2014 Romanian presidential election
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 53.18% (first round) 64.11% (second round) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
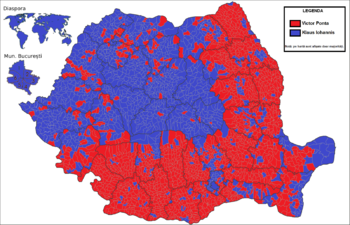
 The results of the presidential election, showing the vote strength by county in the second round. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Part of the Politics series |
 |
|---|
|
|
Presidential elections were held in Romania in 2014. They were the seventh presidential elections held in post-1989 Romania. In the first round of the elections on 2 November, the top two of the fourteen candidates qualified in a run-off on 16 November. These candidates were Victor Ponta, former Prime Minister and ex-leader of the Social Democratic Party (PSD) who won around 40% of the vote in the first round, and Klaus Iohannis, then mayor of Sibiu (German: Hermannstadt) and leader of the Christian Liberal Alliance (ACL), who won around 30% in the first round respectively.[1] Following large protests on how Ponta's government organized the elections in the diaspora, Klaus Iohannis staged a surprising come-back and won the run-off with 54.5%, or more than a million votes than his contender.
Ponta, who had been previously serving as Prime Minister of Romania since May 2012, ran his campaign on promoting an alleged national reconciliation message of a "great union" between all Romanians,[2] defending his governance as balanced, with both progressive and right-wing measures, and promising to end the "era" established by the then incumbent president, Traian Băsescu. However, his government faced some indirect international criticism, with U.S. Assistant Secretary of State Victoria Nuland criticizing in October 2014 what she called the "cancer of democratic regression and corruption" in several Central and Southeast Europe nations and with politicians who "protect the corrupt office holders from prosecution and bypass parliament as often as it suits them".[3] Iohannis, a Transylvanian Saxon (therefore part of the community of the Germans of Romania), focused his campaign on judicial independence and fiscal relaxation,[4] and promised to promote "Romania of thoroughness" and a "Romania of things well done," while blaming the country's economic and political problems on the regional governance of the Social Democratic Party (PSD), the so-called "barons".[5]
The electoral campaign ran between 3 October and 1 November and was overshadowed by several corruption scandals (Microsoftgate,[6] EADS, illegal retrocessions)[7] involving key figures of PSD,[8] but also the candidate Elena Udrea.[9] Outgoing President Traian Băsescu accused Victor Ponta of being an undercover spy, incompatible under the Romanian legislation with a public position,[1] while Klaus Iohannis faced accusations of incompatibility filed by the National Integrity Agency after September, 2013. Following very long voting times and large numbers of people who couldn't vote before the closing of polls in diaspora, large protests were staged in multiple cities across Romania and at Romanian embassies before the second round. This was regarded as both incapacity and unwillingness of Ponta's government to organize fair elections, and led to a surprisingly large turnout of over 64% (largest since 1996), and a surprise win for Iohannis in the second round.
Background
[edit]
Traian Băsescu won the last presidential election in 2009 and was sworn in for his second term on 21 December 2009. According to the Article 83 of the Constitution of Romania, the "term of office of the President of Romania is five years, being exercised from the date the oath was taken,"[10] but only for up to two terms.
The dates were decided by the government in February:[11]
- 5 September: the Supreme Court announced the composition of the Central Electoral Bureau for the presidential election, composed of judges from the High Court of Cassation and Justice appointed by lot, representatives of the Permanent Electoral Authority and of the political parties.[12] Judge Veronica Năstasie is elected president of the Central Electoral Bureau.[13]
- 23 September: last day for submitting candidacies and the electoral insignia of the candidates.
- 24 September: the Central Electoral Bureau validated all the 14 submitted candidacies.[14]
- 3 October–1 November: electoral campaign.[15]
- 2 November, 7 a.m.–9 p.m.: first round of the presidential election, with over 18.3 million people in the country and 530,000 Romanians abroad expected to go to the polls.[12]
- 6 November: validation and publication of the election results in the Official Monitor.[16]
- 7–15 November: electoral campaign for second round.
- 16 November 7 a.m.–9 p.m.: second round of the presidential election.
- 21 November: validation and publication of the election results in the Official Gazette.[16]
Candidates
[edit]
Fourteen candidates submitted to the Central Electoral Bureau files with the number of signatures collected from citizens (at least 200,000) by 23 September 2014: Victor Ponta, Klaus Iohannis, Monica Macovei, Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu, Teodor Meleșcanu, Elena Udrea, Dan Diaconescu, Hunor Kelemen, Zsolt Szilágyi, Corneliu Vadim Tudor, Constantin Rotaru, William Brînză, Mirel Mircea Amariței and Gheorghe Funar.[17]
The left-wing parties designated a single candidate: Victor Ponta, the current Prime Minister. He was rated with the best chance of winning the election by main opinion polls. On the other hand, the main right-wing parties, strengthened under the Christian Liberal Alliance, have designated Klaus Iohannis, the second favorite of the opinion polls. However, the so-called "right wing" was still divided, with many newly formed parties with small number of members designating their own presidential candidates, such as Elena Udrea, candidate from the People's Movement Party and supported by the Christian Democratic National Peasants' Party. There were four independent candidates: former Prime Minister Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu, former Minister of Justice Monica Macovei, former Chief of the Foreign Intelligence Service Teodor Meleșcanu and former Mayor of Cluj-Napoca Gheorghe Funar.
This was a record number of candidates since 1996, since in 2000, 2004 and 2009, only 12 candidates were admitted each election.[18] Likewise, this was the first time women candidates (Elena Udrea and Monica Macovei) ran for the position of president of the country and the first time three ethnics of the national minorities figure on the ballot papers. A number of people announced they would be running was greater, but they failed to gather the 200,000 signatures needed for the submission of the candidature to the Central Electoral Bureau by the 23 September deadline, such as Ioan Ghișe.
Several candidates had announced their intention to run for president, but eventually withdrew in favor of other candidates:
- Crin Antonescu, interim President of Romania in 2012: one of the leading figures of the Social Liberal Union (USL), Antonescu was the joint candidate of the political alliance, but he stepped down as President of PNL and announced the withdrawal of his candidature following the split of USL in February 2014 and the poor results of PNL in the European Parliament election.
- Mihai Răzvan Ungureanu, former Prime Minister of Romania: Ungureanu was a candidate for the Civic Force, but withdrew after the party he led was absorbed into the Christian Liberal Alliance in July 2014.
- Cristian Diaconescu, former Presidential Adviser of Traian Băsescu: he was elected as official candidate of newly formed People's Movement Party, but withdrew from the presidential race to support his party colleague, Elena Udrea, who scored higher in the opinion polls.[19]
- Cătălin Predoiu, former Minister of Justice: he was the official candidate of PDL, after winning an internal election, but after the merger of PNL and PDL, an election was organized to determine the candidate of the alliance, where he lost to Klaus Iohannis.
| Image | Candidate | Candidature launched | Candidature registered by the Central Electoral Bureau |
Alliance | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Victor Ponta | 12 September 2014[20] | 18 September 2014[21] | PSD–UNPR–PC Alliance | Social Democratic Party |
| National Union for the Progress of Romania | |||||
| Conservative Party | |||||

|
Klaus Iohannis | 11 August 2014[22] | 22 September 2014[23] | Christian Liberal Alliance | National Liberal Party |
| Democratic Liberal Party | |||||
| Civic Force | |||||
| Democratic Forum of Germans in Romania | |||||
 |
Monica Macovei | 5 August 2014[24] | 22 September 2014[25] | — | Independent |
 |
Hunor Kelemen | 17 July 2014[26] | 24 September 2014[27] | — | Democratic Alliance of Hungarians in Romania |

|
Elena Udrea | 19 August 2014[28] | 24 September 2014[29] | PMP–PNȚCD Alliance | People's Movement Party |
| Christian Democratic National Peasants' Party | |||||
 |
Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu | 23 July 2014[30] | 24 September 2014[31] | — | Independent1 |
 |
William Brînză | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[33] | — | Romanian Ecologist Party |
| Constantin Rotaru | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[34] | — | Socialist Alternative Party | |
 |
Corneliu Vadim Tudor | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[35] | — | Greater Romania Party |
 |
Dan Diaconescu | 12 October 2013[36] | 24 September 2014[37] | — | People's Party – Dan Diaconescu |
| Gheorghe Funar | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[38] | — | Independent2 | |
 |
Zsolt Szilágyi | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[39] | — | Hungarian People's Party of Transylvania |
| Mirel Mircea Amariței | 23 September 2014[32] | 24 September 2014[40] | — | PRODEMO Party | |
 |
Teodor Meleșcanu | 23 September 2014[41] | 24 September 2014[42] | — | Independent |
1Tăriceanu's Liberal Reformist Party led was not registered at the time, so he decided to run as an independent.
2At the time of the election there was an ongoing dispute between Corneliu Vadim Tudor and Gheorghe Funar as to who is the legitimate leader of the Greater Romania Party. Because Corneliu Vadim Tudor appeared as the leader of the party in the Register of Political Parties kept at the Bucharest Tribunal, Gheorghe Funar ran as an independent.
Campaign
[edit]

Victor Ponta launched his campaign on his birthday, in a huge rally on the National Arena. Over 70,000 people from across the country attended the rally.[43] One of the stadium lawns was covered with four large panels inscribed with the slogan "Proud to be Romanians" and depicting Romanian folk motifs.[44] Many opposing political analysts, members of the opposition and even President Traian Băsescu have likened the event to the rallies in the communist period dedicated to Nicolae Ceaușescu or, more recently, those dedicated to Kim Jong-un, the Supreme Leader of North Korea.[45][46] Likewise, he was criticized by PMP candidate Elena Udrea for the cost of organizing such an event which, she said, was around 2 million euros.[47]
Klaus Iohannis launched his campaign in front of the Government, in the presence of up to 30,000 people. The special guest of the event was the Secretary General of the EPP, Antonio López-Istúriz White, who stated that "Victor Ponta cannot and should not become president of the European Romania".[48] The vast majority of Romanians are Eastern Orthodox Christians like Ponta, while Iohannis is Protestant. Commenting on a poll, according to which 58.22% of the respondents said for them the religion of the President mattered, while 39.81% said they were indifferent to the issue, Ponta said he did not believe that a candidate for President "has a problem if he is Orthodox or is not of Romanian ethnicity".[49] Iohannis has reacted strongly to the statement by his rival, saying that bringing the issue of religion is a "painful attempt" to poison the campaign.[49] Iohannis' slogan in the presidential campaign was "less talk, more things done", alluding to frequent television appearances of his rival, Victor Ponta.[50] In his presidential program are mentioned, among others: deepening of the strategic partnership with the United States, allocation of 2% of GDP for defense, 6% for health and 6% for education, restructuring of the management system of EU funds, development of the capital market, keeping the flat tax, return of VAT to 19%, etc.[51] Iohannis proposes a liberal economy based on competitiveness and prosperity, encouragement of a highly developed agriculture, connection of Romania to the Western world through infrastructure or decentralization, as "vector of modernization". Likewise, for Klaus Iohannis, the European path of the Republic of Moldova is a national priority.[52]
Elena Udrea launched her campaign for the presidency through an anti-governmental march attended by 10,000 people.[53] She expressed her intention to dissolve the Parliament and form a new Government, in the eventuality that she would win the election.[54] Udrea is supported by outgoing President Traian Băsescu[55] who intended to join the party Udrea leads at the end of his mandate in December.[56]
During the early days following the first round of the 2 November election, that saw the two main candidates from all opinion polls facing off in a 16 November runoff, several of the candidates that fell short of acceding into the second round have declared their support for one of the two remaining candidates. Prime Minister and PSD leader Victor Ponta, who came first with 40.4% of the votes ahead of Sibiu mayor and ACL candidate Klaus Iohannis who earned a distant 30.3%, received the backing of the second runner-up, former premier and Senate president Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu, from the Liberal Reformist Party, who would also have been Ponta's proposal to replace him as Prime Minister, had Ponta won.[57]
Other candidates who also publicly declared their support for Ponta were: Dan Diaconescu, from PP-DD, Corneliu Vadim Tudor, from PRM and independent candidate Teodor Meleșcanu. Despite UDMR's presence in the government led by Ponta, Hunor Kelemen expressed neutrality and recommended Hungarian electorate "vote according to their own beliefs". He said that UDMR can't support Victor Ponta in the second round because the Social Democrats have allied with PRM, an ultra-nationalist party, with which UDMR had several conflicts over time.[58] Internationally, Ponta received support from many current Prime Ministers across Europe, like the Moldovan premier Iurie Leancă, Italian Prime Minister Matteo Renzi, Serbian premier Aleksandar Vučić,[59] Slovakian Prime Minister Robert Fico,[60] Czech premier Bohuslav Sobotka,[61] Georgian premier Irakli Garibashvili and Albanian Prime Minister Edi Rama,[62] among others. Also, the Party of European Socialists expressed clear support for the candidature of Ponta to the Romanian presidency.[63] Others were Sigmar Gabriel (Germany, SPD),[64] Elio Di Rupo (Belgium, Parti Socialiste),[65] Gianni Pittella (Italy)[66] and Martin Schulz (President of the European Parliament).[67]
Iohannis announced that he would not negotiate with other candidates, though he needed as much as 21% of the votes to recuperate and win. Elena Udrea, from the PMP–PNȚCD Alliance, didn't avowedly express her support for Klaus Iohannis, but stated that the vote on 16 November should be anti-Ponta.[68] On the other hand, independents Monica Macovei and Mirel Mircea Amariței, as well as PPMT-backed Zsolt Szilágyi announced their support for Iohannis. Likewise, Iohannis enjoyed international support from the European People's Party[69] and German Chancellor Angela Merkel.[70][71]
Victor Ponta and key figures of his party accused Klaus Iohannis of wanting to separate Transylvania from the rest of Romania, because Iohannis won a large majority of the votes on 2 November in the intra-Carpathian region.[72] Iohannis criticized these statements, describing them as "cretinisms". He also said that the idea of "breaking Transylvania" was "totally false, from another century and harmful", and came up because "people like the PRM are coopted for some votes".[73] This topic was intensively discussed in local media. Many political commentators consider that dissimilar cultural heritage that each of the regions of Romania has is an exponent of the different vote expressed by Transylvania, Banat, Bukovina, Crișana and Maramureș, as opposed to Moldavia, Wallachia and Dobruja.[74]
Opinion polls
[edit]First round
[edit]The problem of the seriousness and confidence in the opinion polls in the political domain is extremely controversial in Romania. Many people, especially members and supporters of the opposition,[75][76] consider that the political affiliations of the directors of the main opinion polling firms have a significant impact in their results.[77] For example, Sociopol is led by Mirel Palada, former spokesman for the government of Victor Ponta,[78] while GSSC Avangarde is led by sociologist Marius Pieleanu, a confidant of the Conservative Party.[78] The honorary president of CSCI is Bogdan Teodorescu, one of the strategists of Victor Ponta's campaign during these presidential elections.[78] The main shareholder of IRES is Vasile Dâncu, former PSD senator.[78] But not only the ruling party has tangents with the opinion polls. CCSCC published the results of a fictional survey during the European Parliament election of 25 May 2014, at liberal Horea Uioreanu's command, subsequently taken into custody for corruption.[79]
Several opinion polls were conducted in the period preceding official announcement of the 14 candidates. Many of them showed Crin Antonescu instead of Klaus Iohannis or Cristian Diaconescu instead of Elena Udrea. In the polls also figured Mihai Răzvan Ungureanu and Cătălin Predoiu, which withdrew their candidacies after the political events in the summer of 2014. The following table displays the main candidates (at least 1%) and evolution of their percentages.
| Poll source | Date | Ponta (USD) |
Iohannis (ACL) |
Tăriceanu (Ind.) |
Udrea (PMP) |
Diaconescu (PP-DD) |
Kelemen (UDMR) |
Macovei (M10) |
Vadim (PRM) |
Meleșcanu (Ind.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRES | 29 October 2014 | 41% | 30% | 6% | 7% | 2% | 3% | 6% | 3% | 2% |
| CSCI | 27–29 October 2014 | 40% | 29% | 8% | 6% | 3% | 3% | 5% | 2% | 3% |
| CSCI | 20–25 October 2014 | 41% | 27% | 8% | 5% | 5% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 2% |
| CCSCC | 21–24 October 2014 | 36% | 30% | 6% | 6% | 4% | 3% | 7% | 2% | 3% |
| IRES | 23 October 2014 | 43% | 30% | 6% | 8% | 1% | 2% | 5% | 2% | 3% |
| Sociopol | 18–20 October 2014 | 41% | 28% | 7% | 6% | 4% | 4% | 4% | 3% | 2% |
| INSCOP | 2–8 October 2014 | 40.6% | 30.1% | 6.2% | 6.7% | 2% | 2.5% | 4.6% | 1.7% | 4.6% |
| GSSC Avangarde | 28 September–3 October 2014 | 42% | 28% | 8% | 5% | 2% | 4% | 4% | 2% | 4% |
| AB Research Grup | 20–25 September 2014 | 42% | 23% | 11% | 6% | 4% | 3% | 5% | 2% | 1% |
| CCSCC | 19–24 September 2014 | 38% | 32% | 7% | 8% | 3% | 4% | 5% | ||
| Sociopol | 20–23 September 2014 | 42% | 26% | 9% | 6% | 5% | 3% | 3% | 4% | 1% |
| CSCI | 15–18 September 2014 | 42% | 27% | 9% | 6% | 5% | 4% | 3% | 2% |
Graphical summary
[edit]The following graph depicts the evolution of the standing of each candidate in the poll aggregators from September to October 2014.
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Second round
[edit]| Poll source | Date | Ponta (USD) |
Iohannis (ACL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| INSCOP | 1–7 May 2014 | 51.7% | 48.3% |
| Operations Research | 5–10 June 2014 | 59% | 41% |
| The Political Rating Agency | 16–22 June 2014 | 55% | 45% |
| INSCOP | 1–6 July 2014 | 52.8% | 47.2% |
| BCS | 3–12 July 2014 | 49.6% | 50.4% |
| IRSOP | 10–17 July 2014 | 49% | 43% |
| CCSCC[permanent dead link] | 17–23 July 2014 | 51% | 49% |
| GSSC Avangarde | 25 August–3 September 2014 | 55% | 45% |
| INSCOP | 30 August–4 September 2014 | 54% | 46% |
| CSCI | 15–18 September 2014 | 57% | 43% |
| CCSCC[permanent dead link] | 19–24 September 2014 | 52% | 48% |
| GSSC Avangarde | 28 September–3 October 2014 | 57% | 43% |
| INSCOP | 2–8 October 2014 | 53.5% | 46.5% |
| IRES | 14 October 2014 | 55% | 45% |
| CCSCC | 21–24 October 2014 | 50% | 50% |
| CSCI | 27–29 October 2014 | 55% | 45% |
| CSCI | 5 November 2014 | 55% | 45% |
| CURS-Avangarde | 7–9 November 2014 | 54% | 46% |
Results
[edit]The first round of voting was held on 2 November. Because no candidate obtained the support of more than 50% of registered voters, a second round was scheduled to be held two weeks later, on 16 November, with Victor Ponta and Klaus Iohannis running against each other.
Elena Udrea, Monica Macovei and Kelemen Hunor openly endorsed Iohannis in the second round. Dan Diaconescu positioned himself against Ponta, without openly endorsing Iohannis. Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu and Teodor Meleșcanu openly endorsed Ponta in the second round.
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Klaus Iohannis | Christian Liberal Alliance (PNL–PDL) | 2,881,406 | 30.38 | 6,288,769 | 54.43 | |
| Victor Ponta | PSD–UNPR–PC Alliance | 3,836,093 | 40.44 | 5,264,383 | 45.57 | |
| Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu | Independent | 508,572 | 5.36 | |||
| Elena Udrea | PMP–PNȚCD Alliance | 493,376 | 5.20 | |||
| Monica Macovei | Independent | 421,648 | 4.45 | |||
| Dan Diaconescu | People's Party – Dan Diaconescu | 382,526 | 4.03 | |||
| Corneliu Vadim Tudor | Greater Romania Party | 349,416 | 3.68 | |||
| Hunor Kelemen | Democratic Alliance of Hungarians in Romania | 329,727 | 3.48 | |||
| Teodor Meleșcanu | Independent | 104,131 | 1.10 | |||
| Zsolt Szilágyi | Hungarian People's Party of Transylvania | 53,146 | 0.56 | |||
| Gheorghe Funar | Independent | 45,405 | 0.48 | |||
| William Brînză | Ecologist Party of Romania | 43,194 | 0.46 | |||
| Constantin Rotaru | Socialist Alternative Party | 28,805 | 0.30 | |||
| Mirel Mircea Amariței | PRODEMO Party | 7,895 | 0.08 | |||
| Total | 9,485,340 | 100.00 | 11,553,152 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 9,485,340 | 97.55 | 11,553,152 | 98.58 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 237,761 | 2.45 | 166,111 | 1.42 | ||
| Total votes | 9,723,101 | 100.00 | 11,719,263 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 18,284,066 | 53.18 | 18,280,994 | 64.11 | ||
| Source: ROAEP | ||||||
By county
[edit]First round
[edit]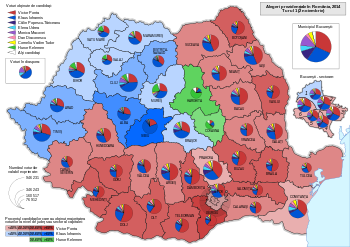

| County | Ponta (PSD) |
Iohannis (ACL) |
Tăriceanu (Ind.) |
Udrea (PMP) |
Macovei (Ind.) |
Kelemen (UDMR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alba | 27.43% | 52.57% | 3.88% | 3.91% | 2.29% | 2.37% |
| Arad | 29.48% | 44.55% | 4.12% | 4.92% | 2.83% | 3.94% |
| Argeș | 49.75% | 20.99% | 8.04% | 5.69% | 2.97% | <1% |
| Bacău | 48.64% | 26.23% | 4.82% | 4.65% | <1% | <1% |
| Bihor | 32.24% | 37.31% | <1% | <1% | <1% | 11.8% |
| Bistrița-Năsăud | 36.28% | 44.68% | 3.53% | 3.6% | 2.21% | 3.02% |
| Botoșani | 55.59% | 22.09% | <1% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
| Brașov | 30.75% | 39% | 7.04% | 4.24% | 5.64% | 3.65% |
| Brăila | 51.54% | 20.09% | 6.03% | 5.24% | 3.23% | <1% |
| Bucharest | 31.74% | 27.24% | <1% | <1% | 12% | <1% |
| Buzău | 54.21% | 19.9% | <1% | 6.06% | <1% | <1% |
| Caraș-Severin | 43.03% | 34.48% | 4.07% | 4.45% | 2.19% | <1% |
| Călărași | 49.76% | 27.36% | 3.55% | 4.22% | 2.3% | <1% |
| Cluj | 23.79% | 42.53% | 3.53% | 3.6% | 2.21% | 3.02% |
| Constanța | 37.36% | 29.41% | 4.63% | 8.07% | 6.38% | <1% |
| Covasna | 13.69% | 14.9% | <1% | 2.7% | <1% | 50.41% |
| Dâmbovița | 52.54% | 23.78% | 3.96% | 5.42% | 2.63% | <1% |
| Dolj | 54.78% | 23.11% | <1% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
| Galați | 48.11% | 24.97% | 5.97% | 5.12% | 4.2% | <1% |
| Giurgiu | 61.32% | 15.4% | 4.98% | 5.45% | 1.84% | <1% |
| Gorj | 50.25% | 24.38% | 5.65% | 5.84% | 1.52% | <1% |
| Harghita | 8.13% | 10.76% | <1% | 2.6% | <1% | 62.97% |
| Hunedoara | 43.59% | 31.64% | 5.52% | 4.69% | <1% | <1% |
| Ialomița | 53.61% | 18.99% | 5.1% | 5.27% | 2.82% | <1% |
| Iași | 43.46% | 29.73% | 5.43% | 4.81% | 6.05% | <1% |
| Ilfov | 39.97% | 27.71% | 7.56% | 5.93% | 6.5% | <1% |
| Maramureș | 36.46% | 36.55% | 4.15% | 6.28% | 3.24% | 3.29% |
| Mehedinți | 57.4% | 21.1% | 5.3% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
| Mureș | 26.49% | 32.02% | <1% | <1% | <1% | 22.96% |
| Neamț | 49.42% | 22.65% | 4.55% | 7.26% | 3.66% | <1% |
| Olt | 59.99% | 18.94% | 3.31% | 4.3% | 1.32% | <1% |
| Prahova | 39.41% | 27.71% | 8.4% | 6.72% | 4.55% | <1% |
| Satu Mare | 31.63% | 32.37% | 5.34% | 3.14% | 1.54% | 18.69% |
| Sălaj | 32.15% | 34.53% | 3.15% | 3.86% | 1.89% | 16.77% |
| Sibiu | 19.35% | 69.87% | 2.3% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
| Suceava | 43.84% | 32.63% | 4.72% | 5.7% | 2.37% | <1% |
| Teleorman | 57.92% | 23.24% | 3.2% | 3.84% | <1% | <1% |
| Timiș | 29.66% | 42.03% | 5.2% | 5.95% | 6.19% | <1% |
| Tulcea | 42.76% | 26.25% | 3.59% | 9.29% | 3.63% | <1% |
| Vaslui | 54.03% | 21.55% | 3.92% | 5.56% | <1% | <1% |
| Vâlcea | 44.32% | 34.42% | 5.82% | 4.1% | 1.78% | <1% |
| Vrancea | 49.95% | 26.82% | 3.33% | 5.71% | 2.81% | <1% |
| Overseas voters | 15.89% | 46.17% | 2.95% | 9.78% | 15.2% | <1% |
| Sources: Știrile Pro TV, Știrile Pro TV | ||||||
Second round
[edit]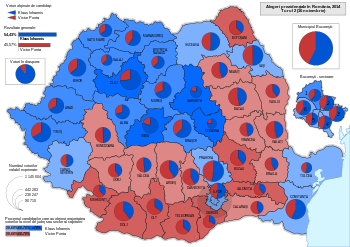
| County | Ponta (PSD) |
Iohannis (ACL) |
|---|---|---|
| Alba | 30.4% | 69.59% |
| Arad | 34.12% | 65.88% |
| Argeș | 59.27% | 40.73% |
| Bacău | 53.55% | 46.45% |
| Bihor | 36.51% | 63.48% |
| Bistrița-Năsăud | 37.73% | 62.26% |
| Botoșani | 62.72% | 37.27% |
| Brașov | 36.9% | 63.09% |
| Brăila | 57.94% | 42.05% |
| Bucharest | 42.67% | 57.33% |
| Buzău | 60.9% | 39.1% |
| Caraș-Severin | 48.06% | 51.93% |
| Călărași | 55.18% | 44.81% |
| Cluj | 26.18% | 73.82% |
| Constanța | 42.93% | 57.07% |
| Covasna | 22.05% | 77.95% |
| Dâmbovița | 58.08% | 41.92% |
| Dolj | 60.6% | 39.39% |
| Galați | 54.02% | 45.98% |
| Giurgiu | 68.38% | 31.62% |
| Gorj | 58.29% | 41.7% |
| Harghita | 20.22% | 79.78% |
| Hunedoara | 50.37% | 49.63% |
| Ialomița | 61.4% | 38.6% |
| Iași | 49.33% | 50.66% |
| Ilfov | 48.18% | 51.82% |
| Maramureș | 39.72% | 60.27% |
| Mehedinți | 63.26% | 36.73% |
| Mureș | 31.36% | 68.63% |
| Neamț | 54.95% | 45.05% |
| Olt | 64.77% | 35.22% |
| Prahova | 47.53% | 52.46% |
| Satu Mare | 34.79% | 65.2% |
| Sălaj | 37.06% | 62.93% |
| Sibiu | 20.51% | 79.48% |
| Suceava | 48.49% | 51.5% |
| Teleorman | 63.42% | 36.57% |
| Timiș | 33.26% | 66.73% |
| Tulcea | 47.36% | 52.63% |
| Vaslui | 59.7% | 40.03% |
| Vâlcea | 50.66% | 49.34% |
| Vrancea | 53.77% | 46.22% |
| Overseas voters | 10.26% | 89.73% |
| Sources: HotNews.ro, Gândul | ||
Confirmation of results
[edit]On 21 November 2014, the Constitutional Court confirmed the results of the election and validated the election of Klaus Iohannis as President of Romania.[80][81]
Reactions
[edit]Protests
[edit]
Several protests broke out in many cities abroad with large communities of Romanians. In Paris, London, Chișinău, Munich, Stuttgart, Vienna, Turin and other cities, Romanians expressed their dissatisfaction concerning the hindering of the voting process and closure before 9 p.m. of the polling stations.[82] Protesters demanded the resignation of Foreign Minister Titus Corlățean and booed the Romanian Government led by PSD candidate Victor Ponta. In Paris, the Romanian Embassy was assaulted by angry protesters. However, the situation defused after the intervention of special forces.[82]
Protests in solidarity with Romanian diaspora also took place in major Romanian cities.[83][84] Organized on Facebook, the protests attracted between 10,000 and 15,000 people in Cluj-Napoca, 5,000 in Timișoara, 4,000 in Bucharest,[85] 2,000 in Craiova and Sibiu, 1,000 in Arad.[86] Many of the protesters were students, young people, intellectuals and people with higher education. They demanded fair elections and Victor Ponta's resignation as PM, whose image was associated with cartoon figures like Mickey Mouse and Pinocchio. Counter-protests organized by sympathizers of PSD also took place in Galați, Alba Iulia, Bistrița, Bacău, Craiova and Brașov, but were attended by fewer people.[87]
During a campaign visit at Millenium Hall, Baia Mare, on 6 November, Victor Ponta was booed by hundreds of people protesting against his disinformation and manipulation uttered at his rival, Klaus Iohannis, and condemning the statements in previous days of the premier and ministers Liviu Dragnea, Titus Corlățean and Bogdan Stanoevici regarding the unfolding of voting process in diaspora.[88] In order to avoid any incidents, Prime Minister Victor Ponta was evacuated from the building by SPP agents and local policemen using a van-minibus.[89]
Victor Ponta accused rival party ACL of organizing the protests, but ACL denied these accusations. Moreover, leaders of ACL and candidate Klaus Iohannis saluted "the civic spirit of all Romanians who in recent days have protested (...) against candidate Victor Ponta's attempt to manipulate the Romanians vote".[90]
Poor organization of the second round in diaspora, but also violent dispersal of Romanian voters after the polls closed angered people in Romania that gathered in their tens of thousands in the largest protest against Ponta's government since the demonstrations against the Roșia Montană Project in the autumn of 2013.
Post-election
[edit]Dear Romanians, all of you have been heroes today.
Klaus Iohannis, after the publication of first exit-polls[91]
The final result was widely seen as a surprise, as all polls before the second round showed Ponta as a clear favorite over Iohannis.[92][93][94][95][96] Ponta did not give a speech at 9 p.m. when the polling ended, and a few hours later he conceded defeat, declaring that "the people are always right" and congratulating Klaus Iohannis over the phone.[93][97] Cristian Ghinea of the Romanian Center for European Policies considered that "Iohannis did a poor job in the two debates, but Ponta mobilized the people against himself (...) He ran a dirty campaign which blew up in his face",[93] while Sergiu Miscoiu, an analyst, thought that "a major mistake was ostracizing the diaspora".[94] Ponta ruled out quitting as prime minister until the parliamentary elections in 2016.[94] Only about 10% of diaspora ended up voting for Ponta.[98]
Upon closing of the polls in Romania, Klaus Iohannis thanked voters for the high turnout and asked the Government to extend the voting period in diaspora to allow everyone in line to vote. Later in the evening, when the victory became clear, he went to University Square, Bucharest, where up to 20,000 people were celebrating, and declared that "we took our country back".[98][99] On Monday morning Iohannis declared that he will be a free president that will represent all Romanians.[100][101]
Following the elections, a wave of resignations occurred in the PSD.[102][103][104] Foreign Minister Teodor Meleșcanu also resigned following the diaspora voting fiasco, thus setting a record for the shortest term as minister in Romania's post-Communist history, having served for only eight days.[105] PSD senator Mircea Geoană, who ran unsuccessfully against Traian Băsescu in the 2009 presidential elections, characterized the result as a "dramatic moment for the Romanian Left" and warned that the PSD needs to "reinvent itself".[106] President-elect Iohannis stated that he want to topple the government.[107] In this regard, PNL leaders intend to file a motion of censure at the beginning of 2015.
International
[edit] U.S. Government congratulated President-elect Klaus Iohannis for his appointment, but also "Romanians, who went to the polls in large numbers, both in country and abroad, in an exemplary demonstration of civic participation".[108]
U.S. Government congratulated President-elect Klaus Iohannis for his appointment, but also "Romanians, who went to the polls in large numbers, both in country and abroad, in an exemplary demonstration of civic participation".[108] Joseph Daul, President of the European People's Party, congratulated Klaus Johannis for the victory in the presidential election, specifying it is "an excellent news" for Romania and the European Union. He stated that Iohannis "will maintain Romania on the democratic way and will lead it in the interest of the Romanian people". On the other hand, Daul expressed disappointment with the "bad conditions" of voting in diaspora.[109] Likewise, the European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker has sent to President-elect of Romania, Klaus Iohannis, a congratulatory letter expressing eagerness to work with the new head of state and government of the country for implementation of the EU agenda, focusing on jobs, investment, competitiveness and growth.[110]
Joseph Daul, President of the European People's Party, congratulated Klaus Johannis for the victory in the presidential election, specifying it is "an excellent news" for Romania and the European Union. He stated that Iohannis "will maintain Romania on the democratic way and will lead it in the interest of the Romanian people". On the other hand, Daul expressed disappointment with the "bad conditions" of voting in diaspora.[109] Likewise, the European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker has sent to President-elect of Romania, Klaus Iohannis, a congratulatory letter expressing eagerness to work with the new head of state and government of the country for implementation of the EU agenda, focusing on jobs, investment, competitiveness and growth.[110] British PM David Cameron also sent Iohannis a congratulatory letter. In reply, Iohannis thanked for it and assured Cameron of strengthening the bilateral relations between the two countries.[111]
British PM David Cameron also sent Iohannis a congratulatory letter. In reply, Iohannis thanked for it and assured Cameron of strengthening the bilateral relations between the two countries.[111] German President Joachim Gauck congratulated Klaus Iohannis for victory in the presidential election and assured that Germany would continue to support Romania on track of important reforms, particularly in terms of strengthening the rule of law.[112] Chancellor Angela Merkel also congratulated Iohannis, stressing that together will deepen bilateral relations.[112]
German President Joachim Gauck congratulated Klaus Iohannis for victory in the presidential election and assured that Germany would continue to support Romania on track of important reforms, particularly in terms of strengthening the rule of law.[112] Chancellor Angela Merkel also congratulated Iohannis, stressing that together will deepen bilateral relations.[112] "I am pleased to address my sincere congratulations and my wishes of success in fulfilling your high mission", said French President François Hollande in a letter sent to Klaus Iohannis. The letter also shows: "Together with you, I want to build a more prosperous, fairer and stronger, able Europe, at times when faces various crises in its neighborhood, to spread its characteristic values, namely democracy and respect for the rule of law".[113]
"I am pleased to address my sincere congratulations and my wishes of success in fulfilling your high mission", said French President François Hollande in a letter sent to Klaus Iohannis. The letter also shows: "Together with you, I want to build a more prosperous, fairer and stronger, able Europe, at times when faces various crises in its neighborhood, to spread its characteristic values, namely democracy and respect for the rule of law".[113] Spokesman for the Russian Foreign Ministry, Alexander Lukashevich, expressed Moscow's position on the presidential election, expressing the hope that, after the election of Klaus Iohannis, the two countries will register a "major change" in their relations after the break caused by "Bucharest's criticism over Moscow's policies" concerning the Ukrainian conflict, but also other international issues.[114]
Spokesman for the Russian Foreign Ministry, Alexander Lukashevich, expressed Moscow's position on the presidential election, expressing the hope that, after the election of Klaus Iohannis, the two countries will register a "major change" in their relations after the break caused by "Bucharest's criticism over Moscow's policies" concerning the Ukrainian conflict, but also other international issues.[114] President of Hungary, János Áder, conveyed his congratulations to Iohannis for victory in the presidential election. In a letter sent to Iohannis, János Áder requested a meeting between the two leaders to discuss issues of mutual interest and to analyze the directions of bilateral cooperation.[115]
President of Hungary, János Áder, conveyed his congratulations to Iohannis for victory in the presidential election. In a letter sent to Iohannis, János Áder requested a meeting between the two leaders to discuss issues of mutual interest and to analyze the directions of bilateral cooperation.[115]
Gallery
[edit]-
Victor Ponta and Italian Prime Minister Matteo Renzi at a debate on Antena 3, 13 November. Klaus Iohannis did not attend the debate.
-
Klaus Iohannis and Victor Ponta at a debate on Realitatea TV, moderated by Rareș Bogdan (center)
-
Submission of Victor Ponta's candidacy for presidential election at the Central Electoral Bureau
-
Victor Ponta launching his candidacy on National Arena, in the presence of his wife Daciana Sârbu (right) and 70,000 other people
Controversies
[edit]The candidate of Christian Liberal Alliance, Klaus Iohannis, publicly asked Prime Minister Victor Ponta for the cancellation of Ordinance 45 of 2014, that amends the legislation on presidential elections,[116] affirming that these changes might lead to electoral fraud by favoring multiple voting.[117] In this regard, PNL brought to trial the Government.[118] Cristian Diaconescu, then the presidential candidate of PMP, notified by letter the Venice Commission about this issue.[119]
In September, the candidacies of Victor Ponta and Monica Macovei were contested at the Constitutional Court, but the complaints were rejected by the court.[120] On the other hand, the National Integrity Agency (ANI) announced in April 2013 that it believed Klaus Iohannis was in a 'state of incompatibility',[121] because he has been the representative of Sibiu in the General Meeting of Shareholders of SC Apă Canal SA Sibiu (since 5 August 2010) and of SC Piețe SA (since 30 April 2009), which contravenes legal provisions governing conflicts of interest.[122] Iohannis repeatedly said that ANI's claims to that effect were mistaken.[citation needed]
Iohannis was also attacked by his rivals, especially Victor Ponta, on the topic of the provenance of his six estates. Many supporters of PSD and TV stations with some sympathies for this party stated that Iohannis bought these houses illicitly,[123] statements which were later refuted by Iohannis. He explained that he has bought the six houses by "honest work" and that the money to purchase them originated either from his own sources – salaries, tutoring, rents - or from money received from his parents and parents-in-law or from loans from friends.[124]
Diaspora voting
[edit]The first round of voting was marked by a scandal concerning the small number of polling stations in countries with large communities of Romanian citizens. 294 polling stations were organized in 95 states,[125] given that over 3 million Romanians with voting right are living and working abroad. In cities like London, Paris, Madrid, Vienna, Munich, Stuttgart, Turin, Rome or Chișinău huge queues of voters were reported at embassies or other polling stations.[126][127] They claim they were prevented from exercising their right to vote, inasmuch as thousands of voters were locked outside the embassies and could not vote until the polls closed.[128] Presidential candidates Klaus Iohannis, Elena Udrea and Monica Macovei urged the prolongation of the voting process in these countries.[129][130] Moreover, the Presidential Administration demanded in a release the immediate resignation of Foreign Minister Titus Corlățean and Minister Delegate for Romanians Abroad Bogdan Stanoevici for poor organization of election in diaspora.[131] Likewise, independent candidate Gheorghe Funar submitted an application to the President of BEC, demanding the cancellation of the first round of voting and its resumption because he considers that the equality of citizens before the law was not ensured, and the right to vote of Romanians abroad was seriously violated.[132] These problems determined Gunther Krichbaum, the chairman of the Commission for European Affairs in the Bundestag to declare that the issue at stake does not concern "possible difficulties in the organisation of elections, but a wilful hindrance of the free expression of the votes", based on the current leftist government's knowledge of the fact that "Romanians living abroad have the tendency to vote with the parties and candidates of the centre-right".[133] Irregularities were also reported in the country's major university centers, where students were forced to form queues of hundreds of people or were redirected to other polling stations, as the standardized affidavit forms had run out.[134]
Angry voters staged spontaneous protests in front of the polling stations in Paris, Vienna, London, Madrid, New York City, Strasbourg and many other locations, chanting slogans like "Down with Ponta!", "Plagiarized vote" or "We want to vote".[135] In Paris, Vienna, London and Turin protests escalated in storming embassies and consulates. Spirits were calmed only after the intervention of law enforcement.[136]
Under pressure from street protests that followed the first round, Titus Corlățean resigned on 10 November.[137] Prime Minister Victor Ponta proposed former presidential candidate Teodor Meleșcanu to occupy this position. The same day, Meleșcanu took the oath in front of President Traian Băsescu at the Cotroceni Palace.[138]
Despite measures taken by new Minister of Foreign Affairs, the scandal in the first round repeated in the second one, but in higher proportions. Kilometer-long queues were reported in several European cities, including Paris, Strasbourg, London, Dublin, Brussels, Oslo, Bonn, Munich, Stuttgart, Turin, Rome and Madrid.[139] Once more, ACL and Monica Macovei urged the prolongation of voting process.[140] Spontaneous protests broke out again in front of embassies and consulates in major European cities. Protesters expressed anger over Ponta's government and poor organization of the election.[141] Shortly after the polls closed, angry voters forced the entrances into the embassies and consulates, to be able to exercise their right to vote. In Paris and Turin, things degenerated into street fighting between voters and law enforcement.[142] Displeased voters were dispersed by police with tear gas and batons.[143] Four people were injured and one arrested after the intervention of Carabinieri in Turin.[144] Having followed the election process, the chairman of the Commission for European Affairs in Bundestag, Gunther Krichbaum, suggested that the voting rights of Romanian citizens had been hindered to such an extent, that the Diaspora voting problems should be investigated as "fraud", and that Victor Ponta should withdraw from office, having lost all authority to serve the public, in any position or qualification.[145][146]
Undercover officer allegations
[edit]In a worsening institutional conflict between the Presidency and the Government, outgoing President Traian Băsescu accused Prime Minister Victor Ponta of serving as an undercover intelligence officer between 1997 and 2001.[147][148] Ponta dismissed the charge as "all lies".[149] His rival Klaus Iohannis demanded an immediate clarification of the situation,[150] while the Minister of Justice Robert Cazanciuc labelled Băsescu's statements as "campaign statements", and the topic as "ridiculous".[151]
Espionage was already a talking point during the electoral campaign. Teodor Meleșcanu, who ran the Foreign Intelligence Service, resigned in September and joined the presidential race as an independent candidate one day later. Around the same time, Robert Turcescu, a popular television anchor, confessed live on air that he had been an undercover lieutenant-colonel for an espionage service and resigned his post.[152] Under Romanian law, outing oneself as a spy is illegal, but prosecutors did not press charges.
Alleged electoral bribe
[edit]Members of PMP and PNL expressed outrage over the announced distribution of 18 kg of food to more than 6.5 million people during the electoral campaign, in October and November.[153] In a press release, PNL stated that "in the mad rush for votes for presidential candidate Victor Ponta, PSD doesn't have the slightest reluctance to use EU funds for masked electoral bribe". This initiative was endorsed by the Ministry of European Funds, who published on 20 September a notice of auction in which the Romanian government said it wants to provide 6,652,986 food packages within the Fund of European aid for the most deprived persons.[citation needed] More specifically, over 150,000 food packages would be sent to each county, totaling 100 million euros.[citation needed] PNL argues that the way this auction is organized raises serious questions about its legality. The Minister for European Funds, Eugen Teodorovici, said that EU funds are not used for electoral purposes and any claims of their diversion is "misinformation".[citation needed]
President Traian Băsescu repeatedly stated that Victor Ponta "bribes the electorate" and "makes electoral alms from borrowed money".[154] In a press conference critical to Victor Ponta and Klaus Iohannis, Băsescu mentioned the figure of 4.8 billion euros, money that would go towards electoral alms and will be paid by the population.[155]
During a large meeting in Iași, Klaus Iohannis mentioned that Ponta's figure is on each pole and tree, asking rhetorically where the money for his campaign came from. He also stated that every Romanian pays Ponta's campaign from the taxes and dues he introduced.[156] During the same meeting, Iohannis refuted all rumors regarding his intentions to cut the pensions after the election, after many pensioners received flyers in the mail, with messages such as "Only Ponta protects the pensions" and "Klaus Iohannis wants to cut your pension" written on them.[157] In a press release, ACL accused PSD that it engages in a campaign against Klaus Iohannis by misinforming and deceiving voters.[158] The Romanian Post signed contracts with PSD, but also with PMP, Macovei and Tăriceanu, agreeing to send newspapers, catalogs, leaflets, brochures and other electoral advertising materials to homes around the country.[159] Over 4 million anti-Iohannis flyers were distributed by the Romanian Post, totaling up to 50,000 euros.[160]
Vote rigging in Moldova
[edit]Sebastian Ghiță, PSD deputy and Victor Ponta's fellow, would be part of a pyramidal mechanism of defrauding the 2014 presidential election, according to prosecutors from the National Anticorruption Directorate, Ploiești branch. He would have given money from illegal deals to persuade voters from Moldova to elect Ponta as president.[161][162]
Sebastian Ghiță would hand in the PSD headquarters in Bucharest 400,000 euros to Alin Petran, an intermediary sent over the Prut to gather the necessary votes.[163] Subsequently, the intermediary has recruited ten coordinators who, in turn, managed 200 people. Each was responsible to provide between 50 and 100 votes to the social democrat candidate. Electors who demonstrated that voted with Victor Ponta received watches, clothes or food.[164] Total costs of these operations were estimated at 350,000 euros.[165][166] Investigators also determined that Sebastian Ghiță and his friends would have created a database that included 20,000 Romanian citizens from Moldova, with voting rights in the 2014 presidential election. According to a witness, Victor Ponta was aware "about this fraudulent attempt to win the presidential election".[163]
As of 24 June 2015, Sebastian Ghiță is prosecuted for influence peddling, money laundering and bribing the voters.[167] Moreover, Ghiță is forbidden to exercise his function of deputy, a premiere in the Romanian justice, but also to talk with Victor Ponta or to leave Ploiești.[166] Ghiță accuses a "prosecutors coup", in an attempt to overthrow the Ponta Government.[168]
Cyber attacks
[edit]In a debate organized by the PNL parliamentary group on 12 February 2015, Marcel Opriș, head of the Special Telecommunications Service (STS), stated that during the presidential election were used cyber attacks for political purposes,[169] being involved a Romanian television through which a signal was given for "a devastating qualified attack for IT-ists".[170] PNL deputy Mihăiță Calimente announced he'll propose at the Defence Commission of the Chamber of Deputies as the director of STS to be heard on this subject.[171]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Andra Timu (2 November 2014). "Romania Votes in Presidential Election With Ponta in Lead". Bloomberg.
- ^ "Romania to elect new president after 'wretched' campaign". EUobserver. 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Discurs dur al Victoriei Nuland la adresa liderilor central-europeni: Protejați parlamentarii corupți și demonizaţi societatea civilă". Digi24 (in Romanian). 3 October 2014.
- ^ "DEZBATERE IOHANNIS - PONTA. Cearta pe pensii, salarii, imunitate si votul diasporei. Cine a "castigat" meciul pe internet". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Peter Janku, Robert Schwartz (1 November 2014). "Democracy put to the test in Romania". Deutsche Welle.
- ^ "'Microsoftgate' scandal rocks Romania". EurActiv. 3 October 2014.
- ^ "Romanian Prime Minister's father-in-law prosecuted in EUR 300 mln illegal forest restitution case". Romania-Insider.com. 16 October 2014. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ^ Radu-Sorin Marinaș (20 October 2014). "Romania starts corruption investigation of ruling-party bosses". Yahoo! News.
- ^ "Presa germană aruncă bomba: Candidatul la Președinția Romaniei, Elena Udrea, și persoane de rang înalt din Germania, implicați în scandalul EADS-Microsoft". Jurnalul Național (in Romanian). 28 October 2014. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ^ Constitution of Romania, Article 83 Archived 2018-05-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ G.S. (2 February 2014). "Ponta: Alegeri europarlamentare la 25 mai. Alegeri prezidențiale la 2 și 16 noiembrie". Antena 3.
- ^ a b Adrian Ilie (16 September 2014). "ALEGERI PREZIDENȚIALE 2014. Calendarul scrutinului pentru Cotroceni. Cine RISCĂ SĂ NU INTRE în cursă". România TV (in Romanian).
- ^ "Proces-verbal încheiat azi 06.09.2014 cu ocazia constituirii Biroului Electoral Central" (PDF). Central Electoral Bureau (in Romanian). 6 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- ^ "Alegeri prezidențiale 2014: BEC a validat candidaturile - cine este, oficial, în cursa pentru Cotroceni". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 24 September 2014.
- ^ Laura Mitran (11 September 2014). "Campania pentru alegerile prezidențiale în audiovizual, între 3 octombrie și 1 noiembrie. CNA a decis că va fi gratuită". Mediafax (in Romanian).
- ^ a b "Cine poate ajunge președinte. Calendar electoral 2014". Gândul (in Romanian). 8 September 2014.
- ^ "14 competitori și-au depus candidatura pentru alegerile prezidențiale. SONDAJ: Cine va fi președintele României?". Gândul (in Romanian). 24 September 2014.
- ^ Bratu Iulian (4 October 2014). "ALEGERI PREZIDENȚIALE 2014: Cei mai mulți prezidențiabili, din 1996. Câți candidați s-au înscris la alegerile prezidențiale de după Revoluție". DC News (in Romanian).
- ^ Roxana Mihăilă (16 September 2014). "Internal party struggles will form the backdrop to Romania's presidential election in November". London School of Economics and Political Science.
- ^ "Victor Ponta a primit oficial susținerea PSD pentru prezidențiale". Digi24 (in Romanian). 12 September 2014.
- ^ "DECIZIE privind înregistrarea candidaturii domnului VICTOR-VIOREL PONTA, propusă de Alianța Electorală PSD – UNPR – PC, la alegerile pentru Președintele României din anul 2014" (PDF). Central Electoral Bureau (in Romanian). 17 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ Larisa Ciută, Andreea Udrea (11 August 2014). "ANUNȚUL OFICIAL. Klaus Iohannis este candidatul PNL și PDL la prezidențiale. PDL a acordat VOT COVÂRȘITOR pentru susținerea lui Iohannis". Evenimentul Zilei (in Romanian).
- ^ "DECIZIE privind înregistrarea candidaturii domnului KLAUS-WERNER IOHANNIS, propusă de Alianța Creștin-Liberală Partidul Național Liberal-Partidul Democrat Liberal, la alegerile pentru Președintele României din anul 2014" (PDF). Central Electoral Bureau (in Romanian). 20 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ Andreea Nicolae (5 August 2014). "Monica Macovei candidează la prezidențiale ca independent". România Liberă (in Romanian).
- ^ "DECIZIE privind înregistrarea candidaturii independente a doamnei MONICA-LUISA MACOVEI la alegerile pentru Președintele României din anul 2014" (PDF). Central Electoral Bureau (in Romanian). 20 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "Alegeri prezidențiale 2014. Kelemen Hunor va fi candidatul UDMR". Știrile Pro TV (in Romanian). 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ A.C. (19 August 2014). "Elena Udrea, desemnată candidatul PMP la alegerile prezidențiale: Îi voi cere președintelui să mă susțină în această competiție". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Larisa Ciută (23 July 2014). "Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu: Mă angajez în proiectul PLR, candidând la alegerile prezidențiale". Evenimentul Zilei (in Romanian).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b c d e f "Biroul Electoral Central: 14 competitori şi-au depus candidatura pentru alegerile prezidenţiale". Mediafax.ro. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Vasile Magradean (12 October 2013). "Dan Diaconescu, primul loc pe lista PPDD la europarlamentare și candidat la prezidențiale". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Teodor Meleșcanu și-a depus candidatura: Voi depune toată energia ca țara să revină la normalitate". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 23 September 2014. Archived from the original on 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2014-09-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ I.R. (20 September 2014). "Victor Ponta și-a lansat candidatura la prezidențiale, de ziua sa, în fața a zeci de mii de oameni, pe Arena Națională: Sunt Victor Viorel Ponta. Vă chem să fim împreună în bătălia pentru marea unire a românilor". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "PONTA, lansare cu fast, pe Arena Națională: "Mi-e teamă să nu vă dezamăgesc!"". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 20 September 2014.
- ^ Valentina Postelnicu (21 September 2014). "Băsescu, despre lansarea lui Ponta: Omul ăsta și-a pierdut cumpătul și controlul. Va fi vai de noi cu un președinte ca Ponta, Kim Jong-Un". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Theodora Șopaltă (20 September 2014). "Ponta, comparat cu "pigmeul" Kim Jong Un: Își construiește cultul mărețului conducător". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ "Elena Udrea: Ponta a organizat o manifestare ale cărei costuri întrec orice imaginație: 2 milioane de euro". Evenimentul Zilei (in Romanian). 20 September 2014.
- ^ Andi Manciu (27 September 2014). "Klaus Iohannis s-a lansat în cursa pentru Cotroceni din fața Guvernului. "Nu sunt un om al scandalului și al spectacolului"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ a b "Ethnic German candidate brings suspense to Romania's presidential race". EurActiv.com. 18 August 2014.
- ^ "Romania's presidential election: Ponta vs the liberals and the ladies". The Economist. 6 September 2014.
- ^ "Principalele puncte din programul prezidențial al lui Klaus Iohannis". HotNews.ro (in Romanian). 29 September 2014.
- ^ Camelia Badea (3 October 2014). "Klaus Iohannis - Ce promite". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ Mădălina Mihalache, Noémi Varga (28 September 2014). "Alegeri prezidențiale 2014. Elena Udrea și-a lansat candidatura cu un marș: Nu sunt un om perfect, dar voi fi cel mai bun președinte". Adevărul (in Romanian).
- ^ Paul Filimon (17 October 2014). "Elena Udrea: Voi dizolva Parlamentul și voi propune un nou premier, cu un nou Guvern". România Liberă (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 25 October 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "Băsescu, la Cotroceni, campanie pentru Udrea: Rămân consecvent în a susține candidatul PMP". Jurnalul Național (in Romanian). 13 October 2014. Archived from the original on 27 October 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ I.C. (22 October 2014). "Elena Udrea: Traian Băsescu se va înscrie în PMP în 22 decembrie". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Alex Varzaru (4 November 2014). "Tăriceanu îl susține pe Ponta și refacerea USL: Bătălia nu este câștigată". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ Georgeta Filip (6 November 2014). "Deși este la guvernare, UDMR nu-l susține pe Ponta. Vezi de ce". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ "Aleksandar Vucic îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Robert Fico îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Bohuslav Sobotka îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Edi Rama îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "PM Victor Ponta launched his candidacy for Romania's Presidency". Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "Sigmar Gabriel îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Elio Di Rupo îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Gianni Pittella îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ "Martin Schulz îl susține pe VICTOR PONTA". YouTube.
- ^ Emma Toader (7 November 2014). "Udrea: Votul în turul II trebuie să fie anti-Ponta, dar nu sunt adepta "răului cel mai mic"". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "PPE îl va susține pe Klaus Iohannis". Digi24 (in Romanian). 11 November 2014.
- ^ Iulia Marin (13 November 2014). "Klaus Iohannis, la Adevărul Live: Mă susține Angela Merkel. Mi-a trimis și o scrisoare". Adevărul (in Romanian).
- ^ "Deutsche Bundeskanzlerin unterstützt Klaus Johannis". Siebenbürgische zeitung. 2014-11-14. Retrieved 2014-11-17.
- ^ "Romanian presidential runoff sets pugnacious PM against 'civilized' Transylvanian mayor". Fox News. 13 November 2014.
- ^ "Iohannis, despre acuzaţiile că ar vrea să rupă Ardealul: Astea nu sunt afirmații politice, ci cretinisme". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian). 7 November 2014.
- ^ "Cum s-a rupt România după primul tur al prezidențialelor: "Ar fi bine dacă Sudul și Estul ar refuza pomenile. Țara asta chiar merită niște timpuri mai bune"". Adevărul (in Romanian). 14 November 2014.
- ^ Ela Giurgea (5 June 2014). "Senator PDL: PSD și aliații săi răsplătesc din bani europeni manipulările sondajelor de opinie". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Ponta crește de la o săptămână la alta, în sondajele firmelor apropiate de PSD". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 27 October 2014.
- ^ Horațiu Pepine (17 October 2014). "Sondajele sunt falsificate, dar nu oricum". Deutsche Welle (in Romanian).
- ^ a b c d "Alegeri prezidențiale 2014: Cine face sondajele de opinie". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 6 October 2014.
- ^ Andreea Unturică (31 May 2014). "DNA: Uioreanu a primit 5.000 de euro mită de la Bene, care a plătit un studiu de piață fictiv". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2014-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2014-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b Cătălina Mihai (3 November 2014). "Votul în diaspora: cozi uriașe, ștampile puține, proteste, porți închise înainte de 21:00". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Luiza Ilie (14 November 2014). "Thousands protest in Romania ahead of presidential run-off vote". Reuters.
- ^ "Romania sees protests ahead of elections". Euronews. 15 November 2014. Archived from the original on 19 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ Cristina Răduță (15 November 2014). "Bucureștenii ies din nou în stradă, după ce ieri s-au plimbat până la sediul PSD peste 4.000 de oameni. "Avem o armă mai puternică decât voi toți la un loc: democrația"". Adevărul (in Romanian).
- ^ Andrei Luca Popescu, Adriana Stanca (14 November 2014). "Zeci de mii de români au ieșit în stradă pentru un vot corect în turul doi. HARTA PROTESTELOR din marile orașe. GÂNDUL A TRANSMIS LIVE". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ "Mitinguri masive în toată țara împotriva lui Ponta / În Cluj s-au adunat circa 10.000 de oameni / Câteva mii de protestatari din București au scandat la sediul PSD - Ieși afară, javră ordinară / Ponta, nu reziști nici cu mii de securiști! / Ponta, ce-a pățit procurorul Panait?". HotNews.ro (in Romanian). 14 November 2014.
- ^ Lucian Gheorghiu (6 November 2014). "Victor Ponta, scos cu duba ca să fie ferit de un grup de protestatari". Cotidianul.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Ponta, huiduit și scos cu duba din mulțime". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 7 November 2014.
- ^ Andi Manciu (9 November 2014). "Predoiu îi acuză pe Ponta și Corlățean de complot. "ACL nu a fost implicată în proteste"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ "Iohannis: Dragi români, aţi fost nişte eroi. Votul a decurs fenomenal, o prezenţă enormă. Nu mi-e teamă. Vă mulţumesc tuturor". Mediafax.ro.
- ^ "Iohannis wins Romanian election - FT.com". Financial Times. 17 November 2014.
- ^ a b c Gillet, Kit (November 17, 2014). "Favorite Concedes Presidency in Romania (Published 2014)". The New York Times.
- ^ a b c "Romanian presidential election victory for centre-right candidate Klaus Iohannis". Telegraph.co.uk. 16 November 2014.
- ^ "Surprise presidential victory for Romania's Iohannis". Yahoo News. 17 November 2014.
- ^ "Klaus Iohannis Wins Romania Presidential Vote - Novinite.com - Sofia News Agency". www.novinite.com.
- ^ "Victor Ponta loses to Klaus Iohannis in Romania's presidential run-off". The Independent. 16 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2022-05-01.
- ^ a b "Klaus Iohannis, castigator: Ne-am luat tara inapoi. Klaus Iohannis e noul presedinte al Romaniei". Realitatea.NET. November 17, 2014.
- ^ "Klaus Iohannis a fost in Piata Universitatii si le-a multumit oamenilor: "Am castigat! Ne-am luat tara inapoi"". stirileprotv.ro.
- ^ "Iohannis, prima declaraţie oficială: Dragi români, vă mulţumesc. Voi fi un preşedinte liber, vă voi reprezenta pe voi. SOLICITĂRILE lui Iohannis". Mediafax.ro.
- ^ Otilia, Luca (November 17, 2014). "Klaus Iohannis: Dragi români, vă mulțumesc". Evenimentul Zilei.
- ^ "Prima demisie dupa alegeri: Gabriel Zetea, presedintele PSD Maramures, a demisionat". 17 November 2014. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ "Demisii în PSD Constanţa după rezultatul "dezastruos" al alegerilor prezidenţiale. Radu Mazăre se mai gândeşte". Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ "DEMISII pe bandă în PSD, după votul din Diaspora". 19 November 2014. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ "Ministrul Afacerilor Externe, Teodor Melescanu, si-a dat marti demisia si a stabilit un record national: a fost ministrul plin cu cel mai scurt mandat din istoria post decembrista, adica 8 zile". Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ "Avertismentul lui Geoană: Situaţia PSD, mai gravă decât în 2004; votul negativ a fost de o intensitate fără precedent". Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ Andrea Tarquini (3 December 2014). "Iohannis: "La mia Romania vuole un'Europa forte"". La Repubblica (in Italian).
- ^ "Guvernul SUA îl felicită pe Klaus Iohannis pentru alegerea ca președinte". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian). 21 November 2014.
- ^ Cătălina Mihai (17 November 2014). "Joseph Daul: Victoria lui Klaus Iohannis - o veste excelentă pentru România și pentru UE". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Claudiu Zamfir (21 November 2014). "Președintele CE îl felicită pe Iohannis: De-abia aștept să lucrez cu dumneavoastră și cu Guvernul la implementarea agendei strategice pentru UE". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Klaus Iohannis îl asigură pe David Cameron de întregul său sprijin pentru întărirea relațiilor bilaterale". Digi24 (in Romanian). 4 December 2014.
- ^ a b Cătălina Mihai (18 November 2014). "Președintele și cancelarul Germaniei l-au felicitat pe Iohannis. Gauck: Vom sprijini România în consolidarea statului de drept. Merkel: Vom aprofunda relațiile bilaterale". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "F. Hollande l-a felicitat pe K. Iohannis: Îmi face plăcere să vă invit la Paris, în funcție de agenda dumneavoastră". Digi24 (in Romanian). 19 November 2014.
- ^ Mihaela Stoica (20 November 2014). "Primul mesaj al Rusiei după câștigarea alegerilor de către Klaus Iohannis". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ Mihai Drăghici (18 November 2014). "Președintele Ungariei, Janos Ader, l-a felicitat pe Klaus Iohannis". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Klaus Iohannis îi cere premierului Victor Ponta amânarea alegerilor prezidențiale din toamnă". B1.ro (in Romanian). 11 August 2014. Archived from the original on 10 October 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ "K. Iohannis cere anularea HG care stabilește data prezidențialelor: Nu e normal ca Guvernul să creeze un avantaj pentru V. Ponta". Digi24 (in Romanian). 11 August 2014.
- ^ Avram Eliza (5 August 2014). "Iohannis: PNL dă în judecată Guvernul pentru ordonanța care modifică Legea electorală". România Liberă (in Romanian).
- ^ "PMP sesizează Comisia de la Veneția cu privire la legea pentru alegerea președintelui". B1.ro (in Romanian). 28 June 2014. Archived from the original on 10 October 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ "Candidaturile lui Ponta și Macovei, CONTESTATE. CCR le-a RESPINS". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Dosarul de incompatibilitate al lui Klaus Iohannis: Înalta Curte a stabilit termenul de judecată". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Curtea Supremă a amânat procesul lui Iohannis cu ANI pentru 30 septembrie". Știrile Pro TV (in Romanian). 25 September 2014.
- ^ "România TV a început "EXECUȚIA" lui Iohannis". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 10 June 2014. Archived from the original on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- ^ Cristian Andrei (20 October 2014). "Iohannis explică sursa banilor pentru cele șase case: părinți, socri, meditații, salariu, chirii, împrumuturi". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ Cătălina Mihai (31 October 2014). "ALEGERI PREZIDENȚIALE 2014: În străinătate sunt 294 de secții. Primii votează cei din Noua Zeelandă". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ V.O. (3 November 2014). "Romanian voters abroad humiliated: government organisers forced them to wait for hours in long queues in European cities in presidential poll". HotNews.ro.
- ^ "Chaos at Romania's voting polls abroad: long queues, protests". Romania-Insider.com. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 7 November 2014.
- ^ Anna Dubuis (3 November 2014). "Hundreds of Romanians locked outside London Embassy 'denied their right to vote'". London Evening Standard.
- ^ "Alegeri prezidențiale 2014. Monica Macovei cere prelungirea programului în secțiile de votare din străinătate și a depus mai multe contestații". Yahoo! News (in Romanian). 2 November 2014. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ Paul Filimon (2 November 2014). "Klaus Iohannis a denunțat PROASTA ORGANIZARE a alegerilor în țară și diaspora. A cerut BEC prelungirea votării". România Liberă (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 30 November 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ "TRAIAN BĂSESCU cere DEMISIA miniștrilor CORLĂȚEAN și STANOEVICI". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 2 November 2014.
- ^ "Funar cere anularea și reluarea primului tur al alegerilor prezidențiale". Agerpres (in Romanian). 2 November 2014. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ "The chairman of the Commission for European Affairs in Bundestag writes to Juncker: the sections outside Romania received indications from Bucharest to hinder the vote", Actmedia.eu/daily/the-chairman-of-the-commission-for-european-affairs-in-bundestag-writes-to-juncker-the-sections-outside-romania-received-indications-from-bucharest-to-hinder-the-vote/54970, retrieved 29 November 2014
- ^ Andreea Ofițeru (3 November 2014). "Apelul studenților din Regie care nu au putut vota: "Vrem să votăm! Asta e democrația lui Ponta?"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ Clarice Dinu (2 November 2014). "ALEGERI PREZIDENȚIALE 2014. Mii de români au protestat la Londra, scandând "Jos Ponta!", "Vot plagiat" și "Vrem să votăm"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ Irina Olteanu, Cristian Soitu (3 November 2014). "Românii au forțat votul după închiderea urnelor la Paris, Viena și Londra - jandarmii au intervenit". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ Radu-Sorin Marinaș (10 November 2014). "Romanian foreign minister resigns in election row". Reuters.
- ^ "Teodor Meleșcanu a depus jurământul de învestitură în funcția de ministru de Externe. Băsescu: Demisia lui Corlățean a intervenit prea târziu. Îl numesc pe Meleșcanu "datorită urgenței"". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian). 10 November 2014.
- ^ Alina Matis (16 November 2014). ""FIȚI EROI ÎN TURUL DOI!". Statul își bate joc și azi de românii din străinătate. Imagini cu cozile umilinței. UPDATE: Campania PSD acuză presa că induce "sentimentul că nu e organizat corect votul": "Sunt secții goale!"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ I.C. (16 November 2014). "ACL cere Biroului Electoral Central prelungirea programului de votare în străinătate". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Diana Toea (16 November 2014). "Diaspora votează: Circa 10.000 de români, la coadă în Londra". Ziare.com (in Romanian).
- ^ Andra Timu, Edith Balazs (16 November 2014). "Johannis Wins Romania Presidency in Double-Digit Comeback". Bloomberg.
- ^ "Italian and French police evict Romanian voters from Romanian embassies using tear gas". Reddit. 16 November 2014.
- ^ "Efectul organizării alegerilor în diaspora: Patru răniți și un român arestat la Torino, după intervenția polițiștilor la o secție de votare". B1.ro (in Romanian). 17 November 2014. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- ^ Ioana Ene Dogioiu (21 November 2014), "Inalt oficial de la Berlin: Ponta nu mai este calificat pentru nicio responsabilitate in stat", Ziare.com, retrieved 29 November 2014
- ^ Official Blog, para. 4, "Home", Gunther-krichbaum.de/, retrieved 29 November 2014
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Luiza Ilie (14 October 2014). "Romania president says PM was an undercover spy". Reuters.
- ^ Andrew Higgins (31 October 2014). "Spy Allegations in a Presidential Race Conjure Romania's Authoritarian Past". The New York Times.
- ^ Alison Mutler (14 October 2014). "Romanian President Accuses PM of Being an Ex-Spy". ABC News.
- ^ V.M. (14 October 2014). "Klaus Iohanis, despre scandalul Ponta - ofițer acoperit SIE: Îi solicit lui Victor Ponta să clarifice în fața națiunii situația domniei sale". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Romanian president says prime-minister acted as secret intelligence officer". Business Review. 14 October 2014.
- ^ "Jurnalistul Robert Turcescu a mărturisit că a fost ofițer acoperit. C. T. Popescu: Sunt uluit de acest delir mistic". Digi24 (in Romanian). 21 September 2014.
- ^ Dorina Lascăr (5 October 2014). "Licitație ilegală cu fonduri europene pentru mită electorală mascată în 6,6 milioane pachete cu 18 kg de alimente". Nașul TV (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 6 October 2014.
- ^ Paul Filimon (13 October 2014). "Traian Băsescu: Ponta și Iohannis sunt mincinoși și corupți. Nu îl susțin nici pe Ponta și nici pe Iohannis. Susțin candidatul PMP. Toată populația României îi plătește campania lui Ponta. Nu mai vorbim despre moralitatea lui Iohannis care are un proces deschis cu ANI. Nu îi consider pe niciunul demn de a fi președinte". România Liberă (in Romanian).
- ^ Irina Tacu, Valentina Postelnicu (13 October 2014). "Băsescu: Nu-i susțin și nu îi voi susține nici pe Ponta, nici pe Iohannis la prezidențiale. Rămân consecvent în a o susține pe Elena Udrea. DECLARAȚIILE președintelui". Mediafax.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ "Iohannis: De unde provin banii de campanie ai lui Ponta? Sunt bani din taxe și impozite, bani din corupție?". Realitatea.net (in Romanian). 18 October 2014.
- ^ Nicoleta Nicolau (18 October 2014). "Pensionarii denunță "campania denigratoare" pe care PSD o face prin poștă". Ziua de Constanța (in Romanian).
- ^ "PSD și Poșta Română, acuzați că trimit pensionarilor pliante anti-Iohannis". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 15 October 2014.
- ^ "Poșta Română: Sunt contracte și cu Macovei, Udrea și Tăriceanu pe distribuirea de material electoral". Mediafax (in Romanian). 20 October 2014.
- ^ Cristian Andrei (4 December 2014). "Cât l-au costat pe Ponta cei 4 milioane de fluturaşi anti-Iohannis, împărţiţi de Poşta Română cu talonul de pensie". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ "DNA: Sebastian Ghita a cumparat cu bani negri alegatori pentru Ponta in R.Moldova". Ziare.com (in Romanian). 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Romania: From Frying Pan to Legal Fire". The New York Times. 24 June 2015.
- ^ a b "EXCLUSIV. S. Ghiță, mecanism piramidal pentru fraudă la prezidențiale. Martor: Victor Ponta era la curent". Digi24 (in Romanian). 24 June 2015.
- ^ Popescu, Andrei Luca; Ilie, Daciana (24 June 2015). "Finanţarea campaniei lui Victor Ponta în Republica Moldova, INVESTIGATĂ de procurori. Sponsorul Sebastian Ghiţă, la ieşirea de la DNA: "Voi depune plângere la Procurorul General împotriva oamenilor care vor o lovitură de palat în România"". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ "Romanian premier's aide indicted for corruption charges". The Washington Post. 24 June 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015.
- ^ a b Hera, Mona (24 June 2015). "Sebastian Ghiţă, urmărit pentru trafic de influenţă, spălare de bani şi coruperea alegătorilor: "Mi se interzice să părăsesc Ploieştiul, probabil pentru a fi umilit. Am interdicţie de a vorbi cu Victor Ponta"". Mediafax (in Romanian).
- ^ "Cele trei masuri luate de DNA impotriva lui Sebastian Ghita. Cum ar fi corupt alegatorii cu tigai de pe piata neagra". Stirile Pro TV (in Romanian). 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Ghita anunta o "lovitura de palat a procurorilor". Imperiul PSD contraataca: ce replica pentru DNA au social-democratii". Stirile Pro TV (in Romanian). 25 June 2015.
- ^ Andi Manciu (12 February 2015). "Directorul STS: La prezidențiale au fost atacuri cibernetice în scop politic, fiind implicat un post TV". Gândul (in Romanian).
- ^ R. M. (12 February 2015). "Marcel Opriș (STS): Atacurile cibernetice pot fi folosite în scopuri politice; un episod s-a petrecut în perioada prezidențialelor". HotNews.ro (in Romanian).
- ^ Paul Dumitrescu (12 February 2015). "Opriș: Un atac cibernetic s-a petrecut în perioada prezidențialelor". Cotidianul.ro (in Romanian).
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Romanian presidential elections, 2014 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Romanian presidential elections, 2014 at Wikimedia Commons










