Oxandrolone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604024 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 97% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 9 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary:90%; Fecal:7% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.158 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
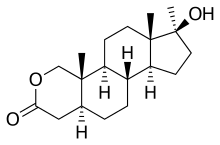
| Formula | C19H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 306.44 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Oxandrolone, also known as oxandrin, is a drug first synthesized by Raphael Pappo while at Searle Laboratories, now Pfizer Inc., under the trademark Anavar, and introduced into the United States in 1964. It is a synthetic anabolic steroid derivative of dihydrotestosterone with an oxygen atom replacing the 2 carbon and methylation in the 17 position.
Biological effects
In contrast with some other steroids with a methyl group in the 17-alpha position, the liver toxicity of oxandrolone is low.[medical citation needed] Studies have shown that a daily dose of 20 mg oxandrolone used in the course of 12 weeks had only a negligible impact on the increase of liver enzymes.[2][3] As a DHT derivative, oxandrolone does not aromatize, and thus does not cause gynecomastia.[medical citation needed] It also does not significantly influence the body's normal testosterone production (HPTA axis) at low dosages (20 mg). When dosages are high, the human body reacts by reducing the production of luteinizing hormone after perceiving endogenous testosterone production as too high; this in turn eliminates further stimulation of Leydig cells in the testicles, causing testicular atrophy.[medical citation needed]
In a randomized, double-blind study, patients with 40% total body surface area burns were selected to receive standard burn care plus oxandrolone, or without oxandrolone. Those treated with oxandrolone showed improved body composition, preserved muscle mass and reduced hospital stay time.[4]
History
The drug was prescribed to promote muscle regrowth in disorders which cause involuntary weight loss, and is used as part of treatment for HIV/AIDS. It had also been shown to be partially successful in treating cases of osteoporosis. However, in part due to bad publicity from its abuses by bodybuilders, production of Anavar was discontinued by Searle Laboratories in 1989. It was picked up by Bio-Technology General Corporation, now Savient Pharmaceuticals who, following successful clinical trials in 1995, released it under the tradename Oxandrin.
It was subsequently approved for orphan drug status by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating alcoholic hepatitis, Turner syndrome, and HIV-induced weight loss. It is also indicated as an offset to protein catabolism caused by long-term administration of corticosteroids. In addition, the drug has shown positive results in treating anemia and hereditary angioedema. Because of its potential for abuse, it is categorized as a Schedule III controlled substance in the United States.
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Schroeder ET, Zheng L, Yarasheski KE, Qian D, Stewart Y, Flores C, Martinez C, Terk M, Sattler FR (March 2004). "Treatment with oxandrolone and the durability of effects in older men". J. Appl. Physiol. 96 (3): 1055–62. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00808.2003. PMID 14578370.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Grunfeld C, Kotler DP, Dobs A, Glesby M, Bhasin S (March 2006). "Oxandrolone in the treatment of HIV-associated weight loss in men: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study". J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 41 (3): 304–14. doi:10.1097/01.qai.0000197546.56131.40. PMID 16540931.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jeschke MG, Finnerty CC, Suman OE, Kulp G, Mlcak RP, Herndon DN (September 2007). "The effect of oxandrolone on the endocrinologic, inflammatory, and hypermetabolic responses during the acute phase postburn". Ann. Surg. 246 (3): 351–60, discussion 360–2. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e318146980e. PMC 1959346. PMID 17717439.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
- Earthman CP, Reid PM, Harper IT, Ravussin E, Howell WH (2002). "Body cell mass repletion and improved quality of life in HIV-infected individuals receiving oxandrolone". JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 26 (6): 357–65. doi:10.1177/0148607102026006357. PMID 12405647.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Hart DW, Wolf SE, Ramzy PI, Chinkes DL, Beauford RB, Ferrando AA, Wolfe RR, Herndon DN (April 2001). "Anabolic effects of oxandrolone after severe burn". Ann. Surg. 233 (4): 556–64. doi:10.1097/00000658-200104000-00012. PMC 1421286. PMID 11303139.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Przkora R, Herndon DN, Suman OE (January 2007). "The effects of oxandrolone and exercise on muscle mass and function in children with severe burns". Pediatrics. 119 (1): e109–16. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1548. PMC 2367234. PMID 17130281.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Demling RH, DeSanti L (December 2003). "Oxandrolone induced lean mass gain during recovery from severe burns is maintained after discontinuation of the anabolic steroid". Burns. 29 (8): 793–7. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2003.08.003. PMID 14636753.
External links
- Oxandrin Homepage, savientpharma.com (retrieved 23 October 2009)* Oxandrin Label, fda.gov (retrieved 23 October 2009)
- "Oxandrolone Side Effects, Interactions and Information". drugs.com.
