Provinces of Vietnam
 |
|---|
|
|
| Administrative units of Vietnam |
|---|
| Province-level |
| District-level |
| Commune-level |
| Village-level |
Vietnam is divided into 58 provinces (Template:Lang-vi) and 5 municipalities existing at the same level as provinces ([thành phố trực thuộc trung ương] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The provinces are divided into districts ([huyện] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), provincial cities ([thành phố trực thuộc tỉnh] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), and district-level towns ([thị xã] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), which are subdivided into commune-level towns ([thị trấn] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) or communes ([xã] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The municipalities are divided into rural districts ([huyện] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) and urban districts ([quận] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), which are subdivided into wards ([phường] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)).
Governance
People's Council
Vietnamese provinces are controlled by a People's Council, elected by the inhabitants. The number of councilors varies from province to province, depending on the population of that province. The People's Council appoints a People's Committee, which acts as the executive arm of the provincial government. This arrangement is a somewhat simplified version of the situation in Vietnam's national government. Provincial governments are expected to be subordinate to the central government.
People's Committee
The People's Committee is, as mentioned previously, the executive arm of a provincial government, and is responsible for formulating and implementing policy. It may be thought of as the equivalent of a cabinet. The People's Committee will have a Chairman and a Vice-Chairman, and between nine and eleven ordinary members.
List and statistics
Template:Vietnam Provinces Image Map
According to the census results of April 1, 2009, the population of Vietnam is 85,789,573 people. The most populous top-level administrative unit in Vietnam is Hồ Chí Minh City, one of the five centrally governed cities. It has 7,123,340 people living within its official boundaries. The second most populous administrative unit is the recently expanded Hà Nội with 6,448,837 people. Prior to the expansion of the capital city, this rank belonged to Thanh Hóa with 3,400,239 people. The least populous is Bắc Kạn, a mountainous province in the remote northeast with 294,660 people.[1]
In terms of land area, the largest province is Nghệ An, which runs from the city of Vinh up the wide Sông Cả valley. The smallest is Bắc Ninh, located in the populous Red River Delta region.
The following is a table of Vietnam's provinces broken down by population and area, April 1, 2009.[2]
See also List of postal codes in Vietnam
Regions
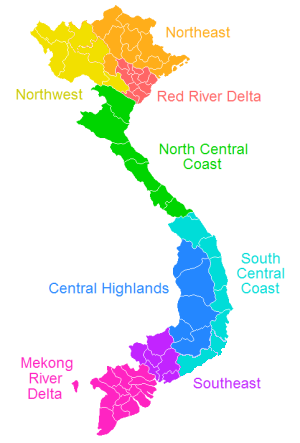
The Vietnamese government often groups the various provinces into eight regions. These regions are not always used, and alternative classifications are possible. The regions include:
Northwest (Tây Bắc Bộ) contains four inland provinces in the west of Vietnam's northern part. Two of them border with Laos, and one borders China.
Northeast (Đông Bắc Bộ) contains eleven provinces (many of which are mountainous) that lie to north of the highly populated Red River lowlands.
Red River Delta (Đồng Bằng Sông Hồng) contains nine provinces that are small but populous – based around the Red River, including the national capital Hanoi, and the municipality of Hải Phòng (both of which are independent of any provincial government).
North Central Coast (Bắc Trung Bộ) contains six provinces in the northern half of Vietnam's narrow central part. All provinces in this region stretch from the coast in the east to Laos in the west.
South Central Coast (Nam Trung Bộ) contains eight coastal provinces in the southern half of Vietnam's central part. Vietnam is wider at this point than in the North Central Coast region, so the inland areas are separate provinces. The region also includes the independent municipality of Đà Nẵng.
Central Highlands (Tây Nguyên) contains the five inland provinces (much of whose terrain is mountainous) of south-central Vietnam, mostly inhabited by ethnic minorities, although many Viet people live there as well.
Southeast (Đông Nam Bộ) contains those parts of lowland southern Vietnam which are north of the Mekong Delta. There are seven provinces, plus the independent municipality of Ho Chi Minh City (formerly Saigon).
Mekong Delta (Đồng Bằng Sông Cửu Long) is Vietnam's southernmost region, and contains twelve mostly small but populous provinces in the delta of the Mekong, plus the independent municipality of Cần Thơ. The other name of this region is Southwestern (Tây Nam Bộ).
Historical provinces of Vietnam
- Hà Nam Ninh - then divided into 3 provinces: Hà Nam, Nam Định and Ninh Bình
- Hà Sơn Bình (divided into Hà Tây and Hòa Bình - then on August 1, 2008, Hà Tây and 4 communities of Hòa Bình became a part of expanded capital city Hà Nội)
- Hà Bắc Province - divided into Bắc Giang Province and Bắc Ninh Province
- Châu Đốc
- Long Hồ
- Nghệ Tĩnh (divided into Nghệ An and Hà Tĩnh), most noted for being the site of the Nghe Tinh Soviet Republic declared September 1930 and lasted into 1931, a short-lived bastion against colonial French rule.
- Minh Hai (divided into Cà Mau and Bạc Liêu)
- Vĩnh Phú (divided into Vĩnh Phúc and Phú Thọ
- Hà Tây - annexed into Hà Nội since August 1, 2008.
