Commonwealth realm: Difference between revisions
→Religious role of the monarch: remove see also link - wikilink already to Monarchy of Canada within section |
→Historical development: add in Chronology - still being worked on hence tagged with incomplete list - being somewhat bold and happy to discuss if others don't like |
||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
The principle of fully separate and equal realms was followed in all future grants of independence. Other realms achieved independence through the "[[Wind of Change (speech)|winds of change]]" that swept through Africa in the 1960s, the collapse of the [[Federation of the West Indies]] in 1961, or at later dates. The latest country to become a Commonwealth realm was [[Saint Kitts and Nevis]], upon independence in 1983. All these realms had previously been British colonies. When [[Papua New Guinea]] became independent of Australia in 1975, this was the first (and so far the last) time a Commonwealth realm was created that had never been made up of British colonies in its entirety. Most of these realms became independent with full constitutional autonomy, although in some cases certain links to the United Kingdom were voluntarily retained, such as the right of appeal to the [[Privy Council of the United Kingdom]]. |
The principle of fully separate and equal realms was followed in all future grants of independence. Other realms achieved independence through the "[[Wind of Change (speech)|winds of change]]" that swept through Africa in the 1960s, the collapse of the [[Federation of the West Indies]] in 1961, or at later dates. The latest country to become a Commonwealth realm was [[Saint Kitts and Nevis]], upon independence in 1983. All these realms had previously been British colonies. When [[Papua New Guinea]] became independent of Australia in 1975, this was the first (and so far the last) time a Commonwealth realm was created that had never been made up of British colonies in its entirety. Most of these realms became independent with full constitutional autonomy, although in some cases certain links to the United Kingdom were voluntarily retained, such as the right of appeal to the [[Privy Council of the United Kingdom]]. |
||
===Chronology=== |
|||
{{incompletelist}} |
|||
{| border="2" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse" |
|||
|- bgcolor="#efefef" |
|||
! Monarch!! Reign |
|||
|- bgcolor="#ffddaa" |
|||
|colspan="9" align="center"|'''[[House of Hanover]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[Victoria of the United Kingdom|Victoria]]<ref>[http://www.heraldry.ca/misc/coatArmsCanada.htm The Canadian Heraldry Society states: "...Her Majesty, Queen Victoria, [was] Queen of Canada and all her other realms. Queen Victoria was the first Monarch of the confederation of provinces that became known as the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867."</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Queen Victoria bw.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[6 February]] [[1840]] - [[Treaty of Waitangi]] signed by representatives of the British Crown and various [[Māori]] chiefs from the northern [[North Island]] of [[New Zealand]]. The Treaty established a British governor in New Zealand, recognised Māori ownership of their lands and other properties, and gave Māori the rights of British subjects. The first of the three articles of the English version grants the [[British monarchy|Queen of the United Kingdom]] sovereignty over New Zealand. The English and Māori versions differ. This has made it difficult to interpret the Treaty and continues to undermine its effect. One of the critical differences revolves around the interpretation of the Māori words; Kāwanatanga (literally, governorship) which is ceded to the Queen in the first article, and [[Rangatiratanga]] (literally chieftainship) which is retained by the chiefs in the second article. Few Māori had good understanding of either sovereignty or 'governorship' and thus it has been questioned whether Māori fully understood that they were ceding sovereignty to the British Crown. |
|||
*? date - Signed [[Constitution Act, 1867|British North America Act, 1867]] and proclaimed [[Ottawa]] as Canada's capital city |
|||
*[[July 1]], [[1867]] - [[Canadian Confederation]], at which time Canada was deemed to have become a kingdom in its own right |
|||
*1871 - [[Belize]] made a [[Crown colony]] of [[British Honduras]] |
|||
*[[January 1]] [[1901]] - Victoria became the first monarch to reign over the [[Commonwealth of Australia]] when the [[Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act 1900]] came into force |
|||
*[[January 22]], [[1901]] - death |
|||
|- bgcolor="#ffddaa" |
|||
|colspan="9" align="center"|'''[[Saxe-Coburg and Gotha#House|House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[Edward VII of the United Kingdom|Edward VII]] [[Image:Edward VII in coronation robes.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[January 22]] [[1901]] - succeeded to the throne |
|||
*[[9 September]] [[1907]] - The proclamation of the [[Dominion of New Zealand]] by Edward VII brought the [[Monarchy of New Zealand]] into being. Originally, these monarchs reigned in their right as British sovereigns, but the sovereign's New Zealand role is now completely separate from the same person's role as monarch of her other Commonwealth realms. |
|||
*[[May 6]] [[1910]] - died |
|||
|- bgcolor="#ffddaa" |
|||
|colspan="9" align="center"|'''House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha''' (1910-17), then '''[[House of Windsor]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[George V of the United Kingdom|George V]] [[Image:George V of the united Kingdom.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[May 6]], [[1910]] |
|||
*1921 - [[Royal Arms of Canada]] proclaimed |
|||
*1926 - At the [[Imperial Conferences|Imperial Conference]], the governments of the Dominions and of the [[United Kingdom]] endorsed the [[Balfour Declaration, 1926|Balfour Declaration of 1926]], which declared that the Dominions were autonomous members of the British Empire, equal to each other and to the United Kingdom. |
|||
*? date - Signed [[Statute of Westminster 1931|Statute of Westminster, 1931]]. The Statute gave legal effect to the Balfour Declaration and other decisions made at the Imperial Conferences. Most importantly, it declared that the [[Parliament of the United Kingdom]] no longer had any legislative authority over the Dominions. The Statute took effect immediately over Canada, South Africa and the [[Irish Free State]]. However, Australia, New Zealand and [[Dominion of Newfoundland|Newfoundland]] had to ratify the Statute through legislation before it would apply to them. Canada also requested certain exemptions from the Statute in regard to the Canadian Constitution. |
|||
**the concept of the state being in a full [[personal union]] with the United Kingdom and other [[Commonwealth realm]]s did not emerge until the passage of the Statute of Westminster. <ref>Zines, ''The High Court and the Constitution'', 4th ed. (1997) at 314: "The Queen as monarch of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand is in a position resembling that of the King of Scotland and of England between 1603 and 1707 when two independent countries had a common sovereign"; the relationship between England and Scotland during those years is described as a [[personal union]].</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title = The Status of the British Commonwealth in International Law|author = P. E. Corbett|journal = The University of Toronto Law Journal|volume = 3|Number = 2|date = 1940|pages 348-359|url = http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0042-0220%281940%293%3A2%3C348%3ATSOTBC%3E2.0.CO%3B2-J}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title = The End of Dominion Status|author = F. R. Scott|journal = The American Journal of International Law|volume = 38|number = 1|date = January 1944|pages = 34-49|url = http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9300%28194401%2938%3A1%3C34%3ATEODS%3E2.0.CO%3B2-B}}</ref><ref>[http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/cases/cth/HCA/1999/30.html R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999] HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]</ref> Since that time, the Canadian Crown has been recognized as legally distinct from the crowns of the other [[Commonwealth realm]]s, meaning that, for example, Canada has a distinct national monarch.<ref>The [[Court of Appeal of England and Wales|English Court of Appeal]] ruled in 1982, while "there is only one person who is the Sovereign within the British Commonwealth... in matters of law and government the Queen of the United Kingdom, for example, is entirely independent and distinct from the Queen of Canada." [http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/cases/cth/HCA/1999/30.html R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999] HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"| |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[January 20]], [[1936]] - dies |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[Edward VIII of the United Kingdom|Edward VIII]] [[Image:A030596.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[January 20]], [[1936]] - succeeds the throne |
|||
*[[December 11]], [[1936]] - signs an instrument of [[Edward VIII abdication crisis|abdication]]. The British Parliament passes [[His Majesty's Declaration of Abdication Act 1936]] on behalf of the UK, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. The King performs his last act as sovereign by giving [[royal assent]] to the Act. |
|||
*[[December 12]] - [[Executive Authority (External Relations) Act 1936]] passed by Irish Free State which declared that the abdication took effect on December 12th |
|||
*1937 - [[Succession to the Throne Act 1937]] : Act of the Canadian Parliament that ratified Canadian consent to His Majesty's Declaration of Abdication Act 1936<ref>{{cite web|url = http://www.sfu.ca/~aheard/324/Independence.html#_ednref77 | title = Canadian Independence| date = 1990 | last = Heard | first = Andrew | publisher = Simon Fraser University|accessdate = 2008-04-10| quote = The legislative confusion which followed the abdication of King Edward VIII in December of 1936 was an important step in the evolution of Dominion status, because it demonstrated that the Imperial Crown could be an entirely divisible entity in law. All the Dominion governments had been warned that the King was about to abdicate the throne; indeed, the Canadian government sent a cable urging him to put his duty as King ahead of his desire to abdicate and marry Wallace Simpson. The news that the Instrument of Abdication had been signed was cabled to all the Dominion governments. Australia's Parliament was in session at the time and gave its formal assent to British legislation, as required by the convention recited in the preamble of the Statute of Westminster. The governments of New Zealand, Canada, and South Africa gave their consents as their Parliaments were not in session; the British Parliament passed an Abdication Act on the following day, December 11th, that gave legal effect to the Instrument of Abdication and brought George VI to the throne.<br/> The divisibility of the Crown became a matter of law in some jurisdictions, however, through the actions of two Dominion Parliaments. The Irish Free State passed an Act declaring that the abdication took effect on December 12th, while the South African Parliament later passed an Act that declared that the abdication had taken effect in South Africa on December 10th. When the Canadian Parliament met in the new year, it passed an Act giving its assent to the British legislation. The assumption of this legislative authority was legally redundant because the British Act was undoubtedly already in force in Canada; it complied with the requirements of s.4 of the Statute of Westminster by containing a reference to the fact that it was being enacted with the request and consent of Canada, and a proclamation announcing that the accession to the Throne had also been duly made by the Governor General. But as Clokie observed about the Canadian Act, "Whether necessary or not, it was clearly designed to demonstrate Canada's equality with Britain in the British Commonwealth and to display the Canadian aspect of the monarchy". Even though the courts in South Africa and the Irish Free State would recognise the divisibility of the Crown and the authority of their own laws on the succession, these measures had no practical effect outside those two Dominions. As far as Canada, New Zealand, and Australia were concerned, the Crown remained a legal unity since their new monarch came to the throne through British legislation.}}</ref> |
|||
*Maintained a private [[ranch]] in Canada |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[George VI of the United Kingdom|George VI]] [[Image:King George VI of England, formal photo portrait, circa 1940-1946.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[December 11]], [[1936]] - Prince Albert, Duke of York, becomes King |
|||
*? date - First reigning monarch to enter Canada. Coined the phrase "King of Canada" |
|||
*[[9 October]] [[1942]] - [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942]] receives assent by the Australian Governor General, Lord Gowrie: the act formally adopted the Statute of Westminster 1931. The act stated it was considered to have had effect since [[3 September]] [[1939]], the beginning of [[World War II]]. |
|||
*[[25 November]] [[1947]] - New Zealand passed the [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1947]] ratifying the 1931 Statute of Westminster. |
|||
*[[21 December]] [[1948]] - [[Republic of Ireland Act 1948]] signed by the president of Ireland |
|||
*[[18 April]] [[1949]] - date of effect of the [[Republic of Ireland Act 1948]] which vested the powers possessed by the king in the president of Ireland. It abolished the remaining roles of the [[Monarchy of Ireland|King of Ireland]] (a king shared with the United Kingdom and other Dominions of the Commonwealth) in the government of the state. |
|||
*1949 - [[Ireland Act 1949]] - British Act of Parliament dealing with the consequences of Ireland becoming a republic: main provision of the Act was the acceptance that the declaration of a Republic of Ireland had meant that that state had "ceased to be part...of His Majesty's dominions" |
|||
*[[February 6]], [[1952]] - dies |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center"|[[Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom|Elizabeth II]] [[Image:Queen of canada wob.jpg|100px]] |
|||
| align="left"| |
|||
*[[February 6]], [[1952]] - Elizabeth was [[Proclamation of accession of Elizabeth II|proclaimed Queen]] in Canada first, by the [[Queen's Privy Council for Canada]].<ref>{{cite web| url = http://archives.cbc.ca/IDD-1-69-70/life_society/new_queen/| title = Canada's New Queen| publisher = [[Canadian Broadcasting Corporation|CBC]]| accessdaymonth = 22 August| accessyear = 2007}}</ref> Her British proclamation was read at [[St. James's Palace]] the following day. |
|||
*First to be officially titled separately as Queen of Canada<ref>http://canada.gc.ca/howgoc/queen/quind_e.html 1</ref> |
|||
*[[2 June]] [[1953]] - Elizabeth II's [[Coronation of the British monarch|coronation]] took place in [[Westminster Abbey]]. Her coronation gown, commissioned from [[Norman Hartnell]], was embroidered with the floral emblems of the countries of the Commonwealth: the [[Tudor rose]] of [[England]], the Scots [[thistle]], the Welsh [[leek]], [[shamrock]] of Ireland, [[Acacia|wattle]] of Australia, the [[maple leaf]] of Canada, the New Zealand [[fern]], South Africa's [[protea]], two [[Nelumbo nucifera|lotus flower]]s for [[India]] and Ceylon, and Pakistan's [[wheat]], [[cotton]] and [[jute]].<ref>[http://www.nga.gov.au/ByAppointment/ National Gallery of Australia: By Appointment: Norman Hartnell's sample for the Coronation dress of Queen Elizabeth II]</ref> |
|||
*1953-54 - the Queen and Prince Philip made a six-month, around the world tour, becoming the first monarch to circumnavigate the globe. She also became the first reigning monarch of Australia, New Zealand and Fiji to visit those nations. |
|||
*October 1957 - she became the first [[Monarchy in Canada|Canadian monarch]] to open a session of that nation's [[Parliament of Canada|parliament]]. She made another [[state visit]] to the United States, as [[Monarchy in Canada|Queen of Canada]], hosting the return dinner for [[President of the United States|President]] [[Dwight D. Eisenhower]] at the [[Canadian Embassy in Washington]]. |
|||
*February 1961 - she visited [[Ankara]] with [[Cemal Gursel]], and later toured [[India]], [[Iran]], [[Pakistan]] and [[Nepal]] for the first time. |
|||
*[[30 November]] [[1966]] - [[Monarchy of Barbados]] established when the country was proclaimed fully independent, via constitutional patriation, by the Queen. |
|||
*[[10 july]] [[1973]] - [[Monarchy of the Bahamas]] formed when Bahamians full independence within the Commonwealth of Nations. |
|||
*[[1 August]] [[1976]] - [[Trinidad and Tobago]] ceased to be a Commonwealth realm and became a [[Commonwealth republic]] through constitutional amendment. |
|||
*[[21 September]] [[1981]] - [[Monarchy of Belize]] established when the country was granted its independence from the United Kingdom by Queen Elizabeth II to form Belize as a kingdom in its own right. |
|||
*[[1 November]] [[1981]] - [[Monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda]] established when the country was proclaimed fully independent, via constitutional patriation, by the Queen. |
|||
* – Present |
|||
|} |
|||
==Former Commonwealth realms/dominions== |
==Former Commonwealth realms/dominions== |
||
Revision as of 06:44, 11 April 2008
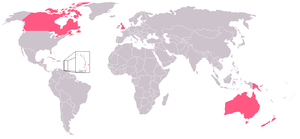
A Commonwealth realm is any one of 16 sovereign states within the Commonwealth of Nations with Elizabeth II as their respective monarch.[1] These countries, with a combined area totalling 18.8 million km² (excluding Antarctic claims), and with a combined population of 131 million,[2] are independent kingdoms in personal union,[3][4][5][6] with the one sovereign being separately and equally monarch of each state.[7] While the term Dominion has never been officially revoked, it has been replaced by use of the word realm, beginning in the 1950s, so as to reflect the relationship of equality amongst all 16 countries.
Commonwealth realms are each members of, but distinguished from, the Commonwealth of Nations, which is an organisation of mostly former British colonies.[1] Within the Commonwealth, there is no difference in status between the Commonwealth realms and other Commonwealth members.
Current Commonwealth realms
Note: The table can be sorted alphabetically or chronologically using the "><" icon.
| Flag | Country | Monarchy | Date1 | Queen's Title | Royal Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | Monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda | 1981 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Antigua and Barbuda and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | None | |
| Australia | Monarchy of Australia | 1942 2 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Australia and Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | ||
| The Bahamas | Monarchy of The Bahamas | 1973 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of the Commonwealth of the Bahamas and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | None | |
| Barbados | Monarchy of Barbados | 1966 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Barbados and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | ||
| Belize | Monarchy of Belize | 1981 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Belize and of Her Other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Canada | Monarchy of Canada | 1931 | In English: Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, of the United Kingdom, Canada and Her other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith.
In French: Elizabeth Deux, par la grâce de Dieu Reine du Royaume-Uni, du Canada et de ses autres royaumes et territoires, Chef du Commonwealth, Défenseur de la Foi.[8] |
||
| Grenada | Monarchy of Grenada | 1974 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and of Grenada and Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Jamaica | Monarchy of Jamaica | 1962 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Jamaica and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | ||
| New Zealand | Monarchy of New Zealand | 1947 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of New Zealand and Her Other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith | File:Royal Standard of New Zealand.svg | |
| Papua New Guinea | Monarchy of Papua New Guinea | 1975 | Elizabeth the Second, Queen of Papua New Guinea and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | Monarchy of Saint Kitts and Nevis | 1983 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Christopher and Nevis and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Saint Lucia | Monarchy of Saint Lucia | 1979 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Lucia and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Monarchy of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1979 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Solomon Islands | Monarchy of the Solomon Islands | 1978 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of the Solomon Islands and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| Tuvalu | Monarchy of Tuvalu | 1978 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Tuvalu and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| United Kingdom | Monarchy of the United Kingdom | n/a3 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and of Her other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith |
2Adoption of Statute of Westminster was declared retroactive to 1939.
3Not applicable to the United Kingdom as it was the realm from which other realms have become independent.
Under the 1981 Cook Islands Constitution, the Queen in Right of New Zealand is head of state, but any change in the succession made by New Zealand would have no effect in the Cook Islands unless separately ratified there. This effectively makes the Realm of New Zealand a personal union of the Cook Islands and New Zealand.
Relationship of the realms
Any alteration by the United Kingdom Parliament in the law touching the succession to the throne would, except perhaps in the case of Papua New Guinea, be ineffective to alter the succession to the throne in respect of, and in accordance with the law of, any other independent member of the Commonwealth which was within the Queen’s realms at the time of such alteration. Therefore it is more than mere constitutional convention that requires that the assent of the Parliament of each member of the Commonwealth within the Queen’s realms be obtained in respect of any such alteration in the law.
— Monarchist League of New Zealand Chairman, Professor Noel Cox
The Commonwealth realms are sovereign states, united only in the voluntary and symmetric sharing of the institution of the monarchy,[9] the succession, and the Queen herself, in a symmetrical fashion; this means the Commonwealth realms are in personal union with one another.[10][11][12][13] The United Kingdom no longer holds any legislative power over any country besides itself, although some countries continue to use the British Judicial Committee of the Privy Council as part of their judiciary.
The Crown in the Commonwealth realms
The personal union of these sovereign states has created the scenario wherein the Crown has both a separate and a shared character, being an institution that operates separately within the jurisdiction of each Commonwealth realm, with the Queen in right of each realm being a distinct legal person, acting on the advice only of the government of that state. The Crown is thus unitary through its shared character, but divided in its jurisdictional operation, meaning that in different contexts, Crown may mean the Crown as shared or the Crown in each realm considered separately.
The monarchy is therefore no longer an exclusively British institution, although it may often be called British for historical reasons, for convenience, or for political (usually republican) purposes.[14] One Canadian constitutional scholar, Dr. Richard Toporoski, stated on this: "I am perfectly prepared to concede, even happily affirm, that the British Crown no longer exists in Canada, but that is because legal reality indicates to me that in one sense, the British Crown no longer exists in Britain: the Crown transcends Britain just as much as it does Canada. One can therefore speak of 'the British Crown' or 'the Canadian Crown' or indeed the 'Barbadian' or 'Tuvaluan' Crown, but what one will mean by the term is the Crown acting or expressing itself within the context of that particular jurisdiction".[15] Expressing this concept, through the proclamation of Elizabeth II's new titles in 1952, in each realm the Queen is known by the title appropriate for that realm; for example, in Barbados she is known as "Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, Queen of Barbados," or, simply, the Queen of Barbados.
As a consequence of this relationship, any alterations to the line of succession to the throne must be approved by the parliaments of all the realms in order to guarantee continuity of a single monarch.[16] For example, there have been suggestions of removing the religious requirements from the Act of Settlement, which currently defines the succession. In practice, since each realm is a sovereign state, this requires the voluntary cooperation of all 16 of the realms. Alternatively, a realm could choose to end its participation in the personal union.
In realms other than the United Kingdom, the Queen normally exercises only those powers related to her appointment of a Governor-General, usually on the advice of the prime minister of the realm concerned; in the Solomon Islands and Tuvalu the Prime Minister is required to consult the legislature in confidence; in Papua New Guinea the Governor-General is nominated to the Queen by parliamentary vote. In some realms certain other powers are reserved exclusively for her, such as the appointment of extra senators to the Canadian Senate. The monarch is also represented by a Governor in each state of Australia, by a Lieutenant Governor in each province of Canada, and by a Queen's Representative in the Cook Islands. In these cases, she is represented in her role as Queen in right of Australia, Canada, and New Zealand respectively. Within the United Kingdom, the Queen appoints Counsellors of State to perform her duties in her absence. These officials exercise almost all the powers of the constitutional monarch with mostly symbolic, figurehead duties, but they also have reserve powers, called the Royal Prerogative.
From a cultural standpoint, the shared nature of the Crown is less clear. In all realms, the sovereign's name and image continue to play a prominent role in political institutions and symbols. For example, her effigy usually appears on coins and banknotes,[citation needed] and an oath of allegiance to the Queen is usually required from politicians, judges, and new citizens. Some argue, however, that the Crown within their particular country remains essentially British and primarily of the United Kingdom, whereas others emphasise the Crown as a shared link between the Commonwealth realms, with the Crown in right of their own nation as having specific domestic characteristics.
Monarch's role in the realms
Though the Queen's constitutional position is virtually identical in each realm, she lives in the United Kingdom. Consequently, the constitutional duties she personally exercises as Queen of the UK are in other realms generally performed by a Governor-General, who serves as her representative. The extent to which these duties are explicitly assigned to the Governor-General, rather than the Queen, varies from realm to realm, but the Queen does act personally in right of any of her other realms when required, for example when issuing Letters Patent, or on occasions of significant political importance. Similarly, the monarch usually performs ceremonial duties in the Commonwealth realms to mark historically significant events during visits at least once every five or six years, meaning she is present in a number of her realms outside the UK every other year, or on behalf of those realms abroad. She is also represented at various ceremonial events throughout all the realms by other members of the Royal Family, such as the Queen's children, grandchildren or cousin, who also reside in the United Kingdom, but act on behalf of the government of the particular realm they're in; meaning the Royal Family also has both a unitary and divided nature. The other realms may receive two to three such visits each year.
The personal union arrangement has led to situations where the monarch has a potential or actual conflict of interest. For example, Queen Elizabeth II, in 1984, while on a state visit to Jordan representing the United Kingdom, made a speech expressing opinions of the British government that did not reflect the view of her Australian government. This raised questions in Australia about the propriety of such an action,[17] though the Queen was clearly not representing Australia at that time. Another documented situation was when Elizabeth II was in Latin America to promote British goods at the same time a Canadian ministerial trip to the same area was underway to promote Canadian products. The External Affairs Minister at the time, Mitchell Sharp, stated on the situation: "We couldn't ask Her Majesty to perform the function she was performing for Britain on that Latin American trip because the Queen is never recognized as Queen of Canada, except when she is in Canada."[18] However, the Queen subsequently represented Canada abroad on a number of following occasions.[19][20]
More serious potential conflicts of interest have arisen in connection with matters of war and peace. In 1939, South Africa and Canada declared war a few days after the UK did, so that George VI, as king of all three countries, was, for a few days, simultaneously at war and at peace with Germany. In South Africa the declaration of war had followed an initial declaration of neutrality which had precipitated a political crisis resulting in the replacement of the prime minister. Ireland (as the Irish Free State had renamed itself in 1937), which was arguably a Dominion until 1949, remained neutral throughout the war and the King had to validate the German consul's credentials. (No possibility of such a conflict of interest arose with Australia or New Zealand. The Australian Prime Minister, Robert Menzies stated that, as a result of the British declaration of war, Australia was also at war with Germany; New Zealand made a separate declaration of war which was timed to coincide with the British declaration.)
A more extreme example is the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947. George VI, as head of state of both warring nations, was, in a legal sense, at war with himself. In 1983, during the invasion of Grenada, Queen Elizabeth was the Queen of Grenada while it was being invaded by many other Caribbean countries of which she was also queen. Additionally, the invasion was also opposed by several other countries in which she was queen, notably the United Kingdom, Canada and Belize.
An important role of a governor-general is to act in such situations in a way that avoids placing the sovereign in such a conflict of interest. In practice, this may require a governor-general to take a controversial action entirely on his or her own initiative through the exercise of reserve powers. The Grenada invasion was formally initiated by an invitation for American forces to invade, issued by the Governor-General, Sir Paul Scoon; this action was deliberately undertaken without informing the Queen. Similarly, when Sir John Kerr dismissed the Australian government in 1975, he did not inform the Queen of his intent to do so. This was possible because the Australian constitution invested this power in the Governor-General, not the sovereign. The Governor-General may also have wished to avoid being dismissed by the Queen on the advice of the Australian Prime Minister.
Religious role of the monarch
In some realms, the Queen is the sovereign "by grace of God," and, in the United Kingdom, is the Supreme Governor of the Church of England. The coronation itself takes place within the context of a church service, at Westminster Abbey, imbued with theological, as well as constitutional, meaning. In some realms, the Queen retains the ancient title Fidei Defensor, a title first granted in 1521 by Pope Leo X to King Henry VIII, prior to the Reformation. Most other Commonwealth nations have removed those words from the Queen's title.[21]
The Church of England remains the established church in England; archbishops and bishops are formally appointed by the British monarch and sit in the House of Lords as Lords Spiritual. In practice, the monarch delegates authority in the Church of England to the Archbishop of Canterbury. Certain churches (known as Royal Peculiars) have royal patronage, and are outside the normal diocesan administrative structures; the best-known example is Westminster Abbey. There are six royal chapels outside of the UK.
The role of the sovereign differs considerably in the other three Home Nations of the United Kingdom. In Scotland, the Church of Scotland, with a Presbyterian system of church government, is recognised in law as the "national church" in which the Queen is an ordinary member. Her first act as monarch was to swear to uphold and protect the reformed church in Scotland; a similar oath for England had to wait for the coronation. The Queen has attended the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland on several occasions, most recently in 1977 and 2002, although, in most years, she appoints a Lord High Commissioner to represent her. Unusually for the Church of Scotland, Glasgow Cathedral and Dunblane Cathedral are both owned by the Crown. The Queen also appoints her own Chaplains from both the Church of England and the Church of Scotland.
In Wales, Northern Ireland, and the other realms, there is no official religion established by law. The Church in Wales and the Church of Ireland were both disestablished, in 1920 and 1871 respectively. Though Canadian coins are minted with the inscription D.G. Regina (Queen by the Grace of God) around her portrait, and her Canadian title includes the phrase "Defender of the Faith", Elizabeth II, as Queen of Canada, plays no religious role in the country.
Royal family
As with the sovereign, a single royal family is shared by the Commonwealth realms. Though there is no strict legal or formal definition of who is or is not a member of the Royal Family,[22] the Royal Family is loosely defined as the extended family of the monarch. The group is most commonly referred to as the British Royal Family, for reasons historical, political, and of convenience. The casual use of this term, however, outside of the United Kingdom, can conflict with official national titles, such as in Canada.[23]
The Queen and other members of the Royal Family regularly perform public duties in the sixteen realms. As the Crown within these countries is a legally separate entity, official activities of the Royal Family are funded in these countries individually, through the ordinary legislative budgeting process. Members of the Royal Family each engage in hundreds of public engagements yearly, as formally recorded in the Court Circular, to honour, encourage and learn about the achievements or endeavours of individuals, institutions and enterprises in a variety of areas of life. As representatives of the Queen, they often also join the nation in commemorating historical events, holidays, celebratory and tragic occurrences. They also sponsor or participate in numerous charitable, cultural and social activities. Their work draws public attention to amicable relations within and between the Commonwealth and other nations. Their presence, activities and traditional roles constitute the apex of a modern royal court. Throughout their lives they draw enormous media coverage in the form of photographic, written and televised commentary on their activities, family relationships, rites of passage, personalities, attire, behaviour, and public roles.
- Further information: British Royal Family and Canadian Royal Family
Flags
Flags of the Queen in Commonwealth realms

The Queen uses various royal standards depending on which realm she is in, or acting on behalf of. She has standards for Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Jamaica, Barbados, and the United Kingdom. Each is a banner of the country's coat of arms with the Royal Cypher in the centre, and a crowned E for Elizabeth, save for the UK one, which does not have a cypher. She also has a personal flag as Head of the Commonwealth, which is used for general Commonwealth purposes, or when visiting Commonwealth countries of which she is not head of state. The Queen formerly had flags for Sierra Leone, Mauritius, Malta, and Trinidad and Tobago, but when these countries became republics they became obsolete.
- See also: Royal Standard of Australia, Royal Standard of Barbados, Royal Standard of Canada, Royal Standard of Jamaica, Royal Standard of New Zealand, Royal Standard of Scotland, and Royal Standard of the United Kingdom
Flags of Governors-General
Similarly, each of the Governors-General has a personal flag, all except one featuring a lion passant on top of a royal crown, with the name of the country written in capitals on a scroll underneath. The only one different is that of the Governor General of Canada, in which the lion is not on a crown, but wearing one, and bears a maple leaf in one paw; the scroll is also absent from the Canadian design.
Historical development
Fourteen of the current Commonwealth realms, and all of the former realms, are former British colonies that have evolved into independent countries. The exceptions are the United Kingdom itself and Papua New Guinea, which was formed in 1975 as a union of the former German New Guinea, which had been administered by Australia as an international trusteeship before independence, and the former British New Guinea, which had legally been a British possession, though administered on the United Kingdom's behalf by Australia (as "Papua") since 1905.
The possibility that a British colony might become a new kingdom was first mooted in the 1860s, when it was proposed that the Canadian Confederation might become known as the Kingdom of Canada. In the face of opposition from the Colonial Office and the United States, however, the self-governing confederation created in 1867 became officially known as the Dominion of Canada.
During the latter part of the 19th century, various other colonies became self-governing. At the Imperial Conference of 1907, the Canadian Prime Minister, Wilfrid Laurier, insisted on the need for a formula to differentiate between the crown colonies and the self-governing colonies. The term Dominion, which till this time had applied uniquely to Canada, was extended to cover all self-governing colonies, which at that time included Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, the Cape Colony, Natal and Transvaal. Shortly afterwards, in 1910, the three South African colonies merged with the Orange River Colony to form the Union of South Africa. In 1921, they were joined by the Irish Free State which had unwillingly accepted Dominion status as a condition of concluding peace with the United Kingdom.
Although the Dominions were self-governing, their ability to legislate remained theoretically subject to the British Parliament, and the Monarch of the United Kingdom nominally reigned over them as a single imperial domain, with a governor-general representing the British government in each Dominion; the United Kingdom retained responsibility for their foreign policy and defence. In practice, this unitary model continued to erode. The international role of the Dominions increased as a result of their participation and sacrifices in the First World War, which prompted Robert Borden, Prime Minister of Canada, and Jan Smuts, the South African Minister of Defence, to demand that the Dominions be given full recognition at the Versailles conference as "autonomous nations of an Imperial commonwealth." As a result, the Dominions were separate signatories to the Treaty of Versailles, and obtained seats in the League of Nations, together with India. In 1920, Canada exchanged envoys with the United States, and in 1923 it concluded a treaty in its own right: the Halibut Fisheries Treaty. In 1925, the Dominions refused to be bound by the British signature to the Treaty of Locarno.
The Balfour Declaration of 1926, embodying agreements reached at the 1926 Imperial Conference formally recognised that in practice the Dominions had in recent years evolved into full sovereignty, by declaring that they were autonomous and equal in status to the UK. As a result, each of the governments of the Dominions established a separate and direct relationship with the Monarchy, with the governor-general now acting as a personal representative of the Sovereign. The first result of the new convention was the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927, which implicitly recognised the Irish Free State as separate from the United Kingdom, and the King as king of each Dominion rather than the British king in each Dominion.[verification needed]
The Balfour Declaration was legally implemented in 1931 by the Statute of Westminster, which granted formal legislative independence to the Dominions, with some minor reservations that were in practice never enforced. Canada, the Union of South Africa, and the Irish Free State all immediately obtained legislative independence from the United Kingdom through the statute. In some Dominions, adoption of the Statute was subject to ratification by the Dominion parliament. Australia and New Zealand achieved the same status after their parliaments ratified the Statute, in 1942 and 1947, respectively (Australia's ratification being back-dated to 1939). The statute also covered Newfoundland, but it was never ratified there, and the dominion reverted to colonial status in 1934, eventually joining Canada in 1949.
The Statute of Westminster retained some residual constitutional functions for the Westminster parliament, such as the right to legislate for a Dominion by request, and reserving the right to alter certain aspects of the constitutions of some Dominions. The Irish Free State gradually eroded these rights after 1936, and they finally lapsed there when it formally became a republic in 1949. South Africa became a republic in 1961, which also severed its remaining constitutional links to the United Kingdom. Canada completed this process in 1982 in cooperation with the United Kingdom, and Australia did the same in 1986.
Although the Dominions were now effectively independent kingdoms under a common monarch, and acted increasingly independently of the United Kingdom, their citizens retained a common citizenship, which was defined in terms of allegiance to the Sovereign, without regard to the Dominion of residence. Although Canada (in 1921) and the Irish Free State (in 1935) had passed their own nationality legislation, this concept did not come into question until the Canadian Citizenship Act of 1946. This resulted in an agreement in 1947 that each Commonwealth member was free to pass their own citizenship legislation, so that their citizens only owed allegiance to the Crown in right of his or her own country.
The next stage in the creation of the Commonwealth realms took place with the dissolution of the Indian Empire. The possibility that a colony might be granted independence without even remaining in the Commonwealth was recognised for the first time in the Cripps Declaration of 1942, and the decision by Burma to become an independent republic outside the Commonwealth in 1948 met with no opposition. India and Pakistan became independent as Dominions in order to accelerate the process while keeping them in the Commonwealth, so that they could complete their constitutions as independent nations. Ceylon, which, as a crown colony, was originally promised "fully responsible status within the British Commonwealth of Nations", was formally granted independence as a Dominion to assure it of equal status with India and Pakistan. Ceylon became the last newly independent colony to be entitled a Dominion. Finally, the London Declaration of 1949 established the formula by which republics could remain within the Commonwealth if they so chose. This process finally established the principle that former colonies, once granted independence, whether as republics or under the Crown, were fully equal in status to each other and to the United Kingdom.
As these constitutional developments were taking place, the British government was concerned with how to represent them. At the 1948 Prime Ministers Conference, the term Dominion was avoided in favour of Commonwealth country; at the same time, the term "British Commonwealth" was replaced by "Commonwealth of Nations"; in both cases to avoid the subordination implied by the older terms. The final step was the recognition of each Dominion under the Crown as a Commonwealth realm. This was initiated by the UK's proclamation of the accession of Elizabeth II in 1952, issued at St. James Palace, which declared her to be Queen "of this Realm, and of her other Realms and Territories". It also marked the first inclusion of the title Head of the Commonwealth, and the first reference to "representatives of other Members of the Commonwealth" as among those proclaiming. Following this, the phrase "British Dominions beyond the Seas" was replaced with "her other Realms and Territories" within each of Elizabeth's titles, the latter using the medieval French word "realm" (from royaume) to replace the previous use of Dominion.
In 1953, a Royal Style and Titles Act was passed separately in each of the seven realms then existing except Pakistan, which gave formal recognition to the separateness and the equality of the realms by entitling the Queen as "Queen of [realm] and her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth" (thus overturning the convention laid out on this point in the Statute of Westminster). South Africa and Ceylon (now called Sri Lanka) adopted this formula immediately, while Australia, Canada and New Zealand recognised the monarch as also being queen of the United Kingdom in her title. At her Coronation she took a separate oath for each realm. At the time, it was argued that the whole point was to reflect the established fact that the Crown was now legally divisible and all the realms were legally equal in status. In the Commons debate, Patrick Gordon Walker stated: "We in this country have to abandon... any sense of property in the Crown. The Queen, now, clearly, explicitly and according to title, belongs equally to all her realms and to the Commonwealth as a whole".
The principle of fully separate and equal realms was followed in all future grants of independence. Other realms achieved independence through the "winds of change" that swept through Africa in the 1960s, the collapse of the Federation of the West Indies in 1961, or at later dates. The latest country to become a Commonwealth realm was Saint Kitts and Nevis, upon independence in 1983. All these realms had previously been British colonies. When Papua New Guinea became independent of Australia in 1975, this was the first (and so far the last) time a Commonwealth realm was created that had never been made up of British colonies in its entirety. Most of these realms became independent with full constitutional autonomy, although in some cases certain links to the United Kingdom were voluntarily retained, such as the right of appeal to the Privy Council of the United Kingdom.
Chronology
This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. |
| Monarch | Reign | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| House of Hanover | ||||||||
| Victoria[24] |
| |||||||
| House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha | ||||||||
Edward VII 
|
| |||||||
| House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1910-17), then House of Windsor | ||||||||
George V 
|
| |||||||
| ||||||||
Edward VIII 
|
| |||||||
George VI 
|
| |||||||
Elizabeth II 
|
| |||||||
Former Commonwealth realms/dominions

Following their independence from the United Kingdom, most Commonwealth countries retained the Queen as head of state, although some became independent as republics and others under resident monarchs. With time, some Commonwealth realms moved to become republics, adopting new constitutions or passing constitutional amendments removing the monarch as their head of state, and replacing the Governor-General with an elected or appointed president.
This was especially true in post-colonial Africa, whose leaders, during a time of strong anti-imperialist attitudes, preferred not to continue in a personal union relationship with other nations, opting instead to establish a resident Head of State. Most African realms became republics within a few years of independence. However, they remained within the Commonwealth, following the 1949 London Declaration, which had allowed India to recognise the British Monarch as "Head of the Commonwealth", but not as Head of State. India became a full-fledged Republic within the Commonwealth in 1950. In Pakistan the Monarch continued to reign until 1956, when Pakistan became the first "Islamic Republic", and the last governor-general became the country's first President.
In some former Commonwealth realms, including Malta, Trinidad and Tobago, and Mauritius, the new office of President was (and remains) a post similar in concept to that of the monarch's, including addressing Parliament in a form analogous to a Speech from the Throne. But in others, such as Ghana, Malawi, and Gambia, the Presidency was a politically active executive post, usually first held by the last Prime Minister. In the latter cases not only was the monarchy abolished, but so was the entire Westminster system of parliamentary government as well.
When the white minority government of Rhodesia issued its Unilateral Declaration of Independence in 1965, it affirmed its loyalty to the Queen as 'Queen of Rhodesia', a title to which she had not consented, which she did not accept, and which was not recognised internationally. Her representative in the colony, Governor Sir Humphrey Gibbs, immediately dismissed Prime Minister Ian Smith from office, but this was ignored and an 'Officer Administering the Government' was appointed to perform the Governor's constitutional duties. In 1970, Smith's government declared Rhodesia a republic.
When mention of the United Kingdom was removed from the Queen's titles in Australia in 1973, the government of the state of Queensland, concerned that this action was a first step towards declaring Australia to be a republic, sought to declare her "Queen of Australia, Queensland and her Other Realms and Territories", in order to ensure that the Monarchy would at least be entrenched in Queensland. The action was blocked by the High Court of Australia in the so-called Queen of Queensland case in 1974. However, it highlighted the fact that the relation of the Australian states to the Crown was then independent of the relation of the Commonwealth to the Crown, and was one of the actions which eventually led to the Australia Act of 1986. While no other state has attempted to achieve status as a realm, the possibility was raised by both sides during the debate on the Republican Referendum of 1999 that a decision to make the country a republic might lead to the creation of separate monarchies in one or more of the individual states.
The Queen's position as Queen of Grenada remained unaffected by the overthrow of Prime Minister Eric Gairy by the left-wing Maurice Bishop in 1979, and the Governor-General remained in office. Following the United States-led Operation Urgent Fury in Grenada in October 1983, in the wake of Bishop's violent overthrow, the Governor-General oversaw the holding of new elections and the restoration of parliamentary democracy.
In Fiji, the change to a republic in 1987 came as a result of a military coup, rather than out of any republican sentiment, as Fiji's indigenous chiefs had voluntarily ceded their country to the Crown. Even when Fiji was not a member of the Commonwealth, symbols of the monarchy remained, including the Queen's portrait on banknotes and coins, and, unlike in the United Kingdom, the Queen's Official Birthday is a public holiday. When Fiji was readmitted to the Commonwealth, the issue of reinstating the Queen as Head of State was raised, but not pursued, although the country's Great Council of Chiefs reaffirmed that the Queen was still the country's 'Paramount Chief'.
Other former British colonies, protectorates, mandates and trust territories followed different paths. Burma, Sudan, Cyprus, Zambia, Botswana, South Yemen, Somaliland, Nauru, the Seychelles, Dominica, Kiribati, Zimbabwe, Namibia, and Vanuatu became republics on independence from Britain, and were thus never Commonwealth realms. Nor were Egypt, Jordan, Iraq, Malaya, Zanzibar, the Maldives, Sikkim, Brunei, Tonga, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, the Trucial States, Swaziland, or Lesotho, all of which had their own monarchies, many of them having been British protectorates. Hyderabad, which unsuccessfully attempted to establish its independence in 1947 separately from India, and Kalat, which similarly tried to remain independent from Pakistan, also had their own monarchies.
Other former colonies did not become Commonwealth realms because they became part of larger entities rather than achieving independence. The mandate of Palestine was divided between Israel, Jordan, and Egypt in 1948. Newfoundland, although a dominion covered by the Statute of Westminster, never became a Commonwealth realm because it never ratified the Statute. Instead, it reverted to colonial status in 1934 and became a province of Canada in 1949. The British-administered, former Italian territories of Cyrenaica and Tripolitania merged with the French-administered Fezzan to form the kingdom of Libya in 1951. Eritrea, a former Italian colony administered by the United Kingdom after World War II under the authority of the United Nations, was federated with Ethiopia in 1952. In 1961, Northern Cameroons was absorbed into Nigeria, and Southern Cameroons into Cameroon. In 1963, the crown colonies of Singapore, Sarawak and North Borneo joined Malaya (independent in 1957) to form Malaysia which has its own monarchy. Hong Kong became a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of the People's Republic of China in 1997. Finally, some former colonies that are now independent countries were never Commonwealth realms because they were formed from a successor state, rather than achieving independence from Britain directly. Singapore, which was part of Malaysia until 1965, and Bangladesh, which was East Pakistan until 1971, fall into this category.
The former Commonwealth dominions/realms, the intervals in which they were dominions/realms, and the constitutional reasons why they ceased to be dominions/realms, are as follows:
| Flag1 | Country | From | To | Presidency | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceylon2 | 1948 | 1972 | originally ceremonial, now executive | new constitution | |
| Fiji | 1970 | 1987 | ceremonial | military coup | |
| Gambia | 1965 | 1970 | ceremonial | referendum | |
| Ghana | 1957 | 1960 | ceremonial | referendum | |
| Guyana | 1966 | 1970 | executive | constitutional amendment | |
| India[34] | 1947 | 1950 | ceremonial | new constitution | |
| Ireland[35] | 1931 | 1936/1949 | ceremonial | act of parliament (See also: Irish head of state from 1936-1949). | |
| Kenya | 1963 | 1964 | executive | new constitution | |
| Malawi | 1964 | 1966 | executive | new constitution | |
| Malta | 1964 | 1974 | ceremonial | constitutional amendment | |
| Mauritius | 1968 | 1992 | ceremonial | constitutional amendment | |
| Nigeria | 1960 | 1963 | originally ceremonial, now executive | constitutional amendment | |
| Pakistan | 1947 | 1956 | originally ceremonial, now executive | new constitution | |
| Rhodesia3 | 1965 | 1970 | ceremonial | new constitution | |
| Sierra Leone | 1961 | 1971 | executive | new constitution | |
| South Africa | 1931 | 1961 | originally ceremonial, now executive | referendum | |
| Tanganyika4 | 1961 | 1962 | executive | new constitution | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 1962 | 1976 | ceremonial | new constitution | |
| Uganda | 1962 | 1963 | originally ceremonial, now executive | constitutional amendment |
1Flags are those in use at the time the country was a Commonwealth realm. Ceylonese flag changed in 1951. Rhodesian flag changed in 1968.
2Now Sri Lanka.
3Now Zimbabwe. De facto realm but not de jure, mostly unrecognised internationally, and not a Commonwealth member. See discussion above.
4Now part of Tanzania.
Public perceptions
The evolving crown
Historically, proponents of the monarchy were generally supportive of the institution as a symbolic link to the United Kingdom. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries most politicians in the Dominions supported their economic and military ties with the UK, tended to view British culture and attitudes as favourable, and encouraged their prominence in the newly developing societies. Still, there were difficulties when the United Kingdom's broader imperial policies were enforced at the expense of the interests of various Dominions: for example, the Alaska Boundary Dispute. Maintaining allegiance to the British monarch was thus seen as a natural thing for many residents, and membership in the British Empire, even with a secondary constitutional status, was considered more desirable than independence.
The decline in the imperial mentality led to a gradual process of removing residual legislative and judicial ties and establishing a separate citizenship. Since the 1980s, none of the fifteen other Commonwealth realms has retained any strong constitutional links to the United Kingdom. The perceived role of the Crown has evolved to reflect these changes. Modern proponents of the monarchy outside the United Kingdom downplay the historical "British" aspect of the monarchy, and instead focus on the Queen as head of state of an independent nation. There has thus been a fundamental shift wherein the United Kingdom acting as a cultural connection has diminished and today when each realm is encouraged to think of the Queen as "their own," serving a role independent of any other obligations in other countries, yet still serving as a personal link to countries with a shared history.
Debate on the monarchy
In recent years, there has been some debate about the continuing practice of sharing a monarch. Although many seem to view the Queen's current role as head of state with passive indifference, some see the monarch as an apolitical unifying body, whether within their own nation, throughout the Commonwealth realms, or both, while others still view the Queen as an obstacle to true "independence" from the United Kingdom, or to their country's status as a sovereign state.
Proponents argue that their respective realm is already an independent kingdom where the sovereign, depicted on the currency, and to whom oaths are given, is monarch constitutionally, and specifically of said nation, asserting that any confusion about this can be eliminated with education, and argue that monarchy, with its history and traditions, is the basis for the national identity of their realm. That the sovereign obtains and maintains their position through constitutional law, supported by the elected representatives of the people, illustrates to monarchists that constitutional monarchy is a democratic institution. It is also argued that problems with outdated legislation that does not conform to modern views and beliefs can be solved by repealing or altering the laws (as has been done in other monarchies like the Netherlands), not by removing the entire institution of the monarchy itself.
Opponents to the monarchy argue that the symbolism of the institution makes an independent nation look "subsidiary" to the United Kingdom, and can be confusing and anachronistic. Others, including republicans in the United Kingdom itself, argue that having a hereditary head of state does not advance the principles of liberal democracy. Some also argue that the Queen's role as Supreme Governor of the Church of England conflicts with the secular principles commonly espoused in their constitutions and human rights legislation, though strictly this has no relevance outside England.
Today several realms have both a republican movement and a monarchist league, which serve as self-proclaimed outlets of debate in the media.
Monarchism
Though loyalist societies existed before the beginning of republican movements in various Commonwealth realms, the start of republican rumblings in the 1960s caused these groups to either shift their focus from a purely societal, celebratory organisation to one which also defended the Crown against abolition.
- In 1943 the International Monarchist League was formed in the United Kingdom as an organisation dedicated to the preservation of constitutional monarchy worldwide, but mainly focused on the Commonwealth realms. In combination with the Constitutional Monarchy Association, the group works to support and strengthen the monarchy in Britain. Supporters of the British monarchy include former Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, former MP Lord Forsyth, and notable figures such as Libby Purves.
- In Australia the Australian Monarchist League, founded in 1943, became actively involved in the campaign against an Australian republic in 1999, and Australians for Constitutional Monarchy was founded in 1992 for the same purpose. These groups view the fact that 55% of Australians voted against a republic as a definitive end to the republic debate. Australian politicians like former Prime Minister John Howard, MP Tony Abbott, and various members of the political parties, continue to support the Australian Crown.
- New Zealand saw the Monarchist League of New Zealand emerge in 1995. People like the former Prime Minister Jenny Shipley, and Peter Tapsell, former Speaker of the New Zealand House of Representatives, opposed any moves for New Zealand to become a republic.
- The Monarchist League of Canada was formed in 1970 to oppose moves by the Lester Pearson and Pierre Trudeau governments that diminished the visibility of the Canadian monarchy, and later attempts to push constitutional changes which would make the Governor General head of state above the Queen. Amongst political circles there is little republican drive, former Prime Minister Jean Chrétien stating "It's a system that works pretty well." Other supporters of the Canadian Crown include Senator Serge Joyal, former Deputy Prime Minister Sheila Copps, former Alberta Premier Ralph Klein, and former Saskatchewan Premier Roy Romanow.
Republicanism
Contemporary Commonwealth realm republican sentiment tends to be quite different in nature from the sentiment in countries that abolished the monarchy at or shortly after independence. The remaining realms have shared the Crown for much longer, in some cases over a hundred years. The debate in such countries is thus more complicated, in terms of both the political and cultural ramifications that a change to the status quo could bring. There are varying arguments by republicans in each modern realm for the abolition of their monarchy.
- In Australia, former Labor Prime Minister Paul Keating made clear his intention to make the country a republic by 2001. A referendum held in 1999 proposing, inter alia, the election of a president by Parliament, was defeated. Republicans attribute this defeat to lack of support for the proposed model, not to strength of support for the monarchy. More recently, the republic issue did not feature prominently in the 2007 election won by Kevin Rudd, but Labor policy is to hold a non-binding plebiscite, although it won't be a priority in their first term.[36]
- In neighbouring New Zealand, Prime Minister Helen Clark and Jim Bolger, a previous prime minister, have also voiced their support for republicanism, and a Republican Movement has been established.
- There has also been anti-monarchical expression in Canada, but there has been little sign of change in the immediate future. An organised republican movement, Citizens for a Canadian Republic, was established in 2002.
- In the Caribbean, P.J. Patterson and Owen Arthur, former Prime Ministers of Jamaica and Barbados, respectively, each had tentative plans to make their countries republics but met resistance from opposition parties over the role and selection of a new head of state. Arthur had announced that a republic referendum would be held in Barbados in late 2008. Both men, however, have since left their offices and neither of their respective political parties currently control their governments.
- Tuvalu's prime minister announced his government intended to hold a referendum by June 2005 on whether or not that country should become a republic[37], but one was not held.
- In Papua New Guinea, Peter Ipatas, Governor of the Enga Province, has called for the country to become a republic and the governor-general's office to be replaced by a president.[38]
In April 2005, four republican organisations within the Commonwealth launched Common Cause, an alliance of Commonwealth republican movements. The four member organisations include the Australian Republican Movement, Citizens for a Canadian Republic, the Republican Movement of Aotearoa New Zealand and Republic in the United Kingdom.
See also
Monarchies of the realms
- Monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda
- Monarchy of Australia
- Monarchy of The Bahamas
- Monarchy of Barbados
- Monarchy of Belize
- Monarchy of Canada
- Monarchy of Grenada
- Monarchy of Jamaica
- Monarchy of New Zealand
- Monarchy of Papua New Guinea
- Monarchy of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Monarchy of Saint Lucia
- Monarchy of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Monarchy of the Solomon Islands
- Monarchy of Tuvalu
- Monarchy of the United Kingdom
Other
- Commonwealth of Nations
- States headed by Elizabeth II
- Dominion
- self-governing colony
- Crown Colony
- Monarchy
- Personal union
- Republicanism in Australia
- Republicanism in Canada
- Republicanism in New Zealand
External links
- The Commonwealth Secretariat official site
- The Commonwealth - UK government site
Commonwealth
- United Commonwealth Main all-Commonwealth group
- Common Cause A Commonwealth Alliance of Republican Movements
- Res Publica : The Commonwealth international anti-monarchy Web directory
Australia
- Australian Monarchist League (traditionalist constitutional monarchists)
- Australian Republican Movement
- No Republic - Australians for Constitutional Monarchy (Moderate constitutional monarchists)
Canada
- Canadian Monarchy - The Official Site
- Canadian Monarchist ONLINE
- Citizens for a Canadian Republic
- Monarchist League of Canada
New Zealand
References
- V. Bogdanor, The Monarchy and the Constitution (Oxford, 1995)
- P. McIntyre, "The Strange Death of Dominion Status", Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History 27:2 (1999) 193-212
Footnotes
- ^ a b Buckingham Palace: Queen and Commonwealth
- ^ Figures totaled from 2007 CIA World Fact Book.
- ^ Zines, The High Court and the Constitution, 4th ed. (1997) at 314: "The Queen as monarch of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand is in a position resembling that of the King of Scotland and of England between 1603 and 1707 when two independent countries had a common sovereign"; the relationship between England and Scotland during those years is described as a personal union.
- ^ P. E. Corbett (1940). "The Status of the British Commonwealth in International Law". The University of Toronto Law Journal. 3.
{{cite journal}}: Text "pages 348-359" ignored (help); Unknown parameter|Number=ignored (|number=suggested) (help) - ^ F. R. Scott (January 1944). "The End of Dominion Status". The American Journal of International Law. 38 (1): 34–49.
- ^ R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999 HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]
- ^ The Court of Appeal of England and Wales ruled in 1982, while "there is only one person who is the Sovereign within the British Commonwealth... in matters of law and government the Queen of the United Kingdom, for example, is entirely independent and distinct from the Queen of Canada." R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999 HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]
- ^ http://laws.justice.gc.ca/fr/ShowDoc/cs/R-12/se:1::se:2/20070110/fr Parliament of Canada, "Loi sur les titres royaux", as of 2007-11-23.
- ^ Trepanier, Peter; Canadian Parliamentary Review: Some Visual Aspects of the Monarchical Tradition; Vol. 27, No. 2; 2004
- ^ Zines, The High Court and the Constitution, 4th ed. (1997) at 314: "The Queen as monarch of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand is in a position resembling that of the King of Scotland and of England between 1603 and 1707 when two independent countries had a common sovereign"; the relationship between England and Scotland during those years is described as a personal union.
- ^ P. E. Corbett (1940). "The Status of the British Commonwealth in International Law". The University of Toronto Law Journal. 3.
{{cite journal}}: Text "pages 348-359" ignored (help); Unknown parameter|Number=ignored (|number=suggested) (help) - ^ F. R. Scott (January 1944). "The End of Dominion Status". The American Journal of International Law. 38 (1): 34–49.
- ^ R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999 HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]
- ^ Rt. Hon. Don McKinnon, Commonwealth Secretary General; Center for Strategic and International Studies, Washington, D.C.; Thursday, May 25, 2006
- ^ Dr. Toporoski, Richard; Monarchy Canada: The Invisible Crown; Summer, 1996
- ^ Statute of Westminster, 1931; 22 George V, c. 4 (U.K.); 11th December, 1931
- ^ Sir Robert Menzies Lecture Trust: Lecture by Sir Zelman Cohen, 1995
- ^ Sharp, Mitchell; Which Reminds Me..., A Memoir; Toronto: University of Toronto Press; 1994; p. 223
- ^ ABC News: Britain, France, Canada Mark WWI Battle; April 9, 2007
- ^ Canadian Monarchist News: Canadian Confusion at Juneau Beach; Summer, 2004
- ^ The International Who's Who : Royal Families, United Kingdom
- ^ Heraldica: FAQ
- ^ Department of National Defence: The Honours, Flags and Heritage Structure of the Canadian Forces; pg 281
- ^ The Canadian Heraldry Society states: "...Her Majesty, Queen Victoria, [was Queen of Canada and all her other realms. Queen Victoria was the first Monarch of the confederation of provinces that became known as the Dominion of Canada on July 1, 1867."
- ^ Zines, The High Court and the Constitution, 4th ed. (1997) at 314: "The Queen as monarch of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand is in a position resembling that of the King of Scotland and of England between 1603 and 1707 when two independent countries had a common sovereign"; the relationship between England and Scotland during those years is described as a personal union.
- ^ P. E. Corbett (1940). "The Status of the British Commonwealth in International Law". The University of Toronto Law Journal. 3.
{{cite journal}}: Text "pages 348-359" ignored (help); Unknown parameter|Number=ignored (|number=suggested) (help) - ^ F. R. Scott (January 1944). "The End of Dominion Status". The American Journal of International Law. 38 (1): 34–49.
- ^ R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999 HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]
- ^ The English Court of Appeal ruled in 1982, while "there is only one person who is the Sovereign within the British Commonwealth... in matters of law and government the Queen of the United Kingdom, for example, is entirely independent and distinct from the Queen of Canada." R v Foreign Secretary; Ex parte Indian Association, QB 892 at 928; as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999 HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998]
- ^ Heard, Andrew (1990). "Canadian Independence". Simon Fraser University. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
The legislative confusion which followed the abdication of King Edward VIII in December of 1936 was an important step in the evolution of Dominion status, because it demonstrated that the Imperial Crown could be an entirely divisible entity in law. All the Dominion governments had been warned that the King was about to abdicate the throne; indeed, the Canadian government sent a cable urging him to put his duty as King ahead of his desire to abdicate and marry Wallace Simpson. The news that the Instrument of Abdication had been signed was cabled to all the Dominion governments. Australia's Parliament was in session at the time and gave its formal assent to British legislation, as required by the convention recited in the preamble of the Statute of Westminster. The governments of New Zealand, Canada, and South Africa gave their consents as their Parliaments were not in session; the British Parliament passed an Abdication Act on the following day, December 11th, that gave legal effect to the Instrument of Abdication and brought George VI to the throne.
The divisibility of the Crown became a matter of law in some jurisdictions, however, through the actions of two Dominion Parliaments. The Irish Free State passed an Act declaring that the abdication took effect on December 12th, while the South African Parliament later passed an Act that declared that the abdication had taken effect in South Africa on December 10th. When the Canadian Parliament met in the new year, it passed an Act giving its assent to the British legislation. The assumption of this legislative authority was legally redundant because the British Act was undoubtedly already in force in Canada; it complied with the requirements of s.4 of the Statute of Westminster by containing a reference to the fact that it was being enacted with the request and consent of Canada, and a proclamation announcing that the accession to the Throne had also been duly made by the Governor General. But as Clokie observed about the Canadian Act, "Whether necessary or not, it was clearly designed to demonstrate Canada's equality with Britain in the British Commonwealth and to display the Canadian aspect of the monarchy". Even though the courts in South Africa and the Irish Free State would recognise the divisibility of the Crown and the authority of their own laws on the succession, these measures had no practical effect outside those two Dominions. As far as Canada, New Zealand, and Australia were concerned, the Crown remained a legal unity since their new monarch came to the throne through British legislation. - ^ "Canada's New Queen". CBC.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessdaymonth=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ http://canada.gc.ca/howgoc/queen/quind_e.html 1
- ^ National Gallery of Australia: By Appointment: Norman Hartnell's sample for the Coronation dress of Queen Elizabeth II
- ^ A Dominion and not a Commonwealth Realm
- ^ A Dominion and not a Commonwealth Realm
- ^ Unions won't rule us: Rudd - National - smh.com.au
- ^ Tuvalu may drop Queen as head of state - Scotsman.com News
- ^ Radio New Zealand International (10 December 2003). "A PNG provincial governor calls for a republic and president". Retrieved 2007-08-01.

