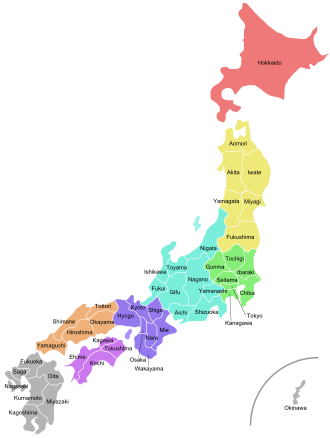
Prefectures of Japan
| Prefecture 都道府県 Todōfuken | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary State |
| Location | Japan |
| Number | 47 |
| Populations | 584,982 (Tottori) – 12,059,237 (Tōkyō) |
| Areas | 1,861.7 km2 (718.8 sq mi) (Kagawa) – 83,453.6 km2 (32,221.6 sq mi) (Hokkaido) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
The Prefectures of Japan (都道府県, Todōfuken) consist of 47 prefectures. They form the first level of jurisdiction and administrative division of Japan. They consist of 43 prefectures (県, ken) proper, two urban prefectures (府, fu, Osaka and Kyoto), one "circuit" or "territory" (道, dō, Hokkaido) and one "metropolis" (都, to, Tokyo). The Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the provinces of Japan in 1868.[1]
Each prefecture's chief executive is a directly-elected governor (知事, chiji). Ordinances and budgets are enacted by a unicameral assembly (議会, gikai) whose members are elected for four-year terms.
Under the current Local Autonomy Law, each prefecture is subdivided into cities (市, shi) and districts (郡, gun) and each district into towns (町, chō/machi) and villages (村, son/mura). For example, Hokkaido has 14 subprefectures that act as branch offices (支庁, shichō) of the prefecture. Some other prefectures also have branch offices that carry out prefectural administrative functions outside the capital. Tokyo, the capital of Japan, is a merged city-prefecture; a metropolis, it has features of both cities and prefectures.
Background
| Administrative divisions of Japan |
|---|
| Prefectural |
| Prefectures |
| Sub-prefectural |
| Municipal |
| Sub-municipal |
The West's use of "prefecture" to label these Japanese regions stems from 16th-century Portuguese explorers' and traders' use of "prefeitura" to describe the fiefdoms they encountered there. Its original sense in Portuguese, however, was closer to "municipality" than "province". (Today, in turn, Japan uses its word ken (県), meaning "prefecture", to identify Portuguese districts while in Brazil the word "Prefeitura" is used to refer to a City Hall.)
Those fiefs were headed by a local warlord or family. Though the fiefs have long since been dismantled, merged, and reorganized multiple times, and been granted legislative governance and oversight, the rough translation stuck.
The Meiji government established the current system in July 1871 with the abolition of the han system and establishment of the prefecture system (廃藩置県 haihan-chiken). Although there were initially over 300 prefectures, many of them being former han territories, this number was reduced to 72 in the latter part of 1871, and 47 in 1888. The Local Autonomy Law of 1947 gave more political power to prefectures, and installed prefectural governors and parliaments.
In 2003, then-Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi proposed that the government consolidate the current prefectures into about 10 regional states. The plan called for each region to have greater autonomy than existing prefectures. This process would reduce the number of sub-prefecture administrative regions and cut administrative costs.[2] The Japanese government is also considering a plan to merge several groups of prefectures, creating a sub-national administrative division system consisting of between nine and 13 states, and giving these states more local autonomy than the prefectures currently enjoy.[3] As of August 2012[update], no reorganization has been scheduled.
Powers
Japan is a unitary state. The central government delegates many functions (such as education and the police force) to the prefectures and municipalities, but retains the overall right to control them. Although local government expenditure accounts for 70 percent of overall government expenditure, the central government controls local budgets, tax rates, and borrowing.[4]
Types of prefecture
Historically, during the Edo period, the Tokugawa shogunate established bugyō-ruled zones (奉行支配地) around the nine largest cities in Japan, and 302 township-ruled zones (郡代支配地) elsewhere. When the Meiji government began to create the prefectural system in 1868, the nine bugyō-ruled zones became fu (府), while the township-ruled zones and the rest of the bugyo-ruled zones became ken (県). Later, in 1871, the government designated Tokyo, Osaka, and Kyoto as fu, and relegated the other fu to the status of ken. During World War II, in 1943, Tokyo became a to, a new type of pseudo-prefecture.
Despite the differences in terminology, there is little functional difference between the four types of local governments. The sub-national governments are sometimes collectively referred to as to-dō-fu-ken (都道府県) in Japanese, which is a simple combination of the four terms.
To
Tokyo is referred to as to (都), which is often translated as "metropolis." The Japanese government translates Tōkyō-to as "Tokyo Metropolis" in almost all cases, and the government is officially called the "Tokyo Metropolitan Government". But there are some people who call Tōkyō-to "Tokyo Prefecture" in English.
Following the abolition of the han system, Tōkyō-fu (an urban prefecture like Kyoto and Osaka) encompassed a number of cities, the largest of which was Tokyo City. Tokyo City was divided into 15 wards. In 1943, Tokyo City was abolished, Tōkyō-fu became Tōkyō-to, and Tokyo's wards became the special wards, local authorities falling directly under the prefecture in hierarchy, each with their own elected assemblies (kugikai) and mayors (kuchō). A number of suburban villages and towns were converted to wards, bringing the total number of special wards to 35. The reorganization's aim was to consolidate the administration of the area around the capital by eliminating the extra level of authority in Tokyo. The central government wanted to have greater control over Tokyo due to Japan's deteriorating position in World War II and the possibility of emergency in the metropolis.
After the war, Japan was forced to decentralize Tokyo again, following the general terms of democratization outlined in the Potsdam Declaration. Many of Tokyo's special governmental characteristics disappeared during this time, and the wards took on an increasingly municipal status in the decades following the surrender. Administratively, today's special wards are almost indistinguishable from other municipalities.
The postwar reforms also changed the map of Tokyo significantly: In 1947, the 35 wards were reorganized into the 23 special wards, because[citation needed] many of its citizens had either died during the war, left the city, or been drafted and didn't return.
There are some differences in terminology between Tokyo and other prefectures: police and fire departments are called chō (庁) instead of honbu (本部), for instance. But the only functional difference between Tōkyō-to and other prefectures is that Tokyo administers wards as well as cities. Today, since the special wards have almost the same degree of independence as Japanese cities, the difference in administration between Tokyo and other prefectures is fairly minor.
In Osaka, several prominent politicians led by Tōru Hashimoto, mayor of Osaka City and former governor of Osaka Prefecture, are currently proposing an Osaka Metropolis plan, under which Osaka City, and possibly other neighboring cities, would be replaced by special wards similar to Tokyo's.
Dō
Hokkaido is referred to as a dō (道) or circuit. This term was originally used to refer to Japanese regions consisting of several provinces (e.g. the Tōkaidō east-coast region, and Saikaido west-coast region). This was also a historical usage of the character in China. (In Korea, this historical usage is still used today and was kept during the period of Japanese rule.)
Hokkaido, the only remaining dō today, was not one of the original seven dō (it was known as Ezo in the pre-modern era). Its current name is believed to originate from Matsuura Takeshiro, an early Japanese explorer of the island. Since Hokkaido did not fit into the existing dō classifications, a new dō was created to cover it.
The Meiji government originally classified Hokkaido as a "Settlement Envoyship" (開拓使 kaitakushi), and later divided the island into three prefectures (Sapporo, Hakodate, and Nemuro). These were consolidated into a single Hokkaido Department (北海道庁 Hokkaido-chō) in 1886, at prefectural level but organized more along the lines of a territory. In 1947, the department was dissolved, and Hokkaido became a full-fledged prefecture. The -ken suffix was never added to its name, so the -dō suffix came to be understood to mean "prefecture."
When Hokkaido was incorporated, transportation on the island was still underdeveloped, so the prefecture was split into several "sub-prefectures" (支庁 shichō) that could fulfill administrative duties of the prefectural government and keep tight control over the developing island. These sub-prefectures still exist today, although they have much less power than they possessed before and during World War II: they now exist primarily to handle paperwork and other bureaucratic functions.
"Hokkaido Prefecture" is, technically speaking, a redundant term, although it is occasionally used to differentiate the government from the island itself. The prefecture's government calls itself the "Hokkaido Government" rather than the "Hokkaido Prefectural Government".
Fu
Osaka and Kyoto Prefectures are referred to as fu (府). The Classical Chinese character from which this is derived implies a core urban zone of national importance. Before World War II, different laws applied to fu and ken, but this distinction was abolished after the war, and the two types of prefecture are now functionally the same.
Ken
43 of the 47 prefectures are referred to as ken (県). The Classical Chinese character from which this is derived carries a rural or provincial connotation, and an analogous character is used to refer to the counties of China, counties of Taiwan and districts of Vietnam.
Lists of prefectures
The different systems of parsing frame the ways in which Japanese prefectures are perceived:
By Japanese ISO
The prefectures are also often grouped into eight regions (Chihō). Those regions are not formally specified, they do not have elected officials, nor are they corporate bodies. But the practice of ordering prefectures based on their geographic region is traditional.[1] This ordering is mirrored in Japan's International Organization for Standardization (ISO) coding.[5] From north to south (numbering in ISO 3166-2:JP order), the prefectures of Japan and their commonly associated regions are:
| Hokkaidō | Tōhoku | Kantō | Chūbu | Kansai | Chūgoku | Shikoku | Kyūshū |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Hokkaidō |
2. Aomori |
8. Ibaraki |
15. Niigata |
24. Mie |
31. Tottori |
40. Fukuoka |
By English name
- The default alphabetic order in this sortable table can be altered to mirror the traditional Japanese regions and ISO parsing.
| Prefecture | Kanji | Capital | Region | Major Island | Population¹ | Area² | Density³ | Distr. | Municip. | ISO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 愛知県 | Nagoya | Chūbu | Honshu | 7,484,094 | 5,172.4 | 1,446.9 | 7 | 54 | JP-23 | |
| 秋田県 | Akita | Tōhoku | Honshu | 1,022,839 | 11,637.54 | 87.9 | 6 | 25 | JP-05 | |
| 青森県 | Aomori | Tōhoku | Honshu | 1,308,649 | 9,645.4 | 135.7 | 8 | 40 | JP-02 | |
| 千葉県 | Chiba | Kantō | Honshu | 6,224,027 | 5,157.64 | 1,206.8 | 6 | 54 | JP-12 | |
| 愛媛県 | Matsuyama | Shikoku | Shikoku | 1,385,840 | 5,676.1 | 244.2 | 7 | 20 | JP-38 | |
| 福井県 | Fukui | Chūbu | Honshu | 787,099 | 4,190.43 | 187.8 | 7 | 17 | JP-18 | |
| 福岡県 | Fukuoka | Kyushu | Kyushu | 5,102,871 | 4,986.4 | 1,023.4 | 12 | 60 | JP-40 | |
| 福島県 | Fukushima | Tōhoku | Honshu | 1,913,606 | 13,783.75 | 138.8 | 13 | 59 | JP-07 | |
| 岐阜県 | Gifu | Chūbu | Honshu | 2,032,533 | 10,621.29 | 191.4 | 9 | 42 | JP-21 | |
| 群馬県 | Maebashi | Kantō | Honshu | 1,973,476 | 6,362.28 | 310.2 | 7 | 35 | JP-10 | |
| 広島県 | Hiroshima | Chūgoku | Honshu | 2,844,963 | 8,479.38 | 335.5 | 5 | 23 | JP-34 | |
| 北海道 | Sapporo | Hokkaido | Hokkaido | 5,383,579 | 83,424.22 | 68.6 | 66 | 180 | JP-01 | |
| 兵庫県 | Kōbe | Kansai | Honshu | 5,536,989 | 8,400.9 | 659.1 | 8 | 41 | JP-28 | |
| 茨城県 | Mito | Kantō | Honshu | 2,917,857 | 6,096.93 | 478.6 | 7 | 44 | JP-08 | |
| 石川県 | Kanazawa | Chūbu | Honshu | 1,154,343 | 4,186.15 | 275.8 | 5 | 19 | JP-17 | |
| 岩手県 | Morioka | Tōhoku | Honshu | 1,279,814 | 15,275.01 | 83.8 | 10 | 33 | JP-03 | |
| 香川県 | Takamatsu | Shikoku | Shikoku | 976,756 | 1,876.73 | 520.5 | 5 | 17 | JP-37 | |
| 鹿児島県 | Kagoshima | Kyushu | Kyushu | 1,648,752 | 9,188.1 | 179.4 | 8 | 43 | JP-46 | |
| 神奈川県 | Yokohama | Kantō | Honshu | 9,127,323 | 2,415.81 | 3,778.2 | 6 | 33 | JP-14 | |
| 高知県 | Kōchi | Shikoku | Shikoku | 728,461 | 7,103.91 | 102.5 | 6 | 34 | JP-39 | |
| 熊本県 | Kumamoto | Kyushu | Kyushu | 1,786,969 | 7,409.32 | 241.2 | 9 | 45 | JP-43 | |
| 京都府 | Kyoto | Kansai | Honshu | 2,610,140 | 4,612.2 | 565.9 | 6 | 26 | JP-26 | |
| 三重県 | Tsu | Kansai | Honshu | 1,815,827 | 5,774.39 | 314.5 | 7 | 29 | JP-24 | |
| 宮城県 | Sendai | Tōhoku | Honshu | 2,334,215 | 7,282.14 | 320.5 | 10 | 35 | JP-04 | |
| 宮崎県 | Miyazaki | Kyushu | Kyushu | 1,104,377 | 7,735.31 | 142.8 | 6 | 26 | JP-45 | |
| 長野県 | Nagano | Chūbu | Honshu | 2,099,759 | 13,561.56 | 154.8 | 14 | 77 | JP-20 | |
| 長崎県 | Nagasaki | Kyushu | Kyushu | 1,377,780 | 4,132.32 | 333.4 | 4 | 21 | JP-42 | |
| 奈良県 | Nara | Kansai | Honshu | 1,365,008 | 3,690.94 | 369.8 | 7 | 39 | JP-29 | |
| 新潟県 | Niigata | Chūbu | Honshu | 2,305,098 | 12,584.1 | 183.2 | 9 | 30 | JP-15 | |
| 大分県 | Ōita | Kyushu | Kyushu | 1,166,729 | 6,340.61 | 184 | 3 | 18 | JP-44 | |
| 岡山県 | Okayama | Chūgoku | Honshu | 1,922,181 | 7,114.62 | 270.2 | 10 | 27 | JP-33 | |
| 沖縄県 | Naha | Kyushu | Ryukyu Islands | 1,434,138 | 2,281 | 628.7 | 5 | 41 | JP-47 | |
| 大阪府 | Ōsaka | Kansai | Honshu | 8,838,908 | 1,904.99 | 4,639.9 | 5 | 43 | JP-27 | |
| 佐賀県 | Saga | Kyushu | Kyushu | 833,245 | 2,440.64 | 341.4 | 6 | 20 | JP-41 | |
| 埼玉県 | Saitama | Kantō | Honshu | 7,261,271 | 3,797.75 | 1,912 | 8 | 63 | JP-11 | |
| 滋賀県 | Ōtsu | Kansai | Honshu | 1,413,184 | 4,017.38 | 351.8 | 3 | 19 | JP-25 | |
| 島根県 | Matsue | Chūgoku | Honshu | 694,188 | 6,708.23 | 103.5 | 5 | 19 | JP-32 | |
| 静岡県 | Shizuoka | Chūbu | Honshu | 3,701,181 | 7,778.7 | 475.8 | 5 | 35 | JP-22 | |
| 栃木県 | Utsunomiya | Kantō | Honshu | 1,974,671 | 6,408.09 | 308.2 | 5 | 26 | JP-09 | |
| 徳島県 | Tokushima | Shikoku | Shikoku | 756,063 | 4,146.93 | 182.3 | 8 | 24 | JP-36 | |
| 東京都 | Tokyo[6] | Kantō | Honshu | 13,513,734 | 2,190.9 | 6,168.1 | 1 | 39 | JP-13 | |
| 鳥取県 | Tottori | Chūgoku | Honshu | 573,648 | 3,507.05 | 163.6 | 5 | 19 | JP-31 | |
| 富山県 | Toyama | Chūbu | Honshu | 1,066,883 | 4,247.61 | 251.2 | 2 | 15 | JP-16 | |
| 和歌山県 | Wakayama | Kansai | Honshu | 963,850 | 4,724.68 | 204 | 6 | 30 | JP-30 | |
| 山形県 | Yamagata | Tōhoku | Honshu | 1,122,957 | 9,323.15 | 120.4 | 8 | 35 | JP-06 | |
| 山口県 | Yamaguchi | Chūgoku | Honshu | 1,405,007 | 6,112.3 | 229.9 | 4 | 19 | JP-35 | |
| 山梨県 | Kōfu | Chūbu | Honshu | 835,165 | 4,464.99 | 187 | 5 | 27 | JP-19 |
Notes: ¹ as of 2015; ² km²; ³ per km²
Former prefectures
1870s
See this Japanese Wikipedia article for all the changes back then.
1880s
| Prefecture | Japanese | Year of Abolishment | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kanazawa | 金沢県 | 1869 | Renamed as Ishikawa |
| Sendai | 仙台県 | 1871 | Renamed as Miyagi |
| Morioka | 盛岡県 | 1872 | Renamed as Iwate |
| Nagoya | 名古屋県 | 1872 | Renamed as Aichi |
| Nukata | 額田県 | 1872 | Merged into Aichi |
| Nanao | 七尾県 | 1872 | Merged into Ishikawa and Shinkawa |
| Iruma | 入間県 | 1973 | Merged into Kumagaya and Kanagawa |
| Inba | 印旛県 | 1873 | Merged into Chiba |
| Kisarazu | 木更津県 | 1873 | Merged into Chiba |
| Utsunomiya | 宇都宮県 | 1873 | Merged into Tochigi |
| Asuwa | 足羽県 | 1873 | Merged into Tsuruga |
| Kashiwazaki | 柏崎県 | 1873 | Merged into Niigata |
| Ichinoseki→Mizusawa→Iwai | 一関県→水沢県→磐井県 | 1875 | Merged into Iwate and Miyagi |
| Okitama | 置賜県 | 1875 | Merged into Yamagata |
| Shinji | 新治県 | 1875 | Merged into Ibaraki and Chiba |
| Sakata→Tsuruoka | 酒田県→鶴岡県 | 1876 | Merged into Yamagata |
| Taira→Iwasaki | 平県→磐前県 | 1876 | Merged into Fukushima and Miyagi |
| Wakamatsu | 若松県 | 1876 | Merged into Fukushima |
| Tsukama | 筑摩県 | 1876 | Merged into Nagano and Gifu |
| Tsuruga | 敦賀県 | 1876 | Merged into Ishikawa and Shiga |
| Shinkawa | 新川県 | 1876 | Merged into Ishikawa |
| Sakai | 堺県 | 1881 | Merged into Osaka |
| Ashigara | 足柄県 | 1876 | Merged into Kanagawa and Shizuoka |
| Kumagaya | 熊谷県 | 1876 | Merged into Gunma and Saitama |
| Aikawa | 相川県 | 1876 | Merged into Niigata |
| Hamamatsu | 浜松県 | 1876 | Merged into Shizuoka |
| Hakodate | 函館県 | 1886 | Merged into Hokkaido |
| Sapporo | 札幌県 | 1886 | Merged into Hokkaido |
| Nemuro | 根室県 | 1886 | Merged into Hokkaido |
| Tokyo | 東京府 | 1943 | Reorganized as Tokyo Metropolis (東京都) |
Territories lost after World War II
Note: Due to the division of Korea, Kōgen (Kangwon/Gangwon) and Keiki (Gyeonggi) are divided between North Korea and South Korea. While each Korea has its own Kangwon/Gangwon Province, the North Korean portion of Gyeonggi has been absorbed into other provinces.
See also
- List of Japanese prefectures by population
- List of Japanese prefectures by GDP
- List of Japanese prefectures by area
- List of prefectural capitals in Japan
- List of Prefecture songs of Japan
- ISO 3166-2 codes for Japan
- List of prefectural governors in Japan
General
References
- ^ a b Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric, 2002: "Provinces and prefectures" in Japan encyclopedia, p. 780.
- ^ Mabuchi, Masaru, "Municipal Amalgamation in Japan", World Bank, 2001.
- ^ "Doshusei Regional System" National Association for Research Advancement.
- ^ Mochida, "Local Government Organization and Finance: Japan", in Shah, Anwar (2006). Local Governance in Industrial Countries. World Bank.
- ^ See ISO 3166
- ^ 都庁の所在地 Shinjuku is the location of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Office.But Tokyo is not a "municipality". Therefore, for the sake of convenience, the notation of prefectural is "Tokyo".

