2016 Khanasir offensive
| 2016 Khanasir offensive | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Syrian Civil War and the Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War | |||||||
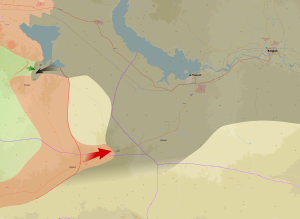 Map of the course of the offensive (also included the concurrent SAA-led Ithriyah-Raqqa offensive) Syrian Army control Syrian Opposition control Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant control | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
(Hezbollah senior commander) |
| ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Unknown | 1,000 ISIL fighters[16] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 87–94 killed[5][19] |
150 killed (per SOHR)[5] 400–450 killed (per pro-gov. sources)[19][20] | ||||||
The 2016 Khanasir offensive was a military operation conducted by ISIL and Jund al-Aqsa, during the Syrian Civil War, with the aim of cutting the Syrian government's only supply route to the northern part of the Aleppo Governorate, which runs through the town of Khanasir.
The offensive
At 10 p.m. on 21 February, the offensive was launched by ISIL.[21] By the next day, a joint attack by militants from both ISIL and al-Qaeda-linked Jund al-Aqsa captured the village of Rasm Al-Nafal, as well as two other points along the Khanasir-Aleppo Road,[4] cutting the Syrian government's only supply route to Aleppo city.[22] The jihadists then proceeded to additionally seize six other villages and a hill.[23][24] A convoy of reinforcements from the town of As-Safira, consisting of the pro-government Palestinian militia Liwa Al-Quds was sent to reopen the road[1] and by the end of the day they had recaptured the hill.[23]
On 23 February, two contingents of the Syrian Army's special forces unit, known as the Tiger Forces, were also sent to help in reestablishing control of the road. Meanwhile, ISIL launched an assault on the town of Khanasir, commanded by Mahmutcan Ateş, which began with a failed suicide car-bomb attack against a checkpoint in its outskirts.[17] Throughout the morning, the military recaptured four out of seven positions they had lost on the road, but ultimately ISIL managed to capture Khanasir.[25] In the afternoon,[26] the Tiger Forces launched a general counteroffensive with a missile barrage, followed by a tank assault. The Syrian Army waited before entering the villages ISIL had captured, until Russian airstrikes had dissipated.[27] The counterattack was launched from two flanks, with the Tiger Forces and Hezbollah assaulting Rasm Al-Nafal from the north, while the Army and the Liwaa Al-Quds Brigade advanced from the south towards Khanasir.[3] By the evening, government forces recaptured Syria Tel Hill (Tal Syria Tel), outside Khanasir,[28] and Rasm Al-Nafal.[8]
The following morning, the Syrian Army re-entered Khanasir and one other village.[26] Later, they managed to seize Tal Za’rour hill, while also advancing to the central district of Khanasir.[29] At this time, the cutting of the road by ISIL caused prices of food and medical supplies in Aleppo city to raise dramatically.[30] On 25 February, the Tiger Forces and their allies recaptured Khanasir, while several hills outside the town were still ISIL-held.[7][31][32] The Army then advanced north of Khanasir and captured the nearby village of Al-Mughayrat,[33] along with four hilltops north of it (including the large Talat Al-Bayda hill).[7] At the same time, government forces advancing from the north seized Shilallah al-Kabeera, which they breached the previous day with the help of Russian airstrikes.[34][35] By the end of the day, government troops reached two more villages and started preparing for a new assault on the next morning.[7]
Early on 26 February, the Syrian Army made more advances, recapturing three villages.[18][36][37] The advances nearly besieged ISIL forces in a pocket of villages southwest of Lake Jabbul.[38] Later in the day, the Army captured the remaining four villages that ISIL held,[9] thus clearing the road to Aleppo.[39] However, elsewhere, ISIL took control of a village near al-Hamam Mountain, that overlooks the supply road.[40] Government forces reportedly re-secured the village the following day.[10][41]
On 28 February, the Syrian Army captured two villages and two mountain points, near Khanasir.[41][42] At the same time, elsewhere the Syrian Army captured the last point on the Sheikh Hilal-Ithriya Road that was held by ISIL.[11] On 29 February, the road to Aleppo city was once again reopened.[43]
Aftermath
Between 9 and 10 March, government forces captured 13 villages previously held by ISIL, near the southern bank of Lake Jabbūl,[44] forcing ISIL to set up a new defensive line east of the lake.[45]
On 14 April, ISIL launched another offensive on Khanasir,[46] and by the following day they captured hills near the town,[47] the Duraham Oil Field[48] and 10 villages. They also seized a large cache of weapons, ammunition and several armored vehicles.[49] On 16 April, Syrian Army reinforcements were sent to the area,[50] and by the evening they recaptured all of the territory lost, except the oil field.[51]
Between 26 January and 12 February 2017, heavy fighting took place near Khanasir with back-and-forth fighting.[52][53][54] On 12 February, 39 pro-government fighters and at least 12 ISIL militants were killed in an attack by ISIL east of Khanasir and south of Jabboul lake.[55] Towards the end of February, the Republican Guard seized the village of Umm Miyal, east of the highway, along with the adjacent hills.[56]
See also
References
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (22 February 2016). "Breaking: Government reinforcements sent to reopen strategic supply route to Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "Complete battlefield report from southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ a b Chris Tomson (25 February 2016). "Syrian Army attacks ISIS from two flanks as to reopen Aleppo supply road - Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ a b c d Leith Fadel (22 February 2016). "ISIS, rebels attack the Syrian Army together in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ^ a b c "نحو 250 قتلوا من قوات النظام ومسلحين موالين لها وتنظيم "الدولة الإسلامية" وفصائل أخرى خلال الهجوم الأخير على طريق الإمداد الاستراتيجي حلب – خناصر – أثريا". المرصد السورى لحقوق الإنسان. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Perry, Tom. "Islamic State tightens grip on Syrian government road to Aleppo". Reuters. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e Leith Fadel (25 February 2016). "Tiger Forces recapture the important city of Khanasser from ISIS". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "Breaking: Tiger Forces capture strategic village from ISIS in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b c Leith Fadel (25 February 2016). "Major road along the Government supply route to Aleppo has been liberated from ISIS". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (27 February 2016). "Government forces inch closer to liberating the only supply route to Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 27 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (28 February 2016). "Syrian Army reopens vital supply route to Aleppo after routing ISIS". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 4 September 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "ISIS captures the strategic village of Khanasser in northeast Hama". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "Senior Hezbollah commander killed in Aleppo". Syrian Observatory For Human Rights. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (4 March 2016). "Top ISIS commander in Aleppo killed". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ "Hassan Aboud, an ISIS Commander, Dies From Battlefield Wounds". The New York Times. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ a b Chris Tomson (23 February 2016). "Government supply line to Aleppo utterly cut due to blitz offensive by ISIS - Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 March 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "Tiger Forces deploy to southeast Aleppo amid ISIL assault on Khanasser". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b c Leith Fadel (26 February 2016). "Tiger Forces liberate 3 villages from ISIS in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 27 February 2016.
- ^ a b Chris Tomson (2 March 2016). "SouthFront: "400 ISIS fighters and 87 Syrian soldiers die in Aleppo offensive"". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 4 September 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ "Farsnews". Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "ISIS cuts two different government supply routes". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (22 February 2016). "ISIS cuts the only government supply line to Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (22 February 2016). "Syrian Army regains strategic point in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "Syrian government supply route to Aleppo still cut as fierce clashes continue". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "ISIS cuts off government supply line to Aleppo - Business Insider". Business Insider. 23 February 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (24 February 2016). "Tiger Forces enter strategic city of Khanasser". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "Tiger Forces launch counter-offensive against ISIS in southeast Aleppo: photos & video". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 February 2016). "Tiger Forces recapture important Khanasser hills from ISIS". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (24 February 2016). "Tiger Forces overwhelm ISIS and recapture several hilltops near Khanasser". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ jack. "Prices of food and medical supplies raise dramatically in Aleppo city". Syrian Observatory For Human Rights. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "Syrian army retakes key town on road to Aleppo from IS". AFP. 25 February 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ "Regime forces take control on Khanaser". SOHR. 25 February 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (25 February 2016). "Tiger Forces liberate more villages from ISIS in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (25 February 2016). "Tiger Forces liberate important village from ISIS in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ "قوات النظام تتقدم مجدداً قرب طريق خناصر – حلب وقذائف تستهدف أحياء في المدينة واشتباكات عنيفة في غربها". المرصد السورى لحقوق الإنسان. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Bassem Mroue and Zeina Karam (26 February 2016). "In push ahead of truce, Syrian troops take villages from IS". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 27 February 2016. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ^ "أكثر من 132 قتيلاً خلال 4 أيام من معارك طريق خناصر بريف حلب وتنظيم "الدولة الإسلامية" يستمر في السيطرة على تلال وقرى". المرصد السورى لحقوق الإنسان. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Chris Tomson (25 February 2016). "ISIS suddenly trapped as Syrian Army pushes to recapture Aleppo supply route – Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 28 August 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ^ "UPDATE: Russia, Syria Step Up Strikes As Ceasefire Deadline Approaches". London South East. 26 February 2016. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ^ "Dozens of airstrikes target Aleppo city's vicinity and countryside, and more than 150 people killed in Khanasser road clashes". SOHR. 26 February 2016. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ^ a b "At least 26 from the regime forces were killed in the clash near the road of Khanasser – Athrayya in the southeastern countryside of Aleppo". Syrian Observatory For Human Rights. 29 February 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (28 February 2016). "Syrian Army captures strategic village in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (29 February 2016). "Syrian Army officially reopens strategic supply route to Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (10 March 2016). "Syrian Army liberates 3 more villages from ISIS in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Chris Tomson (10 March 2016). "ISIS retreats towards Raqqa as government forces widen Aleppo supply line - Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (15 April 2016). "ISIS captures 7 more villages near the government supply line to Aleppo - Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ "Islamic State advances near Turkish border and east of Aleppo". Reuters. 15 April 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (15 April 2016). "ISIS advances on the Khanasser Highway: Burj Al-Atshanah captured". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Chris Tomson (16 April 2016). "ISIS seizes Russian tank and war booty in blitz offensive in eastern Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (16 April 2016). "Syrian Army reinforcements arrive to Khanasser to drive back ISIS: Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Leith Fadel (17 April 2016). "Syrian Army recaptures several villages in southeast Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Fadel, Leith (2017-01-26). "Syrian Army foils major ISIS offensive in southeast Aleppo: map". AMN - Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. Archived from the original on 2017-05-16. Retrieved 2017-01-27.
- ^ Tomson, Chris (7 February 2017). "Syrian Army secures main road along Jabbul Lake as ISIS pulls out of eastern Aleppo". Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ Tomson, Chris (8 February 2017). "ISIS launches deadly attack on Syrian Army supply line to Aleppo". Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ أكثر من 50 قتيلاً غالبيتهم من المسلحين الموالين للنظام ومن قوات النظام خلال 36 ساعة من المعارك العنيفة شرق خناصر بريف حلب الجنوبي الشرقي
- ^ Fadel, Leith (2017-02-26). "Pressure mounting on ISIS in east Aleppo as Syrian Army units advance east of Khanasser". AMN - Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. Archived from the original on 2017-10-21. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- February 2016 events in Syria
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war in 2016
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war involving the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war involving the al-Nusra Front
- As-Safira District
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war involving the Syrian government
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war involving Hezbollah
- Military operations of the Syrian civil war involving Russia
