United States involvement in regime change: Difference between revisions
m →2006-Present: Syria: link |
→2010s: add Venezuela |
||
| Line 404: | Line 404: | ||
The U.S. has been supporting the [[Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen|intervention by Saudi Arabia]] in the [[Yemeni Civil War (2015–present)|Yemeni Civil War]]. The Yemeni Civil War began in 2015 between two sides, each claiming at that time to support the legitimate government of [[Yemen]]:<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/143295/asher-orkaby/houthi-who |work=Foreign Affairs |title=Houthi Who? |first=Asher |last=Orkaby |date=March 25, 2015 |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150327115828/http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/143295/asher-orkaby/houthi-who |archivedate=March 27, 2015}}</ref> [[Houthis|Houthi]] forces, which control the capital [[Sana'a]] and had supported former president [[Ali Abdullah Saleh]], fighting against forces based in [[Aden]] and loyal to the government of [[Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Yemen in Crisis |url=http://www.cfr.org/yemen/yemen-crisis/p36488 |publisher=Council on Foreign Relations |date=July 8, 2015 |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150509030311/http://www.cfr.org/yemen/yemen-crisis/p36488 |archivedate=May 9, 2015}}</ref> The Saudi-led offensive is aimed at restoring Hadi to power, and is allied with various local factions.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html |title=Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen |first1=Giorgio |last1=Cafiero |first2=Daniel |last2=Wagner |date=September 24, 2015}}</ref> The Saudi Arabian-led intervention has been widely condemned due to its widespread bombing of urban and other civilian areas, including schools and [[hospital]]s.<ref>[http://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170210052642/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html |date=February 10, 2017 }}, ''Huffington Post'', "Despite the international community's condemnation of Saudi Arabia's bombing of civilian areas in Yemen, ..."</ref><ref name="news-vice-com_2016-01-05_SCB">{{cite news |last=Oakford |first=Samuel |title=The Saudi Coalition Bombed A Rehabilitation Center for Blind People in Yemen |publisher=[[Vice News]] |date=January 5, 2016 |url=https://news.vice.com/article/saudi-arabia-bombed-a-rehabilitation-center-for-blind-people-in-yemen}}</ref><ref name="MEE_2016-01-05_YCF">{{cite web |last=MacDonald |first=Alex |title=Yemen centre for blind 'hit in Saudi coalition air raid' |publisher=[[Middle East Eye]] |date=January 5, 2016 |url=http://www.middleeasteye.net/news/saudi-led-coalition-airstrikes-reportedly-hit-centre-blind-yemen-capital-128298478 |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6eMrc6cDM |archivedate=January 7, 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> The U.S. military provides targeting assistance and intelligence and logistical support for the Saudi-led bombing campaign,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/middle_east/report-yemens-embattled-president-flees-stronghold-as-rebels-advance/2015/03/25/e0913ae2-d2d5-11e4-a62f-ee745911a4ff_story.html |title=Saudi Arabia launches air attacks in Yemen |work=[[The Washington Post]] |date=March 25, 2015}}</ref> including aerial refueling.<ref>[https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-03-26/yemeni-bombing-led-by-saudis-is-backed-by-u-s-logistics-spying "U.S. Backs Saudi-Led Yemeni Bombing With Logistics, Spying"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170406183021/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-03-26/yemeni-bombing-led-by-saudis-is-backed-by-u-s-logistics-spying |date=April 6, 2017 }}, [[Bloomberg News]], March 26, 2015</ref><ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32211550 "Yemen conflict: US boosts arms supplies for Saudi-led coalition"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180702212047/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32211550 |date=July 2, 2018 }}. [[BBC News]]. April 8, 2015.</ref> The US also provides weapons and bombs,<ref>[http://www.aljazeera.com/news/2015/04/expediting-arms-supplies-saudi-led-coalition-150407152205321.html "US steps up arms for Saudi campaign in Yemen"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150710003749/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/2015/04/expediting-arms-supplies-saudi-led-coalition-150407152205321.html |date=July 10, 2015 }}, [[Al Jazeera]], April 8, 2015</ref> including, according to a Human Rights Watch (HRW) report, [[Cluster munition|cluster bombs]] [[Convention on Cluster Munitions|outlawed]] in much of the world and used by Saudi Arabia in the conflict.<ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32572408 "Yemen: Saudi Arabia used cluster bombs, rights groups says"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180704190515/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32572408 |date=July 4, 2018 }}. [[BBC News]]. May 3, 2015.</ref><ref name="UK-RTS_2015-12-22_UBS">{{cite news |last=Nichols |first=Michelle |title=U.N. blames Saudi-led coalition for most attacks on Yemeni civilians |agency=Reuters UK |date=December 22, 2015 |url=http://uk.reuters.com/article/uk-yemen-security-un-idUKKBN0U51UZ20151222 |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6e1dGmEZF |archivedate=December 24, 2015 |url-status=live}}</ref> The United States also supports the war effort on the ground with Green Berets on the Yemen border with Saudi Arabia tasked initially to help the Saudis secure the border and later expanded to help locate and destroy Houthi ballistic missile caches and launch sites in what Senator [[Tim Kaine]] called a “purposeful blurring of lines between train and equip missions and combat.”<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/05/03/us/politics/green-berets-saudi-yemen-border-houthi.html|title=Army Special Forces Secretly Help Saudis Combat Threat From Yemen Rebels|first1=Helene|last1=Cooper|first2=Thomas|last2=Gibbons-Neff|first3=Eric|last3=Schmitt|date=May 3, 2018|newspaper=The New York Times}}</ref> The US has been criticized for providing weapons and bombs knowing that Saudi bombing has been indiscriminately targeting civilians and violating the [[laws of war]].<ref name="mcclatchydc.com">{{cite news |url=http://www.mcclatchydc.com/news/nation-world/world/article25835662.html |title=Saudi airstrikes in Yemen violate laws of war, rights group says |publisher=[[The McClatchy Company|McClatchy DC]]}}</ref><ref name="lieu">{{cite news |last=Norton |first=Ben |authorlink=Ben Norton |date=March 17, 2016 |title='Look like war crimes to me': Congressman raises concerns over U.S. support for Saudi war in Yemen |url=http://www.salon.com/2016/03/17/look_like_war_crimes_to_me_congressman_raises_concerns_over_u_s_support_for_saudi_war_in_yemen/ |work=[[Salon (website)|Salon]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Steve Visser |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2016/08/20/middleeast/us-military-yemen-saudi-led-coalition/index.html |title=US military distances itself from Saudi-led war in Yemen |publisher=CNN |date=August 21, 2016}}</ref> It has been suggested that the U.S. government is legally a "[[co-belligerent]]" in the conflict, in which case U.S. military personnel could be prosecuted for [[war crime]]s,<ref name=[[Reuters]]-20161010>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-saudi-yemen-idUSKCN12A0BQ |title=Exclusive: As Saudis bombed Yemen, U.S. worried about legal blowback |author=Warren Strobel, Jonathan Landay |agency=[[Reuters]] |date=October 10, 2016}}</ref><ref name=justsecurity-20150327>{{cite web |url=https://www.justsecurity.org/21524/international-law-saudi-operation-storm-resolve-yemen/ |title=International Law on the Saudi-Led Military Operations in Yemen |author=Nathalie Weizmann |publisher=Just Security |date=March 27, 2015}}</ref><ref>[https://www.hrw.org/news/2016/03/21/yemen-embargo-arms-saudi-arabia "Yemen: Embargo Arms to Saudi Arabia"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170131053621/https://www.hrw.org/news/2016/03/21/yemen-embargo-arms-saudi-arabia |date=January 31, 2017 }} [[Human Rights Watch]], March 21, 2106</ref><ref>{{cite news |last= Wintour|first=Patrick|date=September 3, 2019 |title=UK, US and France may be complicit in Yemen war crimes – UN report|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/sep/03/uk-us-and-france-may-be-complicit-in-yemen-war-crimes-un-report|work=[[The Guardian]] |location= |access-date=October 19, 2019}}</ref> and a [[U.S. Senate|U.S. senator]] has accused the U.S. of complicity in Yemen's humanitarian catastrophe, with [[Famine in Yemen|millions facing starvation]].<ref>"[https://theintercept.com/2017/11/14/congress-yemen-war-unauthorized/ Congress Votes to Say It Hasn't Authorized War in Yemen, Yet War in Yemen Goes On] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180107231800/https://theintercept.com/2017/11/14/congress-yemen-war-unauthorized/ |date=2018-01-07 }}", ''The Intercept'', November 14, 2017</ref><ref>{{cite news |date=July 19, 2018 |title=PBS Report from Yemen: As Millions Face Starvation, American-Made Bombs Are Killing Civilians |url=https://www.democracynow.org/2018/7/19/pbs_report_from_yemen_as_millions |work=[[Democracy Now!]] |access-date=August 5, 2018}}</ref> As of May 2018, the civil war is at a stalemate, and 13 million Yemeni civilians face starvation, according to the UN.<ref>{{cite news|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|date=October 15, 2018 |title=Yemen could be 'worst famine in 100 years'|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/av/world-middle-east-45857729/yemen-could-be-worst-famine-in-100-years|work=BBC |location= |access-date=October 15, 2018}}</ref> |
The U.S. has been supporting the [[Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen|intervention by Saudi Arabia]] in the [[Yemeni Civil War (2015–present)|Yemeni Civil War]]. The Yemeni Civil War began in 2015 between two sides, each claiming at that time to support the legitimate government of [[Yemen]]:<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/143295/asher-orkaby/houthi-who |work=Foreign Affairs |title=Houthi Who? |first=Asher |last=Orkaby |date=March 25, 2015 |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150327115828/http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/143295/asher-orkaby/houthi-who |archivedate=March 27, 2015}}</ref> [[Houthis|Houthi]] forces, which control the capital [[Sana'a]] and had supported former president [[Ali Abdullah Saleh]], fighting against forces based in [[Aden]] and loyal to the government of [[Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Yemen in Crisis |url=http://www.cfr.org/yemen/yemen-crisis/p36488 |publisher=Council on Foreign Relations |date=July 8, 2015 |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150509030311/http://www.cfr.org/yemen/yemen-crisis/p36488 |archivedate=May 9, 2015}}</ref> The Saudi-led offensive is aimed at restoring Hadi to power, and is allied with various local factions.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html |title=Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen |first1=Giorgio |last1=Cafiero |first2=Daniel |last2=Wagner |date=September 24, 2015}}</ref> The Saudi Arabian-led intervention has been widely condemned due to its widespread bombing of urban and other civilian areas, including schools and [[hospital]]s.<ref>[http://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170210052642/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/giorgio-cafiero/saudi-arabia-and-alqaeda-_b_8184338.html |date=February 10, 2017 }}, ''Huffington Post'', "Despite the international community's condemnation of Saudi Arabia's bombing of civilian areas in Yemen, ..."</ref><ref name="news-vice-com_2016-01-05_SCB">{{cite news |last=Oakford |first=Samuel |title=The Saudi Coalition Bombed A Rehabilitation Center for Blind People in Yemen |publisher=[[Vice News]] |date=January 5, 2016 |url=https://news.vice.com/article/saudi-arabia-bombed-a-rehabilitation-center-for-blind-people-in-yemen}}</ref><ref name="MEE_2016-01-05_YCF">{{cite web |last=MacDonald |first=Alex |title=Yemen centre for blind 'hit in Saudi coalition air raid' |publisher=[[Middle East Eye]] |date=January 5, 2016 |url=http://www.middleeasteye.net/news/saudi-led-coalition-airstrikes-reportedly-hit-centre-blind-yemen-capital-128298478 |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6eMrc6cDM |archivedate=January 7, 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> The U.S. military provides targeting assistance and intelligence and logistical support for the Saudi-led bombing campaign,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/middle_east/report-yemens-embattled-president-flees-stronghold-as-rebels-advance/2015/03/25/e0913ae2-d2d5-11e4-a62f-ee745911a4ff_story.html |title=Saudi Arabia launches air attacks in Yemen |work=[[The Washington Post]] |date=March 25, 2015}}</ref> including aerial refueling.<ref>[https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-03-26/yemeni-bombing-led-by-saudis-is-backed-by-u-s-logistics-spying "U.S. Backs Saudi-Led Yemeni Bombing With Logistics, Spying"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170406183021/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-03-26/yemeni-bombing-led-by-saudis-is-backed-by-u-s-logistics-spying |date=April 6, 2017 }}, [[Bloomberg News]], March 26, 2015</ref><ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32211550 "Yemen conflict: US boosts arms supplies for Saudi-led coalition"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180702212047/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32211550 |date=July 2, 2018 }}. [[BBC News]]. April 8, 2015.</ref> The US also provides weapons and bombs,<ref>[http://www.aljazeera.com/news/2015/04/expediting-arms-supplies-saudi-led-coalition-150407152205321.html "US steps up arms for Saudi campaign in Yemen"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150710003749/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/2015/04/expediting-arms-supplies-saudi-led-coalition-150407152205321.html |date=July 10, 2015 }}, [[Al Jazeera]], April 8, 2015</ref> including, according to a Human Rights Watch (HRW) report, [[Cluster munition|cluster bombs]] [[Convention on Cluster Munitions|outlawed]] in much of the world and used by Saudi Arabia in the conflict.<ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32572408 "Yemen: Saudi Arabia used cluster bombs, rights groups says"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180704190515/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-32572408 |date=July 4, 2018 }}. [[BBC News]]. May 3, 2015.</ref><ref name="UK-RTS_2015-12-22_UBS">{{cite news |last=Nichols |first=Michelle |title=U.N. blames Saudi-led coalition for most attacks on Yemeni civilians |agency=Reuters UK |date=December 22, 2015 |url=http://uk.reuters.com/article/uk-yemen-security-un-idUKKBN0U51UZ20151222 |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6e1dGmEZF |archivedate=December 24, 2015 |url-status=live}}</ref> The United States also supports the war effort on the ground with Green Berets on the Yemen border with Saudi Arabia tasked initially to help the Saudis secure the border and later expanded to help locate and destroy Houthi ballistic missile caches and launch sites in what Senator [[Tim Kaine]] called a “purposeful blurring of lines between train and equip missions and combat.”<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/05/03/us/politics/green-berets-saudi-yemen-border-houthi.html|title=Army Special Forces Secretly Help Saudis Combat Threat From Yemen Rebels|first1=Helene|last1=Cooper|first2=Thomas|last2=Gibbons-Neff|first3=Eric|last3=Schmitt|date=May 3, 2018|newspaper=The New York Times}}</ref> The US has been criticized for providing weapons and bombs knowing that Saudi bombing has been indiscriminately targeting civilians and violating the [[laws of war]].<ref name="mcclatchydc.com">{{cite news |url=http://www.mcclatchydc.com/news/nation-world/world/article25835662.html |title=Saudi airstrikes in Yemen violate laws of war, rights group says |publisher=[[The McClatchy Company|McClatchy DC]]}}</ref><ref name="lieu">{{cite news |last=Norton |first=Ben |authorlink=Ben Norton |date=March 17, 2016 |title='Look like war crimes to me': Congressman raises concerns over U.S. support for Saudi war in Yemen |url=http://www.salon.com/2016/03/17/look_like_war_crimes_to_me_congressman_raises_concerns_over_u_s_support_for_saudi_war_in_yemen/ |work=[[Salon (website)|Salon]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Steve Visser |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2016/08/20/middleeast/us-military-yemen-saudi-led-coalition/index.html |title=US military distances itself from Saudi-led war in Yemen |publisher=CNN |date=August 21, 2016}}</ref> It has been suggested that the U.S. government is legally a "[[co-belligerent]]" in the conflict, in which case U.S. military personnel could be prosecuted for [[war crime]]s,<ref name=[[Reuters]]-20161010>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-saudi-yemen-idUSKCN12A0BQ |title=Exclusive: As Saudis bombed Yemen, U.S. worried about legal blowback |author=Warren Strobel, Jonathan Landay |agency=[[Reuters]] |date=October 10, 2016}}</ref><ref name=justsecurity-20150327>{{cite web |url=https://www.justsecurity.org/21524/international-law-saudi-operation-storm-resolve-yemen/ |title=International Law on the Saudi-Led Military Operations in Yemen |author=Nathalie Weizmann |publisher=Just Security |date=March 27, 2015}}</ref><ref>[https://www.hrw.org/news/2016/03/21/yemen-embargo-arms-saudi-arabia "Yemen: Embargo Arms to Saudi Arabia"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170131053621/https://www.hrw.org/news/2016/03/21/yemen-embargo-arms-saudi-arabia |date=January 31, 2017 }} [[Human Rights Watch]], March 21, 2106</ref><ref>{{cite news |last= Wintour|first=Patrick|date=September 3, 2019 |title=UK, US and France may be complicit in Yemen war crimes – UN report|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/sep/03/uk-us-and-france-may-be-complicit-in-yemen-war-crimes-un-report|work=[[The Guardian]] |location= |access-date=October 19, 2019}}</ref> and a [[U.S. Senate|U.S. senator]] has accused the U.S. of complicity in Yemen's humanitarian catastrophe, with [[Famine in Yemen|millions facing starvation]].<ref>"[https://theintercept.com/2017/11/14/congress-yemen-war-unauthorized/ Congress Votes to Say It Hasn't Authorized War in Yemen, Yet War in Yemen Goes On] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180107231800/https://theintercept.com/2017/11/14/congress-yemen-war-unauthorized/ |date=2018-01-07 }}", ''The Intercept'', November 14, 2017</ref><ref>{{cite news |date=July 19, 2018 |title=PBS Report from Yemen: As Millions Face Starvation, American-Made Bombs Are Killing Civilians |url=https://www.democracynow.org/2018/7/19/pbs_report_from_yemen_as_millions |work=[[Democracy Now!]] |access-date=August 5, 2018}}</ref> As of May 2018, the civil war is at a stalemate, and 13 million Yemeni civilians face starvation, according to the UN.<ref>{{cite news|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|date=October 15, 2018 |title=Yemen could be 'worst famine in 100 years'|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/av/world-middle-east-45857729/yemen-could-be-worst-famine-in-100-years|work=BBC |location= |access-date=October 15, 2018}}</ref> |
||
====2019: Venezuela==== |
|||
The U.S. efforts for regime change in Venezuela intensified in January 2019 with the increase of crippling sanctions, diplomatic pressure, and warnings.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.npr.org/2019/02/22/696057482/trumps-venezuela-moves-follow-long-history-of-intervention-in-latin-america|title=Trump's Venezuela Moves Follow Long History Of Intervention In Latin America|website=NPR.org|language=en|access-date=2019-12-29}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.ft.com/content/68e2d152-6c2f-11e9-a9a5-351eeaef6d84|title=US commitment to regime change in Venezuela tested|last=Williams|first=Aime|date=2019-05-01|work=Financial Times|access-date=2019-12-29|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2019/02/trump-learned-to-love-regime-change-venezuela/581878/|title=Trump’s Affinity for Strongmen Has a Big Exception|last=Gilsinan|first=Uri Friedman, Kathy|date=2019-02-02|website=The Atlantic|language=en-US|access-date=2019-12-29}}</ref> Mark Weisenbrot writing for the New Republic said the sanctions (which he considers illegal) are a "plan to starve Venezuela into submission." <ref>{{Cite news|url=https://newrepublic.com/article/153283/reality-behind-trumps-coalition-regime-change-venezuela|title=The Reality Behind Trump’s Coalition for Regime Change in Venezuela|last=Weisbrot|first=Mark|date=2019-03-13|work=The New Republic|access-date=2019-12-29|issn=0028-6583}}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 17:40, 29 December 2019
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (November 2019) |
United States involvement in regime change has entailed both overt and covert actions aimed at altering, replacing, or preserving foreign governments. In the latter half of the 19th century, the U.S. government initiated actions for regime change mainly in Latin America and the southwest Pacific, including the Spanish–American and Philippine–American wars. At the onset of the 20th century the United States shaped or installed friendly governments in many countries around the world, including neighbors Panama, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
During World War II, the United States helped overthrow many Nazi Germany or imperial Japanese puppet regimes. Examples include regimes in the Philippines, Korea, the Eastern portion of China, and much of Europe. United States forces were also instrumental in ending the rule of Adolf Hitler over Germany and of Benito Mussolini over Italy.
In the aftermath of World War II, the U.S. government struggled with the Soviet Union for global leadership and influence within the context of the Cold War. It expanded the geographic scope of its actions beyond its traditional area of operations, Central America and the Caribbean. Significant operations included the U.S. and UK-orchestrated 1953 Iranian coup d'état, the 1961 Bay of Pigs Invasion targeting Cuba, and support for the overthrow of Sukarno by General Suharto in Indonesia. In addition, the U.S. has interfered in the national elections of many countries, including in Japan in the 1950s and 1960s to keep its preferred center-right Liberal Democratic Party in power using secret funds, in the Philippines to orchestrate the campaign of Ramon Magsaysay for president in 1953, and in Lebanon to help Christian parties in the 1957 elections using secret cash infusions.[1] According to one study, the U.S. executed at least 81 overt and covert known interventions in foreign elections during the period 1946–2000.[2] Another study found that the U.S. engaged in 64 covert and six overt attempts at regime change during the Cold War.[3]
Also after World War II, the United States in 1945 ratified[4] the UN Charter, the preeminent international law document,[5] which legally bound the U.S. government to the Charter's provisions, including Article 2(4), which prohibits the threat or use of force in international relations, except in very limited circumstances.[6] Therefore, any legal claim advanced to justify regime change by a foreign power carries a particularly heavy burden.[7]
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the United States has led or supported wars to determine the governance of a number of countries. Stated U.S. aims in these conflicts have included fighting the War on Terror as in the ongoing Afghan war, or removing dictatorial and hostile regimes in the Iraq War and the 2011 military intervention in Libya.
Pre-1887 Interventions
1860s
1865-1867: Mexico
While the United States was in the American Civil War, France, and other countries, took the opportunity to invade Mexico, to collect debts. France then installed Hapsburg prince Maximilian I as the Emperor of Mexico. After the Civil war ended the United States began supporting the Liberal forces of Benito Juarez against the forces of Maximilian. The United States began sending and dropping arms into Mexico and many Americans fought alongside Juarez. Eventually Juarez and the Liberals took back power and executed Maximillian I.[8][9][10] The United States was against it and had invoked the Monroe Doctrine. William Seward even said afterwards "The Monroe Doctrine, which eight years ago was merely a theory, is now an irreversible fact."[11]
1887–1912: U.S. Empire, Expansionism, and The Roosevelt Administration
1880s
1887–1889: Samoa

In the 1880s, Samoa was a monarchy with two rival claimants to the throne, Malietoa Laupepa or Mata'afa Iosefo. The Samoan crisis was a confrontation between the United States, Germany and Great Britain from 1887 to 1889, with the powers backing rival claimants to the throne of the Samoan Islands which became the First Samoan Civil War.[12] The powers eventually agreed that Laupepa would become king. After the powers withdrew, the civil war went on until 1894, when Laupepa secured his power.
1890s

1893: Kingdom of Hawaii
Anti-monarchs, mostly Americans, in Hawaii, engineered the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii. On January 17, 1893, the native monarch, Queen Lili'uokalani, was overthrown. Hawaii was initially reconstituted as an independent republic, but the ultimate goal of the action was the annexation of the islands to the United States, which was finally accomplished in 1898.
1898–1902: Cuba
After the explosion of The Maine the United States declared war on Spain, starting the Spanish–American War.[13] The United States invaded and occupied Spanish-ruled Cuba in 1898. Many in the United States did not want to annex Cuba and passed the Teller Amendment, forbidding annexation. Cuba was occupied by the U.S. run by military governor Leonard Wood during the first occupation from 1898-1902, after the end of the war. The Platt Amendment was passed later on outlining U.S. Cuban relations. It said the U.S. could intervene anytime against a government that was not approved, forced Cuba to accept U.S. influence, and limited Cuban abilities to make foreign relations.[14] The United States forced Cuba to accept the terms of the Platt Amendment, by putting it into their constitution.[15] After the occupation Cuba and the U.S. would sign the Cuban-American Treaty of Relations in 1903, further agreeing.[16] The amendment would be the main policy of rule until 1934 and would justify later intervention from 1906 to 1909, in 1912, and from 1917 to 1922.
1900s
1903: Panama

In 1903, the U.S. aided the secession of Panama from the Republic of Colombia. The secession was engineered by a Panamanian faction backed by the Panama Canal Company, a French–US corporation whose aim was the construction of a waterway across the Isthmus of Panama thus connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. In 1903, the U.S. signed the Hay-Herrán Treaty with Colombia, granting the United States use of the Isthmus of Panama in exchange for financial compensation.[17][18] amidst the Thousand Days' War. The Panama Canal was already under construction, and the Panama Canal Zone was carved out and placed under United States sovereignty. The US did not transfer the zone back to Panama until 2000.
1903–1925: Honduras

In what became known as the "Banana Wars," between the end of the Spanish–American War in 1898 and the inception of the Good Neighbor Policy in 1934, the U.S. staged many military invasions and interventions in Central America and the Caribbean.[19] The United States Marine Corps, which most often fought these wars, developed a manual called The Strategy and Tactics of Small Wars in 1921 based on its experiences. On occasion, the Navy provided gunfire support and Army troops were also used. The United Fruit Company and Standard Fruit Company dominated Honduras' key banana export sector and associated land holdings and railways. The U.S. staged invasions and incursions of US troops in 1903 (supporting a coup by Manuel Bonilla), 1907 (supporting Bonilla against a Nicaraguan-backed coup), 1911 and 1912 (defending the regime of Miguel R. Davila from an uprising), 1919 (peacekeeping during a civil war, and installing the caretaker government of Francisco Bográn), 1920 (defending the Bográn regime from a general strike), 1924 (defending the regime of Rafael López Gutiérrez from an uprising) and 1925 (defending the elected government of Miguel Paz Barahona) to defend US interests.[20] Writer O. Henry coined the term "Banana republic" in 1904 to describe Honduras.
1906-1909: Cuba
Tomás Estrada Palma became the first president of Cuba after the U.S. withdrew. He was a member of the Republican Party of Havana. He was re-elected in 1905 unopposed, however the Liberals accused him of electoral fraud. Fighting began between the Liberals and Republicans. Due to the tensions he resigned on September 28, 1906, and his government collapsed soon afterwards. U.S. Secretary of State William Howard Taft invoked the Platt Amendment and the 1903 treaty, under approval of Theodore Roosevelt, invading the country, and occupying it. The country would be governed by Charles Edward Magoon during the occupation. They oversaw the election of Jose Miguel Gomez in 1909, and afterwards withdrew from the country.[21]
1909–1910: Nicaragua
Governor Juan Jose Estrada, member of the conservative party, led a revolt against the president, Jose Santos Zelaya, member of the liberal party. This became what is known as the Estrada’s Rebellion. The United States supported the conservative forces, because Zelaya had wanted to work with Germany or Japan to build a new canal through the country. The U.S. controlled the Panama Canal, and did not want competition from another country outside of the Americas. Thomas P Moffat, a US council in Bluefields, Nicaragua would give overt support, in conflict with the US trying to only give covert support. Direct intervention would be pushed by the secretary of state Philander Knox. Two Americans were executed by Zelaya for their participation with the conservatives. Seeing an opportunity the United States became directly involved in the rebellion and sent in troops, which landed on the Caribbean coast. On December 14, 1909 Zelaya was forced to resign under diplomatic pressure from America and fled Nicaragua. Before Zelaya fled, he along with the liberal assembly choose Jose Madriz to lead Nicaragua. The U.S. refused to recognize Madriz. The conservatives eventually beat back the liberals and forced Madriz to resign. Estrada than became the president. Thomas C Dawson was sent as a special agent to the country and determined that any election held would bring the liberals into power, so had Estrada set up a constituent assembly to elect him instead. In August 1910 Estrada became president of Nicaragua under U.S. recognition, agreeing to certain conditions from the U.S. After the intervention, the U.S. and Nicaragua signed a treaty on June 6, 1911. [22][23][24]
1912–1941: The Wilson Administration, World War I, and The Interwar Period
1910s

1912–1933: Nicaragua
In the years after the Estrada rebellion, conflict between the liberals and conservatives continued. U.S. loans and business were under threat. Estrada was forced to resign by the Minister of War General Luis Mena and conservative Vice President Adolfo Diaz replaced him. Diaz was aligned with the U.S. and this made him unpopular with the Nicaraguan populace and Mena. Mena forced the cabinet to name him the successor to Diaz, but the U.S. did not recognize the decision. Due to this Mena led a rebellion with the liberals against Diaz declaring himself president of Nicaragua.
The Taft administration sent in troops into Nicaragua and occupied the country. When the Wilson administration came into power, they extended the stay and took complete financial and governmental control of the country, leaving a heavily armed legation. U.S. president Calvin Coolidge removed troops from the country, leaving a legation and Adolfo Diaz in charge of the country. Rebels ended up capturing the town with the legation and Diaz requested troops came back, which they did a few months after leaving. The U.S. government fought against rebels lead by Augusto Cesar Sandino. Franklin Delano Roosevelt pulled out because the U.S. could no longer afford to keep troops in the country due to the Great Depression. The second intervention in Nicaragua would become one of the longest wars in United States history. The United States left the US friendly Somoza family in charge, and in 1934 they would kill Sandino.[25]

1915–1934: Haiti
The U.S. occupied Haiti from 1915 to 1934. U.S.-based banks had lent money to Haiti and the banks requested U.S. government intervention. In an example of "gunboat diplomacy," the U.S. sent its navy to intimidate to get its way.[26] Eventually, in 1917, the U.S. installed a new government and dictated the terms of a new Haitian constitution of 1917 that instituted changes that included an end to the prior ban on land ownership by non-Haitians. The Cacos (military group) were originally armed militias of formerly enslaved persons who rebelled and took control of mountainous areas following the Haitian Revolution in 1804. Such groups fought a guerrilla war against the U.S. occupation in what were known as the "Caco Wars."[27]

1916–1924: Dominican Republic
U.S. marines invaded the Dominican Republic and occupied it from 1916 to 1924, and this was preceded by US military interventions in 1903, 1904, and 1914. The US Navy installed its personnel in all key positions in government and controlled the Dominican army and police.[28] Within a couple of days, the constitutional president, Juan Isidro Jimenes, resigned.[29]
1917–1919: Germany


After the release of the Zimmerman Telegram the United States joined the First World War on April 6, 1917, declaring war on the German Empire.[30] The Wilson Administration made a requirement of surrender be the abdication of the Kaiser and the creation of a German Republic. Woodrow Wilson had made U.S. policy to "Make the World Safe for Democracy". Germany surrendered November 11, 1918.[31] Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicated on November 28, 1918.[32] While the United States did not ratify it, the Treaty of Versailles in 1919 had much input from the United States. It mandated for Kaiser Wilhelm II to be removed from the government and tried, though the second part was never carried out.[33] Germany would than became the Weimar Republic. The United States signed the U.S.-German peace Treaty in 1921, solidifying the agreements made previously to the rest of the Entente with the U.S.[34]
1917–1920: Austria-Hungary
On December 7, 1917, the United States declared war on Austria-Hungary as part of World War I.[35] Austria-Hungary surrendered on November 3, 1918.[36] Austria became a republic and signed Treaty of Saint Germain in 1919 effectively dissolved Austria-Hungary.[37] The Treaty disallowed Austria to ever unite with Germany. Even though the United States had much effect on the treaty it did not ratify it and instead signed the U.S.-Austrian Peace Treaty in 1921, solidifying their new borders and government to the United States.[38] After brief civil strife, Hungary became a monarchy without a monarch, instead governed by a Regent. Hungary signed the Treaty of Trianon, in 1920 with the Entente, without the United States.[39] They signed the U.S.-Hungarian Peace Treaty in 1921 solidifying their status and borders with the United States.[40]
1918–1920: Russia
After the new Bolshevik government withdrew from World War I, the U.S. military together with forces of its Allies invaded Russia in 1918. Approximately 250,000 invading soldiers, including troops from Europe, the US and the Empire of Japan invaded Russia to aid the White Army against the Red Army of the new Soviet government in the Russian civil war. The invaders launched the North Russia invasion from Arkhangelsk and the Siberia invasion from Vladivostok. The invading forces included 13,000 U.S. troops whose mission after the end of World War I included the toppling of the new Soviet government and the restoration of the previous Tsarist regime. U.S. and other Western forces were unsuccessful in this aim and withdrew by 1920 but the Japanese military continued to occupy parts of Siberia until 1922 and the northern half of Sakhalin until 1925.[41]
1941–1945: World War II and the aftermath
1940s
1941: Panama
In 1931 Arnulfo Arias overthrew president Florencio Harmodio Arosemena and put his brother Harmodio Arias Madrid into power. in 1940 Arias became the president of Panama. Arias was an open fascist and admirer of Adolf Hitler. He and his brother sought to bring Panama into the influence of the Axis and take control of the Panama canal away from the United States.[42] While the United States has not yet entered the war, tensions were already increasing with the Axis. The United States knew that if war broke out, which it most likely would and did, the Panama canal would be strategically important.
The United States government used its contacts in the Panama National Guard, which the U.S. had earlier trained, to orchestrate a coup against the government of Panama in October 1941. The U.S. had requested that the government of Panama allow it to build over 130 new military installations inside and outside of the Panama Canal Zone, and the government of Panama refused this request at the price suggested by the U.S.[43] President Arnulfo Arias fled the country and Ricardo Adolfo de la Guardia Arango, the leader of the coup and a friend of the US government, became president.[44]
1941–1949: China

On 1 August 1941, the United States, angered by Japanese atrocities in the second Sino-Japanese War, imposed an oil embargo on Japan. This led to the Attack on Pearl Harbor, causing the United States to join the Allies in World War II. The U.S. government provided military, logistical and other aid to the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) army led by Chiang Kai-shek in its campaign against the Japanese, until the Japanese surrender to the United States in August 1945. This surrender brought to an end the Japanese Puppet state of Manchukuo and the Japanese-dominated Wang Jingwei regime.[45]
After the Japanese surrender, the US continued to support the KMT. The US airlifted many KMT troops from central China to Manchuria. Approximately 50,000 U.S. troops were sent to guard strategic sites in Hupeh and Shandong. The U.S. trained and equipped KMT troops, and transported Korean troops and even enemy imperial Japanese troops back to help KMT forces to occupy Chinese zones and to contain Communist-controlled areas.[46] President Harry Truman explained that: "It was perfectly clear to us that if we told the Japanese to lay down their arms immediately and march to the seaboard, the entire country would be taken over by the Communists. We therefore had to take the unusual step of using the enemy as a garrison until we could airlift Chinese National troops to South China and send Marines to guard the seaports."[47] Within less than two years after the Sino-Japanese War, the KMT had received $4.43 billion from the United States—most of which was military aid.[46][48]
1943–1946: Italy
In July–August 1943, the US participated in the Allied invasion of Sicily, spearheaded by the U.S. Seventh Army, under Lieutenant General George S. Patton, in which over 2000 US servicemen were killed,[49] initiating the Italian Campaign which conquered Italy from the fascist regime of Benito Mussolini and its Nazi German allies. Mussolini was arrested by order of King Victor Emmanuel III, provoking a civil war. The king appointed Pietro Badoglio as new Prime Minister. Badoglio stripped away the final elements of Fascist rule by banning the National Fascist Party, then signed an armistice with the Allied armed forces. Italy's military outside of the peninsula itself collapsed, its occupied and annexed territories fell under German control. Italy capitulated to the Allies on 3 September 1943. The northern half of the country was occupied by the Germans with Italian fascists help and made a collaborationist puppet state, while the south was governed by monarchist forces, which fought for the Allied cause as the Italian Co-Belligerent Army.[50] partisans (many former Royal Italian Army soldiers) of disparate political ideologies that operated all over Italy. Rome was taken in June 1944. In April 1945, the Italian Partisans' Committee of Liberation declared a general uprising. On 28 April 1945, Benito Mussolini was executed by Italian partisans, two days before Adolf Hitler's suicide, the Germans surrendered Italy. There followed a rapid succession of anti-fascist prime ministers, the abdication of the King in May 1946, the one-month reign of Umberto II, the 1946 Italian institutional referendum which brought monarchy to an end and inaugurated the current Italian Republic and the 1946 Italian general election won by Christian Democrats.
1944–1946: France

British, Canadian and United States forces were the critical participants in Operation Goodwood and Operation Cobra, leading to a military breakout which ended the Nazi occupation of France. The actual Liberation of Paris was accomplished by French forces. The French formed the Provisional Government of the French Republic in 1944, leading to the formation of the French Fourth Republic in 1946.
The liberation of France is celebrated regularly up to the present day.[51][52]
1944–1945: Belgium

In the wake of the 1940 invasion, Germany established the Reichskommissariat of Belgium and Northern France to govern Belgium. United States, Canadian, British, and other Allied forces ended the Nazi occupation of most of Belgium in September 1944. The Belgian Government in Exile under Prime Minister Hubert Pierlot returned on 8 September.[53]
In December, American forces suffered over 80,000 casualties defending Belgium from a German counterattack in the Battle of the Bulge. By February 1945, all of Belgium was in Allied hands.[54]
The year 1945 was chaotic. Pierlot resigned, and Achille Van Acker of the Belgian Socialist Party formed a new government. There were riots over the Royal Question—the return of King Leopold III. Although the war continued, Belgians were again in control of their own country.[55]
1944–1945: Netherlands
During the Nazi occupation, the Netherlands was governed by the Reichskommissariat Niederlande, headed by Arthur Seyss-Inquart. British, Canadian, and American forces liberated portions of the Netherlands in September 1944. However, after the failure of Operation Market Garden, the liberation of the largest cities had to wait until the last weeks of the European war. The occupied portions of the Netherlands suffered a famine that Winter. British and American forces crossed the Rhine on 23 March 1945, and Canadian forces in their wake then entered the Netherlands from the East. The remaining German forces in the Netherlands surrendered on 5 May, which is celebrated as Liberation Day in the Netherlands. Queen Wilhelmina returned on 2 May, and elections were held in 1946, leading to a new government headed by Louis Beel.[56][57]
1944–1954: Philippines

United States landings in 1944 ended the Japanese occupation of the Philippines.[58] After the Japanese were defeated, the United States fulfilled a wartime promise by granting independence to the Philippines. Sergio Osmeña formed a Filipino government.
The United States helped defeat the pro-communist peasant uprising, called the Hukbalahap Rebellion, or Huk Rebellion.[59]
1945–1949: Germany
The United States took part in the Denazification of the Western portion of Germany. Former Nazis were subjected to varying levels of punishment, depending on what the US thought of their levels of guilt. Eisenhower initially estimated that the process would take 50 years.[60] Depending on a former Nazi's level of culpability, punishments could range from a fine (for those judged least culpable), to denial of permission to work as anything but a manual laborer, to imprisonment and even death for the most severe offenders, such as those convicted in the Nuremberg Trials. At the end of 1947, for example, the Allies held 90,000 Nazis in detention; another 1,900,000 were forbidden to work as anything but manual laborers.[61]
As Germans took more and more responsibility for Germany, they pushed for an end to the denazification process, and the Americans allowed this. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany, also known as West Germany, was formed and took responsibility for denazification. For most former Nazis, the process came to an end with amnesty laws passed in 1951.[62] The ultimate outcome of denazification was the creation of a parliamentary democracy in West Germany.[63]
1945–1955: Austria
Austria was annexed to Germany in the 1938 Anschluss. As German citizens, many Austrians fought on the side of Germany during World War 2. After the Allied victory, the Allies treated Austria as a victim of Nazi aggression, rather than as a perpetrator. The United States Marshall Plan provided aid.[64]
The 1955 Austrian State Treaty re-established Austria as a free, democratic, and sovereign state. It was signed by representatives of the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France. It provided for the withdrawal of all occupying troops and guaranteed Austrian neutrality in the Cold War.[65]

1945–1952: Japan
After the Allied victory in World War 2, Japan was occupied by Allied forces under the command of Douglas MacArthur. In 1946, the Japanese Diet ratified a new Constitution of Japan that followed closely a 'model copy' prepared by MacArthur's command,[66] and was promulgated as an amendment to the old Prussian-style Meiji Constitution. The constitution renounced aggressive war and was accompanied by liberalization of many areas of Japanese life.
While liberalizing life for most Japanese, the Allies tried many Japanese war criminals and executed some, while granting amnesty to the family of Emperor Hirohito.[67]
The occupation was ended by the Treaty of San Francisco.[67] It laid the groundwork for the Japanese economic miracle. Japanese industrial production had fallen in 1946 to 27.6% of the pre-war level, but regained this pre-war level in 1951 and reached 350% in 1960.[68]
1945–1948: South Korea

The Empire of Japan surrendered to the United States in August 1945, ending the Japanese rule of Korea. Under the leadership of Lyuh Woon-Hyung committees throughout Korea formed to coordinate transition to Korean independence. On August 28, 1945 these committees formed the temporary national government of Korea, naming it the People's Republic of Korea (PRK) a couple of weeks later.[69][70] On September 8, 1945, the United States government landed forces in Korea and thereafter established the United States Army Military Government in Korea (USAMGK) to govern Korea south of the 38th parallel north. The USAMGK outlawed the PRK government. The military governor Lieutenant-General John R. Hodge later said that "one of our missions was to break down this Communist government".[71][72]
In May 1948, Syngman Rhee, who had previously lived in the United States, won the election for President, which had been boycotted by most other politicians.[73]
1945–1991: Cold War era
1940s
1947–1949: Greece

By the Summer of 1944, Communist partisans, then known as the Greek People's Liberation Army (ELAS), had liberated nearly all of Greece outside of Athens from Axis occupation, while also attacking and defeating rival non-Communist partisan groups. On 12 August 1944, German forces retreated from the Athens area two days ahead of British landings there, ending the Axis occupation of Greece.
The British military together with Greek forces under control of the Greek government then fought for control of the country in the Greek Civil War against the Communists, who at that time were known as the Democratic Army of Greece (DSE). By early 1947, the British government could no longer afford the huge cost of financing the war against DSE, and pursuant to the October 1944 Percentages Agreement between Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin, Greece was to remain part of the Western sphere of influence. Accordingly, the British requested the US government to step in and the U.S. flooded the country with military equipment, military advisers and weapons.[74]: 553–554 [75]: 129 [76][77] With increased U.S. military aid, by September 1949 the Greek government eventually won.[78]: 616–617
1947–1970s: Italy

British and United States military pressure led the King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy to dismiss Benito Mussolini in July 1943. The king replaced him with Pietro Badoglio, who then made peace with the Allies. The Germans responded by taking control of much of Italy and forming the Italian Social Republic, a puppet state. The region controlled by the Social Republic shrank under the continuing Allied military campaign, surrendering on 1 May 1945.[79]
In 1947, the US-backed Christian Democrats (DC), led by Alcide De Gasperi, were losing popularity, and the Communist Party of Italy (PCI) was growing particularly fast due to its organizing efforts supporting sharecroppers in Sicily, Tuscany and Umbria, movements which were also bolstered by the reforms of Fausto Gullo, the Communist minister of agriculture.[80] The DC engineered the expulsion of all left-wing ministers from the cabinet on May 31. The PCI would not have a national position in government again for twenty years. De Gasperi did this under pressure from US Secretary of State George Marshall, who'd informed him that anti-communism was a pre-condition for receiving American aid,[81][80] and Ambassador James C. Dunn who had directly asked de Gasperi to dissolve the parliament and remove the PCI.[82]
The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) acknowledged giving $1 million to Italian centrist parties for the 1948 election. The CIA also publishing forged letters in order to discredit the leaders of the Italian Communist Party (PCI). U.S. agencies undertook a campaign of writing ten million letters, made numerous short-wave radio broadcasts and funded the publishing of books and articles, all of which warned the Italians of what was believed to be the consequences of a communist victory. Time magazine backed the campaign for U.S. domestic audiences, featuring the Christian Democracy Party leader and Prime Minister Alcide De Gasperi on its cover and in its lead story on April 19, 1948.[83][84][85] Meanwhile, the US secretly convinced the British Labour Party to pressure social democrats to end their support for PCI, and foster a devastating split in the Italian Socialist Party.[86]
CIA ultimately spent at least $65 million helping elect Italian politicians.[87]
1949-1953: Albania

Albania was in chaos after World War II and the country was not as focused on in peace time conferences very much in comparison to other European nations, while having suffered high casualties.[88] It was threatened by its larger neighbors with annexation. After Yugoslavia dropped out of the East Bloc, the small country of Albania was geographically isolated from the rest of the East Bloc.[89]
The United States and United Kingdom took advantage of the situation and recruited anti-communist Albanians who had fled after the USSR invaded. The US and UK formed the “Free Albania” National Committee, made up of many of the emigres. Albanians, recruited, were trained by the U.S. and UK., infiltrated the country, multiple times. Eventually the operation was found out and many of the agents fled, were executed, or were tried. The operation would become a failure.The operation was declassified in 2006, due to the Nazi War Crimes Disclosure Act and is now available in the National Archives. [90][91]
1949: Syria

The democratically elected government of Shukri al-Quwatli was overthrown by a junta led by the Syrian Army chief of staff at the time, Husni al-Za'im, who became President of Syria on April 11, 1949. Za'im had extensive connections to CIA operatives,[92] although the exact nature of U.S. involvement in the coup remains highly controversial.[93][94][95] The construction of the Trans-Arabian Pipeline, which had been held up in the Syrian parliament, was approved by Za'im, the new president, just over a month after the coup.[96]
1950s
1952: Egypt
In February 1952, following January's violent riots in Cairo amid widespread nationalist discontent over the continued British occupation of the Suez Canal and Egypt's defeat in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, CIA officer Kermit Roosevelt Jr. was dispatched by the State Department to meet with Farouk I of the Kingdom of Egypt. American policy at that time was to convince Farouk to introduce reforms that would weaken the appeal of Egyptian radicals and stabilize Farouk's grip on power. The U.S. was notified in advance of the successful July coup led by nationalist and anti-communist Egyptian military officers (the "Free Officers") that replaced the Egyptian monarchy with the Republic of Egypt under the leadership of Mohamed Naguib and Gamal Abdel Nasser. CIA officer Miles Copeland Jr. recounted in his memoirs that Roosevelt helped coordinate the coup during three prior meetings with the plotters (including Nasser, the future Egyptian president); this has not been confirmed by declassified documents but is partially supported by circumstantial evidence. Roosevelt and several of the Egyptians said to have been present in these meetings denied Copeland's account; another U.S. official, William Lakeland, said its veracity is open to question. Hugh Wilford notes that "whether or not the CIA dealt directly with the Free Officers prior to their July 1952 coup, there was extensive secret American-Egyptian contact in the months after the revolution."[97][98]
1953: Iran
The 1953 Iranian coup d'état, (known in Iran as the "28 Mordad coup"[99]) was the overthrow of the democratically elected government of Iranian Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh on August 19, 1953, orchestrated by the intelligence agencies of the United Kingdom (under the name "Operation Boot") and the United States (under the name "TPAJAX Project").[100][101][102][103] The coup saw the transition of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi from a constitutional monarch to an authoritarian one who relied heavily on United States government support to hold on to power until his own overthrow in February 1979.[104]
1954: Guatemala

In a CIA operation code named Operation PBSUCCESS, the U.S. government executed a coup that was successful in overthrowing the democratically-elected government of President Jacobo Árbenz and installed Carlos Castillo Armas, the first of a line of right-wing dictators, in its place.[105][106][107] Not only was it done for the ideological purpose of containment, but the CIA had been approached by the United Fruit Company as it saw possible loss in profits due to the situation of workers in the country, i.e., the introduction of anti-exploitation laws. [108] The perceived success of the operation made it a model for future CIA operations because the CIA lied to the president of the United States when briefing him regarding the number of casualties.[109]
1955–1960: Laos

The U.S. government took over funding of the military budget of the Royal Lao Government in its civil war against the Pathet Lao communist movement, which had taken control of a part of the country. The US paid for 100% of the government's military budget and by 1957 was paying the salaries of the Royal Lao Army. Also the US set up the covert Programs Evaluation Office to field US civilian personnel with former US military experience because a treaty the US had signed expressly forbade US military advisors.[110][111] By July 1959 however, the US sent in US commando units dressed as civilians to train the Royal Lao Army.[112] These interventions did not result in regime change.
1956-1957: Syria
In 1956 Operation Straggle was a coup plot against Syria. The CIA made plans for a coup for late October 1956 to topple the Syrian government. The plan entailed takeover by the Syrian military of key cities and border crossings.[113][114][115] The plan was postponed when Israel invaded Egypt in October 1956 and US planners thought their operation would be unsuccessful at a time when the Arab world is fighting "Israeli aggression." The operation was uncovered and American plotters had to flee the country.[116]
In 1957 Operation Wappen was a coup plan against Syria. A second coup attempt the following year called for assassination of key senior Syrian officials, staged military incidents on the Syrian border to be blamed on Syria and then to be used as pretext for invasion by Iraqi and Jordanian troops, an intense US propaganda campaign targeting the Syrian population, and "sabotage, national conspiracies and various strong-arm activities" to be blamed on Damascus.[117][118][115][119] This operation failed when Syrian military officers paid off with millions of dollars in bribes to carry out the coup revealed the plot to Syrian intelligence. The U.S. Department of State denied accusation of a coup attempt and along with US media accused Syria of being a "satellite" of the USSR.[118][120][121]
There was also an assassination plot later, called "The Preffered Plan", in 1957 against many leaders in Syria. There would be a Free Syria committee set up and outside invasion would be encouraged. However this plan was never put through.[122]
1957–1959: Indonesia

As a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement and host of the April 1955 Bandung Conference, Indonesia was charting a course toward an independent foreign policy that was not militarily committed to either side in the Cold War.[123][124] Starting in 1957, the CIA supported a failed coup plan by rebel Indonesian military officers. CIA pilots, such as Allen Lawrence Pope, piloted planes operated by CIA front organization Civil Air Transport (CAT) that bombed civilian and military targets in Indonesia. The CIA instructed CAT pilots to target commercial shipping in order to frighten foreign merchant ships away from Indonesian waters, thereby to weaken the Indonesian economy and thus to destabilize the democratically elected government of Indonesia. The CIA aerial bombardment resulted in the sinking of several commercial ships[125] and the bombing of a marketplace that killed many civilians.[126] The coup attempt failed at that time[127] and U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower denied any U.S. involvement.[128]
1958: Lebanon

The U.S. launched Operation Blue Bat in July 1958 to intervene in the 1958 Lebanon crisis. This was the first application of the Eisenhower Doctrine, according to which the U.S. was to intervene to protect regimes it considered threatened by international communism. The goal of the operation was to bolster the pro-Western Lebanese government of President Camille Chamoun against internal opposition and threats from Syria and Egypt.[citation needed]
1959: Iraq
Richard Sale of United Press International, citing Adel Darwish and other experts, has reported that the October 1959 assassination attempt on Iraqi Prime Minister Abd al-Karim Qasim involving a young Saddam Hussein and other Ba'athist conspirators was a collaboration between the CIA and Egyptian intelligence.[129] Bryan R. Gibson has challenged the veracity of Sale and Darwish, citing declassified documents that indicate the CIA was blindsided by the timing of the assassination attempt on Qasim and that the National Security Council "had just reaffirmed [its] nonintervention policy" six days before it occurred.[130] Although the assassination attempt failed after Saddam (who was only supposed to provide cover) opened fire on Qasim—forcing Saddam to spend more than three years in exile in the Egyptian-led United Arab Republic (UAR) under threat of death if he returned to Iraq—it led to widespread exposure for Saddam and the Ba'ath within Iraq, where both had previously languished in obscurity, and later became a crucial part of Saddam's public image during his tenure as President of Iraq.[131][132] It is possible that Saddam visited the U.S. embassy in Cairo during his exile.[133] A former high-ranking U.S. official told Marion Farouk–Sluglett and Peter Sluglett that Iraqi Ba'athists, including Saddam, "had made contact with the American authorities in the late 1950s and early 1960s."[134]
1960s
1960-1961: Congo-Leopoldville
Patrice Lumumba was elected the first Prime Minister of the Republic of Congo, now the Democratic Republic of Congo, in May 1960, and in June 1960 achieved full independence from Belgium. Belgium started supporting separatist movements in the country against him, in order to keep power over resources in the region, starting the Congo Crisis. Lumumba called in the United Nations to help him, but the U.N. force only agreed to keep peace and not stop the separatist movements. Lumumba than agreed to receive help from the USSR in order to stop the separatists, worrying the United States, due to the supply of Uranium in the country. At first The Eisenhower Administration attempted to poison him with his toothpaste, but this was abandoned.[135] The United States encouraged the Belgians and Mobutu Sese Seko, a colonel in the army, to overthrow him which they did on September 14, 1960. After being locked in prison Mobutu sent him to Katanga, one of the areas launching an insurgency, and he was executed soon after on January 17, 1961.[136]
1960: Laos
On August 9, 1960, Captain Kong Le with his paratroop battalion seized control of the administrative capital city of Vientiane in a bloodless coup on a "Neutralist" platform with the stated aims of ending the civil war raging in Laos, ending foreign interference in the country, ending the corruption caused by foreign aid, and better treatment for soldiers.[137][138] With CIA support, Field Marshal Sarit Thanarat, the prime minister of Thailand, set up a covert Thai military advisory group, called Kaw Taw. Kaw Taw together with the CIA orchestrated a November 1960 counter-coup against the new Neutralist government in Vientiane, supplying artillery, artillerymen, and advisers to General Phoumi Nosavan, first cousin of Sarit. It also deployed the CIA-sponsored Police Aerial Reinforcement Unit (PARU) to operations within Laos.[139] With the help of CIA front organization Air America to airlift war supplies and with other U.S. military assistance and covert aid from Thailand, General Phoumi Nosavan's forces captured Vientiane in November 1960.[140][141]
1961: Dominican Republic

In May 1961, the ruler of the Dominican Republic, Rafael Trujillo was murdered with weapons supplied by the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).[142][143] An internal CIA memorandum states that a 1973 Office of Inspector General investigation into the murder disclosed "quite extensive Agency involvement with the plotters." The CIA described its role in "changing" the government of the Dominican Republic as a 'success' in that it assisted in moving the Dominican Republic from a totalitarian dictatorship to a Western-style democracy."[144][145] Juan Bosch, an earlier recipient of CIA funding, was elected president of the Dominican Republic in 1962, and was deposed in 1963.[146]
1960s: Cuba
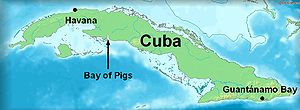
The CIA orchestrated a force composed of CIA-trained Cuban exiles to invade Cuba with support and equipment from the US military, in an attempt to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro. The invasion was launched in April 1961, three months after John F. Kennedy assumed the presidency in the United States. The Cuban armed forces, trained and equipped by Eastern Bloc nations, defeated the invading combatants within three days.
Operation MONGOOSE was a year-long U.S. government effort to overthrow the government of Cuba.[147] The operation included economic warfare, including an embargo against Cuba, "to induce failure of the Communist regime to supply Cuba's economic needs," a diplomatic initiative to isolate Cuba, and psychological operations "to turn the peoples' resentment increasingly against the regime."[148] The economic warfare prong of the operation also included the infiltration of CIA operatives to carry out many acts of sabotage against civilian targets, such as a railway bridge, a molasses storage facilities, an electric power plant, and the sugar harvest, notwithstanding Cuba's repeated requests to the United States government to cease its armed operations.[149][148] In addition, the CIA orchestrated a number of assassination attempts against Fidel Castro, head of government of Cuba, including attempts that entailed CIA collaboration with the American mafia.[150][151][152]
1961–1975: Laos

The United States intervened in the Laotian Civil War against the Pathet Lao communist movement of Laos headed by Prince Souphanouvong, so as to preserve the royalist faction that had been favored by the French and to destroy a Viet Cong supply line known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail. In this proxy war, the two sides received major external support from the two world superpowers. The U.S. government tried to keep the war secret from the American population by having the CIA Special Activities Division (Operation Millpond, Operation Barrel Roll and Operation Steel Tiger) orchestrate the war and by using tribesmen of the Hmong people that it trained, armed and paid to wage the war.[153][154][155] U.S. military support was critical, and for example, in 1962, in the Battle of Luang Namtha, the Laotian military came close to collapse but the war effort was saved by a major U.S. effort. One of the U.S.'s foremost Laotian military leaders in the field was general Vang Pao, a Hmong leader and commander of Military Region 2 in northern Laos. The Hmong people, based primarily in an area known as the Golden Triangle, needed to transport out the opium poppy they cultivated as their primary cash crop, so Air America, a CIA front, "began flying opium from mountain villages north and east of the Plain of Jars to CIA asset Hmong General Vang Pao's headquarters at Long Tieng."[156] The Hmong "tribesmen continued to grow, as they had for generations, the opium poppy....The [heroine refinery] lab's production was soon being ferried out on the planes of the CIA's front airline, Air America." [157][158][159][160][161] The CIA never denied the allegation but asserted that trading in opium was legal in Laos until 1971 and that opium was the sole cash crop of isolated Hmong hill tribes and one of their few medicines.[162] The U.S. military withdrew from Vietnam and French Indochina in April 1975 in what is remembered most vividly in the United States as the Fall of Saigon, and the Pathet Lao took over the country in the same year. Prince Souphanouvong, leader of the U.S. enemy, became president of Laos.[163]
1961–1964: Brazil
When the president of Brazil resigned in August 1961, he was lawfully succeeded by João Belchior Marques Goulart, the democratically elected vice president of the country.[164] João Goulart was a proponent of democratic rights, the legalization of the Communist Party, and economic and land reforms, but the US government insisted that he impose a program of economic austerity. The United States government implemented a plan with the code name Operation Brother Sam for the destabilization of Brazil, by cutting off aid to the Brazilian government, providing aid to state governors of Brazil who opposed the new president, and encouraging senior Brazilian military officers to seize power and to back army chief of staff General Humberto de Alencar Castelo Branco as coup leader.[164][165] General Branco led the April 1964 overthrow of the constitutional government of President João Goulart and was installed as first president of the military regime, immediately declaring a state of siege and arresting more than 50,000 political opponents within the first month of seizing power, while the US government expressed approval and re-instituted aid and investment in the country.[166]
1963: Iraq
Several sources, notably Said Aburish, have alleged that the February 1963 coup that resulted in the formation of a Ba'athist government in Iraq was "masterminded" by the CIA.[167] No declassified U.S. documents have verified this allegation.[168] Tareq Y. Ismael, Jacqueline S. Ismael, and Glenn E. Perry state that "Ba'thist forces and army officers overthrew Qasim on February 8, 1963, in collaboration with the CIA."[169] Conversely, Gibson argues that "the preponderance of evidence substantiates the conclusion that the CIA was not behind the February 1963 B'athist coup."[170] The U.S. offered material support to the new Ba'athist government after the coup, despite an anti-communist purge and Iraqi atrocities against Kurdish rebels and civilians.[171] Because of this, Nathan Citino asserts: "Although the United States did not initiate the 14 Ramadan coup, at best it condoned and at worst it contributed to the violence that followed."[172] The Ba'athist government collapsed in November 1963 over the question of unification with Syria (where a rival branch of the Ba'ath Party had seized power in March).[173] There has been a great deal of academic discussion regarding allegations from King Hussein of Jordan and others that the CIA (or other U.S. agencies) provided the Ba'athist government with lists of communists and other leftists, who were then arrested or killed by the Ba'ath Party's militia—the National Guard.[174] Gibson and Hanna Batatu emphasize that the identities of Iraqi Communist Party members were publicly known and that the Ba'ath would not have needed to rely on U.S. intelligence to identify them, whereas Citino considers the allegations plausible because the U.S. embassy in Iraq had actually compiled such lists, and because Iraqi National Guard members involved in the purge received training in the U.S.[175][176][177] U.S. official Robert Komer wrote to President John F. Kennedy on February 8, 1963 that the Iraqi coup "is almost certainly a net gain for our side... CIA had excellent reports on the plotting, but I doubt either they or UK should claim much credit for it."[178]
1963: South Vietnam
Although the United States was allied with South Vietnam during the Vietnam War, the Kennedy administration had grown increasingly frustrated with South Vietnamese President Ngo Dinh Diem's corrupt and repressive rule. In light of Diem's refusal to adopt reforms, American officials debated whether they should support efforts to replace him. These debates resulted in the dispatch of Cable 243 on August 24, 1963, which instructed United States Ambassador to South Vietnam, Henry Cabot Lodge Jr., to "examine all possible alternative leadership and make detailed plans as to how we might bring about Diem's replacement if this should become necessary". Lodge and his liaison officer, Lucien Conein, established contact with discontented Army of the Republic of Vietnam officers and stimulated their resolve to overthrow Diem. These efforts culminated in a coup d'etat on November 2, 1963, during which Diem and his brother were assassinated.[179]
The Pentagon Papers concluded that "Beginning in August of 1963 we variously authorized, sanctioned and encouraged the coup efforts of the Vietnamese generals and offered full support for a successor government. In October we cut off aid to Diem in a direct rebuff, giving a green light to the generals. We maintained clandestine contact with them throughout the planning and execution of the coup and sought to review their operational plans and proposed new government."[180]
1965–66: Dominican Republic

In the Dominican Civil War, a junta led by President Joseph Donald Reid Cabral was battling "constitutionalist" or "rebel" forces who advocated restoring to power the Dominican Republic's first ever democratically elected president, President Juan Emilio Bosch Gaviño, whose term had been cut short by a coup. The U.S. launched "Operation Power Pack," a US military operation to interpose the US military between the rebels and the junta's forces so as to prevent the rebel's advance and possibly victory.[181][182] Most civilian advisers had recommended against immediate intervention hoping that the junta could bring an end to the civil war but US President Lyndon B. Johnson took the advice of his Ambassador in Santo Domingo, William Tapley Bennett, who suggested that the US intervene.[183] Chief of Staff General Wheeler told a subordinate: "Your unannounced mission is to prevent the Dominican Republic from going Communist."[184] A fleet of 41 US vessels was sent to blockade the island as the US invaded. Ultimately, 42,000 soldiers and marines were ordered to the Dominican Republic and the US occupied the country.[185]
1965–1967: Indonesia

Junior army officers and the commander of the palace guard of President Sukarno accused senior Indonesian military brass of planning a CIA-backed coup against President Sukarno and killed six senior generals on October 1, 1965. General Muhammad Suharto and other senior military officers attacked the junior officers on the same day and accused the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI) of orchestrating the killing of the six generals.[186] The army launched a propaganda campaign based on lies and riled up civilian mobs to attack those believed to be PKI supporters and other political opponents. Indonesian government forces with collaboration of some civilians perpetrated mass killings over many months. The CIA acknowledged that "in terms of the number of people killed, the anti-PKI massacres in Indonesia rank as one of the worst mass murders of the 20th Century."[187] Estimates of the number of civilians killed range from a half million to a million[188][189][190] but more recent estimates put the figure at two to three million.[191][192] US Ambassador Marshall Green encouraged the military leaders to act forcefully against the political opponents.[187] In 2017, declassified documents from the U.S. Embassy in Jakarta have confirmed that the US had detailed, ongoing knowledge of the mass killings and actively facilitated and encouraged them for its own geopolitical interests.[193][194][195][196] US diplomats admitted to journalist Kathy Kadane in 1990 that they had provided the Indonesian army with thousands of names of alleged PKI supporters and other alleged leftists, and that the U.S. officials then checked off from their lists those who had been murdered.[197][198] President Sukarno's base of support was largely annihilated, imprisoned and the remainder terrified, and thus he was forced out of power in 1967, replaced by an authoritarian military regime led by General Suharto.[199][200] Some scholars are now referring to the mass killings as a genocide.[201][202][203]
1967: Greece
On 21 April 1967, just weeks before the scheduled elections, a group of right-wing army officers led by Brigadier General Stylianos Pattakos and Colonels George Papadopoulos and Nikolaos Makarezos seized power in a coup d'etat.[204] The coup leaders placed tanks in strategic positions in Athens, effectively gaining complete control of the city.
At the same time, a large number of small mobile units were dispatched to arrest leading politicians, authority figures, and ordinary citizens suspected of left-wing sympathies, according to lists prepared in advance. One of the first to be arrested was Lieutenant General Grigorios Spandidakis, Commander-in-Chief of the Greek Army. The colonels persuaded Spandidakis to join them, having him activate a previously-drafted action plan to move the coup forward. By the early morning hours, the whole of Greece was in the hands of the colonels. All leading politicians, including acting Prime Minister Panagiotis Kanellopoulos, had been arrested and were held incommunicado by the conspirators. At 6:00 a.m. EET, Papadopoulos announced that eleven articles of the Greek constitution were suspended.[205]
The left of center Center Union Party founder, Georgios Papandreou was arrested after a nighttime raid at his villa in Kastri, Attica. Andreas was arrested at around the same time, after seven soldiers armed with fixed bayonets and a machine gun forcibly entered his home. Andreas Papandreou escaped to the roof of his house, but surrendered after one of the soldiers held a gun to the head of his then-fourteen-year-old son George Papandreou.[205] Gust Avrakotos, a high-ranking CIA officer in Greece who was close with the colonels, allegedly advised them to "shoot the motherfucker because he's going to come back to haunt you".[206]
U.S. critics of the coup included then-Senator Lee Metcalf, who criticized the Johnson Administration for providing aid to a "military regime of collaborators and Nazi sympathizers". Phillips Talbot, the U.S. ambassador in Athens, disapproved of the coup, complaining that it represented "a rape of democracy", to which John M. Maury, the CIA station chief in Athens, answered, "How can you rape a whore?"[205] The CIA claims the timing of the coup apparently caught the agency by surprise.[207]
1970s
1970–1973: Chile

The democratically elected President Salvador Allende was overthrown by the Chilean armed forces and national police. This followed an extended period of social and political unrest between the right dominated Congress of Chile and Allende, as well as economic warfare waged by the U.S. government.[208] As a prelude to the coup, the chief of staff of the Chilean army, René Schneider, a general dedicated to preserving the constitutional order, was assassinated in 1970 during a botched kidnapping attempt backed by the CIA.[209][210] The regime of Augusto Pinochet that came to power with the coup is notable for having, by conservative estimates, disappeared some 3200 political dissidents, imprisoned 30,000 (many of whom were tortured), and forced some 200,000 Chileans into exile.[211][212][213] The CIA, through Project FUBELT (also known as Track II), worked secretly to engineer the conditions for the coup. The U.S. initially denied any involvement however many relevant documents have been declassified in the decades since.
1970: Cambodia
In March 1970 Prince Norodom Sihanouk, head of a political movement known as Sangkum that was first ushered to power by the 1955 parliamentary election, was overthrown by the right wing politician General Lon Nol. The overthrow followed Cambodia's constitutional process and most accounts emphasize the primacy of Cambodian actors in Sihanouk's removal. Historians are divided about the extent of U.S. involvement in or foreknowledge of the ouster, but an emerging consensus posits some culpability on the part of U.S. military intelligence.[214] There is evidence that "as early as late 1968" Lon Nol floated the idea of a coup to U.S. military intelligence to obtain a U.S. consent and military support for action against Prince Sihanouk and his government.[215] The coup succeeded in installing Lon Nol in power but further destabilized the country and ushered in the years of civil war between the right wing government in Phnom Penh backed by the United States and communist forces backed by the Viet Cong.[216][page needed]
1971: Bolivia

The U.S. government supported the 1971 coup led by General Hugo Banzer that toppled President Juan José Torres of Bolivia.[217][218] Torres had displeased Washington by convening an "Asamblea del Pueblo" (People's Assembly or Popular Assembly), in which representatives of specific proletarian sectors of society were represented (miners, unionized teachers, students, peasants), and more generally by leading the country in what was perceived as a left wing direction. Banzer hatched a bloody military uprising starting on August 18, 1971 that succeeded in taking the reins of power by August 22, 1971. After Banzer took power, the U.S. provided extensive military and other aid to the Banzer dictatorship as Banzer cracked down on freedom of speech and dissent, tortured thousands, "disappeared" and murdered hundreds, and closed labor unions and the universities.[219][220] Torres, who had fled Bolivia, was kidnapped and assassinated in 1976 as part of Operation Condor, the US-supported campaign of political repression and state terrorism by South American right-wing dictators.[221][222][223]
1972–1975: Iraq
The U.S. secretly provided millions of dollars for the Kurdish insurgency supported by Iran against the Iraqi government.[224][225] The U.S. role was so secret even the US State Department and the U.S. "40 Committee," created to oversee covert operations, were not informed. The troops of the Kurdish Democratic Party were led by Mustafa Barzani. Notably, unbeknownst to the Kurds, this was a covert regime change action the US wanted to fail, intended only to drain the resources of the country.[226][227] The U.S. abruptly ceased support for the Kurds in 1975 and, despite Kurdish pleas for help, refused to extend even humanitarian aid to the thousands of Kurdish refugees created as a result of the collapse of the insurgency.[228][229][230]
1977–1988: Pakistan

Operation Fair Play was the code name for the 5 July 1977 coup by Pakistan Chief of Army Staff General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq, overthrowing the government of Prime Minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto. The coup itself was bloodless, and was preceded by social unrest and political conflict between the ruling leftist Pakistan Peoples Party government of Bhutto, and the right-wing Islamist opposition Pakistan National Alliance which accused Bhutto of rigging the 1977 general elections. In announcing the coup, Zia promised "free and fair elections" within 90 days, but these were repeatedly postponed on the excuse of accountability and it was not until 1985 that ("party-less") general elections were held. Zia himself stayed in power for eleven years until his death in a plane crash.
The coup was a watershed event in the Cold War and in the history of the country. The coup took place nearly six years after the 1971 war with India which ended with the secession of East Pakistan as Bangladesh. The period following the coup saw the "Islamisation of Pakistan" and Pakistan's involvement with the Afghan Mujahideen (funded by US and Saudi Arabia) in the war against the Soviets in Afghanistan.
1979–1993: Cambodia

Cambodia was invaded by Vietnam and the KUFNS (Kampuchean United Front for National Salvation), overthrowing in January 1979 the genocidal regime of the Khmer Rouge headed by Pol Pot. Khmer Rouge forces retreated to the jungles near the Thai border and waged a war of insurgency against the People's Republic of Kampuchea (PRK), headed by Heng Samrin, which had been installed in the capital city of Phnom Penh by the Vietnamese.[231] The U.S. government wanted to remove the PRK government and provided millions of dollars of annual food aid to 20,000-40,000 Khmer Rouge insurgents in Khmer Rouge bases in Thailand. The aid was managed by an organization staffed by U.S. Central Intelligence Agency personnel.[232] U.S. National Security Advisor Zbigniew Brzezinski "concocted the idea of persuading Thailand to cooperate fully with China in efforts to rebuild the Khmer Rouge."[233][234] Brzezinski acknowledged that "I encourage[d] the Chinese to support [Khmer Rouge leader] Pol Pot ... we could never support him, but China could." Brzezinski subsequently stated: "The Chinese were aiding Pol Pot, but without any help or arrangement from the United States. Moreover, we told the Chinese explicitly that in our view Pol Pot was an abomination and that the United States would have nothing to do with him—directly or indirectly."[235][236][237][233][238] Also, the United States voted for the Khmer Rouge to remain the official representative of the country in the United Nations even though after 1978 Khmer Rouge bases were positioned in just a small part of the country and across the border in Thailand.[235] Some have also found evidence that notwithstanding public condemnation of the Khmer Rouge, the U.S. offered military support to the organization.[239] The U.S. and China helped set up, armed and trained a coalition waging a war of insurgency comprising three major guerrilla groups: the FUNCINPEC (Front Uni National pour un Cambodge Indépendant, Neutre, Pacifique, et Coopératif); the KPLNF (Khmer People's National Liberation Front); and the PDK (Party of Democratic Kampuchea, the Khmer Rouge under the nominal presidency of Khieu Samphan), but direct U.S. military support for the Khmer Rouge guerrillas is officially denied by the U.S. government.[240][241] Peace efforts began in 1989 and a peace agreement was forged in October 1991. Vietnamese forces withdrew and the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) enforced the ceasefire and disarmament.[242]
1979–1989: Afghanistan

In what was known as "Operation Cyclone," the U.S. government secretly provided weapons and funding for a collection of warlords and several factions of Jihadi guerrillas known as the Mujahideen of Afghanistan fighting to overthrow the Afghan government and the Soviet military forces that supported it. Through the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) of Pakistan, the US channeled training, weapons and money for Afghan fighters, including Jihadists who later became known as the Taliban, and at an estimated cost of $800 million for as many as 35,000 Arab foreign fighters.[243][244][245][246] Afghan Arabs also "benefited indirectly from the CIA's funding, through the ISI and resistance organizations."[247][248] Some of the CIA's greatest Afghan beneficiaries were Arabist commanders such as Jalaluddin Haqqani and Gulbuddin Hekmatyar who were key allies of Osama Bin Laden over many years.[249][250][251] Some of the CIA-funded militants would become part of Al Qaeda later on, and included Osama bin Laden, according to former Foreign Secretary Robin Cook and other sources.[252][253][254][255][256] However, these allegations are rejected by Steve Coll ("If the CIA did have contact with bin Laden during the 1980s and subsequently covered it up, it has so far done an excellent job"),[257] Peter Bergen ("The theory that bin Laden was created by the CIA is invariably advanced as an axiom with no supporting evidence"),[258] and Jason Burke ("It is often said that bin Laden was funded by the CIA. This is not true, and, indeed, would have been impossible given the structure of funding that General Zia ul–Haq, who had taken power in Pakistan in 1977, had set up").[259] Although Operation Cyclone officially ended in 1989 with the withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan, U.S. government funding for the Mujahideen continued through 1992, when the Mujahideen overran the Afghan government in Kabul.[260]
1980s
1980–1989: Poland

Unlike the Carter Administration, the Reagan policies supported the Solidarity movement in Poland, and—based on CIA intelligence—waged a public relations campaign to deter what the Carter administration felt was "an imminent move by large Soviet military forces into Poland."[261] Michael Reisman from Yale Law School named operations in Poland as one of the covert actions of CIA during Cold War.[262] Colonel Ryszard Kukliński, a senior officer on the Polish General Staff was secretly sending reports to the CIA.[263] The CIA transferred around $2 million yearly in cash to Solidarity, for a total of $10 million over five years. There were no direct links between the CIA and Solidarnosc, and all money was channeled through third parties.[264] CIA officers were barred from meeting Solidarity leaders, and the CIA's contacts with Solidarnosc activists were weaker than those of the AFL-CIO, which raised $300,000 from its members, which were used to provide material and cash directly to Solidarity, with no control of Solidarity's use of it. The U.S. Congress authorized the National Endowment for Democracy to promote democracy, and the NED allocated $10 million to Solidarity.[265]
When the Polish government launched martial law in December 1981, however, Solidarity was not alerted. Potential explanations for this vary; some believe that the CIA was caught off guard, while others suggest that American policy-makers viewed an internal crackdown as preferable to an "inevitable Soviet intervention."[266] CIA support for Solidarity included money, equipment and training, which was coordinated by Special Operations.[267] Henry Hyde, U.S. House intelligence committee member, stated that the USA provided "supplies and technical assistance in terms of clandestine newspapers, broadcasting, propaganda, money, organizational help and advice".[268] Initial funds for covert actions by CIA were $2 million, but soon after authorization were increased and by 1985 CIA successfully infiltrated Poland.[269]
1980–1992: El Salvador
The government of El Salvador fought a bloody civil war against the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN), an umbrella organization of leftist political opposition groups, and against leaders of agricultural cooperatives, labor leaders and others who advocated for land reform and better conditions for "campesinos" (tenant farmers and other agrarian laborers) that supported the FMLN. The Salvadoran army organized military death squads to terrorize the rural civil population to cease its support for the FMLN.[270] Government forces killed more than 75,000 civilians during the war 1980–1992.[271][272][273][274][275][276] The U.S. government provided military training and weapons for the Salvadoran military. The Atlacatl Battalion, a counter-insurgency battalion, was organized in 1980 at the US Army School of the Americas and had a leading role in the "scorched earth" military policy against the FLMN and the rural villages that supported it. Atlacatl soldiers were equipped and directed by U.S. military advisers operating in El Salvador.[277][278][279] The Atlacatl battalion also participated in the El Mozote massacre in December 1981.[280] By May 1983, US officers took over positions in the top levels of the Salvadoran military, were making critical decisions and running the war.[281][282][283][284] A US Congressional fact finding commission found that the Salvadoran military's "drying up the ocean" policy of repression entailed eliminating "entire villages from the map, to isolate the guerrillas, and deny them any rural base off which they can feed."[285] The "drying up the ocean" or "scorched earth" strategy was based on tactics similar to those being employed by the junta's counter-insurgency in neighboring Guatemala and were primarily derived and adapted from U.S. strategy during the Vietnam War and taught by American military advisors.[286][287]
1981–1982: Chad
In 1975 as part of the First Chadian Civil War, the military overthrew François Tombalbaye and installed Felix Malloum as head of state. Hissène Habré was appointed Prime minister, and attempted to overthrow the government in February 1979, failing, and being forced out. In 1979 Malloum resigned and Goukouni Oueddei became head of state. Oueddei agreed to share power with Habre, appointing him Minister of Defense, but fighting resumed soon after. Habre was exiled to Sudan in 1980.[288]
At the time the U.S. government wanted a bulwark against Muammar Gaddafi in Libya, and saw Chad, Libya's southern neighbor, as a good option. Chad and Libya had recently signed an agreement to attempt to end their border conflict and "to work to achieve full unity between the two countries", which the United States was against. The United States also saw Oueddei as too close to Gaddafi. Habre was already pro-western and pro-American, as well as against Oueddei. The Reagan administration gave him covert support through the CIA when he returned in 1981 to continue fighting, and he overthrow Goukouni Oueddi on June 7, 1982, making himself the new president of Chad.[289]
Donald Norland, the US ambassador, said, "The CIA was so deeply involved in bringing Habré to power I can't conceive they didn't know what was going on, but there was no debate on the policy and virtually no discussion of the wisdom of doing what we did."[290]
Human Rights Watch obtained and revealed documents which stated that the CIA trained and equipped the Documentation and Security Directorate (DDS), Chad's secret police. The Chadian Truth Commission found the United States provided monetary aid to the DDS and to regional intelligence agencies that hunted down Habre’s political opponents afterwards, inside and outside the country.[291] Habre, who was dubbed "Africa's Pinochet" by Human Rights Watch, was convicted of crimes against humanity by a Senegalese court in 2016 for ordering the murder of 40,000 political opponents and the torture of hundreds of thousands of others while in power.[292][293]
1982–1989: Nicaragua

The U.S. government attempted to topple the government of Nicaragua by secretly arming, training and funding the Contras, a rebel group based in Honduras that was created to sabotage Nicaragua and to destabilize the Nicaraguan government.[294][295][296][297] As part of the training, the CIA distributed a detailed manual entitled "Psychological Operations in Guerrilla War," which instructed the Contras, among other things, on how to blow up public buildings, to assassinate judges, to create martyrs, and to blackmail ordinary citizens.[298] In addition to orchestrating the Contras, the U.S. government also blew up bridges and mined Corinto harbor, causing the sinking of several civilian Nicaraguan and foreign ships and many civilian deaths.[299][300][301][302] After the Boland Amendment made it illegal for the U.S. government to provide funding for Contra activities, the administration of President Reagan secretly sold arms to the Iranian government to fund a secret U.S. government apparatus that continued illegally to fund the Contras, in what became known as the Iran-Contra affair.[303] The U.S. continued to arm and train the Contras even after the Sandinista government of Nicaragua won the elections of 1984.[304][305]

1983: Grenada
In what the U.S. government called Operation Urgent Fury, the U.S. military invaded the tiny island nation of Grenada to remove the Marxist government of Grenada that the Reagan Administration found objectionable.[306][307] The United Nations General Assembly called the U.S. invasion "a flagrant violation of international law"[308] but a similar resolution widely supported in the United Nations Security Council was vetoed by the U.S.[309][310]
1989: Panama

In December 1989, in a military operation code-named Operation Just Cause, the U.S. invaded Panama. President George H. W. Bush launched the war ten years after the Torrijos–Carter Treaties were ratified to transfer control of the Panama Canal from the United States to Panama by the year 2000. The U.S. deposed de facto Panamanian leader, general, and dictator Manuel Noriega and brought him to the United States, president-elect Guillermo Endara was sworn into office, and the Panamanian Defense Force was dissolved.
1991–present: Post-Cold War
1990s
1991: Kuwait

After Iraq invaded Kuwait in August 1990, the US government strenuously lobbied governments represented on the UN Security Council to support a resolution authorizing UN members states to use "all necessary means" for removing Iraqi forces from Kuwait.[311] UN Security Council Resolution 678, including such language, was passed and the US assembled a 34 state coalition force to invade. The operation was launched in January 1991 under US code name "Operation Desert Storm". The U.S.-led coalition repelled the Iraqi forces from Kuwait and returned to power the emir, Sheikh Jaber al-Ahmad al-Sabah.[312]
1991: Haiti
Eight months after what was widely considered the first honest election held in Haiti,[313] the newly elected President Jean-Bertrand Aristide was deposed by the Haitian army. It is alleged by some that the CIA "paid key members of the coup regime forces, identified as drug traffickers, for information from the mid-1980s at least until the coup."[314] Coup leaders Cédras and François had received military training in the United States.[315]
1991–2003: Iraq

Following the Persian Gulf War in 1991, the U.S. government successfully advocated that the pre-war sanctions[316] be made more comprehensive, which the UN Security Council did in April 1991 by adopting Resolution 687.[317][318] After the UN imposed the tougher sanctions, U.S. officials stated in May 1991—when it was widely expected that the Iraqi government of Saddam Hussein faced collapse[319][320]—that the sanctions would not be lifted unless Saddam was ousted.[321][322][323] In the subsequent president's administration, U.S. officials took the position that the sanctions could be lifted if Iraq complied with all of the UN resolutions it was violating, not just with UN weapons inspections.[324] The effects of the sanctions on the Iraqi civilian population, including the child mortality rate, were disputed at the time. Whereas it was widely believed at the time that the sanctions caused a major rise in child mortality, recent research has shown that commonly cited data were fabricated by the Iraqi government and that "there was no major rise in child mortality in Iraq after 1990 and during the period of the sanctions."[325][326][327][328][329]
1994–2000: Iraq
The CIA launched DBACHILLES, a coup d'état operation against the Iraqi government, recruiting Ayad Allawi, who headed the Iraqi National Accord, a network of Iraqis who opposed the Saddam Hussein government, as part of the operation. The network included Iraqi military and intelligence officers but was penetrated by people loyal to the Iraqi government.[330][331][332] Also using Ayad Allawi and his network, the CIA directed a government sabotage and bombing campaign in Baghdad between 1992 and 1995, against targets that—according to the Iraqi government at the time—killed many civilians including people in a crowded movie theater.[333] The CIA bombing campaign may have been merely a test of the operational capacity of the CIA's network of assets on the ground and not intended to be the launch of the coup strike itself.[333] The coup was unsuccessful, but Ayad Allawi was later installed as prime minister of Iraq by the Iraq Interim Governing Council, which had been created by the U.S.-led coalition following the March 2003 invasion and occupation of Iraq. As a non-covert measure, the U.S. in 1998 enacted the "Iraq Liberation Act," which states, in part, that "It should be the policy of the United States to support efforts to remove the regime headed by Saddam Hussein from power in Iraq," and appropriated funds for U.S. aid "to the Iraqi democratic opposition organizations."[334]
1997–98: Indonesia
The Clinton administration saw an opportunity to oust Indonesian President Suharto when his rule over Indonesia became increasingly precarious in the aftermath of the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis. American officials sought to exacerbate Indonesia's monetary crisis by having the International Monetary Fund oppose Suharto's efforts to establish a currency board to stabilize the rupiah, thereby provoking discontent. IMF Director Michel Camdessus boasted that, "We created the conditions that obliged President Suharto to leave his job". Former US Secretary of State Lawrence Eagleburger would later remark, "We were fairly clever in that we supported the IMF as it overthrew [Suharto]. Whether that was a wise way to proceed is another question. I'm not saying Mr. Suharto should have stayed, but I kind of wish he had left on terms other than because the IMF pushed him out."[335][336] Hundreds would die in the crisis that followed.
2000s
2000: Yugoslavia
From the period of 1998 to 2000, just over $100,000,000 was channeled from the U.S. State Department through Quangos to opposition parties in order to bring about regime change in Yugoslavia.[337] Following issues regarding the results of the Yugoslav elections of 2000, the U.S. State Department heavily supported opposition groups such as Otpor! through the supply of promotional material and also, consulting services via Quangos.[338] United States involvement served to speed up and organize dissent through exposure, resources, moral and material encouragement, technological aid and professional advice.[337] This campaign was one of the factors contributing to the Bulldozer Revolution and thus the overthrow of the long-standing president Slobodan Milošević on October 5, 2000.[337]
2003: Iraq
The Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that began in March 2003. A United States-led military coalition invaded the country and overthrew the Iraqi government.
2006–07: Palestinian territories
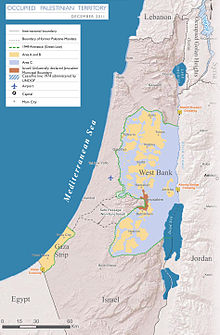
The U.S. government pressured the Fatah faction of the Palestinian leadership to topple the Hamas government of Prime Minister Ismail Haniyeh.[339][340][341] The Bush Administration was displeased with the government that the majority of the Palestinian people elected in the January Palestinian legislative election of 2006.[339][340][342] The U.S. government set up a secret training and armaments program that received tens of millions of dollars in Congressional funding, but also, like in the Iran-contra scandal, a more secret Congress-circumventing source of funding for Fatah to launch a bloody war against the Haniyeh government.[339][343][344] The war was brutal, with many casualties and with Fatah kidnapping and torturing civilian leaders of Hamas, sometimes in front of their own families, and setting fire to a university in Gaza. When the government of Saudi Arabia attempted to negotiate a truce between the sides so as to avoid a wide-scale Palestinian civil war, the U.S. government pressured Fatah to reject the Saudi plan and to continue the effort to topple the Haniyeh government.[339] Ultimately, the Haniyeh government was prevented from ruling over all of the Palestinian territories, with Hamas retreating to the Gaza strip and Fatah retreating to the West Bank.
2006-Present: Syria

Since 2006, the State Department has funneled at least $6 million to the anti-government satellite channel Barada TV, associated with the exile group Movement for Justice and Development in Syria. This secret backing continued under the Obama administration, even as the US publicly rebuilt relations with Bashar Al-Assad.[345][346]
In April 2011, after the outbreak of the Syrian civil war in early 2011, three "key U.S. Senators", Republicans John McCain and Lindsay Graham, and Independent Joe Lieberman, said in a joint statement, urged Obama to "state unequivocally" that "it is time to go".[347] In August, 2011, the U.S. government called on Syrian President Bashar Al Assad to "step aside" and imposed an oil embargo against the Syrian government to bring it to its knees.[348][349][350] Starting in 2013, the U.S. also provided training, weapons and cash to Syrian vetted "moderate" rebels,[351][352] and in 2014, the Supreme Military Council.[353][354] In 2015, Obama reaffirmed that "Assad must go".[355]
In March 2017 Ambassador Nikki Haley told a group of reporters that the US's priority in Syria was no longer on "getting Assad out."[356] Earlier that day at a news conference in Ankara, Secretary of State Rex Tillerson also said that the "longer term status of President Assad will be decided by the Syrian people."[357] While the US Defense Department's program to aid predominantly Kurdish rebels fighting the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) continued, it was revealed in July 2017 that US President Trump had ordered a "phasing out" of the CIA's support for anti-Assad rebels.[358]
In October 2017, Rex Tillerson declared that "the reign of the Assad family is coming to an end" despite recent battlefield gains by Assad's forces.[359] In April 2018, Army General James Votel told lawmakers he did not know whether 'Assad must go' remained a U.S. policy objective; Lindsay Graham responded "If you don't know I doubt if anybody knows, …"; and it was reported that the Trump administration has indicated that ousting Assad is no longer a specific policy goal but it cannot envision political stability if he remains.[360]
2007: Iran
In 2007, the Bush administration requested and received funding from Congress for covert actions in Iran that, according to a presidential finding that Bush signed, had the goal of undermining Iran's religious leadership. One source who was familiar with the contents of the memorandum told The New Yorker that the operations were focused on "undermining Iran's nuclear ambitions and trying to undermine the government through regime change."[361][additional citation(s) needed][neutrality is disputed]
2009: Honduras
On June 28, 2009 the Honduran military removed president Manuel Zelaya from Honduras and sent him to Costa Rica. Previously the U.S. embassy stopped an earlier planned coup, but this coup was not stopped by the embassy. The military and congress set up a new election that excluded Zelaya. The State Department under Hillary Clinton, supported the election under the leaders after the coup. The Obama administration condemned the coup, but still allowed the military to proceed with their new elections. Clinton stated in her memoir “Hard Choices”, “[the state department] strategized a plan for free and fair could be held quickly and legitimately, which would render the question of Zelaya moot.” This quote was written out of later editions of the book. Colonel Andrew Papp, present at some of the meeting, said the main concern was that the military "is very friendly with the U.S." and that while the U.S. government tried to help him the problem "was we didn't really like the guy". Evidence of it has been broken by WikiLeaks and The Intercept.[362][363]
2010s
2011: Libya
In 2011, Libya had been ruled by Socialist and Pan-Africanist dictator Muammar Gaddafi since 1969. In February 2011, amid the "Arab Spring", a revolution broke out against him, spreading from the second city Benghazi (where an interim government was set up on 27 February), to the capital Tripoli, sparking Libyan Civil War (2011). On 17 March, United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 was adopted, authorizing a no-fly zone over Libya, and "all necessary measures" to protect civilians.[364] Two days later, France, the United States and the United Kingdom launched the 2011 military intervention in Libya with Operation Odyssey Dawn, US and British naval forces firing over 110 Tomahawk cruise missiles,[365] the French and British Air Forces[366] undertaking sorties across Libya and a naval blockade by Coalition forces.[367] A coalition of 27 states from Europe and the Middle East soon joined the NATO-led intervention, as Operation Unified Protector. The Gaddafi government collapsed in August, leaving the National Transitional Council as the de facto government, with UN recognition. Gaddafi was captured and killed in October by National Transitional Council forces and NATO action ceased. Instability continued, ultimately leading to the Libyan Civil War (2014–present).
2015–Present: Yemen

The U.S. has been supporting the intervention by Saudi Arabia in the Yemeni Civil War. The Yemeni Civil War began in 2015 between two sides, each claiming at that time to support the legitimate government of Yemen:[368] Houthi forces, which control the capital Sana'a and had supported former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, fighting against forces based in Aden and loyal to the government of Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.[369] The Saudi-led offensive is aimed at restoring Hadi to power, and is allied with various local factions.[370] The Saudi Arabian-led intervention has been widely condemned due to its widespread bombing of urban and other civilian areas, including schools and hospitals.[371][372][373] The U.S. military provides targeting assistance and intelligence and logistical support for the Saudi-led bombing campaign,[374] including aerial refueling.[375][376] The US also provides weapons and bombs,[377] including, according to a Human Rights Watch (HRW) report, cluster bombs outlawed in much of the world and used by Saudi Arabia in the conflict.[378][379] The United States also supports the war effort on the ground with Green Berets on the Yemen border with Saudi Arabia tasked initially to help the Saudis secure the border and later expanded to help locate and destroy Houthi ballistic missile caches and launch sites in what Senator Tim Kaine called a “purposeful blurring of lines between train and equip missions and combat.”[380] The US has been criticized for providing weapons and bombs knowing that Saudi bombing has been indiscriminately targeting civilians and violating the laws of war.[381][382][383] It has been suggested that the U.S. government is legally a "co-belligerent" in the conflict, in which case U.S. military personnel could be prosecuted for war crimes,[384][385][386][387] and a U.S. senator has accused the U.S. of complicity in Yemen's humanitarian catastrophe, with millions facing starvation.[388][389] As of May 2018, the civil war is at a stalemate, and 13 million Yemeni civilians face starvation, according to the UN.[390]
2019: Venezuela
The U.S. efforts for regime change in Venezuela intensified in January 2019 with the increase of crippling sanctions, diplomatic pressure, and warnings.[391][392][393] Mark Weisenbrot writing for the New Republic said the sanctions (which he considers illegal) are a "plan to starve Venezuela into submission." [394]
See also
- Criticism of United States foreign policy
- Foreign electoral intervention
- Foreign interventions by the United States
- Latin America–United States relations
- Russia involvement in regime change
- Timeline of United States military operations
- United States involvement in regime change in Latin America
- Human rights violations by the CIA#Assassination and targeted killing
Notes
- ^ "The Long History of the US Interfering with Elections Elsewhere". October 13, 2016. Archived from the original on June 16, 2017.
{{cite news}}: Text "workThe Washington Post" ignored (help) - ^ The New York Times, February 17, 2019, "Russia Isn't the Only One Meddling in Elections, We Do It, Too," https://www.nytimes.com/2018/02/17/sunday-review/russia-isnt-the-only-one-meddling-in-elections-we-do-it-too.html Archived February 19, 2018, at the Wayback Machine citing Conflict Management and Peace Science, September 19, 2016 "Partisan Electoral Interventions by the Great Powers: Introducing the PEIG Dataset," http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0738894216661190
- ^ O’Rourke, Lindsey A. (November 29, 2019). "The Strategic Logic of Covert Regime Change: US-Backed Regime Change Campaigns during the Cold War". Security Studies. 0: 1–36. doi:10.1080/09636412.2020.1693620. ISSN 0963-6412.
- ^ United Nations Foundation, August 20, 2015, "The American Ratification of the UN Charter," http://unfoundationblog.org/the-american-ratification-of-the-un-charter/ Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Mansell, Wade and Openshaw, Karen, "International Law: A Critical Introduction," Chapter 5, Hart Publishing, 2014, https://books.google.com/booksid=XYrqAwAAQBAJ&pg=PT140
- ^ "All Members shall refrain in their international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state." United Nations, "Charter of the United Nations," Article 2(4), http://www.un.org/en/sections/un-charter/chapter-i/index.html Archived October 28, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Fox, Gregory, "Regime Change," 2013, Oxford Public International Law, Max Planck Encyclopedia of Public International Law, Sections C(12) and G(53)–(55), Archived November 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Falcke Martin, Percy (1914). Maximilian in Mexico. The story of the French intervention (1861–1867). New York City, New York, United States: C. Scribner's sons.
- ^ Robert H. Buck, Captain, Recorder. Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States Commandery of the state of Colorado, Denver. 10 April 1907. Indiana State Library.
- ^ Hart, James Mason (2002). Empire and Revolution: The American in Mexico Since the Civil War. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-90077-4.
- ^ Manning, William R.; Callahan, James Morton; Latané, John H.; Brown, Phillip; Slayden, James L.; Wheless, Joseph; Scott, James Brown (April 25, 1914). "Statements, Interpretations, and Applications of the Monroe Doctrine and of More or Less Allied Doctrines". American Society of International Law. 8. JSTOR 25656497.
- ^ Stevenson, Robert Louis (1892). A Footnote to History: Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa. BiblioBazaar. ISBN 978-1-4264-0754-3.
- ^ Declaration of War with Spain, 1898 (H.R. 10086), United States Senate
- ^ "Transcript of the Platt Amendment". Our Documents.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ US archives online Archived 2015-04-23 at the Wayback Machine, Date of ratification by Cuba
- ^ "Platt Amendment (1903)". Our Documents.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ This Day in History, "November 3: 1903 Panama Declares Independence," https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/panama-declares-independence Archived March 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ In a state speech in December 1903, President Theodore Roosevelt put the number of "revolutions, rebellions, insurrections, riots, and other outbreaks" in Panama at 53, within the space of 57 years. in "Theodore Roosevelt's third state of the union address":http://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Theodore_Roosevelt%27s_Third_State_of_the_Union_Address Archived May 2, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gilderhusrt, Mark T. (2000). The Second Century: U.S.–Latin American Relations Since 1889. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 49.
- ^ Becker, Marc. "History of U.S. Interventions in Latin America". www2.truman.edu.
- ^ Vitor II, MAJ Bruce A. "Under the Shadow of the Big Stick: U.S. Intervention in Cuba, 1906-1909". United States Army.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Humanities, National Endowment for the (December 1, 1909). "The citizen. (Honesdale, Pa.) 1908-1914, December 01, 1909, Image 1". ISSN 2166-7705. Retrieved December 1, 2019.
- ^ "US Intervention in Nicaragua 1911/1912". US Department of State.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Langley, Lester D. (1983). The Banana Wars: An Inner History of American Empire, 1900–1934. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky.
- ^ Musicant, Ivan (1990). The Banana Wars: A History of United States Military Intervention in Latin America from the Spanish–American War to the Invasion of Panama. New York: MacMillan Publishing. ISBN 978-0-02-588210-2.
- ^ David Healy, "Gunboat Diplomacy in the Wilson Era: The U.S. Navy in Haiti, 1915–1916," (Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1976)
- ^ Giles A. Hubert, War and the Trade Orientation of Haiti, https://www.jstor.org/stable/pdfplus/1053341.pdf
- ^ United States Naval Institute (1879). Proceedings of the United States Naval Institute. Annapolis, MD. p. 239.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Atkins, G. Pope; Larman Curtis Wilson. (1998). The Dominican Republic and the United States: From Imperialism to Transnationalism. Athens, GA: Univ. of Georgia Press. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-8203-1930-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ S.J. Res. 1 : Declaration of War with Germany, WW1, United States Senate
- ^ "Armistice: The End of World War I,1918". EyeWitness to History. 2004.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Primary Documents - Kaiser Wilhelm II's Abdication Proclamation, 28 November 1918". First World War.com. November 28, 1918.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Primary Documents - Treaty of Versailles, 28 June 1919". First World War.com. June 28, 1919.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Primary Documents - U.S. Peace Treaty with Germany, 25 August 1921". First World War.com. August 25, 1921.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ H.J.Res.169: Declaration of War with Austria-Hungary, WWI, United States Senate
- ^ Armistice Convention with Austria-Hungary
- ^ "Saint-Germain, Treaty of". International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Primary Documents - U.S. Peace Treaty with Austria, 24 August 1921". First World War.com. August 24, 1921.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Trianon, Treaty of". International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Primary Documents - U.S. Peace Treaty with Hungary, 29 August 1921". First World War.com. August 29, 1921.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Beyer, Rick, "The Greatest Stories Never Told" 2003: A&E Television Networks / The History Channel, pp. 152–153, ISBN 0060014016
- ^ Quijano, Robyn. "Arnulfo Arias : Nazi, terrorist, murderer" (PDF). Larouchepub.com.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Coatsworth, John. H. "Central America and the United States: The Clients and the Colossus," Twayne Publishers, New York: 1994, pp. 45, 225
- ^ The Stanford Daily, "Panamanian President Ousted in Coup d'Etat," Volume 100, Issue 15, October 10, 1941, https://stanforddailyarchive.com/cgi-bin/stanford?a=d&d=stanford19411010-01.2.38 Archived March 13, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Ferris, John; Mawdsley, Evan (2015). The Cambridge History of the Second World War, Volume I: Fighting the War. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ a b Nguyễn Anh Thái (chief author); Nguyễn Quốc Hùng; Vũ Ngọc Oanh; Trần Thị Vinh; Đặng Thanh Toán; Đỗ Thanh Bình (2002). Lịch sử thế giới hiện đại (in Vietnamese). Ho Chi Minh City: Giáo Dục Publisher. pp. 320–322. 8934980082317.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Harry S. Truman, "Memoirs, Vol. Two: Years of Trial and Hope," 1946–1953 (Great Britain 1956), p. 66
- ^ p. 23, U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II, William Blum, Zed Books 2004 London.
- ^ Hart, Basil H. Liddel (1970). A History of the Second World War. London, Weidenfeld Nicolson. p. 627.
- ^ Gianni Oliva, I vinti e i liberati: 8 settembre 1943-25 aprile 1945 : storia di due anni, Mondadori, 1994.
- ^ "60ème Anniversaire de la Libération - La Libération de Paris - Sénat".
- ^ "Bal de célébration des 70 ans de la libération de Paris sur le Parvis de l'Hôtel de Ville".
- ^ Peter Schrijvers (2012). "'A Modern Liberation'. Belgium and the Start of the American Century, 1944-1946". European Journal of American Studies. 7 (2). doi:10.4000/ejas.9695.
- ^ "Battle of The Bulge - HistoryNet". www.historynet.com.
- ^ Conway, Martin (2012). The Sorrows of Belgium: Liberation and Political Reconstruction, 1944–1947. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-969434-1.
- ^ Saunders, Tim (2006). Operation Plunder. Battleground Europe. Barnsley, UK: Pen & Sword. ISBN 1-84415-221-9.
- ^ "Operation Market Garden". National Army Museum. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Smith, Robert Ross (2005). Triumph in the Philippines: The War in the Pacific. University Press of the Pacific. ISBN 1-4102-2495-3.
- ^ "The Hukbalahap Insurrection: A Case Study of a Successful Anti-Insurgency Operation in the Philippines". history.army.mil. Retrieved December 11, 2018.
- ^ Norgaard, Noland. (October 13, 1945). "Eisenhower Claims 50 Years Needed to Re-Educate Nazis". The Oregon Statesman. p. 2. Retrieved November 9, 2014 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ Herbert Hoover's press release of The President's Economic Mission to Germany and Austria, Report No. 1: German Agriculture and Food Requirements, February 28, 1947. pg. 2
- ^ Art, David (2005). The Politics of the Nazi Past in Germany and Austria. Cambridge University Press. pp. 53–55. ISBN 978-0521673242.
- ^ "Formation of the Federal Republic of Germany". Retrieved March 11, 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|encyclopedia=ignored (help) - ^ Sorel, Eliot, and Pier Carlo Padoan. The Marshall Plan: Lessons Learned for the 21st Century. Paris: OECD, 2008. 15-16. Print.
- ^ "Austrian State Treaty, 1955". 2001-2009.state.gov. July 18, 2008. Retrieved June 15, 2017.
- ^ Takemae, Eiji 2002, p. xxxvii.
- ^ a b Dower, John. 'Embracing Defeat. Penguin, 1999. ISBN 978-0-14-028551-2. p. 246.
- ^ Ichiro, Nakayama (1964). Industrialization of Japan. Tokyo. p. 7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Hart-Landsberg, Martin, Korea: Division, Reunification, & U.S. Foreign Policy, Monthly Review Press (1998), p. 65
- ^ Cumings, Bruce, The Origins of the Korean War, Liberation and the Emergence of Separate Regimes, 1945–1947, Princeton University Press (1981), p. 88
- ^ Cumings, Bruce, "The Autumn Uprising," The Origins of the Korean War, Liberation and the Emergence of Separate Regimes, 1945–1947, Princeton University Press(1981)
- ^ Korea Times, June 15, 2015, "Korea Neglects Memory of Provisional Government,"http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/nation/2016/03/180_180890.html Archived January 8, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 66, 69. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ McCullough, David (1992). Truman. New York: Simon & Schuster.
- ^ Patterson, James T. (1996). Grand Expectations. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Panourgia, Neni, "Dangerous Citizens: The Greek Left and The Terror of the State," (New York: Fordham University Press, 2009) Chapter 5. 1946–1949: Emphýlios, Witness of the Mountains, available online at: https://dangerouscitizens.columbia.edu/1946-1949/witness-of-the/1/index.html Archived December 25, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Iatrides, John O., and Nicholas X. Rizopoulos, "The International Dimension of the Greek Civil War," World Policy Journal (2000): 87–103. in JSTOR Archived August 7, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Herring, George C. (2008). From Colony to Superpower: U.S. Foreign Relations Since 1776. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-507822-0.
- ^ Churchill, Winston (2002) [1959]. The Second World War. London: Pimlico. ISBN 0712667024.
- ^ a b Ginsborg, A History of Contemporary Italy, pp. 106–113
- ^ Ciment, James (March 27, 2015). Encyclopedia of Conflicts Since World War II. ISBN 9781317471851 – via books.google.com.
- ^ Corke, Sarah-Jane (September 12, 2007). US Covert Operations and Cold War Strategy: Truman, Secret Warfare and the CIA, 1945-53. Routledge. pp. 47–48. ISBN 9781134104130.
- ^ "How to Hang On", Time, April 19, 1948
- ^ "CNN Cold War Episode 3: Marshall Plan. Interview with F. Mark Wyatt, former CIA operative in Italy during the election". CNN. 1998–1999. Archived from the original on August 31, 2001. Retrieved July 17, 2006.
- ^ CIA memorandum to the Forty Committee (National Security Council), presented to the Select Committee on Intelligence, United States House of Representatives (the Pike Committee) during closed hearings held in 1975. The bulk of the committee's report that contained the memorandum was leaked to the press in February 1976 and first appeared in book form as CIA – The Pike Report (Nottingham, England, 1977). The memorandum appears on pp. 204–05 of this book.
- ^ Pedaliu, E. (October 23, 2003). Britain, Italy and the Origins of the Cold War. Springer. pp. 57–62. ISBN 9780230597402.
- ^ "CIA Covert Aid to Italy Averaged $5 Million Annually from Late 1940s to Early 1960s, Study Finds | National Security Archive". nsarchive.gwu.edu. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ "Albania in World War II". World War II Database.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Sovietization of Yugoslavia and Albania". YouTube. The Cold War. June 22, 2019 – via YouTube.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Albanian Dossier: CIA and British MI6 in Albania". Albanian Canadian League Information Service.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Within Record Group 263. A user's guide is available to assist researchers in locating the documents.
- ^ "H-Diplo Roundtable on "America's Great Game: The CIA's Secret Arabists and the Shaping of the Modern Middle East" | H-Diplo | H-Net". networks.h-net.org. Retrieved March 5, 2019.
- ^ Wilford, Hugh (2013). America's Great Game: The CIA's Secret Arabists and the Making of the Modern Middle East. Basic Books. pp. 101, 103. ISBN 9780465019656.
Predictably, this version of events has proven highly controversial ... In fact, most of the available evidence indicates that it was the Kurd himself [Za'im] who took the initiative in plotting his coup.
- ^ Rathmell, Andrew (January 1996). "Copeland and Za'im: Re-evaluating the Evidence". Intelligence and National Security. 11 (1): 89–105. doi:10.1080/02684529608432345. cf. Quandt, William B. (January 28, 2009). "Capsule Review: Secret War in the Middle East: The Covert Struggle for Syria, 1949-1961". Foreign Affairs. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
For example, the author does not believe that the Husni Zaim coup of 1949 was primarily the work of the cia, despite such claims by cia operatives; he does, however, provide considerable detail on the plotting against Syria by Turkey, Iraq, and the United States in 1957.
- ^ Stuster, J. Dana (August 20, 2013). "Mapped: The 7 Governments the U.S. Has Overthrown". Foreign Policy. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
Despite continued speculation about the CIA's role in a 1949 coup to install a military government in Syria, the ouster of Iranian Prime Minister Mohammed Mossadegh is the earliest coup of the Cold War that the U.S. government has acknowledged.
- ^ Gendzier, Irene L. (2006). Notes from the Minefield: United States Intervention in Lebanon and the Middle East, 1945-1958. Columbia University Press. pp. 97–99. ISBN 9780231140119.
- ^ Wilford, Hugh (2013). America's Great Game: The CIA's Secret Arabists and the Making of the Modern Middle East. Basic Books. pp. 135–139. ISBN 9780465019656.
- ^ Holland, Matthew F. (1996). America and Egypt: From Roosevelt to Eisenhower. Praeger. pp. 26–29. ISBN 978-0-275-95474-1.
- ^ The date of the coup in the Persian calendar.
- ^ Clandestine Service History: Overthrow of Premier Mossadeq of Iran, Mar. 1954: p. iii.
- ^ Ends of British Imperialism: The Scramble for Empire, Suez, and Decolonization. I.B.Tauris. 2007. pp. 775 of 1082. ISBN 978-1-84511-347-6.
- ^ New York Times, 2000, "Secrets of History: The United States in Iran," https://www.nytimes.com/library/world/mideast/041600iran-cia-index.html Archived January 20, 2013, at WebCite
- ^ CIA declassifies more of "Zendebad, Shah!" – internal study of 1953 Iran coup, Danielle Siegel and Malcolm Byrne, National Security Archive, Feb. 12, 2018.
- ^ U.S. foreign policy in perspective: clients, enemies and empire. David Sylvan, Stephen Majeski, p. 121.
- ^ Blakeley, Ruth (2009). State Terrorism and Neoliberalism: The North in the South. Routledge. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-415-68617-4.
- ^ Coatsworth, John. H. "Central America and the United States: The Clients and the Colossus," Twayne Publishers, New York: 1994, pp. 58, 226
- ^ Kornbluh, Peter; Doyle, Kate, eds. "CIA and Assassinations: The Guatemala 1954 Documents", National Security Archive Electronic Briefing Book overview, Washington, D.C.: National Security Archive, http://nsarchive.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB4/index.html Archived November 24, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "(DELETED) MEMO TO JAMES LAY FROM (DELETED) RE GUATEMALA 1954 COUP | CIA FOIA (foia.cia.gov)". www.cia.gov. Retrieved April 29, 2019.
- ^ Kornbluh, Peter; Doyle, Kate, eds. "CIA and Assassinations: The Guatemala 1954 Documents", National Security Archive Electronic Briefing Book Document 5, Washington, D.C.: National Security Archive, http://nsarchive.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB4/index.html Archived November 24, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Conboy, Kenneth J., "War in Laos, 1954–1975" (Squadron/Signal Publications, 1994), p. 5
- ^ Castle, Timothy, "At War in the Shadow of Vietnam: United States Military Aid to the Royal Lao Government, 1955–1975," (New York: Columbia University Press, 1993), p. 18
- ^ Conboy, Kenneth J., "War in Laos, 1954–1975" (Squadron/Signal Publications, 1994), pp. 7, 13
- ^ Saunders, Bonnie, "The United States and Arab Nationalism: The Syrian Case, 1953–1960," (Westport, CT: Greenwood, 1996), p. 49
- ^ Sylvan, David and Majeski, Stephen, "U.S. Foreign Policy in Perspective: Clients, Enemies and Empire," (New York: Routledge, 2009) http://us-foreign-policy-perspective.org/index.php?id=328&L=0 Archived April 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Blum, William, "Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II," (Monroe, ME: Common Courage Press, 1995), pp. 86–87
- ^ Saunders, Bonnie, "The United States and Arab Nationalism: The Syrian Case, 1953–1960," (Westport, CT: Greenwood, 1996), p. 51
- ^ The Guardian, September 26, 2003, "Macmillan Backed Syria Assassination Plot, Documents Show White House and No. 10 Conspired over Oil-Fuelled Invasion Plan," https://www.theguardian.com/politics/2003/sep/27/uk.syria1 Archived June 3, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b John Prados, Safe for Democracy: The Secret Wars of the CIA (Chicago: Rowman & Littlefield, 2006), p. 164 [1]
- ^ Jones, Matthew. "The 'Preferred Plan': The Anglo-American Working Group Report on Covert Action in Syria, 1957," Intelligence and National Security 19(3), Autumn 2004, pp. 404–406
- ^ Dorril, Stephen, "MI6: Inside the Covert World of Her Majesty's Secret Intelligence Service," (New York: Touchstone, 2000), p. 656 656
- ^ Blum, William, "Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II," (Monroe, ME: Common Courage Press, 1995), pp. 88–91
- ^ Ben Fenton, "Macmillan backed Syria assassination plot: Documents show White House and No 10 conspired over oil-fuelled invasion plan"; The Guardian, 26 September 2003.
- ^ Daily News (Sri Lanka), "Bandung Conference of 1955 and the Resurgence of Asia and Africa," archived at: https://web.archive.org/web/20120513090833/http://www.dailynews.lk/2005/04/21/fea01.htm
- ^ Kahin, George McTurnan, "The Asian-African Conference: Bandung, Indonesia, April 1955" (Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1956)
- ^ Conboy, Kenneth; Morrison, James (1999) "Feet to the Fire CIA Covert Operations in Indonesia, 1957–1958," (Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 1999), p. 155, ISBN 1557501939
- ^ Conboy, Kenneth; Morrison, James (1999) "Feet to the Fire CIA Covert Operations in Indonesia, 1957–1958," (Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 1999), p. 131, ISBN 1557501939
- ^ Los Angeles Times, October 29, 1994, "CIA's Covert Indonesia Operation in the 1950s Acknowledged by U.S.," http://articles.latimes.com/1994-10-29/news/mn-56121_1_state-department Archived January 19, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Stone, Oliver and Kuznick, Peter, "The Untold History of the United States" (New York: Simon & Schuster, Inc., 2012), pp. 347–348
- ^ Sale, Richard (April 10, 2003). "Exclusive: Saddam Key in Early CIA Plot". United Press International. Retrieved April 2, 2018.
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. xvii, 25–26, 31, 200, 208. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Karsh, Efraim; Rautsi, Inari (2002). Saddam Hussein: A Political Biography. Grove Press. pp. 15–22, 25. ISBN 978-0-8021-3978-8.
- ^ Makiya, Kanan (1998). Republic of Fear: The Politics of Modern Iraq, Updated Edition. University of California Press. p. 118. ISBN 978-0-520-92124-5.
- ^ Karsh, Efraim; Rautsi, Inari (2002). Saddam Hussein: A Political Biography. Grove Press. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-0-8021-3978-8.
- ^ Farouk–Sluglett, Marion; Sluglett, Peter (2001). Iraq Since 1958: From Revolution to Dictatorship. I.B. Tauris. p. 327. ISBN 9780857713735.
- ^ Kettle, Martin (August 10, 2000). "President 'ordered murder' of Congo leader". The Guardian. London, England.
- ^ Sherer, Lindsey (January 16, 2015). "U.S. foreign policy and its Deadly Effect on Patrice Lumumba". Washington State University.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ US Library of Congress, Federal Research Division, Library of Congress Country Studies, "Laos: The Attempt to Restore Neutrality," https://web.archive.org/web/20041031091831/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd%2Fcstdy%3A%40field%28DOCID%2Bla0039%29
- ^ Castle, Timothy, "At War in the Shadow of Vietnam: United States Military Aid to the Royal Lao Government, 1955–1975," (New York: Columbia University Press, 1993), pp. 32–33
- ^ Castle, Timothy, "At War in the Shadow of Vietnam: United States Military Aid to the Royal Lao Government, 1955–1975," (New York: Columbia University Press, 1993), pp. 33–35, 40, 59
- ^ US Library of Congress, Federal Research Division, Library of Congress Country Studies, "Laos: The Attempt to Restore Neutrality," https://web.archive.org/web/20041031091831/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd%2Fcstdy%3A%40field%28DOCID%2Bla0039%29
- ^ Castle, Timothy, "At War in the Shadow of Vietnam: United States Military Aid to the Royal Lao Government, 1955–1975," (New York: Columbia University Press, 1993), pp. 21–25, 27
- ^ Kross, Peter (December 9, 2018). "The Assassination of Rafael Trujillo". Sovereign Media. Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- ^ "The Kaplans of the CIA - Approved For Release 2001/03/06 CIA-RDP84-00499R001000100003-2" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency. November 24, 1972. pp. 3–6. Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- ^ CIA "Family Jewels" Memo, 1973 (see page 434) Family Jewels (Central Intelligence Agency)
- ^ Ameringer, Charles D. (January 1, 1990). U.S. Foreign Intelligence: The Secret Side of American history (1990 ed.). Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0669217803.
- ^ Iber, Patrick (April 24, 2013). ""Who Will Impose Democracy?": Sacha Volman and the Contradictions of CIA Support for the Anticommunist Left in Latin America". Diplomatic History. 37 (5): 995–1028. doi:10.1093/dh/dht041.
- ^ Office of the Historian, United States Department of State, Foreign Relations of the United States, 1961–63, Volume X, Cuba, January 1961–September 1962, "291. Program Review by the Chief of Operations, Operation Mongoose (Lansdale)," January 18, 1962, https://history.state.gov/historicaldocuments/frus1961-63v10/d291 Archived October 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Office of the Historian, United States Department of State, Foreign Relations of the United States, 1961–63, Volume X, Cuba, January 1961–September 1962, "291. Program Review by the Chief of Operations, Operation Mongoose (Lansdale)," January 18, 1962, pp. 711–17, https://history.state.gov/historicaldocuments/frus1961-63v10/d291 Archived October 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Domínguez, Jorge I. "The @#$%& Missile Crisis (Or, What Was 'Cuban' About US Decisions During the Cuban Missile Crisis)," Diplomatic History: The Journal of the Society for Historians of Foreign Relations, Vol. 24, No. 2, Spring 2000: 305–15
- ^ Johnson, M. Alex (June 26, 2007). "CIA acknowledges Castro plot went to the top". NBC News.
- ^ Escalante Font, Fabián, "Executive Action: 634 Ways to Kill Fidel Castro," Melbourne: Ocean Press, 2006
- ^ Campbell, Duncan (August 2, 2006). "638 ways to kill Castro". The Guardian.
- ^ "Stephen M Bland | Journalist and Author | Central Asia Caucasus". stephenmbland. Archived from the original on November 26, 2016.
- ^ Uppsala Conflict Data Program (November 2, 2011). "Laos". Uppsala University Department of Peace and Conflict Research.
In October 1953, the Franco-Lao Treaty of Amity and Association transferred power....
- ^ "Brief Chronology, 1959–1963". Foreign Office Files: United States of America, Series Two: Vietnam, 1959–1975; Part 2: Laos, 1959–1963.
October 22 Franco-Lao Treaty of Amity and Association
- ^ McCoy, Alfred (1972). The Politics of Heroin in Southeast Asia. Harper & Row. pp. 263–264. ISBN 0060129018.
Air America began flying opium from mountain villages north and east of the Plain of Jars to Gen. Vang Pao's headquarters at Long Tieng.
- ^ The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade, by Alfred W. McCoy, with Cathleen B. Read and Leonard P. Adams II, 2003, p. 385 ISBN 1-55652-483-8
- ^ "Opium Throughout History". PBS.
- ^ Cockburn, Alexander; Jeffrey St. Clair (1998). "9". Whiteout, the CIA, drugs and the press. New York: Verso. ISBN 1-85984-258-5.
- ^ Robbins, Christopher (1985). The Ravens. New York: Crown. p. 94. ISBN 0-9646360-0-X.
- ^ "Air America and Drugs in Laos". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Undercover Armies: CIA and Surrogate Warfare in Laos. Center for the Study of Intelligence. 206. pp. 535–547. Classified control no. C05303949.
{{cite book}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Souphanouvong, Prince. The Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed.. Columbia University Press
- ^ a b Stone and Kuznick (2012, pp. 343–344) citingCrandall, Britta H. (2011), Hemispheric Giants: The Misunderstood History of U.S.–Brazilian Relations, Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 978-1-4422-0787-5 and Schmitz, David F. (1999), Thank God they're on our side: the United States and right-wing dictatorships, 1921–1965, U. of North Carolina Press, p. 98, ISBN 978-0-8078-2472-6 and Schmitz, David F. (1999), Thank God They're on Our Side: The United States and Right-Wing Dictatorships, 1921–1965, U. North Carolina Press, pp. 272–273
- ^ National Security Archive, April 2, 2014, "Brazil Marks 50th Anniversary of Military Coup, On 50th anniversary, Archive Posts New Kennedy Tape Transcripts on Coup Plotting against Brazilian President Joao Goulart," https://nsarchive2.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB465/
- ^ Stone and Kuznick (2012, pp. 343–344) citing Hellman, Robert G.; Rosenbaum, H. Jon (1975), Latin America: The Search for a New International Role, Wiley, p. 80
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 57, 220. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Hahn, Peter (2011). Missions Accomplished?: The United States and Iraq Since World War I. Oxford University Press. p. 48. ISBN 978-0-19-533338-1.
- ^ Ismael, Tareq Y.; Ismael, Jacqueline S.; Perry, Glenn E. (2016). Government and Politics of the Contemporary Middle East: Continuity and Change (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 240. ISBN 978-1-317-66282-2.
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 52–54, 57–58, 200. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 59–61, 68–72, 80. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Citino, Nathan J. (2017). "The People's Court". Envisioning the Arab Future: Modernization in US-Arab Relations, 1945–1967. Cambridge University Press. p. 222. ISBN 978-1-108-10755-6.
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 77–79. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Farouk–Sluglett, Marion; Sluglett, Peter (2001). Iraq Since 1958: From Revolution to Dictatorship. I.B. Tauris. p. 86. ISBN 9780857713735.
Although individual leftists had been murdered intermittently over the previous years, the scale on which the killings and arrests took place in the spring and summer of 1963 indicates a closely coordinated campaign, and it is almost certain that those who carried out the raid on suspects' homes were working from lists supplied to them. Precisely how these lists had been compiled is a matter of conjecture, but it is certain that some of the Ba'th leaders were in touch with American intelligence networks, and it is also undeniable that a variety of different groups in Iraq and elsewhere in the Middle East had a strong vested interest in breaking what was probably the strongest and most popular communist party in the region.
- ^ Batatu, Hanna (1978). The Old Social Classes and the Revolutionary Movements of Iraq. Princeton University Press. pp. 985–987. ISBN 978-0-86356-520-5.
- ^ Gibson, Bryan R. (2015). Sold Out? US Foreign Policy, Iraq, the Kurds, and the Cold War. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 59. ISBN 978-1-137-48711-7.
- ^ Citino, Nathan J. (2017). "The People's Court". Envisioning the Arab Future: Modernization in US–Arab Relations, 1945–1967. Cambridge University Press. pp. 220–222. ISBN 978-1-108-10755-6.
- ^ Komer, Robert (February 8, 1963). "Secret Memorandum for the President". Retrieved May 1, 2017.
- ^ Kinzer, Stephen (2007). Overthrow: America's Century of Regime Change from Hawaii to Iraq. New York: Henry Holt and Company. pp. 158–166. ISBN 978-1-4299-0537-4.
- ^ "U.S. and Diem's Overthrow: Step by Step". The New York Times. July 1, 1971. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
- ^ Stanford University, Fearon, James and Laitin, David, June 27, 2006, "Dominican Republic (Dominican RepublicRN1.2)," pp. 4–6, https://web.stanford.edu/group/ethnic/Random%20Narratives/Dominican%20RepublicRN1.2.pdf Archived March 13, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ New York Times, November 2, 2001, "Juan Bosch, 92, Freely Elected Dominican President, Dies," https://www.nytimes.com/2001/11/02/world/juan-bosch-92-freely-elected-dominican-president-dies.html Archived August 29, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Stephen G. Rabe, "The Johnson Doctrine", Presidential Studies Quarterly 36
- ^ "Foreign Relations of the United States, 1964–1968 Volume XXXII, Dominican Republic; Cuba; Haiti; Guyana, Document 43". US Dept. of State. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Encyclopedia of the Cold War: A Political, Social, and Military History, 2013, p. 267
- ^ Stone, Oliver and Kuznick, Peter, "The Untold History of the United States" (New York, Simon & Schuster, Inc., 2012), p. 350 citing David F. Schmitz, "The United States and Right-Wing Dictatorships, 1965–1989" (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006), p. 45
- ^ a b Mark Aarons (2007). "Justice Betrayed: Post-1945 Responses to Genocide." In David A. Blumenthal and Timothy L. H. McCormack (eds). The Legacy of Nuremberg: Civilising Influence or Institutionalised Vengeance? (International Humanitarian Law). Archived January 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 9004156917 p. 81.
- ^ Robinson, Geoffrey B. (2018). The Killing Season: A History of the Indonesian Massacres, 1965–66. Princeton University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4008-8886-3.
- ^ Melvin, Jess (2018). The Army and the Indonesian Genocide: Mechanics of Mass Murder. Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-138-57469-4.
- ^ Time Magazine, September 30, 2015, The Memory of Savage Anticommunist Killings Still Haunts Indonesia, 50 Years On Archived March 1, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Time
- ^ Indonesia's killing fields Archived February 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine Al Jazeera, December 21, 2012.
- ^ Gellately, Robert; Kiernan, Ben (July 2003). The Specter of Genocide: Mass Murder in Historical Perspective. Cambridge University Press. pp. 290–291. ISBN 978-0-521-52750-7.
- ^ "Files reveal US had detailed knowledge of Indonesia's anti-communist purge". The Associated Press via The Guardian. October 17, 2017. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
- ^ Melvin, Jess (October 20, 2017). "Telegrams confirm scale of US complicity in 1965 genocide". Indonesia at Melbourne. University of Melbourne. Retrieved July 27, 2018.
The new telegrams confirm the US actively encouraged and facilitated genocide in Indonesia to pursue its own political interests in the region, while propagating an explanation of the killings it knew to be untrue.
- ^ Scott, Margaret (October 26, 2017). "Uncovering Indonesia's Act of Killing". The New York Review of Books. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
According to Simpson, these previously unseen cables, telegrams, letters, and reports "contain damning details that the U.S. was willfully and gleefully pushing for the mass murder of innocent people."
- ^ Bevins, Vincent (October 20, 2017). "What the United States Did in Indonesia". The Atlantic. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ Kadane, Kathy (May 21, 1990). "U.S. Officials' Lists Aided Indonesian Bloodbath in '60s". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
- ^ Robinson, Geoffrey B. (2018). The Killing Season: A History of the Indonesian Massacres, 1965–66. Princeton University Press. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-4008-8886-3.
a US Embassy official in Jakarta, Robert Martens, had supplied the Indonesian Army with lists containing the names of thousands of PKI officials in the months after the alleged coup attempt. According to the journalist Kathy Kadane, "As many as 5,000 names were furnished over a period of months to the Army there, and the Americans later checked off the names of those who had been killed or captured." Despite Martens later denials of any such intent, these actions almost certainly aided in the death or detention of many innocent people. They also sent a powerful message that the US government agreed with and supported the army's campaign against the PKI, even as that campaign took its terrible toll in human lives.
- ^ Simpson, Bradley (2010). Economists with Guns: Authoritarian Development and U.S.–Indonesian Relations, 1960–1968. Stanford University Press. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-8047-7182-5.
Washington did everything in its power to encourage and facilitate the army-led massacre of alleged PKI members, and U.S. officials worried only that the killing of the party's unarmed supporters might not go far enough, permitting Sukarno to return to power and frustrate the [Johnson] Administration's emerging plans for a post-Sukarno Indonesia. This was efficacious terror, an essential building block of the neoliberal policies that the West would attempt to impose on Indonesia after Sukarno's ouster.
- ^ Stone, Oliver and Kuznick, Peter, "The Untold History of the United States" (New York: Simon & Schuster, Inc., 2012), p. 352
- ^ Melvin, Jess (2017). "Mechanics of Mass Murder: A Case for Understanding the Indonesian Killings as Genocide". Journal of Genocide Research. 19 (4): 487–511. doi:10.1080/14623528.2017.1393942.
- ^ Robinson, Geoffrey B. (2018). The Killing Season: A History of the Indonesian Massacres, 1965–66. Princeton University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-4008-8886-3.
- ^ McGregor, Katharine; Melvin, Jess; Pohlman, Annie, eds. (2018). The Indonesian Genocide of 1965: Causes, Dynamics and Legacies (Palgrave Studies in the History of Genocide). Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-3-319-71454-7.
- ^ "American/World History 1967-1968". Historycentral.com. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ^ a b c Ganser, Daniele (2005). NATO's secret armies: Operation Gladio and Terrorism in Western Europe. Routledge. p. 216.
- ^ Charlie Wilson's War, George Crile, 2003, Grove/Atlantic.
- ^ Weiner, Tim (2007), Legacy of Ashes: The History of the CIA, Doubleday, p. 383.
- ^ Peter Kornbluh. "Chile and the United States: Declassified Documents Relating to the Military Coup, September 11, 1973".
- ^ CIA Admits Involvement in Chile. ABC News. September 20
- ^ Dinges, John (2005). The Condor Years: How Pinochet And His Allies Brought Terrorism To Three Continents. The New Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-1-56584-977-8.
- ^ [2] Archived March 22, 2015, at the Wayback Machine Valech Report
- ^ Gómez-Barris, Macarena (2010). "Witness Citizenship: The Place of Villa Grimaldi in Chilean Memory". Sociological Forum. 25 (1): 34. doi:10.1111/j.1573-7861.2009.01155.x.
- ^ "El campo de concentración de Pinochet cumple 70 años". El País. December 3, 2008.
- ^ Clymer, Kenton (2004). The United States and Cambodia, 1969–2000: A Troubled Relationship. Routledge. pp. 21–23. ISBN 978-0415326025.
Sihanouk's dismissal (which followed constitutional forms, rather than a blatant military coup d'état) immediately produced much speculation as to its causes. ... most others see at least some American involvement.
- ^ Kiernan, Ben (2004). How Pol Pot Came to Power: Colonialism, Nationalism, and Communism in Cambodia, 1930–1975. Yale University Press. p. 300. ISBN 9780300102628.
Prince Sihanouk has long claimed that the American CIA 'masterminded' the coup against him. ... There is in fact no evidence of CIA involvement in the 1970 events, but a good deal of evidence points to a role played by sections of the US military establishment and the Army Special Forces.
- ^ Clymer, Kenton (2004). The United States and Cambodia, 1969–2000: A Troubled Relationship. Routledge. ISBN 978-0415326025.
- ^ North American Congress on Latin America (NACLA) September 25, 2007, "Alliance for Power: U.S. Aid to Bolivia Under Banzer," https://nacla.org/article/alliance-power-us-aid-bolivia-under-banzer Archived March 17, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Huffington Post, October 23, 2008 updated on May 25, 2011, "U.S. Intervention in Bolivia," https://www.huffingtonpost.com/stephen-zunes/us-intervention-in-bolivi_b_127528.html Archived January 21, 2017, at the Wayback Machine reposted from Foreign Policy in Focus
- ^ BBC News, March 5, 2009, "Hidden Cells Reveal Bolivia's Dark Past," http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/7925694.stm Archived March 10, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Guardian, May 5, 2002, "Hugo Banzer: Former President and Dictator of Bolivia Who Headed a Brutal Military Regime," https://www.theguardian.com/news/2002/may/06/guardianobituaries.bolivia Archived July 21, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ National Security Archive March 8, 2013, "Operation Condor on Trial: Legal Proceeding on Latin American Rendition and Assassination Program Open in Buenos Aires," https://nsarchive2.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB416/ Archived March 17, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Blakeley, Ruth (2009). State Terrorism and Neoliberalism: The North in the South. Routledge. p. 22 & 23. ISBN 978-0-415-68617-4.
- ^ McSherry, J. Patrice (2011). "Chapter 5: "Industrial repression" and Operation Condor in Latin America". In Esparza, Marcia; Henry R. Huttenbach; Daniel Feierstein (eds.). State Violence and Genocide in Latin America: The Cold War Years (Critical Terrorism Studies). Routledge. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-415-66457-8.
- ^ Michael M. Gunter, Conflict Quarterly, Fall 1992, "Influences on the Kurdish Insurgency in Iraq," p. 8
- ^ Los Angeles Times, April 14, 1991, "A People Betrayed: Twice Before, Washington Let Kurds Die to Promote Foreign-Policy Designs. Now it's the Bush Administration Doing the Deed Archived 2016-03-07 at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ Michael M. Gunter, Conflict Quarterly, Fall 1992, "Influences on the Kurdish Insurgency in Iraq," p. 10
- ^ "Even in the context of covert action, ours was a cynical enterprise," according to the 1976 final report of the Pike Committee, the Congressional committee that investigated US intelligence operations. Los Angeles Times, April 14, 1991, "People Betrayed: Twice Before, Washington Let Kurds Die to Promote Foreign-Policy Designs. Now it's the Bush Administration Doing the Deed"
- ^ Michael M. Gunter, Conflict Quarterly, Fall 1992, "Influences on the Kurdish Insurgency in Iraq," p. 11
- ^ The Los Angeles Times, April 14, 1991, "People Betrayed: Twice Before, Washington Let Kurds Die to Promote Foreign-Policy Designs. Now it's the Bush Administration Doing the Deed"
- ^ "Chile President Pinera to ask Obama for Pinochet files". BBC News. March 23, 2011.
- ^ "UNTAC in Cambodia – from Occupation, Civil War and Genocide to Peace" (PDF). Max-Planck-Institut. Retrieved November 26, 2015.
- ^ Covert Action Quarterly, Fall 1997, Issue 62, p. 6, archived at "The Long Secret Alliance: Uncle Sam and Pol Pot"
- ^ a b CovertAction Quarterly, "On the Side of Pol Pot: U.S. Supports Khmer Rouge," Issue 34, Summer 1990, p. 37, archived at [3]
- ^ Covert Action Quarterly, Fall 1997, Issue 62, p. 5-6, archived at "The Long Secret Alliance: Uncle Sam and Pol Pot"
- ^ a b Becker, Elizabeth (April 17, 1998). "Death of Pol Pot: The Diplomacy; Pol Pot's End Won't Stop U.S. Pursuit of His Circle". The New York Times. cf. Lewis, Daniel (May 26, 2017). "Zbigniew Brzezinski, National Security Advisor to President Jimmy Carter, Dies at 89". The New York Times.
- ^ Brzezinski, Zbigniew (April 22, 1998). "Pol Pot's Evil Had Many Faces; China Acted Alone". The New York Times.
- ^ Hodgson, Godfrey (May 28, 2017). "Zbigniew Brzezinski obituary". The Guardian.
- ^ "S China Sea 'an existential issue to legitimise CCP rule'". Today. Singapore. March 31, 2016. Singaporean diplomat Bilahari Kausikan, recalled: "ASEAN wanted elections but the U.S. supported the return of a genocidal regime. Did any of you imagine that the U.S. once had in effect supported genocide?"
- ^ Haas, Michael, "Cambodia, Pol Pot, and the United States: The Faustian Pact," (New York: Praeger, 1991) pp. 17, 28–29
- ^ "Vietnam's invasion of Cambodia and the PRK's rule constituted a challenge on both the national and international political level. On the national level, the Khmer People's Revolutionary Party's rule gave rise..." (PDF). Max-Planck-Institut.
- ^ David P. Chandler, "A History of Cambodia," (Westview Press, 2008)
- ^ US Department of State. Country Profile of Cambodia.
- ^ Washington Post, December 27, 2007, "Sorry Charlie This is Michael Vickers's War," https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/12/27/AR2007122702116.html Archived November 26, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Riedel, Bruce 2014, "What We Won: America's Secret War in Afghanistan, 1979–1989," Brookings Institution Press. pp. ix–xi, 21–22, 98–105
- ^ Newsweek, October 1, 2001, Evan Thomas, "The Road to September 11," "The Road to September 11". October 2001. Archived from the original on November 22, 2013. Retrieved September 2, 2016.
- ^ The National Security Archive, October 9, 2001, "U.S. Analysis of The Soviet War in Afghanistan: Declassified," https://nsarchive2.gwu.edu//NSAEBB/NSAEBB57/us.html
- ^ Ewans, Martin (December 1, 2004). Conflict in Afghanistan: Studies in Asymmetric Warfare. Routledge. ISBN 9781134294817 – via Google Books.
- ^ Ewans, Sir Martin; Ewans, Martin (September 5, 2013). Afghanistan – A New History. Routledge. ISBN 9781136803390 – via Google Books.
- ^ Bergen, Peter; Tiedemann, Katherine (February 14, 2013). Talibanistan. ISBN 9780199893096 – via books.google.com.
- ^ "The Haqqani History: Bin Ladin's Advocate Inside the Taliban". nsarchive.gwu.edu.
- ^ Kepel, Gilles (August 9, 2018). Jihad: The Trail of Political Islam. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 9781845112578 – via Google Books.
- ^ Cook, Robin (July 8, 2005). "The struggle against terrorism cannot be won by military means". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on July 10, 2005. Retrieved July 8, 2005.
- ^ "During the anti-Soviet jihad Bin Laden and his fighters received American and Saudi funding. Some analysts believe Bin Laden himself had security training from the CIA." BBC News, July 20, 2004, "Al-Qaeda's Origins and Links," http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/1670089.stm Archived March 24, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "By 1984, he Osama bin Laden was running a front organization known as Maktab al-Khidamar – the MAK – which funneled money, arms and fighters from the outside world into the Afghan war. What the CIA bio conveniently fails to specify (in its unclassified form, at least) is that the MAK was nurtured by Pakistan's state security services, the Inter-Services Intelligence agency, or ISI, the CIA's primary conduit for conducting the covert war against Moscow's occupation." "So bin Laden, along with a small group of Islamic militants from Egypt, Pakistan, Lebanon, Syria and Palestinian refugee camps all over the Middle East, became the 'reliable' partners of the CIA in its war against Moscow." NBC News, August 24, 1998, "Bin Laden Comes Home to Roost: His CIA Ties Are Only the Beginning of a Woeful Story," http://www.nbcnews.com/id/3340101/t/bin-laden-comes-home-roost/#.WsHDwYXfjvY Archived July 18, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "...bin Laden's Office of Services, set up to recruit overseas for the war, received some US cash." The Guardian, January 17, 1999 "Frankenstein the CIA Created," https://www.theguardian.com/world/1999/jan/17/yemen.islam Archived December 3, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "And some of the same warriors who fought the Soviets with the C.I.A.'s help are now fighting under Mr. bin Laden's banner." New York Times, August 24, 1998 "Afghan Camps, Hidden in Hills, Stymied Soviet Attacks for Years," https://www.nytimes.com/1998/08/24/world/afghan-camps-hidden-in-hills-stymied-soviet-attacks-for-years.html Archived April 2, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Coll, Steve (2004). Ghost Wars: The Secret History of the CIA, Afghanistan, and Bin Laden, from the Soviet Invasion to September 10, 2001. Penguin Group. pp. 87. ISBN 978-1-59420-007-6.
- ^ Bergen, Peter (2006). The Osama bin Laden I Know: An Oral History of al Qaeda's Leader. Simon & Schuster. pp. 60–61. ISBN 978-0-7432-9592-5.
- ^ Burke, Jason (2004). Al-Qaeda: Casting a Shadow of Terror. I.B. Tauris. p. 59. ISBN 978-1-85043-666-9.
- ^ Crile, George (2003) Charlie Wilson's War: The Extraordinary Story of the Largest Covert Operation in History, Atlantic Monthly Press, p. 519
- ^ Douglas J. MacEachin. "US Intelligence and the Polish Crisis 1980-1981". CIA.
- ^ Looking to the Future: Essays on International Law in Honor of W. Michael Reisman
- ^ Richard T. Davies, "The CIA and the Polish Crisis of 1980–1981." Journal of Cold War Studies (2004) 6#3 pp: 120-123. online
- ^ Gregory F. Domber (2008). Supporting the Revolution: America, Democracy, and the End of the Cold War in Poland, 1981--1989. ProQuest. p. 199. ISBN 9780549385165., revised as Domber 2014, p. 110 [4].
- ^ Domber, Gregory F. (August 28, 2014), What Putin Misunderstands about American Power, University of California Press Blog, University of North Carolina Press
{{citation}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ MacEachin, Douglas J. "US Intelligence and the Polish Crisis 1980–1981." CIA. June 28, 2008.
- ^ Cover Story: The Holy Alliance By Carl Bernstein Sunday, June 24, 2001
- ^ Branding Democracy: U.S. Regime Change in Post-Soviet Eastern Europe Gerald Sussman, page 128
- ^ Executive Secrets: Covert Action and the Presidency William J. Daugherty. page 201-203
- ^ Larsen, Neil (2010). "Thoughts on Violence and Modernity in Latin America". In Grandin & Joseph, Greg & Gilbert (ed.). A Century of Revolution. Durham & London: Duke University Press. pp. 381–393.
- ^ The Center for Justice and Accountability, "El Salvador, 12 Years of Civil War," http://cja.org/where-we-work/el-salvador/ Archived March 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Report of the UN Truth Commission on El Salvador (Report). United Nations. April 1, 1993.
- ^ El Salvador, In Depth: Negotiating a settlement to the conflict, Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, Uppsala, Sweden: Uppsala University, retrieved May 24, 2013,
While nothing of the aid delivered from the US in 1979 was earmarked for security purposes, the 1980 aid for security only summed US$6.2 million, close to two-thirds of the total aid in 1979.
- ^ Danner, Mark (1993). The Massacre at El Mozote. Vintage Books. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-679-75525-8.
- ^ Maurice Lemoine (March 19, 2009), "El Salvador : des guérilleros au pouvoir", Le Monde diplomatique, retrieved January 22, 2017
- ^ NACLA, Revolution Brews cited in McClintock, Michael (1985). The American Connection: State Terror and Popular Resistance in El Salvador. Zed Books. ISBN 978-0-86232-259-5., p. 270
- ^ "A Year of Reckoning: El Salvador a Decade After the Assassination of Archbishop Romero" Human Rights Watch, 1990, pp. 224–225
- ^ "How U.S. Advisors Run the War in El Salvador" Philadelphia Inquirer, May 29, 1983
- ^ "How U.S. Actions Helped Hide Salvador Human Rights Abuses" Archived January 29, 2018, at the Wayback Machine New York Times, March 21, 1993
- ^ "From Madness to Hope: the 12-year war in El Salvador: Report of the Commission on the Truth for El Salvador" (PDF). Commission on the Truth for El Salvador. March 15, 1993. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ The Philadelphia Inquirer, May 29, 1983, How U.S. Advisers Run The War in El Salvador," http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_multi=PI%7C&p_product=PHNP&p_theme=phnp&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&s_dispstring=Title%28HOW%20U.S.%20ADVISERS%20RUN%20THE%20WAR%20IN%20EL%20SALVADOR%29%20AND%20date%28all%29&p_field_advanced-0=title&p_text_advanced-0=%28%22HOW%20U.S.%20ADVISERS%20RUN%20THE%20WAR%20IN%20EL%20SALVADOR%22%29Êl_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:DÊl_useweights=no
- ^ "El Salvador Accountability and Human Rights: the Report of the United Nations Commission on the Truth for El Salvador," Human Rights Watch, August 10, 1993
- ^ Michael Smith (2007). Killer Elite. Macmillan. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-312-36272-0.
- ^ The Daily Beast, November 9, 2014, "Bringing El Salvador Nun Killers to Justice: More than 30 Years Later, Justice Closes in on the Salvadorans Behind the Rape and Murder of American Nuns," https://www.thedailybeast.com/bringing-el-salvador-nun-killers-to-justice Archived January 13, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Central America, 1981: report to the Committee on Foreign Affairs, U.S. House of Representatives" Gerry E. Studds, William Woodward, United States. Congress. House. Committee on Foreign Affairs, 1981
- ^ Michael McClintock (1992), Instruments of Statecraft: U.S. Guerrilla Warfare, Counterinsurgency, and Counterterrorism, 1940–1990 Web project by Michael McClintock based on the 1992 book by the same name published by Pantheon Books, a division of Random House, Inc.
- ^ Torture techniques used to interrogate prisoners made use of techniques detailed in secret US counter-insurgency manuals and, when US planners proposed a similar counter-insurgency program for dealing with the Iraq insurgency after the 2003 US-led regime change in Iraq, it was referred to as "the Salvador Option".Tom Gibb (January 27, 2005). "Salvador Option Mooted for Iraq". BBC News. and Thomas Blanton; Peter Kornbluh (December 5, 2004). "Prisoner Abuse: Patterns from the Past". The National Security Archive.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Collelo, Thomas, ed. (1990) [December 1988]. Chad: a country study (PDF) (Second ed.). Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 24–31.
- ^ "U.S.-Backed Chadian Dictator Hissène Habré Faces War Crimes Trial in Historic Win for His Victims". Democracy Now!. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ^ Farah, Douglas (November 27, 2000). "Chad's Torture Victims Pursue Habre in Court". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ^ Avenue, Human Rights Watch | 350 Fifth; York, 34th Floor | New; t 1.212.290.4700, NY 10118-3299 USA |. "Hissène Habré". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Schemm, Paul (May 30, 2016). "In landmark trial, former Chad dictator found guilty of crimes against humanity". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 3, 2019.
- ^ Ba, Diadie (May 30, 2016). "Chad's ex-leader Habre, Cold War-era ally of West, gets life in prison for atrocities". Reuters. Retrieved December 3, 2019.
- ^ National Security Decision Directive 17 (NSD-17), January 1982, https://fas.org/irp/offdocs/nsdd/nsdd-17.pdf Archived April 24, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Presidential Finding authorizing paramilitary activities, December 1981, http://www.brown.edu/Research/Understanding_the_Iran_Contra_Affair/documents/d-all-45.pdf Archived October 30, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ New York Times, February 22, 1985, "President Asserts Goal Is to Remove Sandinista Regime," https://www.nytimes.com/1985/02/22/us/president-asserts-goal-is-to-remove-sandinista-regime.html Archived August 14, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Terrorism Research and Analysis Consortium, "Contras," http://www.trackingterrorism.org/group/contras Archived October 19, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Facts on File World News Digest, October 19, 1984, "U.S. Orders Probe of CIA Terror Manual," archived at Live Journal: http://bailey83221.livejournal.com/60879.html#2c Archived May 31, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Woodward, Bob, "Veil, The Secret Wars of the CIA," 1987 New York: Simon & Schuster
- ^ Gilbert, Dennis, "Sandinistas: The Party and The Revolution," Oxford: Basil Blackwell, 1988, p. 167
- ^ Los Angeles Times, March 5, 1986, "Setback for Contras : CIA Mining of Harbors 'a Fiasco,'" http://articles.latimes.com/1985-03-05/news/mn-12633_1_harbor-mining Archived December 18, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ International Court of Justice, Nicaragua v. United States of America, June 27, 1986, "Cour internationale de Justice - International Court of Justice | International Court of Justice". Archived from the original on March 1, 2015. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ^ New York Times, July 10, 1987, "Iran-Contra Hearings; Boland Amendments: What They Provided," https://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/10/world/iran-contra-hearings-boland-amendments-what-they-provided.html Archived May 31, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ BBC News, June 27, 1986, "BBC On This Day – 5 – 1984: Sandinistas claim election victory,"http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/june/27/newsid_2520000/2520169.stm Archived September 22, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ New York Times, November 16, 1984, "Nicaraguan Vote: 'Free, Fair, Hotly Contested,'" https://www.nytimes.com/1984/11/16/opinion/l-nicaraguan-vote-free-fair-hotly-contested-089345.html Archived July 1, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ New York Times, March 30, 1984, "Medals Outnumber G.I.s in Grenada Assault," https://www.nytimes.com/1984/03/30/world/medals-outnumber-gi-s-in-grenada-assault.html Archived February 13, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Stuart, Richard W., 2008, "Operation Urgent Fury: The Invasion of Grenada, October 1983" U.S. Army, http://www.history.army.mil/html/books/grenada/urgent_fury.pdf Archived September 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Nations General Assembly Resolution 38/7, November 2, 1983, http://www.un.org/en/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/38/7 Archived November 11, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Global Policy Forum, Foreign Policy in Focus, Zunes, Stephen, October 2003, "The U.S. Invasion of Grenada: A Twenty Year Retrospective," https://www.globalpolicy.org/component/content/article/155/25966.html Archived May 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Nations Security Council vetoes, October 28, 1983, http://research.un.org/en/docs/sc/quick/ Archived October 19, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Global Policy Reform, "Baker Twists Arms of Yemen, Colombia and Malaysia," https://www.globalpolicy.org/component/content/article/167/35359.html Archived September 2, 2009, at the Wayback Machine citing James A. Baker III, The Politics of Diplomacy: Revolution, War and Peace, 1989–1992 (New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1995), pp. 317–320
- ^ New York Times, March 15, 1991, "After the War: Kuwait; Kuwaiti Emir, Tired and Tearful, Returns to His Devastated Land," https://www.nytimes.com/1991/03/15/world/after-war-kuwait-kuwaiti-emir-tired-tearful-returns-his-devastated-land.html Archived October 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ French, Howard W. (December 18, 1990). "Haitians Overwhelmingly Elect Populist Priest to the Presidency". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- ^ Whitney, Kathleen Marie (1996). "Sin, Fraph, and the CIA: U.S. Covert Action in Haiti". Southwestern Journal of Law and Trade in the Americas. 3 (2): 303–32 [p. 320].
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Whitney 1996, p. 321
- ^ United Nations Security Council Resolution 661 of adopted 6 August 6, 1991, https://fas.org/news/un/iraq/sres/sres0661.htm Archived September 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Nations, UN Security Council Resolution 687, April 8, 1991, http://www.un.org/Depts/unmovic/documents/687.pdf Archived October 20, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ New York Times Magazine, July 27, 2003, "Were Sanctions Right?," https://www.nytimes.com/2003/07/27/magazine/were-sanctions-right.html Archived October 14, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Makiya, Kanan (1998). Republic of Fear: The Politics of Modern Iraq, Updated Edition. University of California Press. p. xv. ISBN 978-0-520-92124-5.
- ^ cf. "A Gulf War Exclusive: President Bush Talking with David Frost". Retrieved February 26, 2017.
George H. W. Bush: Everybody felt that Saddam Hussein could not stay in office—certainly not stay in office as long as he's stayed in office. I miscalculated—I thought he'd be gone. But I wasn't alone! People in the Arab world felt, with unanimity, that he would be out of there. I think all observers felt that (event occurs at 45:14).
- ^ "My view is we don't want to lift these sanctions as long as Saddam Hussein is in power," said President George H. W. Bush, The New York Times, May 21, 1991, "Bush Links End of Trading Ban To Hussein Exit," https://www.nytimes.com/1991/05/21/world/after-the-war-bush-links-end-of-trading-ban-to-hussein-exit.html Archived August 7, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Press International, May 20, 1991, "U.S. Taking Tough Stand Against Saddam Hussein," http://www.upi.com/Archives/1991/05/20/US-taking-tough-stand-against-Saddam-Hussein/1946674712000/ Archived October 19, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Additional U.S. government officials' statements setting Saddam Hussein's ouster as the precondition for the cessation of sanctions against Iraq, including statements by Robert Gates, Director of the Central Intelligence Agency, are provided in Gordon, Joy, 2010 "Invisible War: The United States and the Iraq Sanctions," Harvard University Press, http://www.hup.harvard.edu/catalog.php?isbn=978-0674035713 Archived April 27, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Autopsy of a Disaster: The U.S. Sanctions Policy on Iraq". Institute for Public Accuracy. November 13, 1998. Retrieved February 26, 2017. For example, United States Secretary of State Madeleine Albright stated in March 1997 that "Our view, which is unshakable, is that Iraq must prove its peaceful intentions. It can only do that by complying with all of the Security Council resolutions to which it is subjected"; National Security Adviser Sandy Berger stated in November 1997 that "It's been the U.S. position since the Bush administration that Saddam Hussein comply—has to comply with all of the relevant Security Council resolutions"; and UN ambassador Bill Richardson stated in December 1997 that "Our policy is clear. We believe that Saddam Hussein should comply with all the Security Council resolutions, and that includes 1137, those that deal with the UNSCOM inspectors, those that deal with human rights issues, those that deal with prisoners of war with Kuwait, those that deal with the treatment of his own people. We think that there are standards of international behavior."
- ^ Iraq surveys show 'humanitarian emergency' Archived August 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine UNICEF Newsline August 12, 1999
- ^ Rubin, Michael (December 2001). "Sanctions on Iraq: A Valid Anti-American Grievance?". 5 (4). Middle East Review of International Affairs: 100–15. Archived from the original on October 28, 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Spagat, Michael (September 2010). "Truth and death in Iraq under sanctions" (PDF). Significance.
- ^ Dyson, Tim; Cetorelli, Valeria (July 1, 2017). "Changing views on child mortality and economic sanctions in Iraq: a history of lies, damned lies and statistics". BMJ Global Health. 2 (2): e000311. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2017-000311. ISSN 2059-7908. PMC 5717930. PMID 29225933. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 7, 2017.
- ^ "Saddam Hussein said sanctions killed 500,000 children. That was 'a spectacular lie.'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on August 4, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Association of Former Intelligence Officers (May 19, 2003), US Coup Plotting in Iraq, Weekly Intelligence Notes 19-03
- ^ "The CIA And the Coup That Wasn't". The Washington Post. May 16, 2003.
- ^ "With CIA's Help, Group in Jordan Targets Saddam; U.S. Funds Support Campaign To Topple Iraqi Leader From Afar". The Washington Post. June 23, 1996.
- ^ a b "Ex-C.I.A. Aides Say Iraq Leader Helped Agency in 90's Attacks". The New York Times. June 9, 2004.
The Iraqi government at the time claimed that the bombs, including one it said exploded in a movie theater, resulted in many civilian casualties ... One former Central Intelligence Agency officer who was based in the region, Robert Baer, recalled that a bombing during that period 'blew up a school bus; school children were killed.' Mr. Baer ... said he did not recall which resistance group might have set off that bomb. Other former intelligence officials said Dr. Allawi's organization was the only resistance group involved in bombings and sabotage at that time. But one former senior intelligence official recalled that 'bombs were going off to no great effect.' 'I don't recall very much killing of anyone,' the official said.
- ^ Pub.L. 105–338, https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/PLAW-105publ338/html/PLAW-105publ338.htm Archived March 29, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, 112 Stat. 3178, https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/STATUTE-112/pdf/STATUTE-112-Pg3178.pdf Archived September 22, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, enacted October 31, 1998
- ^ Hanke, Steve (July 6, 2017). "20th Anniversary, Asian Financial Crisis: Clinton, The IMF And Wall Street Journal Toppled Suharto". Forbes. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
- ^ Tyson, James L. (February 10, 1999). "'Dollar diplomacy' rises again as foreign-policy tool". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
- ^ a b c Ray Jennings (2011). "346. Serbia's October Revolution: Evaluating International Efforts Promoting Democratic Breakthrough". Global Europe Program. Retrieved January 28, 2016.
- ^ Nicholas Thompson (2001). "This Ain't Your Momma's CIA". Washington Monthly. Archived from the original on January 9, 2007.
- ^ a b c d Vanity Fair, March 3, 2008, "The Gaza Bombshell," http://www.vanityfair.com/news/2008/04/gaza200804 Archived January 28, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Christian Science Monitor, May 25, 2007, "Israel, US, and Egypt Back Fatah's Fight Against Hamas," http://www.csmonitor.com/2007/0525/p07s02-wome.html Archived October 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Times (UK), November 18, 2006, "Diplomats Fear US wants to Arm Fatah for 'War on Hamas'"
- ^ The Times (UK), November 18, 2006, "Diplomats Fear US Wants to Arm Fatah for 'War on Hamas'"
- ^ The Middle East Online, January 31, 2007, http://www.middle-east-online.com/english/?id=19358 Archived October 30, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ San Francisco Chronicle, December 14, 2006, "U.S. Training Fatah in Anti-Terror Tactic – Underlying Motive Is to Counter Strength of Hamas, Analysts Say," http://www.sfgate.com/news/article/U-S-training-Fatah-in-anti-terror-tactics-2465370.php Archived December 3, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "U.S. secretly backed Syrian opposition groups, cables released by WikiLeaks show". The Washington Post.
- ^ Bandeira, Luiz Alberto Moniz (May 30, 2017). The Second Cold War: Geopolitics and the Strategic Dimensions of the USA. Springer. pp. 54–55. ISBN 978-3-319-54888-3.
- ^ "Assad must go, U.S. Republicans say". Newspapers.com. Agence France Presse. April 29, 2011. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
We urge President Obama to state unequivocally, as he did in the case of (Libyan leader Moammar) Gadhafi and Egyptian president Hosni) Mubarak — that it is time for Assad to go.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Council on Foreign Relations, August 18, 2011, "Calling for Regime Change in Syria," http://www.cfr.org/syria/calling-regime-change-syria/p25677 Archived November 13, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Wall Street Journal, August 19, 2011, "World Leaders Urge Assad to Resign: Obama Imposes New Embargo on Syrian Oil Sales as Europe Considers Similar Measures; Crackdown on Protests Persists," https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424053111903639404576516144145940136 Archived November 19, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Guardian, January 25, 2015, "US Changes Its Tune on Syrian Regime Change as Isis Threat Takes Top Priority, Washington Still Hopes Bashar al-Assad Will Be Removed from Power, But Is No Longer Insisting on It As A Precondition for Peace, https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2015/jan/25/us-syrian-regime-change-isis-priority Archived 2016-11-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ National Public Radio, April 23, 2014, "CIA Is Quietly Ramping Up Aid To Syrian Rebels, Sources Say," https://www.npr.org/sections/parallels/2014/04/23/306233248/cia-is-quietly-ramping-up-aid-to-syrian-rebels-sources-say Archived April 18, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Guardian, March 8, 2013, "West Training Syrian Rebels in Jordan Exclusive: UK and French Instructors Involved in US-Led Effort to Strengthen Secular Elements in Syria's Opposition, Say Sources," https://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/mar/08/west-training-syrian-rebels-jordan Archived December 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Abouzeid, Rania (September 26, 2013). "Syrian Opposition Groups Stop Pretending". The New Yorker. ISSN 0028-792X. Archived from the original on March 9, 2018. Retrieved May 9, 2018.
- ^ Atwan, Abdel Bari (September 8, 2015). Islamic State: The Digital Caliphate. Univ of California Press. ISBN 9780520289284 – via Google Books.
- ^ Nelson, Colleen McCain (November 19, 2015). "Obama Says Syrian Leader Bashar al-Assad Must Go". WSJ. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ RT https://www.rt.com/usa/382869-un-haley-assad-syria/ Archived March 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Yahoo 7 News https://au.news.yahoo.com/world/a/34856857/tillerson-says-assads-fate-up-to-syrian-people/#page1 Archived March 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jaffe, Greg; Entous, Adam (July 19, 2017). "Trump ends covert CIA program to arm anti-Assad rebels in Syria, a move sought by Moscow". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 20, 2017.
- ^ "Rex Tillerson again insists Syrian leader Bashar Assad must go". Newspapers.com. Associated Press. October 26, 2017. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ DeYoung, Karen; Ryan, Missy (April 10, 2018). "Strike on Assad for use of chemical agents unlikely to advance wider U.S. goals in Syria". Washington Post. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ The New Yorker, July 8, 2008, Seymour Hersh, "Preparing the Battlefield, The Bush Administration Steps Up Its Secret Moves Against Iran," http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2008/07/07/preparing-the-battlefield Archived December 4, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Johnston, Jake (August 29, 2017). "How Pentagon Officials May Have Encouraged a 2009 Coup in Honduras". The Intercept. Retrieved November 30, 2019.
- ^ Naiman, Robert; Director, ContributorPolicy; Policy, Just Foreign (February 19, 2016). "Did Secretary of State Hillary Clinton Enable the Coup in Honduras?". HuffPost. Retrieved November 30, 2019.
{{cite web}}:|first2=has generic name (help) - ^ "Security Council Approves 'No-Fly Zone' over Libya, Authorizing 'All Necessary Measures' To Protect Civilians in Libya, by a Vote of Ten For, None Against, with Five Abstentions". United Nations. March 17, 2011. Archived from the original on March 19, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2011.
- ^ "Libya Live Blog". Al Jazeera. March 19, 2011. Archived from the original on March 19, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2011.
- ^ "Libya: US, UK and France attack Gaddafi forces". BBC News. March 20, 2011. Archived from the original on March 20, 2011. Retrieved March 20, 2011.
- ^ "French Fighter Jets Deployed over Libya". CNN. March 19, 2011. Archived from the original on March 22, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2011.
- ^ Orkaby, Asher (March 25, 2015). "Houthi Who?". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on March 27, 2015.
- ^ "Yemen in Crisis". Council on Foreign Relations. July 8, 2015. Archived from the original on May 9, 2015.
- ^ Cafiero, Giorgio; Wagner, Daniel (September 24, 2015). "Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen".
- ^ Saudi Arabia and al-Qaeda Unite in Yemen Archived February 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Huffington Post, "Despite the international community's condemnation of Saudi Arabia's bombing of civilian areas in Yemen, ..."
- ^ Oakford, Samuel (January 5, 2016). "The Saudi Coalition Bombed A Rehabilitation Center for Blind People in Yemen". Vice News.
- ^ MacDonald, Alex (January 5, 2016). "Yemen centre for blind 'hit in Saudi coalition air raid'". Middle East Eye. Archived from the original on January 7, 2016.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia launches air attacks in Yemen". The Washington Post. March 25, 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Backs Saudi-Led Yemeni Bombing With Logistics, Spying" Archived April 6, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Bloomberg News, March 26, 2015
- ^ "Yemen conflict: US boosts arms supplies for Saudi-led coalition" Archived July 2, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. BBC News. April 8, 2015.
- ^ "US steps up arms for Saudi campaign in Yemen" Archived July 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Al Jazeera, April 8, 2015
- ^ "Yemen: Saudi Arabia used cluster bombs, rights groups says" Archived July 4, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. BBC News. May 3, 2015.
- ^ Nichols, Michelle (December 22, 2015). "U.N. blames Saudi-led coalition for most attacks on Yemeni civilians". Reuters UK. Archived from the original on December 24, 2015.
- ^ Cooper, Helene; Gibbons-Neff, Thomas; Schmitt, Eric (May 3, 2018). "Army Special Forces Secretly Help Saudis Combat Threat From Yemen Rebels". The New York Times.
- ^ "Saudi airstrikes in Yemen violate laws of war, rights group says". McClatchy DC.
- ^ Norton, Ben (March 17, 2016). "'Look like war crimes to me': Congressman raises concerns over U.S. support for Saudi war in Yemen". Salon.
- ^ Steve Visser (August 21, 2016). "US military distances itself from Saudi-led war in Yemen". CNN.
- ^ Warren Strobel, Jonathan Landay (October 10, 2016). "Exclusive: As Saudis bombed Yemen, U.S. worried about legal blowback". Reuters.
- ^ Nathalie Weizmann (March 27, 2015). "International Law on the Saudi-Led Military Operations in Yemen". Just Security.
- ^ "Yemen: Embargo Arms to Saudi Arabia" Archived January 31, 2017, at the Wayback Machine Human Rights Watch, March 21, 2106
- ^ Wintour, Patrick (September 3, 2019). "UK, US and France may be complicit in Yemen war crimes – UN report". The Guardian. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
- ^ "Congress Votes to Say It Hasn't Authorized War in Yemen, Yet War in Yemen Goes On Archived 2018-01-07 at the Wayback Machine", The Intercept, November 14, 2017
- ^ "PBS Report from Yemen: As Millions Face Starvation, American-Made Bombs Are Killing Civilians". Democracy Now!. July 19, 2018. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
- ^ "Yemen could be 'worst famine in 100 years'". BBC. October 15, 2018. Retrieved October 15, 2018.
- ^ "Trump's Venezuela Moves Follow Long History Of Intervention In Latin America". NPR.org. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
- ^ Williams, Aime (May 1, 2019). "US commitment to regime change in Venezuela tested". Financial Times. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Gilsinan, Uri Friedman, Kathy (February 2, 2019). "Trump's Affinity for Strongmen Has a Big Exception". The Atlantic. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weisbrot, Mark (March 13, 2019). "The Reality Behind Trump's Coalition for Regime Change in Venezuela". The New Republic. ISSN 0028-6583. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
Bibliography
- Bass, Gary J. (2008). Freedom's Battle: The Origins of Humanitarian Intervention. Knopf Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-307-26929-4.
- Bert, Wayne (2016). American Military Intervention in Unconventional War: From the Philippines to Iraq. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-33781-7.
- Blakeley, Ruth (2009). State Terrorism and Neoliberalism: The North in the South. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-68617-4.
- Blum, William (2003). Killing Hope: US Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II. Zed Books. ISBN 978-1-84277-369-7.
- Bruzzese, Anthony (2008). The Origins of Intervention: America, Italy, and the Fight Against Communism, 1947–1953. ISBN 978-0-494-46952-1.
- Cooley, Alexander (2012). Great Games, Local Rules: The New Power Contest in Central Asia. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-981200-4.
- Cullinane, Michael (2012). Liberty and American Anti-Imperialism: 1898–1909. Springer. ISBN 978-1-137-00257-0.
- Foner, Philip (1972). The Spanish-Cuban-American War and the Birth of American Imperialism Vol. 1: 1895–1898. NYU Press. ISBN 978-0-85345-266-9.
- Foner, Philip (1972). The Spanish-Cuban-American War and the Birth of American Imperialism Vol. 2: 1898–1902. NYU Press. ISBN 978-0-85345-267-6.
- Fouskas, Vassilis; Gökay, Bülent (2005). The New American Imperialism: Bush's War on Terror and Blood for Oil. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-275-98476-2.
- Grow, Michael (2008). U.S. Presidents and Latin American Interventions: Pursuing Regime Change in the Cold War. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-1586-5.
- Harland, Michael (2013). Democratic Vanguardism: Modernity, Intervention, and the Making of the Bush Doctrine. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-7970-3.
- Hiro, Dilip (2014). War Without End: The Rise of Islamist Terrorism and Global Response. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-48556-5.
- Kinzer, Stephen (2006). Overthrow: America's Century of Regime Change from Hawaii to Iraq. Times Books. ISBN 978-0-8050-8240-1.
- Little, Douglas (2009). American Orientalism: The United States and the Middle East since 1945. University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-7761-6.
- Little, Douglas (2016). Us versus Them: The United States, Radical Islam, and the Rise of the Green Threat. UNC Press Books. ISBN 978-1-4696-2681-9.
- Maurer, Noel (2013). The Empire Trap: The Rise and Fall of U.S. Intervention to Protect American Property Overseas, 1893–2013. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-4660-3.
- McPherson, Alan (2016). A Short History of U.S. Interventions in Latin America and the Caribbean. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-95400-3.
- McPherson, Alan (2013). Encyclopedia of U.S. Military Interventions in Latin America. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-59884-260-9.
- North, David (2016). A Quarter Century of War. Mehring Books. ISBN 978-1-893638-69-3.
- Parmar, Inderjeet; Cox, Michael (2010). Soft Power and US Foreign Policy: Theoretical, Historical and Contemporary Perspectives. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-15048-8.
- Sandstrom, Karl (July 18, 2013). Local Interests and American Foreign Policy: Why International Interventions Fail. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-04165-6.
- Schoonover, Thomas (2013). Uncle Sam's War of 1898 and the Origins of Globalization. University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 978-0-8131-4336-1.
- Sullivan, Michael (2008). American adventurism abroad: invasions, interventions, and regime changes since World War II. Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 978-1-4051-7075-8.
- Wilford, Hugh (2008). The Mighty Wurlitzer: How the CIA Played America. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-04517-0.
- Wilford, Hugh (2013). America's Great Game: The CIA's Secret Arabists and the Shaping of the Modern Middle East. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-01965-6.
