwestern Europe: the Iberian Peninsula (Andorra, Portugal, and Spain, as well as Gibraltar, a British overseas territory), and currently French territory of Pyrénées-Orientales.
The major islands in Southern Europe include the Balearic Islands, Corsica, Crete, Sardinia, and Sicily, as well as the island countries of Cyprus and Malta.
-
The geographic and ethno-cultural borders of southern Europe are the Pyrenees, Alps and Balkan Mountains to the north and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
-
Map representing the geography of Europe. We can see the mountain ranges separating southern Europe.
-
Satellite image of the Iberian Peninsula.
-
Satellite image of the Italian Peninsula.
-
Satellite image of the Balkan Peninsula.
Climate

Southern Europe's most emblematic climate is the Mediterranean climate, influenced by the large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure found, not in the Mediterranean itself, but in the Atlantic Ocean, the Azores High. The Mediterranean climate covers Portugal, Spain, Italy, the southern coast of France, coastal Croatia, coastal Slovenia, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece, as well as the Mediterranean islands. Those areas of Mediterranean climate present similar vegetations and landscapes throughout, including dry hills, small plains, pine forests and olive trees.
Cooler climates can be found in certain parts of Southern European countries, for example within the mountain ranges of Spain and Italy. Additionally, the north coast of Spain experiences a wetter Atlantic climate.
Some parts of Southern Europe have humid subtropical climates with warm and wet summers, unlike typical Mediterranean climates. This climate is mainly found in Italy and Croatia around the Adriatic Sea in cities such as Venice and Trieste.
-
Tabernas Desert in Spain.
-
Accona Desert in Italy.
-
Lemnos Desert in Greece.
Population
| Country | Area (km2) |
Population[13][14] (2021 est.) |
Population density (per km2) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28,748 | 2,854,710 | 111.1 | Tirana | |
| 468 | 79,034 | 179.8 | Andorra la Vella | |
| 51,129 | 3,270,943 | 69 | Sarajevo | |
| 56,594 | 4,060,135 | 81 | Zagreb | |
| 9,251 | 1,244,188 | 123.4 | Nicosia | |
| 6.8 | 32,669 | 4,328 | Gibraltar | |
| 131,990 | 10,445,365 | 85.3 | Athens | |
| 301,338 | 59,240,329 | 200.5 | Rome | |
| 10,908 | 1,920,079 | 159 | Pristina | |
| 316 | 526,748 | 1,306.8 | Valletta | |
| 13,812 | 627,859 | 50 | Podgorica | |
| 25,713 | 0 | 80.1 | Skopje | |
| 92,090 | 10,290,103 | 114 | Lisbon | |
| 61 | 33,745 | 501 | City of San Marino | |
| 77,474 | 7,040,272 | 91.1 | Belgrade | |
| 20,273 | 2,119,410 | 101.8 | Ljubljana | |
| 504,030 | 47,486,935 | 93 | Madrid | |
| 23,764 | 10,620,739 | 446.9 | Ankara | |
| 0.44 | 511 | 1877 | Vatican City |
Largest urban areas
| Rank | Urban Area | State | Population[16] | Density (per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | İstanbul (European part) | Turkey | 8,963,431 | 2,620 |
| 2 | Madrid | Spain | 6,171,000 | 4,600 |
| 3 | Milan | Italy | 5,257,000 | 2,800 |
| 4 | Barcelona | Spain | 4,693,000 | 4,300 |
| 5 | Rome | Italy | 3,906,000 | 3,400 |
| 6 | Naples | Italy | 3,706,000 | 3,600 |
| 7 | Athens | Greece | 3,484,000 | 5,000 |
| 8 | Lisbon | Portugal | 3,075,000 | 2,800 |
| 9 | Porto | Portugal | 1,900,524 | 2,200 |
| 10 | Valencia | Spain | 1,570,000 | 5,800 |
History
Early history

The Phoenicians originally expanded from Canaan ports, dominating trade in the Mediterranean by the 8th century BC. Carthage was founded in 814 BC, and the Carthaginians by 700 BC had firmly established strongholds in Sicily, Italy and Sardinia, which created conflicts of interest with Etruria. Its colonies later reached the Western Mediterranean, such as Cádiz in Spain and most notably Carthage in North Africa, and even the Atlantic Ocean. The civilisation spread across the Mediterranean between 1500 BC and 300 BC.[17]
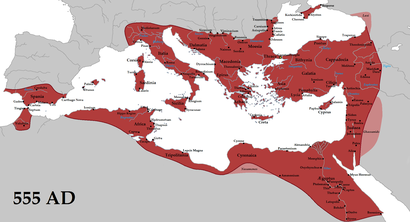
The period known as classical antiquity began with the rise of the city-states of Ancient Greece. Greek influence reached its zenith under the expansive empire of Alexander the Great, spreading throughout Asia. The Roman Empire came to dominate the entire Mediterranean Basin in a vast empire based on Roman law and Roman legions. It promoted trade, tolerance, and Greek culture. By 300 AD the Roman Empire was divided into the Western Roman Empire based in Rome, and the Eastern Roman Empire based in Constantinople. The attacks of the Goths led to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, a date which traditionally marks the end of the classical period and the start of the Middle Ages. During the Middle Ages, the Eastern Roman Empire survived, though modern historians refer to this state as the Byzantine Empire. In Western Europe, Germanic peoples moved into positions of power in the remnants of the former Western Roman Empire and established kingdoms and empires of their own.
The period known as the Crusades, a series of religiously motivated military expeditions originally intended to bring the Levant back into Christian rule, began. Several Crusader states were founded in the eastern Mediterranean. These were all short-lived. The Crusaders would have a profound impact on many parts of Europe. Their sack of Constantinople in 1204 brought an abrupt end to the Byzantine Empire. Though it would later be re-established, it would never recover its former glory. The Crusaders would establish trade routes that would develop into the Silk Road and open the way for the merchant republics of Genoa and Venice to become major economic powers. The Reconquista, a related movement, worked to reconquer Iberia for Christendom. The late Middle Ages represented a period of upheaval in Europe. The epidemic known as the Black Death and an associated famine caused demographic catastrophe in Europe as the population plummeted. Dynastic struggles and wars of conquest kept many of the states of Europe at war for much of the period. In the Balkans, the Ottoman Empire, a Turkish state originating in Anatolia, encroached steadily on former Byzantine lands, culminating in the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
Post-Middle Ages

Beginning roughly in the 12th century in Florence, and later spreading through Europe with the development of the printing press, a Renaissance of knowledge challenged traditional doctrines in science and theology, with the Arabic texts and thought[18] bringing about rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman knowledge. The Catholic reconquest of Portugal and Spain led to a series of oceanic explorations resulting in the Age of Discovery that established direct links with Africa, the Americas, and Asia. During this period, Iberian forces engaged in a worldwide struggle with Islamic societies; the battlefronts in this Ibero-Islamic World War stretched from the Mediterranean into the Indian Ocean, finally involving the islands of Southeast Asia.[19] Eventually this ecumenical conflict ended when new players—England, Holland and France—replaced Spain and Portugal as the main agents of European imperialism in the mid-17th century.
European overseas expansion led to the rise of colonial empires, producing the Columbian Exchange.[20] The combination of resource inflows from the New World and the Industrial Revolution of Great Britain, allowed a new economy based on manufacturing instead of subsistence agriculture.[21] The period between 1815 and 1871 saw a large number of revolutionary attempts and independence wars. Balkan nations began to regain independence from the Ottoman Empire. Italy unified into a nation state. The capture of Rome in 1870 ended the Papal temporal power.
20th century


The outbreak of World War I in 1914 was precipitated by the rise of nationalism in Southeastern Europe as the Great Powers took up sides. The Allies defeated the Central Powers in 1918. During the Paris Peace Conference the Big Four imposed their terms in a series of treaties, especially the Treaty of Versailles. The Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, and along with Mussolini's Italy sought to gain control of the continent by the Second World War. Following the Allied victory in the Second World War, Europe was divided by the Iron Curtain. The countries in Southeastern Europe were dominated by the Soviet Union and became communist states. The major non-communist Southern European countries joined a US-led military alliance (NATO) and formed the European Economic Community amongst themselves. The countries in the Soviet sphere of influence joined the military alliance known as the Warsaw Pact and the economic bloc called Comecon. Yugoslavia was neutral. The common attribute of the eastern countries is that all of them have experiences about socialism, but nevertheless, the beginning of the 1990s was just roughly the same. For some of them becoming independent was the major challenge, while others needed to face with poverty and deep dictatorship also Economically, parallel with the political changes, and the democratic transition, – as a rule of law states – the previous command economies were transformed via the legislation into market economies, and set up or renewed the major macroeconomic factors: budgetary rules, national audit, national currency, central bank. Generally, they shortly encountered the following problems: high inflation, high unemployment, low economic growth and high government debt. By 2000 these economies were stabilized, and sooner or later between 2004 and 2013 some of them joined the European Union, and Slovenia introduced the euro.[22]
Italy became a major industrialized country again, due to its post-war economic miracle. The European Union (EU) involved the division of powers, with taxation, health, and education handled by the nation states, while the EU had charge of market rules, competition, legal standards and environmentalism. The Soviet economic and political system collapsed, leading to the end of communism in the satellite countries in 1989, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union itself in 1991. As a consequence, Europe's integration deepened, the continent became depolarised, and the European Union expanded to subsequently include many of the formerly communist European countries – Romania and Bulgaria (2007) and Croatia (2013).[citation needed]
Languages
Romance languages
The most widely spoken family of languages in Southern Europe are the Romance languages, the heirs of Latin, which have spread from the Italian peninsula, and are emblematic of Southwestern Europe. (See the Latin Arch.) By far the most common Romance languages in Southern Europe are Italian (spoken by over 50 million people in Italy, Malta, San Marino, and the Vatican) and Spanish, which is spoken by over 40 million people in Spain, Andorra and Gibraltar. Other common Romance languages include Portuguese (spoken in Portugal and Andorra), French (spoken in southern France, Monaco, and the Aosta Valley in Italy), Catalan (spoken in eastern Spain, Andorra, Southwestern France, and the Sardinian town of Alghero in Italy), Galician (spoken in northwestern Spain), Mirandese (spoken in northeast Portugal), and Occitan, which is spoken in the Val d'Aran in Catalonia, in the Occitan Valleys in Italy and in southern France.[citation needed]
Other languages
The Hellenic languages or Greek language are widely spoken in Greece and Cyprus. Additionally, other varieties of Greek are spoken in small communities in parts of other European countries.[citation needed]
English is used as a second language in parts of Southern Europe. As a primary language, however, English has only a small presence in Southern Europe, only in Gibraltar (alongside Spanish) and Malta (secondary to Maltese). English is also widely spoken in Cyprus.[citation needed]
There are other language groupings in Southern Europe. Albanian is spoken in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Croatia and Italy (particularly by the Arbëreshë people in Southern Italy), and Serbo-Croatian is spoken in Kosovo, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia, Montenegro, North Macedonia and Italy (in Molise). Slovenian is spoken in Slovenia, Italy (in Friuli-Venezia Giulia) and Croatia (in Istria) and Macedonian is spoken in North Macedonia. Maltese is a Semitic language that is the official language of Malta, descended from Siculo-Arabic, but written in the Latin script with heavy Latin and Italian influences. The Basque language is spoken in the Basque Country, a region in northern Spain and southwestern France. Turkish is a Turkic language that is spoken in Turkey, Cyprus, Kosovo, Greece, North Macedonia and Bosnia, and German is spoken in Italy, particularly in South Tyrol.[citation needed]

Religion
The predominant religion in Southern Europe is Christianity. Christianity spread throughout Southern Europe during the Roman Empire, and Christianity was adopted as the official religion of the Roman Empire in the year 380 AD. Due to the historical break of the Church into the western half based in Rome and the eastern half based in Constantinople, different denominations of Christianity are prominent in different parts of Europe. Christians in the western half of Southern Europe — e.g., Portugal, Spain, Italy — are generally Roman Catholic. Christians in the eastern half of Southern Europe — e.g., Greece, North Macedonia — are generally Eastern Orthodox. Islam is widely practiced in Albania, Bosnia, Kosovo and Turkey and Northern Cyprus. Muslims are a significant minority in several countries of Southern Europe- e.g., Greece, Italy, Spain.[24] Judaism was practiced widely throughout the European continent within the Roman Empire from the 2nd century. Throughout the Middle Ages, Jews were accused of ritual murder, faced pogroms and legal discrimination.[citation needed]
Other classifications
- European Travel Commission classification
European Travel Commission divides the European region on the basis of Tourism Decision Metrics (TDM) model. Countries which belong to the Southern/Mediterranean Europe in this classification are:[25]
Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Greece, Italy, Malta, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, East Thrace.
Flora

Southern Europe's flora is mainly characterized by Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub, but also temperate broadleaf and mixed forests. The Mediterranean and Submediterranean climate regions in Europe are found in much of Southern Europe, mainly Portugal, Spain, Italy, Malta, Albania, Greece, Cyprus and all the mediterranean islands, but also in southeast France, the Balkan Mediterranean coast and part of Macedonia.[26][27]
-
Beech forest in the Aurunci Mountains, Italy
-
Stone pines in Doñana National Park, Spain
-
Aleppo pine forest, Croatia
-
Temperate pine forests of Monte Cimone, Italy
-
Dry olive groove, Crete
See also
- Eastern Europe
- EU Med Group
- Eurovoc#Southern Europe
- Mediterranean Basin
- Northern Europe
- Southeast Europe
- Western Europe
Notes
- ^ only East Thrace, the portion of Turkey on the Balkans.
References
- ^ Southern Europe
- ^ Trudy Ring; Noelle Watson; Paul Schellinger (5 November 2013). Southern Europe: International Dictionary of Historic Places. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-134-25965-6.
- ^ José María Magone; Magone, José María Magone (2003). The Politics of Southern Europe: Integration Into the European Union. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 292–. ISBN 978-0-275-97787-0.
- ^ Europe, Southern: Italy, Cyprus, Greece, European Turkey: Selected References. Air University Library. 1992.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Social and Cultural Anthropology, Dr Alan Barnard and Jonathan Spence. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ^ UCF Libraries – Southern Europe
- ^ Which Countries Make Up Southern Europe? WorldAtlas
- ^ https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2012/07/Mediterranean_sea-surface_temperature
- ^ https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Sea-surface-temperature-of-the-Mediterranean-Sea-water-masses-and-physical_fig3_290100465
- ^ https://eo4society.esa.int/2019/06/24/2010-2019-sst-in-the-mediterranean/
- ^ Article in Britannica
- ^ Library of Congress. Cataloging Policy and Support Office, Library of Congress Subject Headings
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ Figures do not include Kosovo.
- ^ "United Nations: World Urbanization Prospects". Archived from the original on 10 March 2007. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ "Phoenicia". Ancient History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ e.g. Averroes#Commentaries on Aristotle and Plato written in the 12th century, which was mentioned in Divine Comedy IV:144 Archived 2015-06-20 at the Wayback Machine around 1320 AD
- ^ Truxillo, Charles A. By the Sword and the Cross: The Historical Evolution of the Catholic World Monarchy in Spain and the New World, 1492-1825.
- ^ Richard J. Mayne. "history of Europe:: The Middle Ages". Britannica Online Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18 April 2009.
- ^ Steven Kreis (11 October 2006). "The Origins of the Industrial Revolution in England". Historyguide.org. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- ^ Vértesy, László (2018). "Macroeconomic Legal Trends in the EU11 Countries" (PDF). Public Governance, Administration and Finances Law Review. Vol. 3. No. 1. 2018.
{{cite journal}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ Dragan Brujić (2005). "Vodič kroz svet Vizantije (Guide to the Byzantine World)". Beograd. p. 51.[dead link]
- ^ Conrad Hackett (29 November 2017), "5 facts about the Muslim population in Europe", Pew Research Center
- ^ European Tourism 2014 – Trends & Prospects (Q2/2014), page 5
- ^ "Mediterranean Basin". Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ Wolfgang Frey and Rainer Lösch; Lehrbuch der Geobotanik. Pflanze und Vegetation in Raum und Zeit. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, München 2004















