COVID-19 pandemic in Tonga
| COVID-19 pandemic in Tonga | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Map of the COVID-19 pandemic in Tonga (as of 16 August 2022[update])
10,000+ Confirmed cases
1,000-9,999 Confirmed cases
100-999 Confirmed cases
10–99 Confirmed cases
1–9 Confirmed cases
No confirmed cases | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Tonga |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Arrival date | 29 October 2021 (3 years, 2 weeks and 6 days ago) |
| Confirmed cases | 14,135[1] |
| Active cases | 1,042 |
| Recovered | 13,066[1] |
Deaths | 12 |
| Government website | |
| http://www.health.gov.to/content/covid-19-daily-update | |
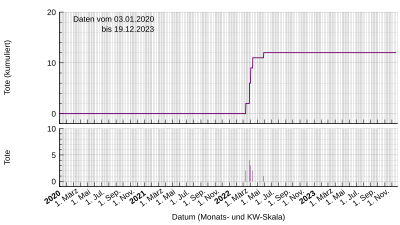
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Tonga on 29 October 2021 with a traveller who tested positive in quarantine.[2][3] Several more cases were found in January and February 2022 in a minor outbreak during the aftermath of the 2022 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha'apai eruption and tsunami as other countries delivered aid. These are currently the only cases in the country so far; Tonga has followed a "Covid-free" policy.[3]
Background
A novel coronavirus that caused a respiratory illness was identified in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, in December 2019, and was reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) on 31 December 2019, which confirmed its concern on 12 January 2020. WHO declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January, and a pandemic on 11 March.[4][5]
The case fatality rate of COVID-19[6][7] is much lower than that of SARS, a related disease which emerged in 2002, but its transmission has been significantly greater, leading to a much greater total death toll.[8][6]
Timeline
March 2020
On 27 March 2020, Prime Minister Pohiva Tu'i'onetoa announced that the country would be under a lockdown from 29 March through 5 April.[9]
As a precautionary measure, various travel and quarantining restrictions have been put in place.[10] Cruise ships and yachts have also been banned from docking in the country.[11]
July to September 2021
As of 24 August 2021, according to the WHO, there were zero confirmed COVID-19 cases; and as of 15 August, 51,816 vaccine doses were administered.[12]
October to December 2021
On 29 October, Tonga reported its first confirmed case, who was a seasonal worker returning from Christchurch in New Zealand.[2] On 1 November, the Tongan government imposed a seven-day lockdown on the main island of Tongatapu. Public gatherings except funerals were banned while most economic activities apart from banks and essential services were ordered to close down. The sale of alcohol was also banned. In response to the new reported case, there were reports of long queues outside vaccination centers, banks, Western Union outlets and shops.[13][14] During the lockdown, 124 people were arrested for violating those restrictions.[15]
January to March 2022
As of 16 January 2022, there was only one case in Tonga, who had recovered from the virus.[16]
The country's zero-COVID policy has caused complications with international aid following the Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha'apai volcano eruption in 2022.[3] To keep the country virus-free, an Australian aid flight had to return to base after detecting a case midflight, while HMAS Adelaide made plans to stay at sea after 23 members of her crew tested positive for COVID-19.[17]
On 1 February, the Tongan Prime Minister Siaosi Sovaleni and Minister of Health Dr Saia Piukala confirmed that two positive cases had been detected in port workers at the wharf in Nuku'alofa. The two workers and their families went into isolation at an army base. The Tongan Government confirmed that the island country would go into lockdown at 6 pm on 2 February.[18][19] By 4 February, a few contacts of the port workers (one's wife and two children as well as a possible fourth contact) had also tested positive, while one of the port workers tested negative on a second test.[20]
As of 5 February 2022, there were 7 cases in Tonga, including 5 active cases and 2 recoveries.[16] In response to the rise in new cases, the Tongan Government extended the lockdown until 6pm on 6 February 2022 local time.[21]
On 7 February, the Tongan Government extended the nationwide lockdown by two weeks in response to rising cases.[22]
As of 8 February 2022, there were 15 cases in Tonga, including 13 active cases and 2 recoveries.[16]
By 9 February, Tonga had reported 20 new cases in the past 24 hours, bringing the total number to 34. Clusters were reported in Pili, Fasi, Vaini, Sopu, and Hala'ano. At least three cases had recovered.[23]
As of 12 February, there are 66 cases in Tonga, including 64 active cases and 2 have been cured.[16]
On 14 February, New Zealand eliminated Tonga from its quarantine free travel list due to rising cases. Tongans entering NZ from 15 February will have to undergo rapid antigen testing. Those entering New Zealand from 22 February will be required to self-isolate for seven days and to take rapid antigen testing. By 14 February, Tonga had reported a total of 139 cases, with 75 reported over the previous three days.[24]
As of 16 February, there were 130 cases in Tonga, including 121 active cases and 9 have recovered.[16]
As of 20 February, there are 234 cases in Tonga, including 196 active cases and 38 have recovered.[16]
As of 26 February, there are 355 cases in Tonga, including 177 active cases and 178 have recovered.[16]
As of 4 March, there are 645 cases in Tonga, including 342 active cases and 303 have recovered.[16]
As of 10 March, there were 1220 cases in Tonga, including 854 active cases and 366 have been cured.[16]
On 11 March 2022, Tonga reported its first death from this virus. As of 11 March, there were 1382 cases in Tonga, including 442 active cases and 938 recoveries and 2 deaths.[16]
As of 15 March, there were 2072 cases in Tonga, including 705 active cases and 1365 recoveries and 2 deaths.[16]
By 18 March, Tonga reported a total of 1,819 active cases and two deaths. In response to rising cases, Sovaleni announced that the Tongan Government would impose a "hard lockdown" including closing businesses for a week and limiting travel to visiting health facilities and plantations.[25]
As of 19 March, there are 2788 cases in Tonga, including 964 active cases and 1822 cures and 2 deaths.[16]
April to June 2022
- As of 8 April, there were 7665 cases in Tonga, including 1923 active cases and 5733 cures and 9 deaths.[16]
- As of 12 April, there were 8444 cases in Tonga, including 1790 active cases and 6645 recoveries and 9 deaths.[16]
- As of 14 April, there were 8761 cases, including 1850 active cases and 6900 cures and 11 fatalities.[16]
- As of 19 April, there were 9106 cases, including 1473 active cases and 7622 cures and 11 deaths.[16]
- As of 26 April, there were 9697 cases, including 1259 active cases and 8427 recoveries and 11 deaths.[16]
- As of 2 May, there were 10196 cases, including 1262 active cases and 8923 recoveries and 11 fatal cases.[16]
- As of 12 May, there were 10950 cases, including 954 active cases and 9985 cures and 11 deaths.[16]
- As of 26 May, there were 11500 cases, including 614 active cases and 10875 cures and 11 deaths.[16]
- As of 14 June, there are 11909 cases, including 380 active cases and 11517 cures and 12 deaths.[16]
- As of 23 June, there are 12079 cases, including 846 active cases and 11821 cures and 12 deaths.[16]
July to September 2022
- As of 8 July, there are 12382 casesin Tonga, including 147 active cases and 12223 recoveries and 12 deaths.[16]
- As of 19 July, there are 12439 cases, including 144 active cases and 12283 recoveries and 12 fatal cases.[16]
- As of 26 August, there are 15235 cases, including 906 active cases and 14317 cures and 12 deaths.[16]
- As of 8 September, there are 16182 cases, including 532 active cases and 15638 cures and 12 fatalities.[16]
COVID-19 vaccination
On 5 August 2021, the Tongan government introduced legislation amending the Public Health Act to allow compulsory COVID-19 vaccination. The bill passed its first reading by a 17 to 0 votes.[26]
By 2 February 2022, 85 percent of Tonga's eligible population had been double vaccinated. Following the early February outbreak, Australia and New Zealand confirmed that they would fast track shipments of vaccine doses to Tonga.[19]
By 18 March 2022, 98% of Tonga's population had received their first dose; 90% their second dose; and 47% had received their booster shot.[25]
Statistics
| Division | Cases | Active | Recovered | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'Eua | 224 | 122 | 102 | |
| Haʻapai | 930 | 47 | 883 | [27] |
| Ongo Niua (Niuafo'ou) | 49 | 46 | 3 | |
| Ongo Niua (Niuatoputapu) | 159 | 70 | 89 | |
| Tongatapu | 11,177 | 757 | 10,394 | |
| Vavaʻu | 1,597 | 0 | 1,595 | |
| 5/5 | 14,136 | 1,042 | 13,066 | [28] |
See also
References
- ^ a b "COVID-19 Coronavirus - Update". Virusncov.com. 15 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2020-03-12. Retrieved 15 February 2022.
- ^ a b Dreaver, Barbara (29 October 2021). "Tonga's Cabinet to meet after first Covid case arrives from NZ". 1 News. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2021.
- ^ a b c Fildes, Nic (18 January 2022). "Tonga volcano relief effort complicated by 'Covid-free' policy". Financial Times. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ Elsevier. "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ Weiss, Matt Reynolds and Sabrina (2020-05-27). "How coronavirus started and what happens next, explained". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ a b "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus | Imperial News | Imperial College London". Imperial News. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID)". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists - Coronavirus". www.wfsahq.org. 25 June 2020. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "Tonga declares lockdown starting this weekend". Radio New Zealand. 27 March 2020. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Sweeping restrictions introduced across the Pacific". Radio New Zealand. 17 March 2020. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ "Tonga toughens travel advisory". Matangi Tonga. 17 March 2020. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Tonga: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data". covid19.who.int. 24 August 2021. Retrieved 25 August 2021.
- ^ "Tonga lockdown begins, schools and shops closed". Radio New Zealand. 2 November 2021. Archived from the original on 2 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ Tora, Iliesa (1 November 2021). "Panic, lockdown and a rush to vaccinate in Tonga as first Covid case recorded". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 1 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ "Police in Tonga arrest more than 100 during Covid-19 lockdown". Radio New Zealand. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z "Reported Cases and Deaths by Country, Territory, or Conveyance". Worldometer. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID cases reported on Australian aid vessel sailing to virus-free Tonga". Reuters. 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Tonga to enter lockdown after port workers test positive for Covid-19". Radio New Zealand. 1 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ a b "Two community cases of Covid-19 confirmed in Tonga". 1 News. 2 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2 February 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ^ "Aid to volcano-hit Tonga brings 1st COVID outbreak, lockdown". ABC News. Retrieved 2022-02-04.
- ^ "Tonga extends lockdown". Radio New Zealand. 5 February 2022. Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 6 February 2022.
- ^ "Tonga extends lockdown". Radio New Zealand. 7 February 2022. Archived from the original on 7 February 2022. Retrieved 15 February 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 in Tonga: 20 new cases of virus, active cases now total 33". Stuff. 9 February 2022. Archived from the original on 9 February 2022. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Arrivals from Tonga will soon have to self-isolate due to rising Covid-19 cases". Radio New Zealand. 14 February 2022. Archived from the original on 14 February 2022. Retrieved 15 February 2022.
- ^ a b "Stricter lockdown rules to be enforced in Tonga". Radio New Zealand. 18 March 2022. Archived from the original on 18 March 2022. Retrieved 18 March 2022.
- ^ "In brief: news from around the Pacific". Radio New Zealand. 5 August 2021. Archived from the original on 12 August 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 reaches Ha'apai". Matangitonga. 2022-03-24. Retrieved 2022-03-26.
- ^ "COVID-19 Daily Update | Ministry of Health". www.health.gov.to. Retrieved 2022-04-25.