From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Wikipedia list article
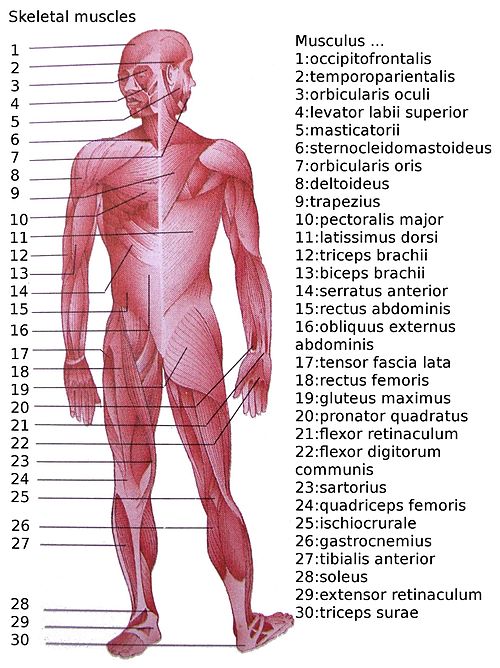
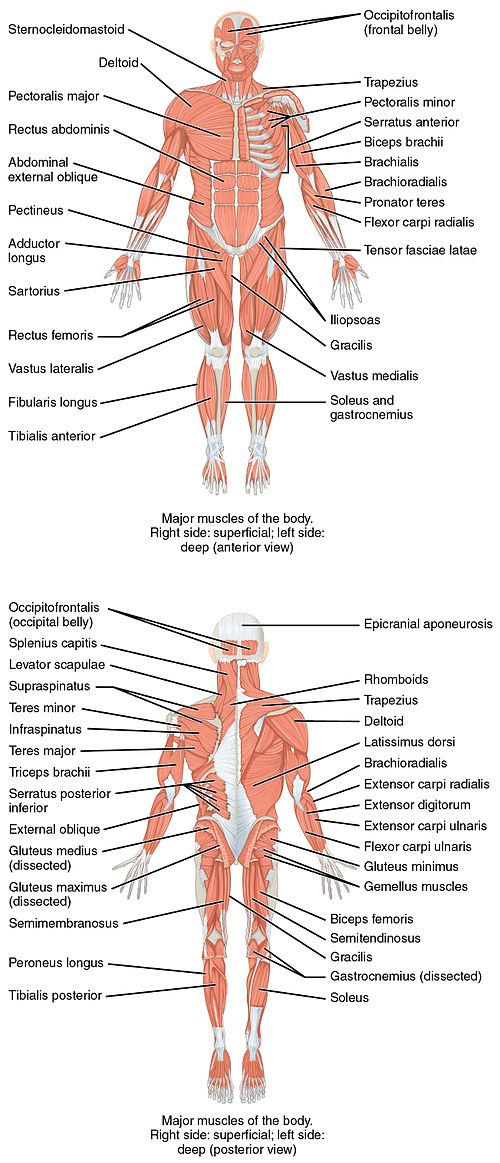
This is a table of skeletal muscles of the human anatomy .
There are around 640 skeletal muscles within the typical human body.[ 1] [ 2] bilateral muscles, found on both sides, resulting in approximately 320 pairs of muscles, as presented
in this article. Nevertheless, the exact number is difficult to define because different sources group muscles differently, e.g. regarding what is defined as different parts of a single muscle or as several muscles.
The muscles of the human body can be categorized into a number of groups which include muscles relating to the head and neck, muscles of the torso or trunk, muscles of the upper limbs, and muscles of the lower limbs.
The action refers to the action of each muscle from the standard anatomical position . In other positions, other actions may be performed.
These muscles are described using anatomical terminology .
Head
Ear
Nose
Mouth
Mastication
Tongue
Extrinsic muscle
Intrinsic
Soft palate
Pharynx
Larynx
Neck
Clavicular
Suprahyoid
Infrahyoid
Neck
Anterior
Lateral
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
scalene muscles cervical vertebrae first and second ribs
ascending cervical artery (branch of inferior thyroid artery )cervical nerves (C3 , C4 , C5 , C6 , C7 elevation of ribs I&II
anterior C3 -C6 first rib ascending cervical artery (branch of inferior thyroid artery )ventral ramus of C5 , C6 When the neck is fixed, elevates the first rib to aid in breathing or when the rib is fixed, bends the neck forward and sideways and rotates it to the opposite side
medius C2 -C6 first rib ascending cervical artery (branch of inferior thyroid artery )ventral rami of the third to eighth cervical spinal nerves
Elevate 1st rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side
posterior transverse processes of C4 – C6
2nd rib
ascending cervical artery , superficial cervical artery C6 , C7 , C8 Elevate 2nd rib, tilt the neck to the same side
levator scapulae Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4Superior part of medial border of scapula
dorsal scapular artery cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5)Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula
rectus capitis lateralis upper surface of the transverse process of the atlas (C1)
under surface of the jugular process of the occipital bone
C1
obliquus capitis superior lateral mass of atlas lateral half of the inferior nuchal line
suboccipital nerve
obliquus capitis inferior spinous process of the axis
lateral mass of atlas suboccipital nerve
Posterior
Torso
Back
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
erector spinae on the spines of the last four thoracic vertebrae
both the spines of the most cranial thoracic vertebrae and the cervical vertebrae
lateral sacral artery posterior branch of spinal nerve extends the vertebral column
rectus abdominis muscle
iliocostalis lateral sacral artery
longissimus transverse process transverse process lateral sacral artery posterior branch of spinal nerve rectus abdominis muscle
spinalis spinous process spinous process lateral sacral artery posterior branch of spinal nerve rectus abdominis muscle
latissimus dorsi spinous processes of thoracic T6 -T12 , thoracolumbar fascia , iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs
floor of intertubercular groove of the humerus
subscapular artery , dorsal scapular artery thoracodorsal nerve pulls the forelimb dorsally and caudally
deltoid , trapezius
transversospinales transverse process spinous process posterior branches
semispinalis thoracis (dorsi) transverse processes of the sixth to the tenth thoracic vertebrae
spinous processes of the upper four thoracic and lower two cervical vertebrae
semispinalis cervicis (colli) transverse processes of the upper five or six thoracic vertebræ
cervical spinous processes, from the axis to the fifth
semispinalis capitis (complexus) transversal process of lower cervical and higher thoracal columna
area between superior and inferior nuchal line
greater occipital nerve Extends the head
multifidus sacrum , erector spinae aponeurosis , PSIS , and iliac crest spinous process posterior branch of spinal nerve Stabilizes vertebrae in local movements of vertebral column
rotatores transverse process spinous process posterior branch
interspinales spinous process spinous process posterior rami of spinal nerves Extension , flexion and rotation of vertebral column.
intertransversarii transverse process transverse process above
anterior rami of spinal nerves Lateral flexion of trunk
Splenius muscles
capitis ligamentum nuchae, spinous process of C7 -T6
Mastoid process of temporal and occipital bone
C3 , C4 Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head
cervicis spinous processes of T3 -T6 transverse processes of C1 , C2 , C3 C5 , C6
Chest
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
intercostals ribs 1–11
ribs 2–12
intercostal arteries intercostal nerves
external intercostal arteries intercostal nerves Inhalation internal
internal rib – inferior borderrib – superior borderintercostal arteries intercostal nerves hold ribs steady
external
innermost intercostal arteries intercostal nerves Elevate ribs
subcostales inner surface of one rib
inner surface of the second or third rib above, near its angle
intercostal nerves
transversus thoracis costal cartilages of last 3–4 ribs, body of sternum, xiphoid processribs /costal cartilages 2–6intercostal arteries intercostal nerves depresses ribs
levatores costarum transverse processes of C7 to T12 vertebraesuperior surfaces of the ribs immediately inferior to the preceding vertebrae
dorsal rami – C8 , T1 , T2 , T3 , T4 , T5 , T6 , T7 , T8 , T9 , T10 , T11 Assists in elevation of the thoracic rib cage
Serratus posterior muscles
inferior vertebrae T11 – L3
the inferior borders of the 9th through 12th ribs
intercostal arteries intercostal nerves depress the lower ribs, aiding in expiration
superior nuchal ligament (or ligamentum nuchae) and the spinous processes of the vertebrae C7 through T3the upper borders of the 2nd through 5th ribs
intercostal arteries 2nd through 5th intercostal nerves
elevate the ribs which aids in inspiration
diaphragm pericardiacophrenic artery , musculophrenic artery , inferior phrenic arteries phrenic and lower intercostal nerves respiration
Abdomen
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
transversus abdominis ribs and the iliac crest inserts into the pubic tubercle via the conjoint tendon, also known as the falx inguinalis
intercostal nerves T7 , T8 , T9 , T10 , T11 , subcostal nerve (T12 ), iliohypogastric nerve , ilioinguinal nerve , genitofemoral nerve compress the ribs and viscera, providing thoracic and pelvic stability
rectus abdominis pubis costal cartilages of ribs 5–7, xiphoid process of sternum inferior epigastric artery segmentally by thoraco-abdominal nerves (T7 , T8 , T9 , T10 , T11 , T12 )
flexion of trunk /lumbar vertebrae erector spinae
pyramidalis pubic symphysis and pubic crest linea alba subcostal nerve (T12 )tensing the linea alba
cremaster inguinal ligament cremasteric artery genital branch of genitofemoral nerve raise and lower the scrotum
quadratus lumborum iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament last rib and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae lumbar arteries , iliolumbar artery anterior branches of T12 , L1 , L2 , L3 , L4
Alone, lateral flexion of vertebral column ; Together, depression of thoracic rib cage
Oblique muscles
external Lower 8 costae
Crista iliaca , ligamentum inguinale intercostal nerves T5 , T6 , T7 , T8 , T9 , T10 , T11 , subcostal nerve (T12 )Rotates torso
internal inguinal ligament , iliac crest and the lumbodorsal fascia linea alba , xiphoid process and the inferior ribs.intercostal nerves T8 , T9 , T10 , T11 , subcostal nerve (T12 ), iliohypogastric nerve , ilioinguinal nerve Compresses abdomen and rotates vertebral column
Pelvis
Perineum
Upper limbs
Vertebral column
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
trapezius down the midline, from the external occipital protuberance , the nuchal ligament , the medial part of the superior nuchal line , and the spinous processes of the vertebrae C7-T12
at the shoulders, into the lateral third of the clavicle , the acromion process and into the spine of the scapula
transverse cervical artery major nerve supply is the cranial nerve XI . cervical nerves C3 and C4 receive information about pain in this muscle
retraction and elevation of scapula .Serratus anterior muscle
latissimus dorsi spinous processes of thoracic T6 -T12 , thoracolumbar fascia , iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs
floor of intertubercular groove of the humerus
subscapular artery , dorsal scapular artery thoracodorsal nerve pulls the forelimb dorsally and caudally
deltoid , trapezius
rhomboids nuchal ligaments , spinous processes of C7-T5 vertebrae medial border of the scapula dorsal scapular artery dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5 )Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity . fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall .Serratus anterior muscle
rhomboid major spinous processes of the T2 to T5 vertebraemedial border of the scapula , inferior to the insertion of rhomboid minor muscle dorsal scapular artery dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5 )Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity . It also fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall .Serratus anterior muscle
rhomboid minor nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7- to T1 vertebrae medial border of the scapula , superior to the insertion of rhomboid major muscle dorsal scapular artery dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5 )Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity . It also fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall .Serratus anterior muscle
levator scapulae posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4 vertebraesuperior part of medial border of scapula
dorsal scapular artery cervical nerve (C3 , C4 ) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5 )Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula
Thoracic walls
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
pectoralis major anterior surface of the medial half of the clavicle .Sternocostal head : anterior surface of the sternum , the superior six costal cartilages
intertubercular groove of the humerus pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial trunk lateral pectoral nerve and medial pectoral nerve Clavicular head : C5 and C6 Sternocostal head : C7 , C8 and T1 Clavicular head : flexes the humerus Sternocostal head : extends the humerusadducts and medially rotates the humerus . It also draws the scapula anteriorly and inferiorly.
pectoralis minor 3rd to 5th ribs , near their costal cartilages
medial border and superior surface of the coracoid process of the scapula
Pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial trunk Medial pectoral nerves (C8 , T1 )stabilizes the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against the thoracic wall
subclavius first rib subclavian groove of clavicle thoracoacromial artery , clavicular branchnerve to subclavius Depresses the clavicle
serratus anterior fleshy slips from the outer surface of upper 8 or 9 ribs
costal aspect of medial margin of the scapula lateral thoracic artery (upper part), thoracodorsal artery (lower part)long thoracic nerve (from roots of brachial plexus C5 , C6 , C7 )protract and stabilize scapula , assists in upward rotationRhomboid major , Rhomboid minor , Trapezius
Shoulder
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
deltoid clavicle , acromion , spine of the scapula deltoid tuberosity of humerus primarily posterior circumflex humeral artery
Axillary nerve shoulder abduction , flexion and extension Latissimus dorsi
teres major posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the scapula
medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
Subscapular and circumflex scapular arteriesLower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6 )Internal rotation of the humerus
Rotator cuff
supraspinatus supraspinous fossa of scapula superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus
suprascapular artery suprascapular nerve abduction of arm and stabilizes humerus infraspinatus , teres minor , pectoralis major , and latissimus dorsi
infraspinatus infraspinous fossa of the scapula middle facet of greater tubercle of the humerus
suprascapular and circumflex scapular arteries suprascapular nerve Lateral rotation of arm & Adduction of arm and stabilizes humerus subscapularis , pectoralis major , and latissimus dorsi
teres minor lateral border of the scapula inferior facet of greater tubercle of the humerus
posterior circumflex humeral artery and the circumflex scapular artery axillary nerve laterally rotates and adducts the armsubscapularis , pectoralis major , and latissimus dorsi
subscapularis subscapular fossa lesser tubercle of humerus subscapular artery upper subscapular nerve , lower subscapular nerve (C5 , C6 )rotates medially humerus ; stabilizes shoulder infraspinatus and teres minor
Arm
Anterior compartment
Posterior compartment
Forearm
Anterior compartment
Superficial
Deep
Posterior compartment
Superficial
Deep
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
supinator Lateral epicondyle of the humerus , supinator crest of ulna , radial collateral ligament , annular ligament Lateral proximal radial shaft
radial recurrent artery posterior interosseus nerve (C7 , C8 )supinates forearm Pronator teres , Pronator quadratus
extensor indicis ulna index finger (extensor hood )posterior interosseous nerve (C7 , C8 )extends index finger , wrist
Anatomical snuff box
abductor pollicis longus ulna , radial styloid process first metacarpal posterior interosseous nerve (C7 , C8 )abduction , extension of thumb Adductor pollicis muscle
extensor pollicis brevis radius thumb , proximal phalanx posterior interosseous artery posterior interosseous nerve (C7 , C8 )extension of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint Flexor pollicis longus muscle , Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
extensor pollicis longus ulna thumb , distal phalanx posterior interosseous nerve (C7 , C8 )extension of the thumb (metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal )Flexor pollicis longus muscle , Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
Hand
Lateral volar
Thenar
Lower limb
Iliac region
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
iliopsoas iliac fossa (iliacus ), sacrum (iliacus), spine (T12 , L1 , lumbar vertebra , Psoas major , psoas minor )[ 3] femur —lesser trochanter (psoas major/minor), shaft below lesser trochanter (iliacus), tendon of psoas major & femur (iliacus)[ 3] medial femoral circumflex artery , iliolumbar artery femoral nerve , Lumbar nerves L1 , L2 flexion of hip (psoas major/minor, iliacus), spine rotation (psoas major/minor)Gluteus maximus , posterior compartment of thigh
psoas major transverse processes, bodies and discs of T12-L5
in the lesser trochanter of the femur
Iliolumbar artery Lumbar plexus via anterior branches of L1 , L2 , L3 [ 4] flexes and rotates laterally thigh Gluteus maximus
psoas minor Side of T11 +L1 and IV Disc between
Pectineal line and iliopectineal eminence L1 Weak trunk flexor
Gluteus maximus
iliacus iliac fossa lesser trochanter of femur medial femoral circumflex artery , Iliolumbar artery femoral nerve (L2 , L3 [ 4] flexes hip[ 5]
Gluteus maximus
Gluteal
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
tensor fasciae latae iliac crest iliotibial tract primarily lateral circumflex femoral artery , Superior gluteal artery
Superior gluteal nerve (L4 , L5 )Thigh – flexion , medial rotation . Trunk stabilization.
Gluteal muscles
gluteus maximus muscle Gluteal surface of ilium , lumbar fascia , sacrum , sacrotuberous ligament
Gluteal tuberosity of the femur , iliotibial tract superior and inferior gluteal arteries inferior gluteal nerve (L5 , S1 , S2 nerve roots)external rotation and extension of the hip joint , supports the extended knee through the iliotibial tract , chief antigravity muscle in sitting Iliacus , Psoas major , Psoas minor
gluteus medius muscle Gluteal surface of ilium , under gluteus maximus
Greater trochanter of the femur superior gluteal artery superior gluteal nerve (L4 , L5 , S1 nerve roots)abduction of the hip ; preventing adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh .lateral rotator group
minimus Gluteal surface of ilium , under gluteus medius .
Greater trochanter of the femur superior gluteal artery superior gluteal nerve (L4 , L5 , S1 nerve roots)Works in concert with gluteus medius: abduction of the hip; preventing adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh.
lateral rotator group
lateral rotator group at or below the acetabulum of the ilium
on or near the greater trochanter of the femur
Inferior gluteal artery , Lateral sacral artery , Superior gluteal artery Obturator nerve , nerve to the Piriformis , nerve to quadratus femoris lateral rotation of hipGluteus minimus muscle , Gluteus medius muscle
piriformis sacrum greater trochanter Inferior gluteal artery , Lateral sacral artery , Superior gluteal artery nerve to the Piriformis (S1 and S2 nerve roots)[ 6] laterally rotate (outward) the thigh
obturator externus obturator foramen and obturatory membrane medial aspect of greater trochanter of femur
obturator artery posterior branch of obturator nerve (L3 , L4 )adduct thigh , rotate laterally thigh
obturator internus Ischiopubic ramus & obturator membrane medial aspect of the Greater trochanter
Nerve to obturator internus (L5 , S1 , S2 )Abducts & rotates laterally thigh , and stabiliser of the hip during walking
inferior gemellus Ischial tuberosity Obturator internus tendonNerve to Quadratus femoris (L4 , L5 , S1 )Rotates laterally thigh
superior gemellus spine of the ischium Obturator internus tendonNerve to obturator internus (L5 , S1 , S2 )Rotates laterally thigh
quadratus femoris ischial tuberosity intertrochanteric crest inferior gluteal artery nerve to quadratus femoris (L4 , L5 , -S1 )lateral rotation of thigh
Thigh
Anterior compartment
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
biceps femoris long head: tuberosity of the ischium , short head: linea aspera , femur [ 7]
the head of the fibula [ 7] lateral tibial condyle
inferior gluteal artery , perforating arteries , popliteal artery long head: medial (tibial) part of sciatic nerve , short head: lateral (common fibular) part of sciatic nerve [ 7]
flexes knee joint , laterally rotates leg at knee (when knee is flexed), extends hip joint (long head only)[ 7] Quadriceps muscle
semitendinosus tuberosity of the ischium[ 7]
pes anserinus inferior gluteal artery , perforating arteries sciatic [ 7] tibial , L5 , S1 , S2 )flexes knee, extends hip joint, medially rotates leg at knee[ 7]
Quadriceps muscle
semimembranosus tuberosity of the ischium[ 7]
Medial surface of tibia [ 7]
profunda femoris , gluteal artery sciatic nerve [ 7] flexes knee, extends hip joint, medially rotates leg at knee[ 7]
Quadriceps muscle
Leg
Anterior compartment
Posterior compartment
Superficial
Deep
Lateral compartment
Peroneus (Fibularis) muscles :
Dorsal
Plantar
First layer
Second layer
Third layer
Fourth layer
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Artery
Nerve
Action
Antagonist
Plantar interossei muscles Tendons of Plantar Interossei
The muscles then continue distally along the foot and insert in the proximal phalanges III-V. The muscles cross the metatarsophalangeal joint of toes III-V so the insertions correspond with the origin and there is no crossing between toes.
Plantar Artery, and Dorsal Metatarsal Artery
lateral plantar nerve Since the intersseous muscles cross on the metatarsophalangeal joint, then they act on that specific joint and cause adduction of toes III, IV, and V.[1] Adduction itself is not of extreme importance to the toes, but these muscles work together with the dorsal interosseous muscles in flexion of the foot. They also work together to strengthen the metatarsal arch.[2]
Dorsal interossei of the foot
|}
−
−
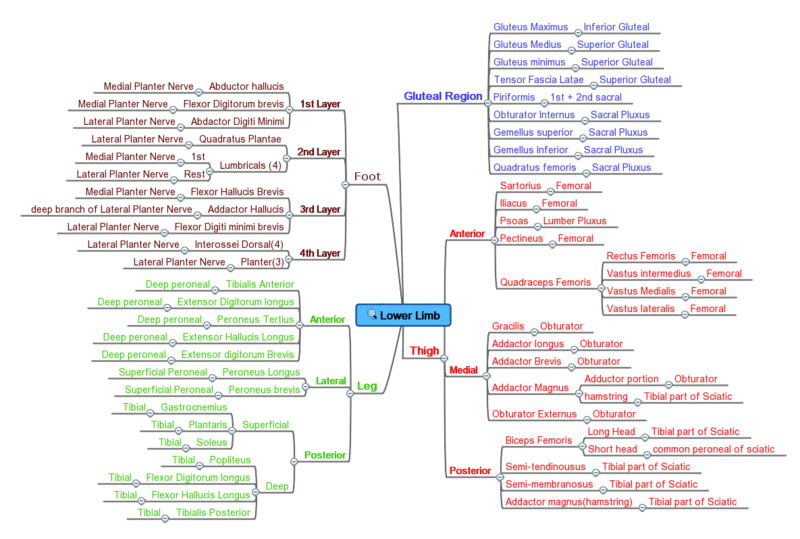
Innervation overview
−
Mind Map showing a summary of Upper Limb Muscle Innervation
−
−
See also
References
^ Brooks, Susan V. (2003-12-01). "Current topics for teaching skeletal muscle physiology". Advances in Physiology Education . 27 (1–4): 171–182. doi :10.1152/advan.00025.2003 . ISSN 1043-4046 . PMID 14627615 . ^ John., Stewart, Gregory (2009). "Chapter 8: Skeletal muscles". The skeletal and muscular systems ISBN 9781604133653 OCLC 277118444 . {{cite book }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link )^ a b exrx.net ^ a b Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 193
^ Gosling, J. A., Harris, P. F., Humpherson, J. R., Whitmore I., & Willan P. L. T. 2008. Human Anatomy Color Atlas and Text Book. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier. page 200
^ Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 217
^ a b c d e f g h i j k Gosling 2008, p. 273 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Gosling et al. 2008, p. 266 ^ MedicalMnemonics .com : 255
External links