Alaproclate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 255.74 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alaproclate (developmental code name GEA-654) is a drug that was being developed as an antidepressant by the Swedish pharmaceutical company Astra AB (now AstraZeneca) in the 1970s. It acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and along with zimelidine and indalpine, was one of the first of its kind. Development was discontinued due to the observation of liver complications in rodent studies. In addition to its SSRI properties, alaproclate has been found to act as a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, but does not have discriminative stimulus properties similar to phencyclidine.[1][2]
Synthesis
Method for Treatment of Senile Dementia:[3]
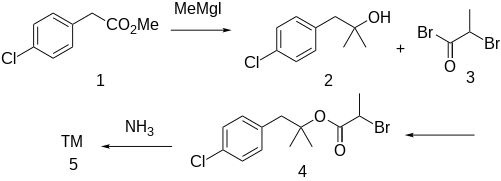
The Grignard reaction between methyl 4-chlorophenylacetate [52449-43-1] (1) with methylmagnesium iodide gives 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-2-propanol [5468-97-3] (2). Acylation with 2-bromopropionyl bromide [563-76-8] (3) gives [1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-methylpropan-2-yl] 2-bromopropanoate, CID:13695101 (3). Displacement of halogen with ammonia leads to alaproclate (4).
See also
References
- ^ Wilkinson A, Courtney M, Westlind-Danielsson A, Hallnemo G, Akerman KE (December 1994). "Alaproclate acts as a potent, reversible and noncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor coupled ion flow". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 271 (3): 1314–9. PMID 7996440.
- ^ Nicholson KL, Balster RL (November 2003). "Evaluation of the phencyclidine-like discriminative stimulus effects of novel NMDA channel blockers in rats". Psychopharmacology. 170 (2): 215–24. doi:10.1007/s00213-003-1527-6. PMID 12851738. S2CID 30803162.
- ^ Ulf H. A. Lindberg, Sven-Ove gren, U.S. patent 4,469,707 (1984 to Astra Lakemedel Aktiebolag).
- ^ Lindberg, Ulf Henrik (1978). "Inhibitors of neuronal monoamine uptake. 2. Selective inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake by .alpha.-amino acid esters of phenethyl alcohols". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 21 (5): 448–456. doi:10.1021/jm00203a008.
- ^ Ulf M. A. Lindberg, Svante B. Ross, Seth-Olov Thorberg, Sven O. / gren, U.S. patent 4,237,311 & U.S. patent 4,331,684 (1980 & 1982 both to Astra Lakemedel Aktiebolag).
- ^ Gawell, Lars (1986). "Synthesis of [14C]alaproclate". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 23 (9): 947–949. doi:10.1002/jlcr.2580230905.
- ^ Bengtsson, Stefan; Gawell, Lars; Högberg, Thomas; Sahlberg, Christer (1985). "Synthesis and 3H NMR of 3H-alaproclate of high specific activity". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 22 (5): 427–435. doi:10.1002/jlcr.2580220503.
