Slavery: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 205.124.163.121 to last revision by Razimantv (HG) |
→Other uses of the term: Removed the mechanical/synchronized-clock use of the term, as the list is expressly framed as being for pejorative uses |
||
| Line 274: | Line 274: | ||
* Some feel that [[military draft]]s and other forms of coerced government labour constitute state-operated slavery.<ref>See the [[Conscription#Slavery|Slavery]] section in the Conscription article for more.</ref><ref>[http://rmf.net/pauldraft.html The Military Draft and Slavery] and [http://www.antiwar.com/paul/paul60.html Conscription Is Slavery] both by [[Ron Paul]]</ref><ref>[http://www.capmag.com/article.asp?ID=2346 An Idea Not Worth Drafting: Conscription is Slavery] by Peter Krembs</ref><ref>[http://www.davidkopel.com/NRO/2001/Nationalized-Slavery.htm Nationalized Slavery; A policy Italy should dump] by [[Dave Kopel]] refers to both the military and [[national service]] requirements of Italy as slavery.</ref> |
* Some feel that [[military draft]]s and other forms of coerced government labour constitute state-operated slavery.<ref>See the [[Conscription#Slavery|Slavery]] section in the Conscription article for more.</ref><ref>[http://rmf.net/pauldraft.html The Military Draft and Slavery] and [http://www.antiwar.com/paul/paul60.html Conscription Is Slavery] both by [[Ron Paul]]</ref><ref>[http://www.capmag.com/article.asp?ID=2346 An Idea Not Worth Drafting: Conscription is Slavery] by Peter Krembs</ref><ref>[http://www.davidkopel.com/NRO/2001/Nationalized-Slavery.htm Nationalized Slavery; A policy Italy should dump] by [[Dave Kopel]] refers to both the military and [[national service]] requirements of Italy as slavery.</ref> |
||
* Some proponents of [[animal rights]] apply the term ''slavery'' to the condition of some or all human-owned animals, arguing that their status is comparable to that of human slaves.<ref name="MSpiegel">Spiegel, Marjorie. ''The Dreaded Comparison: Human and Animal Slavery'', New York: Mirror Books, 1996.</ref> |
* Some proponents of [[animal rights]] apply the term ''slavery'' to the condition of some or all human-owned animals, arguing that their status is comparable to that of human slaves.<ref name="MSpiegel">Spiegel, Marjorie. ''The Dreaded Comparison: Human and Animal Slavery'', New York: Mirror Books, 1996.</ref> |
||
* Sometimes where one mechanism or system controls others, one is called "master" and the others "slaves", for example with a system of coordinated [[clock]]s through a big premises. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 08:21, 15 December 2009
| Part of a series on |
| Forced labour and slavery |
|---|
 |
Slavery is a form of forced labour in which people are considered to be the property of others. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to receive compensation (such as wages). Evidence of slavery predates written records, and has existed to varying extents, forms and periods in almost all cultures and continents.[1] In some societies, slavery existed as a legal institution or socio-economic system, but today it is formally outlawed in nearly all countries and condemned by the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Nevertheless, the practice continues in various forms around the world.[2][3]
The English word slave derives - through Old French and Medieval Latin - from the medieval word for Slavic people of Central and Eastern Europe, who were the last ethnic group to be captured and enslaved in Central Europe.[4][5] For thousands of years, according to Adam Smith and Auguste Comte, a slave was principally defined as a captive or prisoner of war.
History of slavery and the slave trade

Slavery is rare among Hunter gatherer populations, as slavery depends on a system of social stratification. Slavery also requires economic surpluses and a high population density to be viable. Due to these factors, the practice of slavery would have only proliferated after the invention of agriculture during the Neolithic revolution about 11,000 years ago.[6] The earliest records of slavery can be traced to the Code of Hammurabi (ca. 1760 BC), and the Bible refers to it as an established institution.[7] Slavery was known to occur in civilizations as old as Sumer, as well as almost every other ancient civilization, including Ancient Egypt, the Akkadian Empire, Assyria, Ancient Greece, the Roman Empire and the Islamic Caliphate.[8] Such institutions were a mixture of debt-slavery, punishment for crime, the enslavement of prisoners of war, child abandonment, and the birth of slave children to slaves.[9] Records of slavery in Ancient Greece go as far back as Mycenaean Greece. Two-fifths (some authorities say four-fifths) of the population of Classical Athens were slaves.[10] Greek philosophers such as Aristotle accepted the theory of natural slavery, that is, that some men are slaves by nature.[11][12]
As the Roman Republic expanded outward, entire populations were enslaved, thus creating an ample supply from all over Europe and the Mediterranean. Greeks, Illyrians, Berbers, Germans, Britons, Thracians, Gauls, Jews, Arabs, and many more were slaves used not only for labour, but also for amusement (e.g. gladiators and sex slaves). This oppression by an elite minority eventually led to slave revolts (see Roman Servile Wars); the Third Servile War led by Spartacus being the most famous and severe. By the late Republican era, slavery had become a vital economic pillar in the wealth of Rome, as well as a very significant part of Roman society.[13] It is estimated that over 25% of the population of Ancient Rome was enslaved.[14] According to some scholars, slaves represented 35% or more of Italy's population.[15] In the city of Rome alone, under the Roman Empire, there were about 400,000 slaves.[16] During the millennium from the emergence of the Roman Empire to its eventual decline, at least 100 million people were captured or sold as slaves throughout the Mediterranean and its hinterlands.[17]

The early medieval slave trade was mainly confined to the South and East: the Byzantine Empire and the Muslim world were the destinations, pagan Central and Eastern Europe, along with the Caucasus and Tartary, were important sources. Viking, Arab, Greek and Jewish merchants (known as Radhanites) were all involved in the slave trade during the Early Middle Ages.[18][19][20]
Medieval Spain and Portugal were the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians. Periodic raiding expeditions were sent from Al-Andalus to ravage the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In raid against Lisbon, Portugal in 1189, for example, the Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives, while his governor of Córdoba, in a subsequent attack upon Silves, Portugal in 1191, took 3,000 Christian slaves.[21] From the 11th to the 19th century, North African Barbary Pirates engaged in Razzias, raids on European coastal towns, to capture Christian slaves to sell at slave markets in places such as Algeria and Morocco.[22][23]
At the time of the Domesday Book, compiled in 1086, nearly 10% of the English population were slaves.[24] Slavery in early medieval Europe was so common that the Roman Catholic Church repeatedly prohibited it — or at least the export of Christian slaves to non-Christian lands was prohibited at e.g. the Council of Koblenz in 922, the Council of London (1102), and the Council of Armagh (1171).[25] In the 15th century, the Catholic Church legitimised enslavement of non-Christians in overseas territories.[26] In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull Dum Diversas, granting Afonso V of Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens, pagans and any other unbelievers" to hereditary slavery which legitimized the slave trade, at least as a result of war.[27] The approval of slavery under these conditions was reaffirmed and extended in his Romanus Pontifex bull of 1455. However, the Dominican friars who arrived at the Spanish settlement at Santo Domingo strongly denounced the enslavement of the local Indians. Along with other priests, they opposed their treatment as unjust and illegal in an audience with the Spanish king and in the subsequent royal commission.[28]

The Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the Ottoman wars in Europe brought large numbers of Christian slaves into the Islamic world too.[29] After the Battle of Lepanto approximately 12,000 Christian galley slaves were freed from the Ottoman Turks.[30] Eastern Europe suffered a series of Tatar invasions, the goal of which was to loot and capture slaves into jasyr. Seventy-five Crimean Tatar raids were recorded into Poland–Lithuania between 1474-1569.[31] There were more than 100,000 Russian captives in the Kazan Khanate alone in 1551.[32]
The transatlantic slave trade
Slavery was prominent presumably elsewhere in Africa long before the beginnings of the transatlantic slave trade.[33] The maritime town of Lagos, Portugal, was the first slave market created in Portugal for the sale of imported African slaves - the Mercado de Escravos, opened in 1444.[34][35] In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania.[35] By the year 1552 black African slaves made up 10 percent of the population of Lisbon.[36][37] In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas - in the case of Portugal, especially Brazil.[35] In the 15th century one third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold.[38]

Spain had to fight against relatively powerful and hardy civilizations of the New World. However, the Spanish conquest of the indigenous peoples in the Americas was also facilitated by the spread of diseases (e.g. smallpox) due to lack of biological immunity.[39] (although diseases such as syphilis were spread to the Europeans from first nations origins.) Natives were used as forced labour (the Spanish employed the pre-Columbian draft system called the mita),[40] but the diseases caused a labour shortage and so the Spanish colonists were gradually involved in the Atlantic slave trade. The first Europeans to use African slaves in the New World were the Spaniards who labourers on islands such as Cuba and Hispaniola, where the alarming decline in the native population had spurred the first royal laws protecting the native population (Laws of Burgos, 1512-1513). The first African slaves arrived in Hispaniola in 1501.[41] England played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade. The "slave triangle" was pioneered by Francis Drake and his associates. By 1750, slavery was a legal institution in all of the 13 American colonies[42][43], and the profits of the slave trade and of West Indian plantations amounted to 5% of the British economy at the time of the Industrial Revolution. [44]
The Transatlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century, when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by African kingdoms, such as the Oyo empire (Yoruba), the Ashanti Empire, the kingdom of Dahomey,[45] and the Aro Confederacy.[46] Europeans rarely entered the interior of Africa, due to fear of disease and moreover fierce African resistance. The slaves were brought to coastal outposts where they were traded for goods. An estimated 12 million Africans were shipped to the Americas from the 16th to the 19th centuries.[47] Of these, an estimated 645,000 were brought to what is now the United States. The white citizens of Virginia decided to treat the first Africans in Virginia as indentured servants.[48] Over half of all European immigrants to Colonial America during the 17th and 18th centuries arrived as indentured servants.[49] In 1655, John Casor, a black man, became the first legally recognized slave in the present United States.[50] According to the 1860 U.S. census, 393,975 individuals owned 3,950,528 slaves.[51] The largest number of slaves were shipped to Brazil.[52]
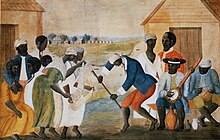
Author Charles Rappleye[who?] argued that
In the West Indies in particular, but also in North and South America, slavery was the engine that drove the mercantile empires of Europe. The institution was as old as time - finding explicit sanction in the Bible, and in the glory days of Greece and Rome - and had flourished, in its modern form, for two hundred years. It appeared, in the eighteenth century, as universal and immutable as human nature.[53]
Slavery in the United States
Although the trans-Atlantic slave trade ended shortly after the American Revolution, slavery remained a central economic institution in the Southern states. All the Northern states passed emancipation acts between 1780 and 1804; most of these arranged for gradual emancipation.[54] In the South, however, slavery expanded with the westward movement of population. Historian Peter Kolchin wrote, "By breaking up existing families and forcing slaves to relocate far from everyone and everything they knew" this migration "replicated (if on a reduced level) many of [the] horrors" of the Atlantic slave trade.[55] Historian Ira Berlin called this forced migration the Second Middle Passage. Characterizing it as the "central event” in the life of a slave between the American Revolution and the Civil War, Berlin wrote that whether they were uprooted themselves or simply lived in fear that they or their families would be involuntarily moved, "the massive deportation traumatized black people, both slave and free."[56] By 1860, 500,000 slaves had grown to 4 million. As long as slavery expanded, it remained profitable and powerful and was unlikely to disappear. Antislavery forces, however, proposed to put it on the path to extinction by stopping further expansion. If it became unprofitable, few people would spend the large sums of cash needed to buy and keep slaves, and the system would fade away quietly as it had in most countries in world history.
Slave population and percentages of the original thirteen colonies in 1770
New Hampshire had 654 slaves and one percent of the total. Massachusetts had 4754 and 2 percent. Connecticut had 5698 and 3 percent. Rhode Island had 3761 and 6 percent. New York had 19062 and 12 percent. New Jersey had 8220 and 7 percent. Pennsylvania had 5561 and 2 percent. Delaware had 1836 and 5 percent. Maryland had 63,818 and 32 percent. Virginia had 187,600 and 42 percent. North Carolina had 69,600 and 35 percent. South Carolina had 75,168 and 61 percent. Georgia had 15,000 and 45 percent
The plantation system, based on tobacco growing in Virginia, North Carolina, and Kentucky, and rice in South Carolina, expanded into lush new cotton lands in Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi—and needed more slaves. But slave importation became illegal in 1808. Although complete statistics are lacking, it is estimated that 1,000,000 slaves moved west from the Old South between 1790 and 1860. Most of the slaves were moved from Maryland, Virginia, and the Carolinas. Michael Tadman, in a 1989 book Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South, indicates that 60-70% of interregional migrations were the result of the sale of slaves. In 1820 a child in the Upper South had a 30% chance to be sold south by 1860.[57]
Political division over slavery was temporarily resolved by the Compromise of 1850 which sought to divide new territories between slave and free states. However, the status of Kansas was left unresolved, producing bloody clashes between pro-slavery and anti-slavery settlers.[58] In 1860, the election of Abraham Lincoln as President on a program of limiting slavery led to the secession of Southern States and the outbreak of the US Civil War. Although Lincoln initially disclaimed any intention to interfere with slavery, the progress of the war produced the Emancipation Proclamation freeing slaves in Southern states still in revolt, and ultimately the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution in December 1865, which ended legalized slavery in the United States.

The Arab slave trade
Historians say the Arab slave trade lasted more than a millennium.[59] Slaves in the Arab World came from many different regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly Zanj), the Caucasus (mainly Circassians),[60] Central Asia (mainly Tartars), and Central and Eastern Europe (mainly Saqaliba).[61]
Ibn Battuta tells us several times that he was given or purchased slaves.[62] Slaves were purchased or captured on the frontiers of the Islamic world and then imported to the major centers, where there were slave markets from which they were widely distributed.[63][64][65] In the 9th and 10th centuries, the black Zanj slaves may have constituted at least a half of the total population in lower Iraq.[66] At the same time, many tens of thousands of slaves in the region were also imported from Central Asia and the Caucasus.[67]
Zanzibar was once East Africa's main slave-trading port, and under Omani Arabs in the 19th century as many as 50,000 slaves were passing through the city each year.[68][69] Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million black African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 AD to 1900 AD,[1][70][71] compared with the 9.4 to 12 million Africans who were taken to the Americas.[1] One of the reasons for the European powers colonizing nearly the entire African continent during the 1880s and 1890s was the desire to end slave trading and slavery in Africa.[72]
Central and Eastern European slaves were generally known as Saqaliba (i.e., Slavs).[73] The Moors, starting in the 8th century, also raided coastal areas around the Mediterranean and Atlantic Ocean, and became known as the Barbary pirates. It is estimated that they captured 1.25 million white slaves from Western Europe and North America between the 16th and 19th centuries.[74][75]
Slave trade in Europe
In Western Europe slavery largely disappeared by the later Middle Ages.[76] The trade of slaves in England was made illegal in 1102.[77] Thralldom in Scandinavia was finally abolished in the mid-14th century.[78] Slavery persisted longer in Eastern Europe. Slavery in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588; they were replaced by the second serfdom. In Kievan Rus and Muscovy, the slaves were usually classified as kholops. Slavery remained a major institution in Russia until the year 1723, when the Peter the Great converted the household slaves into house serfs. Russian agricultural slaves were formally converted into serfs earlier in 1679.[79] Serfs in Russia were freed from their lords by an edict of Alexander II in 1861.[80]
According to Robert Davis between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by Barbary pirates and sold as slaves in North Africa and Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 19th centuries.[81][82] There was also an extensive trade in Christian slaves in the Black Sea region for several centuries until the Crimean Khanate was destroyed by the Russian Empire in 1783.[32] In the 1570s close to 20,000 slaves a year were being sold in the Crimean port of Kaffa.[83] The slaves were captured in southern Russia, Poland-Lithuania, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Circassia by Tatar horsemen in a trade known as the "harvesting of the steppe". Some researchers estimate that altogether more than 3 million people were captured and enslaved during the time of the Crimean Khanate.[84][85] It is estimated that up to 75% of the Crimean population consisted of slaves or freedmen.[33]
Slavery in Africa
In early Islamic states of the western Sudan, including Ghana (750-1076), Mali (1235–1645), Segou (1712–1861), and Songhai (1275-1591), about a third of the population were slaves. In Senegambia, between 1300 and 1900, close to one-third of the population was enslaved. In Sierra Leone in the 19th century about half of the population consisted of slaves. In the 19th century at least half the population was enslaved among the Duala of the Cameroon, the Igbo and other peoples of the lower Niger, the Kongo, and the Kasanje kingdom and Chokwe of Angola. Among the Ashanti and Yoruba a third of the population consisted of slaves. The population of the Kanem (1600–1800) was about a third-slave. It was perhaps 40% in Bornu (1580–1890). Between 1750 and 1900 from one- to two-thirds of the entire population of the Fulani jihad states consisted of slaves. The population of the Sokoto caliphate formed by Hausas in the northern Nigeria and Cameroon was half-slave in the 19th century. Between 65% to 90% population of Arab-Swahili Zanzibar was enslaved. Roughly half the population of Madagascar was enslaved.[86][87] When British rule was first imposed on the Sokoto Caliphate and the surrounding areas in northern Nigeria at the turn of the 20th century, approximately 2 million to 2.5 million people there were slaves.[88] Anti-Slavery Society estimated there were 2 million slaves in Ethiopia in the early 1930s out of an estimated population of between 8 and 16 million.[89]

One of the most famous slave traders on the East African coast was Tippu Tip, who was himself the grandson of an enslaved African. The prazeros slave traders, descendants of Portuguese and Africans, operated along the Zambezi. North of the Zambezi, the waYao and Makua people played a similar role as professional slave raiders and traders. The Nyamwezi slave traders operated further north under the leadership of Msiri and Mirambo.[90]
Slavery in Asia

As late as 1908, women slaves were still sold in the Ottoman Empire.[91] A slave market for captured Russian and Persian slaves was centred in the Central Asian khanate of Khiva.[92] According to Sir Henry Bartle Frere (who sat on the Viceroy's Council), there were an estimated 8 million or 9 million slaves in India in 1841. In Malabar, about 15% of the population were slaves. Slavery was abolished in both Hindu and Muslim India by the Indian Slavery Act V. of 1843.[1][93] In Istanbul about one-fifth of the population consisted of slaves.[33]
In East Asia, the Imperial government formally abolished slavery in China in 1906, and the law became effective in 1910.[94] Slave rebellion in China at the end of the 17th and the beginning of the 18th century was so extensive that owners eventually converted the institution into a female-dominated one.[80] The Nangzan in Tibetan history were hereditary household slaves.[95] Indigenous slaves existed in Korea. Slavery was officially abolished with the Gabo Reform of 1894 but remained extant in reality until 1930. During the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1910) about 30% to 50% of the Korean population were slaves.[96] In late 16th century Japan, slavery was officially banned; but forms of contract and indentured labor persisted alongside the period penal codes' forced labor.[97]
In Southeast Asia, a quarter to a third of the population of some areas of Thailand and Burma were slaves.[1] The hill tribe people in Indochina were "hunted incessantly and carried off as slaves by the Siamese (Thai), the Anamites (Vietnamese), and the Cambodians."[98] The Siamese military expedition had been converted into a slave hunting operation on a large scale.[99]
Abolitionist movements


Slavery has existed, in one form or another, through the whole of recorded human history — as have, in various periods, movements to free large or distinct groups of slaves. According to the Biblical Book of Exodus, Moses led Israelite slaves out of ancient Egypt — possibly the first written account of a movement to free slaves. Later Jewish laws (known as Halacha) prevented slaves from being sold out of the Land of Israel, and allowed a slave to move to Israel if he so desired.
One of the first protests against the enslavement of Africans came from German and Dutch Quakers in Pennsylvania in 1688. One of the most significant milestones in the campaign to abolish slavery throughout the world occurred in England in 1772, with British judge Lord Mansfield, whose opinion in Somersett's Case was widely taken to have held that slavery was illegal in England. This judgement also laid down the principle that slavery contracted in other jurisdictions (such as the American colonies) could not be enforced in England.[100]. In 1777, Vermont became the first portion of what would become the United States to abolish slavery (at the time Vermont was an independent nation). In 1794, under the Jacobins, Revolutionary France abolished slavery.[101] There were celebrations in 2007 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the Abolition of the slave trade in the United Kingdom through the work of the British Anti-Slavery Society. William Wilberforce received much of the credit although the groundwork was an anti-slavery essay by Thomas Clarkson. Wilberforce was also urged by his close friend, Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger, to make the issue his own, and was also given support by reformed Evangelical John Newton. The Slave Trade Act was passed by the British Parliament on 25 March 1807, making the slave trade illegal throughout the British Empire, Wilberforce also campaigned for abolition of slavery in British Empire, which he lived to see in the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. After abolition slave trade act 1807 was passed these campaigners switched to encouraging other countries to follow suit, notably France and the British colonies.
Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard.[102] Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.[103]
In the United States, abolitionist pressure produced a series of small steps towards emancipation. After January 1, 1808, the importation of slaves into the United States was prohibited,[104] but not the internal slave trade, nor involvement in the international slave trade externally. Legal slavery persisted; and those slaves already in the U.S. would not be legally emancipated for another 60 years. Many American abolitionists took an active role in opposing slavery by supporting the Underground Railroad. Violence soon erupted, with the anti-slavery forces led by John Brown, and Bleeding Kansas, involving anti-slavery and pro-slavery settlers, became a symbol for the nationwide clash over slavery. The American Civil War, beginning in 1861, led to the end of slavery in the United States.
In 1863 Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed slaves held in the Confederate States; the 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution (1865) prohibited slavery throughout the country.
In the 1860s, David Livingstone's reports of atrocities within the Arab slave trade in Africa stirred up the interest of the British public, reviving the flagging abolitionist movement. The Royal Navy throughout the 1870s attempted to suppress "this abominable Eastern trade", at Zanzibar in particular.
On December 10, 1948, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which declared freedom from slavery is an internationally recognized human right. Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states:
No one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade shall be prohibited in all their forms.[105]
Chronology of abolition
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
- 1761 Portugal abolishes slavery in mainland Portugal and in Portuguese possessions in India, but not Brazil or Africa,
- 1794 France abolishes slavery (partly-abortively)
- 1804 France re-legalizes slavery
- 1807 Great Britain abolishes slave trade within and to the British Empire
- 1811 Spain abolishes slavery at home and in all colonies except Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Santo Domingo
- 1813 Argentina abolishes slavery
- 1821 Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela abolish slavery
- 1823 Chile abolishes slavery
- 1824 The Federal Republic of Central America abolishes slavery
- 1829 Mexico abolishes slavery
- 1831 Bolivia abolishes slavery
- 1833 British Empire abolishes slavery
- 1842 Uruguay abolishes slavery
- 1848 Slavery abolished in all French and Danish colonies
- 1854 Venezuela abolishes slavery
- 1863 Slavery abolished in Dutch colonies
- 1865 United States abolishes slavery
- 1869 Portugal abolishes slavery in the African colonies
- 1886 Cuba abolishes slavery
- 1888 Brazil abolishes slavery
- 1894 Korea abolishes slavery
- 1905 Siam (Thailand) abolishes slavery
- 1906 China abolishes slavery
- 1923 Afghanistan abolishes slavery
- 1942 Ethiopia abolishes slavery
- 1958 Bhutan abolishes slavery
- 1962 Saudi Arabia abolishes slavery
- 1963 United Arab Emirates abolishes slavery
- 1970 Oman abolishes slavery
- 1981 Mauritania abolishes slavery
Contemporary slavery
Since 1945, debate about the link between economic growth and different relational forms (most notably unfree social relations of production in Third World agriculture) occupied many contributing to discussions in the development decade (the 1960s). This continued to be the case in the mode of production debate (mainly about agrarian transition in India) that spilled over into the 1970s, important aspects of which continue into the present (see the monograph by Brass, 1999, and the 600 page volume edited by Brass and van der Linden, 1997). Central to these discussions was the link between capitalist development and modern forms of unfree labour (peonage, debt bondage, indenture, and chattel slavery (which involves outright ownership of the slave)). Within the domain of political economy, the debate has a long historical lineage, and - accurately presented - never actually went away. Unlike advocacy groups, for which the number of the currently unfree is paramount, those political economists who participated in the earlier debates sought to establish who, precisely, was (or was not) to be included under the rubric of a worker whose subordination constituted a modern form of unfreedom. This element of definition was regarded as an epistemologically necessary precondition to any calculations of how many were to be categorized as relationally unfree.[citation needed]
Though slavery was officially abolished in China in 1910,[106] the practice continues unofficially in some regions.[107][108] Slavery also exists in other countries across the world, including among nations within Africa. Groups such as the American Anti-Slavery Group, Anti-Slavery International, Free the Slaves, the Anti-Slavery Society, and the Norwegian Anti-Slavery Society continue to campaign to rid the world of slavery. Conditions that are considered slavery include debt bondage, indentured servitude, serfdom, domestic servants kept in captivity, adoption in which children are effectively forced to work as slaves, child soldiers, and forced marriage[109].
More people suffer slavery than in the past but slaves are a smaller proportion of the human population. Slaves are cheap and can therefore be treated as expendable. Worldwide slavery is a criminal offence but criminal slave owners can get very high returns for their actions.[110] According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 was $91.2 billion. That is second only to drug trafficking in terms of global, criminal, illicit enterprises. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labor and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave.[111] Approximately forty percent of all slave profits each year are generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4 percent of the world's 29 million slaves.[111]
Human trafficking
Trafficking in human beings (also called human trafficking) is one method of obtaining slaves. Victims are typically recruited through deceit or trickery (such as a false job offer, false migration offer, or false marriage offer), sale by family members, recruitment by former slaves, or outright abduction. Victims are forced into a "debt slavery" situation by coercion, deception, fraud, intimidation, isolation, threat, physical force, debt bondage or even force-feeding with drugs of abuse to control their victims.[112] “Annually, according to U.S. Government-sponsored research completed in 2006, approximately 800,000 people are trafficked across national borders, which does not include millions trafficked within their own countries. Approximately 80 percent of transnational victims are women and girls and up to 50 percent are minors,” reports the U.S. Department of State in a 2008 study.[113]
Whilst the majority of victims are women, and sometimes children, who are forced into prostitution (in which case the practice is called sex trafficking), victims also include men, women and children who are forced into manual labour.[114] Due to the illegal nature of human trafficking, its exact extent is unknown. A U.S. Government report published in 2005, estimates that 600,000 to 800,000 people worldwide are trafficked across borders each year. This figure does not include those who are trafficked internally.[114] Another research effort revealed that between 1.5 million and 1.8 million individuals are trafficked either internally or internationally each year, 500,000 to 600,000 of whom are sex trafficking victims.[111]
Current situation
Although outlawed in nearly all countries, forms of slavery still exist.[2][3] Several estimates of the number of slaves in the world have been provided. According to a broad definition of slavery used by Kevin Bales of Free the Slaves (FTS), an advocacy group linked with Anti-Slavery International, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world.[117] In 2005, the International Labour Organisation provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers in the world,[118]. Siddharth Kara has provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into the following three categories: bonded labour/debt bondage (18.1 million), forced labour (7.6 million), and trafficked slaves (2.7 million).[111] Kara provides a dynamic model to calculate the number of slaves in the world each year, with an estimated 29.2 million at the end of 2009. The weighted average global sales price of a slave is calculated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa.[111]
Enslavement is also taking place in parts of Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.[119] The Middle East Quarterly reports that slavery is still endemic in Sudan.[120] In June and July 2007, 570 people who had been enslaved by brick manufacturers in Shanxi and Henan were freed by the Chinese government.[121] Among those rescued were 69 children.[122] In response, the Chinese government assembled a force of 35,000 police to check northern Chinese brick kilns for slaves, sent dozens of kiln supervisors to prison, punished 95 officials in Shanxi province for dereliction of duty, and sentenced one kiln foreman to death for killing an enslaved worker.[121] In 2008, the Nepalese government abolished the Haliya system of forced labour, freeing about 20,000 people.[123] An estimated 40 million people in India, most of them Dalits or "untouchables", are bonded workers, many working to pay off debts that were incurred generations ago.[124][125]
In Mauritania alone, it is estimated that up to 600,000 men, women and children, or 20% of the population, are enslaved with many used as bonded labour.[126][127] Slavery in Mauritania was criminalized in August 2007.[128] In Niger, slavery is also a current phenomenon. A Nigerien study has found that more than 800,000 people are enslaved, almost 8% of the population.[129][130][131] Pygmies, the people of Central Africa's rain forest,[132] live in servitude to the Bantus.[133] Some tribal sheiks in Iraq still keep blacks, called Abd, which means servant or slave in Arabic, as slaves.[134] Child slavery has commonly been used in the production of cash crops and mining. According to the U.S. Department of State, more than 109,000 children were working on cocoa farms alone in Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) in "the worst forms of child labor" in 2002.[135]
In November 2006, the International Labour Organization announced it will be seeking "to prosecute members of the ruling Myanmar junta for crimes against humanity" over the continuous forced labour of its citizens by the military at the International Court of Justice.[136][137] According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), an estimated 800,000 people are subject to forced labour in Myanmar.[138][139]
The Ecowas Court of Justice is hearing the case of Hadijatou Mani in late 2008, where Ms. Mani hopes to compel the government of Niger to end slavery in its jurisdiction. Cases brought by her in local courts have failed so far.[140]
Apologies
On May 21, 2001, the National Assembly of France passed the Taubira law, recognizing slavery as a crime against humanity. Apologies on behalf of African nations, for their role in trading their countrymen into slavery, remain an open issue since slavery was practiced in Africa even before the first Europeans arrived and the Atlantic slave trade was performed with a high degree of involvement of several African societies. The black slave market was supplied by well-established slave trade networks controlled by local African societies and individuals.[141] Indeed, as already mentioned in this article, slavery persists in several areas of West Africa until the present day.
There is adequate evidence citing case after case of African control of segments of the trade. Several African nations such as the Ashanti of Ghana also Calabar and other southern parts of Nigeria had economies depended solely on the trade. African peoples such as the Imbangala of Angola and the Nyamwezi of Tanzania would serve as middlemen or roving bands warring with other African nations to capture Africans for Europeans.[142]
Several historians have made important contributions to the global understanding of the African side of the Atlantic slave trade. By arguing that African merchants determined the assemblage of trade goods accepted in exchange for slaves, many historians argue for African agency and ultimately a shared responsibility for the slave trade.[143]
The issue of an apology is linked to reparations for slavery and is still being pursued by a number of entities across the world. For example, the Jamaican Reparations Movement approved its declaration and action Plan.
In September, 2006, it was reported[144] that the UK Government may issue a "statement of regret" over slavery, an act that was followed through by a "public statement of sorrow" from Tony Blair on November 27, 2006.[145]
On February 25, 2007 the state of Virginia resolved to 'profoundly regret' and apologize for its role in the institution of slavery. Unique and the first of its kind in the U.S., the apology was unanimously passed in both Houses as Virginia approached the 400th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown, where the first slaves were imported into North America in 1619.[146]
On August 24, 2007, Mayor Ken Livingstone of London, United Kingdom apologized publicly for Britain's role in colonial slave trade. "You can look across there to see the institutions that still have the benefit of the wealth they created from slavery," he said pointing towards the financial district. He claimed that London was still tainted by the horrors of slavery. Jesse Jackson praised Mayor Livingstone, and added that reparations should be made, one of his common arguments.[147]
Reparations
Sporadically there have been movements to achieve reparations for those formerly held as slaves, or sometimes their descendants. Claims for reparations for being held in slavery are handled as a civil law matter in almost every country. This is often decried as a serious problem, since former slaves' relative lack of money means they often have limited access to a potentially expensive and futile legal process. Mandatory systems of fines and reparations paid to an as yet undetermined group of claimants from fines, paid by unspecified parties, and collected by authorities have been proposed by advocates to alleviate this "civil court problem." Since in almost all cases there are no living ex-slaves or living ex-slave owners these movements have gained little traction. In nearly all cases the judicial system has ruled that the statute of limitations on these possible claims has long since expired.
Nonetheless, from time to time misinformation is circulated (often through e-mail) to United States residents describing a $5000 "slavery tax credit," supposedly passed into law under President Bill Clinton's administration during the 1990s, but never announced to the public. No such credit exists, and persons attempting to promote or take advantage of the alleged credit are subject to prosecution.[148] (See Slavery reparations scam for further information.) A similar scam involves a "tax credit" available to Native Americans.
Economics

Economists have attempted to model during which circumstances slavery (and milder variants such as serfdom) appear and disappear. One observation is that slavery becomes more desirable for land owners when land is abundant but labour is not, so paid workers can demand high wages. If labour is abundant but land is scarce, then it becomes more costly for the land owners to have guards for the slaves than to employ paid workers who can only demand low wages due to the competition. Thus first slavery and then serfdom gradually decreased in Europe as the population grew. It was reintroduced in the Americas and in Russia (serfdom) as large new land areas with few people became available.[citation needed]. In his books,Time on the Cross and Without Consent or Contract: the Rise and Fall of American Slavery, Robert Fogel maintains that slavery was in fact a very economical method of production, especially on bigger plantations. Fogel discusses that although immoral and extremely unjust, slavery in the time prior to the Civil War had whites in the South more successful financially than those in the North.
Another observation is slavery is more common when the labour done is relatively simple and thus easy to supervise, such as large scale growing of a single crop. It is much more difficult and costly to check that slaves are doing their best and with good quality when they are doing complex tasks. Therefore, slavery was seen as the most efficient method of production for large scale crops like sugar and cotton, whose output was based on economies of scale. This enabled a gang system of labor to be prominent on large plantations where field hands were monitored and worked with factory-like precision. Each work gang was based on an internal division of labor that not only assigned every member of the gang to a precise task but simultaneously made his or her performance dependent on the actions of the others. The hoe hands chopped out the weeds that surrounded the cotton plants as well as excessive sprouts. The plow gangs followed behind, stirring the soil near the rows of cotton plants and tossing it back around the plants. Thus, the gang system worked like an early version of the assembly line later to be found in factories. [149]
It has also been argued that slavery tends to retard technological advancement, since the focus is on increasing the number of slaves rather than improving the efficiency of labour. Because of this, theoretical knowledge and learning in Greece—and later in Rome—was not applied to ease physical labour or improve manufacturing.[150] Some Russian scholars have argued that the Soviet Union's technological development was hindered by Stalin's use of slave labour.[citation needed]
Adam Smith who was opposed of slavery, colonialism, empire and critical of colonial and slave masters in his minor works and both of his two major works, The Theory of Moral Sentiments and the Wealth of Nations stated that "domestic slavery" in Europe's past was the "vilest of all states"[151],made the generally well known argument that free labor was better than slave labor, and argued further that slavery in Europe ended during the Middle Ages, and only then after both the church and state were separate, independent and strong institutions,[152] that it is nearly impossible to end slavery in a free, democratic and republican forms of governments since many of its legislators or political figures were slave owners, and would not punish themselves, and that slaves would be better able to gain their freedom when there was centralized government, or a central authority like a king or the church.[153] Similar arguments appear later in the works of Auguste Comte, especially when it comes to Adam Smith’s belief in the separation of powers or what Comte called the "separation of the spiritual and the temporal" during the Middle Ages and the end of slavery, and Smith's criticism of masters, past and present. As Smith stated in the Lectures on Jurisprudence, "The great power of the clergy thus concurring with that of the king set the slaves at liberty. But it was absolutely necessary both that the authority of the king and of the clergy should be great. Where ever any one of these was wanting, slavery still continues."
Religion and slavery
Other uses of the term
The word slavery is often used as a pejorative to describe any activity in which one is coerced into performing.
- Many anarchists, socialists, and communists have condemned "wage slavery" or "economic slavery", where workers are forced to choose between selling their labour and facing starvation, poverty or social stigma and a lack of prosperity. This is related to the notion of economic coercion.[citation needed]
- Some libertarians and anarcho-capitalists view government taxation as a form of slavery.[154]
- Some progressives and feminists feel that anti-abortion laws and other government laws that force a woman to carry a pregnancy to term is a form of slavery.
- Some feel that military drafts and other forms of coerced government labour constitute state-operated slavery.[155][156][157][158]
- Some proponents of animal rights apply the term slavery to the condition of some or all human-owned animals, arguing that their status is comparable to that of human slaves.[159]
See also
- Various
|
- Slavery by region
|
|
- Slavery by religion and era
|
- Opposition and resistance
|
|
- Films
|
|
|
Template:Articles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
References
- ^ a b c d e Historical survey > Slave-owning societies. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ a b UN Chronicle | Slavery in the Twenty-First Century
- ^ a b BBC Millions 'forced into slavery'
- ^ "slave", Online Etymology Dictionary, retrieved 26 March 2009
- ^ Merriam-Webster's, retrieved 18 August 2009
- ^ "Slavery". Britannica.
- ^ "Mesopotamia: The Code of Hammurabi".
e.g. Prologue, "the shepherd of the oppressed and of the slaves". Code of Laws #7, "If any one buy from the son or the slave of another man".
- ^ Introduction of Slavery. The Mariners' Museum.
- ^ Demography, Geography and the Sources of Roman Slaves, by W. V. Harris: The Journal of Roman Studies, 1999
- ^ Slavery in Ancient Greece. Britannica Student Encyclopædia.
- ^ Ben Kiernan "Blood and Soil: A World History of Genocide and Extermination from Sparta to Darfur", Yale University Press, 2007, ISBN 0300100981, 9780300100983, Pages 65-68
- ^ Léonie J. Archer (1988). "Slavery and Other Forms of Unfree Labour: And Other Forms of Unfree Labour." History Workshop Centre for Social History (Oxford, England), Published by Routledge,ISBN 0415002036, 9780415002035, Page 28
- ^ Slavery in Ancient Rome
- ^ BBC - History - Resisting Slavery in Ancient Rome
- ^ Schiavone Aldo (2000), The End of the Past. Ancient Rome and the Modern West, Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press, p.112.
- ^ The Romans at Work and Play Western New England College.
- ^ The Roman slave supply Walter Scheidel. Stanford University.
- ^ Slave trade -- Britannica Concise Encyclopedia
- ^ JewishEncyclopedia.com - slave-trade
- ^ Slavery Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- ^ Ransoming Captives in Crusader Spain: The Order of Merced on the Christian-Islamic Frontier
- ^ "British Slaves on the Barbary Coast".
- ^ "Jefferson Versus the Muslim Pirates by Christopher Hitchens, City Journal Spring 2007".
- ^ University of Wisconsin. "Medieval English society". history.wisc.edu. Retrieved 2009-09-05.
- ^ Slavery, serfdom, and indenture through the Middle Ages
- ^ Falola, Toyin; Warnock, Amanda (2007). Encyclopedia of the Middle Passage. Greenwood Publishing. p. 153. ISBN 9780313088292.
- ^ Allard, Paul (1912). "Slavery and Christianity". Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. XIV. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved 4 February 2006.
- ^ Thomas, Hugh (2003). Rivers of Gold: The Rise of the Spanish Empire. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 258–262. ISBN 0297645633.
- ^ Ottoman Dhimmitude
- ^ Famous Battles in History The Turks and Christians at Lepanto
- ^ Davies (2007). Warfare, State and Society on the Black Sea Steppe,1500-1700.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|frist=ignored (|first=suggested) (help) - ^ a b The Crimean Tatars and their Russian-Captive Slaves. Eizo Matsuki, Mediterranean Studies Group at Hitotsubashi University.
- ^ a b c Historical survey > Slave societies. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Goodman, Joan E. (2001). A Long and Uncertain Journey: The 27,000 Mile Voyage of Vasco Da Gama. Mikaya Press, ISBN 096504937X.
- ^ a b c de Oliveira Marques, António Henrique R. (1972). History of Portugal. Columbia University Press, ISBN 0231031599, p. 158-160, 362-370.
- ^ Thomas Foster Earle, K. J. P. Lowe "Black Africans in Renaissance Europe" p.157 Google
- ^ David Northrup, "Africa's Discovery of Europe" p.8 (Google)
- ^ Klein, Herbert. The Atlantic Slave Trade.
- ^ David A. Koplow Smallpox The Fight to Eradicate a Global Scourge
- ^ U.S. Library of Congress
- ^ HEALTH IN SLAVERY
- ^ Scott, Thomas Allan (1995-07). Cornerstones of Georgia history. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 0820317438, 9780820317434.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Thurmond: Why Georgia's founder fought slavery". Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ^ Digital History, Steven Mintz. "Was slavery the engine of economic growth?". Digitalhistory.uh.edu. Retrieved 2009-04-18.
- ^ The Transatlantic Slave Trade Alexander Ives Bortolot. Department of Art History and Archaeology, Columbia University.
- ^ Nigeria - The Slave Trade. Source: U.S. Library of Congress.
- ^ Ronald Segal (1995). The Black Diaspora: Five Centuries of the Black Experience Outside Africa. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 4. ISBN 0-374-11396-3.
It is now estimated that 11,863,000 slaves were shipped across the Atlantic. [Note in original: Paul E. Lovejoy, "The Impact of the Atlantic Slave Trade on Africa: A Review of the Literature," in Journal of African History 30 (1989), p. 368.] ... It is widely conceded that further revisions are more likely to be upward than downward.
- ^ Frontline: Famous Families
- ^ Indentured Servitude in Colonial America. Deanna Barker, Frontier Resources.
- ^ Selling Poor Steven. Philip Burnham, American Heritage Magazine.
- ^ 1860 Census Results, The Civil War Home Page.
- ^ Stephen D. Behrendt, David Richardson, and David Eltis, W. E. B. Du Bois Institute for African and African-American Research, Harvard University. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". Stephen Behrendt (1999). "Transatlantic Slave Trade". Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience. New York: Basic Civitas Books. ISBN 0-465-00071-1.
- ^ Sons Of Providence: The Brown Brothers, the Slave Trade, and the American Revolution By Charles Rappleye. 2006 Simon & Schuster. 978-0743266871
- ^ Richard S. Newman, Transformation of American abolitionism: fighting slavery in the early Republic chapter 1
- ^ Kolchin p. 96
- ^ Berlin pp. 161-162
- ^ Berlin pp. 168-169. Kolchin p. 96. Kolchin notes that Fogel and Engerman maintained that 84% of slaves moved with their families but "most other scholars assign far greater weight ... to slave sales." Ransome (p. 582) notes that Fogel and Engermann based their conclusions on the study of some counties in Maryland in the 1830s and attempt to extrapolate that as reflective of the entire South over the entire period.
- ^ "Bleeding Kansas (United States history)". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Islam and Slavery
- ^ "Horrible Traffic in Circassian Women—Infanticide in Turkey," New York Daily Times, August 6 1856
- ^ Soldier Khan
- ^ Insights into the concept of Slavery
- ^ Historical survey > The international slave trade. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ slave-trade. JewishEncyclopedia.com
- ^ Muslim Slave System in Medieval India, K.S. Lal, Aditya Prakashan, New Delhi
- ^ Slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica's Guide to Black History.
- ^ Slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Swahili Coast. Nationalgeographic.com
- ^ Remembering East African slave raids, BBC News, March 30, 2007
- ^ Focus on the slave trade, BBC News, September 3, 2001
- ^ The Unknown Slavery: In the Muslim world, that is — and it's not over
- ^ "Slavery in Africa". Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2009.
- ^ Lewis. Race and Slavery in the Middle East, Oxford Univ Press 1994.
- ^ When europeans were slaves: Research suggests white slavery was much more common than previously believed
- ^ Davis, Robert. Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500-1800.Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". Stephen Behrendt, "Transatlantic Slave Trade", Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience (New York: Basic Civitas Books, 1999), ISBN 0-465-00071-1.
- ^ Slavery in the Middle Ages. Historymedren.about.com
- ^ The Saxon Slave-Market. First published in Bristol Magazine July 2006.
- ^ Träldom. Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 30. Tromsdalstind – Urakami /159–160, 1920. (In Swedish)
- ^ Historical survey > Ways of ending slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ a b "Slavery (sociology)". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ "Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500-1800". Robert Davis (2004) ISBN 1403945519
- ^ Rees Davies, British Slaves on the Barbary Coast, BBC, July 1, 2003
- ^ Halil Inalcik. "Servile Labor in the Ottoman Empire" in A. Ascher, B. K. Kiraly, and T. Halasi-Kun (eds), The Mutual Effects of the Islamic and Judeo-Christian Worlds: The East European Pattern, Brooklyn College, 1979, pp. 25-43.
- ^ Fisher 'Muscovy and the Black Sea Slave Trade', pp. 580—582. [1]
- ^ Soldier Khan By Mike Bennighof, Ph.D. September 2007
- ^ Welcome to Encyclopædia Britannica's Guide to Black History
- ^ Digital History Slavery Fact Sheets
- ^ Slow Death for Slavery: The Course of Abolition in Northern Nigeria, 1897-1936 (review), Project MUSE - Journal of World History
- ^ a b Twentieth Century Solutions of the Abolition of Slavery
- ^ The East African slave trade. BBC World Service | The Story of Africa.
- ^ Sexual slavery - the harem. BBC - Religion & Ethics
- ^ "The Freeing of the Slaves"
- ^ Historical survey > Slave-owning societies
- ^ "Slavery". Encyclopædia Britannica. May 19, 2009.
- ^ A. Tom Grunfeld, The making of Modern Tibet, Revised Edition, Armonk, New York: M. E. Sharpe, 1996, p. 15.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica - Slavery
- ^ Lewis, James Bryant. (2003). Frontier Contact Between Choson Korea and Tokugawa Japan, p. 31-32.
- ^ "Slavery in Nineteenth-Century Northern Thailand (Page 4 of 6)". Kyoto Review of South East Asia; (Colquhoun 1885:53).
- ^ "Slavery in Nineteenth-Century Northern Thailand: Archival Anecdotes and Village Voices" (Page 3 of 6). The Kyoto Review of South Asia
- ^ S.M.Wise, Though the Heavens May Fall, Pimlico (2005)
- ^ Abolition Movement. Online Encyclopedia
- ^ Sailing against slavery. By Jo Loosemore. BBC - Devon - Abolition
- ^ The West African Squadron and slave trade
- ^ Foner, Eric. "Forgotten step towards freedom," New York Times. December 30, 2007.
- ^ "The law against slavery". Religion & Ethics - Ethical issues. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- ^ Commemoration of the Abolition of Slavery Project
- ^ Chinese Police Find Child Slave
- ^ Convictions in China slave trial
- ^ "Religion & Ethics - Modern slavery: Modern forms of slavery". BBC. 2007-01-30. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ name="slavery1"/
- ^ a b c d e Kara, Siddharth (2008). Sex Trafficking - Inside the Business of Modern Slavery. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0231139601.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Trafficking FAQs – Amnesty International USA
- ^ Lost Daughters - An Ongoing Tragedy in Nepal Women News Network - WNN, Dec 05, 2008
- ^ a b US State Department Trafficking report
- ^ War and Genocide in Sudan
- ^ The Lost Children of Sudan
- ^ Kevin Bales, Disposable People
- ^ A Global Alliance Against Forced Labour.
{{cite book}}: Text "International Labour Organisation" ignored (help) - ^ "Does Slavery Still Exist?". Anti-Slavery Society. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "My Career Redeeming Slaves". MEQ. December 1999. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b "Convictions in China slave trial". BBC. July 17, 2007. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Zhe, Zhu (June 15, 2007). "More than 460 rescued from brick kiln slavery". China Daily. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Nepal abolishes slave labour system". ABC News. September 8, 2008.
- ^ "The Untouchables". CBC Radio.
- ^ "UN report slams India for caste discrimination". CBC News. March 2, 2007.
- ^ Mauritania made slavery illegal last month
- ^ The Abolition season on BBC World Service
- ^ Mauritanian MPs pass slavery law
- ^ The Shackles of Slavery in Niger
- ^ Born to be a slave in Niger
- ^ BBC World Service | Slavery Today
- ^ As the World Intrudes, Pygmies Feel Endangered, New York Times
- ^ Congo's Pygmies live as slaves, newsobserver.com
- ^ IRAQ: Black Iraqis hoping for a Barack Obama win, Los Angeles Times
- ^ U.S. Department of State Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, 2005 Human Rights Report on Côte d'Ivoire
- ^ "ILO seeks to charge Myanmar junta with atrocities". Reuters. 2006-11-16. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- ^ ILO asks Myanmar to declare forced labour banned
- ^ ILO cracks the whip at Yangon
- ^ Critics: Myanmar biofuel drive uses forced labor
- ^ BBC report on Mani case
- ^ Adu Boahen, Topics In West African History p. 110
- ^ Afrikan Involvement In Atlantic Slave Trade, By Kwaku Person-Lynn, Ph.D
- ^ João C. Curto. Álcool e Escravos: O Comércio Luso-Brasileiro do Álcool em Mpinda, Luanda e Benguela durante o Tráfico Atlântico de Escravos (c. 1480-1830) e o Seu Impacto nas Sociedades da África Central Ocidental. Translated by Márcia Lameirinhas. Tempos e Espaços Africanos Series, vol. 3. Lisbon: Editora Vulgata, 2002. ISBN 978-972-8427-24-5.
- ^ What the papers say, BBC News, 2006-09-22
- ^ Blair 'sorrow' over slave trade, BBC News, 2006-11-27
- ^ BBC News, 2007-02-25
- ^ Livingstone breaks down in tears at slave trade memorial
- ^ Barbara Mikkelsen, 'Black Tax' Credit; Snopes.com. Accessed 2009.09.21.
- ^ Lagerlöf, Nils-Petter (2006-11-12). "Slavery and other property rights". Ideas.repec.org. Retrieved 2009-05-06.
- ^ "Technology". History.com. 2008-01-04. Retrieved 2009-05-06.
- ^ Book VII, The Theory of Moral Sentiments
- ^ Slavery and Evangelical Enlightenment by Robert P Forbes in Religion and the Antebellum Debate over Slavery By John R. McKivigan and Mitchell Snay
- ^ Adam Smith and the Virtues of Enlightenment by Charles L. Griswold
- ^ E.g., Machan, Tibor R. (2000). "Tax Slavery". Ludwig von Mises Institute. Retrieved October 9 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ See the Slavery section in the Conscription article for more.
- ^ The Military Draft and Slavery and Conscription Is Slavery both by Ron Paul
- ^ An Idea Not Worth Drafting: Conscription is Slavery by Peter Krembs
- ^ Nationalized Slavery; A policy Italy should dump by Dave Kopel refers to both the military and national service requirements of Italy as slavery.
- ^ Spiegel, Marjorie. The Dreaded Comparison: Human and Animal Slavery, New York: Mirror Books, 1996.
Bibliography
- Fernand Braudel, Civilization and Capitalism, vol. III: The Perspective of the World (1984, originally published in French, 1979.)
- Davis, David Brion. The Problem of Slavery in the Age of Revolution, 1770-1823 (1999)
- Davis, David Brion. The Problem of Slavery in Western Culture (1988)
- Finkelman, Paul. Encyclopedia of Slavery (1999)
- Lal, K. S. Muslim Slave System in Medieval India (1994) ISBN 81-85689-67-9
- Gordon, M. Slavery in the Arab World (1989)
- E. Wyn James, 'Welsh Ballads and American Slavery', Welsh Journal of Religious History, 2 (2007), pp. 59–86. ISSN 0967-3938.
- Jacqueline Dembar Greene, Slavery in Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, (2001), ISBN 0531165388
- Morgan, Kenneth. Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America (2008)
- Nieboer, H. J. (1910). Slavery as an Industrial System
- Postma, Johannes. The Atlantic Slave Trade, (2003)
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed., The Historical Encyclopedia of World Slavery (1997)
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. Slavery in the United States: A Social, Political, and Historical Encyclopedia (2007)
- Shell, Robert Carl-Heinz Children Of Bondage: A Social History Of The Slave Society At The Cape Of Good Hope, 1652-1813 (1994)
- William Linn Westermann, The Slave Systems of Greek and Roman Antiquity (1955), ISBN 0871690403
- Uncited sources
- Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion: The Shell Money of the Slave Trade. African Studies Series 49, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1986.
- The Slavery Reader, ed. by Rigas Doganis, Gad Heuman, James Walvin, Routledge 2003
- Mintz, S. Facts and Myths
- United States
- Berlin, Ira. Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America (1999), most important recent survey
- Blackmon, Douglas A. Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II Doubleday (March 23, 2008), ISBN 0385-50625-2 ISBN 978-0385-50625-0
- Boles, John. Black Southerners: 1619-1869 (1983) brief survey
- Engerman, Stanley L. Terms of Labor: Slavery, Serfdom, and Free Labor (1999)
- Genovese Eugene D. Roll, Jordan Roll (1974), classic study
- Richard H. King, "Marxism and the Slave South", American Quarterly 29 (1977), 117-31, a critique of Genovese
- Escott, Paul D. "Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk about Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Freedom" Journal of Southern History, Vol. 67, 2001
- Parish, Peter J. Slavery: History and Historians (1989)
- Phillips, Ulrich B. American Negro Slavery:A Survey of the Supply, Employment and Control of Negro Labor as Determined by the Plantation Regime (1918; paperback reprint 1966), southern white perspective
- Phillips, Ulrich B. Life and Labor in the Old South (1929)
- Sellers, James B. Slavery in Alabama (1950).
- Sydnor, Charles S. Slavery in Mississippi (1933
- Stampp, Kenneth M. The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South (1956), a rebuttal of U B Philipps
- Vorenberg, Michael . Final Freedom: The Civil War, the Abolition of Slavery, and the Thirteenth Amendment (2001)
- Weinstein, Allen , Frank O. Gatell, and Lewis Sarasohn, eds., American Negro Slavery: A Modern Reader, third ed. (1978)
- Mintz, S. Slavery Facts & Myths, Digital History
- Slavery in the modern era
- Jesse Sage and Liora Kasten, Enslaved: True Stories of Modern Day Slavery, Palgrave Macmillan, 2008 ISBN 9781403974938
- Tom Brass, Marcel van der Linden, and Jan Lucassen, Free and Unfree Labour. Amsterdam: International Institute for Social History, 1993
- Tom Brass, Towards a Comparative Political Economy of Unfree Labour: Case Studies and Debates, London and Portland, OR: Frank Cass Publishers, 1999. 400 pages.
- Tom Brass and Marcel van der Linden, eds., Free and Unfree Labour: The Debate Continues, Bern: Peter Lang AG, 1997. 600 pages. A volume containing contributions by all the most important writers on modern forms of unfree labour.
- Kevin Bales, Disposable People. New Slavery in the Global Economy, Revised Edition, University of California Press 2004, ISBN 0-520-24384-6
- Kevin Bales (ed.), Understanding Global Slavery Today. A Reader, University of California Press 2005, ISBN 0-520-24507-5freak
- Kevin Bales, Ending Slavery: How We Free Today's Slaves, University of California Press 2007, ISBN 978-0-520-25470-1.
- Mende Nazer and Damien Lewis, Slave: My True Story, ISBN 1-58648-212-2. Mende is a Nuba, captured at 12 years old. She was granted political asylum by the British government in 2003.
- Gary Craig, Aline Gaus, Mick Wilkinson, Klara Skrivankova and Aidan McQuade (2007). Contemporary slavery in the UK: Overview and key issues, Joseph Rowntree Foundation. ISBN 978-1-85935-573-2.
- Somaly Mam Foundation
External links
- Historical
- 16 Largest Slaveholders from 1860 Census
- Slavery Resource Guide, from the Library of Congress
- Parliament & The British Slave Trade 1600 - 1807
- Report of the Brown University Steering Committee on Slavery and Justice
- Emory and Oxford College
- Slavery at Princeton
- University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill exhibit
- Yale, Slavery and Abolition
- Slavery Fact Sheets, Digital History
- The West African Squadron and slave trade
- British documents on slave holding and the slave trade, 1788-1793 (DjVu) and Template:PDFlink (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries)
- Slavery - PBS
- Understanding Slavery
- " Slavery in Ethiopia" Abyssinian colonialism and slavery/slavery trade in Abyssinia/Ethiopia
