Anisodamine
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 58.61.144.129 (talk) at 17:29, 11 August 2016. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:29, 11 August 2016 by 58.61.144.129 (talk)
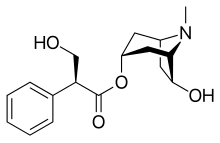 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.962 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H23NO4 |
| Molar mass | 305.37 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Anisodamine, also known as 7β-hydroxyhyoscyamine, is an anticholinergic and α1 adrenergic receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China[1] under the Mandarin Chinese name 山莨菪碱片. It is also a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid found in some plants of the Solanaceae family.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Varma DR, Yue TL (March 1986). "Adrenoceptor blocking properties of atropine-like agents anisodamine and anisodine on brain and cardiovascular tissues of rats". British Journal of Pharmacology. 87 (3): 587–94. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10201.x. PMC 1916562. PMID 2879586.
- ^ Zhang WW, Song MK, Cui YY, et al. (October 2008). "Differential neuropsychopharmacological influences of naturally occurring tropane alkaloids anisodamine versus scopolamine". Neuroscience Letters. 443 (3): 241–5. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.07.048. PMID 18672024.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
