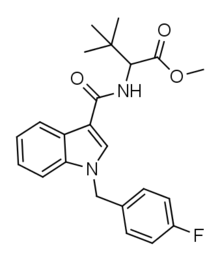
MDMB-FUBICA
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H25FN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 396,46 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
MDMB-FUBICA is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.
It was first detected by the EMCDDA in Sweden in February 2015.[1]
Side effects
MDMB-FUBICA's indazole analogue MDMB-FUBINACA has been linked to at least 1000 hospitalisations and 40 deaths as a consequence of intoxication as of March 2015.[2]
Legality
MDMB-FUBICA is banned in Sweden.[3]
See also
References
- ^ "HAMAROSAN: 2015. ÉVI EURÓPAI KÁBÍTÓSZER - JELENTÉS" (PDF). Hungarian National Focal Point (NFP). June 2015. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ^ "Очередная жертва спайса". Federal Drug Control Service of the Russian Federation. 17 March 2015. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- ^ "23 nya ämnen kan klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara". Folkhälsomyndigheten. 1 June 2015. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
