ADB-4en-PINACA: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
templated cites |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| ATC_prefix = |
| ATC_prefix = |
||
| ATC_suffix = |
| ATC_suffix = |
||
| PubChem = |
| PubChem = 162705324 |
||
| ChemSpiderID = |
| ChemSpiderID = 103835283 |
||
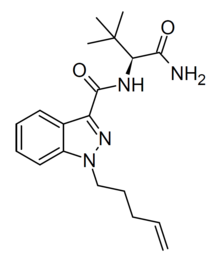
| smiles = NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)c1nn(CCCC=C)c2ccccc21)C(C)(C)C |
| smiles = NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)c1nn(CCCC=C)c2ccccc21)C(C)(C)C |
||
| StdInChI = 1S/C19H26N4O2/c1-5-6-9-12-23-14-11-8-7-10-13(14)15(22-23)18(25)21-16(17(20)24)19(2,3)4/h5,7-8,10-11,16H,1,6,9,12H2,2-4H3,(H2,20,24)(H,21,25) |
| StdInChI = 1S/C19H26N4O2/c1-5-6-9-12-23-14-11-8-7-10-13(14)15(22-23)18(25)21-16(17(20)24)19(2,3)4/h5,7-8,10-11,16H,1,6,9,12H2,2-4H3,(H2,20,24)(H,21,25) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''ADB-4en-PINACA''' is a [[cannabinoid]] [[designer drug]] that has been found as an ingredient in some [[synthetic cannabis]] products, first appearing in early 2021. It is a reasonably potent cannabinoid agonist ''in vitro'' but has not been so widely sold as related compounds such as [[ADB-PINACA]] and [[MDMB-4en-PINACA]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kronstrand R, Norman C, Vikingsson S, Biemans A, Valencia Crespo B, Edwards D, Fletcher D, Gilbert N, Persson M, Reid R, Semenova O, Al Teneiji F, Wu X, Dahlén J, NicDaéid N, Tarbah F, Sutcliffe OB, McKenzie C, Gréen H | display-authors = 6 | title = The metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoids ADB-BUTINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA and their detection in forensic toxicology casework and infused papers seized in prisons | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 14 | issue = 4 | pages = 634–652 | date = April 2022 | pmid = 34811926 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3203 | s2cid = 244490343 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pike E, Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Luo JL, Sparkes E, Cairns EA, Ellison R, Gerona R, Stove CP, Auwärter V, Banister SD | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB<sub>1</sub> receptor activation assays: Part I-Synthesis, analytical characterization, and binding affinity for human CB<sub>1</sub> receptors | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1383–1401 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33787091 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3037 }}</ref><ref name="pmid33769699">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, Banister SD, Auwärter V, Stove CP | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB<sub>1</sub> receptor activation assays-Part II: Structure activity relationship assessment via a β-arrestin recruitment assay | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1402–1411 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33769699 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3035 }}</ref><ref name="pmid33908179">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grafinger KE, Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, Juchli PO, Haschimi B, Pulver B, Banister SD, Stove CP, Auwärter V | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays. Part III: The G protein pathway and critical comparison of different assays | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1412–1429 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33908179 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3054 }}</ref> |
'''ADB-4en-PINACA''' is a [[cannabinoid]] [[designer drug]] that has been found as an ingredient in some [[synthetic cannabis]] products,<ref>{{citation|title=Nuclear magnetic resonance implemented synthetic indole and indazole cannabinoid detection, identification, and quantification|url=https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220026380A1/en}}</ref> first appearing in early 2021. It is a reasonably potent cannabinoid agonist ''in vitro'' but has not been so widely sold as related compounds such as [[ADB-PINACA]] and [[MDMB-4en-PINACA]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kronstrand R, Norman C, Vikingsson S, Biemans A, Valencia Crespo B, Edwards D, Fletcher D, Gilbert N, Persson M, Reid R, Semenova O, Al Teneiji F, Wu X, Dahlén J, NicDaéid N, Tarbah F, Sutcliffe OB, McKenzie C, Gréen H | display-authors = 6 | title = The metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoids ADB-BUTINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA and their detection in forensic toxicology casework and infused papers seized in prisons | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 14 | issue = 4 | pages = 634–652 | date = April 2022 | pmid = 34811926 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3203 | s2cid = 244490343 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pike E, Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Luo JL, Sparkes E, Cairns EA, Ellison R, Gerona R, Stove CP, Auwärter V, Banister SD | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB<sub>1</sub> receptor activation assays: Part I-Synthesis, analytical characterization, and binding affinity for human CB<sub>1</sub> receptors | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1383–1401 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33787091 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3037 }}</ref><ref name="pmid33769699">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, Banister SD, Auwärter V, Stove CP | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB<sub>1</sub> receptor activation assays-Part II: Structure activity relationship assessment via a β-arrestin recruitment assay | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1402–1411 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33769699 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3035 }}</ref><ref name="pmid33908179">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grafinger KE, Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, Juchli PO, Haschimi B, Pulver B, Banister SD, Stove CP, Auwärter V | display-authors = 6 | title = Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays. Part III: The G protein pathway and critical comparison of different assays | journal = Drug Testing and Analysis | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = 1412–1429 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33908179 | doi = 10.1002/dta.3054 }}</ref> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 16:33, 11 June 2022
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 342.443 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
ADB-4en-PINACA is a cannabinoid designer drug that has been found as an ingredient in some synthetic cannabis products,[1] first appearing in early 2021. It is a reasonably potent cannabinoid agonist in vitro but has not been so widely sold as related compounds such as ADB-PINACA and MDMB-4en-PINACA.[2][3][4][5]
See also
References
- ^ Nuclear magnetic resonance implemented synthetic indole and indazole cannabinoid detection, identification, and quantification
- ^ Kronstrand R, Norman C, Vikingsson S, Biemans A, Valencia Crespo B, Edwards D, et al. (April 2022). "The metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoids ADB-BUTINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA and their detection in forensic toxicology casework and infused papers seized in prisons". Drug Testing and Analysis. 14 (4): 634–652. doi:10.1002/dta.3203. PMID 34811926. S2CID 244490343.
- ^ Pike E, Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Luo JL, Sparkes E, et al. (July 2021). "Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays: Part I-Synthesis, analytical characterization, and binding affinity for human CB1 receptors". Drug Testing and Analysis. 13 (7): 1383–1401. doi:10.1002/dta.3037. PMID 33787091.
- ^ Grafinger KE, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, Banister SD, et al. (July 2021). "Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays-Part II: Structure activity relationship assessment via a β-arrestin recruitment assay". Drug Testing and Analysis. 13 (7): 1402–1411. doi:10.1002/dta.3035. PMID 33769699.
- ^ Grafinger KE, Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Ametovski A, Sparkes E, Cairns E, et al. (July 2021). "Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays. Part III: The G protein pathway and critical comparison of different assays". Drug Testing and Analysis. 13 (7): 1412–1429. doi:10.1002/dta.3054. PMID 33908179.
