AM-694: Difference between revisions
m Format plain DOIs using AWB (8087) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{More footnotes|date=May 2011}} |
{{More footnotes|date=May 2011}} |
||
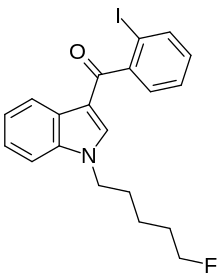
'''AM-694''' (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective [[agonist]] for the [[cannabinoid receptor]] [[Cannabinoid receptor 1|CB<sub>1</sub>]] |
'''AM-694''' (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective [[agonist]] for the [[cannabinoid receptor]] [[Cannabinoid receptor 1|CB<sub>1</sub>]]. It is used in scientific research for mapping the distribution of CB<sub>1</sub> receptors. No public data about AM-694 [[metabolism]] is known{{Citation needed|19. July 2012}}. AM-694 has already emerged as a [[designer drug]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Pharmacology== |
|||
AM-694 has already emerged as a [[designer drug]]. Concerns have been raised{{by whom?|date=May 2011}} over the possible toxicity of this compound, due to its likely metabolism to ω-fluoroalkanoic acids. Studies of the metabolism of related compounds show that the first step is the N-[[dealkylation]] of the indole nitrogen<ref>Zhang Q, Ma P, Cole RB, Wang G. Identification of in vitro metabolites of JWH-015, an aminoalkylindole agonist for the peripheral cannabinoid receptor (CB2) by HPLC-MS/MS. ''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry''. 2006 Nov;386(5):1345-55. PMID 16955257</ref>, which in this case yields 5-fluoropentanoic acid, which is then further metabolised to 3-fluoropropanoic acid. Terminal mono[[fluoroalkane]]s with even numbers of carbons are ultimately metabolized into [[Fluoroacetic acid|fluoroacetate]], which is a potent toxin primarily used as a [[rodenticide]] and has the potential to [[bioaccumulate]]. As AM-694 contains a five carbon chain, fluoroacetate is unlikely to be produced as a metabolite, with the substantially less toxic 3-fluoropropanoic acid being produced instead. The 4-fluorobutyl and 6-fluorohexyl [[Homolog (chemistry)|homologues]] of AM-694 will however produce fluoroacetate as a metabolite and so may be significantly more toxic.<ref>[http://article.pubs.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/ppv/RPViewDoc?issn=1480-3291&volume=34&issue=11&startPage=1532 Millington JE, Pattison FLM. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XII. ESTERS OF ω-FLUOROALCOHOLS. ''Canadian Journal of Chemistry''. 1956 Nov;34(11):1532-1541.]</ref><ref>[http://article.pubs.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/ppv/RPViewDoc?issn=1480-3291&volume=35&issue=2&startPage=141 Pattison FLM, Howell WC, Woolford RG. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XIII. ω-FLUOROALKYL ETHERS. ''Canadian Journal of Chemistry''. 1957 Feb;35(2):141-148.]</ref> Fluoroacetate is also produced in similar fashion by S-dealkylation of [[2C-T-21]], another designer drug, so death from acute fluoroacetate poisoning appears unlikely following consumption of these drugs, with concerns instead relating to the potential for chronic toxicity with extended use. |
|||
| ⚫ | AM-694 is a [[agonist]] for [[cannabinoid receptor]]s. Affinities are: with a [[Dissociation constant|K<sub>i</sub>]] of 0.08nM at [[Cannabinoid receptor 1|CB<sub>1</sub>]] and 18x selectivity over [[Cannabinoid receptor 2 (macrophage)|CB<sub>2</sub>]] with a [[Dissociation constant|K<sub>i</sub>]] 1.44nM.<ref name="WO 2001 28557 A1">{{Ref patent2 | country = WO | number = 200128557 | status = granted | title = Cannabimimetic indole derivatives | pubdate = 2001-04-26 | gdate = 2001-06-07 | pridate= 1999-10-18 | inventor = Makriyannis A, Deng H | assign1= }}</ref> It is unclear what is responsible for this unusually high CB<sub>1</sub> binding affinity, but it makes the [[fluorine-18|<sup>18</sup>F]] [[Isotopic labeling|radiolabelled]] derivative of AM-694 useful for mapping the distribution of CB<sub>1</sub> receptors in the body.<ref>Willis PG, Katoch-Rouse R, Horti AG. Regioselective F-18 radiolabeling of AM694, a CB1 cannabinoid receptor ligand. ''Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals'' 2003;46(9):799-804. {{doi|10.1002/jlcr.720}}</ref>. |
||
===Pharmacokinetics=== |
|||
{{Refimprove section|date=July 2012}} |
|||
{{Main|JWH-018#Pharmacokinetics|l1=Pharmacokinetic data of JWH-018 are generally applicable to AM-694.}} |
|||
AM-694 [[metabolism]] differs only slightly from that of [[JWH-018]]. AM-694 N-[[dealkylation]] produces fluoropentane instead of [[pentane]] (or plain [[alkane]]s in general). It has been speculated that the fluoropentane might function as an [[alkylating agent]] or is further metabolized into toxic [[fluoroacetic acid]]. This is not true since [[fluoroalkane]]s do not act as [[alkylating agent]]s under normal conditions and uneven [[fluoroalkane]] chains metabolize into substantially less toxic [[fluoropropanoic acid]].<ref>[http://article.pubs.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/ppv/RPViewDoc?issn=1480-3291&volume=34&issue=11&startPage=1532 Millington JE, Pattison FLM. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XII. ESTERS OF ω-FLUOROALCOHOLS. ''Canadian Journal of Chemistry''. 1956 Nov;34(11):1532-1541.]</ref><ref>[http://article.pubs.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/ppv/RPViewDoc?issn=1480-3291&volume=35&issue=2&startPage=141 Pattison FLM, Howell WC, Woolford RG. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XIII. ω-FLUOROALKYL ETHERS. ''Canadian Journal of Chemistry''. 1957 Feb;35(2):141-148.]</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 01:44, 19 July 2012
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H19FINO |
| Molar mass | 435.273 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (May 2011) |
AM-694 (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is used in scientific research for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors. No public data about AM-694 metabolism is known[citation needed]. AM-694 has already emerged as a designer drug.
Pharmacology
AM-694 is a agonist for cannabinoid receptors. Affinities are: with a Ki of 0.08nM at CB1 and 18x selectivity over CB2 with a Ki 1.44nM.[1] It is unclear what is responsible for this unusually high CB1 binding affinity, but it makes the 18F radiolabelled derivative of AM-694 useful for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors in the body.[2].
Pharmacokinetics
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2012) |
AM-694 metabolism differs only slightly from that of JWH-018. AM-694 N-dealkylation produces fluoropentane instead of pentane (or plain alkanes in general). It has been speculated that the fluoropentane might function as an alkylating agent or is further metabolized into toxic fluoroacetic acid. This is not true since fluoroalkanes do not act as alkylating agents under normal conditions and uneven fluoroalkane chains metabolize into substantially less toxic fluoropropanoic acid.[3][4]
See also
References
- ^ WO patent 200128557, Makriyannis A, Deng H, "Cannabimimetic indole derivatives", granted 2001-06-07
- ^ Willis PG, Katoch-Rouse R, Horti AG. Regioselective F-18 radiolabeling of AM694, a CB1 cannabinoid receptor ligand. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals 2003;46(9):799-804. doi:10.1002/jlcr.720
- ^ Millington JE, Pattison FLM. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XII. ESTERS OF ω-FLUOROALCOHOLS. Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 1956 Nov;34(11):1532-1541.
- ^ Pattison FLM, Howell WC, Woolford RG. TOXIC FLUORINE COMPOUNDS: XIII. ω-FLUOROALKYL ETHERS. Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 1957 Feb;35(2):141-148.
