Ingles Ferry
Ingles Ferry | |
 Ingles Ferry in 1908 | |
| Location | Radford, Virginia, USA |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 37°6′3″N 80°35′30″W / 37.10083°N 80.59167°W |
| Area | 2 acres (0.81 ha) |
| Built | 1772 (tavern) |
| NRHP reference No. | 69000275[1] |
| VLR No. | 077-0013 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | November 25, 1969 |
| Designated VLR | May 13, 1969[2] |
Ingles Ferry (sometimes referred to as English Ferry) is the site of a historic ferry crossing on the New River in western Virginia, near the city of Radford in Pulaski County, Virginia, United States. A tavern was opened there in 1772 and the ferry served soldiers and civilians until 1948. A bridge was built at the site in 1842 but was burned during the civil war. The tavern and replicas of the 18th-century home of the Ingles family can be seen nearby.
History
The ford was in use by Native Americans when Europeans arrived in the area, and initially was known as Eagle Bottom.[3]: 75 William Ingles and his wife Mary Draper Ingles began developing a farm on the eastern side of the New River a few years after Mary's capture by Shawnee Indians and her subsequent escape in 1755.[4] As early as 1760, William was making money ferrying troops across the New River during the Anglo-Cherokee War,[3]: 74 and, realizing the value of the ferry, purchased the land from Dr. Thomas Walker.[5]: 109 The November 1762 official authorization of Ingles Ferry set fees at 3 pence for man or horse.[3]: 74–75 In 1766, Ingles applied for a license to operate an ordinary (tavern) there.[6]: 99–101 During the first few years of its existence, Indians frequently attacked the farm and ferry,[7]: 84–93 [5]: 7–8 and Ingles constructed a small stockaded blockhouse, which he named Fort Hope, to protect his family and neighbors.[8]: 3
Tavern

With the help of his brother-in-law John Draper, William completed construction of the Ingles Ferry Hill Tavern and blacksmith shop on the Pulaski County side of the river in 1772.[9][6]: 99–101 The tavern was a popular meeting place for travelers, with Daniel Boone,[10] Andrew Jackson and George Rogers Clark among its patrons.[9] In April 1797, Louis Philippe I, Duke of Orléans and future King of France, crossed the river on the ferry, but did not stop at the tavern.[11]: 51 William Clark (of Lewis and Clark) crossed on the ferry at least five times between 1801 and 1820.[3]: 76 [12]: 13
William Ingles was in charge of improving and maintaining the road leading to and from Ingles Ferry, known at the time as Ingle's Ferry Road or English Ferry Road.[13]: 36 It later became a main thoroughfare and was part of as the Great Wagon Road and the Wilderness Road.[14]
On 8 May 1779, Lord Henry Hamilton, a British prisoner of war, was being escorted under guard to Williamsburg and spent the night at the home of William and Mary Ingles. In his journal, Hamilton described the Ingles' home:
- 8th. In the Evening crossed over in a ferry the new river or great Canhawa, and were kindly and hospitably received at the house of Colonel Ingles-- here we rested for an entire day...The Scenery about this house was romantic to a degree, the river very beautyfull, the hills well wooded, the low grounds well improved & well stocked, I thought...Mrs. Ingles had in her early years been carryed off with another young Woman by the Savages...however terror and distress had left so deep an impression on her mind that she appear'd absorbed in a deep melancholy.[15]
By 1780, William Ingles owned 907 acres, 67 cattle,[16] and ten slaves who ran his ferry and worked in his mills or in domestic capacities.[13]: 69 [17] Following his death in 1782, his son Thomas Ingles took over the operation of Ingles Ferry, in partnership with his brother John and his cousin Crockett.[13]: 75 [18]: 51 Mary Draper Ingles died at Ingles Ferry in 1815.[19]

Toll road
After the American Revolutionary War, thousands of immigrants poured through the New River Valley on their way to the newly opened territories in Kentucky and Tennessee.[20]: 6 At times, as many as 30 or 40 wagons and teams would spend the night at the ferry.[12]: 13 In 1805 William's son John Ingles and Andrew Lewis Jr. sponsored a bill before the Virginia General Assembly authorizing the Allegheny Turnpike (now known as the Valley Pike), so that tolls could be collected to support the maintenance of the road and the ferry, "because the cost of maintaining the previous public road in good condition had proved too great a burden." The turnpike, which opened in 1809, was 25 feet wide and more than seven miles in length. A gate and toll house were built near Shawsville.[13]: 79
Thomas Ingles, grandson of William and Mary Draper Ingles, acquired the ferry in 1832. By 1834, an estimated 20,000 people were using the ferry annually, including slaves being transported westward. Geographer George William Featherstonhaugh observed a caravan of 300 slaves crossing the river at Ingles Ferry in 1834.[13]: 75 In the 1830s, Thomas refurbished and enlarged the tavern, which is still standing, and built a ferry house.[6]: 95–100 He and several others incorporated The Lafayette and Ingles Ferry Turnpike Company in 1839.[13]: 115 The state of Virginia macadamized (paved) the road in 1840.[5]: 114
The Ingles Bridge and later years

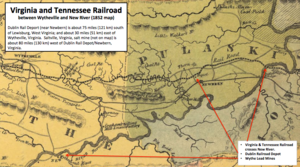
In 1842, Thomas Ingles built a covered bridge across the New River at a cost of $17,000, but he continued to offer a ferry service until 1847.[13]: 76, 116 The bridge was completed in February, 1843[8]: 4 and was 28 feet wide, 20 feet above the water, and 600 feet long.[12]: 16 By 1848, the bridge tolls added up to nearly $1,900 a year, but Ingles stated that "a large portion of the county people are permitted to cross free of charge."[13]: 117 During subsequent years, tolls could exceed $1,000 per month.[12]: 16 [9] Revenue dropped after the construction in 1855 of the Virginia and Tennessee Railroad bridge, about two miles downstream from Ingles Ferry.[5]: 114
On 9 May, 1864, following the Battle of Cloyd's Mountain, the fleeing Confederate artillery crossed the New River on Ingles Bridge.[21]: 52 The bridge was subsequently burned by Union forces,[5]: 114 but the abutments on the west bank can still be seen.[13]: 117 Ingles Ferry was the site of one of the final battles of the Civil War when, on 12 April, 1865 (3 days after the Confederate surrender at Appomattox, Virginia), a detachment of Union troops attempting to rejoin General George Stoneman skirmished with Confederate infantry. The troops had not yet received news of the surrender.[12]: 19 In 1865, the Ingles Ferry was again put into operation and continued until 1939 when the last flat-bottom ferry boat sank with a load of coal.[13]: 76 The ferry was briefly reactivated from 1944-1948.[12]: 56 The 1840 ferry house remained in use until it was destroyed by fire in 1967.[9]
A watercolor sketch by Lewis Miller dated 26 August, 1859 depicts the covered Ingles Bridge and the Ingles farm next to the tavern, as seen from Lovely Mount.[3]: 74
Archaeology
The Ingles Bottom Archeological Sites feature excavations investigating historic and prehistoric occupation of the area, including the Ingles family home, farm,[22] stables, and a family cemetery.[23] John Ingles' 1790 home, known as Ingleside, is also nearby.[24]: 414 Excavations initiated in 1974 covered 1400 square feet and found over 30,000 artifacts from the late 18th century. The dig uncovered a tannery as well as the foundation of the one-room cabin where Mary Draper Ingles lived during her final years, which measured 14.5 feet by 16 feet, and was still standing in 1910. Archaeologists also found evidence of a Native American village dating to 1250-1500 CE, as well as projectile points, bone tools and shellfish remains dating from ca. 3000-1500 BCE.[8]: 4
Legacy
In November 1969, the property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and the Virginia Landmarks Register.[8]: 4 [25][26] The property’s three owners, all direct descendants of Mary Draper Ingles, have donated a permanent conservation easement of the 313-acre tract to the Virginia Outdoors Foundation and the Virginia Department of Historic Resources. The tavern as well as portions of the original Wilderness Road can be seen at the site. Replicas of the 18th-century home of the Ingles family can be seen on the eastern side of the river, and this area was also placed under permanent easement by the owner, another direct descendent of Mary Draper Ingles.[27]
See also
External links
- 2007 Historic Lecture Series: Ingles Tavern & Wilderness Trail, Blacksburg Museum and Cultural Foundation
Bibliography
- Fitzpatrick, Francis Burke. History of Ingles Ferry - 1937. Washington, District of Columbia: Library of Congress Photoduplication Service, 1990. Notes: Microfilm of original typescript (1937, carbon or mimeograph, 65 leaves). Contains history of Ingles Ferry and settlement and biographical sketches of Colonel William Ingles and Mary Draper Ingles.
- John Preston McConnell Library. James Zoll Ingles Ferry Store Ledgers: [Finding Aid]. Radford, Va: McConnell Library Archives and Special Collections, 2011. Summary: This contains two ledgers and a few supporting documents from a store owned by James Zoll that was at or near the site of Ingles Ferry near Radford, and operated ca. 1850-1870s.
- Killen, Linda. Ingles Ferry Ledgers: 1840s to 1880s. [Virginia?]: [L. Killen], 1999. Notes: Includes index. Description: 96 pages; 28 cm. Responsibility: transcribed by Linda Killen.
References
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- ^ "Virginia Landmarks Register". Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Retrieved 5 June 2013.
- ^ a b c d e Jim Page and Sherry Joines Wyatt, "The Nigh and Best Way": The Early Development of Roads in Montgomery County", The Smithfield Review, Volume 21, 2017.
- ^ Ingels History
- ^ a b c d e Hale, John P., Trans-Allegheny Pioneers (West Virginia and Ohio): Historical Sketches of the First White Settlers West of the Alleghenies, 1748 and After (1886), Heritage Books, reprint, 2009.
- ^ a b c Smith, Conway Howard. Colonial Days in the Land that Became Pulaski County. Pulaski County Library Board, 1975.
- ^ History of the Great Kanawha Valley (West Virginia): With Family History and Biographical Sketches: a Statement of Its Natural Resources, Industrial Growth and Commercial Advantages. Westminster, Md: Heritage Books, 2007
- ^ a b c d Junius R. Fishburne, "Nomination form, Ingles Bottom Archaeological Sites," Virginia Department of Historic Resources, June 15, 1976
- ^ a b c d Ingles Ferry, Virginia Department of Historic Resources, June 2, 2022.
- ^ Evan Benjamin and Daniel Holbrook. "Ingles Farm." Clio: Your Guide to History. May 4, 2017. Accessed September 11, 2023.
- ^ Louis Philippe. Diary of My Travels in America: Louis Philippe, King of France, 1830-1848. New York: Delacorte Press, 1977.
- ^ a b c d e f Elmer Johnson, "Radford Then and Now: A Pictorial History," American Bicentennial Commission of Radford, Virginia, 1975
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Montgomery County Reconnaissance Level Survey", Vol. 1, July 1986, Historic Sites Survey: Virginia Division of Historic Landmarks.
- ^ Ann Brush Miller, Betty E. Spillman and Shirley P. Thomas, "Historic Roads of Virginia: Fincastle County Road Orders, 1773-1776," New River Historical Society, 2007
- ^ "Henry Hamilton's Journal: A Prisoner of War, March 8 to June 16, 1779", Indiana Historical Bureau website.
- ^ Richard Osborn, "William Preston and the Revolutionary Settlement", Journal of Backcountry Studies, vol. 3, no. 2, July, 2010.
- ^ 1782 Montgomery County, Virginia Personal Property Tax List
- ^ Kegley, Frederick Bittle., Kegley, Mary B. Early Adventurers on the Western Waters: The New River of Virginia in pioneer days, 1745-1800. Green Publishers, 1980.
- ^ Ryan S. Mays, "The Draper's Meadows Settlement (1746-1756)," Part II, The Smithfield Review, Volume 19, 2015
- ^ Hugh Miller, "Prehistoric and Historic Resources of Montgomery County, Virginia," Virginia Department of Natural Resources, 2 Sept 1989
- ^ Pulaski County Reconnaissance Level Survey, National Park Service, Virginia Department of Historic Resources, September 1985
- ^ "Ingles Farm," Radford Tourism
- ^ "Ingels History: Ingles Ferry, Virginia
- ^ Calder Loth, The Virginia Landmarks Register, Virginia Department of Historic Resources, 1999
- ^ Virginia Outdoors Foundation Archived 2010-01-15 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 16 July 2010
- ^ Virginia Historic Landmarks Commission Staff (May 1969). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory/Nomination: Ingles Ferry" (PDF). Virginia Department of Historic Resources. and Accompanying two photos
- ^ Jason McGarvey, "Historic Ingles Ferry Farm Permanently Protected," Virginia Outdoors Foundation News, August 29, 2009
- National Register of Historic Places in Pulaski County, Virginia
- 1772 establishments in Virginia
- Ferries
- Colony of Virginia
- Pulaski County, Virginia
- Montgomery County, Virginia
- Pre-statehood history of Virginia
- Transportation in Virginia
- Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Virginia




