Dasatinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sprycel |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607063 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1.3 to 5 hours |
| Excretion | Faecal (85%), renal (4%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.228.321 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H26ClN7O2S |
| Molar mass | 488.01 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dasatinib, previously known as BMS-354825, is a cancer drug produced by Bristol-Myers Squibb and sold under the trade name Sprycel. Dasatinib is an oral Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor (inhibits the "Philadelphia chromosome") and Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for first line use in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)[1] and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). It is being evaluated for use in numerous other cancers, including advanced prostate cancer. Dasatinib was developed by collaboration of Bristol-Myers Squibb and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.[2]
Efficacy
In a Phase I dose escalation study published in June 2006, dasatinib was tested in patients who were resistant to or who could not tolerate imatinib.[3] Complete hematological responses[4] were seen in 37 of 40 patients with chronic-phase CML. Major hematologic responses were seen in 31 of 44 patients with accelerated-phase CML, CML in blast crisis, or Ph+ ALL.
Molecular targets
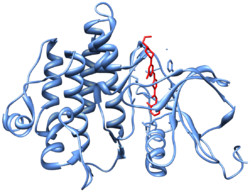
The main targets of dasatinib are BCR/Abl (the "Philadelphia chromosome"), Src, c-Kit, ephrin receptors, and several other tyrosine kinases.
Duration of benefit
Responses were maintained in 95% of patients with chronic-phase CML, with a median follow-up time of >12 months. In patients with accelerated-phase CML, 82% remained in remission, although with a median follow-up of only 5 months. Nearly all patients with CML in blast crisis or Ph+ ALL relapsed within 6 months.
Susceptible genotypes
Responses were seen in patients with all BCR/Abl genotypes, with the exception of T315I mutation, which confers resistance to dasatinib, nilotinib and imatinib in vitro.
Toxicities
Neutropenia and myelosuppression were common toxic effects. Fifteen patients (of 84, i.e. 18%) in the above-mentioned study developed pleural effusions, which were felt to be a side effect of dasatinib. Some of these patients required thoracentesis or pleurodesis to treat the effusions. Other adverse events included mild to moderate diarrhea, peripheral edema, and headache. A small number of patients developed abnormal liver function tests which returned to normal without dose adjustments. Mild hypocalcemia was also noted, but did not appear to cause any significant problems. Several cases of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) were found in patients treated with dasatinib.[6]
Adverse effects
On October 11, 2011 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that dasatinib may increase the risk of a rare but serious condition in which there is abnormally high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension, PAH). Symptoms of PAH may include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling of the body (such as the ankles and legs). In reported cases, patients developed PAH after starting dasatinib, including after more than one year of treatment.
Information about this risk has been added to the Warnings and Precautions section of the Sprycel drug label.[7]
Cost
The Union for Affordable Cancer Treatment objected to the price of dasatinib, in a letter to the U.S. trade representative. The average wholesale price in the U.S. is $367 per day, twice the price in other high income countries. The price in India, where the average annual per capita income is $1,570, and where most patients pay out of pocket, is Rs6627 ($108) a day. Indian manufacturers offered to supply generic versions for $4 a day, but, under pressure from the U.S., the Indian Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion refused to issue a compulsory license.[8]
Bristol-Myers Squibb justified the high prices of cancer drugs with the high R&D costs, but the Union of Affordable Cancer Treatment said that most of the R&D costs came from the U.S. government, including National Institutes of Health funded research and clinical trials, and a 50% tax credit. In England and Wales, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommended against dasatinib because of the high cost-benefit ratio.[8]
The Union for Affordable Cancer Treatment said that "the dasatinib dispute illustrates the shortcomings of US trade policy and its impact on cancer patients."[8]
See also
References
- ^ FDA. "FDA approves additional medical indication for Sprycel". www.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- ^ https://www.otsuka.co.jp/en/company/release/2015/0302_01.html, http://news.bms.com/press-release/rd-news/fda-approves-us-product-labeling-update-sprycel-dasatinib-include-three-year-f, http://news.bms.com/press-release/financial-news/bristol-myers-squibb-announces-extension-us-agreement-abilify-and-estab
- ^ Talpaz M, Shah NP, Kantarjian H, et al. (June 2006). "Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias". N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (24): 2531–41. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa055229. PMID 16775234.
- ^ Complete hematologic response was defined as normal white blood cell and platelet counts, no blasts in the peripheral blood, <5% myelocytes plus metamyelocytes in the peripheral blood, <20% basophils in the peripheral blood, and no extramedullary disease.
- ^ Tokarski, J. S.; Newitt, J. A.; Chang, C. Y.; Cheng, J. D.; Wittekind, M.; Kiefer, S. E.; Kish, K.; Lee, F. Y.; Borzillerri, R.; Lombardo, L. J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klei, H. E. (2006). "The Structure of Dasatinib (BMS-354825) Bound to Activated ABL Kinase Domain Elucidates Its Inhibitory Activity against Imatinib-Resistant ABL Mutants". Cancer Research. 66 (11): 5790–5797. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4187. PMID 16740718.
- ^ NHS - Healthcare News
- ^ FDA: Sprycel (dasatinib): Drug Safety Communication - Risk of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, 10/11/2011.
- ^ a b c Deborah Cohen (4 November 2014). "US trade rep is pressing Indian government to forbid production of generic cancer drug, consortium says". BMJ. 349: g6593. doi:10.1136/bmj.g6593.
External links
- Sprycel (dasatinib) Official Site
- Prescribing information from Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Summary Basis for Approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Freedom of Information Homepage
- Sprycel Summary of Product Characteristics (from the European Medicines Agency Website)
- Discovery of N-(2-Chloro-6-methyl-phenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a Dual Src/Abl Kinase Inhibitor with Potent Antitumor Activity in Preclinical Assays
