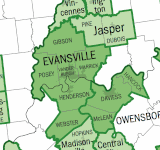
Southwestern Indiana
 2010 Census Population: 474,251 Common names: Southwest Indiana, Tri-State Area, Wabash Valley, Ohio Valley Area Nicknames: The Four Rivers Area 1 Lincoln's Boyhood Home (mainly Spencer Co.), Land that Time Forgot and Keeps Forgetting 1 After Ohio, Patoka, Wabash, and White Rivers or | |
| Largest city Other cities |
Evansville - Jasper - Princeton - Vincennes - Washington |
| Counties | * Daviess * Dubois * Gibson * Knox * Martin * Perry * Pike * Posey * Spencer * Vanderburgh * Warrick |
Southwestern Indiana is an 11-county region of southern Indiana, United States located at the southernmost and westernmost part of the state. As of the 2010 census, the region's combined population is 474,251. Evansville, Indiana's third largest city, is the primary hub for the region as well as the primary regional hub for a tri-state area which includes Kentucky and Illinois. Other regional hubs include Jasper, Vincennes, and Washington.
Geography
Southwestern Indiana's topography is considerably more varied and complex than most of Indiana, including large tracts of forest, marshes, rolling fields, large flat valleys in the west and south, to several chains of low mountains, high hills, and sharp valleys towards the north and east. Every county in Southwestern Indiana is bounded by a river at one point, whether it be by the Wabash River along the west, The Ohio River by the south, the White River, dividing the six northern counties between its two forks, or other smaller rivers. More than 50% of the boundaries of Daviess, Gibson, Knox, Perry, Posey, and Spencer counties are dictated by a river or a creek. Eighty percent of Knox County's boundaries are dictated by either the Wabash River or the White River. Additionally, over half of the area is located within the Wabash Valley Seismic Zone.
Southwestern Indiana has clusters of separate towns of varying sizes and layouts. Vincennes is laid out in the French quadranglar while Jasper and Princeton are laid out in a standard grid. Evansville is laid out in both modes of survey, with its downtown being mapped out from the river and the rest of the city being laid out in the standard grid.
Organizational defining
In addition to various media definitions, Southwestern Indiana is also defined by most Indiana state agencies as well as various commercial and economic regions as an entire area. All of Southwestern Indiana's counties are in Indiana's 8th Congressional District as of 2013. Most of Southwestern Indiana exists in the Roman Catholic Diocese of Evansville and Vincennes as well. Southwestern Indiana makes up realtor region 12 in Indiana, while nine of the counties make up Economic Growth Region 11 with Daviess and Martin in Region 8.[1][2]
In addition, the southern third of Southwestern Indiana exists within the Ohio River Valley American Viticultural Area, the second largest wine appellation in the United States. The Ohio River Valley AVA occupies all of Perry, Posey, Spencer, Vanderburgh, and Warrick counties, nearly 90% of Gibson County, and portions of Pike and Dubois counties in Southwestern Indiana.[3]
Counties
| IN No. |
County Name |
Establishment Date (SW Indiana) (History) (Statehood) |
County Seat |
Time Zone |
Population (2010) (Rank) |
Area sq mi (km2) (Rank) |
Twps |
ZIP code Prefix(es) |
% of Boundary by water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Daviess | February 2, 1818 (10) (29) (14) |
Washington | Eastern | 32,200 (6) |
437 sq mi (1,130 km2) (3) |
10 | 475 | 55% |
| 19 | Dubois | December 20, 1817 (7) (20) (4) |
Jasper | Eastern | 41,889 (3) |
435 sq mi (1,130 km2) (4) |
12 | 475 | 24% |
| 26 | Gibson | April 1, 1813 (2) (8) (T) |
Princeton | Central | 33,503 (5) |
526 sq mi (1,360 km2) (1) |
10 | 475/476 | 59% |
| 42 | Knox | June 6, 1790 (1) (1) (T) |
Vincennes | Eastern | 38,440 (4) |
516 sq mi (1,340 km2) (2) |
10 | 475/478 | 84% |
| 51 | Martin | January 7, 1820 (11) (33) (18) |
Shoals | Eastern | 10,334 (11) |
341 sq mi (880 km2) (10) |
6 | 475 | 18% |
| 62 | Perry | November 1, 1814 (4) (12) (T) |
Tell City | Central | 19,338 (9) |
386 sq mi (1,000 km2) (8) |
7 | 474/475 | 52% |
| 63 | Pike | December 21, 1816 (6) (16) (1) |
Petersburg | Eastern | 12,845 (10) |
342 sq mi (890 km2) (9) |
9 | 475/476 | 35% |
| 65 | Posey | November 11, 1814 (5) (13) (T) |
Mt. Vernon | Central | 25,940 (7) |
429 sq mi (1,110 km2) (5) |
10 | 476 | 63% |
| 74 | Spencer | January 10, 1818 (9) (24) (9) |
Rockport | Central | 20,942 (8) |
401 sq mi (1,040 km2) (7) |
9 | 475/476 | 73% |
| 82 | Vanderburgh | January 7, 1818 (8) (22) (7) |
Evansville | Central | 179,703 (1) |
236 sq mi (610 km2) (11) |
8 | 476/477 | 26% |
| 87 | Warrick | April 30, 1813 (3) (9) (T) |
Boonville | Central | 59,689 (2) |
424 sq mi (1,100 km2) (6) |
10 | 475/476/477 | 19% |
(T) - Establishment Date - Indiana Territory County
Metropolitan and micropolitan areas
Metropolitan area
| Name | Primary City or Cities |
State or States |
County or Counties |
Non-Area County or Counties Influenced |
Area | 2005 Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evansville, IN-KY Metropolitan Statistical Area |
Evansville Henderson Princeton |
Indiana Kentucky |
IN: Gibson, Posey Vanderburgh, Warrick KY: Henderson, Webster |
Illinois: Wabash, White Indiana: Spencer Kentucky: Union |
2,367 sq mi 6,130 km2 |
352,943 |
Micropolitan areas
| Name | Primary City | State or States |
County or Counties |
Area | 2005 Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jasper, IN Micropolitan Statistical Area |
Jasper | Indiana | Dubois Pike |
776 sq mi 2010 km2 |
53,211 |
| Vincennes, IN-IL Micropolitan Statistical Area |
Lawrenceville Vincennes |
Illinois Indiana |
Knox Lawrence |
898 sq mi 2,330 km2 |
54,332 |
| Washington, IN Micropolitan Statistical Area |
Washington | Indiana | Daviess | 437 sq mi 1,130 km2 |
32,200 |
Political status
- As of 2013, All of Southwestern Indiana is now in the 8th Congressional District.

| County | House District(s) |
Senate District(s) |
US House District |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 Daviess | 45th 63rd 64th | 39th 48th | 8th |
| 19 Dubois | 63rd 73rd 74th | 47th 48th | 8th |
| 26 Gibson | 64th 74th 75th | 48th 49th | 8th |
| 42 Knox | 45th 64th | 39th 48th | 8th |
| 51 Martin | 62nd 63rd | 48th | 8th |
| 62 Perry | 73rd 74th | 47th | 8th |
| 63 Pike | 63rd 64th | 48th | 8th |
| 65 Posey | 76th | 49th | 8th |
| 74 Spencer | 74th 78th | 47th | 8th |
| 82 Vanderburgh | 75th 76th 77th 78th | 49th 50th | 8th |
| 87 Warrick | 75th 77th 78th | 47th 50th | 8th |
| Southwestern Indiana | 45th 62nd 63rd 64th 73rd 74th 75th 76th 77th 78th |
39th 47th 48th 49th 50th |
8th |
Highways

Interstate highways
The oldest interstate in the region, this stretch of I-64 has been the primary artery of east-west traffic since entering service around 1983. While relatively flat in Posey, Vanderburgh, and Gibson Counties, it's terrain becomes hillier as it passes through the nearly 30-mile stretch in Warrick County. By the time it approaches U.S. 231, the hills and valleys are sharper, transitioning into the low mountainous conditions found in Perry County as the highway leaves into Crawford County.
The newest interstate in the region, this stretch of I-69 is provides Interstate access to Bloomington and, eventually, to Indianapolis. Like I-64, the terrain around Evansville, is relatively flat, but becomes hillier in northeastern Gibson County, and becomes progressively hillier through Pike County. The stretch of I-69 in Daviess County between Washington and Elnora is actually flatter than the stretch in Vanderburgh County while containing some hilly sections south of Washington, but becomes very hilly northeast of Elnora as the highway approaches Crane and leaves the area into Greene County.
U.S. highways
![]() U.S. Route 41
U.S. Route 41
US 41 extends from Miami, Florida to the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. This four-lane highway serves the western half of the region. US 41 goes through the city of Evansville, becoming six lanes between the Lloyd Expressway and Diamond Avenue. It bypasses Princeton and Vincennes before continuing north towards Terre Haute.
![]() U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50
US 50 extends from Baltimore, Maryland to Sacramento, California. It is a winding two-lane road in the eastern half of the region which becomes a four-lane road in the western half, near Washington, before joining US 41 in the bypass around Vincennes. It intersects with I-69 just east of Washington. It leaves Indiana on the Red Skelton Bridge.
![]() U.S. Route 150
U.S. Route 150
Coterminous with US 50 from Vincennnes to Shoals, it breaks off and heads eastward while US 50 continues northeast.
![]() U.S. Route 231
U.S. Route 231
This now mostly new four-lane road serves the eastern jalf of the region. The route is in a process of relocation as a new four-lane road is under construction from Rockport to Greene County, where it will intersect with Interstate 69.
Interstate 69 - A highway underway
Culture
Annual festivals and celebrations
- April
- Perry County Dogwood Tour - Perry County, Indiana
- May
- Gastoff Spring Festival - Montgomery, Indiana
- Historic Newburgh Wine and Arts Festival - Newburgh, Indiana
- Spirit of Vincennes Rendezvous - Vincennes, Indiana
- June
- Spencer County Fair - Grandview, Indiana
- Haubstadt Somerfest - Haubstadt, Indiana
- Evansville Freedom Festival - Evansville, Indiana
- July
- Germania Männerchor Volksfest - Evansville, Indiana
- Thunder on the Ohio - Evansville, Indiana
- Gibson County Fair - Princeton, Indiana
- Cedar Valley Bluegrass Festival - Derby, Indiana
- Jasper Strassenfest - Jasper, Indiana
- August
- Owensville Watermelon Festival - Owensville, Indiana
- Oakland City Sweetcorn Festival - Oakland City, Indiana
- Tell City Schweizer Fest - Tell City, Indiana
- Knox County Watermelon Festival - Bicknell, Indiana
- Princeton Golden Heritage Days - Princeton, Indiana
- Warrick County Fair - Boonville, Indiana
- Vanderburgh County Fair - Darmstadt, Indiana
- September
- Princeton Labor Day Celebration Princeton, Indiana
- Dale Fall Festival - Dale, Indiana
- Spirit of Vincennes Civil War Days - Vincennes, Indiana
- Fort Branch Fall Days - Fort Branch, Indiana
- Bear Hollow Fall Fest & Dasholz - St. Croix, Indiana
- Gastoff Fall Festival - Montgomery, Indiana
- October
- West Side Nut Club Fall Festival - Evansville, Indiana
- Troy Pioneer Days - Troy, Indiana
- Spencer County Fair Octoberfest - Grandview, Indiana
- Hoosier Heritage Fall Tour - Perry County, Indiana
- Cannelton Heritage Festival - Cannelton, Indiana
- Rome Courthouse Days - Rome, Indiana
- Historic Newburgh Ghost Walks - Newburgh, Indiana
- Old Courthouse Catacombs - Old Vanderburgh County Courthouse
- November and December
- Muster on the Wabash (November) - Vincennes, Indiana (Fort Knox II)
- Santa Claus Christmas Celebration (December) - Santa Claus, Indiana
- Numerous Communities have Thanksgiving and Christmas Parades in November and December. There are also numerous Basketball Tournaments that occur in December, including the Gibson County Toyota Teamwork Classic.
Central Time vs. Eastern Time - an ongoing issue
From 1966 to 2006, the five southwesternmost counties—Gibson, Posey, Spencer, Vanderburgh, and Warrick—observed Central Daylight Time. The six northern and eastern counties—Daviess, Dubois, Knox, Martin, Perry and Pike since 1982—observed a year-round Eastern Standard Time as did much of the rest of the state.
In 2006, Indiana Governor Mitch Daniels pushed through legislation that would put the counties on Eastern Time onto Eastern Daylight Time. This action threw both Southwestern and Northwestern Indiana into chaos as counties started to argue with one another as to whether to return to Central Time or remain on Eastern Time and start observing Eastern Daylight Time. On April 2, 2006, Southwestern Indiana was once again united in one Time Zone, Central Daylight Time.
Not even a month after the change, people began to complain about some of the same problems that people that lived in the original Central Daylight Time counties had been complaining about for years. Most prevalent was the complaint that the Crane Naval Surface Warfare Center had become a "time island". The workers' union of the base subsequently petitioned the Martin County Commissioners to repetition for a change back to Eastern Time. The resulting chain reaction resulted in all of the former Eastern Time counties, along with two Central Time counties, Gibson and Spencer, petitioning for a change to Eastern Time.
On September 20, 2007 after only 15 months and only one winter on Central Time the DOT returned only five of the eight applicants to Eastern Time. Gibson, Perry and Spencer counties did not have enough support to return or to go to Eastern Time. However, three of the five counties, Daviess, Knox, and Pike counties there wasn't that much support either, but "convenience of commerce" was given as the reason for their time changes, despite commute patterns into Evansville and the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana plant in Gibson County, the region's largest employer. In Dubois County, there is a heated disagreement between Huntingburg and Jasper over the topic. Most of Huntingburg's industry and economy is geared towards the Central Time Zone where Owensboro, Kentucky and Spencer County, and the Huntingburg area's largest employers, AK Steel and Holiday World are located. Jasper, on the other hand, insists that the majority of its business is aimed at the Eastern Seaboard and it would be in the interest of the county to return to Eastern Time.[4]
So whether it was supported or not, Daviess, Dubois, Knox, Martin, and Pike returned to Eastern Daylight Time on November 4, 2007, once again dividing Southwestern Indiana. The DOT has stated that it will not hold any more hearings on the subject until the fall of 2008.[5][6]
See also
- Illinois-Indiana-Kentucky Tri-State Area
- Wabash Valley Seismic Zone - The main faultline in the area.
References
- ^ http://www.stats.indiana.edu/maptools/maps/boundary/realtor_regions.gif
- ^ http://www.stats.indiana.edu/maptools/maps/boundary/egr_detailed/Indianamap_2005_egr11.pdf
- ^ http://edocket.access.gpo.gov/cfr_2008/aprqtr/pdf/27cfr9.78.pdf
- ^ "Some counties get OK to move back to Eastern Time zone". Evansville Courier & Press. Retrieved 2008-09-19.
- ^ "Indiana does time warp again". Evansville Courier & Press. Retrieved 2008-09-19.
- ^ "DOT Moves Five Indiana Counties from Central to Eastern Time". U.S. Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on 2008-05-20. Retrieved 2008-09-19.
- Southwestern Indiana
- Regions of Indiana
- Geography of Daviess County, Indiana
- Geography of Dubois County, Indiana
- Geography of Gibson County, Indiana
- Geography of Knox County, Indiana
- Geography of Martin County, Indiana
- Geography of Perry County, Indiana
- Geography of Pike County, Indiana
- Geography of Posey County, Indiana
- Geography of Spencer County, Indiana
- Geography of Vanderburgh County, Indiana
- Geography of Warrick County, Indiana
- Interstate 69