Longyan dialect
| Longyan Min | |
|---|---|
| 龍岩閩語 | |
| Native to | China. |
| Region | Fujian Province |
Native speakers | 740,000 (approx.)[citation needed] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
 Longyan prefecture | |
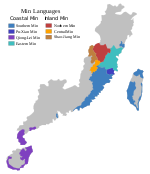
Longyan Min (龍岩閩語), is a variety of Min Chinese spoken in the Longyan region of the southern Chinese province of Fujian. The Longyan Min people had settled in the region from southern part of Fujian Province as early as the Tang dynasty period (618–907). Longyan Min has in the past been influenced by Hakka Chinese due to large numbers of Hakka migrants into the region. As a result, it has limited intelligibility with Southern Min dialects such as Teochew and Hokkien–Taiwanese. Today, Longyan Min is predominantly spoken in Longyan's Xinluo District and Zhangping City. Branner classifies Longyan as Coastal Min, but separate from Southern and Eastern Min.[1] He assigns a similar classification to the dialect of Wan'an township, 50 km north of Longyan.[2] Longyan Hakka on the other hand is spoken in Changting County, Yongding County, Shanghang County, Liancheng County and Wuping County.[3]
References
- ^ Branner, David Prager (1999). "The Classification of Longyan" (PDF). In Simmons, Richard VanNess (ed.). Issues in Chinese Dialect Description and Classification. Journal of Chinese Linguistics monograph series. Vol. 15. pp. 36–83.
- ^ Branner, David Prager (2000). Problems in Comparative Chinese Dialectology — the Classification of Miin and Hakka (PDF). Trends in Linguistics series. Vol. 123. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-015831-1.
- ^ Wurm, Stephen Adolphe; Li, Rong; Baumann, Theo; Lee, Mei W. (1987). Language Atlas of China. Longman. ISBN 978-962-359-085-3.
External links