Kapampangan language
| Kapampangan | |
|---|---|
| Native to | |
| Region | Central Luzon |
Native speakers | 2.9 million |
| Latin (Kapampangan or Spanish variant); Historically written in Matuang Kudlitan | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Regional language in the Philippines |
| Regulated by | Commission on the Filipino Language |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | pam |
| ISO 639-3 | pam |
Kapampangan, also spelled Capampan͠gan, is one of the major languages of the Philippines. It is the language spoken in the province of Pampanga, the southern half of the province of Tarlac and the northern portion of the province of Bataan. Kapampangan is also understood in some barrios of Bulacan and Nueva Ecija and by the Aitas or Aeta of Zambales. The language is also called Pampango, Capampan͠gan, Pampangueño, and Amanung Sisuan. The latter literally means "breastfed language" and is analogous to the term "native language."
History
The word Kapampangan is derived from the rootword pampang which means "river bank." Very little is known about the language prior to the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century. In the 18th century, two books were written by Fr. Diego Bergaño. He authored Vocabulario de la lengua Pampanga[1] and Arte de la lengua Pampanga. The Kapampangan Language produced two literary giants in the 19th century. Father Anselmo Fajardo was noted for his works Gonzalo de Córdova and Comedia Heróica de la Conquista de Granada. Another writer, Juan Crisostomo Soto, was noted for writing many plays. He authored Alang Dios in 1901. The Kapampangan poetical joust "Crissotan" was coined by his fellow literary genius Nobel Prize nominee for peace and literature in the 50's, Amado Yuzon to immortalize his contribution to Pampanga's Literature. [2]
Classification
Kapampangan is one of the Central Luzon languages language within the Austronesian language family. Its closest relatives are the Sambal languages of Zambales province and the Bolinao language spoken in the town of Bolinao, Pangasinan.
These languages share the same reflex /j/ of the Proto-Austronesian consonant *R.
Geographic distribution
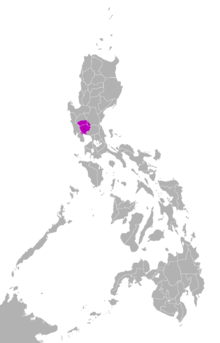
Kapampangan is primarily spoken in the provinces of Pampanga and in the southern towns of the province of Tarlac (Bamban, Capas, Concepcion, San Jose, Gerona, La Paz, Victoria,and Tarlac City). It is also spoken in isolated communities within the provinces of Bataan (Abucay, Dinalupihan, Hermosa, and Samal), Bulacan (San Miguel,San Ildefonso,Hagonoy,Plaridel, Pulilan, and Calumpit), Nueva Ecija (Cabiao, San Isidro, Gapan City and Cabanatuan City), and Zambales (Olongapo City and Subic).
The Philippine Census of 2000 stated that a total of 2,312,870 out of 76,332,470 people spoke Kapampangan as their native language.
Phonology
Standard Kapampangan has 21 phonemes: 15 consonants and five vowels. Some western dialects of Kapampangan have six vowels. Syllable structure is relatively simple. Each syllable contains at least a consonant and a vowel.
Vowels
Kapampangan is complete in vowel phonemes, they are:
- /a/ an open front unrounded vowel similar to English "father"
- /ɛ/ an open-mid front unrounded vowel similar to English "bed"
- /i/ a close front unrounded vowel similar to English "machine"
- /o/ a close-mid back rounded vowel similar to English "forty"
- /u/ a close back rounded vowel similar to English "flute"
In addition to those, some dialects also had /ə/. In some western accents, there is a sixth monophthong phoneme /ɯ/, a close back unrounded vowel, found in for example [atɯp] "roof" and [lalɯm] "deep". However, this sound has merged with /a/ for most Kapampangan speakers.
There are four main diphthongs; /aɪ/, /oɪ/, /aʊ/, and /iʊ/. However, in most dialects, including standard Kapampangan, /aɪ/ and /aʊ/ are reduced to /ɛ/ and /o/, respectively.
The monophthongs have allophones in unstressed and word-final positions:
- /a/ is raised slightly in unstressed positions except final syllables
- Unstressed /i u/ are usually pronounced [ɪ ʊ] as in English "bit" and "book" respectively, except final syllables.
- At the end of a word and declarative sentences, /ɛ/ and /i/ are pronounced [i], and /o/ and /u/ are pronounced [u].
- However, in exclamatory and interogatory statements, /ɛ/ and /i/ are pronounced [ɛ], and /o/ and /u/ are pronounced [o]. Examples:
- "What is this?" is Nanu ine?, not *Nanu ini?
- "Come here!" is Me kene!, not *Me keni!
- "Who is Pedro?" is Ninu i Pedro?, not *Ninu i Pedru?
- "(He) wrote me!" is Silatanan na ko!, not *Silatanan na ku!
Consonants
Below is a chart of Kapampangan consonants. All the stops are unaspirated. The velar nasal occurs in all positions including at the beginning of a word.
Unlike other Philippine languages, Kapampangan lacks the phoneme /h/. "Que" and "C" are commonly use instead of the letter K. For Example: Caluguran da ca. (I love you or You are my friend) Me queni. (Come here)
| Bilabial | Dental / Alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | (ng) ŋ | |||
| Stop | voiceless | p | t | (ts, tiy) tʃ | k | - ʔ |
| voiced | b | d | (diy) dʒ | g | ||
| Fricative | s | (siy) ʃ | ||||
| Flap | ɾ | |||||
| Approximant | l | (y) j | w | |||
- /k/ has a tendency to lenite to [x] between vowels.
- [d] and [ɾ] are allophones in Kapampangan, and thus sometimes interchangeable. So, Nukarin la ring libro? can be Nukarin la ding libro? (Translation: Where are the books?)
- A glottal stop that occurs at the end of a word is often omitted when it's in the middle of a sentence.
Basic words
Some words in Kapampangan:
Numbers
1-isa/metung
2-adwa
3-atlu
4-apat
5-lima
6-anam
7-pitu
8-walu
9-syam/siyam
10-apulu
Sentence:
My name is John-Juan ing lagyu ku
I am here!-Atyu cu queni
Where are you?-Nokarin na'ka?
Who are you?-Ninu y ica?
Words:
I-acu/cacu
You-ica/ceca
we-icami
us-itamu
all of us-itamu ngan
love-caluguran/lugud
angry-mimwa
beautiful-malagu/masanting
beauty-lagu
ugly-matsura
Stress
Stress is phonemic in Kapampangan. Primary stress occurs on either the last or the next-to-last syllable of a word. Vowel lengthening accompanies primary or secondary stress except when stress occurs at the end of a word.
Historical sound changes
In Kapampangan, the Proto-Philippine schwa vowel *ə has merged to /a/ in most dialects of Kapampangan. It is preserved in some western dialects. For example, Proto-Philippine *tanəm is tanam (to plant) in Kapampangan. Compare with Tagalog tanim and Cebuano tanom.
Proto-Philippine *R merged with /j/. For example, the Kapampangan word for "new" is bayu while in Tagalog it is bago and baro in Ilocano.
Grammar
Nouns
While Kapampangan nouns are not inflected, they are usually preceded by case markers. There are three types of case markers: absolutive (nominative), ergative (genitive), and oblique.
Unlike English and Spanish which are nominative-accusative languages, Kapampangan is an ergative-absolutive language. It's a common misconception that Kapampangan is frequently spoken in the passive voice.
Absolutive or nominative markers mark the actor of an intransitive verb and the object of a transitive verb.
Ergative or genitive markers mark the object (usually indefinite) of an intransitive verb and the actor of a transitive one. It also marks possession.
Oblique markers are similar to prepositions in English. It marks things such as location and direction.
Furthermore, noun markers are divided into two classes: one for names of people (personal) and the second for everything else (common).
Below is a chart of case markers.
| Absolutive | Ergative | Oblique | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common singular | ing | -ng, ning |
king |
| Common plural | ding ring |
ring | karing |
| Personal singular | i | -ng | kang |
| Personal plural | di ri |
ri | kari |
Examples:
Dinatang ya ing lalaki.
"The man arrived."
Ikit neng Juan y Maria.
"John saw Maria."
Munta la ri Elena ampon y Robertu quing bale nang Miguel./ Munta la di Elena ampon y Robertu king bale nang Miguel.
"Elena and Roberto will go to Miguel's house."
Nukarin la ring libru?
"Where are the books?"
Ibie ke ing susi kang Carmen.
I will give the key to Carmen.
Pronouns
Kapampangan pronouns are categorized by case: absolutive, ergative, and oblique.
| Absolutive (Independent) |
Absolutive (Enclitic) |
Ergative | Oblique | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | yaku, aku | ku | ku | kanaku, kaku |
| 2nd person singular | ika | ka | mu | keka |
| 3rd person singular | iya, ya | ya | na | keya, kaya |
| 1st person dual | ikata | kata, ta | ta | kekata |
| 1st person plural inclusive | ikatamu, itamu | katamu, tamu | tamu, ta | kekatamu, kekata |
| 1st person plural exclusive | ikami, ike | kami, ke | mi | kekami, keke |
| 2nd person plural | ikayu, iko | kayu, ko | yu | kekayu, keko |
| 3rd person plural | ila | la | da ra |
karela |
Examples
Sinulat ku.
"I wrote."
Silatanan na ku.
"(He or She) wrote me."
Dinatang ya.
"(He or She) has arrived." [Note: Dinatang ya = "He arrived" or "He arrives"; He has arrived = Dinatang ne]
Sabyan me kaku "Tell it to me"
Ninu ing minaus keka?
"Who called you?
Mamasa la.
"They are reading."
Mamangan la ring babi(e)?/Mamangan la ding babi(e)?
"Are the pigs eating?" (literally: "Eating they the pigs?")
Genitive pronouns follow the word they modify. Oblique pronouns can take the place of the genitive pronoun but they precede the word they modify.
Ing bale ku.
Ing kakung bale.
"My house."
The dual pronoun ikata refers to only the first and second persons.
The inclusive pronoun ikatamu refers to the first and second persons. It may also refer to a third person(s).
The exclusive pronoun ikamí refers to the first and third persons but excludes the second.
Ala tang nasi.
"We (you and I) do not have rice." [the word "you" here maybe plural or singular]
Ala tamung nasi.
"We (you and I and someone else) do not have rice." [this is the same as above; "tang" is only a shortcut of "tamung"]
Ala keng nasi.
"We (someone else and I, but not you) do not have rice." [the third person maybe singular or plural, that is, "we" may refer to "He/She and I" or "They and I"]
Furthermore, Kapampangan stands out among many Philippine languages in requiring the presence of the pronoun even if the noun it represents, or the grammatical antecedent, is present.
Dinatang ya i Erning. (not *dinatang i Erning)
"Ernie arrived."
Mamasa la ri Maria at Juan./Mamasa la di Maria at Juan. (not *mamasa ri Maria at Juan/mamasa di Maria at Juan)
"Maria and Juan are reading."
Silatanan na kang José. (not *silatanan kang José)
"José wrote you."
As a comparison, it would be akin to saying *dumating siya si Erning, *bumabasa sila sina Maria at Juan and *sinulatan ka niya ni José in Tagalog.
Special forms
The pronouns ya and la have special forms when they are used in conjunction with the words ati (there is/are) and ala (there is/are not).
Ati yu king Pampanga. (not *Ati ya king Pampanga)
"He is in Pampanga."
Ala lu ring doktor keni./Ala lu ding doktor keni. (not *ala la ring doktor keni/ala la ding doktor keni)
The doctors are no longer here.
Note: for some speakers of Kapampangan (possibly certain dialects), all of the above forms can be used:
Both "ati yu" and "ati ya" are equally right. Plural form ("they are") is "atilu" and "atila".
Both "ala la" and "ala lu" are correct in the plural form. Singular form is "ala ya" and "ala yu"
Pronoun combinations
The order and forms in which Kapampangan pronouns appear in sentences are outlined in the following chart.
Kapampangan pronouns follow a certain order following verbs or particles like negation words. The enclitic pronoun is always first followed by another pronoun or discourse marker.
Ikit da ka.
"I saw you."
Silatanan na ku.
"He wrote to me."
However, the following constructions are incorrect: *ikit ka da and *silatanan ku na
Also, pronouns combine to form one portmanteau pronoun.
Ikit ke. (instead of Ikit ku ya)
"I saw her."
Dinan kong pera. (instead of Dinan ku lang pera.)
"I will give them money." [Actually "Dinan ku la..." is correct; "kong..." is a shortcut of "ku lang..."]
Portmanteau pronouns are not usually used in questions and while using the word naman. Furthermore,
Akakit me? (instead of akakit me?)
Do you see him?
Buri nya naman yan/buri ne murin yan. (instead of buri ne naman yan)
he likes that, too
The chart below outlines the permitted combinations of pronouns. There are blank entries to denote combinations which are deemed impossible.
The column headings (i.e., yaku, ika, etc.) in bold denote pronouns in the absolutive case while the row headings (i.e., ku, mu, etc.) denote pronouns in the ergative case.
| yaku 1 s |
ika 2 s |
ya 3 s |
ikata 1 dual |
ikatamu 1 p inc. |
ikami 1 p exc. |
ikayo 2 p |
ila 3 p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ku 1 s |
(ing sarili ku) | da ka ra ka |
ke keya |
- | - | - | da ko (ra ko) da kayu (ra kayu) |
ko ku la |
| mu 2 s |
mu ku | (ing sarili mu) | me mya |
- | - | mu ke mu kami |
- | mo mu la |
| na 3 s |
na ku | na ka | ne nya (ing sarili na) |
na kata | na katamu | na ke na kami |
na ko na kayu |
no nu la |
| ta 1 dual |
- | - | te tya |
(ing sarili ta) | - | - | - | to ta la |
| tamu 1 p inc. |
- | - | ta ya | - | (ing sarili tamu) | - | - | ta la |
| mi 1 p exc. |
- | da ka ra ka |
mi ya | - | - | (ing sarili mi) | da ko (ra ko) da kayu (ra kayu) |
mi la |
| yu 2 p |
yu ku | - | ye ya |
- | - | yu ke yu kami |
(ing sarili yu) | yo yu la |
| da 3 p |
da ku ra ku |
da ka ra ka |
de (re) dya |
da kata ra kata |
da katamu ra katamu |
da ke (ra ke) da kami (ra kami) |
da ko(ra ko) da kayu (ra kayu) |
do (ro) da la (ra la) (ing sarili da) |
Demonstrative pronouns
Kapampangan's demonstrative pronouns are outlined in the chart below.
This particular system of demonstrative pronouns differs with other Philippine languages by having separate forms for the singular and plural.
| Absolutive | Ergative | Oblique | Locative | Existential | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Nearest to speaker (this, here) |
ini | deni reni |
nini | dareni | canini | careni | oyni | oreni | queni |
| Near speaker & addressee (this, here) |
iti | deti reti |
niti | dareti | caniti | careti | oyti | oreti | queti |
| Nearest addressee (that, there) |
iyan | den ren |
niyan | daren | canyan | caren | oyan | oren | quen |
| Remote (yon, yonder) |
ita | deta reta |
nita | dareta | canita | careta | oyta | oreta | queta |
The demonstrative pronouns ini and iti (as well as their respective forms) both mean "this" but each have distinct uses.
Iti usually refers to something abstract but may also refer to concrete nouns. For example, iting musika (this music), iti ing gagawan mi (this is what we do).
Ini is always concrete and never abstract. For example ining libru (this book), ini ing asu nang Juan (this is Juan's dog).
Furthermore, in their locative forms, keni is used when the person spoken to is not near the subject spoken of. Keti, on the other hand, when the person spoken to is near the subject spoken of. For example, two people in the same country will refer to their country as keti however, they will refer to their respective towns as keni. Both mean here.
Nanu ini?
"What's this?"
Mangabanglu la rening sampaga./Mangabanglu la dening sampaga.
"These flowers smell good."
Ninu ing lalaking ita?
"Who is that man/guy?"
Me keni/munta ka keni.
"Come here."
Ati ku keti/atsu ku keni/atyu ku keni.
"I am here."
Mangan la keta.
"They will eat there."
Ninu ing anak a yan?
"Who is that child?"
Uyta/Oyta ya pala ing salamin mo/mu!
"So that's where your glasses are!"
E ku pa menakit makanyan/makanini.
"I haven't seen one of these before"
Manyaman la ren./Manyaman la den.
Those are delicious.
Ayni/Areni/Oreni la reng adwang regalo para keka.
"Here are the two gifts for you."
Buri daka! "I like You"
Kaluguran daka! " I Love You"
Mangan Tana! "Let's Eat"
Edaka buring mawala! "I don't wannna loose you!"
Verbs
Kapampangan verbs are morphologically complex and take on a variety of affixes reflecting focus, aspect, mode, and others.
Ambiguities and irregularities
Speakers of other Philippine languages find Kapampangan verbs to be more difficult than their own languages' verbs due to some verbs belonging to unpredictable verb classes as well as ambiguity with certain verb forms.
To illustrate this, let's take the rootword sulat (write) which exists in both Tagalog and Kapampangan.
For example:
- susulat means "is writing" in Kapampangan but "will write" in Tagalog.
- sumulat means "will write" in Kapampangan but "wrote" in Tagalog. This form is also the infinitive in both languages.
- sinulat means "wrote" in both languages. However in Kapampangan it's in the actor focus but object focus in Tagalog
The object-focus suffix -an represents two types of focuses. However, the only difference between the two is that one of the conjugations preserves -an in the completed aspect while it is dropped in the other conjugation. Take the two verbs below:
- bayaran (to pay someone): bayaran (will pay someone), babayaran (is paying someone), beyaran (paid someone)
- bayaran (to pay for something): bayaran (will pay for something), babayaran (is paying for something), binayad (paid for something)
Note that other Philippine languages have separate forms. For example, there is -in and -an in Tagalog, -on and -an in Bikol and in most of the Visayan languages, and -en and -an in Ilokano. This is due to historical sound changes concerning Proto-Philippine /*e/ mentioned above.
There are a number of actor-focus verbs which do not use the infix -um- but are usually conjugated like other verbs that do. For example, gawa (to do), bulus (to immerse), terak (to dance), lukas (to take off), sindi (to smoke), saklu (to fetch), takbang (to step), tuki (to accompany), etc. are used instead of *gumawa, *bumulus, *tumerak, *lumukas, *sumindi, *sumaklu, *tumakbang, *tumuki,
Many of the verbs mentioned in the previous paragraph undergo a change of their vowel rather than use the infix -in- (completed aspect). In the actor focus (i.e., -um- verbs), this happens only to verbs having the vowel /u/ in the first syllable. For example, the verb lukas (to take off) is conjugated lukas (will take off), lulukas (is taking off), and likas (took off) (rather than *linukas).
This change of vowel also applies to certain object-focus verbs in the completed aspect. In addition to /u/ becoming /i/, /a/ becomes /e/ in certain cases. For example, dela (brought something) and not *dinala, semal (worked on something) and not *sinamal, and seli (bought) and not *sinali.
Furthermore, there is no written distinction between the two mag- affixes in writing. Magsalita can either mean is speaking or will speak. There is an audible difference, however. [mɐɡsaliˈtaʔ] means "will speak" while [ˌmaːɡsaliˈtaʔ] means "is speaking".
Conjugation chart
Below is a chart of the basic Kapampangan verbal affixes.
| Infinitive & Contemplative |
Progressive | Completed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actor Focus1a | -um- | CV- | -in- |
| Actor Focus1b | - | CV- | -in- -i- |
| Actor Focus1c | m- | mVm- | min- me- |
| Actor Focus2 | mag- | mág- | mig-, meg- |
| Actor Focus3 | ma- | má- | ne- |
| Actor Focus4 | maN- | máN- | meN- |
| Object Focus1 | -an | CV- ... -an | -in- -i- -e- |
| Object Focus2 Benefactive Focus |
i- | iCV- | i- -in- i- -i- i- -e- |
| Object Focus3 Locative Focus |
-an | CV- ... -an | -in- ... -an -i- ... -an -e- ... -an |
| Instrument Focus | ipaN- | páN- | piN-, peN |
| Reason Focus | ka- | ká- | ke- |
Enclitic Particles
1. ba: used optionally in yes-and-no questions and other types of questions.
2. agyaman, man: even, even if, even though.
3. nung: condition particle that expresses unexpected event; if.
4. kanu: reporting or hearsay particle that expresses that the information is second-hand; he said, she said, they said, it was said, allegedly, reportedly, supposedly.
5. din/rin: inclusive particle that adds something to what was said before; also, too.
6. iká: expresses hope, unrealized condition (with verb in completed aspected), used in conditional aspects.
7. itá: expresses uncertainty and unrealized idea; perhaps, probably, seems.
8. mu: limiting particle; only, just.
9. na and pa
- na: now, already, yet, anymore.
- pa: still, else.
10. namán: used in making contrasts and softens requests and emphasis.
11. nanu ita: expresses cause; because, because of.
12. pin: used in affirmations or emphasis and also softens imperatives; indeed.
13. palá: realization particle that expresses that the speaker has realized and/or suddenly remembered something.
14. pu/opu: politeness particle.
Swerti kanu iti kanaku.
It was said that it is lucky to me.
Edukadu ya rin ing nobyu mu./Edukadu ya din ing nobyu mu.
Your boyfriend is also educated.
Existential
To express existence (there is/are) and possession (to have), the word atí is used.
Atí la namang konsyensya.
They also have conscience.
Negation
There are two negation words: alí and alá.
Alí negates verbs and equations. It means no and/or not.
Alí ya seli.
He did not buy.
Alá is the opposite of atí.
Alá na mo kanung lugud.
They say that there is no more love.
But in several statements, e is used instead of "ali."
E ke seli.
I did not buy it.
Interrogative Words
Kumustá is used to inquire how something is (are). It is frequently used as a greeting meaning How are you? It is derived from the Spanish ¿cómo está?
Kumustá na ka?
“How are you?”
Kumustá ya ing pasyenti?
“How is the patient?”
Nanu means what.
Nanu ya ing gagawan mu?
“What are you doing?”
Ninu means who.
Ninu la reng lalake?/Ninu la deng lalake?
“Who are those men?”
Ninu i Jennifer?
“Who is Jennifer?”
Nukarin means where but is used to inquire about the location of an object and not used with verbs.
Nukarin ya ing drayber?
“Where is the driver?”
Note: Drayber is the Kapampangan phonetic spelling of “driver.”
Nukarin ya i Henry?
“Where is Henry?”
Loan words
Kapampangan has a plethora of Spanish loan words, given its more than three hundred years of occupation. Among a few examples are suerti from Spanish suerte (luck), curus from cruz (cross), carni from carne (meat), corsunada from corazonada (crush), casapego from casa fuego (matchbox), and machura from mal hechura (ugly-looking).
Due to the influence of Buddhism and Hinduism from the surrounding islands, Kapampangan also acquired words from Sanskrit. A few examples are:
- alaya "home" from Sanskrit आलय alaya
- kalma "fate" from Sanskrit कर्म karma
- damla "divine law" from Sanskrit धर्म dharma
- mantala "magic formulas" from Sanskrit मन्त्र mantra
- upaya "power" from Sanskrit उपाय upaya
- siuala "voice" from Sanskrit स्वर svara
- lupa "face" from Sanskrit रुपा rupa
- sabla "every" from Sanskrit सर्व sarva
- lawu "eclipse" from Sanskrit राहु rahu
- galura "giant eagle" (a surname) from Sanskrit गरुड garuda
- laksina "south" (a surname) from Sanskrit दक्षिण dakshin
- laksamana "admiral" (a surname) from Sanskrit लक्ष्मण lakshmana
Kapampangan also contains a lot of Chinese especially from Cantonese and Hokkien. Examples are:
- ápû 阿婆 "(maternal) grandmother"
- impû 外婆 "(paternal) grandmother'
- ingkung 外公 "(paternal) grandfather"
- atchi 阿姐 "eldest sister"
- koya 哥仔 "eldest brother"
- susi 鎖匙 "key"
- pansit 便食 "noodles" (lit."instant meal")
- buisit 無衣食 "bad luck" (lit."without clothes and food")
Examples
Some Common Phrases & Sentences
- Kumusta na ka? - How are you?
- Masalese ku pu. - I'm fine.
- Mayap ku pu. - I'm good.
- Nanung lagyu mu? - What is your name?
- Malagu ka talaga! - You are really beautiful.
- Kasanting mo! - You are so handsome!
- Wa - Yes
- Ali - No
- Me keni. (from 'Ume ka keni'). - Come here.
- Buri ku maglawlaw keka. - I wanna love [court] you. <addition by Buenafe A. Briggs - Aug. 8, 2009>
- Kaluguran da ka. - I love you.
- Tabalu keka- literally "I don't know with you." (expression)
- Eku balu.- I don't know.
- Mako na ku. - I am going.
- Mangan ta na, mangan tamu. - Let us eat now, let us eat.
Numbers
| Number | Kapampangan |
|---|---|
| 1 | Metung/Isa |
| 2 | Adua |
| 3 | Atlu |
| 4 | Apat |
| 5 | Lima |
| 6 | Anam |
| 7 | Pitu |
| 8 | Walu |
| 9 | Siyam |
| 10 | Apulu |
| 11 | Labing metung |
| 12 | Labing adua |
| 13 | Labing atlu |
| 14 | Labing apat |
| 15 | Labing lima |
| 20 | Adwang pulu |
| 21 | Adwang pulu't metung |
| 22 | Adwang pulu't adua |
| 30 | Atlung pulu |
| 100 | Dinalan |
| 200 | Aduang dalan |
| 1,000 | Libu / Metung Libu / Metung a Libu |
| 2,000 | Aduang Libu |
| 10,000 | Lacsa |
| 100,000 | Gatus |
| 200,000 | Adwang Dalan Libu / Adwang Dalan A Libu |
| 1,000,000 | Sangyuto |
| 2,000,000 | Aduang Milyun (Modern) |
| 1,000,000,000 | Bilyun / Metung Bilyun / Metung a Bilyun (Modern) |
Traditional Children's Song
Atin ku pung singsing
Metung yang timpukan
Amana ke iti
King indung ibatan [Better = "Kang..."]
Sangkan keng sininup
King metung a caban
Mewala ya iti,
E ku kamalayan.
Ing sukal ning lub ku
Susukdul king banua
Pikurus kung gamat[or the active "Mikurus..."]
Babo ning lamesa
Ninu mang manakit
King singsing cung mana
Kalulung pusu ku
Manginu ya keya.
English Translation:
I once had a ring
With a beautiful gem
I inherited this
From my mother
I stored it as well as I could
In a hopebox
But it just suddenly disappeared
I didn't notice.
The heartache inside me
Is as high as the sky
My crossed hands (as I pray)
Are upon the table
Whoever would find
That inherited ring
[Better: My inherited ring]
My poor heart (that's aching)
Shall forever worship him/her.
See also
References
- ^ Bergaño
- ^ In many gatherings Kapampangans seem more confident and articulate in exchanging views and ideas among their own K[abalen] ‘countrymen’ ... in Tagalog than they would in their own [mother tongue]. For instance, many Catholic priests are now delivering their homilies in the Tagalog language during a Kapampangan liturgy while high school student meetings are conducted in the Tagalog language even if all the participants are Kapampangans. http://www.silinternational.org/asia/philippines/ical/papers/pangilinan-Dispute%20on%20Orthography.pdf
- Bautista, Ma. Lourdes S. 1996. An Outline: The National Language and the Language of Instruction. In Readings in Philippine Sociolinguistics, ed. by Ma. Lourdes S. Bautista, 223. Manila: De La Salle University Press, Inc.
- Bergaño, Diego. 1860. Vocabulario de la Lengua Pampanga en Romance. 2nd ed. Manila: Imprenta de Ramirez y Giraudier.
- Castro, Rosalina Icban. 1981. Literature of the Pampangos. Manila: University of the East Press.
- Fernández, Eligío. 1876. Nuevo Vocabulario, ó Manual de Conversaciónes en Español, Tagálo y Pampángo. Binondo: Imprenta de M. Perez
- Gallárdo, José. 1985-86. Magaral Tang Capampangan. Ing Máyap a Balità, ed. by José Gallárdo, May 1985- June 1986. San Fernando: Archdiocese of San Fernando.
- Henson, Mariano A. 1965. The Province of Pampanga and Its Towns: A.D. 1300-1965. 4th ed. revised. Angeles City: By the author.
- Kitano Hiroaki. 1997. Kapampangan. In Facts About The World’s Major Languages, ed. by Jane Garry. New York: H.W. Wilson. Pre-published copy
- Lacson, Evangelina Hilario. 1984. Kapampangan Writing: A Selected Compendium and Critique. Ermita, Manila: National Historical Institute.
- Manlapaz, Edna Zapanta. 1981. Kapampangan Literature: A Historical Survey and Anthology. Quezon City: Ateneo de Manila Universit Press.
- Panganiban, J.V. 1972. Diksyunaryo-Tesauro Pilipino-Ingles. Quezon City: Manlapaz Publishing Co.
- Pangilinan, Michael Raymon M. 2004. Critical Diacritical. In Kapampangan Magazine, ed. by Elmer G. Cato,32-33, Issue XIV. Angeles City: KMagazine.
- Samson, Venancio. 2004. Problems on Pampango Orthography. In Kapampangan Magazine, ed. by Elmer G. Cato,32-33, Issue XII. Angeles City: KMagazine.
- Tayag, Katoks (Renato). 1985. "The Vanishing Pampango Nation", Recollections and Digressions. Escolta, Manila: Philnabank Club c/o Philippine National Bank.
- Turla, Ernesto C. 1999. Classic Kapampangan Dictionary. Offprint Copy
External links
- 10 ICAL Paper - Issues in Orthography
- 10 ICAL Paper - Importance of Diacritical Marks
- 10 ICAL Paper - Transitivity & Pronominal Clitic Order
- Ethnologue
- Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database
- Bansa.org Kapampangan Dictionary
- Kapampangan in 10 Easy Lessons NB: uses SÚLAT BACÚLUD or the Spanish-derived Orthography
- Dying languages
- State can still save Kapampangan
- Siuala ding Meangubie
- Electronic Kabalen - New Writing on Kapampangan Life & Letters
