Cloud computing: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 236271256 by 75.41.52.92 (talk): not a prominent example |
→Client: adding zonbu |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
A ''cloud client'' is [[computer hardware]] and/or [[computer software]] which relies on [[The Cloud]] for application delivery, or which is specifically designed for delivery of cloud services, and which is in either case essentially useless without it<ref name="nimbus"/>. For example: |
A ''cloud client'' is [[computer hardware]] and/or [[computer software]] which relies on [[The Cloud]] for application delivery, or which is specifically designed for delivery of cloud services, and which is in either case essentially useless without it<ref name="nimbus"/>. For example: |
||
* [[Mobile computing|Mobile]] ([[Android (mobile device platform)|Android]], [[iPhone]]<ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2008/07/17/technology/personaltech/17pogue.html?_r=1&oref=slogin In Sync to Pierce the Cloud]</ref>) |
* [[Mobile computing|Mobile]] ([[Android (mobile device platform)|Android]], [[iPhone]]<ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2008/07/17/technology/personaltech/17pogue.html?_r=1&oref=slogin In Sync to Pierce the Cloud]</ref>) |
||
* [[Thin client]] ([[CherryPal]]) |
* [[Thin client]] ([[CherryPal]], [[Zonbu]]) |
||
* [[Thick client]]/[[Web browser]] ([[Google Chrome]], [[Internet Explorer]], [[Mozilla Firefox]], [[Safari (web browser)|Safari]], [[Konqueror]], [[Opera (web browser)|Opera]]) |
* [[Thick client]]/[[Web browser]] ([[Google Chrome]], [[Internet Explorer]], [[Mozilla Firefox]], [[Safari (web browser)|Safari]], [[Konqueror]], [[Opera (web browser)|Opera]]) |
||
<!-- Please DO NOT list insignificant or poor examples here --> |
<!-- Please DO NOT list insignificant or poor examples here --> |
||
Revision as of 15:50, 6 September 2008
Cloud computing means Internet ('Cloud') based development and use of computer technology ('Computing'). It is a style of computing where IT-related capabilities are provided “as a service”[1], allowing users to access technology-enabled services "in the cloud"[2] without knowledge of, expertise with, or control over the technology infrastructure that supports them[3]. It is a general concept that incorporates software as a service, Web 2.0 and other recent, well-known technology trends, where the common theme is reliance on the Internet for satisfying the computing needs of the users. For example, Google Apps provides common business applications online that are accessed from a web browser, while the software and data is stored on the servers.
Cloud computing is often confused with grid computing (a form of distributed computing whereby a "super and virtual computer" is composed of a cluster of networked, loosely-coupled computers, acting in concert to perform very large tasks), utility computing (the packaging of computing resources, such as computation and storage, as a metered service similar to a traditional public utility such as electricity) and autonomic computing (computer systems capable of self-management)[4]. Indeed many cloud computing deployments are today powered by grids, have autonomic characteristics and are billed like utilities, but cloud computing is rather a natural next step from the grid-utility model[5]. Some successful cloud architectures have little or no centralised infrastructure or billing systems whatsoever including Peer to peer networks like BitTorrent and Skype and Volunteer computing like SETI@home.
The majority of cloud computing infrastructure currently consists of reliable services delivered through next-generation data centers that are built on compute and storage virtualization technologies. The services are accessible anywhere in the world, with The Cloud appearing as a single point of access for all the computing needs of consumers. Commercial offerings need to meet the quality of service requirements of customers and typically offer service level agreements[6]. Open standards and open source software are also critical to the growth of cloud computing[7].
As customers generally do not own the infrastructure, they are merely accessing or renting, they can forego capital expenditure and consume resources as a service, paying instead for what they use. Many cloud computing offerings have adopted the utility computing model which is analogous to how traditional utilities like electricity are consumed, while others are billed on a subscription basis. By sharing "perishable and intangible" computing power between multiple tenants, utilization rates can be improved (as servers are not left idle) which can reduce costs significantly while increasing the speed of application development. A side effect of this approach is that "computer capacity rises dramatically" as customers do not have to engineer for peak loads[8]. Adoption has been enabled by "increased high-speed bandwidth" which makes it possible to receive the same response times from centralized infrastructure at other sites.
The cloud computing "revolution" is being driven by companies like Amazon, Google, Salesforce and Yahoo! as well as traditional vendors including Hewlett Packard, IBM, Intel and Microsoft[9] and adopted by individuals through large enterprises including General Electric, L'Oréal, Procter & Gamble and Valeo[10][11].
History
The Cloud[12] is a metaphor for the Internet[13], derived from its common depiction in network diagrams (or more generally components which are managed by others) as a cloud outline[14].
The underlying concept dates back to 1960 when John McCarthy opined that "computation may someday be organized as a public utility" (indeed it shares characteristics with service bureaus which date back to the 1960s) and the term cloud was already in commercial use in the early 1990s to refer to large ATM networks [15]. By the turn of the 21st century, cloud computing solutions had started to appear on the market [16], though most of the focus at this time was on Software as a service.
Amazon.com played a key role in the development of cloud computing by modernizing their data centers after the dot-com bubble and (having found the new cloud architecture resulted in significant internal efficiency improvements) providing access to their systems by way of Amazon Web Services in 2002 on a utility computing basis[17].
2007 saw increased activity, including Google, IBM and a number of universities embarking on a large scale cloud computing research project[18], around the time the term started gaining popularity in the mainstream press. It was a hot topic by mid-2008 and numerous cloud computing events had been scheduled[19].
In August 2008 Gartner observed that "organisations are switching from company-owned hardware and software assets to per-use service-based models" and that the "projected shift to cloud computing will result in dramatic growth in IT products in some areas and in significant reductions in other areas"[20].
Key characteristics
- Capital expenditure minimized and thus low barrier to entry as infrastructure is owned by the provider and does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Services are typically being available to or specifically targeting retail consumers and small businesses.
- Device and location independence[21] which enables users to access systems regardless of location or what device they are using (eg PC, mobile).
- Multitenancy enabling sharing of resources (and costs) among a large pool of users, allowing for:
- Centralization of infrastructure in areas with lower costs (eg real estate, electricity)
- Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possible load levels)
- Utilization and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 10-20% utilised[17].
- Performance is monitored and consistent but can be affected by insufficient bandwidth or high network load.
- Reliability by way of multiple redundant sites, which makes it suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery[22], however IT and business managers are able to do little when an outage hits them[23].
- Scalability which meets changing user demands quickly, without having to engineer for peak loads. Massive scalability and large user bases are common but not an absolute requirement.
- Security which typically improves due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources, etc. but which raises concerns about loss of control over certain sensitive data. Accesses are typically logged but accessing the audit logs themselves can be difficult or impossible.
- Sustainability through improved resource utilisation, more efficient systems and carbon neutrality[24].
Components
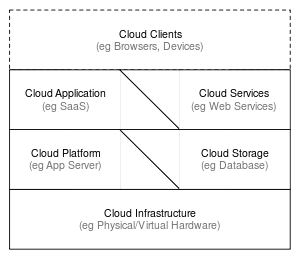
Application
A cloud application leverages The Cloud in software architecture, often eliminating the need to install and run the application on the customer's own computer, thus alleviating the burden of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support. For example:
- Peer-to-peer/volunteer computing (Bittorrent, SETI, Skype)
- Web application (Facebook)
- Software as a service (Google Apps, Salesforce)
- Software plus services (Microsoft Online Services)
Client
A cloud client is computer hardware and/or computer software which relies on The Cloud for application delivery, or which is specifically designed for delivery of cloud services, and which is in either case essentially useless without it[25]. For example:
- Mobile (Android, iPhone[26])
- Thin client (CherryPal, Zonbu)
- Thick client/Web browser (Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Konqueror, Opera)
Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure (eg Infrastructure as a service) is the delivery of computer infrastructure (typically a platform virtualization environment) as a service[27]. For example:
- Full virtualization (GoGrid, Skytap)
- Paravirtualization (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Grid computing (Sun Grid)
Platform
A cloud platform (eg Platform as a service) (the delivery of a computing platform and/or solution stack as a service) facilitates deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers[28]. For example:
Service
A cloud service (eg Web Service) is "software system[s] designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network"[29] which may be accessed by other cloud computing components, software (eg Software plus services) or end users directly[30]. For example:
- Identity (OAuth, OpenID)
- Integration (Amazon Simple Queue Service)
- Mapping (Google Maps, Yahoo! Maps)
- Payments (Amazon Flexible Payments Service, Google Checkout, PayPal)
- Search (Alexa, Google Custom Search, Yahoo! BOSS)
- Others (Amazon Mechanical Turk)
Storage
Cloud storage is the delivery of data storage as a service (including database-like services), often billed on a utility computing basis (eg per gigabyte per month)[31]. For example:
- Database (Amazon SimpleDB, Google App Engine's BigTable datastore)
- Network attached storage (MobileMe iDisk component, Nirvanix CloudNAS)
- Synchronisation (Live Mesh Live Desktop component, MobileMe push functions)
- Web service (Amazon Simple Storage Service, Nirvanix SDN)
Architecture

Cloud architecture[32] is the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing (eg hardware, software) as designed by a cloud architect who typically works for a cloud integrator. It typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over application programming interfaces (usually web services)[33].
This is very similar to the Unix philosophy of having multiple programs doing one thing well and working together over universal interfaces. Complexity is controlled and the resulting systems are more manageable than their monolithic counterparts.
Cloud architecture extends to the client where web browsers and/or software applications are used to access cloud applications.
Roles
Enablers
A cloud enabler facilitates the adoption and use of cloud computing[34]. For example:
- 3PAR utility storage system for utility and cloud computing
- 3tera system software for utility and cloud computing
- Hadoop free Java software framework
- Linux including Red Hat[35]
Providers
A cloud provider or cloud service provider owns and operates live cloud computing systems, typically for third parties. Usually this requires significant resources and expertise in building and managing next generation data centers. Some organisations are realising a subset of the benefits of cloud computing by becoming "internal" cloud providers and servicing themselves, though they do not benefit from the same economies of scale and still have to engineer for peak loads. The barrier to entry is also significantly higher with capital expenditure required and billing and management creates some overhead. Nonetheless, significant operational efficiency and agility advantages can be realised even by small organisations and server consolidation and virtualization rollouts are already well underway[36]. Amazon.com was the first such provider, modernising its data centers which, like most computer networks were using as little as 10% of its capacity at any one time just to leave room for occasional spikes. This allowed small, fast-moving groups to add new features faster and easier, and they went on to open it up to outsiders as Amazon Web Services in 2002 on a utility computing basis[17].
Users
A cloud user is a consumer of cloud computing[25].
The privacy of users in cloud computing has become of increasing concern.[37] [38]
Standards
A cloud standard is one of a number of existing (typically lightweight) open standards that have facilitated the growth of cloud computing, including:
- Application
- Communications (HTTP, XMPP)
- Security (OAuth, OpenID, TLS)
- Syndication (Atom)
- Client
- Infrastructure
- Platform
- Service
- Data (XML, JSON)
- Web Services (REST)
- Storage
Legal issues
In March 2007, Dell applied to trademark the term '"cloud computing" (U.S. Trademark 77,139,082) in the United States. It received a "Notice of Allowance" in July 2008 which was subsequently canceled on August 6, resulting in a formal rejection of the trademark application less than a week later.
In November 2007, the Free Software Foundation released the Affero General Public License, a version of GPLv3 designed to close a perceived legal loophole associated with Free software designed to be run over a network, particularly software as a service. An application service provider is required to release any changes they make to Affero GPL open source code.
See also
References
- ^ Gartner Says Cloud Computing Will Be As Influential As E-business
- ^ What's the Difference Between Cloud Computing and SaaS?
- ^ Distinguishing Cloud Computing from Utility Computing
- ^ What's In A Name? Utility vs. Cloud vs Grid
- ^ I.B.M. to Push ‘Cloud Computing,’ Using Data From Afar
- ^ Rajkumar Buyya1, Chee Shin Yeo1, Srikumar Venugopal1. "Market-Oriented Cloud Computing: Vision, Hype, and Reality for Delivering IT Services as Computing Utilities" (PDF). Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Australia: 9. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Open source fuels growth of cloud computing, software-as-a-service
- ^ Cloud Computing: The Evolution of Software-as-a-Service
- ^ With Their Heads in the Clouds
- ^ Google Apps makes its way into big business
- ^ Google, Inc. Q2 2008 Earnings Call
- ^ Cloud Computing: When Computers Really Do Rule
- ^ What cloud computing really means
- ^ The Internet Cloud
- ^ July, 1993 meeting report from the IP over ATM working group of the IETF
- ^ Internet Critic Takes on Microsoft
- ^ a b c Jeff Bezos' Risky Bet
- ^ Google and I.B.M. Join in ‘Cloud Computing’ Research
- ^ Keep an eye on cloud computing
- ^ Gartner Says Worldwide IT Spending On Pace to Surpass $3.4 Trillion in 2008
- ^ The new geek chic: Data centers
- ^ Cloud Computing: Small Companies Take Flight
- ^ Google Apps Admins Jittery About Gmail, Hopeful About Future
- ^ Google to go carbon neutral by 2008
- ^ a b Nimbus Cloud Guide
- ^ In Sync to Pierce the Cloud
- ^ EMC buys Pi and forms a cloud computing group
- ^ Google angles for business users with 'platform as a service'
- ^ "Web Services Glossary".
- ^ The Emerging Cloud Service Architecture
- ^ Google, Microsoft and Apple building online storage havens: you win
- ^ Building GrepTheWeb in the Cloud, Part 1: Cloud Architectures
- ^ Cloud Maturity Is Accelerating: More Than Just Reaction To The Hype?
- ^ List of Cloud Platforms, Providers and Enablers
- ^ Red Hat chief: 'The clouds will all run Linux'
- ^ ACM Queue - Beyond Server Consolidation
- ^ Carl Hewitt (September/October 2008). "ORGs for Scalable, Robust, Privacy-Friendly Client Cloud Computing". IEEE Intenet Computing. 12 (5).
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ Google Privacy Practices Worse Than ISP Snooping, AT&T Charges
- Chappell, David (August 2008). "A short introduction to cloud platforms" (PDF). David Chappell & Associates: 13. Retrieved 2008-08-20.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
External links
- Guide To Cloud Computing on InformationWeek.com
