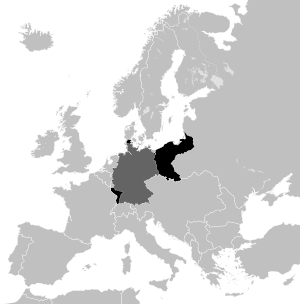
Former eastern territories of Germany
| Territorial evolution of Germany in the 20th century |
|---|
The former eastern territories of Germany (Template:Lang-de) are those provinces or regions east of the current eastern border of Germany (the Oder–Neisse line) which were lost by Germany after World War I and then World War II. The territories lost following World War I include most of the Province of Posen and West Prussia, and further territories lost after World War II include East Prussia, Farther Pomerania, East Brandenburg, Upper Silesia, and almost all of Lower Silesia. All territories lost in both World Wars account for 33% of the former German Empire, while land ceded by Germany after World War II constituted roughly 25% of its pre-war Weimar territory.[1] In present-day Germany, the term usually refers only to the territories lost in World War II,[2] while in Poland the territories acquired from Germany after World War II were dubbed the "Recovered Territories" by the Soviet-installed Polish government.
The post-war border between Germany and Poland along the Oder–Neisse line was formally recognized by East Germany in 1950 by the Treaty of Zgorzelec, under pressure from Stalin. In 1952, recognition of the Oder–Neisse line as a permanent boundary was one of Stalin's conditions for the Soviet Union to agree to a reunification of Germany (see Stalin Note). The offer was rejected by West German Chancellor Konrad Adenauer. The official German government position on the status of former eastern territories of Germany vacated by settled German communities east of the Oder and Neisse rivers was that the areas were "temporarily under Polish [or Soviet] administration." In 1970, West Germany recognised the line as a de facto boundary in the Treaty of Warsaw.
In 1990, as part of the reunification of Germany, West Germany accepted clauses in the Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to Germany whereby Germany renounced all claims to territory east of the Oder-Neisse line.[3] Germany's recognition of the Oder-Neisse line as the border was formalised by the re-united Germany in the German-Polish Border Treaty on November 14, 1990; and by the repeal of Article 23 of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany under which German states outside the Federal Republic could formerly apply for admission. With this repeal the post-1990 boundaries of Germany are closed to further expansion.
Usage

In the Potsdam Agreement the description of the territories transferred is "The former German territories east of the Oder-Neisse line", and permutations on this description are the most commonly used to describe any former territories of Germany east of the Oder-Neisse line.
The name East Germany, a political term, used to be the common colloquial English name for the German Democratic Republic (GDR), and mirrored the common colloquial English term for the other German state of West Germany. When focusing on the period before World War II, "eastern Germany" is used to describe all the territories east of the Elbe (East Elbia), as reflected in the works of sociologist Max Weber and political theorist Carl Schmitt,[4] [5] [6][7] [8] but because of the border changes in the 20th century, after World War II the term "east Germany" and eastern Germany in English has meant the territory of the German Democratic Republic.
In German there is only one usual term,Ostdeutschland, meaning East Germany or Eastern Germany. The rather ambiguous German term never gained prevailing use for the GDR as did the English term. Since Ostdeutschland has been used to denote the post-war and the respective five states of the reunited Germany. However, because people and institutions in the states, traditionally considered as Middle Germany, like the three southern new states Saxony-Anhalt, the Free State of Saxony and the Free State of Thuringia, still use the term Middle Germany when referring to their area and its institutions, the term Ostdeutschland is still ambiguous.[9]
History
Foundation of German Empire, 1871

At the time of the foundation of the German Empire in 1871, theKingdom of Prussia was the largest and dominant part of the empire. Prussian territory east of the Oder-Neisse line included West Prussia and Posen (taken by Prussia in the first two Partitions of Poland in the 18th century), also Silesia, East Brandenburg, and Pomerania. Later, these territories would come to be called in Germany "Ostgebiete des deutschen Reiches" (Eastern territories of the German Empire).
Treaty of Versailles, 1919


The Treaty of Versailles of 1919 that ended World War I restored the independence of Poland, known as the Second Polish Republic, and Germany was compelled to cede territories to it, most of which were taken by Prussia in the three Partitions of Poland, and had been part of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the German Empire for over 100 years. The territories ceded to Poland in 1919 were those with an apparent Polish majority, such as the Province of Posen, the east-southern part of Upper Silesia and the Polish Corridor.
Land transfers in Central Europe as a result of Versailles included:
- Most of Greater Poland ("Province of Posen") and Pomerelia (parts of West Prussia), mostly what the Kingdom of Prussia had taken in the Partitions of Poland was handed over to Poland after the Greater Poland Uprising (this land comprised an area of 53,800 km2 4,224,000 inhabitants (1931) including 510 km2 and 26,000 inhabitants from Upper Silesia).[10]
- The Hlučín Area of Moravian-Silesian Region to Czechoslovakia (316 or 333 km2 and 49,000 people),
- The eastern part of Upper Silesia (including Katowice), to Poland (area 3,214 km2 and 965,000 people),
- The northeastern part of East Prussia, named Memel Territory, which was placed under the control of France (and was later annexed by Lithuania, as the Klaipėda Region),
- The area of Działdowo (Soldau) (area 492 km2[citation needed]) to Poland; a few villages in the eastern part of West Prussia and in the southern part of East Prussia (Warmia and Masuria) to Poland after the East Prussian plebiscite.
- The city of Danzig (Polish Gdańsk) with the delta of the Vistula river at the Baltic Sea, was made the Free City of Danzig under the League of Nations and partially Polish authority (area 1893 km2, 408,000 inhabitants 1929).
German annexation of Hultschin Area and the Memel Territory

In October 1938 Hlučín Area (Hlučínsko in Czech, Hultschiner Ländchen in German) of Moravian-Silesian Region which had been ceded to Czechoslovakia under the Treaty of Versailles was annexed by the Third Reich as a part of areas lost by Czechoslovakia in accordance with the Munich agreement. However, as distinct from other lost Czechoslovakian domains, it was not attached to Sudetengau (administrative region covering Sudetenland) but to Prussia (Upper Silesia).
By late 1938, Lithuania had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum caused a Lithuanian delegation to travel to Berlin, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop signed the Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
German occupation of Poland in World War II, 1939–1945
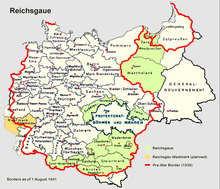
Between the two world wars, many in Germany claimed that the territory ceded to Poland in 1919–1922 should be returned to Germany. This claim was one of the justifications for the German invasion of Poland in 1939, heralding the start of the Second World War. The Third Reich annexed the former German lands, comprising the "Polish Corridor", West Prussia, the Province of Posen, and parts of eastern Upper Silesia. The council of the Free City of Danzig voted to become a part of Germany again, although Poles and Jews were deprived of their voting rights and all non-Nazi political parties were banned. In addition to taking territories lost in 1919, Germany also took additional land that had never been German.
Two decrees by Adolf Hitler (October 8 and October 12, 1939) divided the annexed areas of Poland into administrative units:
- Reichsgau Wartheland (initially Reichsgau Posen), which included the entire Poznań Voivodeship, most of the Łódź Voivodeship, five counties of the Pomeranian Voivodeship, and one county of the Warszawa Voivodeship;
- Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia (initially Reichsgau West Prussia), which consisted of the remaining area of the Pomeranian Voivodeship and the Free City of Danzig;
- Ciechanów District (Regierungsbezirk Zichenau), consisting of the five northern counties of Warszawa Voivodeship (Płock, Płońsk, Sierpc, Ciechanów, and Mława), which became a part of East Prussia;
- Katowice District (Regierungsbezirk Kattowitz), or East Upper Silesia (Ost-Oberschlesien), which included Sosnowiec, Będzin, Chrzanów, and Zawiercie Counties, and parts of Olkusz and Żywiec Counties.
These territories had an area of 94,000 km2 and a population of 10,000,000 people.
The remainder of Polish territory was annexed by the Soviet Union (see Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact) or made into the German-controlled General Government occupation zone.
After the German attack on the Soviet Union in June 1941, the district of Białystok, which included the Białystok, Bielsk Podlaski, Grajewo, Łomża, Sokółka, Volkovysk, and Grodno Counties, was "attached to" (not incorporated into) East Prussia, whilst East Galicia (Distrikt Galizien), which included the cities of Lwów, Stanislawów and Tarnopol, was made part of the General Government.
The Yalta Conference
The final decision to move Poland's boundary westward was made by the United States, United Kingdom and the Soviets at the Yalta Conference in February 1945, shortly before the end of the war. The precise location of the border was left open; the western Allies also accepted in general the principle of the Oder River as the future western border of Poland and of population transfer as the way to prevent future border disputes. The open question was whether the border should follow the Eastern or Lusatian Neisse rivers, and whether Stettin, the traditional seaport of Berlin, should remain German or be included in Poland.
Originally, Germany was to retain Stettin while the Poles were to annex East Prussia with Königsberg.[11] Eventually, however, Stalin decided that he wanted Königsberg as a year-round warm water port for the Soviet Navy and argued that the Poles should receive Stettin instead. The wartime Polish government in exile had little to say in these decisions.[11]

At the Yalta Conference, it was agreed to split Germany into four occupation zones after the war, with a quadripartite occupation of Berlin as well, prior unification of Germany. The status of Poland was discussed, but was complicated by the fact that Poland was at this time under the control of the Red Army. It was agreed to reorganize the Provisionary Polish Government that had been set up by the Red Army through the inclusion of other groups such as the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity and to have democratic elections. This effectively excluded the Polish government-in-exile that had evacuated in 1939. It was agreed that the Polish eastern border would follow the Curzon Line, and Poland would receive substantial territorial compensation in the west from Germany, although the exact border was to be determined at a later time. A "Committee on Dismemberment of Germany" was to be set up. The purpose was to decide whether Germany was to be divided into six nations, and if so, what borders and inter-relationships the new German states were to have.[citation needed]
Potsdam Agreement, 1945
Germany subsequently lost territories east of the Oder-Neisse Line at the end of the War in 1945, when international recognition of its right to jurisdiction over any of these territories was conditionally withdrawn. The "condition" mentioned was the Final German Peace Treaty, which was to set the actual border line, which may or may not have been the Oder-Neisse line. At Potsdam, the assumption by many was that a Final German Peace Treaty was imminent, but this turned out to be incorrect.
After World War II, as agreed at the Potsdam Conference (which met from 17 July until 2 August 1945), all of the areas east of the Oder-Neisse line, whether recognised by the international community as part of Germany until 1939 or occupied by Germany during World War II, were placed under the jurisdiction of other countries.The relevant paragraphs in the Potsdam Agreement are:[12][13][14]
V. City of Koenigsberg and the adjacent area.
The Conference examined a proposal by the Soviet Government to the effect that pending the final determination of territorial questions at the peace settlement, the section of the western frontier of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics which is adjacent to the Baltic Sea should pass from a point on the eastern shore of the Bay of Danzig to the east, north of Braunsberg-Goldap, to the meeting point of the frontiers of Lithuania, the Polish Republic and East Prussia.
The Conference has agreed in principle to the proposal of the Soviet Government concerning the ultimate transfer to the Soviet Union of the City of Koenigsberg and the area adjacent to it as described above subject to expert examination of the actual frontier.
The President of the United States and the British Prime Minister have declared that they will support the proposal of the Conference at the forthcoming peace settlement.
VIII. Poland.
...
The British and United States Governments have taken measures to protect the interest of the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity as the recognized government of the Polish State in the property belonging to the Polish State located in their territories and under their control, whatever the form of this property may be.
...
In conformity with the agreement on Poland reached at the Crimea Conference the three Heads of Government have sought the opinion of the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity in regard to the accession of territory in the north and west which Poland should receive. The President of the National Council of Poland and members of the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity have been received at the Conference and have fully presented their views. The three Heads of Government reaffirm their opinion that the final delimitation of the western frontier of Poland should await the peace settlement.The three Heads of Government agree that, pending the final determination of Poland's western frontier, the former German territories east of a line running from the Baltic Sea immediately west of Swinamunde, and thence along the Oder River to the confluence of the western Neisse River and along the Western Neisse to the Czechoslovak frontier, including that portion of East Prussia not placed under the administration of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in accordance with the understanding reached at this conference and including the area of the former free city of Danzig, shall be under the administration of the Polish State and for such purposes should not be considered as part of the Soviet zone of occupation in Germany. (Emphasis added)
The Allies also agreed that:
XII. Orderly transfer of German populations.
The Three Governments [of the Soviet Union, the United States and Great Britain], having considered the question in all its aspects, recognize that the transfer to Germany of German populations, or elements thereof, remaining in Poland, Czechoslovakia and Hungary, will have to be undertaken. They agree that any transfers that take place should be effected in an orderly and humane manner.
because in the words of Winston Churchill
Expulsion is the method which, in so far as we have been able to see, will be the most satisfactory and lasting. There will be no mixture of populations to cause endless trouble. A clean sweep will be made.[15]
The problem with the status of these territories was that the Potsdam Agreement was not a legally binding treaty, but a memorandum between the USSR, the USA and the UK. It regulated the issue of the eastern German border, which was to be the Oder-Neisse line, but the final article of the memorandum said that the final decisions concerning Germany were subject to a separate peace treaty. This treaty was signed in 1990 as the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany.[16][17]
Post World War II
After the War, the so-called "German question" was an important factor of post-war German and European history and politics. The debate affected Cold War politics and diplomacy and played an important role in the negotiations leading up to the reunification of Germany in 1990. In 1990 Germany officially recognized its present eastern border at the time of its reunification in the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany, ending any residual claims to sovereignty that Germany may have had over any territory east of the Oder-Neisse line.
Between 1945 and 1990 the government of West Germany referred to these territories as "former German territories temporarily under Polish and Soviet administration". This terminology was used in relation to territories of eastern Germany within the 1937 Germany border, and was based on the terminology used in the Potsdam Agreement. It was used only by the Federal Republic of Germany; but the Polish and Soviet governments objected to the obvious implication that these territories should someday revert to Germany. The Polish government preferred to use the phrase "Recovered Territories", asserting a sort of continuity because parts of these territories had centuries previously been ruled by ethnic Poles.
Expulsion of Germans and resettlement

With the rapid advance of the Red Army in the winter of 1944–1945, German authorities desperately evacuated many Germans to west of the Oder–Neisse line. The majority of the remaining German-speaking population east of the Oder–Neisse line (roughly 10 million in the ostgebiete alone) that had not already been evacuated was expelled. Although in the post-war period earlier German sources often cited the number of evacuated and expelled Germans at 16 million and the death toll at between 1.7[18] and 2.5 million,[19] today, the numbers are considered by some historians to be exaggerated and more likely in the range between 400,000 and 600,000.[20] Some present-day estimates place the numbers of German refugees at 14 million of which about half a million died during the evacuations and expulsions.[20][21]
At the same time, Poles from central Poland, expelled Poles from former eastern Poland, Polish returnees from internment and forced labour, Ukrainians were forcibly resettled in Operation Vistula and Jewish Holocaust survivors were settled in German territories gained by Poland, whereas the north of former East Prussia (Kaliningrad Oblast gained by the USSR) was turned into a military zone and subsequently became settled with Russians.
Ostpolitik
In the 1970s, West Germany adopted Ostpolitik in foreign relations, which strove to normalise relations with its neighbours by recognising the realities of the European order of the time,[22] and abandoning elements of the Hallstein Doctrine. West Germany "abandoned, at least for the time being, its claims with respect to German self-determination and reunification, recognising de facto the existence of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) and the Oder-Neisse line."[22] As part of this new approach, West Germany concluded friendship treaties with the Soviet Union (Treaty of Moscow (1970)), Poland (Treaty of Warsaw (1970)), East Germany (Basic Treaty (1972)) and Czechoslovakia (Treaty of Prague (1973)).
Present status
Over the last 20 years, the "German question" has been muted by a number of related phenomena[citation needed]:
- The passage of time resulted in fewer people being left who have firsthand experience of living in these regions under German jurisdiction.
- In the Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to Germany, Germany renounced all claims to territory east the Oder-Neisse line. Germany's recognition of the border was repeated in the German-Polish Border Treaty on November 14, 1990. The treaties were made by both German states and ratified in 1991 by a united Germany.
- The expansion of the European Union to Central Europe in 2004 enabled any German wishing to live and work in Poland, and thus east of the Oder-Neisse line, to do so without requiring a permit. German expellees and refugees became free to visit their former homes and set up residence, though some restrictions remained on the purchase of land and buildings.
- Poland entered the Schengen Area on December 21, 2007, removing all border controls on its border with Germany.
Under Article 1 of the Treaty on Final Settlement, the new united, Germany committed itself to renouncing any further territorial claims beyond the boundaries of East Germany, West Germany and Berlin; "The united Germany has no territorial claims whatsoever against other states and shall not assert any in the future." Furthermore the Basic Law of the Federal Republic was required to be amended to state explicitly that full German unification had now been achieved, such that the new German state comprised the entirety of Germany, and that all constitutional mechanisms should be removed by which any territories outside those boundaries could otherwise subsequently to be admitted; these new constitutional articles being bound by treaty not to be revoked. Article 23 of the Basic Law was repealed, closing off the possibility for any further states to apply for membership of the Federal Republic; while Article 146 was amended to state explicitly that the territory of the newly unified republic comprised the entirety of the German people; "This Basic Law, which since the achievement of the unity and freedom of Germany applies to the entire German people, shall cease to apply on the day on which a constitution freely adopted by the German people takes effect". This was confirmed in the 1990 rewording of the preamble; "Germans..have achieved the unity and freedom of Germany in free self-determination. This Basic Law thus applies to the entire German people." In place of the former Article 23 (under which the states of East Germany had been admitted), a new Article 23 established the constitutional status of accession of the Federal Republic to the European Union; hence with the subsequent accession of Poland to the EU, the constitutional bar on pursuing any claim to territories beyond the Oder-Neisse Line was reinforced. In so far as the former German Reich may be claimed to continue in existence within 'Germany as a whole', former eastern German territories in Poland and Russia are now definitively and permanently excluded from ever again being united with Germany.
In the course of the German reunification, Chancellor Helmut Kohl accepted the territorial changes made after World War II, creating some outrage among the Federation of Expellees, while some Poles were concerned about a possible revival of their 1939 trauma through a "second German invasion", this time with the Germans buying back their land, which was cheaply available at the time. This happened on a smaller scale than many Poles expected, and the Baltic Sea coast of Poland has become a popular German tourist destination. The so-called "homesickness-tourism" which was often perceived as quite aggressive well into the 1990s now tends to be viewed as a good-natured nostalgia tour rather than an expression of anger and desire for the return of the lost territories[citation needed].
Some organisations in Germany continue to claim the territories for Germany or property there for German citizens. The Prussian Trust (or the Prussian Claims Society), that probably has less than a hundred members,[23] re-opened the old dispute when in December 2006, it submitted 23 individual claims against the Polish government to the European Court of Human Rights asking for compensation or return of property appropriated from its members at the end of World War II. An expert report jointly commissioned by the German and Polish governments from specialists in international law have confirmed that the proposed complaints by the Prussian Trust had little hope of success. But the German government cannot prevent such requests being made and the Polish government has felt that the submissions warranted a comment by Anna Fotyga, the Polish Minister of the Foreign Affairs to "express [her] deepest concern upon receiving the information about a claim against Poland submitted by the Prussian Trust to the European Court of Human Rights".[24] On 9 October 2008 the European Court of Human Rights declared the case of Preussische Treuhand v. Poland inadmissible, because the European Convention on Human Rights does not impose any obligations on the Contracting States to return property which was transferred to them before they ratified the Convention.[25]
After the National Democratic Party of Germany, described as a neo-Nazi organisation, won six seats in the parliament of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in September 2006, the leader of the party, Udo Voigt, declared that his party demands Germany in "historical borders" and questioned the current border treaties.[26]
Former eastern territories in German history
The former eastern territories were the scene of numerous notable events in German history, but generally viewed in modern-day Poland as being of 'foreign' rather than local interest.[27]
These include battles such as Frederick the Great’s victories at Mollwitz in 1741, Hohenfriedeberg in 1745, Leuthen (1757) and Zorndorf (1758), and his defeats at Gross-Jägersdorf in 1757 and Kunersdorf in 1759. Historian Norman Davies describes Kunersdorf as "Prussia's greatest disaster" and the inspiration for Christian Tiedge's Elegy to "Humanity butchered by Delusion on the Altar of Blood".[27] In the Napoleonic Wars the Pomeranian town of Kolberg was besieged in 1807 (inspiring a Second World War Nazi propaganda film) while the French Grande Armée was victorious at Eylau in East Prussia in the same year. The Treaties of Tilsit were separately signed in the selfsame town in July 1807 between Napoleon and the Russians and Prussians. The Iron Cross, Germany's highest military honour, was established (though not awarded) by King Frederick William III at Breslau on 17 March 1813.[28] In World War I, Hindenburg won critical victories at Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes, ejecting Russian forces from East Prussia.[27]
Numerous figures in German culture and history (some still living) were either born or resident in the former eastern territories. An inexhaustive list is as follows:[27]
Politicians, statesmen and national leaders
- Friedrich von Gentz
- Adalbert Falk
- Ferdinand Lassalle
- Eduard Lasker
- Catherine the Great, Empress of Russia
- Augusta Victoria, last German Empress
- Leo von Caprivi, Chancellor
- Georg Michaelis, Chancellor
- Gustav Bauer, Chancellor
- Helmuth James Graf von Moltke, jurist
- Egon Krenz, East German leader
- Arthur Zimmermann, German foreign minister, author of the Zimmermann Note
- Otto Landsberg, Justice Minister, one of the signatories of the Treaty of Versailles
- Walther von Lüttwitz, co-leader of the Kapp-Lüttwitz Putsch
- Reinhold Wulle
- Frederick Augustus III, King of Saxony, retired to Sibyllenort in Lower Silesia after his abdication in 1918
- Wilhelm Pieck, first President of East Germany
- Cécil von Renthe-Fink, ambassador, and later plenipotentiary, to Denmark during World War II
- Paul Hensel, politician and champion of the Masurians (not to be confused with Paul Hensel the philosopher)
- Herbert Hupka, CDU politician
- Hans Modrow, last premier of East Germany
- Manfred Stolpe
- Philip, Prince of Eulenburg (implicated in the Harden-Eulenburg Affair)
- Elard von Oldenburg-Januschau
Military figures
- Paul von Hindenburg, Field Marshal, German President
- Hermann von Eichhorn, Field Marshal
- Günther von Kluge, Field Marshal
- Erich von Falkenhayn, General
- Heinz Guderian, General
- Hans-Ulrich Rudel, the highest decorated member of the German Armed Forces
- Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski, SS
- Kurt Daluege, SS
- Manfred von Richthofen (Red Baron), fighter ace
- Kurt Wintgens, fighter ace
- Otto Liman von Sanders, military advisor to the Ottoman Army
- Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, military advisor to the Ottoman Army
- Dietrich von Saucken, General
- Walther Wever, pre-war Commander of the Luftwaffe
- Hyacinth Graf Strachwitz von Groß-Zauche und Camminetz
- Heinrich Freiherr von Lüttwitz
- Helmut Lent, fighter ace
- Günther Radusch, fighter ace
- Walter Schilling, General
- Rudolf Schoenert, fighter ace
- Paul Zorner, fighter ace
- Joachim Müncheberg, fighter ace
- Herbert Kaminski, fighter ace
- Max Näther, fighter ace
- Kurt Student, General
- Erich Fellgiebel, General, conspirator in the 20 July Plot
- Dietrich von Choltitz, last military governor of Paris during World War II
- Felix Steiner, directed troops during the Battle of Berlin
- Hanna Reitsch, aviator
- Melitta Schenk Gräfin von Stauffenberg, aviator
- Johann David Ludwig Graf Yorck von Wartenburg
- Hermann von Boyen
- Walter Nehring
- Hermann Balck
- Friedrich von Mellenthin
- Kuno von Moltke (implicated in the Harden-Eulenburg Affair)
- Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, co-victor over Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo
- Wolf-Dietrich Wilcke, World War II ace
- Gerhard Barkhorn, World War II ace
- Walter Krupinski, World War II ace
- Max von Gallwitz
- Fritz von Below
Scientists and mathematicians
- Wernher von Braun, rocket scientist and space architect
- Ferdinand von Richthofen, geographer and explorer
- David Hilbert
- Max Born
- Walther Nernst
- Paul Ehrlich, immunologist
- Georg von Arco, physicist and radio engineer, cofounder of Telefunken
- Hugo Münsterberg, German-American psychologist
- Paul Gottlieb Nipkow, one of the earliest pioneers of the technology that would lead to modern television
- Emil Krebs, polyglot and Sinologist
- Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus, mathematician. Also the first person to discover a means of manufacturing porcelain in Europe on an industrial scale
- Ferdinand Schichau, engineer
- Fritz Haber, chemist, Nobel laureate
- Günter Blobel, biologist, Nobel laureate
- Alois Alzheimer, who gave his name to Alzheimer's disease
- Johannes Thienemann, founder of the world's first bird observatory
- George K. Kunowsky, astronomer
- Gerhard Domagk, bacteriologist, Nobel laureate
Philosophers and theologians
- Immanuel Kant
- Arthur Schopenhauer
- Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher
- Dietrich Bonhoeffer
- Johann Georg Hamann
- George of Polentz, the first Lutheran bishop
- Johann Gottfried Herder
- Paul Hensel (not to be confused with Paul Hensel the politician)
Historians and archaeologists
- Heinrich Graetz
- Gottfried Bernhardy
- Arthur Milchhöfer
- Theodor Schieder
- Fritz Gause
- Otto Jaekel
- Ferdinand von Roemer
- Bolko von Richthofen
Musicians
- Philipp and Xaver Scharwenka, composers
- Moritz Moszkowski, composer
- George Henschel, singer, pianist, conductor and composer
- Edgar Froese, founder of the electronic music band Tangerine Dream
- Sylvius Leopold Weiss, composer and lutenist
- Otto Klemperer, conductor
- Kurt Masur, conductor
- Johann Sedlatzek, flautist
- Dame Elisabeth Schwarzkopf, German-born Austro-British singer
- Johann Gottfried Piefke, composer of patriotic marches
- Richard Wetz, composer
- John Kay, frontman of Steppenwolf
- Carl Loewe spent much of his career in Stettin
- Georg Riedel, the "East Prussian Bach", much of whose works were lost in the destruction of Königsberg during World War II
- Johann Friedrich Reichardt
- Wilhelm Joseph von Wasielewski
Poets, writers, dramatists, and other cultural figures
- Martin Opitz
- Angelus Silesius
- Andreas Gryphius
- Friedrich von Logau
- Ewald Christian von Kleist
- Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff
- Gustav Freytag
- E. T. A. Hoffmann
- Arnold Zweig
- Gerhart Hauptmann
- Günter Grass
- Bogumil Goltz, humorist
- Walter Bruno Henning, linguist
- Marion Dönhoff
- Emanuel Lasker, World Chess Champion
- Paul Mross, chess master
- Franz von Oppersdorff, a patron of Beethoven
- Robert Wiene, film director (The Cabinet of Dr Caligari)
- Alfred Döblin
- Janosch, popular children's writer (he often refers to his nationality as Silesian)
- Edward Sapir, linguist
- Max von Schenkendorf
Painters and visual artists
- Karl Friedrich Lessing
- Adolph Menzel
- Michael Willmann, "the Silesian Rembrandt"
- Lovis Corinth
- Käthe Kollwitz
Architects
- Richard Konwiarz, designer of the Silesian Arena (Schlesierkampfbahn, now the Olympic Stadium in Wrocław)
- Max Berg, designer of the Centennial Hall
- Carl Ferdinand Langhans, son of Carl Gotthard, built among others the Breslau Opera
- Carl Gotthard Langhans, designer of the Brandenburg Gate
- Hanns Hopp lived in Königsberg for a time and designed many public and private buildings in that city.
- Friedrich Lahrs
Actors and actresses
- Armin Mueller-Stahl
- Matthias Habich
- Veruschka von Lehndorff
- Volker Lechtenbrink
- Hans Heinrich von Twardowski
- Ulli Lommel
- Marianne Hold
Miscellaneous
- Karl Denke, a notorious cannibalistic serial killer who made headlines in Silesia in the 1920s
- Herta Heuwer, inventor of the currywurst
- Rochus Misch, last surviving occupant of the Führerbunker
- Beate Uhse-Rotermund, aviator and founder of the world's first sex shop, Beate Uhse AG
- Ludwig Guttmann, founder of the Paralympic Games
- Hardy Rodenstock, publisher, wine connoisseur (and suspected wine fraud)
- Karl Godulla, industrialist, the "King of Zinc", contributed greatly towards the industrialisation of Silesia
- Prince Franz Wilhelm of Prussia, businessman and member of the House of Hohenzollern, born in Grünberg
- Sophie Charlotte Elisabeth Ursinus, serial killer
- Max Otto Koischwitz, German-American propagandist
- Renate von Natzmer, spy
- Wolfgang Vogel, East German lawyer famous for brokering various spy exchanges during the Cold War
See also
- Former eastern territories of Germany:
- Major treaties affecting the former eastern territories of Germany:
- Territorial changes of Poland and Germany:
- World War II evacuation and expulsion
- Expulsion of Polish people by Germany on those territories
- Evacuation, flight and expulsion of Germans from the those territories:
- Polish settlement:
- Former eastern territories of Germany annexed by the Soviet Union:
- Kaliningrad oblast of Russia (former Northern East Prussia)
- Klaipėda in Lithuania (former Memel territory)
Notes and references
- ^ Demshuk, Andrew. The Lost German East: Forced Migration and the Politics of Memory, 1945-1970. page 52
- ^ see for example msn encarta: "diejenigen Gebiete des Deutschen Reiches innerhalb der deutschen Grenzen von 1937", Meyers Lexikon online: "die Teile des ehemaligen deutschen Reichsgebietes zwischen der Oder-Neiße-Linie im Westen und der Reichsgrenze von 1937 im Osten". Archived 2009-10-31.
- ^ The problem with the status of these territories was that in 1945 the concluding document of the Potsdam Conference was not a legally binding treaty, but a memorandum between the USSR, the USA and the UK. It regulated the issue of the eastern German border, which was to be the Oder-Neisse line, but the final article of the memorandum said that the final decisions concerning Germany were subject to a separate peace treaty. This treaty was signed in 1990 under the name of Treaty on the Final Settlement by both the German states and ratified in 1991 by the united Germany. This ended the legal limbo state which meant that for 45 years, people on both sides of the border could not be sure whether the settlement reached in 1945 might be changed at some future date.
- ^ Cornfield, Daniel B. and Hodson, Randy (2002). Worlds of Work: Building an International Sociology of Work. Springer, p. 223. ISBN 0306466058
- ^ Pollock, Michael. Östereichische Zeitschrift für Soziologie; Zeitschrift für Soziologie,, Jg. 8, Heft 1 (1979); 50-62. 01/1979 Template:De icon
- ^ Baranowsky, Shelley (1995). The Sanctity of Rural Life: Nobility, Protestantism, and Nazism in Weimar Prussia. Oxford University Press, pp. 187-188. ISBN 0195361660
- ^ Schmitt, Carl (1928). Political Romanticism. Transaction Publishers. Preface, p. 11. ISBN 1412844304
- ^ "Each spring, millions of workmen from all parts of western Russia arrived in eastern Germany, which, in political language, is called East Elbia." Viereck, George Sylvester. The Stronghold of Junkerdom, Volume 8. Fatherland Corporation, 1918
- ^ The public broadcaster run by the states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia is Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (lit. in Template:Lang-en), the regional newspaper issued in Halle upon Saale is the Mitteldeutsche Zeitung, and a Protestant regional church body in the area, just recently founded by a merger, is the Evangelische Kirche in Mitteldeutschland (Template:Lang-en).
- ^ The German population in those areas in 1921 was 16.7% in the Poznań region (1910: 27.1%), and 18.8% in the area of Polish Pomorze (1910: 42.5%). [1]
- ^ a b https://web.archive.org/web/20131101211017/http://newyorktelco.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/biuletyn9-10_56-57.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 1, 2013. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003). "Potsdam Agreement, 1945". In Mango, Anthony (ed.). Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: A to F. Vol. 1. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1829–1830. ISBN 9780415939218.
- ^ Krickus, Richard J. (202). The Kaliningrad Question (illustrated ed.). Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 34–35. ISBN 9780742517059.
- ^ Piotrowicz, Ryszard W.; Blay, Sam; Schuster, Gunnar; Zimmermann, Andreas (1997). "The Unification of Germany in International and Domestic Law". German monitor (39). Rodopi: 48–49. ISBN 9789051837551. ISSN 0927-1910.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^
Murphy, Clare (2004-08-02). "WWII expulsions spectre lives on". BBC News. bbc.co.uk. Retrieved June 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Junker, Detlef; Gassert, Philipp; Mausbach, Wilfried; et al., eds. (2004). The United States and Germany in the Era of the Cold War, 1945-1990: A Handbook. Publications of the German Historical Institute Volume 1 of The United States and Germany in the Era of the Cold War 2 Volume Set (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 105. ISBN 9780521791120.
- ^ Piotrowicz et al. 1997, p. 66.
- ^ Hans-Ulrich Wehler (2003). Deutsche Gesellschaftsgeschichte Band 4: Vom Beginn des Ersten Weltkrieges bis zur Gründung der beiden deutschen Staaten 1914–1949 (in German). Munich: C.H. Beck Verlag. ISBN 3-406-32264-6.
- ^ Dagmar Barnouw (2005). The War in the Empty Air: Victims, Perpetrators, and Postwar Germans. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. p. 143. ISBN 0-253-34651-7.
- ^ a b Frank Biess (2006). "Review of Dagmar Barnouw, The War in the Empty Air: Victims, Perpetrators, and Postwar Germans" (pdf). H-Net Reviews: 2.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ Rüdiger Overmans (2004). Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg (German Military Losses in WWII) (in German). Munich: Oldenbourg. pp. 298–300. ISBN 3-486-56531-1.
- ^ a b The Federal Republic of Germany’s Ostpolitik, the European Navigator
- ^ Klaus Ziemer. What Past, What Future? Social Science in Eastern Europe: News letter: Special Issue German-Polish Year 2005/2006, 2005 Issue 4, ISSN 1615-5459 pp. 4–11 (See page 4). Published by the Social Science Information Centre (see Archive)
- ^ Anna Fotyga, the Polish Minister of the Foreign Affairs "I express my deepest concern upon receiving the information about a claim against Poland submitted by the Prussian Trust to the European Court of Human Rights. ...". 21 December 2006
- ^ Decision as to the admissibility Application no. 47550/06 by Preussische Treuhand GMBH & CO. KG A. A. against Poland, by the European Court of Human Rights, 7 October 2008
- ^ Template:Pl iconSzef NPD: chcemy Niemiec w historycznych granicach, 22 września 2006, gazeta.pl
- ^ a b c d Davies, N. (2005) God's Playground. A History of Poland. Volume II: 1795 to the present. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Michael Nungesser. Das Denkmal auf dem Kreuzberg von Karl Friedrich Schinkel, ed. on behalf of the Bezirksamt Kreuzberg von Berlin as catalogue of the exhibition „Das Denkmal auf dem Kreuzberg von Karl Friedrich Schinkel“ in the Kunstamt Kreuzberg / Künstlerhaus Bethanien Berlin, between 25 April and 7 June 1987, Berlin: Arenhövel, 1987, p. 29. ISBN 3-922912-19-2.
Further reading
- Emotions prevail in relations between Germans, Czechs, Poles – poll, Czech Happenings, 21 December 2005
- Jose Ayala Lasso. Speech to the German expellees, Day of the Homeland, Berlin 6 August 2005 Lasso was the first United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (1994–1997)
- Ryszard W. Piotrowicz. The Status of Germany in International Law: Deutschland uber Deutschland? The International and Comparative Law Quarterly, Vol. 38, No. 3 (Jul., 1989), pp. 609–635 "The purpose of this article is to consider the legal status of Germany from 1945 to [1989]"
