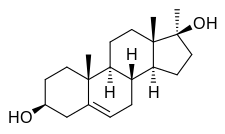
Methandriol
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Crestabolic, Cytobolin, Diandren, Madiol, Stenediol, Mestenediol |
| Other names | Metandriol; Methylandrostenediol; Methylandrostenediole; 17α-Methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.548 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 304.474 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Methandriol (INN) (brand names Crestabolic, Cytobolin, Diandren, Madiol, Stenediol, Mestenediol), also known as methylandrostenediol, as well as 17α-methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is a synthetic, orally active androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) which was developed by Organon and is used in both oral and injectable (as methandriol dipropionate, methandriol propionate, or methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate) formulations.[1][2] It is a 17α-alkylated AAS and the 17α-methylated derivative of the endogenous androgen prohormone androstenediol.[1][2]
History
Methandriol was first synthesized in 1935 along with methyltestosterone and mestanolone.[3][4]
References
- ^ a b J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 794–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 177–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ^ Schänzer W (1996). "Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids". Clin. Chem. 42 (7): 1001–20. PMID 8674183.
- ^ Ruzicka, L.; Goldberg, M. W.; Rosenberg, H. R. (1935). "Sexualhormone X. Herstellung des 17-Methyl-testosterons und anderer Androsten- und Androstanderivate. Zusammenhänge zwischen chemischer Konstitution und männlicher Hormonwirkung". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 18 (1): 1487–1498. doi:10.1002/hlca.193501801203. ISSN 0018-019X.
External links
