Pralsetinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gavreto |
| Other names | BLU-667 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620057 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
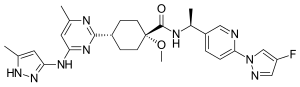
| Formula | C27H32FN9O2 |
| Molar mass | 533.612 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pralsetinib, sold under the brand name Gavreto, is a medication approved[10] for RET mutation-positive medullary thyroid cancer (MTC)[11] and RET fusion-positive differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy.[12] Pralsetinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It is taken by mouth.[12]
The most common adverse reactions include increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), decreased hemoglobin, decreased lymphocytes, decreased neutrophils, increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increased creatinine, increased alkaline phosphatase, fatigue, constipation, musculoskeletal pain, decreased calcium, hypertension, decreased sodium, decreased phosphate, and decreased platelets.[12]
Pralsetinib was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2020,[12][13][14][15][16][excessive citations] and in the European Union in November 2021.[8]
Medical uses
[edit]Pralsetinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as detected by an FDA approved test.[12][15]
History
[edit]Efficacy was investigated in a multicenter, open-label, multi-cohort clinical trial (ARROW, NCT03037385) with 220 participants aged 26-87 whose tumors had RET alterations.[12][15] Identification of RET gene alterations was prospectively determined in local laboratories using either next generation sequencing, fluorescence in situ hybridization, or other tests.[12] The main efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate (ORR) and response duration determined by a blinded independent review committee using RECIST 1.1.[12] The trial was conducted at sites in the United States, Europe and Asia.[15]
Efficacy for RET fusion-positive NSCLC was evaluated in 87 participants previously treated with platinum chemotherapy.[12] The ORR was 57% (95% CI: 46%, 68%); 80% of responding participants had responses lasting 6 months or longer.[12] Efficacy was also evaluated in 27 participants who never received systemic treatment.[12] The ORR for these participants was 70% (95% CI: 50%, 86%); 58% of responding participants had responses lasting 6 months or longer.[12]
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for pralsetinib priority review, orphan drug, and breakthrough therapy designations[12]and granted approval of Gavreto to Blueprint Medicines.[12]
Society and culture
[edit]Legal status
[edit]On 16 September 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a conditional marketing authorization for the medicinal product Gavreto, intended for the treatment of people with rearranged during transfection (RET)-fusion positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).[17] The applicant for this medicinal product is Roche Registration GmbH.[17] Pralsetinib was approved for medical use in the European Union in November 2021.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Gavreto". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 6 April 2023. Archived from the original on 8 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ "Gavreto pralsetinib 100 mg hard capsule bottle (380812)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 30 March 2023. Archived from the original on 8 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ "Gavreto (Roche Products Pty Ltd)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- ^ "Gavreto (Roche Products Pty Ltd)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- ^ https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspar/auspar-gavreto-0 [bare URL]
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Gavreto". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 29 May 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Gavreto- pralsetinib capsule". DailyMed. 9 September 2020. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ a b c "Gavreto EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 14 September 2021. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Gavreto Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Archived from the original on 5 March 2023. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ "FDA approves pralsetinib for RET-altered thyroid cancers". Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 11 June 2021. Archived from the original on 9 January 2023. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Nervo A, Retta F, Ragni A, Piovesan A, Gallo M, Arvat E (2022). "Management of Progressive Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Carcinoma: Current Perspective". Cancer Management and Research. 14: 3047–3062. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S340967. PMC 9584766. PMID 36275786.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "FDA approves pralsetinib for lung cancer with RET gene fusions". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 4 September 2020. Archived from the original on 9 September 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Blueprint Medicines Announces FDA Approval of Gavreto (pralsetinib) for the Treatment of Adults with Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" (Press release). Blueprint Medicines. 4 September 2020. Archived from the original on 9 September 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020 – via PR Newswire.
- ^ "Roche announces FDA approval of Gavreto (pralsetinib) for the treatment of adults with metastatic RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer". Roche (Press release). 7 September 2020. Archived from the original on 9 September 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Drug Trial Snapshot: Gavreto". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 4 September 2020. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Markham A (November 2020). "Pralsetinib: First Approval". Drugs. 80 (17): 1865–1870. doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01427-4. PMID 33136236. S2CID 226223522.
- ^ a b "Gavreto: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2021. Archived from the original on 17 September 2021. Retrieved 17 September 2021. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
External links
[edit]- "Pralsetinib". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute.
- Clinical trial number NCT03037385 for "Phase 1/2 Study of the Highly-selective RET Inhibitor, Pralsetinib (BLU-667), in Patients With Thyroid Cancer, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Other Advanced Solid Tumors (ARROW)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- "Understanding Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)" (PDF).
- "Understanding Metastatic RET-Driven Thyroid Cancers" (PDF).
