Carbutamide
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Ffffrr (talk | contribs) at 00:00, 6 March 2022 (Importing Wikidata short description: "Chemical compound" (Shortdesc helper)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:00, 6 March 2022 by Ffffrr (talk | contribs) (Importing Wikidata short description: "Chemical compound" (Shortdesc helper))
Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.841 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
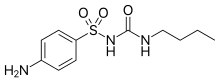
| Formula | C11H17N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 271.33 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Carbutamide (brand name Glucidoral) is an anti-diabetic drug of the sulfonylurea class, developed by Servier.
It is classified as first-generation.[1]
It was patented in 1953 and approved for medical use in 1956.[2]
See also
- Hellmuth Kleinsorge (1920-2001) German medical doctor
References
- ^ Ballagi-Pordány G, Köszeghy A, Koltai MZ, Aranyi Z, Pogátsa G (January 1990). "Divergent cardiac effects of the first and second generation hypoglycemic sulfonylurea compounds". Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 8 (2): 109–14. doi:10.1016/0168-8227(90)90020-T. PMID 2106423.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 449. ISBN 9783527607495.
| Calcium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloride |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Hidden categories:
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- All stub articles
