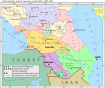
Dagestan
Republic of Dagestan | |
|---|---|
| Республика Дагестан | |
| Anthem: State Anthem of the Republic of Dagestan | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 43°06′N 46°53′E / 43.100°N 46.883°E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal district | North Caucasian[1] |
| Economic region | North Caucasus[2] |
| Capital | Makhachkala |
| Government | |
| • Body | People's Assembly[3] |
| • Head[3] | Vladimir Vasilyev |
| Area | |
| • Total | 50,300 km2 (19,400 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 52nd |
| Population | |
| • Total | 2,910,249 |
| • Estimate (2018)[6] | 3,063,885 (+5.3%) |
| • Rank | 12th |
| • Density | 58/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 45.2% |
| • Rural | 54.8% |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK |
| ISO 3166 code | RU-DA |
| License plates | 05 |
| OKTMO ID | 82000000 |
| Official languages | Russian;[8] Aghul, Avar, Azerbaijani, Chechen, Dargwa, Kumyk, Lezgian, Lak, Nogai, Rutul, Tabasaran, Tat, Tsakhur[9][10] |
| Website | http://www.e-dag.ru/ |

Dagestan (/ˌdæɡɪˈstæn/ or /ˌdæɡɪˈstɑːn/; Template:Lang-ru), officially the Republic of Dagestan (Template:Lang-ru), is a federal subject (a republic) of Russia, located in the North Caucasus region. Its capital and largest city is Makhachkala, centrally located on the Caspian Sea coast.
With a population of 2,910,249,[5] Dagestan is very ethnically diverse and Russia's most heterogeneous republic, with the largest ethnicity constituting less than 30% of the population. Largest among the ethnicities are the Avar, Dargin, Kumyk, Lezgian, Laks, Azerbaijani, Tabasaran, and Chechen.[12] Ethnic Russians comprise about 3.6% of Dagestan's total population.[13] Russian is the primary official language and the lingua franca among the ethnicities.[14]
Dagestan has been a scene of Islamic insurgency, occasional outbreaks of separatism, and ethnic tension since the 1990s. According to the International Crisis Group, the militant Islamist organization Shariat Jamaat is responsible for much of the violence.[15] Much of the tension is rooted in an internal Islamic conflict between traditional Sufi groups advocating secular government and more recently introduced Salafist teachers preaching the implementation of a certain form of Sharia in Dagestan.[citation needed] Its government was dissolved in a major corruption investigation on 5 February 2018, and the region has since been under the direct control of the Russian government.[16][17][18][19]
Toponymy
The word Dagestan is of Turkish and Persian origin. The Turkish word dağ means 'mountain', and the Persian suffix -stan means 'land'.
Some areas of Dagestan were known as Albania, Lezgistan, Avaria, and Tarkov at various times.[20]
Between 1860 and 1920, Dagestan was referred to as Dagestan Oblast, corresponding to the southeastern part of the present-day republic. The current borders were created with the establishment of the Dagestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic in 1921, with the incorporation of the eastern part of Terek Oblast, which is not mountainous but includes the Terek littoral at the southern end of the Caspian Depression.
Names for Dagestan
Official languages
- Russian – Респу́блика Дагеста́н (Respublika Dagestan)
- Avar – Дагъистаналъул Жумгьурият (Daġistanałul Jumhuriyat)
- Dargin – Дагъистанес Республика (Daġistanes Respublika)
- Kumyk – Дагъыстан Джумгьурият (Dağıstan Cumhuriyat)
- Lezgian – Республика Дагъустан (Respublika Daġustan)
- Lak – Дагъустаннал Республика (Daġustannal Respublika)
- Tabasaran – Дагъустан Республика (Daġustan Respublika)
- Rutul – Республика Дагъустан (Respublika Daġustan)
- Aghul – Республика Дагъустан (Respublika Daġustan)
- Tsakhur – Республика Дагъустан (Respublika Daġustan)
- Nogai – Дагыстан Республикасы (Dağıstan Respublikası)
- Chechen – Дехастан пачхьалкъ (Dexastan Paçxalq̇)
- Azerbaijani – Дағыстан Республикасы (Dağıstan Respublikası)
Non-official languages
- Turkish – Dağıstan Cumhuriyeti
- Arabic – جمهورية داغستان (Jumhūrīyat Dāgistān)
- Persian – جمهوری داغستان (Jomhuriye Dâqestân)
- Georgian – დაღესტანის რესპუბლიკა (Daqest’anis Resp’ublik’a)
- Ingush – ДаьгIасте (Däġaste)
- Kalmyk – Дагъсин таңһч (Dag’sin tañhç)
Geography
- the North Caucasus Federal District's republics: Karachay-Cherkessia, Kabardino-Balkaria, North Ossetia-Alania, Ingushetia, Chechnya and Dagestan
- to the north and west: the Southern Federal District
The republic is situated in the North Caucasus mountains. It is the southernmost part of Russia and is bordered on its eastern side by the Caspian Sea.
- Area: 50,300 square kilometers (19,400 sq mi)
- Borders:
- internal: Kalmykia (N), Chechnya (W), and Stavropol Krai (NW)
- international: Azerbaijan (Balakan District, Khachmaz District, Oghuz District, Qabala District, Qakh District, Qusar District, Shaki District and Zaqatala District) (S), Georgia (Kakheti) (SW)
- water: Caspian Sea (E)
- Highest point: Mount Bazardüzü/Bazardyuzyu: 4,446 metres (14,587 ft)
- Maximum north-south distance: 400 kilometers (250 mi)
- Maximum east-west distance: 200 kilometers (120 mi)
Rivers

There are over 1,800 rivers in the republic. Major rivers include:
- Sulak River
- Samur River
- Terek River
- Vladas River
- Ccenter River
Lakes
Dagestan has about 405 kilometers (252 mi) of coastline on the Caspian Sea.
Mountains

Most of the Republic is mountainous, with the Greater Caucasus Mountains covering the south. The highest point is the Bazardüzü/Bazardyuzyu peak at 4,470 meters (14,670 ft) on the border with Azerbaijan. The southernmost point of Russia is located about seven kilometers southwest of the peak. Other important mountains are Diklosmta (4,285 m (14,058 ft)), Gora Addala Shukgelmezr (4,152 m (13,622 ft)) and Gora Dyultydag (4,127 m (13,540 ft)).
Natural resources
Dagestan is rich in oil, natural gas, coal, and many other minerals.
Climate
The climate is hot and dry in the summer but the winters are harsh in the mountain areas.
- Average January temperature: +2 °C (36 °F)
- Average July temperature: +26 °C (79 °F)
- Average annual precipitation: 250 mm (10 in) (northern plains) to 800 mm (31 in) (in the mountains).
Administrative divisions
Dagestan is administratively divided into forty-one districts (raions) and ten cities/towns. The districts are further subdivided into nineteen urban-type settlements, and 363 rural okrugs and stanitsa okrugs.
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2011) |
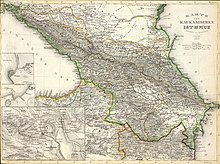


Early 1st millennium
In the first few centuries AD, Caucasian Albania (corresponding to modern Azerbaijan and southern Dagestan) became a vassal and eventually subordinate to the Parthian Empire. With the advent of the Sassanian Empire, it became a satrapy (province) within the vast domains of the empire. In later antiquity, it was a few times fought over by the Roman Empire and the Sassanid Persians as the former sought to contest the latter's rule over the region, without success. Over the centuries, to a relatively large extent, the peoples within the Dagestan territory converted to Christianity alongside Zoroastrianism.

In the 5th century, the Sassanids gained the upper hand, and by the 6th century constructed a strong citadel at Derbent, known henceforward as the Caspian Gates, while the northern part of Dagestan was overrun by the Huns, followed by the Caucasian Avars. During the Sassanian era, southern Dagestan became a bastion of Iranian culture and civilization, with its center at Derbent,[21] and a policy of "Persianisation" can be traced over many centuries.[22]
Islamic influence
In 664, the Persians were succeeded in Derbent by the Arabs, who in the 8th century repeatedly clashed with the Khazars. Although the local population rose against the Arabs of Derbent in 905 and 913, Islam was eventually adopted in urban centers, such as Samandar and Kubachi (Zerechgeran), from where it steadily penetrated into the highlands. By the 15th century, Albanian Christianity had died away, leaving a 10th-century church at Datuna as the sole monument to its existence.

Alternating Persian and Russian rule
As Mongolian authority gradually eroded, new centers of power emerged in Kaitagi and Tarki. In the early 16th century, the Persians (under the Safavids) reconsolidated their rule over the region, which would, intermittently, last till the early 19th century. In the 16th and 17th centuries, legal traditions were codified and mountainous communities (djamaats) obtained a considerable degree of autonomy.
The Russians intensified their hold in the region for the first time in the 18th century, when Peter the Great annexed maritime Dagestan from Safavid Persia in the course of the Russo-Persian War (1722–23). The territories were however returned to Persia in 1735 per the Treaty of Ganja.
Between 1730 and the early course of the 1740s, following his brother's murder in Dagestan, the new Iranian ruler and military genius Nader Shah led a lengthy campaign in swaths of Dagestan in order to fully conquer the region, which was met with considerable success, although he was eventually inflicted several decisive defeats by various of the ethnic groups of Dagestan, forcing him to retreat with his army. From 1747 onwards, the Iranian-ruled part of Dagestan was administered through the Derbent Khanate, with its center at Derbent. The Persian Expedition of 1796 resulted in the Russian capture of Derbent in 1796. However, the Russians were again forced to retreat from the entire Caucasus following internal governmental problems, allowing Iran to capture the territory again.
Russian rule consolidated
In 1806 the khanate voluntarily submitted to Russian authority,[citation needed] but it was not until the aftermath of the Russo-Persian War (1804-1813) that Russian power over Dagestan was confirmed, and that Qajar Iran officially ceded the territory to Russia. In 1813, following Russia's victory in the war, Iran was forced to cede southern Dagestan with its principal city of Derbent, alongside other vast territories in the Caucasus to Russia, conforming with the Treaty of Gulistan.[23] The 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay indefinitely consolidated Russian control over Dagestan and removed Iran from the military equation.[24]
Risings against imperial Russia
The Russian administration, however, disappointed and embittered the highlanders. The institution of heavy taxation, coupled with the expropriation of estates and the construction of fortresses (including Makhachkala), electrified highlanders into rising under the aegis of the Muslim Imamate of Dagestan, led by Ghazi Mohammed (1828–32), Gamzat-bek (1832–34) and Shamil (1834–59). This Caucasian War raged until 1864.

Dagestan and Chechnya profited from the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), to rise together against imperial Russia for the last time (Chechnya rose again at various times throughout the late 19th and 20th centuries).
Soviet era
On 21 December 1917, Ingushetia, Chechnya, and Dagestan declared independence from Russia and formed a single state called the "United Mountain Dwellers of the North Caucasus" (also known as the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus) which was recognized by major world powers. The capital of the new state was moved to Temir-Khan-Shura.[25][26][27] The first prime minister of the state was Tapa Chermoyev, a prominent Chechen statesman. The second prime minister was an Ingush statesman Vassan-Girey Dzhabagiev, who in 1917 also became the author of the constitution of the land, and in 1920 was reelected for a third term.[28] After the Bolshevik Revolution, Ottoman armies occupied Azerbaijan and Dagestan and the region became part of the short-lived Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus. After more than three years of fighting the White movement and local nationalists, the Bolsheviks achieved victory and the Dagestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed on January 20, 1921. Nevertheless, Stalin's industrialization largely bypassed Dagestan and the economy stagnated, making the republic the poorest region in Russia.
Post-Soviet era
In 1999, an Islamist group from Chechnya, led by Shamil Basayev and Ibn Al-Khattab, launched a military invasion of Dagestan, with the aim of creating an "independent Islamic State of Dagestan". The invaders were driven back by the Russian military. As a retaliation, Russian forces subsequently reinvaded Chechnya later that year.[citation needed] Violence in the Republic exploded from the beginning of 2010 to the end of 2012. This upsurge led many people to claim that Dagestan was about to enter into a situation of sectarian civil war.[29] Dagestan became the epicenter of violence in the North Caucasus with Makhachkala, Kaspiisk, Derbent, Khasavyurt, Kizlyar, Sergokala, Untsukul, and Tsumada all becoming hotbeds of militant activities.
Politics

The parliament of Dagestan is the People's Assembly, consisting of 72 deputies elected for a four-year term. The People's Assembly is the highest executive and legislative body of the republic.
The Constitution of Dagestan was adopted on 10 July 2003. According to it, the highest executive authority lies with the State Council, comprising representatives of fourteen ethnicities. The members of the State Council are appointed by the Constitutional Assembly of Dagestan for a term of four years. The State Council appoints the members of the Government.
The ethnicities represented in the State Council are Avars, Dargins, Kumyks, Lezgins, Laks, Azerbaijanis, Tabasarans, Russians, Chechens, Nogais, Aguls, Rutuls, Tsakhurs, and Tats.
Formerly, the Chairman of the State Council was the highest executive post in the republic, held by Magomedali Magomedovich Magomedov until 2006. On 20 February 2006, the People's Assembly passed a resolution terminating this post and disbanding the State Council. Russian president, Vladimir Putin offered the People's Assembly the candidature of Mukhu Aliyev for the newly established post of the president of the Republic of Dagestan. The nomination was accepted by the People's Assembly, and Mukhu Aliyev became the first president of the republic. On 20 February 2010 Aliyev was replaced by Magomedsalam Magomedov. The current head of the republic is Ramazan Abdulatipov (acting until 2013, following the resignation of Magomedov).[30]
Demographics
Because its mountainous terrain impedes travel and communication, Dagestan is unusually ethnically diverse, and still largely tribal. It is Russia's most heterogeneous republic. Dagestan's population is rapidly growing.[31]
Population: 2,910,249 (2010 Census);[5] 2,576,531 (2002 Census);[32] 1,802,579 (1989 Soviet census).[33]
Settlements
Vital statistics

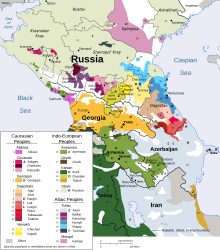

| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 1,438 | 41,381 | 9,543 | 31,838 | 28.8 | 6.6 | 22.1 | |
| 1975 | 1,544 | 42,098 | 10,292 | 31,806 | 27.3 | 6.7 | 20.6 | |
| 1980 | 1,655 | 44,088 | 11,188 | 32,900 | 26.6 | 6.8 | 19.9 | |
| 1985 | 1,744 | 50,053 | 12,010 | 38,043 | 28.7 | 6.9 | 21.8 | |
| 1990 | 1,848 | 48,209 | 11,482 | 36,727 | 26.1 | 6.2 | 19.9 | 3.07 |
| 1991 | 1,906 | 47,461 | 12,062 | 35,399 | 24.9 | 6.3 | 18.6 | 2.94 |
| 1992 | 1,964 | 44,986 | 12,984 | 32,002 | 22.9 | 6.6 | 16.3 | 2.70 |
| 1993 | 2,012 | 41,863 | 14,777 | 27,086 | 20.8 | 7.3 | 13.5 | 2.46 |
| 1994 | 2,117 | 44,472 | 15,253 | 29,219 | 21.0 | 7.2 | 13.8 | 2.45 |
| 1995 | 2,209 | 45,680 | 15,700 | 29,980 | 20.7 | 7.1 | 13.6 | 2.41 |
| 1996 | 2,251 | 42,282 | 15,565 | 26,717 | 18.8 | 6.9 | 11.9 | 2.19 |
| 1997 | 2,308 | 41,225 | 15,662 | 25,563 | 17.9 | 6.8 | 11.1 | 2.10 |
| 1998 | 2,363 | 41,164 | 15,793 | 25,371 | 17.4 | 6.7 | 10.7 | 2.05 |
| 1999 | 2,417 | 38,281 | 16,020 | 22,261 | 15.8 | 6.6 | 9.2 | 1.87 |
| 2000 | 2,464 | 38,229 | 16,108 | 22,121 | 15.5 | 6.5 | 9.0 | 1.82 |
| 2001 | 2,511 | 38,480 | 15,293 | 23,187 | 15.3 | 6.1 | 9.2 | 1.79 |
| 2002 | 2,563 | 41,204 | 15,887 | 25,317 | 16.1 | 6.2 | 9.9 | 1.85 |
| 2003 | 2,609 | 41,490 | 15,929 | 25,561 | 15.9 | 6.1 | 9.8 | 1.81 |
| 2004 | 2,647 | 41,573 | 15,724 | 25,849 | 15.7 | 5.9 | 9.8 | 1.76 |
| 2005 | 2,684 | 40,814 | 15,585 | 25,229 | 15.2 | 5.8 | 9.4 | 1.69 |
| 2006 | 2,721 | 40,646 | 15,939 | 24,707 | 14.9 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 1.64 |
| 2007 | 2,761 | 45,470 | 15,357 | 30,113 | 16.5 | 5.6 | 10.9 | 1.81 |
| 2008 | 2,804 | 49,465 | 15,794 | 33,671 | 17.6 | 5.6 | 12.0 | 1.94 |
| 2009 | 2,850 | 50,416 | 16,737 | 33,679 | 17.7 | 5.9 | 11.8 | 1.92 |
| 2010 | 2,896 | 52,057 | 17,013 | 35,044 | 18.0 | 5.9 | 12.1 | 1.92 |
| 2011 | 2,914 | 54,427 | 16,917 | 37,510 | 18.1 | 5.8 | 12.3 | 1.98 |
| 2012 | 2,931 | 56,186 | 16,642 | 39,492 | 19.1 | 5.7 | 13.4 | 2.03 |
| 2013 | 2,955 | 55,641 | 16,258 | 39,383 | 18.8 | 5.5 | 13.3 | 2.02 |
| 2014 | 2,982 | 56,888 | 16,491 | 40,397 | 19.1 | 5.5 | 13.6 | 2.08 |
| 2015 | 3,003 | 54,724 | 16,132 | 38,592 | 18.2 | 5.4 | 12.8 | 2.02 |
| 2016 | 3,029 | 52,924 | 15,642 | 37,282 | 17.4 | 5.2 | 12.2 | 1.98 |
| 2017 | 3,041 | 50,322 | 15,562 | 34,760 | 16.4 | 5.1 | 11.3 | 1.91 |
Ethnicities
The people of Dagestan include a large variety of ethnicities. According to the 2010 Census,[5] Northeast Caucasians (including Avars, Dargins, Lezgins, Laks, Tabasarans, and Chechens) make up almost 75% of the population of Dagestan. Turkic peoples, Kumyks, Azerbaijanis, and Nogais make up 21%, and Russians 3.6%. Other ethnicities (e.g. Tats) each account for less than 0.4% of the total population.
It should be noted that such groups as the Botlikh, the Andi, the Akhvakhs, the Tsez and about ten other groups were reclassified as Avars between the 1926 and 1939 censuses.[34]
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Avars | 177,189 | 22.5% | 230,488 | 24.8% | 239,373 | 22.5% | 349,304 | 24.5% | 418,634 | 25.7% | 496,077 | 27.5% | 758,438 | 29.4% | 850,011 | 29.4% |
| Dargins | 125,707 | 16.0% | 150,421 | 16.2% | 148,194 | 13.9% | 207,776 | 14.5% | 246,854 | 15.2% | 280,431 | 15.6% | 425,526 | 16.5% | 490,384 | 17.0% |
| Kumyks | 87,960 | 11.2% | 100,053 | 10.8% | 120,859 | 11.4% | 169,019 | 11.8% | 202,297 | 12.4% | 231,805 | 12.9% | 365,804 | 14.2% | 431,736 | 14.9% |
| Lezgians | 90,509 | 11.5% | 96,723 | 10.4% | 108,615 | 10.2% | 162,721 | 11.4% | 188,804 | 11.6% | 204,370 | 11.3% | 336,698 | 13.1% | 385,240 | 13.3% |
| Laks | 39,878 | 5.1% | 51,671 | 5.6% | 53,451 | 5.0% | 72,240 | 5.1% | 83,457 | 5.1% | 91,682 | 5.1% | 139,732 | 5.4% | 161,276 | 5.6% |
| Azerbaijanis | 23,428 | 3.0% | 31,141 | 3.3% | 38,224 | 3.6% | 54,403 | 3.8% | 64,514 | 4.0% | 75,463 | 4.2% | 111,656 | 4.3% | 130,919 | 4.5% |
| Tabasarans | 31,915 | 4.0% | 33,432 | 3.6% | 33,548 | 3.2% | 53,253 | 3.7% | 71,722 | 4.4% | 78,196 | 4.6% | 110,152 | 4.3% | 118,848 | 4.1% |
| Russians | 98,197 | 12.5% | 132,952 | 14.3% | 213,754 | 20.1% | 209,570 | 14.7% | 189,474 | 11.6% | 165,940 | 9.2% | 120,875 | 4.7% | 104,020 | 3.6% |
| Chechens | 21,851 | 2.8% | 26,419 | 2.8% | 12,798 | 1.2% | 39,965 | 2.8% | 49,227 | 3.0% | 57,877 | 3.2% | 87,867 | 3.4% | 93,658 | 3.2% |
| Nogais | 26,086 | 3.3% | 4,677 | 0.5% | 14,939 | 1.4% | 21,750 | 1.5% | 24,977 | 1.5% | 28,294 | 1.6% | 38,168 | 1.5% | 40,407 | 1.4% |
| Aghuls | 7,653 | 1.0% | 20,408 | 2.2% | 6,378 | 0.6% | 8,644 | 0.6% | 11,459 | 0.7% | 13,791 | 0.8% | 23,314 | 0.9% | 28,054 | 1.0% |
| Rutuls | 10,333 | 1.3% | 6,566 | 0.6% | 11,799 | 0.8% | 14,288 | 0.9% | 14,955 | 0.8% | 24,298 | 1.0% | 27,849 | 1.0% | ||
| Tsakhurs | 3,531 | 0.4% | 4,278 | 0.4% | 4,309 | 0.3% | 4,560 | 0.3% | 5,194 | 0.3% | 8,168 | 0.3% | 9,771 | 0.3% | ||
| Others | 43,861 | 5.6% | 52,031 | 5.6% | 61,495 | 5.8% | 63,787 | 4.5% | 57,892 | 3.6% | 58,113 | 3.2% | 25,835 | 1.0% | 19,646 | 0.7% |
| 1 18,430 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[35] | ||||||||||||||||
The indigenous ethnicities of Dagestan are in bold.
There are also 40 or so tiny groups such as the Hinukh, numbering 439, or the Akhvakhs, who are members of a complex family of indigenous Caucasians. Notable are also the Hunzib or Khunzal people who live in only four towns in the interior.
Languages
More than 30 local languages are commonly spoken, most belonging to the Northeast Caucasian language family. Russian became the principal lingua franca in Dagestan during the 20th century;[36] Over 20 of Russia's 131 endangered languages as identified by UNESCO can be found in Dagestan. Most of these endangered languages have Dagestani speakers in the mountainous region on the Dagestan-Georgia border.[37]
Prior to Soviet rule, the literary lingua-franca status to some extent belonged to Classical Arabic.[38] The northern Avar dialect of Khunzakh has also served as a lingua franca in mountainous Dagestan where Avar-related peoples lived.[39] And throughout centuries the Kumyk language had been the lingua-franca for the bigger part of the Northern Caucasus, from Dagestan to Kabarda, until the 1930s.[40][41][42]. Kumyk also had been an official language for communication of Russian Imperial administration with the local peoples.[43]
The first Russian grammar written for Dagestani languages was that for locally international Kumyk[44]. Author Timofey Makarov wrote:
From the peoples speaking Tatar language I liked the most Kumyks, as for their language's distinction and precision, so for their closeness to the European civilization, but most importantly, I take in account that they live on the Left Flank of the Caucasian Front, where we're conducting military actions, and where all the peoples, apart from their own language, speak also Kumyk.
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2016) |
Religion



According to a 2012 survey[45] 83% of the population of Dagestan adheres to Islam, 2.4% to the Russian Orthodox Church, 2% to Caucasian folk religion and other native faiths, 1% are non-denominational Christians. In addition, 9% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 2% is atheist and 0.6% follows other religions or did not answer the question.[45]
Dagestanis are largely Sunni Muslims, of the Shafii rites, that has been in place for centuries. On the Caspian coast, particularly in and around the port city of Derbent, the population (primarily made up of Azerbaijanis) is Shia. There is also a Salafi population, which is often a target of official repression.[47]
A relatively large number of native Tati-speaking Jews – the "Mountain Jews" – were[when?] also present in this same coastal areas. However, since 1991 and the collapse of the Soviet Union, they have migrated to Israel and the United States. These were an extension of much larger Azerbaijani Jewish community across the border in the Azerbaijani districts of Quba and Shamakhi.[48]
The appearance of Sufi mysticism in Dagestan dates back to the 14th century. The two Sufi tariqas that spread in the North Caucasus were the Naqshbandiya and the Qadiriya. The mystic tariqas preached tolerance and coexistence between the diverse people in the region. The Communist total intolerance for any religion after the Communist Revolution of 1917 also suppressed the Sufi movements. Shaykh Said Afandi al-Chirkawi was a prominent scholar, spiritual leader and murshid of Naqshbandi and Shadhili tariqahs in Dagestan until his death.[49]
The number of Christians among the non-Slavic indigenous population is very low, with estimates between 2,000 and 2,500. Most of these are Pentecostal Christians from the Lak ethnicity.[50][51] The largest congregation is Osanna Evangelical Christian Church (Pentecostal) in Makhachkala, with more than 1,000 members.[52]
Economy
The major industries in Dagestan include oil production, engineering, chemicals, machine building, textile manufacturing, food processing, and the timber. Oil deposits are located in the narrow coastal region. The Dagestani oil is of high quality and is delivered to other regions. Dagestan's natural gas production goes mostly to satisfy local needs. Agriculture is varied and includes grain-farming, viticulture and wine-making, sheep-farming, and dairying. The engineering and metalworking industries own 20% of the republic's industrial production assets and employ 25% of all industrial workers. Dagestan's hydroelectric power industry is developing rapidly. There are five power plants on the Sulak River providing hydroelectric power. It has been estimated that Dagestan's total potential hydroelectric power resources are 4.4 billion kW. Dagestan has a well-developed transportation system. Railways connect the capital Makhachkala to Moscow, Astrakhan, and the Azerbaijani capital, Baku. The Moscow-Baku highway also passes through Dagestan, and there are air links with major cities.[53][54]
Conditions for economic development are favorable in Dagestan, but – as of 2006[update] – the republic's low starting level for a successful transition to market relations, in addition to rampant corruption, has made the region highly dependent on its underground economy and the subsidies coming from the central Russian government.[54][55] Corruption in Dagestan is more severe than in other regions of the former Soviet Union and is coupled with a flourishing black market and clan-based economic system.[15]
In 2011 Rostelecom started implementation of WDM-based equipment on the backbone network for data transmission in the Republic of Dagestan. Due to WDM introduction, the fiber-optic communication lines bandwidth increased to 2.5 Gbit/s. Rostelecom invested about 48 million rubles in the project.[56]
Dagestani conflict

Since 2000, Dagestan has been the venue of a low-level guerrilla war, bleeding over from Chechnya; the fighting has claimed the lives of hundreds of federal servicemen and officials—mostly members of local police forces—as well as many Dagestani national rebels and civilians.
More recently, among other incidents:
- On 15 May 2008, two MVD officers were killed and one police officer heavily wounded during an ambush on their vehicle in Gubden.
- On 8 September 2008, Abdul Madzhid and several rebels were killed in an ambush by Russian special forces.
- On 21 October 2008, rebels ambushed a Russian military truck, killing five soldiers and wounding nine others.
- On 6 January 2010, a suicide bomber attempted to blow up a police station in Makhachkala, killing six officers and wounding 14 others.
- On 31 March 2010, 12 people were killed and 18 wounded by two suicide bombings in the town of Kizlyar outside the offices of the local interior ministry and the FSB security agency. The second bomb went off twenty minutes after the first, as a crowd had gathered. In the early hours of the next morning, two people died as a bomb went off in their car, apparently prematurely, near the village of Toturbiikala.
- On 15 July 2010, Pastor Artur Suleimanov, a Muslim convert to Christianity, was murdered by a gunman. The pastor was killed in his car as he was leaving the Hosanna House of Prayer in Makhachkala, according to a religious persecution watchdog group, Voice of the Martyrs, report. Pastor Suleimanov's church is one of the largest Protestant churches in Dagestan. Christians in the Russian Republic of Dagestan, which borders Chechnya, face harassment and intimidation from various groups. Pastor Suleimanov's life had been threatened on several previous occasions.[57]
- On 23 September 2011, Magomed Murtuzaliyev, a high-level law enforcement official, was shot and killed by gunmen.[58]
- On 28 September 2011, seven civilians and a police officer were killed by a car bomb in the village of Hajjalmakhi.[59]
- On 4 May 2012, 12 people were killed in two separate explosions on the outskirts of Makhachkala.[60]
- On 28 August 2012, Sheikh Said Afandi, an influential 75-year-old Sufi cleric, was killed along with six others in a suicide bombing. Afandi, a Sufi Muslim, opposed violent jihad in Dagestan.[61]
Notable people
- Adam Amirilayev, politician.
- Abdulkhakim Ismailov (1916–2010), World War II soldier.
- Abdulrashid Sadulaev – a two-time World Champion (2014, 2015), European Champion (2014), European Games Champion (2015), two time Cadet World Champion (2012, 2013), Golden Grand-Prix Champion, Olympic Gold Medalist (2016).
- Abdusalam Gadisov – Freestyle Wrestling World Champion.
- Adam Saitiev (12 December 1977, Khasavyurt, Dagestan ASSR) – Russia's freestyle wrestler, a Chechen, Russian Master of sports of international class, Honored Master of Sports of Russia (2000), three-time champion of Russia (1999, 2000, 2002), three-time champion Europe (1999, 2000, 2006), two-time world champion (1999, 2002), Olympic champion (2000).
- Ali Aliyev (wrestler) - Avar Dagestani-born Soviet Union freestyle wrestler. He won five world titles.
- Ali Bagautinov – UFC fighter in the flyweight division. Combat Sambo World Champion.
- Bekkhan Goygereyev - wrestler who won the gold medal at the 2013 World Wrestling Championships.
- Buvaisar Saitiev (b. 11 March 1975 in Khasavyurt, Dagestan ASSR) – Russia's freestyle wrestler, three-time Olympic champion, six-time world champion, six-time European champion, five-time Russian champion, seven-time winner of the tournament Krasnoyarsk Ivan Yarygin winner Goodwill Games will. Honored Master of Sports of Russia (1995).
- Dzhabar Askerov - He is the World Muay Thai Council's Muay Thai Welterweight European Champion and K-1 MAX Scandinavia 2008 Tournament Finalist.
- Dzhamal Otarsultanov -won the gold medal in men's freestyle 55 kg at the 2012 London Olympics.
- Eduard Puterbrot (1940–1993) – Dagestan artist and member of the USSR Union of Artists.
- Gasret Aliev - Hero of Soviet Union.
- Gaydarbek Gaydarbekov - boxer of Avar heritage, who has won two Olympic medals in Middleweight including the gold medal at the 2004 games.
- Hizgil Avshalumov (1913–2001) – Soviet novelist, poet, playwright. Wrote in Mountain Jews (Juhuri) and Russian languages.
- Israel Tsvaygenbaum (b. 1961) – Russian-American artist.
- Khabib Nurmagomedov – UFC fighter in the lightweight division and the current undisputed Lightweight champion.
- Khadzhimurad Magomedov - Olympic gold medalist and two time world wrestling champion.
- Kuramagomed Kuramagomedov (b. 1978), freestyle wrestler who competed for Russia in the 2000 Summer Olympics, and won a world title in 1997.
- Magomed Ibragimhalilovich Ibragimov -He competed in the freestyle 85 kg competition at the 2000 Summer Olympics and won the bronze medal.
- Mansur Isaev - In 2012, he won the gold medal in judo at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
- Makhach Murtazaliev - Russian Olympic wrestler who won the bronze medal for Russia at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens.
- Magomed Abdusalamov - is a Russian former heavyweight professional boxer who competed from 2008 to 2013.
- Magomedrasul Gazimagomedov - He won gold medal at the 2015 World Wrestling Championships at Men's freestyle 70 kg.
- Magomedkhan Aratsilov - former wrestler who competed in the 1980 Summer Olympics.
- Magomed Kurbanaliev - Russian freestyle wrestler. World freestyle wrestling champion 2016 in 70 kg.
- Magomed Magomedov - the professional WMC and IMF[clarification needed] Light Heavyweight World Muay Thai Champion.
- Magomedrasul Khasbulaev - (Frodo khasbulaev) mixed martial artist of Avar heritage at one time fought in the Featherweight division for the Bellator Fighting Championships.
- Mavlet Batirov - freestyle wrestler, world and 2-time Olympic champion, who competed in the men's freestyle 55 kg category at the 2004 Summer Olympics and won the gold medal.
- Michail Borisovich Dadashev - (born 1936) Jewish writer and poet, honored economist of the Republic of Dagestan. For 20 years worked as the head of the Tax division in Derbent.
- Murad Umakhanov - Umakhanov competed at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney where he received a gold medal in Freestyle wrestling.
- Mushail Mushailov (1941–2007) – a painter, a member of the USSR Union of Artists and Israel.
- Muslim Salikhov - The only non Chinese "King of sanda". Muslim Salikhov is often acknowledged as one of the best Wushu Sanda competitors in history.
- Nurmagomed Shanavazov - Shanavazov won the Light Heavyweight Silver medal at the 1988 Summer Olympics for the Soviet Union.
- Ramazan Şahin - Olympic Gold Medalist (2008), World Champion (2007) in Freestyle wrestling.
- Rashid Magomedov - UFC fighter in the lightweight division.
- Ruslan Magomedov - UFC fighter in the heavyweight division.
- Rasul Gamzatov (1923–2003) – Avar poet, writer, political activist.
- Rustam Khabilov – UFC fighter in the lightweight division. Combat Sambo World Champion.
- Sagid Murtazaliev - two time World champion, Olympic champion in Freestyle wrestling.
- Saypulla Absaidov - Olympic champion and World Champion 1981 in Freestyle wrestling.
- Sazhid Sazhidov - Russian Olympic wrestler who represented Russia at the world-level from 2003 to 2006. He won the bronze medal at the 2004 Athens Olympics.
- Shamil Zavurov - Combat Sambo World champion (3 time).
- Shirvani Muradov - wrestler, who has won a gold medal at the 2008 Summer Olympics and European champion 2007.
- Sergey Izgiyayev (1922–1972) – Mountain Jew Soviet poet, playwright and translator.
- Suleyman Kerimov - businessman, investor, philanthropist and politician. Featured on Forbes list as one of the richest people in Russia. Founded the Suleyman Kerimov Foundation as a vehicle for his charitable projects.
- Sultan Ibragimov- professional boxer held the WBO heavyweight title from 2007 to 2008. As an amateur he won silver medals at the 2000 Olympics and 2000 European Championships, and bronze at the 2001 World Championships, all in the heavyweight division.
- Tagir Khaybulaev - In the 2012 Summer Olympics, Khaybulaev won a gold medal.
- Tamara Musakhanova (1928–2014) – a sculptor and ceramist, a member of the USSR Union of Artists and Israel.
- Tankho Israelov (1917–1981) – ballet dancer, choreographer, People's Artist of the USSR (1978).
- Vazif Meylanov (1940–2015) – Soviet dissident and political prisoner, political activist.
- Yagutil Mishiev (b. 1927) – Honored Teacher of the Republic of Dagestan and the Russian Federation, publicist, author of books about the history of Derbent.
- Zabit Magomedsharipov (b. 1991) - UFC fighter fighting in the featherweight division.
See also
- Former countries in Europe after 1815
- Insurgency in the North Caucasus
- List of clashes in the North Caucasus
- Music of Dagestan
Notes
- ^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", No. 20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ^ a b Constitution, Article 8
- ^ "Сведения о наличии и распределении земель в Российской Федерации на 01.01.2019 (в разрезе субъектов Российской Федерации)". Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- ^ "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ^ "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ^ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ^ According to Article 11 of the Constitution of Dagestan, the official languages of the republic include "Russian and the languages of the peoples of Dagestan"
- ^ Solntsev et al., pp. XXXIX–XL
- ^ Всероссийский Центральный Исполнительный Комитет. Декрет от 20 января 1921 г. «Об Автономной Дагестанской Социалистической Советской Республике». (All-Russian Central Executive Committee. Decree of January 20, 1921 On Autonomous Dagestan Socialist Soviet Republic. ).
- ^ Dagestan. Most inhabitants speak Caucasian and Turkic languages. In terms of religion, however, Dagestan is homogeneously Muslim. Encyclopædia Britannica (Online edition)
- ^ Heinrich, Hans-Georg; Lobova, Ludmila; Malashenko, Alexei (2011). Will Russia Become a Muslim Society?. Peter Lang. p. 46. ISBN 3631609132. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ Dalby, Andrew (2004). Dictionary of Languages: The Definitive Reference to More Than 400 Languages. Columbia University Press. p. 59. ISBN 0231115695. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ a b Russia’s Dagestan: Conflict Causes Archived March 28, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. International Crisis Group Europe Report N°192. 3 June 2008. Access date: 07 April 2014.
- ^ https://www.rt.com/politics/417983-dagestan-government-dissolved-as-former/ Russia Today - "Dagestan government dissolved amid major corruption investigation"
- ^ http://tass.com/politics/988511 "High-ranking Dagestani officials detained on fraud charges" - Tass Russian News Agency
- ^ https://themoscowtimes.com/news/golden-pistol-seized-raid-dagestani-premier-amid-anti-corruption-crackdown-60393 "Golden Pistol Seized in Anti-Corruption Raid on Dagestani Prime Minister" - The Moscow Times
- ^ https://lenta.ru/articles/2018/02/06/dagestan/ "They held Dagestan for decades. Now they have questions." - Lenta
- ^ Zonn, Igor S.; et al. The Caspian Sea Encyclopedia. Berlin: Springer. p. 280.
- ^ Michael Khodarkovsky (2015). "Bitter Choices: Loyalty and Betrayal in the Russian Conquest of the North Caucasus" Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801462908 pp. 47–52
- ^ "Dagestan". Retrieved June 11, 2015.
- ^ Timothy C. Dowling (2014). Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond pp. 728–730 ABC-CLIO, ISBN 1598849484
- ^ Aksan, Virginia (2014). Ottoman Wars, 1700–1870: An Empire Besieged p. 463. Routledge. ISBN 978-1317884033
- ^ http://1900.ethnia.org/polity.php?ASK_CODE=KC__&ASK_YY=1919&ASK_MM=05&ASK_DD=07&SL=en[permanent dead link]
- ^ Russian Civil War Polities
- ^ Общественное движение ЧЕЧЕНСКИЙ КОМИТЕТ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОГО СПАСЕНИЯ Archived February 23, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Вассан-Гирей Джабагиев Archived February 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Nick Paton Walsh, “Dagestan Edged Closer to Civil War” The Guardian
- ^ "Putin replaces head of South Russian republic of Dagestan". RT. January 28, 2013. Retrieved January 28, 2013.
- ^ Ware, Robert Bruce (March 29, 2008). "Islamic Resistance and Political Hegemony in Dagestan". Retrieved May 28, 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ^ Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- ^ Wixman, Ronald (1984). "The Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook". Armonk, New York: M. E. Sharpe, Inc: 11.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Перепись-2010: русских становится больше (in Russian). Perepis-2010.ru. December 19, 2011. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ^ Beliaev, Edward; Oksana Buranbaeva (2006). Dagestan. New York: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark. p. 89. ISBN 0761420150. Retrieved April 4, 2013.
- ^ Moseley, Christopher (2010). "UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger". United Nations Education, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. UNESCO. Retrieved October 3, 2016.
- ^ Kemper, Michael (2011). "An Island of Classical Arabic in the Caucasus: Dagestan". In Françoise Companjen; László Károly Marácz; Lia Versteegh (eds.). Exploring the Caucasus in the 21st Century: Essays on Culture, History and Politics in a Dynamic Context. Amsterdam: Pallas Publications. pp. 63–90. ISBN 9789089641830. Retrieved April 4, 2013.
- ^ Comrie, Bernard (1981). The Languages of the Soviet Union. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 199. ISBN 0521232309. Retrieved April 4, 2013.
- ^ Pieter Muysken. (2008). Studies in language companion series. From linguistic areas to areal linguistics. Vol. 90. John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 74. ISBN 9789027231000.
- ^ Nansen. Gjennem Kaukasus til Volga (Oslo: Jacob Dybwads Forlag, 1929).
- ^ Н.С.Трубецкой (1925). ""О народах Кавказа"" (статья ed.).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Ярцева В.Н. и др. (ред.) Языки Российской Федерации и соседних государств. Том 2. К-Р, стр. 183
- ^ "Kafkaz Lehçeni Tatar Grammatikası, Makarov 1848". caucasian.space (in Kumyk and Russian). Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved June 28, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Arena: Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia". Sreda, 2012.
- ^ 2012 Arena Atlas Religion Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017. Archived.
- ^ Russia’s crackdown on Salafis may be breeding extremism
- ^ Mountain Jews at World Culture Encyclopedia
- ^ "Biography of Shaykh Said Afandi al-Chirkawi". Islamdag.info. July 22, 2011. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Slavic Center for Law & Justice". SCLJ. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ^ Magomed Gasanov (2001). "On Christianity in Dagestan". Iran & the Caucasus. 5: 79–84. JSTOR 4030847.
- ^ [1] Archived August 11, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Dagestan Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2008. Archived 2009-10-31.
- ^ a b Dagestan Republic Archived September 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine Kommersant 2004-03-10
- ^ Dagestan’s Economic Crisis: Past, Present and Future North Caucasus Weekly 2006-12-31
- ^ Broadband Russia Newslatter
- ^ "The Voice of the Martyrs' Be-A-Voice Network". Be-a-voice.net. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- ^ "Russia: Official Killed in Dagestan". The New York Times. September 23, 2011.
- ^ https://www.nytimes.com/reuters/2011/09/28/world/europe/international-us-russia-dagestan-bomb.html?hp[dead link]
- ^ "BBC News – Dagestan Russia blasts: At least 12 dead in Makhachkala". Bbc.co.uk. May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Sheikh Murdered Over Religious Split Say Analysts | Russia | RIA Novosti". En.rian.ru. August 30, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
References
- В. М. Солнцев и др., ed. (2000). Письменные языки мира: Российская Федерация. Социолингвистическая энциклопедия. (in Russian). Москва: Российская Академия Наук. Институт языкознания. проект №99-04-16158.
- 10 июля 2003 г. «Конституция Республики Дагестан», в ред. Закона №45 от 7 октября 2008 г. (July 10, 2003 Constitution of the Republic of Dagestan, as amended by the Law #45 of October 7, 2008. ).
Further reading
- Catholic Haidak in the Holy Roman Empire (rus)
- Kaziev, Shapi. Imam Shamil. "Molodaya Gvardiya" publishers. Moscow, 2001, 2003, 2006, 2010
- Kaziev, Shapi. Akhoulgo. Caucasian War in the 19th century. The historical novel. Epoch, Publishing house: Makhachkala, 2008. ISBN 978-5-98390-047-9
- Kaziev, Shapi. Caucasian Highlanders. Everyday life of the Caucasian highlanders. 19th century (In the co-authorship with I.Karpeev). "Molodaya Gvardiy" publishers. Moscow, 2003. ISBN 5-235-02585-7
- Kaziev, Shapi. Crash of tyrant. Nader Shah (Крах тирана). The historical novel about Nader Shah. Epoch, Publishing house: Makhachkala, 2009. ISBN 978-5-98390-066-0
External links
- Official governmental website of Dagestan Template:Ru icon
- Egbert Wesselink (1998). "Dagestan (Daghestan): Comprehensive Report". Caspian.net. Archived from the original on October 5, 2001. Retrieved January 15, 2012.
- Dagestan in Iranica Encyclopaedia
- History of Islam in Russia
- "The North Caucasus," Russian Analytical Digest No. 22 (5 June 2007)
- BBC Country Report on Dagestan
- University of Texas maps of the Dagestan region
- Radio Free Europe discusses religious tension in Dagestan
- ISN Case Study: The North Caucasus on the Brink (August 2006)
- Articles on Dagestan, reports from research, photos
- Dagestan in Pictures Template:Ru icon
- Daghestan's Kaitag Embroideries – and Henri Matisse?
- Dagestan Republic News Portal Template:Ru icon