1990s: Difference between revisions
Removed this line from the top of the page: "Chris Guest = The 90s" |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
A combination of factors including the mass mobilization of capital markets through [[neoliberalism]], the beginning of the widespread proliferation of [[new media]] such as the [[Internet]], and the dissolution of the [[Soviet Union]] led to a realignment and reconsolidation of economic and political power across the world, and within countries. Living standards and democratic governance generally improved in many areas of the world, notably East Asia, much of Eastern Europe, Latin America, and South Africa. New ethnic conflicts emerged in Africa, the Caucusus and the Balkans, and signs of any resolution of tensions in the [[Middle East]] remained elusive.<ref>{{cite book | last = Stiglitz | first = Joseph E. | title = The Roaring Nineties | publisher = W. W. Norton & Company | date = 2004 | isbn = 9780393326185 }}</ref> |
A combination of factors including the mass mobilization of capital markets through [[neoliberalism]], the beginning of the widespread proliferation of [[new media]] such as the [[Internet]], and the dissolution of the [[Soviet Union]] led to a realignment and reconsolidation of economic and political power across the world, and within countries. Living standards and democratic governance generally improved in many areas of the world, notably East Asia, much of Eastern Europe, Latin America, and South Africa. New ethnic conflicts emerged in Africa, the Caucusus and the Balkans, and signs of any resolution of tensions in the [[Middle East]] remained elusive.<ref>{{cite book | last = Stiglitz | first = Joseph E. | title = The Roaring Nineties | publisher = W. W. Norton & Company | date = 2004 | isbn = 9780393326185 }}</ref> |
||
The 1990s is considered by many western countries, such as the [[United States]], to be a peaceful time that occurred after the effective end of the [[Cold War]] (1945–1991), but before the |
The 1990s is considered by many western countries, such as the [[United States]], to be a peaceful time that occurred after the effective end of the [[Cold War]] (1945–1991), but before the [[9/11 Attacks]] and the ensuing [[War on Terror]] (2001–present). |
||
==Politics and wars== |
==Politics and wars== |
||
Revision as of 00:10, 30 January 2010

| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
The 1990s, pronounced "the Nineteen Nineties" or abbreviated as "the Nineties", was the decade that started on January 1, 1990 and ended on December 31, 1999. It was the last full decade of both the 20th century and the 2nd millennium.
A combination of factors including the mass mobilization of capital markets through neoliberalism, the beginning of the widespread proliferation of new media such as the Internet, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union led to a realignment and reconsolidation of economic and political power across the world, and within countries. Living standards and democratic governance generally improved in many areas of the world, notably East Asia, much of Eastern Europe, Latin America, and South Africa. New ethnic conflicts emerged in Africa, the Caucusus and the Balkans, and signs of any resolution of tensions in the Middle East remained elusive.[1]
The 1990s is considered by many western countries, such as the United States, to be a peaceful time that occurred after the effective end of the Cold War (1945–1991), but before the 9/11 Attacks and the ensuing War on Terror (2001–present).
Politics and wars
Wars

- The Gulf War - Iraq was left in severe debt after the 1980s war with Iran. President Saddam Hussein accused Kuwait of flooding the market with oil and driving down prices. As a result, on August 2, 1990, Iraqi forces invaded and conquered Kuwait. The UN immediately condemned the action, and a coalition force led by the United States was sent to the Persian Gulf. Aerial bombing of Iraq began in January 1991 (see also Gulf War), and a month later, the UN forces drove the Iraqi army from Kuwait in just four days. In the aftermath of the war, the Kurds in the north of Iraq and the Shiites in the south rose up in revolt, and Saddam Hussein barely managed to hold onto power. Until the US invasion in 2003, Iraq was cut off from much of the world.
- The Congo wars break out in the 1990s:
- The First Congo War takes place in Zaire from 1996 to 1997, resulting in Zairian dictator Mobutu Sese Seko being overthrown from power on May 16, 1997, ending 32 years of his rule. Zaire is renamed the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- The Second Congo War starts in 1998 in central Africa and includes 5 different cultures and 7 different nations. It goes on until 2003.
- The Chechen wars break out in the 1990s:
- The First Chechen War (1994–1996) - the conflict was fought between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria. After the initial campaign of 1994–1995, culminating in the devastating Battle of Grozny, Russian federal forces attempted to seize control of the mountainous area of Chechnya but were set back by Chechen guerrilla warfare and raids on the flatlands in spite of Russia's overwhelming manpower, weaponry, and air support. The resulting widespread demoralization of federal forces, and the almost universal opposition of the Russian public to the conflict, led Boris Yeltsin's government to declare a ceasefire in 1996 and sign a peace treaty a year later.
- The Second Chechen War (1999 - ongoing) - the war was launched by the Russian Federation starting August 26, 1999, in response to the Invasion of Dagestan and the Russian apartment bombings which were blamed on the Chechens. During the war Russian forces largely recaptured the separatist region of Chechnya[2]. The campaign largely reversed the outcome of the First Chechen War, in which the region gained de facto independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria.
- Kargil War (1999) - In May 1999, Pakistan sends troops covertly to occupy strategic peaks in Kashmir. A month later the Kargil War with India results in a political fiasco for Nawaz Sharif, followed by a military withdrawal to the Line of Control. The incident leads to a military coup in October in which the Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif is ousted by Army Chief Pervez Musharraf.
- The Kosovo War (1998–1999):
- War between ethnic-Albanian separatists and Yugoslav military and Serb paramilitary forces in Kosovo begin in 1996 and escalates in 1998 with increasing reports of atrocities taking place.
- In 1999, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) led by the United States launched air attacks against Yugoslavia (then composed of only Serbia and Montenegro) to pressure the Yugoslav government to end its military operations against ethnic Albanian separatists in Kosovo due to accusations of war crimes being committed by Yugoslav military forces working alongside nationalist Serb paramilitary groups. After weeks of bombing, Yugoslavia submits to NATO's demands and NATO forces occupy Kosovo and later UN peacekeeping forces to take control of Kosovo.

- The Yugoslav Wars (1991–2001) - The breakup of Yugoslavia beginning on June 25, 1991 after the republics of Croatia and Slovenia declared independence from Yugoslavia [disambiguation needed] which was followed by the subsequent Yugoslav wars. The Yugoslav Wars would become notorious for numerous war crimes and human rights violations such as ethnic cleansing and genocide committed by all sides, especially by the Serbs.
- War in Slovenia (1991) - a brief military conflict between Slovenian TO (Slovenian Territorial Defence) and the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) following Slovenia's declaration of independence.
- Croatian War of Independence (1991–1995) - the war fought in Croatia between the Croatian government, having declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, and both the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and Serb forces, who established the self-proclaimed Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) within Croatia.
- Bosnian War (1992–1995) - the war involved several ethnically defined factions within Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats as well as a smaller faction in Western Bosnia led by Fikret Abdić. The Siege of Sarajevo (1992 - 1994) marked the most violent urban warfare in Europe since World War II at that time as Serb forces bombard and attack Bosniak controlled and populated areas of the city. War crimes occur including ethnic cleansing and destruction of civilian property.
- The final fighting in Croatian and Bosnian wars ends in 1995 with the success of Croatian military offensives against Serb forces and the mass exodus of Serbs from Croatia in 1995; Serb losses to Croat and Bosniak forces; and finally the signing of the Dayton Agreement which internally partitioned Bosnia and Herzegovina into a Serb republic and a Bosniak-Croat federation.
Internal conflicts

- The Rwandan Genocide - between April 6, 1994 until mid-July 1994 a mass killing of hundreds of thousands of Rwanda's Tutsis and Hutu political moderates occurred by the Hutu dominated government under the Hutu Power ideology. Over the course of approximately 100 days, at least 500,000 people were killed.[3] Estimates of the death toll have ranged between 500,000 and 1,000,000,[4] or as much as 20% of the total population of the country. It resulted in serious criticism of the United Nations and major countries for failing to stop the genocide.
- In Algeria a long period of violence in the north African country starts by the cancellation of the first ever held democratic elections by a group of high ranking army officers.
- The Ethiopian Civil War ends in 1991, ending over twenty years of internal conflict. The end of the war coincides with the collapse of the communist government of Mengistu Haile Mariam and the establishment of a coalition government of various factions.
- Oka Crisis takes place in 1990 involving an armed standoff between people of the Mohawk nation (North American indigenous peoples in Canada), and the Canadian military over a dispute involving land held via treaty to the Mohawk people.
- A large number of the Zapatista indigenous people of Mexico join the Zapatista Army of National Liberation that begins armed conflict with the Mexican government in 1994 and continues through the 1990s.
- The Taliban seize control of Afghanistan in 1996.
- The 1992 Los Angeles riots occurred, with 53 deaths and 5,500 property fires in a 100-square-mile (260 km2) riot zone. The riots were a result of the state court acquittal of three White and one Hispanic L.A. police officers by an all-white jury in a police brutality case involving motorist Rodney King, but in 1993, all four officers were convicted in a federal civil rights case.
- The Pakistan Army overthrows the democratically elected government of Pakistan on October 12, 1999. Army chief Pervez Musharraf takes control of government as Prime Minister of Pakistan; he would dominate Pakistan's political leadership for nine years.
- The Somali Civil War (1991–Present) and the Battle of Mogadishu.
- Somali president Mohamed Siad Barre, who had ruled since 1969, was overthrown in 1991 and the country fell into a state of anarchy and civil war which continues today.
- Severe political deadlock between Russian President Boris Yeltsin and the Supreme Soviet (Russia's parliament at this time) result in Yeltsin ordering the controversial shelling of the Russian parliament building by tanks in 1993.
Terrorist attacks

- The bombings of the World Trade Center and the Oklahoma City bombing leads to awareness in U.S. of domestic and international terrorism as a potential threat.
- The Oklahoma City bombing in 1995, the bombing of a federal building in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, killed 168. Bombing suspect Timothy McVeigh claimed he bombed the building in retaliation for the 1993 Waco massacre.
- After the bombings of U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania by Al-Qaeda militants, U.S. naval military forces launch cruise missile attacks against Al-Qaeda bases in Afghanistan in 1998.
- The Omagh bombing in Omagh, County Tyrone, Northern Ireland which kills 29 civilians and injures hundreds more.
- Ahmed Ressam, an Islamist militant associated with Al-Qaeda is arrested when attempting to cross from Canada to the United States at the Canada-U.S. border on December 14, 1999; it is discovered that he intended to bomb Los Angeles International Airport during millennium celebrations. This is the first major attempted terrorist attack by Al Qaeda on U.S. soil since the 1993 World Trade Center bombing and marked the beginning of a series of attempted terrorist attacks by Al Qaeda against the U.S. that would continue into the 2000s.
Nuclear threats
- The rival countries India and Pakistan in succession reveal their acquisition of nuclear weapons in 1998 with two separate missile tests amid escalating tensions over the disputed region of Kashmir.
Decolonization and Independence
- Great Britain hands sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China on July 1, 1997.
- Portugal hands sovereignty of Macau to the People's Republic of China on December 20, 1999.
- Eritrea gains independence from Ethiopia (1993).
- East Timor breaks away from Indonesian control in 1999, merely a year after the fall of Suharto from power, ending a twenty-four year guerrilla war with more than 200,000 casualties. The UN deploys a peace keeping force, spearheaded by the Australian and New Zealand armed forces. The United States deploys police officers to serve with the International Police element, to help train and equip an East Timorese police force.
- The republics of Croatia and Slovenia declared independence from Yugoslavia [disambiguation needed].
- Dissolution of Czechoslovakia into Czech Republic and Slovakia (1993).
Prominent political events
- the 1990s was an era of spreading democracy.[5] The former countries of the Warsaw Pact moved from totalitarian regimes to democratically elected governments.[5] The same happened in other non-communist countries, such as Taiwan, Chile, South Africa, and Indonesia. Capitalism made great changes to the economies of communist countries like China and Vietnam.
- The ethnic tensions and violence in the former Yugoslavia during the 1990s create a greater sense of ethnic identity of the nations in the new countries, especially involving increased popularity of nationalism.
Africa

- The release of African National Congress leader Nelson Mandela from jail in February 1990 after thirty years of imprisonment for opposing apartheid and white-minority rule in South Africa. This would resolve with the end of Apartheid in South Africa in 1994, marking the end of the original Civil Rights era of the 20th century.
- Nelson Mandela is elected President of South Africa in 1994, becoming the first black-President in South African history ending a long-legacy of apartheid white-rule in the country.
North America
- United States president Bill Clinton was a dominant political figure in international affairs during the 1990s especially with his attempts to negotiate peace in the Middle East and end the ongoing wars occurring in the former Yugoslavia; his promotion of international action to decrease human-created climate change; and his endorsement of advancing free trade in the Americas.
- Lewinsky scandal - US president Bill Clinton was caught in a media-frenzied sex scandal over his intern Monica Lewinsky, first announced on January 21, 1998. After the U.S. House of Representatives impeached Clinton on December 19, 1998 for perjury under oath, following an investigation by federal prosecutor Kenneth Starr, the Senate acquitted Clinton of the charges on February 12, 1999 and he finished his second term.
- Jean-Bertrand Aristide becomes the first democratically elected President of Haiti in 1990.
- Canadian politics is radically altered in the 1993 federal election with the collapse of the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada, (a major political party in Canada since 1867) from being government to only 2 seats and the New Democratic Party collapsing from 44 seats to 9. The Liberal Party of Canada is the only genuine national political party that remains while the regionally based parties such as the Quebec-based Bloc Québécois and the almost entirely Western Canada-based Reform Party of Canada rise from political insignificance to being major political parties.
- After the collapse of the Meech Lake constitutional accord in 1990, the province of Quebec in Canada experienced a rekindled wave of separatism by francophone Québécois nationalists, who sought for Quebec to become an independent country. In 1995, during a referendum on Quebec sovereignty, Quebec voters narrowly reject the vote for independence.
- The 1995 Quebec referendum on sovereignty is held in the predominantly francophone province of Quebec in Canada, a majority anglophone country. If accepted Quebec would become an independent country with an economic association with Canada. The proposal is narrowly rejected by Quebec's voters by 50.4% no, and 49.6% yes.
- California voters passed Proposition 215 in 1996, to legalize cannabis only for medical purposes, the debate over legalization of marijuana in the U.S. goes on today.
- The enactment of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) on January 1, 1994, creating a North American free trade zone consisting of Canada, Mexico, and the United States.
Asia

- Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian Prime Minister Yasser Arafat agree to the Peace Process at the culmination of the Oslo Accords, negotiated by the United States President Bill Clinton on September 13, 1993. By signing the Oslo accords, the Palestine Liberation Organization recognize Israel's right to exist, while Israel permitted the creation of an autonomous Palestinian National Authority consisting of the Gaza Strip and West Bank which was implemented in 1994. Israeli military forces withdraw from the Palestinian territories in compliance with the accord, which marked the end of the First Intifada (a period of violence between Palestinian Arab militants and Israeli armed forces from 1987 to 1993).
- The Palestinian National Authority is created in 1994 in accordance with the Oslo Accords, giving Palestinian Arab people official autonomy over the Gaza Strip and West Bank, though not official independence from Israel.
- In 1994, a peace treaty is signed between Israel and Jordan.
- In July 1994, North Korean leader Kim Il-sung died, having ruled the country since its founding in 1948. His son Kim Jong-il succeeded him, taking over a nation on the brink of complete economic collapse. Famine caused a great number of deaths in the late '90s, and North Korea would gain a reputation for being a major source of money laundering, counterfeiting, and weapons proliferation. The country's ability to produce and sell nuclear weapons became a focus of concern in the international community.
- Aung San Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy in Burma wins a majority of seats in the first free elections in 30 years in 1990, yet the Burmese military junta refuses to relinquish power, beginning an ongoing peaceful struggle throughout the 1990s to the present by Aung San Suu Kyi and her supporters to demand the end of military rule in Burma.
- North Yemen and South Yemen merge to form Yemen in 1991.
Europe
- The Moscow Coup and subsequent break-up of the Soviet Union on December 26, 1991.
- The improvement in relations between the countries of NATO and the former members of the Warsaw Pact ended the Cold War both in Europe and other parts of the world.
- German reunification - Germany reunified on October 3, 1990 as a result of the fall of the Berlin Wall and after integrating the economic structure and provincial governments, focused on modernization of the former communist East. People who were brought up in a communist culture became integrated with those living in democratic western Germany.
- Margaret Thatcher who had been the United Kingdom's Prime Minister since 1979 resigned as Prime Minister on November 22, 1990 after been challenged for the leadership of the Conservative Party by Michael Heseltine because of widespread opposition to the introduction of the controversial Community Charge and the fact that her key allies such as Nigel Lawson and Geoffrey Howe resigned over the deeply sensitive issues of the Maastricht Treaty and Margaret Thatcher's resistance to Britain joining the European Exchange Rate Mechanism. Less than two years later on the infamous Black Wednesday of September 1992, the pound sterling crashed out of the system after the pound fell below the agreed exchange rate with the Deutsche Mark.
- The Belfast Agreement (a.k.a. the Good Friday Agreement) is signed by U.K. and Irish politicians on April 10, 1998, declaring a joint commitment to a peaceful resolution of the territorial dispute between the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom over Northern Ireland.
- The IRA agreed to a truce in 1994. This marked the beginning of the end of 25 years of violence between the IRA and the United Kingdom, and the start of political negotiations.
- The European Union forms in 1992 under the Maastricht Treaty.
South America
- Due to the internal conflict in Peru and the economic crisis, Alberto Fujimori rises to power in Peru and remains in office for eleven years. His administration is marked by economic development but also by numerous human rights violations (La Cantuta massacre, Barrios Altos massacre), and a rampant corruption network set up by Vladimiro Montesinos.
Assassinations

The 1990s were marked by several notable assassinations and assassination attempts:
- 19 September 1990 - The Provisional Irish Republican Army tries to assassinate Air Chief Marshal Sir Peter Terry at his home near Stafford, England. Hit by at least 9 bullets, the former Governor of Gibraltar survives.
- 21 May 1991 - In Sriperumbudur, India, former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi is assassinated.
- 7 August 1991 - Shapour Bakhtiar, former prime minister of Iran, is assassinated.
- 29 June 1992 - A bodyguard assassinates President Mohamed Boudiaf of Algeria.
- April 1993 - The Kuwaiti government claims to uncover an Iraqi assassination plot against former U.S. President George H. W. Bush shortly after his visit to Kuwait. Two Iraqi nationals confess to driving a car-bomb into Kuwait on behalf of the Iraqi Intelligence Service.[6]
- 1 May 1993 - A Tamil Tigers suicide bomber assassinates President Ranasinghe Premadasa of Sri Lanka.
- 29 August 1995 - Eduard Shevardnadze, the Georgian head of state, survives an assassination attempt in Tbilisi.
- 4 November 1995 - Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin is assassinated at a peace rally in Tel Aviv by a radical Jewish militant who opposed the Oslo Accords.
- 2 October 1996 - The former prime minister of Bulgaria, Andrei Lukanov, is assassinated.
- 9 February 1998 - Eduard Shevardnadze, the Georgian head of state, survives an assassination attempt in Tbilisi.
- 16 February 1999 - In Uzbekistan, an apparent assassination attempt against President Islam Karimov takes place at government headquarters.
- 23 March 1999 - Gunmen assassinate Paraguay's Vice President Luis María Argaña.
- 9 April 1999 - Ibrahim Baré Maïnassara, president of Niger, is assassinated.
Disasters
Natural disasters
- The most prominent natural disasters of the decade include: Hurricane Andrew strikes South Florida in August 1992, the crippling super storm of March 1993 along the Eastern Seaboard, the devastating 1994 Northridge earthquake in Los Angeles, the Great Hanshin earthquake in Kobe, Japan in January 1995, the Blizzard of 1996 in the eastern U.S., the US drought of 1999, the deadly Hurricane Mitch which struck Central America in October 1998, and the destructive F-5 Oklahoma City tornado in May 1999, the August 1999 İzmit earthquake in Turkey, and the September 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake in Taiwan.
- A magnitude 7.8 earthquake hit the Philippines on July 16, 1990 and killed around 1000 people in Baguio City.
- July 1995 - Midwestern United States heat wave - An unprecedented heat wave strikes the Midwestern United States for most of the month. Temperatures peak at 106 °F (41 °C), and remain above 94 °F (34 °C) in the afternoon for 5 straight days. At least 739 people die in Chicago alone.
Non-natural disasters
- Gulf War oil spill - the worst oil spill in history, resulting from actions taken during the Gulf War in 1991 by the Iraq military. The oil spill caused considerable damage to wildlife in the Persian Gulf especially in areas surrounding Kuwait and Iraq.
- On December 15, 1991, The Egyptian ferry Salem Express sinks in the Red Sea, killing more than 450.
- On July 26, 1993, Asiana Airlines Flight 733 crashes into Mt. Ungeo in Haenam, South Korea killing 68.
- On June 29, 1995, the Sampoong Department Store collapses in Seoul, South Korea, killing 502.
Economics

- Many countries, institutions, companies, and organizations were prosperous during the 1990s. High-income countries such as the United States, Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea, and those in Western Europe experienced steady economic growth for much of the decade. However, in the former Soviet Union GDP decreased as their economies restructured to produce goods they needed and some capital flight occurred.
- GATT update and creation of the World Trade Organization and other global economic institutions, but opposition by anti-globalization activists showed up in nearly every GATT summit, like the demonstrations in Seattle in December 1999.
- The anti-globalization protests at the World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference of 1999 in Seattle, Washington began on November 30, 1999. This marks the beginning of a steady increase in anti-globalization protests which occurred in the 2000s as well as increasing hostility to neoliberalism.
North America
- The U.S experiences its longest period of economic expansion during the decade. Personal incomes doubled from the recession in 1990, and there was higher productivity overall. After the 1996 Welfare Reform Act there was a reduction of poverty,[7] and the Wall Street stock exchange stayed over the 10,500 mark from 1999 to 2001.
- After the 1992 booming of the US stock market, Alan Greenspan coined the phrase "irrational exuberance".
- The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which phases out trade barriers between the United States, Mexico, and Canada is signed into law by U.S. President Bill Clinton.
Asia
- The government of the People's Republic of China announces major privatization of state-owned industries in September 1997.
- China started the '90s in a bad way, shunned by much of the world after the Tiananmen Square Massacre and controlled by hard line politicians who reigned in private enterprise and attempted to revive old-fashioned propaganda campaigns. Relations with the United States deteriorated sharply, and the Chinese leadership was further embarrassed by the disintegration of communism in Europe. In 1992, Deng Xiaoping travelled to southern China in his last major public appearance to revitalize faith in market economics and stop the country's slide back into Maoism. Afterwards, China recovered, and would experience explosive economic growth during the rest of the decade. In spite of this, dissent continued to be suppressed, and President Jiang Zemin launched a brutal crackdown against the Falun Gong religious sect in 1999. Deng Xiaoping himself died in 1997 at the age of 93. Relations with the US deteriorated again in 1999 after the death of a Chinese journalist during the bombing of Serbia by NATO forces, and allegations of Chinese espionage at the Los Alamos Nuclear Facility.
- South-East Asia economic crisis starting from 1997.
- Financial crisis hits East and Southeast Asia in 1997 and 1998 after a long period of phenomenal economic development, which continues by 1999. This crisis begins to be felt by the end of the decade.
- In Japan, after three decades of economic growth put them in second place in the world's economies, the situation worsened after 1993. The recession went on into the early 2000s, bringing an end to the seemingly unlimited prosperity that the country had hitherto enjoyed.
- The Philippines saw great economic development after the People Power Revolution. The economy gains 5% from its deficit until the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis.
- Less affluent nations such as India, Malaysia, and Vietnam also saw tremendous improvements in economic prosperity and quality of life during the 1990s. Restructuring following the end of the Cold War was beginning. However, there was also the continuation of terrorism in Third World regions that were once the "frontlines" for American and Soviet foreign politics, particularly in Asia.
Europe
- By 1990, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev's reforms were causing major inflation and economic chaos. A coup attempt by hard-liners in August 1991 failed, marking the effective end of the Soviet Union. All its constituent republics declared their independence in 1991, and on Christmas, Gorbachev resigned from office. After 73 years, the Soviet Union had ceased to exist. The new Russian Federation was headed by Boris Yeltsin, and would face severe economic difficulty. Oligarchs took over Russia's energy and industrial sectors, reducing almost half the country to poverty. With a 3% approval rating, Yeltsin had to buy the support of the oligarchs to win reelection in 1996. Economic turmoil and devaluation of the ruble continued, and with heart and alcohol troubles, he stepped down from office on the last day of 1999, handing power to Vladimir Putin.
- Russian financial crisis in the 1990s results in mass hyperinflation and prompts economic intervention from the International Monetary Fund and western countries to help Russia's economy recover.
- Eastern European economies struggled after the fall of communism, but Poland, Hungary, Estonia, and Lithuania saw healthy economic growth rates in the late 1990s.
- The first McDonald's restaurant opens in Moscow in 1990 with then-President of the Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR and future Russian President Boris Yeltsin attending, symbolizing Russia's transition towards a capitalist free market economy and a move towards adopting elements of western culture.
- Oil and gas were discovered in many countries in the former Soviet bloc, leading to economic growth and wider adoption of trade between nations. These trends were also fueled by inexpensive fossil energy, with low petroleum prices caused by a glut of oil. Political stability and decreased militarization due to the winding down of the Cold War led to economic development and higher standards of living for many citizens.
- Much of Europe had serious economic problems including the massive 1995 general strikes in France during its worst recession since World War II and the problems associated with German reunification. The French economy mildly rebounds at the end of the decade as does Germany. During the late 90s, the economies of particularly Spain, Scandinavia and former Eastern Bloc countries accelerate at rapid speed. After the early 1990s recession, the United Kingdom and Ireland experience rapid economic growth that continues throughout the decade. Unemployment is a persistent problem in many countries throughout the 90s.
- With the creation of the E.U. there is freedom of movement between member states, such as the 1992 and 1995 free trade agreements.
- The Euro is adopted by the European Union on January 1, 1999, which begins a process of phasing out national currencies of EU countries.
South America
- The sluggish economies of Brazil, by a new emphasis on free markets for all their citizens, and Mexico, under economist president Ernesto Zedillo elected in 1994, were in their best shape by the late 1990s.
Technology and science
Technology
The 1990s were an incredibly revolutionary decade for digital technology. Cell phone usage was at only a few percent in 1990, and almost non-existent in 1985, but Internet usage in that year was higher; by 1999, more than 50% of some Western countries had Internet access, and more than 25% had cell phone access.
Electronics and communications


- On 6 August 1991, CERN, a pan European organization for particle research, publicized the new World Wide Web project.[8] Although the basic applications and guidelines that make the Internet possible had existed for almost two decades, the network did not gain a public face until the 1990s.
- Y2K spread fear throughout the United States and eventually the world in the last half of the decade particularly 1999 about possible massive computer malfunctions on January 1, 2000. As a result, many people stocked up on supplies for fear of a world wide disaster. Eventually no globally significant computer failures occurred when the clocks rolled over into 2000.
- Advancements in computer modems, ISDN, cable modems, and DSL lead to faster connection to the Internet.
- The Pentium processor is developed by Intel.
- E-mail becomes popular; as a result Microsoft acquires the popular Hotmail webmail service.
- Instant messaging and the Buddy list becomes popular. AIM and ICQ are two early protocols.
- Businesses start to build E-commerce websites; E-commerce-only companies such as Amazon.com, eBay, AOL, and Yahoo! grow rapidly.
- The introduction of affordable, smaller satellite dishes and the DVB-S standard in the mid-1990s expanded satellite television services that carried up to 500 television channels..
- The first MP3 Player, the MPMan, is released in late spring of 1998. It came with 32Mb of flash memory expandable to 64Mb.
- The first GSM network is launched in Finland in 1991.
- Digital SLRs and regular digital cameras become commercially available.
- IBM introduces the 1-inch (25 mm) wide Microdrive hard drive in 170 MB and 340 MB capacities.
- Apple introduces the iMac computer, initiating a trend in computer design towards translucent plastics and multicolor case design, discontinuing many legacy technologies like serial ports, and beginning a resurgence in the company's fortunes that continues unabated to this day.
- CD burner drives are introduced.
- The DVD media format is developed and popularized along with a plethora of Flash memory card standards.
- Pagers are initially popular but ultimately are replaced by mobile phones toward the end of the decade.
- Hand-held satellite phones are introduced towards the end of the decade.
Software
- Microsoft Windows operating systems become virtually ubiquitous on IBM Personal Computers.
- Microsoft introduces Windows NT 3.1, Windows 95 and later Windows 98 to the market, which gain immediate popularity.
- Mac OS X was released in 1999, with the consumer version to be released in 2001.
- The development of Web browsers such as Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer makes surfing the World Wide Web easier and more user friendly.
- The Java programming language is developed by Sun Microsystems.
- Development of the free Linux kernel is started by Linus Torvalds in Finland.
- The Year 2000 problem (commonly known as Y2K), the computer glitch disaster expected to happen on January 1, 2000 is recognized.
Automobiles
The 1990s began with another recession that dampened car sales. General Motors continued to suffer huge losses thanks to an inefficient structure and stale designs. Sales improved with the economy by the mid-'90s, but GM's US market share gradually declined to less than 40% (from a peak of 53% in the '70s). While the new Saturn division fared well, Oldsmobile declined sharply, and attempts to remake the division as a European-style luxury car were unsuccessful.
Cars in the 1990s had a rounder shape than those of the 1970s and 1980s; this style would continue into the 2000s.
Chrysler ran into financial troubles again as the '90s started. Like GM, it too had a stale model lineup (except for the best-selling minivans [disambiguation needed]) that was largely based on the aging K-car platform. In 1992, chairman Lee Iacocca retired, and the company began a remarkable revival, introducing the new LH platform and "Cab-Forward" styling, along with a highly successful redesign of the full-sized Dodge Ram in 1994. Chrysler's minivans continued to dominate the market despite increasing competition. In 1998, Daimler-Benz (the parent company of Mercedes-Benz) merged with Chrysler. The following year, it was decided to retire Plymouth, which had been on a long decline since the '70s. Ford continued to fare well in the '90s, with the second and third generations of the Ford Taurus being named the best selling car in the United States.
Japanese cars continued to be highly successful during the decade. The Honda Accord vied with the Taurus most years for being the best-selling car in the United States. SUVs and trucks became hugely popular during the economic boom in the second half of the decade. Many makes that had never built a truck before started selling SUVs. Car styling during the 1990s became gradually more round and ovoid, the third-generation Taurus and Mercury Sable being some of the more extreme examples. Safety features such as airbags and shoulder belts became mandatory equipment on new cars.
Science


- Physicists develop M-theory.
- Detection of extrasolar planets orbiting stars other than the sun.
- In the United Kingdom, the first cloned mammal, Dolly the sheep was confirmed by the Roslin Institute, and was reported by global media on February 26, 1997. Dolly would trigger a raging controversy on cloning and bioethical concerns regarding possible human cloning continue to this day.
- Human Genome Project begins.
- DNA identification of individuals finds wide application in criminal law.
- Hubble Space Telescope launched in 1990; revolutionizes astronomy. Unfortunately, a flaw in its main mirror caused it to produce fuzzy, distorted images. This was corrected by a shuttle repair mission in 1993.
- Protease inhibitors introduced allowing HAART therapy against HIV; drastically reduces AIDS mortality.
- NASA's spacecraft Pathfinder lands on Mars and deploys a small roving vehicle, Sojourner, which analyzes the planet's geology and atmosphere.
- The Hale-Bopp comet swings past the sun for the first time in 4,200 years in April 1997.
- Development of biodegradable products, replacing products made from styrofoam; advances in methods for recycling of waste products (such as paper, glass, and aluminum).
- Genetically engineered crops are developed for commercial use.
- Discovery of dark matter, dark energy, brown dwarfs, and first confirmation of black holes.
- The Galileo probe orbits Jupiter, studying the planet and its moons extensively.
- The Global Positioning System (GPS) becomes fully operational.
- Proof of Fermat's Last Theorem is discovered by Andrew Wiles.
- Construction started in 1998 on the International Space Station.
Environment
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2010) |
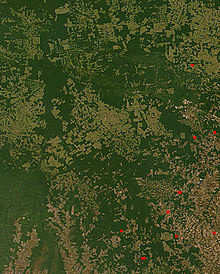
- Large areas of the Amazon Rainforest were deforested during this decade.
- The adoption of the Kyoto Protocol by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change on December 11, 1997.
Society
- The decade started out with Baby boomers from the 1960s finally entering the middle-aged Establishment with a progressive politico-economic message for youth ("peace", "save the earth"; "stop racism"; "greed is bad") mixed or paired with a mostly conservative or "cautious" socio-cultural one ("Believe"; "Jesus is the answer"; "just say no to drugs"; "don't drink, smoke, or do dope"...etc...)[citation needed]
- Youth culture in the 1990s responded to this by embracing both environmentalism and entrepreneurship. Western world fashions reflected this by often turning highly individualistic and/or counter-cultural: tattoos and body piercing gained popularity, and "retro" styles inspired by fashions of the 1960s and 1970s were also prevalent. Some young people became increasingly involved in outdoor activities that combined embracing athletics with the appreciation of nature.
- In 1990, the World Health Organization removed homosexuality from its list of diseases. Increasing acceptance of homosexuality occurs in the western world throughout the 1990s and 2000s.
Third-wave feminism

- Anita Hill and other women testify before the United States Congress on being sexually harassed by Supreme Court nominee Clarence Thomas. Thomas was narrowly confirmed by the United States Senate, but Hill's testimony, and the testimony of other harassed women, begins a national debate on the issue.
- Record numbers of women are elected to high office in the U.S. in 1992, the "Year of the Woman".
- Violence against women takes center stage as an important issue internationally. In the U.S. the Violence Against Women Act was passed, which greatly affected the world community through the United Nations. The law's author, Joe Biden, and UN Ambassador and Secretary of State Madeleine Albright, and Hillary Clinton (see below) become vocal advocates of action against violence against women.
- Women reach great heights of power in the U.S. government. Hillary Rodham Clinton, leading policy proposals, traveling abroad as a State Department representative to 82 nations, advising her husband, and being elected a Senator (in 2000), is the most openly empowered and politically powerful First Lady in American history; Madeleine Albright and Janet Reno take two of the cabinet's top jobs as United States Secretary of State (#1), and United States Attorney General (#4), respectively. Sheila Widnall becomes head and Secretary of the Air Force and Ruth Bader Ginsburg joins Sandra Day O'Connor as the second woman on the U.S. Supreme Court.
- Record numbers of women become tops CEOs worldwide.
- More nations than ever before are led by elected women Presidents and Prime Ministers. Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto's 1988 victory in Pakistan makes women leaders in Muslim states unextraordinary.
Additional significant world-wide events
- Worldwide New Year's Eve celebrations on December 31, 1999 welcoming the year 2000. The 2nd millennium and the 20th century would end on December 31, 2000.
Europe
- 1991 – Soviet Union military troops attack Lithuanian independence supporters in Vilnius. Killed 14 people and wounding 1000.
- In France, Princess Diana and her Arab fiancee were killed in a car accident in August 1997, when under mysterious circumstances, their car crashed in a tunnel.
- Mother Teresa, the Roman Catholic nun who won the Nobel Peace Prize, dies at age 87.
- The birth of the "Second Republic" in Italy, with the Mani Pulite investigations of 1994.
- The Channel Tunnel across the English Channel opens in 1994, connecting France and England. As of 2007 it is the second-longest rail tunnel in the world, but with the undersea section of 37.9 km (23.55 miles) being the longest undersea tunnel in the world.
- The resignation of President Boris Yeltsin on December 31, 1999 resulting in Prime Minister Vladimir Putin's succession to the position.
Americas
- The Columbine High School massacre occurred on April 20, 1999, in Littleton, Colorado when two student gunmen killed 12 students and a teacher before committing suicide, making it the deadliest high school shooting in United States history.
- O. J. Simpson murder case - O. J. Simpson's trial, described in the U.S. media as the "trial of the century" and enormous U.S. media attention is focused on the trial. On October 3, 1995, Simpson was found "not guilty" of double-murder of ex-wife Nicole Brown Simpson and her friend, Ronald Goldman.
- With help from clinical fertility drugs, an Iowa mother, Bobbie McCaughey, gave birth to the first surviving septuplets in 1997. There followed a media frenzy and widespread support for the family.
- John F. Kennedy, Jr., his wife Carolyn Bessette and sister-in-law Lauren Bessette are killed when Kennedy's private plane crashes off the coast of Martha's Vineyard in July 1999.
- Debate on assisted suicide highly publicized by Michigan doctor Jack Kevorkian, charged with multiple counts of homicide of his terminally ill patients through the decade.
- Beer keg registration becomes popular public policy in U.S.
- The 500th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' discovery of the Americas in 1992 was popularly observed, despite controversy and protests against the victimization of Native Americans by Columbus' expeditions. The holiday was labeled by some as racist, in view of Native American experiences of colonialism, slavery, genocide, and cultural destruction.
Asia
- Massive immigration wave of Jews from the Commonwealth of Independent States to Israel - With the end of the Soviet Union, Israel faced a mass influx of Russian Jews, many of whom had high expectations the country was unable to meet. Israel was also barred from participating in the Gulf War, so as to not disrupt the US-Arab alliance.
- The Spratly Islands issue became one of the most controversial in Southeast Asia.
Popular Culture
This article is missing information about Error: you must specify what information is missing.. (January 2010) |
Film
- Oscar winners: Dances with Wolves (1990), The Silence of the Lambs (1991), Unforgiven (1992), Schindler's List (1993), Forrest Gump (1994), Braveheart (1995), The English Patient (1996), Titanic (1997), Shakespeare in Love (1998), American Beauty (1999)
- Some of Hollywood's most notable blockbuster films of the 1990s include: Titanic, Star Wars Episode I: The Phantom Menace, Jurassic Park & The Lost World: Jurassic Park, Independence Day, The Lion King, Forrest Gump, The Sixth Sense, Men in Black, Armageddon, Home Alone, Pulp Fiction, Ghost, Terminator 2: Judgment Day, Aladdin, Twister, Toy Story & II, Saving Private Ryan, Pretty Woman, The Matrix, Mission: Impossible, Dances with Wolves, The Mummy, The Bodyguard and Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves.
- Dogme 95 becomes an important European artistic film movement by the end of the decade.
- The movie Titanic becomes a cultural phenomenon throughout the world, and eventually becomes the highest grossing movie of all time grossing over $1.8 billion, worldwide.[9]
Television

TV shows, mostly sitcoms, were popular with the American audience. Series like Friends and Seinfeld turned TV in new directions and defined the humor of the decade.
Beverly Hills, 90210 ran throughout the entire decade from 1990–2000 and established the teen soap genre paving the way for Dawson's Creek, Felicity, and other shows that are currently airing today. The show was then remade and renamed simply '90210' and premiered in 2008.
Baywatch, a hugely popular TV show that dominated throughout the nineties, became the most watched TV show in history and made huge impact on pop culture.
The U.S. animated television comedy series The Simpsons becomes a huge domestic and international success in the 1990s. The show has made it beyond 2010 and has become an institution of pop culture, and has spawned the animated sitcom genre, inspiring racier shows such as Beavis and Butthead along with South Park and Family Guy, the latter two of which began in the late 1990s and lasted past 2009.
Anime became very popular. Shows like Sailor Moon, Dragonball Z, Pokemon led people into embracing the Japanese culture around the world.
Reality television began on MTV; this would grow in importance in the western world in the 2000s.
Music

- The 1990s were a decade of many diverse scenes in music, however they are perhaps best known for teen pop and electronic dance music, and for being the decade that hip hop and alternative rock became mainstream.
- Grunge music, and the culture marketed around it, born out of the Pacific Northwest American states of Washington and Oregon, becomes a fad in 1991 with the success of Nirvana and similar groups following. The style would come to be strongly associated with the 1990s by the 2000s.
- In the UK the uniquely British alternative rock Britpop genre emerged as part of the more general Cool Britannia culture. The Britrock band Oasis was formed in 1991. Female icons of Cool Britannia, the "Spice Girls", manage to do what the britpop boys couldn't manage and break America, taking the world by storm and becoming the most commercially successful British Group since The Beatles[10][11]. Their impact brings about a widespread invasion of teen pop acts around the world[12][13] such as Britney Spears, 'N Sync, Backstreet Boys and Hanson who come to prominence into the new millennium.
- The Tibetan Freedom Concert brings 120,000 people together in the interest of increased human rights and autonomy for Tibet from China.
- Freddie Mercury, Kurt Cobain, Tupac Shakur, and The Notorious B.I.G. are the most publicized music-related deaths of the decade, in 1991, 1994, 1996, and 1997 respectively.
- Controversy surrounded The Prodigy with the release of the track 'Smack My Bitch Up'. The National organization for Women(NOW) claimed that the track was "advocating violence against women" due to the lyrics of that song. The music video (directed by Jonas Åkerlund) featured a first-person POV of someone going clubbing, indulging in large amounts of drugs and alcohol, getting into fist fights with men, abusing women and picking up a prostitute. At the end of the video the camera pans over to a mirror, revealing the subject to be a woman.
- The rave movement that emerged in the late 1980s rises incredibly in the early to mid 1990s, and continues to exist as late as 2010.
Computer and video games

- Popular notable video games of the 1990s include: Super Mario World, Super Mario 64, The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time, Gran Turismo, Mario Kart 64, Half-Life, Super Mario Kart, Tomb Raider series, Metal Gear series, Final Fantasy series, Crash Bandicoot series, Street Fighter II, Myst, Commander Keen series, Test Drive series, Monkey Island, Civilization, Dune series, Mortal Kombat series, Warcraft series, Rayman series, Duke Nukem 3D, Tekken series, StarCraft, Unreal series and Counter-Strike.
- 3-D graphics become the standard by end of decade. Although FPSs had long since seen the transition to full 3D, other genres begin to copy this trend by the end of the decade.
- Lara Croft became a video game sex symbol, becoming a recognizable figure in the entertainment industry throughout the late 1990s.
- The console wars, primarily between Sega (Mega Drive, marketed as the Sega Genesis in North America, introduced in 1988) and Nintendo (Super NES, introduced in 1990), sees the entrance of Sony with the PlayStation in 1994, which becomes the first successful CD-based console (as opposed to cartridges). By the end of the decade, Sega's hold on the market becomes tenuous after the end of the Saturn in 1998 and the Dreamcast in 2001.
- Mario as Nintendo's mascot finds a rival in Sega's Sonic the Hedgehog with the release of the original game on the Genesis in 1991.
- Arcade games rapidly decrease in popularity.[14]
- Fighting games like Capcom's Street Fighter II, Sega's futuristic Virtua Fighter, and especially the more violent Mortal Kombat from Acclaim prompted the video game industry to adopt a game rating system, and hundreds of knock-offs are widely popular in mid-to-late 1990s.

- Sony's PlayStation becomes the top selling game console and changes the standard media storage type from cartridges to compact discs in consoles.
- Doom (1993) bursts onto the world scene and instantly popularizes the FPS genre, and even how games are played, as Doom is among the first games to feature multiplayer capabilities. It is not until Quake (1996), however, that game developers begin to take multiplayer features into serious consideration when making games. Half-Life (1998) features the next evolutionary step in the genre with continual progression of the game (no levels in the traditional sense) and an entirely in-person view, and becomes one of the most popular computer games in history.
- The real-time strategy (RTS) genre is introduced in 1992 with the release of Dune II. Warcraft: Orcs & Humans (1994) popularizes the genre, with Command & Conquer and Warcraft II: Tides of Darkness in 1995 setting up the first major real-time strategy competition and popularizing multiplayer capabilities in RTS games. StarCraft in 1998 becomes the second best-selling computer game of all time. It remains among the most popular multiplayer RTS games to this day, especially in South Korea. Homeworld in 1999 becomes the first successful 3d RTS game. The rise of the RTS genre is often credited with the fall of the turn-based strategy (TBS) genre, popularized with Civilization in 1991.
- Final Fantasy first debuted (in North America) in 1990 for the NES, and remains among the most popular video game franchises, with 12 new titles to date, with another in development, plus numerous spin-offs, sequels, movies and related titles. Final Fantasy VII, released in 1997, especially popularized the series.
- Zelda continues its massive popularity with a series of groundbreaking releases, including A Link to the Past in 1991 and Ocarina of Time in 1998, both of which are considered some of the greatest and most influential games of all time.[15][16]
- Massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs) see their entrance into the computer game world with Ultima Online in 1997, although they don't gain widespread popularity until EverQuest and Asheron's Call in 1999. MMORPGs go on to become among the most popular genres in the 2000s.
- Pokémon entered the world scene with the release of the original Game Boy Pokémon Red and Pokémon Green games in Japan in 1996, later changed to Pokémon Red and Pokémon Blue for worldwide release in 1998. It soon becomes popular in the U.S. spurring the term Pokémania and is adapted into a popular children's anime series and trading card game, among other media forms.
- Resident Evil is released in 1996 and becomes the most popular survival-horror series in video gaming well into the next decade.
Sports
- 21-year-old golfer Tiger Woods wins the Masters Tournament by a record 12 strokes; becoming both the youngest and the first American of multiracial descent to win the Masters.
- Major League Baseball players went on strike in August 12, 1994, thus ended the season, canceled the World Series the first time in 90 years, and went on until March 29, 1995 when players and team owners in agreement.
- American NBA Basketball player Michael Jordan becomes a major sports and pop culture icon idolized by millions worldwide. He revolutionizes sports marketing through deals with companies such as Gatorade, Hanes, McDonald's and Nike.
- American cyclist Lance Armstrong wins his first Tour de France in 1999, less than two years after battling testicular cancer.
- American boxer George Foreman regains the world Heavyweight title, twenty years after losing it to Muhammad Ali, by knocking out Michael Moorer in ten rounds in 1994, also becoming the oldest boxer to win the world Heavyweight title.
Architecture

- Petronas Twin Towers becomes the tallest man-made structure ever built after it officially opened on August 31, 1999.
Art
Literature
Fashion

- The Rachel, Jennifer Aniston's hairstyle on the hit show Friends, becomes a cultural phenomenon with millions of women copying it worldwide.
- Leonardo DiCaprio popularises the long fringe and cropped back hairstyle in fashion and culture amongst teenage boys in the late 1990s after the success of the movies, Titanic and Romeo + Juliet.
- The model 1300 Wonderbra style has a resurgence of popularity in Europe in 1992 which kicks off a multinational media sensation, the 1994 re-introduction of "The Wonderbra" brand, and a spike in push-up, plunge bras around the world.
- Additional fashion trends of the 1990s include the Tamagotchi ,Rollerblades, Pogs and Dr. Martens shoes.
Miscellaneous
- Feminism is one of the core defining elements of 1990s pop culture, and the overall image of the decade. You go, girl! was a popular phrase in the media as feminism became more widely accepted and publicized with the Spice Girls, the WNBA, women's boxing, Girl Power, Sex and the City, and others showcasing modern femininity and challenged the problem of sexism. Girl Power and feminism were not considered as "cool" in the 2000s, though its legacy lasted in the female-dominated culture it ushered in.
- Anime and manga become popular and known in the mainstream. Previously restricted to fringe or niche circles within existing science fiction and comic book fandom, anime and manga fandom in the west begins expanding and organizing its own fan conventions such as Otakon and Katsucon. Such conventions have continued to expand covering gaming, cosplay, and J-pop as well as other elements of Japanese and east Asian culture in general.
People
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2010) |
World leaders


- George H. W. Bush (United States)
- Bill Clinton (United States)
- Mikhail Gorbachev (Soviet Union)
- Boris Yeltsin (Russia)
- Nelson Mandela (South Africa)
- Saddam Hussein (Iraq)
- François Mitterrand (France)
- Jacques Chirac (France)
- Yitzhak Rabin (Israel)
- Benjamin Netanyahu (Israel)
- Ehud Barak (Israel)
- Yasser Arafat (Palestinian Authority)
- John Major (United Kingdom)
- Tony Blair (United Kingdom)
- John Howard (Australia)
- Gerhard Schröder (Germany)
- Helmut Kohl (Germany)
- Mohammad Khatami (Iran)
- Deng Xiaoping (China)
- Jiang Zemin (China)
- Akihito (Japan)
- P. V. Narasimha Rao (India)
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee (India)
Entertainers
Musicians
|
|
Bands
|
|
Sports figures
See also
- 1990s in music
- 1990s in fashion
- 1990s in television
- 1990s in science and technology
- 1990s in video gaming
- 1990s in literature
- Generation X were young adults or teenagers during this decade.
- Generation Y were children, pre-teens or born in this decade.
- 20th century
References
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2004). The Roaring Nineties. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 9780393326185.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org, Second Chechnya War - 1999-???
- ^ Des Forges, Alison (1999). Leave None to Tell the Story: Genocide in Rwanda. Human Rights Watch. ISBN 1-56432-171-1. Retrieved 2007-01-12.
- ^ See, e.g., Rwanda: How the genocide happened, BBC, April 1, 2004, which gives an estimate of 800,000, and OAU sets inquiry into Rwanda genocide, Africa Recovery, Vol. 12 1#1 (August 1998), page 4, which estimates the number at between 500,000 and 1,000,000. 7 out of every 10 Tutsis were killed.
- ^ a b Sorin Antohi and Vladimir Tismăneanu, "Independence Reborn and the Demons of the Velvet Revolution" in Between Past and Future: The Revolutions of 1989 and Their Aftermath, Central European University Press. ISBN 963-9116-71-8. p.85.
- ^ Error in Webarchive template: Empty url.
- ^ "The Urban Institute | Welfare Reform: Ten Years Later". Archived from the original on 2009-05-08. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Grossman, Lev (31 March 2003). "How the Web Was Spun". Time Magazine. Archived from the original on 18 July 2009. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
Berners-Lee's computer faithfully logged the exact second the site was launched: 2:56:20 p.m., Aug. 6, 1991.
- ^ "Titanic (1997)". Archived from the original on 2009-05-27. Retrieved 2009-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.bbc.co.uk/pressoffice/pressreleases/stories/2007/10_october/19/spice.shtml
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/may/31/newsid_2494000/2494855.stm
- ^ "Teen Pop Music: A Guide". Archived from the original on 2009-09-04. Retrieved 2009-08-26.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://allmusic.com/cg/amg.dll?p=amg&sql=77:7232
- ^ Wolf, Mark J.P. (2008). "Arcade Games of the 1990s and Beyond". The video game explosion: a history from PONG to PlayStation and beyond. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 135. ISBN 031333868X. OCLC 154776597. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
The decline of arcade video games would come back in the 1990s, despite attempts to redefine the arcade experience and attract players back to the arcade.
- ^ "The Greatest Games of All-Time: The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past". GameSpot. 2006-03-17. Retrieved 2007-03-07.
- ^ "The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time (Inducted 2008)". IGN Entertainment, Inc. Archived from the original on 18 July 2009. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
Get past the fact that it is one of the few videogames to ever get a score of 10 on IGN, and you'll be left with a deep, engaging and rewarding tale

