Fluroxene
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.344 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
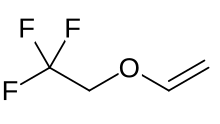
| Formula | C4H5F3O |
| Molar mass | 126.077 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fluroxene (INN, USAN; brand name Fluoromar), or 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl vinyl ether, is a volatile, inhalational anesthetic, and was the first halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetic to be introduced.[1][2] It was synthesized in 1951, and was introduced for clinical use in 1954, but was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 1974 due to its potential flammability and accumulating evidence that it could cause organ toxicity.[2][1][3] In any case, prior to being discontinued, it had largely been superseded by halothane.[4]
See also
References
- ^ a b Robert K. Stoelting; Simon C. Hillier (11 January 2012). Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 142–. ISBN 978-1-4511-6583-8.
- ^ a b Paul G Barash; Bruce F Cullen; Robert K Stoelting; Michael Cahalan; M Christine Stock (1 January 2011). Clinical Anesthesia. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 113–. ISBN 978-1-4511-2297-8.
- ^ Monte Lichtiger; Frank Moya (1 January 1978). Introduction to the practice of anesthesia. Medical Dept., Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-06-141534-0.
- ^ Acta anaesthesiologica Belgica. Acta Medica Belgica. 1974.
